A representation of the 3D structure of the protein myoglobin showing turquoise α-helices. This protein was the first to have its structure solved by X-ray crystallography. Towards the right-center among the coils, a prosthetic group called a heme group (shown in gray) with a bound oxygen molecule (red).
Proteins are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules
from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another
primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.
A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide.
A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides,
containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be
proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by post-translational modification,
which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability,
activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes
proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.
Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life
and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an
average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal or misfolded
proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for
destruction or due to being unstable.
Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. In animals, proteins are needed in the diet to provide the essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized. Digestion breaks the proteins down for use in the metabolism.
Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering
has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification.
Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.
Biochemistry
Resonance structures of the peptide bond that links individual amino acids to form a protein polymer
Most proteins consist of linear polymers built from series of up to 20 different L-α- amino acids. All proteinogenic amino acids possess common structural features, including an α-carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a variable side chain are bonded. Only proline
differs from this basic structure as it contains an unusual ring to the
N-end amine group, which forces the CO–NH amide moiety into a fixed
conformation. The side chains of the standard amino acids, detailed in the list of standard amino acids,
have a great variety of chemical structures and properties; it is the
combined effect of all of the amino acid side chains in a protein that
ultimately determines its three-dimensional structure and its chemical
reactivity.
The amino acids in a polypeptide chain are linked by peptide bonds. Once linked in the protein chain, an individual amino acid is called a residue, and the linked series of carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms are known as the main chain or protein backbone.
The peptide bond has two resonance forms that contribute some double-bond character and inhibit rotation around its axis, so that the alpha carbons are roughly coplanar. The other two dihedral angles in the peptide bond determine the local shape assumed by the protein backbone. The end with a free amino group is known as the N-terminus or amino terminus, whereas the end of the protein with a free carboxyl group is known as the C-terminus or carboxy terminus (the sequence of the protein is written from N-terminus to C-terminus, from left to right).
The words protein, polypeptide, and peptide are a little ambiguous and can overlap in meaning. Protein is generally used to refer to the complete biological molecule in a stable conformation, whereas peptide
is generally reserved for a short amino acid oligomers often lacking a
stable three-dimensional structure. However, the boundary between the
two is not well defined and usually lies near 20–30 residues. Polypeptide can refer to any single linear chain of amino acids, usually regardless of length, but often implies an absence of a defined conformation.
Interactions
Proteins can interact with many types of molecules, including with other proteins, with lipids, with carboyhydrates, and with DNA.
Abundance in cells
It has been estimated that average-sized bacteria contain about 2 million proteins per cell (e.g. E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus). Smaller bacteria, such as Mycoplasma or spirochetes contain fewer molecules, on the order of 50,000 to 1 million. By contrast, eukaryotic cells are larger and thus contain much more protein. For instance, yeast cells have been estimated to contain about 50 million proteins and human cells on the order of 1 to 3 billion. The concentration of individual protein copies ranges from a few molecules per cell up to 20 million.
Not all genes coding proteins are expressed in most cells and their
number depends on, for example, cell type and external stimuli. For
instance, of the 20,000 or so proteins encoded by the human genome, only
6,000 are detected in lymphoblastoid cells. Moreover, the number of proteins the genome encodes correlates well with the organism complexity. Eukaryotes have 15,000, bacteria have 3,200, archaea have 2,400, and viruses have 42 proteins on average coded in their respective genomes.
Synthesis
Biosynthesis
A ribosome produces a protein using mRNA as template
The DNA sequence of a gene encodes the amino acid sequence of a protein
Proteins are assembled from amino acids using information encoded in genes. Each protein has its own unique amino acid sequence that is specified by the nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding this protein. The genetic code is a set of three-nucleotide sets called codons and each three-nucleotide combination designates an amino acid, for example AUG (adenine-uracil-guanine) is the code for methionine. Because DNA
contains four nucleotides, the total number of possible codons is 64;
hence, there is some redundancy in the genetic code, with some amino
acids specified by more than one codon. Genes encoded in DNA are first transcribed into pre-messenger RNA (mRNA) by proteins such as RNA polymerase. Most organisms then process the pre-mRNA (also known as a primary transcript) using various forms of Post-transcriptional modification to form the mature mRNA, which is then used as a template for protein synthesis by the ribosome. In prokaryotes the mRNA may either be used as soon as it is produced, or be bound by a ribosome after having moved away from the nucleoid. In contrast, eukaryotes make mRNA in the cell nucleus and then translocate it across the nuclear membrane into the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis
then takes place. The rate of protein synthesis is higher in
prokaryotes than eukaryotes and can reach up to 20 amino acids per
second.
The process of synthesizing a protein from an mRNA template is known as translation. The mRNA is loaded onto the ribosome and is read three nucleotides at a time by matching each codon to its base pairing anticodon located on a transfer RNA molecule, which carries the amino acid corresponding to the codon it recognizes. The enzyme aminoacyl tRNA synthetase "charges" the tRNA molecules with the correct amino acids. The growing polypeptide is often termed the nascent chain. Proteins are always biosynthesized from N-terminus to C-terminus.
The size of a synthesized protein can be measured by the number of amino acids it contains and by its total molecular mass, which is normally reported in units of daltons (synonymous with atomic mass units),
or the derivative unit kilodalton (kDa). The average size of a protein
increases from Archaea to Bacteria to Eukaryote (283, 311, 438 residues
and 31, 34, 49 kDa respecitvely) due to a bigger number of protein domains constituting proteins in higher organisms. For instance, yeast proteins are on average 466 amino acids long and 53 kDa in mass. The largest known proteins are the titins, a component of the muscle sarcomere, with a molecular mass of almost 3,000 kDa and a total length of almost 27,000 amino acids.
Chemical synthesis
Short proteins can also be synthesized chemically by a family of methods known as peptide synthesis, which rely on organic synthesis techniques such as chemical ligation to produce peptides in high yield. Chemical synthesis allows for the introduction of non-natural amino acids into polypeptide chains, such as attachment of fluorescent probes to amino acid side chains. These methods are useful in laboratory biochemistry and cell biology,
though generally not for commercial applications. Chemical synthesis is
inefficient for polypeptides longer than about 300 amino acids, and the
synthesized proteins may not readily assume their native tertiary structure. Most chemical synthesis methods proceed from C-terminus to N-terminus, opposite the biological reaction.
Structure
The
crystal structure of the chaperonin, a huge protein complex. A single
protein subunit is highlighted. Chaperonins assist protein folding.
Three possible representations of the three-dimensional structure of the protein triose phosphate isomerase. Left: All-atom representation colored by atom type. Middle: Simplified representation illustrating the backbone conformation, colored by secondary structure. Right:
Solvent-accessible surface representation colored by residue type
(acidic residues red, basic residues blue, polar residues green,
nonpolar residues white).
Most proteins fold into unique 3-dimensional structures. The shape into which a protein naturally folds is known as its native conformation.
Although many proteins can fold unassisted, simply through the chemical
properties of their amino acids, others require the aid of molecular chaperones to fold into their native states. Biochemists often refer to four distinct aspects of a protein's structure:
- Primary structure: the amino acid sequence. A protein is a polyamide.
- Secondary structure: regularly repeating local structures stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The most common examples are the α-helix, β-sheet and turns. Because secondary structures are local, many regions of different secondary structure can be present in the same protein molecule.
- Tertiary structure: the overall shape of a single protein molecule; the spatial relationship of the secondary structures to one another. Tertiary structure is generally stabilized by nonlocal interactions, most commonly the formation of a hydrophobic core, but also through salt bridges, hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds, and even posttranslational modifications. The term "tertiary structure" is often used as synonymous with the term fold. The tertiary structure is what controls the basic function of the protein.
- Quaternary structure: the structure formed by several protein molecules (polypeptide chains), usually called protein subunits in this context, which function as a single protein complex.
Proteins are not entirely rigid molecules. In addition to these
levels of structure, proteins may shift between several related
structures while they perform their functions. In the context of these
functional rearrangements, these tertiary or quaternary structures are
usually referred to as "conformations", and transitions between them are called conformational changes. Such changes are often induced by the binding of a substrate molecule to an enzyme's active site,
or the physical region of the protein that participates in chemical
catalysis. In solution proteins also undergo variation in structure
through thermal vibration and the collision with other molecules.
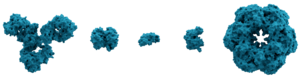
Molecular surface of several proteins showing their comparative sizes. From left to right are: immunoglobulin G (IgG, an antibody), hemoglobin, insulin (a hormone), adenylate kinase (an enzyme), and glutamine synthetase (an enzyme).
Proteins can be informally divided into three main classes, which correlate with typical tertiary structures: globular proteins, fibrous proteins, and membrane proteins. Almost all globular proteins are soluble and many are enzymes. Fibrous proteins are often structural, such as collagen, the major component of connective tissue, or keratin, the protein component of hair and nails. Membrane proteins often serve as receptors or provide channels for polar or charged molecules to pass through the cell membrane.
A special case of intramolecular hydrogen bonds within proteins,
poorly shielded from water attack and hence promoting their own dehydration, are called dehydrons.
Protein domains
Many proteins are composed of several protein domains, i.e. segments of a protein that fold into distinct structural units. Domains usually also have specific functions, such as enzymatic activities (e.g. kinase) or they serve as binding modules (e.g. the SH3 domain binds to proline-rich sequences in other proteins).
Sequence motif
Short amino acid sequences within proteins often act as recognition sites for other proteins. For instance, SH3 domains typically bind to short PxxP motifs (i.e. 2 prolines [P], separated by 2 unspecified amino acids
[x], although the surrounding amino acids may determine the exact
binding specificity). A large number of such motifs has been collected
in the Eukaryotic Linear Motif (ELM) database.
Cellular functions
Proteins are the chief actors within the cell, said to be carrying out the duties specified by the information encoded in genes. With the exception of certain types of RNA,
most other biological molecules are relatively inert elements upon
which proteins act. Proteins make up half the dry weight of an Escherichia coli cell, whereas other macromolecules such as DNA and RNA make up only 3% and 20%, respectively. The set of proteins expressed in a particular cell or cell type is known as its proteome.
The enzyme hexokinase is shown as a conventional ball-and-stick molecular model. To scale in the top right-hand corner are two of its substrates, ATP and glucose.
The chief characteristic of proteins that also allows their diverse
set of functions is their ability to bind other molecules specifically
and tightly. The region of the protein responsible for binding another
molecule is known as the binding site
and is often a depression or "pocket" on the molecular surface. This
binding ability is mediated by the tertiary structure of the protein,
which defines the binding site pocket, and by the chemical properties of
the surrounding amino acids' side chains. Protein binding can be
extraordinarily tight and specific; for example, the ribonuclease inhibitor protein binds to human angiogenin with a sub-femtomolar dissociation constant (less than 10−15 M) but does not bind at all to its amphibian homolog onconase
(greater than 1 M). Extremely minor chemical changes such as the addition of a
single methyl group to a binding partner can sometimes suffice to nearly
eliminate binding; for example, the aminoacyl tRNA synthetase specific to the amino acid valine discriminates against the very similar side chain of the amino acid isoleucine.
Proteins can bind to other proteins as well as to small-molecule substrates. When proteins bind specifically to other copies of the same molecule, they can oligomerize
to form fibrils; this process occurs often in structural proteins that
consist of globular monomers that self-associate to form rigid fibers. Protein–protein interactions also regulate enzymatic activity, control progression through the cell cycle, and allow the assembly of large protein complexes
that carry out many closely related reactions with a common biological
function. Proteins can also bind to, or even be integrated into, cell
membranes. The ability of binding partners to induce conformational
changes in proteins allows the construction of enormously complex signaling networks.
As interactions between proteins are reversible, and depend heavily on
the availability of different groups of partner proteins to form
aggregates that are capable to carry out discrete sets of function,
study of the interactions between specific proteins is a key to
understand important aspects of cellular function, and ultimately the
properties that distinguish particular cell types.
Enzymes
The best-known role of proteins in the cell is as enzymes, which catalyze
chemical reactions. Enzymes are usually highly specific and accelerate
only one or a few chemical reactions. Enzymes carry out most of the
reactions involved in metabolism, as well as manipulating DNA in processes such as DNA replication, DNA repair, and transcription.
Some enzymes act on other proteins to add or remove chemical groups in a
process known as posttranslational modification. About 4,000 reactions
are known to be catalyzed by enzymes. The rate acceleration conferred by enzymatic catalysis is often enormous—as much as 1017-fold increase in rate over the uncatalysed reaction in the case of orotate decarboxylase (78 million years without the enzyme, 18 milliseconds with the enzyme).
The molecules bound and acted upon by enzymes are called substrates.
Although enzymes can consist of hundreds of amino acids, it is usually
only a small fraction of the residues that come in contact with the
substrate, and an even smaller fraction—three to four residues on
average—that are directly involved in catalysis. The region of the enzyme that binds the substrate and contains the catalytic residues is known as the active site.
Dirigent proteins are members of a class of proteins that dictate the stereochemistry of a compound synthesized by other enzymes.
Cell signaling and ligand binding
Ribbon diagram of a mouse antibody against cholera that binds a carbohydrate antigen
Many proteins are involved in the process of cell signaling and signal transduction. Some proteins, such as insulin, are extracellular proteins that transmit a signal from the cell in which they were synthesized to other cells in distant tissues. Others are membrane proteins that act as receptors
whose main function is to bind a signaling molecule and induce a
biochemical response in the cell. Many receptors have a binding site
exposed on the cell surface and an effector domain within the cell,
which may have enzymatic activity or may undergo a conformational change detected by other proteins within the cell.
Antibodies are protein components of an adaptive immune system whose main function is to bind antigens, or foreign substances in the body, and target them for destruction. Antibodies can be secreted into the extracellular environment or anchored in the membranes of specialized B cells known as plasma cells.
Whereas enzymes are limited in their binding affinity for their
substrates by the necessity of conducting their reaction, antibodies
have no such constraints. An antibody's binding affinity to its target
is extraordinarily high.
Many ligand transport proteins bind particular small biomolecules
and transport them to other locations in the body of a multicellular
organism. These proteins must have a high binding affinity when their ligand
is present in high concentrations, but must also release the ligand
when it is present at low concentrations in the target tissues. The
canonical example of a ligand-binding protein is haemoglobin, which transports oxygen from the lungs to other organs and tissues in all vertebrates and has close homologs in every biological kingdom. Lectins are sugar-binding proteins which are highly specific for their sugar moieties. Lectins typically play a role in biological recognition phenomena involving cells and proteins. Receptors and hormones are highly specific binding proteins.
Transmembrane proteins can also serve as ligand transport proteins that alter the permeability of the cell membrane to small molecules and ions. The membrane alone has a hydrophobic core through which polar or charged molecules cannot diffuse. Membrane proteins contain internal channels that allow such molecules to enter and exit the cell. Many ion channel proteins are specialized to select for only a particular ion; for example, potassium and sodium channels often discriminate for only one of the two ions.
Structural proteins
Structural proteins confer stiffness and rigidity to otherwise-fluid biological components. Most structural proteins are fibrous proteins; for example, collagen and elastin are critical components of connective tissue such as cartilage, and keratin is found in hard or filamentous structures such as hair, nails, feathers, hooves, and some animal shells. Some globular proteins can also play structural functions, for example, actin and tubulin are globular and soluble as monomers, but polymerize to form long, stiff fibers that make up the cytoskeleton, which allows the cell to maintain its shape and size.
Other proteins that serve structural functions are motor proteins such as myosin, kinesin, and dynein, which are capable of generating mechanical forces. These proteins are crucial for cellular motility of single celled organisms and the sperm of many multicellular organisms which reproduce sexually. They also generate the forces exerted by contracting muscles and play essential roles in intracellular transport.
Methods of study
The activities and structures of proteins may be examined in vitro, in vivo, and in silico. In vitro
studies of purified proteins in controlled environments are useful for
learning how a protein carries out its function: for example, enzyme kinetics studies explore the chemical mechanism of an enzyme's catalytic activity and its relative affinity for various possible substrate molecules. By contrast, in vivo experiments can provide information about the physiological role of a protein in the context of a cell or even a whole organism. In silico studies use computational methods to study proteins.
Protein purification
To perform in vitro analysis, a protein must be purified away from other cellular components. This process usually begins with cell lysis, in which a cell's membrane is disrupted and its internal contents released into a solution known as a crude lysate. The resulting mixture can be purified using ultracentrifugation, which fractionates the various cellular components into fractions containing soluble proteins; membrane lipids and proteins; cellular organelles, and nucleic acids. Precipitation by a method known as salting out can concentrate the proteins from this lysate. Various types of chromatography
are then used to isolate the protein or proteins of interest based on
properties such as molecular weight, net charge and binding affinity. The level of purification can be monitored using various types of gel electrophoresis if the desired protein's molecular weight and isoelectric point are known, by spectroscopy if the protein has distinguishable spectroscopic features, or by enzyme assays if the protein has enzymatic activity. Additionally, proteins can be isolated according to their charge using electrofocusing.
For natural proteins, a series of purification steps may be
necessary to obtain protein sufficiently pure for laboratory
applications. To simplify this process, genetic engineering
is often used to add chemical features to proteins that make them
easier to purify without affecting their structure or activity. Here, a
"tag" consisting of a specific amino acid sequence, often a series of histidine residues (a "His-tag"), is attached to one terminus of the protein. As a result, when the lysate is passed over a chromatography column containing nickel,
the histidine residues ligate the nickel and attach to the column while
the untagged components of the lysate pass unimpeded. A number of
different tags have been developed to help researchers purify specific
proteins from complex mixtures.
Cellular localization
Proteins in different cellular compartments and structures tagged with green fluorescent protein (here, white)
The study of proteins in vivo is often concerned with the
synthesis and localization of the protein within the cell. Although many
intracellular proteins are synthesized in the cytoplasm and membrane-bound or secreted proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, the specifics of how proteins are targeted
to specific organelles or cellular structures is often unclear. A
useful technique for assessing cellular localization uses genetic
engineering to express in a cell a fusion protein or chimera consisting of the natural protein of interest linked to a "reporter" such as green fluorescent protein (GFP). The fused protein's position within the cell can be cleanly and efficiently visualized using microscopy, as shown in the figure opposite.
Other methods for elucidating the cellular location of proteins
requires the use of known compartmental markers for regions such as the
ER, the Golgi, lysosomes or vacuoles, mitochondria, chloroplasts, plasma
membrane, etc. With the use of fluorescently tagged versions of these
markers or of antibodies to known markers, it becomes much simpler to
identify the localization of a protein of interest. For example, indirect immunofluorescence
will allow for fluorescence colocalization and demonstration of
location. Fluorescent dyes are used to label cellular compartments for a
similar purpose.
Other possibilities exist, as well. For example, immunohistochemistry
usually utilizes an antibody to one or more proteins of interest that
are conjugated to enzymes yielding either luminescent or chromogenic
signals that can be compared between samples, allowing for localization
information. Another applicable technique is cofractionation in sucrose
(or other material) gradients using isopycnic centrifugation.
While this technique does not prove colocalization of a compartment of
known density and the protein of interest, it does increase the
likelihood, and is more amenable to large-scale studies.
Finally, the gold-standard method of cellular localization is immunoelectron microscopy.
This technique also uses an antibody to the protein of interest, along
with classical electron microscopy techniques. The sample is prepared
for normal electron microscopic examination, and then treated with an
antibody to the protein of interest that is conjugated to an extremely
electro-dense material, usually gold. This allows for the localization
of both ultrastructural details as well as the protein of interest.
Through another genetic engineering application known as site-directed mutagenesis,
researchers can alter the protein sequence and hence its structure,
cellular localization, and susceptibility to regulation. This technique
even allows the incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins,
using modified tRNAs, and may allow the rational design of new proteins with novel properties.
Proteomics
The total complement of proteins present at a time in a cell or cell type is known as its proteome, and the study of such large-scale data sets defines the field of proteomics, named by analogy to the related field of genomics. Key experimental techniques in proteomics include 2D electrophoresis, which allows the separation of a large number of proteins, mass spectrometry, which allows rapid high-throughput identification of proteins and sequencing of peptides (most often after in-gel digestion), protein microarrays, which allow the detection of the relative levels of a large number of proteins present in a cell, and two-hybrid screening, which allows the systematic exploration of protein–protein interactions. The total complement of biologically possible such interactions is known as the interactome. A systematic attempt to determine the structures of proteins representing every possible fold is known as structural genomics.
Bioinformatics
A vast array of computational methods have been developed to analyze the structure, function, and evolution of proteins.
The development of such tools has been driven by the large amount
of genomic and proteomic data available for a variety of organisms,
including the human genome.
It is simply impossible to study all proteins experimentally, hence
only a few are subjected to laboratory experiments while computational
tools are used to extrapolate to similar proteins. Such homologous proteins can be efficiently identified in distantly related organisms by sequence alignment. Genome and gene sequences can be searched by a variety of tools for certain properties. Sequence profiling tools can find restriction enzyme sites, open reading frames in nucleotide sequences, and predict secondary structures. Phylogenetic trees can be constructed and evolutionary hypotheses developed using special software like ClustalW regarding the ancestry of modern organisms and the genes they express. The field of bioinformatics is now indispensable for the analysis of genes and proteins.
Structure determination
Discovering the tertiary structure of a protein, or the quaternary
structure of its complexes, can provide important clues about how the
protein performs its function and how it can be affected, i.e. in drug design. As proteins are too small to be seen under a light microscope, other methods have to be employed to determine their structure. Common experimental methods include X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy, both of which can produce structural information at atomic
resolution. However, NMR experiments are able to provide information
from which a subset of distances between pairs of atoms can be
estimated, and the final possible conformations for a protein are
determined by solving a distance geometry problem. Dual polarization interferometry is a quantitative analytical method for measuring the overall protein conformation and conformational changes due to interactions or other stimulus. Circular dichroism is another laboratory technique for determining internal β-sheet / α-helical composition of proteins. Cryoelectron microscopy is used to produce lower-resolution structural information about very large protein complexes, including assembled viruses; a variant known as electron crystallography can also produce high-resolution information in some cases, especially for two-dimensional crystals of membrane proteins. Solved structures are usually deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), a freely available resource from which structural data about thousands of proteins can be obtained in the form of Cartesian coordinates for each atom in the protein.
Many more gene sequences are known than protein structures.
Further, the set of solved structures is biased toward proteins that can
be easily subjected to the conditions required in X-ray crystallography, one of the major structure determination methods. In particular, globular proteins are comparatively easy to crystallize
in preparation for X-ray crystallography. Membrane proteins and large
protein complexes, by contrast, are difficult to crystallize and are
underrepresented in the PDB. Structural genomics
initiatives have attempted to remedy these deficiencies by
systematically solving representative structures of major fold classes. Protein structure prediction
methods attempt to provide a means of generating a plausible structure
for proteins whose structures have not been experimentally determined.
Structure prediction and simulation
Constituent
amino-acids can be analyzed to predict secondary, tertiary and
quaternary protein structure, in this case hemoglobin containing heme units
Complementary to the field of structural genomics, protein structure prediction develops efficient mathematical models
of proteins to computationally predict the molecular formations in
theory, instead of detecting structures with laboratory observation. The most successful type of structure prediction, known as homology modeling,
relies on the existence of a "template" structure with sequence
similarity to the protein being modeled; structural genomics' goal is to
provide sufficient representation in solved structures to model most of
those that remain.
Although producing accurate models remains a challenge when only
distantly related template structures are available, it has been
suggested that sequence alignment is the bottleneck in this process, as quite accurate models can be produced if a "perfect" sequence alignment is known. Many structure prediction methods have served to inform the emerging field of protein engineering, in which novel protein folds have already been designed. A more complex computational problem is the prediction of intermolecular interactions, such as in molecular docking and protein–protein interaction prediction.
Mathematical models to simulate dynamic processes of protein folding and binding involve molecular mechanics, in particular, molecular dynamics. Monte Carlo techniques facilitate the computations, which exploit advances in parallel and distributed computing (for example, the Folding@home project which performs molecular modeling on GPUs). In silico simulations discovered the folding of small α-helical protein domains such as the villin headpiece and the HIV accessory protein. Hybrid methods combining standard molecular dynamics with quantum mechanical mathematics explored the electronic states of rhodopsins.
Protein disorder and unstructure prediction
Many proteins (in Eucaryota ~33%) contain large unstructured but biologically functional segments and can be classified as intrinsically disordered proteins. Predicting and analyzing protein disorder is, therefore, an important part of protein structure characterization.
Nutrition
Most microorganisms and plants can biosynthesize all 20 standard amino acids, while animals (including humans) must obtain some of the amino acids from the diet. The amino acids that an organism cannot synthesize on its own are referred to as essential amino acids. Key enzymes that synthesize certain amino acids are not present in animals—such as aspartokinase, which catalyses the first step in the synthesis of lysine, methionine, and threonine from aspartate.
If amino acids are present in the environment, microorganisms can
conserve energy by taking up the amino acids from their surroundings and
downregulating their biosynthetic pathways.
In animals, amino acids are obtained through the consumption of
foods containing protein. Ingested proteins are then broken down into
amino acids through digestion, which typically involves denaturation of the protein through exposure to acid and hydrolysis by enzymes called proteases. Some ingested amino acids are used for protein biosynthesis, while others are converted to glucose through gluconeogenesis, or fed into the citric acid cycle. This use of protein as a fuel is particularly important under starvation conditions as it allows the body's own proteins to be used to support life, particularly those found in muscle.
In animals such as dogs and cats, protein maintains the health
and quality of the skin by promoting hair follicle growth and
keratinization, and thus reducing the likelihood of skin problems
producing malodors.
Poor-quality proteins also have a role regarding gastrointestinal
health, increasing the potential for flatulence and odorous compounds in
dogs because when proteins reach the colon in an undigested state, they
are fermented producing hydrogen sulfide gas, indole, and skatole.
Dogs and cats digest animal proteins better than those from plants but
products of low-quality animal origin are poorly digested, including
skin, feathers, and connective tissue.
History and etymology
Proteins were recognized as a distinct class of biological molecules in the eighteenth century by Antoine Fourcroy and others, distinguished by the molecules' ability to coagulate or flocculate under treatments with heat or acid. Noted examples at the time included albumin from egg whites, blood serum albumin, fibrin, and wheat gluten.
Proteins were first described by the Dutch chemist Gerardus Johannes Mulder and named by the Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1838. Mulder carried out elemental analysis of common proteins and found that nearly all proteins had the same empirical formula, C400H620N100O120P1S1.
He came to the erroneous conclusion that they might be composed of a
single type of (very large) molecule. The term "protein" to describe
these molecules was proposed by Mulder's associate Berzelius; protein is
derived from the Greek word πρώτειος (proteios), meaning "primary", "in the lead", or "standing in front", + -in. Mulder went on to identify the products of protein degradation such as the amino acid leucine for which he found a (nearly correct) molecular weight of 131 Da. Prior to "protein", other names were used, like "albumins" or "albuminous materials" (Eiweisskörper, in German).
Early nutritional scientists such as the German Carl von Voit
believed that protein was the most important nutrient for maintaining
the structure of the body, because it was generally believed that "flesh
makes flesh." Karl Heinrich Ritthausen extended known protein forms with the identification of glutamic acid. At the Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station a detailed review of the vegetable proteins was compiled by Thomas Burr Osborne. Working with Lafayette Mendel and applying Liebig's law of the minimum in feeding laboratory rats, the nutritionally essential amino acids were established. The work was continued and communicated by William Cumming Rose. The understanding of proteins as polypeptides came through the work of Franz Hofmeister and Hermann Emil Fischer in 1902. The central role of proteins as enzymes in living organisms was not fully appreciated until 1926, when James B. Sumner showed that the enzyme urease was in fact a protein.
The difficulty in purifying proteins in large quantities made
them very difficult for early protein biochemists to study. Hence, early
studies focused on proteins that could be purified in large quantities,
e.g., those of blood, egg white, various toxins, and digestive/metabolic enzymes obtained from slaughterhouses. In the 1950s, the Armour Hot Dog Co. purified 1 kg of pure bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A
and made it freely available to scientists; this gesture helped
ribonuclease A become a major target for biochemical study for the
following decades.
John Kendrew with model of myoglobin in progress
Linus Pauling is credited with the successful prediction of regular protein secondary structures based on hydrogen bonding, an idea first put forth by William Astbury in 1933. Later work by Walter Kauzmann on denaturation, based partly on previous studies by Kaj Linderstrøm-Lang, contributed an understanding of protein folding and structure mediated by hydrophobic interactions.
The first protein to be sequenced was insulin, by Frederick Sanger, in 1949. Sanger correctly determined the amino acid sequence of insulin, thus conclusively demonstrating that proteins consisted of linear polymers of amino acids rather than branched chains, colloids, or cyclols. He won the Nobel Prize for this achievement in 1958.
The first protein structures to be solved were hemoglobin and myoglobin, by Max Perutz and Sir John Cowdery Kendrew, respectively, in 1958. As of 2017, the Protein Data Bank has over 126,060 atomic-resolution structures of proteins. In more recent times, cryo-electron microscopy of large macromolecular assemblies and computational protein structure prediction of small protein domains are two methods approaching atomic resolution.