A rocket (from Italian: rocchetto, lit. 'bobbin/spool') is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere.
Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity.
Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Significant scientific, interplanetary and industrial use did not occur until the 20th century, when rocketry was the enabling technology for the Space Age, including setting foot on the Moon. Rockets are now used for fireworks, missiles and other weaponry, ejection seats, launch vehicles for artificial satellites, human spaceflight, and space exploration.
Chemical rockets are the most common type of high power rocket, typically creating a high speed exhaust by the combustion of fuel with an oxidizer. The stored propellant can be a simple pressurized gas or a single liquid fuel that disassociates in the presence of a catalyst (monopropellant), two liquids that spontaneously react on contact (hypergolic propellants), two liquids that must be ignited to react (like kerosene (RP1) and liquid oxygen, used in most liquid-propellant rockets), a solid combination of fuel with oxidizer (solid fuel), or solid fuel with liquid or gaseous oxidizer (hybrid propellant system). Chemical rockets store a large amount of energy in an easily released form, and can be very dangerous. However, careful design, testing, construction and use minimizes risks.
History
In China, gunpowder-powered rockets evolved in medieval China under the Song dynasty by the 13th century. They also developed an early form of multiple rocket launcher during this time. The Mongols adopted Chinese rocket technology and the invention spread via the Mongol invasions to the Middle East and to Europe in the mid-13th century. According to Joseph Needham, the Song navy used rockets in a military exercise dated to 1245. Internal-combustion rocket propulsion is mentioned in a reference to 1264, recording that the "ground-rat", a type of firework, had frightened the Empress-Mother Gongsheng at a feast held in her honor by her son the Emperor Lizong. Subsequently, rockets are included in the military treatise Huolongjing, also known as the Fire Drake Manual, written by the Chinese artillery officer Jiao Yu in the mid-14th century. This text mentions the first known multistage rocket, the 'fire-dragon issuing from the water' (Huo long chu shui), thought to have been used by the Chinese navy.
Medieval and early modern rockets were used militarily as incendiary weapons in sieges. Between 1270 and 1280, Hasan al-Rammah wrote al-furusiyyah wa al-manasib al-harbiyya (The Book of Military Horsemanship and Ingenious War Devices), which included 107 gunpowder recipes, 22 of them for rockets. In Europe, Roger Bacon mentioned firecrackers made in various parts of the world in the Opus Majus of 1267. Between 1280 and 1300, the Liber Ignium gave instructions for constructing devices that are similar to firecrackers based on second hand accounts. Konrad Kyeser described rockets in his military treatise Bellifortis around 1405.
The name "rocket" comes from the Italian rocchetta, meaning "bobbin" or "little spindle", given due to the similarity in shape to the bobbin or spool used to hold the thread from a spinning wheel. Leonhard Fronsperger and Conrad Haas adopted the Italian term into German in the mid-16th century; "rocket" appears in English by the early 17th century. Artis Magnae Artilleriae pars prima, an important early modern work on rocket artillery, by Casimir Siemienowicz, was first printed in Amsterdam in 1650.
The Mysorean rockets were the first successful iron-cased rockets, developed in the late 18th century in the Kingdom of Mysore (part of present-day India) under the rule of Hyder Ali.
The Congreve rocket was a British weapon designed and developed by Sir William Congreve in 1804. This rocket was based directly on the Mysorean rockets, used compressed powder and was fielded in the Napoleonic Wars. It was Congreve rockets to which Francis Scott Key was referring, when he wrote of the "rockets' red glare" while held captive on a British ship that was laying siege to Fort McHenry in 1814. Together, the Mysorean and British innovations increased the effective range of military rockets from 100 to 2,000 yards (91 to 1,829 m).
The first mathematical treatment of the dynamics of rocket propulsion is due to William Moore (1813). In 1814 Congreve published a book in which he discussed the use of multiple rocket launching apparatus. In 1815 Alexander Dmitrievich Zasyadko constructed rocket-launching platforms, which allowed rockets to be fired in salvos (6 rockets at a time), and gun-laying devices. William Hale in 1844 greatly increased the accuracy of rocket artillery. Edward Mounier Boxer further improved the Congreve rocket in 1865.
William Leitch first proposed the concept of using rockets to enable human spaceflight in 1861. Leitch's rocket spaceflight description was first provided in his 1861 essay "A Journey Through Space", which was later published in his book God's Glory in the Heavens (1862). Konstantin Tsiolkovsky later (in 1903) also conceived this idea, and extensively developed a body of theory that has provided the foundation for subsequent spaceflight development.
The British Royal Flying Corps designed a guided rocket during World War I. Archibald Low stated "...in 1917 the Experimental Works designed an electrically steered rocket… Rocket experiments were conducted under my own patents with the help of Cdr. Brock." The patent "Improvements in Rockets" was raised in July 1918 but not published until February 1923 for security reasons. Firing and guidance controls could be either wire or wireless. The propulsion and guidance rocket eflux emerged from the deflecting cowl at the nose.
In 1920, Professor Robert Goddard of Clark University published proposed improvements to rocket technology in A Method of Reaching Extreme Altitudes. In 1923, Hermann Oberth (1894–1989) published Die Rakete zu den Planetenräumen (The Rocket into Planetary Space). Modern rockets originated in 1926 when Goddard attached a supersonic (de Laval) nozzle to a high pressure combustion chamber. These nozzles turn the hot gas from the combustion chamber into a cooler, hypersonic, highly directed jet of gas, more than doubling the thrust and raising the engine efficiency from 2% to 64%. His use of liquid propellants instead of gunpowder greatly lowered the weight and increased the effectiveness of rockets.
In 1921 the Soviet research and development laboratory Gas Dynamics Laboratory began developing solid-propellant rockets, which resulted in the first launch in 1928, which flew for approximately 1,300 metres. These rockets were used in 1931 for the world's first successful use of rockets for jet-assisted takeoff of aircraft and became the prototypes for the Katyusha rocket launcher, which were used during World War II.
In 1929, Fritz Lang's German science fiction film Woman in the Moon was released. It showcased the use of a multi-stage rocket, and also pioneered the concept of a rocket launch pad (a rocket standing upright against a tall building before launch having been slowly rolled into place) and the rocket-launch countdown clock. The Guardian film critic Stephen Armstrong states Lang "created the rocket industry". Lang was inspired by the 1923 book The Rocket into Interplanetary Space by Hermann Oberth, who became the film's scientific adviser and later an important figure in the team that developed the V-2 rocket. The film was thought to be so realistic that it was banned by the Nazis when they came to power for fear it would reveal secrets about the V-2 rockets.
In 1943 production of the V-2 rocket began in Germany. It was designed by the Peenemünde Army Research Center with Wernher von Braun serving as the technical director. The V-2 became the first artificial object to travel into space by crossing the Kármán line with the vertical launch of MW 18014 on 20 June 1944. Doug Millard, space historian and curator of space technology at the Science Museum, London, where a V-2 is exhibited in the main exhibition hall, states: "The V-2 was a quantum leap of technological change. We got to the Moon using V-2 technology but this was technology that was developed with massive resources, including some particularly grim ones. The V-2 programme was hugely expensive in terms of lives, with the Nazis using slave labour to manufacture these rockets". In parallel with the German guided-missile programme, rockets were also used on aircraft, either for assisting horizontal take-off (RATO), vertical take-off (Bachem Ba 349 "Natter") or for powering them (Me 163, see list of World War II guided missiles of Germany). The Allies' rocket programs were less technological, relying mostly on unguided missiles like the Soviet Katyusha rocket in the artillery role, and the American anti tank bazooka projectile. These used solid chemical propellants.
The Americans captured a large number of German rocket scientists, including Wernher von Braun, in 1945, and brought them to the United States as part of Operation Paperclip. After World War II scientists used rockets to study high-altitude conditions, by radio telemetry of temperature and pressure of the atmosphere, detection of cosmic rays, and further techniques; note too the Bell X-1, the first crewed vehicle to break the sound barrier (1947). Independently, in the Soviet Union's space program research continued under the leadership of the chief designer Sergei Korolev (1907–1966).
During the Cold War rockets became extremely important militarily with the development of modern intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). The 1960s saw rapid development of rocket technology, particularly in the Soviet Union (Vostok, Soyuz, Proton) and in the United States (e.g. the X-15). Rockets came into use for space exploration. American crewed programs (Project Mercury, Project Gemini and later the Apollo programme) culminated in 1969 with the first crewed landing on the Moon – using equipment launched by the Saturn V rocket.
Types
Rocket vehicles are often constructed in the archetypal tall thin "rocket" shape that takes off vertically, but there are actually many different types of rockets including:
- tiny models such as balloon rockets, water rockets, skyrockets or small solid rockets that can be purchased at a hobby store
- missiles
- space rockets such as the enormous Saturn V used for the Apollo program
- rocket cars
- rocket bike
- rocket-powered aircraft (including rocket assisted takeoff of conventional aircraft – RATO)
- rocket sleds
- rocket trains
- rocket torpedoes
- rocket-powered jet packs
- rapid escape systems such as ejection seats and launch escape systems
- space probes
Design
A rocket design can be as simple as a cardboard tube filled with black powder, but to make an efficient, accurate rocket or missile involves overcoming a number of difficult problems. The main difficulties include cooling the combustion chamber, pumping the fuel (in the case of a liquid fuel), and controlling and correcting the direction of motion.
Components
Rockets consist of a propellant, a place to put propellant (such as a propellant tank), and a nozzle. They may also have one or more rocket engines, directional stabilization device(s) (such as fins, vernier engines or engine gimbals for thrust vectoring, gyroscopes) and a structure (typically monocoque) to hold these components together. Rockets intended for high speed atmospheric use also have an aerodynamic fairing such as a nose cone, which usually holds the payload.
As well as these components, rockets can have any number of other components, such as wings (rocketplanes), parachutes, wheels (rocket cars), even, in a sense, a person (rocket belt). Vehicles frequently possess navigation systems and guidance systems that typically use satellite navigation and inertial navigation systems.
Engines
Rocket engines employ the principle of jet propulsion. The rocket engines powering rockets come in a great variety of different types; a comprehensive list can be found in the main article, Rocket engine. Most current rockets are chemically powered rockets (usually internal combustion engines, but some employ a decomposing monopropellant) that emit a hot exhaust gas. A rocket engine can use gas propellants, solid propellant, liquid propellant, or a hybrid mixture of both solid and liquid. Some rockets use heat or pressure that is supplied from a source other than the chemical reaction of propellant(s), such as steam rockets, solar thermal rockets, nuclear thermal rocket engines or simple pressurized rockets such as water rocket or cold gas thrusters. With combustive propellants a chemical reaction is initiated between the fuel and the oxidizer in the combustion chamber, and the resultant hot gases accelerate out of a rocket engine nozzle (or nozzles) at the rearward-facing end of the rocket. The acceleration of these gases through the engine exerts force ("thrust") on the combustion chamber and nozzle, propelling the vehicle (according to Newton's Third Law). This actually happens because the force (pressure times area) on the combustion chamber wall is unbalanced by the nozzle opening; this is not the case in any other direction. The shape of the nozzle also generates force by directing the exhaust gas along the axis of the rocket.
Propellant
Rocket propellant is mass that is stored, usually in some form of propellant tank or casing, prior to being used as the propulsive mass that is ejected from a rocket engine in the form of a fluid jet to produce thrust. For chemical rockets often the propellants are a fuel such as liquid hydrogen or kerosene burned with an oxidizer such as liquid oxygen or nitric acid to produce large volumes of very hot gas. The oxidiser is either kept separate and mixed in the combustion chamber, or comes premixed, as with solid rockets.
Sometimes the propellant is not burned but still undergoes a chemical reaction, and can be a 'monopropellant' such as hydrazine, nitrous oxide or hydrogen peroxide that can be catalytically decomposed to hot gas.
Alternatively, an inert propellant can be used that can be externally heated, such as in steam rocket, solar thermal rocket or nuclear thermal rockets.
For smaller, low performance rockets such as attitude control thrusters where high performance is less necessary, a pressurised fluid is used as propellant that simply escapes the spacecraft through a propelling nozzle.
Pendulum rocket fallacy
The first liquid-fuel rocket, constructed by Robert H. Goddard, differed significantly from modern rockets. The rocket engine was at the top and the fuel tank at the bottom of the rocket, based on Goddard's belief that the rocket would achieve stability by "hanging" from the engine like a pendulum in flight. However, the rocket veered off course and crashed 184 feet (56 m) away from the launch site, indicating that the rocket was no more stable than one with the rocket engine at the base.
Uses
Rockets or other similar reaction devices carrying their own propellant must be used when there is no other substance (land, water, or air) or force (gravity, magnetism, light) that a vehicle may usefully employ for propulsion, such as in space. In these circumstances, it is necessary to carry all the propellant to be used.
However, they are also useful in other situations:
Military
Some military weapons use rockets to propel warheads to their targets. A rocket and its payload together are generally referred to as a missile when the weapon has a guidance system (not all missiles use rocket engines, some use other engines such as jets) or as a rocket if it is unguided. Anti-tank and anti-aircraft missiles use rocket engines to engage targets at high speed at a range of several miles, while intercontinental ballistic missiles can be used to deliver multiple nuclear warheads from thousands of miles, and anti-ballistic missiles try to stop them. Rockets have also been tested for reconnaissance, such as the Ping-Pong rocket, which was launched to surveil enemy targets, however, recon rockets have never come into wide use in the military.
Science and research
Sounding rockets are commonly used to carry instruments that take readings from 50 kilometers (31 mi) to 1,500 kilometers (930 mi) above the surface of the Earth. The first images of Earth from space were obtained from a V-2 rocket in 1946 (flight #13).
Rocket engines are also used to propel rocket sleds along a rail at extremely high speed. The world record for this is Mach 8.5.
Spaceflight
Larger rockets are normally launched from a launch pad that provides stable support until a few seconds after ignition. Due to their high exhaust velocity—2,500 to 4,500 m/s (9,000 to 16,200 km/h; 5,600 to 10,100 mph)—rockets are particularly useful when very high speeds are required, such as orbital speed at approximately 7,800 m/s (28,000 km/h; 17,000 mph). Spacecraft delivered into orbital trajectories become artificial satellites, which are used for many commercial purposes. Indeed, rockets remain the only way to launch spacecraft into orbit and beyond. They are also used to rapidly accelerate spacecraft when they change orbits or de-orbit for landing. Also, a rocket may be used to soften a hard parachute landing immediately before touchdown (see retrorocket).
Rescue
Rockets were used to propel a line to a stricken ship so that a Breeches buoy can be used to rescue those on board. Rockets are also used to launch emergency flares.
Some crewed rockets, notably the Saturn V and Soyuz, have launch escape systems. This is a small, usually solid rocket that is capable of pulling the crewed capsule away from the main vehicle towards safety at a moments notice. These types of systems have been operated several times, both in testing and in flight, and operated correctly each time.
This was the case when the Safety Assurance System (Soviet nomenclature) successfully pulled away the L3 capsule during three of the four failed launches of the Soviet moon rocket, N1 vehicles 3L, 5L and 7L. In all three cases the capsule, albeit uncrewed, was saved from destruction. Only the three aforementioned N1 rockets had functional Safety Assurance Systems. The outstanding vehicle, 6L, had dummy upper stages and therefore no escape system giving the N1 booster a 100% success rate for egress from a failed launch.
A successful escape of a crewed capsule occurred when Soyuz T-10, on a mission to the Salyut 7 space station, exploded on the pad.
Solid rocket propelled ejection seats are used in many military aircraft to propel crew away to safety from a vehicle when flight control is lost.
Hobby, sport, and entertainment
A model rocket is a small rocket designed to reach low altitudes (e.g., 100–500 m (330–1,640 ft) for 30 g (1.1 oz) model) and be recovered by a variety of means.
According to the United States National Association of Rocketry (nar) Safety Code, model rockets are constructed of paper, wood, plastic and other lightweight materials. The code also provides guidelines for motor use, launch site selection, launch methods, launcher placement, recovery system design and deployment and more. Since the early 1960s, a copy of the Model Rocket Safety Code has been provided with most model rocket kits and motors. Despite its inherent association with extremely flammable substances and objects with a pointed tip traveling at high speeds, model rocketry historically has proven to be a very safe hobby and has been credited as a significant source of inspiration for children who eventually become scientists and engineers.
Hobbyists build and fly a wide variety of model rockets. Many companies produce model rocket kits and parts but due to their inherent simplicity some hobbyists have been known to make rockets out of almost anything. Rockets are also used in some types of consumer and professional fireworks. A water rocket is a type of model rocket using water as its reaction mass. The pressure vessel (the engine of the rocket) is usually a used plastic soft drink bottle. The water is forced out by a pressurized gas, typically compressed air. It is an example of Newton's third law of motion.
The scale of amateur rocketry can range from a small rocket launched in one's own backyard to a rocket that reached space. Amateur rocketry is split into three categories according to total engine impulse: low-power, mid-power, and high-power.
Hydrogen peroxide rockets are used to power jet packs, and have been used to power cars and a rocket car holds the all time (albeit unofficial) drag racing record.
Corpulent Stump is the most powerful non-commercial rocket ever launched on an Aerotech engine in the United Kingdom.
Flight
Launches for orbital spaceflights, or into interplanetary space, are usually from a fixed location on the ground, but would also be possible from an aircraft or ship.
Rocket launch technologies include the entire set of systems needed to successfully launch a vehicle, not just the vehicle itself, but also the firing control systems, mission control center, launch pad, ground stations, and tracking stations needed for a successful launch or recovery or both. These are often collectively referred to as the "ground segment".
Orbital launch vehicles commonly take off vertically, and then begin to progressively lean over, usually following a gravity turn trajectory.
Once above the majority of the atmosphere, the vehicle then angles the rocket jet, pointing it largely horizontally but somewhat downwards, which permits the vehicle to gain and then maintain altitude while increasing horizontal speed. As the speed grows, the vehicle will become more and more horizontal until at orbital speed, the engine will cut off.
All current vehicles stage, that is, jettison hardware on the way to orbit. Although vehicles have been proposed which would be able to reach orbit without staging, none have ever been constructed, and, if powered only by rockets, the exponentially increasing fuel requirements of such a vehicle would make its useful payload tiny or nonexistent. Most current and historical launch vehicles "expend" their jettisoned hardware, typically by allowing it to crash into the ocean, but some have recovered and reused jettisoned hardware, either by parachute or by propulsive landing.
When launching a spacecraft to orbit, a "dogleg" is a guided, powered turn during ascent phase that causes a rocket's flight path to deviate from a "straight" path. A dogleg is necessary if the desired launch azimuth, to reach a desired orbital inclination, would take the ground track over land (or over a populated area, e.g. Russia usually does launch over land, but over unpopulated areas), or if the rocket is trying to reach an orbital plane that does not reach the latitude of the launch site. Doglegs are undesirable due to extra onboard fuel required, causing heavier load, and a reduction of vehicle performance.
Noise
Rocket exhaust generates a significant amount of acoustic energy. As the supersonic exhaust collides with the ambient air, shock waves are formed. The sound intensity from these shock waves depends on the size of the rocket as well as the exhaust velocity. The sound intensity of large, high performance rockets could potentially kill at close range.
The Space Shuttle generated 180 dB of noise around its base. To combat this, NASA developed a sound suppression system which can flow water at rates up to 900,000 gallons per minute (57 m3/s) onto the launch pad. The water reduces the noise level from 180 dB down to 142 dB (the design requirement is 145 dB). Without the sound suppression system, acoustic waves would reflect off of the launch pad towards the rocket, vibrating the sensitive payload and crew. These acoustic waves can be so severe as to damage or destroy the rocket.
Noise is generally most intense when a rocket is close to the ground, since the noise from the engines radiates up away from the jet, as well as reflecting off the ground. This noise can be reduced somewhat by flame trenches with roofs, by water injection around the jet and by deflecting the jet at an angle.
For crewed rockets various methods are used to reduce the sound intensity for the passengers, and typically the placement of the astronauts far away from the rocket engines helps significantly. For the passengers and crew, when a vehicle goes supersonic the sound cuts off as the sound waves are no longer able to keep up with the vehicle.
Physics
Operation
The effect of the combustion of propellant in the rocket engine is to increase the internal energy of the resulting gases, utilizing the stored chemical energy in the fuel. As the internal energy increases, pressure increases, and a nozzle is used to convert this energy into a directed kinetic energy. This produces thrust against the ambient environment to which these gases are released. The ideal direction of motion of the exhaust is in the direction so as to cause thrust. At the top end of the combustion chamber the hot, energetic gas fluid cannot move forward, and so, it pushes upward against the top of the rocket engine's combustion chamber. As the combustion gases approach the exit of the combustion chamber, they increase in speed. The effect of the convergent part of the rocket engine nozzle on the high pressure fluid of combustion gases, is to cause the gases to accelerate to high speed. The higher the speed of the gases, the lower the pressure of the gas (Bernoulli's principle or conservation of energy) acting on that part of the combustion chamber. In a properly designed engine, the flow will reach Mach 1 at the throat of the nozzle. At which point the speed of the flow increases. Beyond the throat of the nozzle, a bell shaped expansion part of the engine allows the gases that are expanding to push against that part of the rocket engine. Thus, the bell part of the nozzle gives additional thrust. Simply expressed, for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, according to Newton's third law with the result that the exiting gases produce the reaction of a force on the rocket causing it to accelerate the rocket.
In a closed chamber, the pressures are equal in each direction and no acceleration occurs. If an opening is provided in the bottom of the chamber then the pressure is no longer acting on the missing section. This opening permits the exhaust to escape. The remaining pressures give a resultant thrust on the side opposite the opening, and these pressures are what push the rocket along.
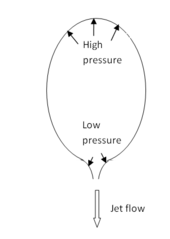
The shape of the nozzle is important. Consider a balloon propelled by air coming out of a tapering nozzle. In such a case the combination of air pressure and viscous friction is such that the nozzle does not push the balloon but is pulled by it. Using a convergent/divergent nozzle gives more force since the exhaust also presses on it as it expands outwards, roughly doubling the total force. If propellant gas is continuously added to the chamber then these pressures can be maintained for as long as propellant remains. Note that in the case of liquid propellant engines, the pumps moving the propellant into the combustion chamber must maintain a pressure larger than the combustion chamber – typically on the order of 100 atmospheres.
As a side effect, these pressures on the rocket also act on the exhaust in the opposite direction and accelerate this exhaust to very high speeds (according to Newton's Third Law). From the principle of conservation of momentum the speed of the exhaust of a rocket determines how much momentum increase is created for a given amount of propellant. This is called the rocket's specific impulse. Because a rocket, propellant and exhaust in flight, without any external perturbations, may be considered as a closed system, the total momentum is always constant. Therefore, the faster the net speed of the exhaust in one direction, the greater the speed of the rocket can achieve in the opposite direction. This is especially true since the rocket body's mass is typically far lower than the final total exhaust mass.
Forces on a rocket in flight
The general study of the forces on a rocket is part of the field of ballistics. Spacecraft are further studied in the subfield of astrodynamics.
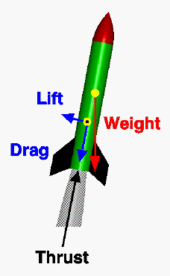
Flying rockets are primarily affected by the following:
- Thrust from the engine(s)
- Gravity from celestial bodies
- Drag if moving in atmosphere
- Lift; usually relatively small effect except for rocket-powered aircraft
In addition, the inertia and centrifugal pseudo-force can be significant due to the path of the rocket around the center of a celestial body; when high enough speeds in the right direction and altitude are achieved a stable orbit or escape velocity is obtained.
These forces, with a stabilizing tail (the empennage) present will, unless deliberate control efforts are made, naturally cause the vehicle to follow a roughly parabolic trajectory termed a gravity turn, and this trajectory is often used at least during the initial part of a launch. (This is true even if the rocket engine is mounted at the nose.) Vehicles can thus maintain low or even zero angle of attack, which minimizes transverse stress on the launch vehicle, permitting a weaker, and hence lighter, launch vehicle.
Drag
Drag is a force opposite to the direction of the rocket's motion relative to any air it is moving through. This slows the speed of the vehicle and produces structural loads. The deceleration forces for fast-moving rockets are calculated using the drag equation.
Drag can be minimised by an aerodynamic nose cone and by using a shape with a high ballistic coefficient (the "classic" rocket shape—long and thin), and by keeping the rocket's angle of attack as low as possible.
During a launch, as the vehicle speed increases, and the atmosphere thins, there is a point of maximum aerodynamic drag called max Q. This determines the minimum aerodynamic strength of the vehicle, as the rocket must avoid buckling under these forces.
Net thrust
- Underexpanded
- Ideally expanded
- Overexpanded
- Grossly overexpanded
A typical rocket engine can handle a significant fraction of its own mass in propellant each second, with the propellant leaving the nozzle at several kilometres per second. This means that the thrust-to-weight ratio of a rocket engine, and often the entire vehicle can be very high, in extreme cases over 100. This compares with other jet propulsion engines that can exceed 5 for some of the better engines.
It can be shown that the net thrust of a rocket is:
where:
The effective exhaust velocity is more or less the speed the exhaust leaves the vehicle, and in the vacuum of space, the effective exhaust velocity is often equal to the actual average exhaust speed along the thrust axis. However, the effective exhaust velocity allows for various losses, and notably, is reduced when operated within an atmosphere.
The rate of propellant flow through a rocket engine is often deliberately varied over a flight, to provide a way to control the thrust and thus the airspeed of the vehicle. This, for example, allows minimization of aerodynamic losses and can limit the increase of g-forces due to the reduction in propellant load.
Total impulse
Impulse is defined as a force acting on an object over time, which in the absence of opposing forces (gravity and aerodynamic drag), changes the momentum (integral of mass and velocity) of the object. As such, it is the best performance class (payload mass and terminal velocity capability) indicator of a rocket, rather than takeoff thrust, mass, or "power". The total impulse of a rocket (stage) burning its propellant is:
When there is fixed thrust, this is simply:
The total impulse of a multi-stage rocket is the sum of the impulses of the individual stages.
Specific impulse
| Rocket | Propellants | Isp, vacuum (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Space Shuttle liquid engines |
LOX/LH2 | 453 |
| Space Shuttle solid motors |
APCP | 268 |
| Space Shuttle OMS |
NTO/MMH | 313 |
| Saturn V stage 1 |
LOX/RP-1 | 304 |
As can be seen from the thrust equation, the effective speed of the exhaust controls the amount of thrust produced from a particular quantity of fuel burnt per second.
An equivalent measure, the net impulse per weight unit of propellant expelled, is called specific Impulse, , and this is one of the most important figures that describes a rocket's performance. It is defined such that it is related to the effective exhaust velocity by:
where:
Thus, the greater the specific impulse, the greater the net thrust and performance of the engine. is determined by measurement while testing the engine. In practice the effective exhaust velocities of rockets varies but can be extremely high, ~4500 m/s, about 15 times the sea level speed of sound in air.
Delta-v (rocket equation)
The delta-v capacity of a rocket is the theoretical total change in velocity that a rocket can achieve without any external interference (without air drag or gravity or other forces).
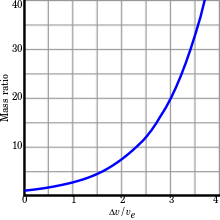
When is constant, the delta-v that a rocket vehicle can provide can be calculated from the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation:
where:
When launched from the Earth practical delta-vs for a single rockets carrying payloads can be a few km/s. Some theoretical designs have rockets with delta-vs over 9 km/s.
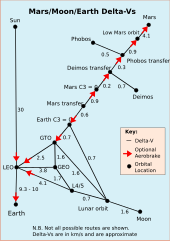
The required delta-v can also be calculated for a particular manoeuvre; for example the delta-v to launch from the surface of the Earth to low Earth orbit is about 9.7 km/s, which leaves the vehicle with a sideways speed of about 7.8 km/s at an altitude of around 200 km. In this manoeuvre about 1.9 km/s is lost in air drag, gravity drag and gaining altitude.
The ratio is sometimes called the mass ratio.
Mass ratios
Almost all of a launch vehicle's mass consists of propellant. Mass ratio is, for any 'burn', the ratio between the rocket's initial mass and its final mass. Everything else being equal, a high mass ratio is desirable for good performance, since it indicates that the rocket is lightweight and hence performs better, for essentially the same reasons that low weight is desirable in sports cars.
Rockets as a group have the highest thrust-to-weight ratio of any type of engine; and this helps vehicles achieve high mass ratios, which improves the performance of flights. The higher the ratio, the less engine mass is needed to be carried. This permits the carrying of even more propellant, enormously improving the delta-v. Alternatively, some rockets such as for rescue scenarios or racing carry relatively little propellant and payload and thus need only a lightweight structure and instead achieve high accelerations. For example, the Soyuz escape system can produce 20 g.
Achievable mass ratios are highly dependent on many factors such as propellant type, the design of engine the vehicle uses, structural safety margins and construction techniques.
The highest mass ratios are generally achieved with liquid rockets, and these types are usually used for orbital launch vehicles, a situation which calls for a high delta-v. Liquid propellants generally have densities similar to water (with the notable exceptions of liquid hydrogen and liquid methane), and these types are able to use lightweight, low pressure tanks and typically run high-performance turbopumps to force the propellant into the combustion chamber.
Some notable mass fractions are found in the following table (some aircraft are included for comparison purposes):
| Vehicle | Takeoff mass | Final mass | Mass ratio | Mass fraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ariane 5 (vehicle + payload) | 746,000 kg (~1,645,000 lb) | 2,700 kg + 16,000 kg (~6,000 lb + ~35,300 lb) | 39.9 | 0.975 |
| Titan 23G first stage | 117,020 kg (258,000 lb) | 4,760 kg (10,500 lb) | 24.6 | 0.959 |
| Saturn V | 3,038,500 kg (~6,700,000 lb) | 13,300 kg + 118,000 kg (~29,320 lb + ~260,150 lb) | 23.1 | 0.957 |
| Space Shuttle (vehicle + payload) | 2,040,000 kg (~4,500,000 lb) | 104,000 kg + 28,800 kg (~230,000 lb + ~63,500 lb) | 15.4 | 0.935 |
| Saturn 1B (stage only) | 448,648 kg (989,100 lb) | 41,594 kg (91,700 lb) | 10.7 | 0.907 |
| Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer | 10,024.39 kg (22,100 lb) | 1,678.3 kg (3,700 lb) | 6.0 | 0.83 |
| V-2 | 13,000 kg (~28,660 lb) (12.8 ton) |
|
3.85 | 0.74 |
| X-15 | 15,420 kg (34,000 lb) | 6,620 kg (14,600 lb) | 2.3 | 0.57 |
| Concorde | ~181,000 kg (400,000 lb) |
|
2 | 0.5 |
| Boeing 747 | ~363,000 kg (800,000 lb) |
|
2 | 0.5 |
Staging
Thus far, the required velocity (delta-v) to achieve orbit has been unattained by any single rocket because the propellant, tankage, structure, guidance, valves and engines and so on, take a particular minimum percentage of take-off mass that is too great for the propellant it carries to achieve that delta-v carrying reasonable payloads. Since Single-stage-to-orbit has so far not been achievable, orbital rockets always have more than one stage.
For example, the first stage of the Saturn V, carrying the weight of the upper stages, was able to achieve a mass ratio of about 10, and achieved a specific impulse of 263 seconds. This gives a delta-v of around 5.9 km/s whereas around 9.4 km/s delta-v is needed to achieve orbit with all losses allowed for.
This problem is frequently solved by staging—the rocket sheds excess weight (usually empty tankage and associated engines) during launch. Staging is either serial where the rockets light after the previous stage has fallen away, or parallel, where rockets are burning together and then detach when they burn out.
The maximum speeds that can be achieved with staging is theoretically limited only by the speed of light. However the payload that can be carried goes down geometrically with each extra stage needed, while the additional delta-v for each stage is simply additive.
Acceleration and thrust-to-weight ratio
From Newton's second law, the acceleration, , of a vehicle is simply:
where m is the instantaneous mass of the vehicle and is the net force acting on the rocket (mostly thrust, but air drag and other forces can play a part).
As the remaining propellant decreases, rocket vehicles become lighter and their acceleration tends to increase until the propellant is exhausted. This means that much of the speed change occurs towards the end of the burn when the vehicle is much lighter. However, the thrust can be throttled to offset or vary this if needed. Discontinuities in acceleration also occur when stages burn out, often starting at a lower acceleration with each new stage firing.
Peak accelerations can be increased by designing the vehicle with a reduced mass, usually achieved by a reduction in the fuel load and tankage and associated structures, but obviously this reduces range, delta-v and burn time. Still, for some applications that rockets are used for, a high peak acceleration applied for just a short time is highly desirable.
The minimal mass of vehicle consists of a rocket engine with minimal fuel and structure to carry it. In that case the thrust-to-weight ratio of the rocket engine limits the maximum acceleration that can be designed. It turns out that rocket engines generally have truly excellent thrust to weight ratios (137 for the NK-33 engine; some solid rockets are over 1000 ), and nearly all really high-g vehicles employ or have employed rockets.
The high accelerations that rockets naturally possess means that rocket vehicles are often capable of vertical takeoff, and in some cases, with suitable guidance and control of the engines, also vertical landing. For these operations to be done it is necessary for a vehicle's engines to provide more than the local gravitational acceleration.
Energy
Energy efficiency
The energy density of a typical rocket propellant is often around one-third that of conventional hydrocarbon fuels; the bulk of the mass is (often relatively inexpensive) oxidizer. Nevertheless, at take-off the rocket has a great deal of energy in the fuel and oxidizer stored within the vehicle. It is of course desirable that as much of the energy of the propellant end up as kinetic or potential energy of the body of the rocket as possible.
Energy from the fuel is lost in air drag and gravity drag and is used for the rocket to gain altitude and speed. However, much of the lost energy ends up in the exhaust.
In a chemical propulsion device, the engine efficiency is simply the ratio of the kinetic power of the exhaust gases and the power available from the chemical reaction:
100% efficiency within the engine (engine efficiency ) would mean that all the heat energy of the combustion products is converted into kinetic energy of the jet. This is not possible, but the near-adiabatic high expansion ratio nozzles that can be used with rockets come surprisingly close: when the nozzle expands the gas, the gas is cooled and accelerated, and an energy efficiency of up to 70% can be achieved. Most of the rest is heat energy in the exhaust that is not recovered. The high efficiency is a consequence of the fact that rocket combustion can be performed at very high temperatures and the gas is finally released at much lower temperatures, and so giving good Carnot efficiency.
However, engine efficiency is not the whole story. In common with the other jet-based engines, but particularly in rockets due to their high and typically fixed exhaust speeds, rocket vehicles are extremely inefficient at low speeds irrespective of the engine efficiency. The problem is that at low speeds, the exhaust carries away a huge amount of kinetic energy rearward. This phenomenon is termed propulsive efficiency ().
However, as speeds rise, the resultant exhaust speed goes down, and the overall vehicle energetic efficiency rises, reaching a peak of around 100% of the engine efficiency when the vehicle is travelling exactly at the same speed that the exhaust is emitted. In this case the exhaust would ideally stop dead in space behind the moving vehicle, taking away zero energy, and from conservation of energy, all the energy would end up in the vehicle. The efficiency then drops off again at even higher speeds as the exhaust ends up traveling forwards – trailing behind the vehicle.
From these principles it can be shown that the propulsive efficiency for a rocket moving at speed with an exhaust velocity is:
And the overall (instantaneous) energy efficiency is:
For example, from the equation, with an of 0.7, a rocket flying at Mach 0.85 (which most aircraft cruise at) with an exhaust velocity of Mach 10, would have a predicted overall energy efficiency of 5.9%, whereas a conventional, modern, air-breathing jet engine achieves closer to 35% efficiency. Thus a rocket would need about 6x more energy; and allowing for the specific energy of rocket propellant being around one third that of conventional air fuel, roughly 18x more mass of propellant would need to be carried for the same journey. This is why rockets are rarely if ever used for general aviation.
Since the energy ultimately comes from fuel, these considerations mean that rockets are mainly useful when a very high speed is required, such as ICBMs or orbital launch. For example, NASA's Space Shuttle fired its engines for around 8.5 minutes, consuming 1,000 tonnes of solid propellant (containing 16% aluminium) and an additional 2,000,000 litres of liquid propellant (106,261 kg of liquid hydrogen fuel) to lift the 100,000 kg vehicle (including the 25,000 kg payload) to an altitude of 111 km and an orbital velocity of 30,000 km/h. At this altitude and velocity, the vehicle had a kinetic energy of about 3 TJ and a potential energy of roughly 200 GJ. Given the initial energy of 20 TJ, the Space Shuttle was about 16% energy efficient at launching the orbiter.
Thus jet engines, with a better match between speed and jet exhaust speed (such as turbofans—in spite of their worse )—dominate for subsonic and supersonic atmospheric use, while rockets work best at hypersonic speeds. On the other hand, rockets serve in many short-range relatively low speed military applications where their low-speed inefficiency is outweighed by their extremely high thrust and hence high accelerations.
Oberth effect
One subtle feature of rockets relates to energy. A rocket stage, while carrying a given load, is capable of giving a particular delta-v. This delta-v means that the speed increases (or decreases) by a particular amount, independent of the initial speed. However, because kinetic energy is a square law on speed, this means that the faster the rocket is travelling before the burn the more orbital energy it gains or loses.
This fact is used in interplanetary travel. It means that the amount of delta-v to reach other planets, over and above that to reach escape velocity can be much less if the delta-v is applied when the rocket is travelling at high speeds, close to the Earth or other planetary surface; whereas waiting until the rocket has slowed at altitude multiplies up the effort required to achieve the desired trajectory.
Safety, reliability and accidents
The reliability of rockets, as for all physical systems, is dependent on the quality of engineering design and construction.
Because of the enormous chemical energy in rocket propellants (greater energy by weight than explosives, but lower than gasoline), consequences of accidents can be severe. Most space missions have some problems. In 1986, following the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, American physicist Richard Feynman, having served on the Rogers Commission, estimated that the chance of an unsafe condition for a launch of the Shuttle was very roughly 1%; more recently the historical per person-flight risk in orbital spaceflight has been calculated to be around 2% or 4%.
In May 2003 the astronaut office made clear its position on the need and feasibility of improving crew safety for future NASA crewed missions indicating their "consensus that an order of magnitude reduction in the risk of human life during ascent, compared to the Space Shuttle, is both achievable with current technology and consistent with NASA's focus on steadily improving rocket reliability".
Costs and economics
The costs of rockets can be roughly divided into propellant costs, the costs of obtaining and/or producing the 'dry mass' of the rocket, and the costs of any required support equipment and facilities.
Most of the takeoff mass of a rocket is normally propellant. However propellant is seldom more than a few times more expensive than gasoline per kilogram (as of 2009 gasoline was about $1/kg [$0.45/lb] or less), and although substantial amounts are needed, for all but the very cheapest rockets, it turns out that the propellant costs are usually comparatively small, although not completely negligible. With liquid oxygen costing $0.15 per kilogram ($0.068/lb) and liquid hydrogen $2.20/kg ($1.00/lb), the Space Shuttle in 2009 had a liquid propellant expense of approximately $1.4 million for each launch that cost $450 million from other expenses (with 40% of the mass of propellants used by it being liquids in the external fuel tank, 60% solids in the SRBs).
Even though a rocket's non-propellant, dry mass is often only between 5–20% of total mass, nevertheless this cost dominates. For hardware with the performance used in orbital launch vehicles, expenses of $2000–$10,000+ per kilogram of dry weight are common, primarily from engineering, fabrication, and testing; raw materials amount to typically around 2% of total expense. For most rockets except reusable ones (shuttle engines) the engines need not function more than a few minutes, which simplifies design.
Extreme performance requirements for rockets reaching orbit correlate with high cost, including intensive quality control to ensure reliability despite the limited safety factors allowable for weight reasons. Components produced in small numbers if not individually machined can prevent amortization of R&D and facility costs over mass production to the degree seen in more pedestrian manufacturing. Amongst liquid-fueled rockets, complexity can be influenced by how much hardware must be lightweight, like pressure-fed engines can have two orders of magnitude lesser part count than pump-fed engines but lead to more weight by needing greater tank pressure, most often used in just small maneuvering thrusters as a consequence.
To change the preceding factors for orbital launch vehicles, proposed methods have included mass-producing simple rockets in large quantities or on large scale, or developing reusable rockets meant to fly very frequently to amortize their up-front expense over many payloads, or reducing rocket performance requirements by constructing a non-rocket spacelaunch system for part of the velocity to orbit (or all of it but with most methods involving some rocket use).
The costs of support equipment, range costs and launch pads generally scale up with the size of the rocket, but vary less with launch rate, and so may be considered to be approximately a fixed cost.
Rockets in applications other than launch to orbit (such as military rockets and rocket-assisted take off), commonly not needing comparable performance and sometimes mass-produced, are often relatively inexpensive.