From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The
shape of the universe is the
local and
global geometry of the
universe. The local features of the geometry of the universe are primarily described by its
curvature, whereas the
topology
of the universe describes general global properties of its shape as of a
continuous object. The shape of the universe is related to
general relativity which describes how
spacetime is curved and bent by mass and energy.
Cosmologists distinguish between the
observable universe
and the global universe. The observable universe consists of the part
of the universe that can, in principle, be observed by light reaching
Earth within the age of the universe. It encompasses a region of space
which
currently forms a ball centered at Earth of estimated radius 46 billion light-years (4.4
×10
26 m). This does not mean the universe is 46 billion years old; in fact the universe
is believed to be 13.799 billion years old but
space itself has also expanded causing the
size of the observable universe
to be as stated. (However, it is possible to observe these distant
areas only in their very distant past, when the distance light had to
travel was much less). Assuming an
isotropic nature, the observable universe is similar for all contemporary vantage points.
According to the book
Our Mathematical Universe[clarification needed], the shape of the global universe can be explained with three categories:
[1]
- Finite or infinite
- Flat (no curvature), open (negative curvature), or closed (positive curvature)
- Connectivity, how the universe is put together, i.e., simply connected space or multiply connected.
There are certain logical connections among these properties. For
example, a universe with positive curvature is necessarily finite.
[2]
Although it is usually assumed in the literature that a flat or
negatively curved universe is infinite, this need not be the case if the
topology is not the trivial one.
[2]
The exact shape is still a matter of debate in
physical cosmology, but experimental data from various, independent sources (
WMAP,
BOOMERanG, and
Planck for example) confirm that the observable universe is flat with only a 0.4% margin of error.
[3][4][5] Theorists have been trying to construct a formal mathematical model of the shape of the universe. In formal terms, this is a
3-manifold model corresponding to the spatial section (in
comoving coordinates) of the 4-dimensional
spacetime of the universe. The model most theorists currently use is the
Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker
(FLRW) model. Arguments have been put forward that the observational
data best fit with the conclusion that the shape of the global universe
is infinite and flat,
[6] but the data are also consistent with other possible shapes, such as the so-called
Poincaré dodecahedral space[7][8] and the Sokolov–Starobinskii space (quotient of the
upper half-space model of hyperbolic space by 2-dimensional lattice).
[9]
Shape of the observable universe
As stated in the introduction, there are two aspects to consider:
- its local geometry, which predominantly concerns the curvature of the universe, particularly the observable universe, and
- its global geometry, which concerns the topology of the universe as a whole.
The observable universe can be thought of as a sphere that extends
outwards from any observation point for 46.5 billion light years, going
farther back in time and more
redshifted the more distant away one looks. Ideally, one can continue to look back all the way to the
Big Bang; in practice, however, the farthest away one can look using light and other
electromagnetic radiation is the
cosmic microwave background (CMB), as anything past that was opaque. Experimental investigations show that the observable universe is very close to
isotropic and
homogeneous.
If the observable universe encompasses the entire universe, we may be
able to determine the global structure of the entire universe by
observation. However, if the observable universe is smaller than the
entire universe, our observations will be limited to only a part of the
whole, and we may not be able to determine its global geometry through
measurement. From experiments, it is possible to construct different
mathematical models of the global geometry of the entire universe all of
which are consistent with current observational data and so it is
currently unknown whether the observable universe is identical to the
global universe or it is instead many orders of magnitude smaller than
it. The universe may be small in some dimensions and not in others
(analogous to the way a
cuboid
is longer in the dimension of length than it is in the dimensions of
width and depth). To test whether a given mathematical model describes
the universe accurately, scientists look for the model's novel
implications—what are some phenomena in the universe that we have not
yet observed, but that must exist if the model is correct—and they
devise experiments to test whether those phenomena occur or not. For
example, if the universe is a small closed loop, one would expect to see
multiple images of an object in the sky, although not necessarily
images of the same age.
Cosmologists normally work with a given
space-like slice of spacetime called the
comoving coordinates,
the existence of a preferred set of which is possible and widely
accepted in present-day physical cosmology. The section of spacetime
that can be observed is the backward
light cone (all points within the
cosmic light horizon, given time to reach a given observer), while the related term
Hubble volume
can be used to describe either the past light cone or comoving space up
to the surface of last scattering. To speak of "the shape of the
universe (at a point in time)" is
ontologically naive from the point of view of
special relativity alone: due to the
relativity of simultaneity
we cannot speak of different points in space as being "at the same
point in time" nor, therefore, of "the shape of the universe at a point
in time". However, the
comoving coordinates
(if well-defined) provide a strict sense to those by using the time
since the Big Bang (measured in the reference of CMB) as a distinguished
universal time.
Curvature of the universe
The
curvature is a quantity describing how the geometry of a space differs locally from the one of the
flat space. The curvature of any locally
isotropic space (and hence of a locally isotropic universe) falls into one of the three following cases:
- Zero curvature (flat); a drawn triangle's angles add up to 180° and the Pythagorean theorem holds; such 3-dimensional space is locally modeled by Euclidean space E3.
- Positive curvature; a drawn triangle's angles add up to more than
180°; such 3-dimensional space is locally modeled by a region of a 3-sphere S3.
- Negative curvature; a drawn triangle's angles add up to less than
180°; such 3-dimensional space is locally modeled by a region of a hyperbolic space H3.
Curved geometries are in the domain of
Non-Euclidean geometry.
An example of a positively curved space would be the surface of a
sphere such as the Earth. A triangle drawn from the equator to a pole
will have at least two angles equal 90°, which makes the sum of the 3
angles greater than 180°. An example of a negatively curved surface
would be the shape of a
saddle or mountain pass. A triangle drawn on a saddle surface will have the sum of the angles adding up to less than 180°.
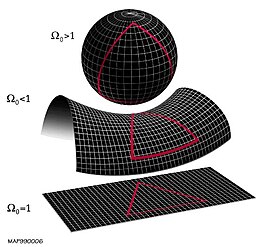
The local geometry of the universe is determined by whether the
density parameter Ω is greater than, less than, or equal to 1.
From top to bottom: a
spherical universe with
Ω > 1, a
hyperbolic universe with
Ω < 1, and a
flat universe with
Ω = 1.
These depictions of two-dimensional surfaces are merely easily
visualizable analogs to the 3-dimensional structure of (local) space.
General relativity
explains that mass and energy bend the curvature of spacetime and is
used to determine what curvature the universe has by using a value
called the
density parameter, represented with Omega (
Ω).
The density parameter is the average density of the universe divided by
the critical energy density, that is, the mass energy needed for a
universe to be flat. Put another way,
- If Ω = 1, the universe is flat
- If Ω > 1, there is positive curvature
- if Ω < 1 there is negative curvature
One can experimentally calculate this
Ω
to determine the curvature two ways. One is to count up all the
mass-energy in the universe and take its average density then divide
that average by the critical energy density. Data from
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) as well as the
Planck spacecraft give values for the three constituents of all the mass-energy in the universe – normal mass (
baryonic matter and
dark matter), relativistic particles (
photons and
neutrinos), and
dark energy or the
cosmological constant:
[10][11]
Ω
mass ≈ 0.315±0.018
Ω
relativistic ≈ 9.24×10
−5
Ω
Λ ≈ 0.6817±0.0018
Ω
total= Ω
mass + Ω
relativistic + Ω
Λ= 1.00±0.02
The actual value for critical density value is measured as ρ
critical= 9.47×10
−27 kg m
−3. From these values, within experimental error, the universe seems to be flat.
Another way to measure Ω is to do so geometrically by measuring an
angle across the observable universe. We can do this by using the
CMB
and measuring the power spectrum and temperature anisotropy. For an
intuition, one can imagine finding a gas cloud that is not in thermal
equilibrium due to being so large that light speed cannot propagate the
thermal information. Knowing this propagation speed, we then know the
size of the gas cloud as well as the distance to the gas cloud, we then
have two sides of a triangle and can then determine the angles. Using a
method similar to this, the
BOOMERanG experiment has determined that the sum of the angles to 180° within experimental error, corresponding to an Ω
total ≈ 1.00±0.12.
[12]
These and other astronomical measurements constrain the spatial
curvature to be very close to zero, although they do not constrain its
sign. This means that although the local geometries of spacetime are
generated by the theory of relativity based on
spacetime intervals, we can approximate
3-space by the familiar
Euclidean geometry.
The
Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker (FLRW) model using
Friedmann equations is commonly used to model the universe. The FLRW model provides a curvature of the universe based on the mathematics of
fluid dynamics,
that is, modeling the matter within the universe as a perfect fluid.
Although stars and structures of mass can be introduced into an "almost
FLRW" model, a strictly FLRW model is used to approximate the local
geometry of the observable universe. Another way of saying this is that
if all forms of
dark energy
are ignored, then the curvature of the universe can be determined by
measuring the average density of matter within it, assuming that all
matter is evenly distributed (rather than the distortions caused by
'dense' objects such as galaxies). This assumption is justified by the
observations that, while the universe is "weakly"
inhomogeneous and
anisotropic (see the
large-scale structure of the cosmos), it is on average homogeneous and
isotropic.
Global universe structure
Global structure covers the
geometry and the
topology
of the whole universe—both the observable universe and beyond. While
the local geometry does not determine the global geometry completely, it
does limit the possibilities, particularly a geometry of a constant
curvature. The universe is often taken to be a
geodesic manifold, free of
topological defects;
relaxing either of these complicates the analysis considerably. A
global geometry is a local geometry plus a topology. It follows that a
topology alone does not give a global geometry: for instance, Euclidean
3-space and
hyperbolic 3-space have the same topology but different global geometries.
As stated in the introduction, investigations within the study of the global structure of the universe include:
- Whether the universe is infinite or finite in extent
- Whether the geometry of the global universe is flat, positively curved, or negatively curved
- Whether the topology is simply connected like a sphere or multiply connected, like a torus[13]
Infinite or finite
One
of the presently unanswered questions about the universe is whether it
is infinite or finite in extent. For intuition, it can be understood
that a finite universe has a finite volume that, for example, could be
in theory filled up with a finite amount of material, while an infinite
universe is unbounded and no numerical volume could possibly fill it.
Mathematically, the question of whether the universe is infinite or
finite is referred to as
boundedness. An infinite universe (unbounded metric space) means that there are points
arbitrarily far apart: for any distance
d, there are points that are of a distance at least
d apart. A finite universe is a bounded metric space, where there is some distance
d such that all points are within distance
d of each other. The smallest such
d is called the diameter of the universe, in which case the universe has a well-defined "volume" or "scale."
With or without boundary
Assuming a finite universe, the universe can either have an edge or no edge. Many finite mathematical spaces, e.g., a
disc,
have an edge or boundary. Spaces that have an edge are difficult to
treat, both conceptually and mathematically. Namely, it is very
difficult to state what would happen at the edge of such a universe. For
this reason, spaces that have an edge are typically excluded from
consideration.
However, there exist many finite spaces, such as the
3-sphere and
3-torus, which have no edges. Mathematically, these spaces are referred to as being
compact without boundary. The term compact basically means that it is finite in extent ("bounded") and
complete.
The term "without boundary" means that the space has no edges.
Moreover, so that calculus can be applied, the universe is typically
assumed to be a
differentiable manifold. A mathematical object that possesses all these properties, compact without boundary and differentiable, is termed a
closed manifold. The 3-sphere and 3-torus are both closed manifolds.
Curvature
The curvature of the universe places constraints on the topology. If the spatial geometry is
spherical,
i.e., possess positive curvature, the topology is compact. For a flat
(zero curvature) or a hyperbolic (negative curvature) spatial geometry,
the topology can be either compact or infinite.
[14]
Many textbooks erroneously state that a flat universe implies an
infinite universe; however, the correct statement is that a flat
universe that is also
simply connected implies an infinite universe.
[14] For example, Euclidean space is flat, simply connected, and infinite, but the
torus is flat, multiply connected, finite, and compact.
In general,
local to global theorems in
Riemannian geometry
relate the local geometry to the global geometry. If the local geometry
has constant curvature, the global geometry is very constrained, as
described in
Thurston geometries.
The latest research shows that even the most powerful future
experiments (like SKA, Planck..) will not be able to distinguish between
flat, open and closed universe if the true value of cosmological
curvature parameter is smaller than 10
−4. If the true value of the cosmological curvature parameter is larger than 10
−3 we will be able to distinguish between these three models even now.
[15]
Results of the
Planck mission released in 2015 show the cosmological curvature parameter, Ω
K, to be 0.000±0.005, consistent with a flat universe.
[16]
Universe with zero curvature
In a universe with zero curvature, the local geometry is
flat. The most obvious global structure is that of
Euclidean space, which is infinite in extent. Flat universes that are finite in extent include the
torus and
Klein bottle.
Moreover, in three dimensions, there are 10 finite closed flat
3-manifolds, of which 6 are orientable and 4 are non-orientable. These
are the
Bieberbach manifolds. The most familiar is the aforementioned
3-torus universe.
In the absence of dark energy, a flat universe expands forever but at
a continually decelerating rate, with expansion asymptotically
approaching zero. With dark energy, the expansion rate of the universe
initially slows down, due to the effect of gravity, but eventually
increases. The
ultimate fate of the universe is the same as that of an open universe.
A flat universe can have
zero total energy.
Universe with positive curvature
A positively curved universe is described by
elliptic geometry, and can be thought of as a three-dimensional
hypersphere, or some other
spherical 3-manifold (such as the
Poincaré dodecahedral space), all of which are quotients of the 3-sphere.
Poincaré dodecahedral space, a positively curved space, colloquially described as "soccerball-shaped", as it is the quotient of the 3-sphere by the
binary icosahedral group, which is very close to
icosahedral symmetry, the symmetry of a soccer ball. This was proposed by
Jean-Pierre Luminet and colleagues in 2003
[7][17] and an optimal orientation on the sky for the model was estimated in 2008.
[8]
Universe with negative curvature
Universe in an expanding sphere. The galaxies farthest away are moving fastest and hence experience length contraction and so become smaller to an
observer in the centre.
A hyperbolic universe, one of a negative spatial curvature, is described by
hyperbolic geometry,
and can be thought of locally as a three-dimensional analog of an
infinitely extended saddle shape. There are a great variety of
hyperbolic 3-manifolds, and their classification is not completely understood. Those of finite volume can be understood via the
Mostow rigidity theorem.
For hyperbolic local geometry, many of the possible three-dimensional
spaces are informally called "horn topologies", so called because of the
shape of the
pseudosphere, a canonical model of hyperbolic geometry. An example is the
Picard horn, a negatively curved space, colloquially described as "funnel-shaped".
[9]
Curvature: open or closed
When
cosmologists speak of the universe as being "open" or "closed", they
most commonly are referring to whether the curvature is negative or
positive. These meanings of open and closed are different from the
mathematical meaning of open and closed used for sets in topological
spaces and for the mathematical meaning of open and closed manifolds,
which gives rise to ambiguity and confusion. In mathematics, there are
definitions for a
closed manifold (i.e., compact without boundary) and
open manifold
(i.e., one that is not compact and without boundary). A "closed
universe" is necessarily a closed manifold. An "open universe" can be
either a closed or open manifold. For example, in the
Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker
(FLRW) model the universe is considered to be without boundaries, in
which case "compact universe" could describe a universe that is a closed
manifold.
Milne model ("spherical" expanding)
If one applies
Minkowski space-based
special relativity to expansion of the universe, without resorting to the concept of a
curved spacetime, then one obtains the Milne model. Any spatial section of the universe of a constant age (the
proper time elapsed from the Big Bang) will have a negative curvature; this is merely a
pseudo-Euclidean geometric fact analogous to one that
concentric spheres in the
flat Euclidean space are nevertheless curved. Spatial geometry of this model is an unbounded
hyperbolic space. The entire universe is contained within a
light cone, namely the future cone of the Big Bang. For any given moment
t> 0 of
coordinate time (assuming the Big Bang has
t = 0), the entire universe is bounded by a
sphere of radius exactly
c t. The apparent paradox of an infinite universe contained within a sphere is explained with
length contraction: the galaxies farther away, which are travelling away from the observer the fastest, will appear thinner.
This model is essentially a
degenerate FLRW for
Ω = 0.
It is incompatible with observations that definitely rule out such a
large negative spatial curvature. However, as a background in which
gravitational fields (or gravitons) can operate, due to diffeomorphism
invariance, the space on the macroscopic scale, is equivalent to any
other (open) solution of Einstein's field equations.
 bits of binary information, encoded on a boundary to that region, a closed surface of area
bits of binary information, encoded on a boundary to that region, a closed surface of area  . The information is evenly distributed on the surface with each bit requiring an area equal to
. The information is evenly distributed on the surface with each bit requiring an area equal to  , the so-called Planck area, from which
, the so-called Planck area, from which  can thus be computed:
can thus be computed: is the Planck length. The Planck length is defined as:
is the Planck length. The Planck length is defined as: is the universal gravitational constant,
is the universal gravitational constant,  is the speed of light, and
is the speed of light, and  is the reduced Planck constant. When substituted in the equation for
is the reduced Planck constant. When substituted in the equation for  we find:
we find: of a system with
of a system with  degrees of freedom in terms of its energy
degrees of freedom in terms of its energy  such that:
such that: is the Boltzmann constant. This is the equivalent energy for a mass
is the Boltzmann constant. This is the equivalent energy for a mass  according to:
according to:.
,
 is that acceleration, which for a mass
is that acceleration, which for a mass  would be attributed to a force
would be attributed to a force  according to Newton's second law of motion:
according to Newton's second law of motion:.
 , the surface area would be given by:
, the surface area would be given by:.
.