Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers – specifically polypeptides – formed from sequences of amino acids, the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid monomer may also be called a residue indicating a repeating unit of a polymer. Proteins form by amino acids undergoing condensation reactions, in which the amino acids lose one water molecule per reaction in order to attach to one another with a peptide bond. By convention, a chain under 30 amino acids is often identified as a peptide, rather than a protein. To be able to perform their biological function, proteins fold into one or more specific spatial conformations driven by a number of non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic packing. To understand the functions of proteins at a molecular level, it is often necessary to determine their three-dimensional structure. This is the topic of the scientific field of structural biology, which employs techniques such as X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and dual polarisation interferometry to determine the structure of proteins.
Protein structures range in size from tens to several thousand amino acids. By physical size, proteins are classified as nanoparticles, between 1–100 nm. Very large protein complexes can be formed from protein subunits. For example, many thousands of actin molecules assemble into a microfilament.
A protein usually undergoes reversible structural changes in performing its biological function. The alternative structures of the same protein are referred to as different conformations, and transitions between them are called conformational changes.
Levels of protein structure
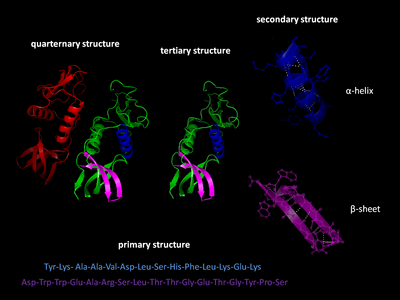
There are four distinct levels of protein structure.
Primary structure
The primary structure of a protein refers to the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. The primary structure is held together by peptide bonds that are made during the process of protein biosynthesis. The two ends of the polypeptide chain are referred to as the carboxyl terminus (C-terminus) and the amino terminus (N-terminus) based on the nature of the free group on each extremity. Counting of residues always starts at the N-terminal end (NH2-group), which is the end where the amino group is not involved in a peptide bond. The primary structure of a protein is determined by the gene corresponding to the protein. A specific sequence of nucleotides in DNA is transcribed into mRNA, which is read by the ribosome in a process called translation. The sequence of amino acids in insulin was discovered by Frederick Sanger, establishing that proteins have defining amino acid sequences. The sequence of a protein is unique to that protein, and defines the structure and function of the protein. The sequence of a protein can be determined by methods such as Edman degradation or tandem mass spectrometry. Often, however, it is read directly from the sequence of the gene using the genetic code. It is strictly recommended to use the words "amino acid residues" when discussing proteins because when a peptide bond is formed, a water molecule is lost, and therefore proteins are made up of amino acid residues. Post-translational modifications such as phosphorylations and glycosylations are usually also considered a part of the primary structure, and cannot be read from the gene. For example, insulin is composed of 51 amino acids in 2 chains. One chain has 31 amino acids, and the other has 20 amino acids.
Secondary structure
Secondary structure refers to highly regular local sub-structures on the actual polypeptide backbone chain. Two main types of secondary structure, the α-helix and the β-strand or β-sheets, were suggested in 1951 by Linus Pauling. These secondary structures are defined by patterns of hydrogen bonds between the main-chain peptide groups. They have a regular geometry, being constrained to specific values of the dihedral angles ψ and φ on the Ramachandran plot. Both the α-helix and the β-sheet represent a way of saturating all the hydrogen bond donors and acceptors in the peptide backbone. Some parts of the protein are ordered but do not form any regular structures. They should not be confused with random coil, an unfolded polypeptide chain lacking any fixed three-dimensional structure. Several sequential secondary structures may form a "supersecondary unit".
Tertiary structure
Tertiary structure refers to the three-dimensional structure created by a single protein molecule (a single polypeptide chain). It may include one or several domains. The α-helices and β-pleated-sheets are folded into a compact globular structure. The folding is driven by the non-specific hydrophobic interactions, the burial of hydrophobic residues from water, but the structure is stable only when the parts of a protein domain are locked into place by specific tertiary interactions, such as salt bridges, hydrogen bonds, and the tight packing of side chains and disulfide bonds. The disulfide bonds are extremely rare in cytosolic proteins, since the cytosol (intracellular fluid) is generally a reducing environment.
Quaternary structure
Quaternary structure is the three-dimensional structure consisting of the aggregation of two or more individual polypeptide chains (subunits) that operate as a single functional unit (multimer). The resulting multimer is stabilized by the same non-covalent interactions and disulfide bonds as in tertiary structure. There are many possible quaternary structure organisations. Complexes of two or more polypeptides (i.e. multiple subunits) are called multimers. Specifically it would be called a dimer if it contains two subunits, a trimer if it contains three subunits, a tetramer if it contains four subunits, and a pentamer if it contains five subunits. The subunits are frequently related to one another by symmetry operations, such as a 2-fold axis in a dimer. Multimers made up of identical subunits are referred to with a prefix of "homo-" and those made up of different subunits are referred to with a prefix of "hetero-", for example, a heterotetramer, such as the two alpha and two beta chains of hemoglobin.
Domains, motifs, and folds in protein structure
Proteins are frequently described as consisting of several structural units. These units include domains, motifs, and folds. Despite the fact that there are about 100,000 different proteins expressed in eukaryotic systems, there are many fewer different domains, structural motifs and folds.
Structural domain
A structural domain is an element of the protein's overall structure that is self-stabilizing and often folds independently of the rest of the protein chain. Many domains are not unique to the protein products of one gene or one gene family but instead appear in a variety of proteins. Domains often are named and singled out because they figure prominently in the biological function of the protein they belong to; for example, the "calcium-binding domain of calmodulin". Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimera proteins. A conservative combination of several domains that occur in different proteins, such as protein tyrosine phosphatase domain and C2 domain pair, was called "a superdomain" that may evolve as a single unit.
Structural and sequence motifs
The structural and sequence motifs refer to short segments of protein three-dimensional structure or amino acid sequence that were found in a large number of different proteins
Supersecondary structure
Tertiary protein structures can have multiple secondary elements on the same polypeptide chain. The supersecondary structure refers to a specific combination of secondary structure elements, such as β-α-β units or a helix-turn-helix motif. Some of them may be also referred to as structural motifs.
Protein fold
A protein fold refers to the general protein architecture, like a helix bundle, β-barrel, Rossmann fold or different "folds" provided in the Structural Classification of Proteins database. A related concept is protein topology.
Protein dynamics and conformational ensembles
Proteins are not static objects, but rather populate ensembles of conformational states. Transitions between these states typically occur on nanoscales, and have been linked to functionally relevant phenomena such as allosteric signaling and enzyme catalysis. Protein dynamics and conformational changes allow proteins to function as nanoscale biological machines within cells, often in the form of multi-protein complexes. Examples include motor proteins, such as myosin, which is responsible for muscle contraction, kinesin, which moves cargo inside cells away from the nucleus along microtubules, and dynein, which moves cargo inside cells towards the nucleus and produces the axonemal beating of motile cilia and flagella. "[I]n effect, the [motile cilium] is a nanomachine composed of perhaps over 600 proteins in molecular complexes, many of which also function independently as nanomachines...Flexible linkers allow the mobile protein domains connected by them to recruit their binding partners and induce long-range allostery via protein domain dynamics. "
Proteins are often thought of as relatively stable tertiary structures that experience conformational changes after being affected by interactions with other proteins or as a part of enzymatic activity. However, proteins may have varying degrees of stability, and some of the less stable variants are intrinsically disordered proteins. These proteins exist and function in a relatively 'disordered' state lacking a stable tertiary structure. As a result, they are difficult to describe by a single fixed tertiary structure. Conformational ensembles have been devised as a way to provide a more accurate and 'dynamic' representation of the conformational state of intrinsically disordered proteins.
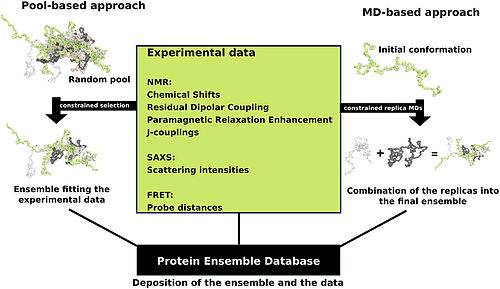
Protein ensemble files are a representation of a protein that can be considered to have a flexible structure. Creating these files requires determining which of the various theoretically possible protein conformations actually exist. One approach is to apply computational algorithms to the protein data in order to try to determine the most likely set of conformations for an ensemble file. There are multiple methods for preparing data for the Protein Ensemble Database that fall into two general methodologies – pool and molecular dynamics (MD) approaches (diagrammed in the figure). The pool based approach uses the protein’s amino acid sequence to create a massive pool of random conformations. This pool is then subjected to more computational processing that creates a set of theoretical parameters for each conformation based on the structure. Conformational subsets from this pool whose average theoretical parameters closely match known experimental data for this protein are selected. The alternative molecular dynamics approach takes multiple random conformations at a time and subjects all of them to experimental data. Here the experimental data is serving as limitations to be placed on the conformations (e.g. known distances between atoms). Only conformations that manage to remain within the limits set by the experimental data are accepted. This approach often applies large amounts of experimental data to the conformations which is a very computationally demanding task.
The conformational ensembles were generated for a number of highly dynamic and partially unfolded proteins, such as Sic1/Cdc4, p15 PAF, MKK7, Beta-synuclein and P27
Protein folding
As it is translated, polypeptides exit the ribosome mostly as a random coil and folds into its native state. The final structure of the protein chain is generally assumed to be determined by its amino acid sequence (Anfinsen's dogma).
Protein stability
Thermodynamic stability of proteins represents the free energy difference between the folded and unfolded protein states. This free energy difference is very sensitive to temperature, hence a change in temperature may result in unfolding or denaturation. Protein denaturation may result in loss of function, and loss of native state. The free energy of stabilization of soluble globular proteins typically does not exceed 50 kJ/mol. Taking into consideration the large number of hydrogen bonds that take place for the stabilization of secondary structures, and the stabilization of the inner core through hydrophobic interactions, the free energy of stabilization emerges as small difference between large numbers.
Protein structure determination
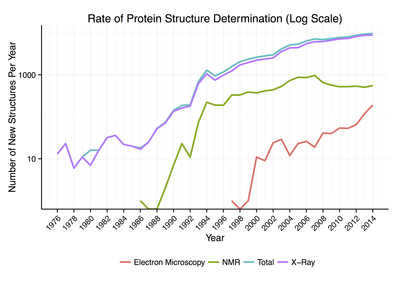
Around 90% of the protein structures available in the Protein Data Bank have been determined by X-ray crystallography. This method allows one to measure the three-dimensional (3-D) density distribution of electrons in the protein, in the crystallized state, and thereby infer the 3-D coordinates of all the atoms to be determined to a certain resolution. Roughly 7% of the known protein structures have been obtained by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques. For larger protein complexes, cryo-electron microscopy can determine protein structures. The resolution is typically lower than that of X-ray crystallography, or NMR, but the maximum resolution is steadily increasing. This technique is still a particularly valuable for very large protein complexes such as virus coat proteins and amyloid fibers.
General secondary structure composition can be determined via circular dichroism. Vibrational spectroscopy can also be used to characterize the conformation of peptides, polypeptides, and proteins. Two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy has become a valuable method to investigate the structures of flexible peptides and proteins that cannot be studied with other methods. A more qualitative picture of protein structure is often obtained by proteolysis, which is also useful to screen for more crystallizable protein samples. Novel implementations of this approach, including fast parallel proteolysis (FASTpp), can probe the structured fraction and its stability without the need for purification. Once a protein's structure has been experimentally determined, further detailed studies can be done computationally, using molecular dynamic simulations of that structure.
Protein structure databases
A protein structure database is a database that is modeled around the various experimentally determined protein structures. The aim of most protein structure databases is to organize and annotate the protein structures, providing the biological community access to the experimental data in a useful way. Data included in protein structure databases often includes 3D coordinates as well as experimental information, such as unit cell dimensions and angles for x-ray crystallography determined structures. Though most instances, in this case either proteins or a specific structure determinations of a protein, also contain sequence information and some databases even provide means for performing sequence based queries, the primary attribute of a structure database is structural information, whereas sequence databases focus on sequence information, and contain no structural information for the majority of entries. Protein structure databases are critical for many efforts in computational biology such as structure based drug design, both in developing the computational methods used and in providing a large experimental dataset used by some methods to provide insights about the function of a protein.
Structural classifications of proteins
Protein structures can be grouped based on their structural similarity, topological class or a common evolutionary origin. The Structural Classification of Proteins database and CATH database provide two different structural classifications of proteins. When the structural similarity is large the two proteins have possibly diverged from a common ancestor, and shared structure between proteins is considered evidence of homology. Structure similarity can then be used to group proteins together into protein superfamilies. If shared structure is significant but the fraction shared is small, the fragment shared may be the consequence of a more dramatic evolutionary event such as horizontal gene transfer, and joining proteins sharing these fragments into protein superfamilies is no longer justified. Topology of a protein can be used to classify proteins as well. Knot theory and circuit topology are two topology frameworks developed for classification of protein folds based on chain crossing and intrachain contacts respectively.
Computational prediction of protein structure
The generation of a protein sequence is much easier than the determination of a protein structure. However, the structure of a protein gives much more insight in the function of the protein than its sequence. Therefore, a number of methods for the computational prediction of protein structure from its sequence have been developed. Ab initio prediction methods use just the sequence of the protein. Threading and homology modeling methods can build a 3-D model for a protein of unknown structure from experimental structures of evolutionarily-related proteins, called a protein family.