Marine ecosystems are the largest of Earth's aquatic ecosystems and exist in waters that have a high salt content. These systems contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have a lower salt content. Marine waters cover more than 70% of the surface of the Earth and account for more than 97% of Earth's water supply and 90% of habitable space on Earth. Seawater has an average salinity of 35 parts per thousand of water. Actual salinity varies among different marine ecosystems. Marine ecosystems can be divided into many zones depending upon water depth and shoreline features. The oceanic zone is the vast open part of the ocean where animals such as whales, sharks, and tuna live. The benthic zone consists of substrates below water where many invertebrates live. The intertidal zone is the area between high and low tides. Other near-shore (neritic) zones can include mudflats, seagrass meadows, mangroves, rocky intertidal systems, salt marshes, coral reefs, lagoons. In the deep water, hydrothermal vents may occur where chemosynthetic sulfur bacteria form the base of the food web.
Marine ecosystems are characterized by the biological community of organisms that they are associated with and their physical environment. Classes of organisms found in marine ecosystems include brown algae, dinoflagellates, corals, cephalopods, echinoderms, and sharks.
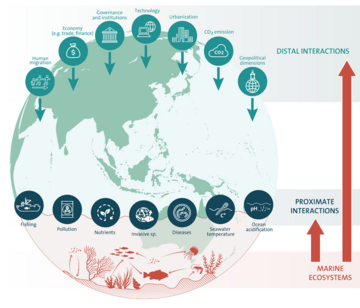
Marine ecosystems are important sources of ecosystem services and food and jobs for significant portions of the global population. Human uses of marine ecosystems and pollution in marine ecosystems are significantly threats to the stability of these ecosystems. Environmental problems concerning marine ecosystems include unsustainable exploitation of marine resources (for example overfishing of certain species), marine pollution, climate change, and building on coastal areas. Moreover, much of the carbon dioxide causing global warming and heat captured by global warming are absorbed by the ocean, ocean chemistry is changing through processes like ocean acidification which in turn threatens marine ecosystems. Because of these opportunities in marine ecosystems for humans and the threats created by humans, the international community has prioritized "Life below water" as Sustainable Development Goal 14 to "Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development".
Coastal ecosystems
International attention to address the threats of coasts has been captured in Sustainable Development Goal 14 "Life Below Water" which sets goals for international policy focused on preserving coastal ecosystems and supporting more sustainable economic practices for coastal communities. Likewise, the United Nations has declared 2021-2030 the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, but restoration of coastal ecosystems has received insufficient attention.
Coral reefs
Coral reefs are one of the most well-known marine ecosystems in the world, with the largest being the Great Barrier Reef. These reefs are composed of large coral colonies of a variety of species living together. The corals from multiple symbiotic relationships with the organisms around them.
Mangroves
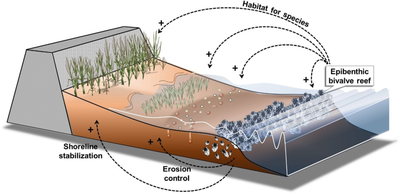
Mangroves are trees or shrubs that grow in low-oxygen soil near coastlines in tropical or subtropical latitudes. They are an extremely productive and complex ecosystem that connects the land and sea. Mangroves consist of species that are not necessarily related to each other and are often grouped for the characteristics they share rather than genetic similarity. Because of their proximity to the coast, they have all developed adaptions such as salt excretion and root aeration to live in salty, oxygen-depleted water. Mangroves can often be recognized by their dense tangle of roots that act to protect the coast by reducing erosion from storm surges, currents, wave, and tides. The mangrove ecosystem is also an important source of food for many species as well as excellent at sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere with global mangrove carbon storage is estimated at 34 million metric tons per year.
Seagrass meadows
Seagrasses form dense underwater meadows which are among the most productive ecosystems in the world. They provide habitats and food for a diversity of marine life comparable to coral reefs. This includes invertebrates like shrimp and crabs, cod and flatfish, marine mammals and birds. They provide refuges for endangered species such as seahorses, turtles, and dugongs. They function as nursery habitats for shrimps, scallops and many commercial fish species. Seagrass meadows provide coastal storm protection by the way their leaves absorb energy from waves as they hit the coast. They keep coastal waters healthy by absorbing bacteria and nutrients, and slow the speed of climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide into the sediment of the ocean floor.
Seagrasses evolved from marine algae which colonized land and became land plants, and then returned to the ocean about 100 million years ago. However, today seagrass meadows are being damaged by human activities such as pollution from land runoff, fishing boats that drag dredges or trawls across the meadows uprooting the grass, and overfishing which unbalances the ecosystem. Seagrass meadows are currently being destroyed at a rate of about two football fields every hour.
Kelp forests
Kelp forests occur worldwide throughout temperate and polar coastal oceans. In 2007, kelp forests were also discovered in tropical waters near Ecuador.
Physically formed by brown macroalgae, kelp forests provide a unique habitat for marine organisms and are a source for understanding many ecological processes. Over the last century, they have been the focus of extensive research, particularly in trophic ecology, and continue to provoke important ideas that are relevant beyond this unique ecosystem. For example, kelp forests can influence coastal oceanographic patterns and provide many ecosystem services.
However, the influence of humans has often contributed to kelp forest degradation. Of particular concern are the effects of overfishing nearshore ecosystems, which can release herbivores from their normal population regulation and result in the overgrazing of kelp and other algae. This can rapidly result in transitions to barren landscapes where relatively few species persist. Already due to the combined effects of overfishing and climate change, kelp forests have all but disappeared in many especially vulnerable places, such as Tasmania's east coast and the coast of Northern California. The implementation of marine protected areas is one management strategy useful for addressing such issues, since it may limit the impacts of fishing and buffer the ecosystem from additive effects of other environmental stressors.
Estuaries
Estuaries occur where there is a noticeable change in salinity between saltwater and freshwater sources. This is typically found where rivers meet the ocean or sea. The wildlife found within estuaries is unique as the water in these areas is brackish - a mix of freshwater flowing to the ocean and salty seawater. Other types of estuaries also exist and have similar characteristics as traditional brackish estuaries. The Great Lakes are a prime example. There, river water mixes with lake water and creates freshwater estuaries. Estuaries are extremely productive ecosystems that many humans and animal species rely on for various activities. This can be seen as, of the 32 largest cities in the world, 22 are located on estuaries as they provide many environmental and economic benefits such as crucial habitat for many species, and being economic hubs for many coastal communities. Estuaries also provide essential ecosystem services such as water filtration, habitat protection, erosion control, gas regulation nutrient cycling, and it even gives education, recreation and tourism opportunities to people.
Lagoons
Lagoons are areas that are separated from larger water by natural barriers such as coral reefs or sandbars. There are two types of lagoons, coastal and oceanic/atoll lagoons. A coastal lagoon is, as the definition above, simply a body of water that is separated from the ocean by a barrier. An atoll lagoon is a circular coral reef or several coral islands that surround a lagoon. Atoll lagoons are often much deeper than coastal lagoons. Most lagoons are very shallow meaning that they are greatly affected by changed in precipitation, evaporation and wind. This means that salinity and temperature are widely varied in lagoons and that they can have water that ranges from fresh to hypersaline. Lagoons can be found in on coasts all over the world, on every continent except Antarctica and is an extremely diverse habitat being home to a wide array of species including birds, fish, crabs, plankton and more. Lagoons are also important to the economy as they provide a wide array of ecosystem services in addition to being the home of so many different species. Some of these services include fisheries, nutrient cycling, flood protection, water filtration, and even human tradition.
Salt marsh
Salt marshes are a transition from the ocean to the land, where fresh and saltwater mix. The soil in these marshes is often made up of mud and a layer of organic material called peat. Peat is characterized as waterlogged and root-filled decomposing plant matter that often causes low oxygen levels (hypoxia). These hypoxic conditions causes growth of the bacteria that also gives salt marshes the sulfurous smell they are often known for. Salt marshes exist around the world and are needed for healthy ecosystems and a healthy economy. They are extremely productive ecosystems and they provide essential services for more than 75 percent of fishery species and protect shorelines from erosion and flooding. Salt marshes can be generally divided into the high marsh, low marsh, and the upland border. The low marsh is closer to the ocean, with it being flooded at nearly every tide except low tide. The high marsh is located between the low marsh and the upland border and it usually only flooded when higher than usual tides are present. The upland border is the freshwater edge of the marsh and is usually located at elevations slightly higher than the high marsh. This region is usually only flooded under extreme weather conditions and experiences much less waterlogged conditions and salt stress than other areas of the marsh.
Intertidal zones
Intertidal zones are the areas that are visible and exposed to air during low tide and covered up by saltwater during high tide. There are four physical divisions of the intertidal zone with each one having its distinct characteristics and wildlife. These divisions are the Spray zone, High intertidal zone, Middle Intertidal zone, and Low intertidal zone. The Spray zone is a damp area that is usually only reached by the ocean and submerged only under high tides or storms. The high intertidal zone is submerged at high tide but remains dry for long periods between high tides. Due to the large variance of conditions possible in this region, it is inhabited by resilient wildlife that can withstand these changes such as barnacles, marine snails, mussels and hermit crabs. Tides flow over the middle intertidal zone two times a day and this zone has a larger variety of wildlife. The low intertidal zone is submerged nearly all the time except during the lowest tides and life is more abundant here due to the protection that the water gives.
Ocean surface
Organisms that live freely at the surface, termed neuston, include keystone organisms like the golden seaweed Sargassum that makes up the Sargasso Sea, floating barnacles, marine snails, nudibranchs, and cnidarians. Many ecologically and economically important fish species live as or rely upon neuston. Species at the surface are not distributed uniformly; the ocean's surface harbours unique neustonic communities and ecoregions found at only certain latitudes and only in specific ocean basins. But the surface is also on the front line of climate change and pollution. Life on the ocean's surface connects worlds. From shallow waters to the deep sea, the open ocean to rivers and lakes, numerous terrestrial and marine species depend on the surface ecosystem and the organisms found there.
The ocean's surface acts like a skin between the atmosphere above and the water below, and harbours an ecosystem unique to this environment. This sun-drenched habitat can be defined as roughly one metre in depth, as nearly half of UV-B is attenuated within this first meter. Organisms here must contend with wave action and unique chemical and physical properties. The surface is utilised by a wide range of species, from various fish and cetaceans, to species that ride on ocean debris (termed rafters). Most prominently, the surface is home to a unique community of free-living organisms, termed neuston (from the Greek word, υεω, which means both to swim and to float. Floating organisms are also sometimes referred to as pleuston, though neuston is more commonly used). Despite the diversity and importance of the ocean's surface in connecting disparate habitats, and the risks it faces, not a lot is known about neustonic life.
A stream of airborne microorganisms circles the planet above weather systems but below commercial air lanes. Some peripatetic microorganisms are swept up from terrestrial dust storms, but most originate from marine microorganisms in sea spray. In 2018, scientists reported that hundreds of millions of viruses and tens of millions of bacteria are deposited daily on every square meter around the planet.
Deep sea and sea floor
The deep sea contains up to 95% of the space occupied by living organisms. Combined with the sea floor (or benthic zone), these two areas have yet to be fully explored and have their organisms documented.
Ecosystem services
In addition to providing many benefits to the natural world, marine ecosystems also provide social, economic, and biological ecosystem services to humans. Pelagic marine systems regulate the global climate, contribute to the water cycle, maintain biodiversity, provide food and energy resources, and create opportunities for recreation and tourism. Economically, marine systems support billions of dollars worth of capture fisheries, aquaculture, offshore oil and gas, and trade and shipping.
Ecosystem services fall into multiple categories, including supporting services, provisioning services, regulating services, and cultural services.
Threats
Human activities affect marine life and marine habitats through overfishing, habitat loss, the introduction of invasive species, ocean pollution, ocean acidification and ocean warming. These impact marine ecosystems and food webs and may result in consequences as yet unrecognised for the biodiversity and continuation of marine life forms.
According to the IPCC (2019), since 1950 "many marine species across various groups have undergone shifts in geographical range and seasonal activities in response to ocean warming, sea ice change and biogeochemical changes, such as oxygen loss, to their habitats."
It has been estimated only 13% of the ocean area remains as wilderness, mostly in open ocean areas rather than along the coast.Human exploitation and development
Coastal marine ecosystems experience growing population pressures with nearly 40% of people in the world living within 100 km of the coast. Humans often aggregate near coastal habitats to take advantage of ecosystem services. For example, coastal capture fisheries from mangroves and coral reef habitats are estimated to be worth a minimum of $34 billion per year. Yet, many of these habitats are either marginally protected or not protected. Mangrove area has declined worldwide by more than one-third since 1950, and 60% of the world's coral reefs are now immediately or directly threatened. Human development, aquaculture, and industrialization often lead to the destruction, replacement, or degradation of coastal habitats.
Moving offshore, pelagic marine systems are directly threatened by overfishing. Global fisheries landings peaked in the late 1980s, but are now declining, despite increasing fishing effort. Fish biomass and average trophic level of fisheries landing are decreasing, leading to declines in marine biodiversity. In particular, local extinctions have led to declines in large, long-lived, slow-growing species, and those that have narrow geographic ranges. Biodiversity declines can lead to associated declines in ecosystem services. A long-term study reports the decline of 74–92% of catch per unit effort of sharks in Australian coastline from the 1960s to 2010s.
Pollution
Marine pollution occurs when substances used or spread by humans, such as industrial, agricultural and residential waste, particles, noise, excess carbon dioxide or invasive organisms enter the ocean and cause harmful effects there. The majority of this waste (80%) comes from land-based activity, although marine transportation significantly contributes as well. Since most inputs come from land, either via the rivers, sewage or the atmosphere, it means that continental shelves are more vulnerable to pollution. Air pollution is also a contributing factor by carrying off iron, carbonic acid, nitrogen, silicon, sulfur, pesticides or dust particles into the ocean. The pollution often comes from nonpoint sources such as agricultural runoff, wind-blown debris, and dust. These nonpoint sources are largely due to runoff that enters the ocean through rivers, but wind-blown debris and dust can also play a role, as these pollutants can settle into waterways and oceans. Pathways of pollution include direct discharge, land runoff, ship pollution, atmospheric pollution and, potentially, deep sea mining.
The types of marine pollution can be grouped as pollution from marine debris, plastic pollution, including microplastics, ocean acidification, nutrient pollution, toxins and underwater noise. Plastic pollution in the ocean is a type of marine pollution by plastics, ranging in size from large original material such as bottles and bags, down to microplastics formed from the fragmentation of plastic material. Marine debris is mainly discarded human rubbish which floats on, or is suspended in the ocean. Plastic pollution is harmful to marine life.Invasive species
- Global aquarium trade
- Ballast water transport
- Aquaculture
Climate change
- Warming temperatures
- Increased frequency/intensity of storms
- Ocean acidification
- Sea level rise