Priestley by Ellen Sharples (1794)
During his lifetime, Priestley's considerable scientific reputation rested on his invention of soda water, his writings on electricity,
and his discovery of several "airs" (gases), the most famous being what
Priestley dubbed "dephlogisticated air" (oxygen). However, Priestley's
determination to defend phlogiston theory and to reject what would become the chemical revolution eventually left him isolated within the scientific community.
Priestley's science was integral to his theology, and he consistently tried to fuse Enlightenment rationalism with Christian theism. In his metaphysical texts, Priestley attempted to combine theism, materialism, and determinism, a project that has been called "audacious and original". He believed that a proper understanding of the natural world would promote human progress and eventually bring about the Christian millennium. Priestley, who strongly believed in the free and open exchange of ideas, advocated toleration and equal rights for religious Dissenters, which also led him to help found Unitarianism in England. The controversial nature of Priestley's publications, combined with his outspoken support of the French Revolution,
aroused public and governmental suspicion; he was eventually forced to
flee in 1791, first to London and then to the United States, after a mob
burned down his Birmingham home and church. He spent his last ten years in Northumberland County, Pennsylvania.
A scholar and teacher throughout his life, Priestley also made significant contributions to pedagogy, including the publication of a seminal work on English grammar
and books on history, and he prepared some of the most influential
early timelines. These educational writings were among Priestley's most
popular works. It was his metaphysical works, however, that had the most
lasting influence, being considered primary sources for utilitarianism by philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham, John Stuart Mill, and Herbert Spencer.
Early life and education (1733–55)
Priestley's birthplace (since demolished) in Fieldhead, Birstall, West Yorkshire – about six miles (10 km) southwest of Leeds
Priestley was born to an established English Dissenting family (i.e. they did not conform to the Church of England) in Birstall, near Batley in the West Riding of Yorkshire. He was the oldest of six children born to Mary Swift and Jonas Priestley, a finisher
of cloth. To ease his mother's burdens, Priestley was sent to live with
his grandfather around the age of one. He returned home, five years
later, after his mother died. When his father remarried in 1741,
Priestley went to live with his aunt and uncle, the wealthy and
childless Sarah and John Keighley, 3 miles (4.8 km) from Fieldhead. Because Priestley was precocious—at the age of four he could flawlessly recite all 107 questions and answers of the Westminster Shorter Catechism—his
aunt sought the best education for the boy, intending him for the
ministry. During his youth, Priestley attended local schools where he
learned Greek, Latin, and Hebrew.
Around 1749, Priestley became seriously ill and believed he was dying. Raised as a devout Calvinist, he believed a conversion experience
was necessary for salvation, but doubted he had had one. This emotional
distress eventually led him to question his theological upbringing,
causing him to reject election and to accept universal salvation. As a result, the elders of his home church, the Independent Upper Chapel of Heckmondwike, refused him admission as a full member.
Priestley's illness left him with a permanent stutter and he gave
up any thoughts of entering the ministry at that time. In preparation
for joining a relative in trade in Lisbon, he studied French, Italian, and German in addition to Aramaic, and Arabic. He was tutored by the Reverend George Haggerstone, who first introduced him to higher mathematics, natural philosophy, logic, and metaphysics through the works of Isaac Watts, Willem 's Gravesande, and John Locke.
Daventry Academy
Priestley eventually decided to return to his theological studies and, in 1752, matriculated at Daventry, a Dissenting academy.
Because he had already read widely, Priestley was allowed to skip the
first two years of coursework. He continued his intense study; this,
together with the liberal atmosphere of the school, shifted his theology
further leftward and he became a Rational Dissenter.
Abhorring dogma and religious mysticism, Rational Dissenters emphasised
the rational analysis of the natural world and the Bible.
Priestley later wrote that the book that influenced him the most, save the Bible, was David Hartley's Observations on Man (1749). Hartley's psychological, philosophical, and theological treatise postulated a material theory of mind.
Hartley aimed to construct a Christian philosophy in which both
religious and moral "facts" could be scientifically proven, a goal that
would occupy Priestley for his entire life. In his third year at
Daventry, Priestley committed himself to the ministry, which he
described as "the noblest of all professions".
Needham Market and Nantwich (1755–61)
Title page of Rudiments of English Grammar (1761)
Robert Schofield, Priestley's major modern biographer, describes his first "call" in 1755 to the Dissenting parish in Needham Market, Suffolk, as a "mistake" for both Priestley and the congregation.
Priestley yearned for urban life and theological debate, whereas
Needham Market was a small, rural town with a congregation wedded to
tradition. Attendance and donations dropped sharply when they discovered
the extent of his heterodoxy.
Although Priestley's aunt had promised her support if he became a
minister, she refused any further assistance when she realised he was no
longer a Calvinist.
To earn extra money, Priestley proposed opening a school, but local
families informed him that they would refuse to send their children. He
also presented a series of scientific lectures titled "Use of the
Globes" that was more successful.
Sweetbriar Hall plaque
Priestley's Daventry friends helped him obtain another position and in 1758 he moved to Nantwich, Cheshire, living at Sweetbriar Hall
in the town's Hospital Street; his time there was happier. The
congregation cared less about Priestley's heterodoxy and he successfully
established a school. Unlike many schoolmasters of the time, Priestley
taught his students natural philosophy
and even bought scientific instruments for them. Appalled at the
quality of the available English grammar books, Priestley wrote his own:
The Rudiments of English Grammar (1761). His innovations in the description of English grammar, particularly his efforts to dissociate it from Latin grammar, led 20th-century scholars to describe him as "one of the great grammarians of his time". After the publication of Rudiments and the success of Priestley's school, Warrington Academy offered him a teaching position in 1761.
Warrington Academy (1761–1767)
Jasperware cameo of Priestley, Josiah Wedgwood & Sons
Mary Priestley, by Carl F. von Breda (1793); daughter of ironmaster Isaac Wilkinson, sister of industrialist John Wilkinson
In 1761, Priestley moved to Warrington and assumed the post of tutor of modern languages and rhetoric at the town's Dissenting academy,
although he would have preferred to teach mathematics and natural
philosophy. He fitted in well at Warrington, and made friends quickly. These included John Aikin, his sister Anna Laetitia Aikin, and Josiah Wedgwood.
Wedgwood met Priestley in 1762, after a fall from his horse. Wedgwood
and Priestley met rarely, but exchanged letters, advice on chemistry,
and laboratory equipment. Wedgwood eventually created a medallion of
Priestley in cream-on-blue jasperware.
On 23 June 1762, Priestley married Mary Wilkinson of Wrexham. Of his marriage, Priestley wrote:
This proved a very suitable and happy connexion, my wife being a woman of an excellent understanding, much improved by reading, of great fortitude and strength of mind, and of a temper in the highest degree affectionate and generous; feeling strongly for others, and little for herself. Also, greatly excelling in every thing relating to household affairs, she entirely relieved me of all concern of that kind, which allowed me to give all my time to the prosecution of my studies, and the other duties of my station.
On 17 April 1763, they had a daughter, whom they named Sarah after Priestley's aunt.
Educator and historian
All of the books Priestley published while at Warrington emphasised
the study of history; Priestley considered it essential for worldly
success as well as religious growth. He wrote histories of science and
Christianity in an effort to reveal the progress of humanity and,
paradoxically, the loss of a pure, "primitive Christianity".
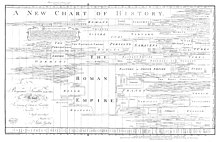
A redacted version of A New Chart of History
(1765); Priestley believed this chart would "impress" upon students "a
just image of the rise, progress, extent, duration, and contemporary
state of all the considerable empires that have ever existed in the
world"
In his Essay on a Course of Liberal Education for Civil and Active Life (1765), Lectures on History and General Policy
(1788), and other works, Priestley argued that the education of the
young should anticipate their future practical needs. This principle of
utility guided his unconventional curricular choices for Warrington's
aspiring middle-class students. He recommended modern languages instead
of classical languages and modern rather than ancient history.
Priestley's lectures on history were particularly revolutionary; he
narrated a providentialist
and naturalist account of history, arguing that the study of history
furthered the comprehension of God's natural laws. Furthermore, his millennial
perspective was closely tied to his optimism regarding scientific
progress and the improvement of humanity. He believed that each age
would improve upon the previous and that the study of history allowed
people to perceive and to advance this progress. Since the study of
history was a moral imperative for Priestley, he also promoted the
education of middle-class women, which was unusual at the time. Some scholars of education have described Priestley as the most important English writer on education between the 17th-century John Locke and the 19th-century Herbert Spencer. Lectures on History was well received and was employed by many educational institutions, such as New College at Hackney, Brown, Princeton, Yale, and Cambridge. Priestley designed two Charts to serve as visual study aids for his Lectures. These charts are in fact timelines; they have been described as the most influential timelines published in the 18th century.
Both were popular for decades, and the trustees of Warrington were so
impressed with Priestley's lectures and charts that they arranged for
the University of Edinburgh to grant him a Doctor of Law degree in 1764.
History of electricity
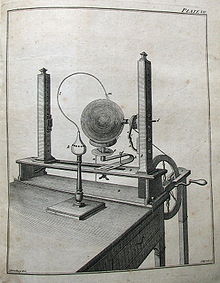
Priestley's "electrical machine for amateur experimentalists", illustrated in the first edition of his Familiar Introduction to the Study of Electricity (1768)
The intellectually stimulating atmosphere of Warrington, often called
the "Athens of the North" (of England) during the 18th century,
encouraged Priestley's growing interest in natural philosophy. He gave
lectures on anatomy and performed experiments regarding temperature with
another tutor at Warrington, his friend John Seddon.
Despite Priestley's busy teaching schedule, he decided to write a
history of electricity. Friends introduced him to the major
experimenters in the field in Britain—John Canton, William Watson, and the visiting Benjamin Franklin—who
encouraged Priestley to perform the experiments he wanted to include in
his history. In the process of replicating others' experiments,
Priestley became intrigued by unanswered questions and was prompted to
undertake experiments of his own design. (Impressed with his Charts and the manuscript of his history of electricity, Canton, Franklin, Watson, and Richard Price nominated Priestley for a fellowship in the Royal Society; he was accepted in 1766.)
In 1767, the 700-page The History and Present State of Electricity was published to positive reviews.
The first half of the text is a history of the study of electricity to
1766; the second and more influential half is a description of
contemporary theories about electricity and suggestions for future
research. Priestley reported some of his own discoveries in the second
section, such as the conductivity of charcoal and other substances and the continuum between conductors and non-conductors.
This discovery overturned what he described as "one of the earliest and
universally received maxims of electricity", that only water and metals
could conduct electricity. This and other experiments on the electrical
properties of materials and on the electrical effects of chemical
transformations demonstrated Priestley's early and ongoing interest in
the relationship between chemical substances and electricity. Based on experiments with charged spheres, Priestley was among the first to propose that electrical force followed an inverse-square law, similar to Newton's law of universal gravitation. However, he did not generalise or elaborate on this, and the general law was enunciated by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb in the 1780s.
Priestley's strength as a natural philosopher was qualitative
rather than quantitative and his observation of "a current of real air"
between two electrified points would later interest Michael Faraday and James Clerk Maxwell as they investigated electromagnetism. Priestley's text became the standard history of electricity for over a century; Alessandro Volta (who later invented the battery), William Herschel (who discovered infrared radiation), and Henry Cavendish (who discovered hydrogen) all relied upon it. Priestley wrote a popular version of the History of Electricity for the general public titled A Familiar Introduction to the Study of Electricity (1768). He marketed the book with his brother Timothy, but unsuccessfully.
Leeds (1767–73)
The
earliest known portrait of Priestley, known as the "Leeds" portrait (c.
1763); except for his membership on the Leeds Library Committee,
Priestley was not active in the town's social life
Perhaps prompted by Mary Priestley's ill health, or financial
problems, or a desire to prove himself to the community that had
rejected him in his childhood, Priestley moved with his family from
Warrington to Leeds in 1767, and he became Mill Hill Chapel's minister. Two sons were born to the Priestleys in Leeds: Joseph junior on 24 July 1768 and William three years later. Theophilus Lindsey, a rector at Catterick, Yorkshire,
became one of Priestley's few friends in Leeds, of whom he wrote: "I
never chose to publish any thing of moment relating to theology, without
consulting him."
Although Priestley had extended family living around Leeds, it does not
appear that they communicated. Schofield conjectures that they
considered him a heretic. Each year Priestley travelled to London to consult with his close friend and publisher, Joseph Johnson, and to attend meetings of the Royal Society.
Minister of Mill Hill Chapel
Priestley had been working on Institutes of Natural and Revealed Religion since his Daventry days.
When Priestley became its minister, Mill Hill Chapel was one of the oldest and most respected Dissenting congregations in England;
however, during the early 18th century the congregation had fractured
along doctrinal lines, and was losing members to the charismatic Methodist movement. Priestley believed that by educating the young, he could strengthen the bonds of the congregation.
In his magisterial three-volume Institutes of Natural and Revealed Religion (1772–74), Priestley outlined his theories of religious instruction. More importantly, he laid out his belief in Socinianism. The doctrines he explicated would become the standards for Unitarians
in Britain. This work marked a change in Priestley's theological
thinking that is critical to understanding his later writings—it paved
the way for his materialism and necessitarianism (the belief that a divine being acts in accordance with necessary metaphysical laws).
Priestley's major argument in the Institutes was that the
only revealed religious truths that could be accepted were those that
matched one's experience of the natural world. Because his views of
religion were deeply tied to his understanding of nature, the text's theism rested on the argument from design. The Institutes shocked and appalled many readers, primarily because it challenged basic Christian orthodoxies, such as the divinity of Christ and the miracle of the Virgin Birth. Methodists in Leeds penned a hymn asking God to "the Unitarian fiend expel / And chase his doctrine back to Hell."
Priestley wanted to return Christianity to its "primitive" or "pure"
form by eliminating the "corruptions" which had accumulated over the
centuries. The fourth part of the Institutes, An History of the Corruptions of Christianity, became so long that he was forced to issue it separately in 1782. Priestley believed that the Corruptions
was "the most valuable" work he ever published. In demanding that his
readers apply the logic of the emerging sciences and comparative history
to the Bible and Christianity, he alienated religious and scientific
readers alike—scientific readers did not appreciate seeing science used
in the defence of religion and religious readers dismissed the
application of science to religion.
Religious controversialist
Priestley engaged in numerous political and religious pamphlet
wars. According to Schofield, "he entered each controversy with a
cheerful conviction that he was right, while most of his opponents were
convinced, from the outset, that he was willfully and maliciously wrong.
He was able, then, to contrast his sweet reasonableness to their
personal rancor", but as Schofield points out Priestley rarely altered his opinion as a result of these debates. While at Leeds he wrote controversial pamphlets on the Lord's Supper and on Calvinist doctrine; thousands of copies were published, making them some of Priestley's most widely read works.
Priestley founded the Theological Repository
in 1768, a journal committed to the open and rational inquiry of
theological questions. Although he promised to print any contribution,
only like-minded authors submitted articles. He was therefore obliged to
provide much of the journal's content himself (this material became the
basis for many of his later theological and metaphysical works). After
only a few years, due to a lack of funds, he was forced to cease
publishing the journal. He revived it in 1784 with similar results.
Defender of Dissenters and political philosopher
His Essay on the First Principles of Government (1768) influenced early 19th-century political philosophers, including Jeremy Bentham.
Many of Priestley's political writings supported the repeal of the Test and Corporation Acts,
which restricted the rights of Dissenters. They could not hold
political office, serve in the armed forces, or attend Oxford and
Cambridge unless they subscribed to the Thirty-nine Articles of the Church of England. Dissenters repeatedly petitioned Parliament to repeal the Acts, arguing that they were being treated as second-class citizens.
Priestley's friends, particularly other Rational Dissenters,
urged him to publish a work on the injustices experienced by Dissenters;
the result was his Essay on the First Principles of Government (1768). An early work of modern liberal political theory
and Priestley's most thorough treatment of the subject, it—unusually
for the time—distinguished political rights from civil rights with
precision and argued for expansive civil rights. Priestley identified
separate private and public spheres, contending that the government
should only have control over the public sphere. Education and religion,
in particular, he maintained, were matters of private conscience and
should not be administered by the state. Priestley's later radicalism
emerged from his belief that the British government was infringing upon
these individual freedoms.
Priestley also defended the rights of Dissenters against the attacks of William Blackstone, an eminent legal theorist, whose Commentaries on the Laws of England
(1765–69) had become the standard legal guide. Blackstone's book stated
that dissent from the Church of England was a crime and that Dissenters
could not be loyal subjects. Furious, Priestley lashed out with his Remarks on Dr. Blackstone's Commentaries (1769), correcting Blackstone's interpretation of the law, his grammar (a highly politicised subject at the time), and history. Blackstone, chastened, altered subsequent editions of his Commentaries:
he rephrased the offending passages and removed the sections claiming
that Dissenters could not be loyal subjects, but he retained his
description of Dissent as a crime.
Natural philosopher: electricity, Optics, and soda water
Optics: The History and Present State of Vision, Light, and Colours, published in 1772, London
Although Priestley claimed that natural philosophy was only a hobby, he took it seriously. In his History of Electricity, he described the scientist as promoting the "security and happiness of mankind". Priestley's science was eminently practical and he rarely concerned himself with theoretical questions; his model was Benjamin Franklin.
When he moved to Leeds, Priestley continued his electrical and chemical
experiments (the latter aided by a steady supply of carbon dioxide from
a neighbouring brewery). Between 1767 and 1770, he presented five
papers to the Royal Society from these initial experiments; the first four papers explored coronal discharges and other phenomena related to electrical discharge,
while the fifth reported on the conductivity of charcoals from
different sources. His subsequent experimental work focused on chemistry
and pneumatics.
Priestley published the first volume of his projected history of experimental philosophy, The History and Present State of Discoveries Relating to Vision, Light and Colours (referred to as his Optics), in 1772.
He paid careful attention to the history of optics and presented
excellent explanations of early optics experiments, but his mathematical
deficiencies caused him to dismiss several important contemporary
theories. Furthermore, he did not include any of the practical sections
that had made his History of Electricity so useful to practising natural philosophers. Unlike his History of Electricity,
it was not popular and had only one edition, although it was the only
English book on the topic for 150 years. The hastily written text sold
poorly; the cost of researching, writing, and publishing the Optics convinced Priestley to abandon his history of experimental philosophy.
Priestley was considered for the position of astronomer on James Cook's second voyage to the South Seas, but was not chosen. Still, he contributed in a small way to the voyage: he provided the crew with a method for making soda water, which he erroneously speculated might be a cure for scurvy. He then published a pamphlet with Directions for Impregnating Water with Fixed Air (1772). Priestley did not exploit the commercial potential of soda water, but others such as J. J. Schweppe made fortunes from it. For his discovery of soda water Priestley has been labelled “the father of the soft drink”, with the beverage company Schweppes regarding him as “the father of our industry”. In 1773, the Royal Society recognised Priestley's achievements in natural philosophy by awarding him the Copley Medal.
Priestley's friends wanted to find him a more financially secure position. In 1772, prompted by Richard Price and Benjamin Franklin, Lord Shelburne
wrote to Priestley asking him to direct the education of his children
and to act as his general assistant. Although Priestley was reluctant to
sacrifice his ministry, he accepted the position, resigning from Mill
Hill Chapel on 20 December 1772, and preaching his last sermon on 16 May
1773.
Calne (1773–80)
A portrait of Priestley commissioned by his publisher and close friend Joseph Johnson from Henry Fuseli (c. 1783)
In 1773, the Priestleys moved to Calne in Wiltshire, and a year later Lord Shelburne and Priestley took a tour of Europe. According to Priestley's close friend Theophilus Lindsey, Priestley was "much improved by this view of mankind at large".
Upon their return, Priestley easily fulfilled his duties as librarian
and tutor. The workload was intentionally light, allowing him time to
pursue his scientific investigations and theological interests.
Priestley also became a political adviser to Shelburne, gathering
information on parliamentary issues and serving as a liaison between
Shelburne and the Dissenting and American interests. When the
Priestleys' third son was born on 24 May 1777, they named him Henry at
the lord's request.
Materialist philosopher
By 1782, at least a dozen hostile refutations were published to Disquisitions relating to Matter and Spirit, and Priestley was branded an atheist.
Priestley wrote his most important philosophical works during his years with Lord Shelburne. In a series of major metaphysical texts published between 1774 and 1780—An Examination of Dr. Reid's Inquiry into the Human Mind (1774), Hartley's Theory of the Human Mind on the Principle of the Association of Ideas (1775), Disquisitions relating to Matter and Spirit (1777), The Doctrine of Philosophical Necessity Illustrated (1777), and Letters to a Philosophical Unbeliever (1780)—he argues for a philosophy that incorporates four concepts: determinism, materialism, causation, and necessitarianism. By studying the natural world, he argued, people would learn how to become more compassionate, happy, and prosperous.
Priestley strongly suggested that there is no mind-body duality,
and put forth a materialist philosophy in these works; that is, one
founded on the principle that everything in the universe is made of
matter that we can perceive. He also contended that discussing the soul
is impossible because it is made of a divine substance, and humanity
cannot perceive the divine. Despite his separation of the divine from
the mortal, this position shocked and angered many of his readers, who
believed that such a duality was necessary for the soul to exist.
Responding to Baron d'Holbach's Système de la Nature (1770) and David Hume's Dialogues Concerning Natural Religion (1779) as well as the works of the French philosophers,
Priestley maintained that materialism and determinism could be
reconciled with a belief in God. He criticised those whose faith was
shaped by books and fashion, drawing an analogy between the scepticism
of educated men and the credulity of the masses.
Maintaining that humans had no free will, Priestley argued that what he called "philosophical necessity" (akin to absolute determinism)
is consonant with Christianity, a position based on his understanding
of the natural world. Like the rest of nature, man's mind is subject to
the laws of causation, Priestley contended, but because a benevolent God
created these laws, the world and the people in it will eventually be
perfected. Evil is therefore only an imperfect understanding of the
world.
Although Priestley's philosophical work has been characterised as "audacious and original", it partakes of older philosophical traditions on the problems of free will, determinism, and materialism. For example, the 17th-century philosopher Baruch Spinoza argued for absolute determinism and absolute materialism. Like Spinoza and Priestley,
Leibniz argued that human will was completely determined by natural laws;
however, unlike them, Leibniz argued for a "parallel universe" of
immaterial objects (such as human souls) so arranged by God that its
outcomes agree exactly with those of the material universe.
Leibniz
and Priestley
share an optimism that God has chosen the chain of events benevolently;
however, Priestley believed that the events were leading to a glorious Millennial conclusion,
whereas for Leibniz the entire chain of events was optimal in and of
itself, as compared with other conceivable chains of events.
Founder of Unitarianism
When Priestley's friend Theophilus Lindsey
decided to found a new Christian denomination that would not restrict
its members' beliefs, Priestley and others hurried to his aid. On 17
April 1774, Lindsey held the first Unitarian service in Britain, at the newly formed Essex Street Chapel in London; he had even designed his own liturgy, of which many were critical. Priestley defended his friend in the pamphlet Letter to a Layman, on the Subject of the Rev. Mr. Lindsey's Proposal for a Reformed English Church (1774),
claiming that only the form of worship had been altered, not its
substance, and attacking those who followed religion as a fashion.
Priestley attended Lindsey's church regularly in the 1770s and
occasionally preached there. He continued to support institutionalised Unitarianism for the rest of his life, writing several Defenses of Unitarianism and encouraging the foundation of new Unitarian chapels throughout Britain and the United States.
Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air
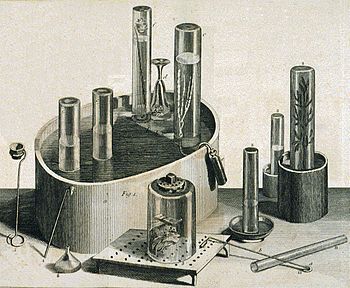
Equipment used by Priestley in his experiments on gases, 1775
Priestley's years in Calne were the only ones in his life dominated
by scientific investigations; they were also the most scientifically
fruitful. His experiments were almost entirely confined to "airs", and
out of this work emerged his most important scientific texts: the six
volumes of Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air (1774–86). These experiments helped repudiate the last vestiges of the theory of four elements, which Priestley attempted to replace with his own variation of phlogiston theory. According to that 18th-century theory, the combustion or oxidation of a substance corresponded to the release of a material substance, phlogiston.
Priestley's work on "airs" is not easily classified. As historian of science Simon Schaffer
writes, it "has been seen as a branch of physics, or chemistry, or
natural philosophy, or some highly idiosyncratic version of Priestley's
own invention".
Furthermore, the volumes were both a scientific and a political
enterprise for Priestley, in which he argues that science could destroy
"undue and usurped authority" and that government has "reason to tremble
even at an air pump or an electrical machine".
Volume I of Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air outlined several discoveries: "nitrous air" (nitric oxide, NO); "vapor of spirit of salt", later called "acid air" or "marine acid air" (anhydrous hydrochloric acid, HCl); "alkaline air" (ammonia, NH3); "diminished" or "dephlogisticated nitrous air" (nitrous oxide, N2O); and, most famously, "dephlogisticated air" (oxygen, O2)
as well as experimental findings that showed plants revitalised
enclosed volumes of air, a discovery that would eventually lead to the
discovery of photosynthesis. Priestley also developed a "nitrous air test" to determine the "goodness of air". Using a pneumatic trough, he would mix nitrous air with a test sample, over water or mercury, and measure the decrease in volume—the principle of eudiometry.
After a small history of the study of airs, he explained his own
experiments in an open and sincere style. As an early biographer writes,
"whatever he knows or thinks he tells: doubts, perplexities, blunders
are set down with the most refreshing candour."
Priestley also described his cheap and easy-to-assemble experimental
apparatus; his colleagues therefore believed that they could easily
reproduce his experiments.
Faced with inconsistent experimental results, Priestley employed
phlogiston theory. This, however, led him to conclude that there were
only three types of "air": "fixed", "alkaline", and "acid". Priestley
dismissed the burgeoning chemistry
of his day. Instead, he focused on gases and "changes in their sensible
properties", as had natural philosophers before him. He isolated carbon monoxide (CO), but apparently did not realise that it was a separate "air".
Discovery of oxygen
The laboratory at Lord Shelburne's estate, Bowood House, in which Priestley discovered oxygen
In August 1774 he isolated an "air" that appeared to be completely
new, but he did not have an opportunity to pursue the matter because he
was about to tour Europe with Shelburne. While in Paris, however,
Priestley managed to replicate the experiment for others, including
French chemist Antoine Lavoisier. After returning to Britain in January 1775, he continued his experiments and discovered "vitriolic acid air" (sulphur dioxide, SO2).
In March he wrote to several people regarding the new "air" that
he had discovered in August. One of these letters was read aloud to the Royal Society,
and a paper outlining the discovery, titled "An Account of further
Discoveries in Air", was published in the Society's journal Philosophical Transactions. Priestley called the new substance "dephlogisticated air", which he made in the famous experiment by focusing the sun's rays on a sample of mercuric oxide.
He first tested it on mice, who surprised him by surviving quite a
while entrapped with the air, and then on himself, writing that it was
"five or six times better than common air for the purpose of
respiration, inflammation, and, I believe, every other use of common
atmospherical air". He had discovered oxygen gas (O2).
William Petty, 2nd Earl of Shelburne – a fellow Unitarian – built a laboratory for the famous dissenter at Bowood House.
Priestley assembled his oxygen paper and several others into a second volume of Experiments and Observations on Air,
published in 1776. He did not emphasise his discovery of
"dephlogisticated air" (leaving it to Part III of the volume) but
instead argued in the preface how important such discoveries were to
rational religion. His paper narrated the discovery chronologically,
relating the long delays between experiments and his initial
puzzlements; thus, it is difficult to determine when exactly Priestley
"discovered" oxygen. Such dating is significant as both Lavoisier and Swedish pharmacist Carl Wilhelm Scheele
have strong claims to the discovery of oxygen as well, Scheele having
been the first to isolate the gas (although he published after
Priestley) and Lavoisier having been the first to describe it as
purified "air itself entire without alteration" (that is, the first to
explain oxygen without phlogiston theory).
In his paper "Observations on Respiration and the Use of the
Blood", Priestley was the first to suggest a connection between blood
and air, although he did so using phlogiston theory.
In typical Priestley fashion, he prefaced the paper with a history of
the study of respiration. A year later, clearly influenced by Priestley,
Lavoisier was also discussing respiration at the Académie des sciences.
Lavoisier's work began the long train of discovery that produced papers
on oxygen respiration and culminated in the overthrow of phlogiston
theory and the establishment of modern chemistry.
Around 1779 Priestley and Shelburne had a rupture, the precise
reasons for which remain unclear. Shelburne blamed Priestley's health,
while Priestley claimed Shelburne had no further use for him. Some
contemporaries speculated that Priestley's outspokenness had hurt
Shelburne's political career. Schofield argues that the most likely
reason was Shelburne's recent marriage to Louisa Fitzpatrick—apparently,
she did not like the Priestleys. Although Priestley considered moving
to America, he eventually accepted Birmingham New Meeting's offer to be their minister.
Both Priestley and Shelburne's families upheld their Unitarian faith for generations.
In December 2013, it was reported that Sir Christopher Bullock – a direct descendant of Shelburne's brother, Thomas Fitzmaurice (MP) – had married his wife, Lady Bullock, née Barbara May Lupton, at London's Unitarian Essex Church in 1917. Barbara Lupton was the second cousin of Olive Middleton, née Lupton, the great grandmother of Catherine, Duchess of Cambridge. In 1914, Olive and Noel Middleton had married at Leeds' Mill Hill Chapel, which Priestly, as its minister, had once guided towards Unitarianism.
Birmingham (1780–91)
In 1780 the Priestleys moved to Birmingham
and spent a happy decade surrounded by old friends, until they were
forced to flee in 1791 by religiously motivated mob violence in what
became known as the Priestley Riots.
Priestley accepted the ministerial position at New Meeting on the
condition that he be required to preach and teach only on Sundays, so
that he would have time for his writing and scientific experiments. As
in Leeds, Priestley established classes for the youth of his parish and
by 1781, he was teaching 150 students. Because Priestley's New Meeting
salary was only 100 guineas, friends and patrons donated money and goods to help continue his investigations. He was elected a Foreign Honorary Member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1782.
Chemical Revolution
One of a set of Lunar Society Moonstones commemorating Priestley at Great Barr, Birmingham
Many of the friends that Priestley made in Birmingham were members of the Lunar Society,
a group of manufacturers, inventors, and natural philosophers who
assembled monthly to discuss their work. The core of the group included
men such as the manufacturer Matthew Boulton, the chemist and geologist James Keir, the inventor and engineer James Watt, and the botanist, chemist, and geologist William Withering. Priestley was asked to join this unique society and contributed much to the work of its members.
As a result of this stimulating intellectual environment, he published
several important scientific papers, including "Experiments relating to
Phlogiston, and the seeming Conversion of Water into Air" (1783). The
first part attempts to refute Lavoisier's challenges to his work on
oxygen; the second part describes how steam is "converted" into air.
After several variations of the experiment, with different substances as
fuel and several different collecting apparatuses (which produced
different results), he concluded that air could travel through more
substances than previously surmised, a conclusion "contrary to all the
known principles of hydrostatics". This discovery, along with his earlier work on what would later be recognised as gaseous diffusion, would eventually lead John Dalton and Thomas Graham to formulate the kinetic theory of gases.
Antoine Lavoisier and his wife, Marie-Anne Pierrette Paulze, by Jacques-Louis David, 1788
In 1777, Antoine Lavoisier had written Mémoire sur la combustion en général, the first of what proved to be a series of attacks on phlogiston theory;
it was against these attacks that Priestley responded in 1783. While
Priestley accepted parts of Lavoisier's theory, he was unprepared to
assent to the major revolutions Lavoisier proposed: the overthrow of
phlogiston, a chemistry based conceptually on elements and compounds, and a new chemical nomenclature.
Priestley's original experiments on "dephlogisticated air" (oxygen),
combustion, and water provided Lavoisier with the data he needed to
construct much of his system; yet Priestley never accepted Lavoisier's
new theories and continued to defend phlogiston theory for the rest of
his life. Lavoisier's system was based largely on the quantitative concept that mass is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions (i.e., the conservation of mass). By contrast, Priestley preferred to observe qualitative
changes in heat, color, and particularly volume. His experiments tested
"airs" for "their solubility in water, their power of supporting or
extinguishing flame, whether they were respirable, how they behaved with
acid and alkaline air, and with nitric oxide and inflammable air, and
lastly how they were affected by the electric spark."
By 1789, when Lavoisier published his Traité Élémentaire de Chimie and founded the Annales de Chimie,
the new chemistry had come into its own. Priestley published several
more scientific papers in Birmingham, the majority attempting to refute
Lavoisier. Priestley and other Lunar Society members argued that the new
French system was too expensive, too difficult to test, and
unnecessarily complex. Priestley in particular rejected its
"establishment" aura. In the end, Lavoisier's view prevailed: his new
chemistry introduced many of the principles on which modern chemistry is founded.
Priestley's refusal to accept Lavoisier's "new chemistry"—such as the conservation of mass—and his determination to adhere to a less satisfactory theory has perplexed many scholars.
Schofield explains it thus: "Priestley was never a chemist; in a
modern, and even a Lavoisierian, sense, he was never a scientist. He was
a natural philosopher, concerned with the economy of nature and
obsessed with an idea of unity, in theology and in nature."
Historian of science John McEvoy largely agrees, writing that
Priestley's view of nature as coextensive with God and thus infinite,
which encouraged him to focus on facts over hypotheses and theories,
prompted him to reject Lavoisier's system.
McEvoy argues that "Priestley's isolated and lonely opposition to the
oxygen theory was a measure of his passionate concern for the principles
of intellectual freedom, epistemic equality and critical inquiry." Priestley himself claimed in the last volume of Experiments and Observations that his most valuable works were his theological ones because they were "superior [in] dignity and importance".
Defender of English Dissenters and French revolutionaries
DOCTOR PHLOGISTON,
The PRIESTLEY politician or the Political Priest
This anti-Priestley cartoon shows him trampling on the Bible and burning documents representing English freedom. "Essays on Matter and Spirit", "Gunpowder", and "Revolution Toasts" bulge from his pockets.
The PRIESTLEY politician or the Political Priest
This anti-Priestley cartoon shows him trampling on the Bible and burning documents representing English freedom. "Essays on Matter and Spirit", "Gunpowder", and "Revolution Toasts" bulge from his pockets.
Although Priestley was busy defending phlogiston theory from the "new
chemists", most of what he published in Birmingham was theological. In
1782 he published the fourth volume of his Institutes, An History of the Corruptions of Christianity, describing how he thought the teachings of the early Christian church had been "corrupted" or distorted.
Schofield describes the work as "derivative, disorganized, wordy, and
repetitive, detailed, exhaustive, and devastatingly argued".
The text addresses issues ranging from the divinity of Christ to the
proper form for the Lord's Supper. Priestley followed up in 1786 with
the provocatively titled book, An History of Early Opinions
concerning Jesus Christ, compiled from Original Writers, proving that
the Christian Church was at first Unitarian. Thomas Jefferson
would later write of the profound effect that these two books had on
him: "I have read his Corruptions of Christianity, and Early Opinions of
Jesus, over and over again; and I rest on them ... as the basis of my
own faith. These writings have never been answered."
Although a few readers such as Jefferson and other Rational Dissenters
approved of the work, it was harshly reviewed because of its extreme
theological positions, particularly its rejection of the Trinity.
In 1785, while Priestley was engaged in a pamphlet war over Corruptions, he also published The Importance and Extent of Free Enquiry, claiming that the Reformation had not really reformed the church. In words that would boil over into a national debate, he challenged his readers to enact change:
Let us not, therefore, be discouraged, though, for the present, we should see no great number of churches professedly unitarian .... We are, as it were, laying gunpowder, grain by grain, under the old building of error and superstition, which a single spark may hereafter inflame, so as to produce an instantaneous explosion; in consequence of which that edifice, the erection of which has been the work of ages, may be overturned in a moment, and so effectually as that the same foundation can never be built upon again ....
Although discouraged by friends from using such inflammatory
language, Priestley refused to back down from his opinions in print and
he included it, forever branding himself as "Gunpowder Joe". After the
publication of this seeming call for revolution in the midst of the French Revolution, pamphleteers stepped up their attacks on Priestley and he and his church were even threatened with legal action.
"A Word of Comfort" by William Dent (dated 22 March 1790). Priestley is preaching in front of Charles James Fox
who asks "Pray, Doctor, is there such a thing as a Devil?", to which
Priestley responds "No" while the devil prepares to attack Priestley
from behind.
In 1787, 1789, and 1790, Dissenters again tried to repeal the Test and Corporation Acts.
Although initially it looked as if they might succeed, by 1790, with
the fears of revolution looming in Parliament, few were swayed by
appeals to equal rights. Political cartoons, one of the most effective
and popular media of the time, skewered the Dissenters and Priestley. In Parliament, William Pitt and Edmund Burke
argued against the repeal, a betrayal that angered Priestley and his
friends, who had expected the two men's support. Priestley wrote a
series of Letters to William Pitt and Letters to Burke in an attempt to persuade them otherwise, but these publications only further inflamed the populace against him.
Dissenters such as Priestley who supported the French Revolution
came under increasing suspicion as scepticism regarding the revolution
grew.
In its propaganda against "radicals", Pitt's administration used the
"gunpowder" statement to argue that Priestley and other Dissenters
wanted to overthrow the government. Burke, in his famous Reflections on the Revolution in France
(1790), tied natural philosophers, and specifically Priestley, to the
French Revolution, writing that radicals who supported science in
Britain "considered man in their experiments no more than they do mice
in an air pump". Burke also associated republican
principles with alchemy and insubstantial air, mocking the scientific
work done by both Priestley and French chemists. He made much in his
later writings of the connections between "Gunpowder Joe", science, and
Lavoisier—who was improving gunpowder for the French in their war against Britain.
Paradoxically, a secular statesman, Burke, argued against science and
maintained that religion should be the basis of civil society, whereas a
Dissenting minister, Priestley, argued that religion could not provide
the basis for civil society and should be restricted to one's private
life.
Birmingham riots of 1791
The attack on Priestley's home, Fairhill, Sparkbrook, Birmingham
The animus that had been building against Dissenters and supporters
of the American and French Revolutions exploded in July 1791. Priestley
and several other Dissenters had arranged to have a celebratory dinner
on the anniversary of the storming of the Bastille,
a provocative action in a country where many disapproved of the French
Revolution and feared that it might spread to Britain. Amid fears of
violence, Priestley was convinced by his friends not to attend. Rioters
gathered outside the hotel during the banquet and attacked the attendees
as they left. The rioters moved on to the New Meeting and Old Meeting
churches—and burned both to the ground. Priestley and his wife fled from
their home; although their son William and others stayed behind to protect their property, the mob overcame them and torched Priestley's house "Fairhill" at Sparkbrook,
destroying his valuable laboratory and all of the family's belongings.
Twenty-six other Dissenters’ homes and three more churches were burned
in the three-day riot.
Priestley spent several days hiding with friends until he was able to
travel safely to London. The carefully executed attacks of the "mob" and
the farcical trials of only a handful of the "leaders" convinced many
at the time—and modern historians later—that the attacks were planned
and condoned by local Birmingham magistrates. When George III
was eventually forced to send troops to the area, he said: "I cannot
but feel better pleased that Priestley is the sufferer for the doctrines
he and his party have instilled, and that the people see them in their
true light."
Hackney (1791–94)
... Lo! Priestley there, patriot, and saint, and sage,
Him, full of years, from his loved native land
Statesmen blood-stained and priests idolatrous
By dark lies maddening the blind multitude
Drove with vain hate ....
From "Religious Musings" (1796) by Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Unable to return to Birmingham, the Priestleys eventually settled in Lower Clapton, a district in Hackney, Middlesex where he gave a series of lectures on history and natural philosophy at the Dissenting academy, the New College at Hackney.
Friends helped the couple rebuild their lives, contributing money,
books, and laboratory equipment. Priestley tried to obtain restitution
from the government for the destruction of his Birmingham property, but
he was never fully reimbursed. He also published An Appeal to the Public on the Subject of the Riots in Birmingham (1791),
which indicted the people of Birmingham for allowing the riots to occur
and for "violating the principles of English government".
The Friends of the People, 15 November 1792, caricaturing Joseph Priestley and Thomas Paine (Science History Institute)
Dumourier Dining in State at St James's, on 15 May 1793 by James Gillray: Priestley bears a mitre-crowned pie, as he, Fox and Sheridan serve Dumourier
The couple's friends urged them to leave Britain and emigrate to
either France or the new United States, even though Priestley had
received an appointment to preach for the Gravel Pit Meeting congregation. Priestley was minister between 1793 and 1794 and the sermons he preached there, particularly the two Fast Sermons, reflect his growing millenarianism,
his belief that the end of the world was fast approaching. After
comparing Biblical prophecies to recent history, Priestley concluded
that the French Revolution was a harbinger of the Second Coming of Christ. Priestley's works had always had a millennial cast, but after the beginning of the French Revolution, this strain increased.
He wrote to a younger friend that while he himself would not see the
Second Coming, his friend "may probably live to see it ... It cannot, I
think be more than twenty years [away]."
Daily life became more difficult for the family: Priestley was burned in effigy along with Thomas Paine;
vicious political cartoons continued to be published about him; letters
were sent to him from across the country, comparing him to the devil
and Guy Fawkes;
tradespeople feared the family's business; and Priestley's Royal
Academy friends distanced themselves. As the penalties became harsher
for those who spoke out against the government, Priestley examined
options for removing himself and his family from England.
Joseph Priestley's son William was presented to the French Assembly and granted letters of naturalization on 8 June 1792. Priestley learned about it from the Morning Chronicle.
A decree of 26 August 1792 by the French National Assembly conferred
French citizenship on Joseph Priestley and others who had "served the
cause of liberty" by their writings. Priestley accepted French citizenship, considering it "the greatest of honours". In the French National Convention election on 5 September 1792, Joseph Priestley was elected to the French National Convention by at least two departments, (Orne and Rhône-et-Loire). However, he declined the honour, on the grounds that he was not fluent in French.
As relations between England and France worsened, however, a removal to France became impracticable.
Following the declaration of war of February 1793, and the Aliens Bill
of March 1793, which forbade correspondence or travel between England
and France, William Priestley left France for America. Joseph
Priestley's sons Harry and Joseph chose to leave England for America in
August 1793. Finally Priestley himself followed with his wife, boarding the Sansom at Gravesend on 7 April 1794. Five weeks after Priestley left, William Pitt's administration began arresting radicals for seditious libel, resulting in the famous 1794 Treason Trials.
Pennsylvania (1794–1804)
Priestley, painted late in life by Rembrandt Peale (c. 1800);[160] Americans knew Priestley less as a man of science and more as a defender of the freedom of the colonies and of Dissenters.
The Priestleys arrived in New York City on 4 June 1794, where they were fêted
by various political factions vying for Priestley's endorsement.
Priestley declined their entreaties, hoping to avoid political discord
in his new country. Before travelling to a new home in the backwoods of Northumberland County, Pennsylvania, at Point township (now the Borough of Northumberland), Dr and Mrs Priestley lodged in Philadelphia, where Priestley gave a series of sermons which led to the founding of the First Unitarian Church of Philadelphia. Priestley turned down an opportunity to teach chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania.
Priestley's son Joseph Priestley Jr. was a leading member of a
consortium that had purchased 300,000 acres of virgin woodland between
the forks of Loyalsock Creek, which they intended to lease or sell in 400-acre plots, with payment deferred to seven annual instalments, with interest. His brothers, William
and Henry, bought a 284-acre plot of woodland which they attempted to
transform into a farm, later called "Fairhill", felling and uprooting
trees, and making lime to sweeten the soil by building their own lime kilns. Henry Priestley died 11 December 1795, possibly of malaria which he may have contracted after landing at New York. Mary Priestley's health, already poor, deteriorated further; although William's wife, Margaret Foulke-Priestley, moved in with the couple to nurse Mary twenty-four hours a day, Mary Priestley died 17 September 1796. Dr Priestley now moved in with his elder son, Joseph Jr., and his wife Elizabeth Ryland-Priestley. Thomas Cooper, whose son, Thomas Jr., was living with the Priestleys, was a frequent visitor.
Since his arrival in America, Priestley had continued to defend his Christian Unitarian
beliefs; now, falling increasingly under the influence of Thomas Cooper
and Elizabeth Ryland-Priestley, he was unable to avoid becoming
embroiled in political controversy. In 1798, when, in response to the Pinckney affair, a belligerent President Adams
sought to enlarge the navy and mobilise the militia into what Priestley
and Cooper saw as a 'standing army', Priestley published an anonymous
newspaper article: Maxims of political arithmetic, which attacked Adams, defended free trade, and advocated a form of Jeffersonian isolationism. In the same year, a small package, addressed vaguely: "Dr Priestley in America," was seized by the Royal Navy on board a neutral Danish boat. It was found to contain three letters, one of which was signed by the radical printer John Hurford Stone. These intercepted letters were published in London, and copied in numerous papers in America.
One of the letters was addressed to "MBP", with a note: "I inclose a
note for our friend MBP—but, as ignorant of the name he bears at present
among you, I must beg you to seal and address it." This gave the
intercepted letters a tinge of intrigue. Fearful lest they be taken as
evidence of him being a 'spy in the interest of France', Priestley sent a
clumsy letter to numerous newspaper editors, in which he naively named
"MBP" (Member of the British Parliament) as Mr. Benjamin Vaughan, who "like me, thought it necessary to leave England, and for some time is said to have assumed a feigned name." William Cobbett, in his Porcupine's Gazette,
20 August 1798, added that Priestley "has told us who Mr MBP is, and
has confirmed me in the opinion of their both being spies in the
interest of France."
The Priestleys' rural Pennsylvania home never became the center of a utopian community, as the expected emigrants could not afford the journey.
Joseph Priestley Jr. left on a visit to England at Christmas 1798,
not returning until August 1800. In his absence, his wife Elizabeth
Ryland-Priestley and Thomas Cooper became increasing close,
collaborating in numerous political essays.
Priestley allowed himself to fall too heavily under Elizabeth and
Cooper's influences, even helping hawk a seditious handbill Cooper had
printed, around Point township, and across the Susquehanna at Sunbury. In September 1799, William Cobbett
printed extracts from this handbill, asserting that: "Dr Priestley has
taken great pains to circulate this address, has travelled through the
country for the purpose, and is in fact the patron of it." He challenged
Priestley to "clear himself of the accusation" or face prosecution." Barely a month later, in November and December 1799, Priestley stepped forward in his own defence, with his Letters to the inhabitants of Northumberland.
Priestley's
original 1804 gravestone in Riverview Cemetery, Northumberland,
Pennsylvania. Visible at right is part of the new stone, placed in front
of it in 1971.
Priestley’s son, William, now living in Philadelphia, was increasingly embarrassed by his father's actions. He confronted his father, expressing John and Benjamin Vaughan’s unease, his own wife's concerns about Elizabeth Ryland-Priestley's dietary care,
and his own concerns at the closeness of Elizabeth Ryland-Priestley and
Thomas Cooper's relationship, and their adverse influence on Dr
Priestley; but this only led to a further estrangement between William
and his sister-in-law. When, a while later, Priestley's household
suffered a bout of food poisoning, perhaps from milk sickness or a bacterial infection,
Elizabeth Ryland-Priestley, falsely accused William of having poisoned
the family's flour. Although this allegation has attracted the attention
of some modern historians, it is believed to be without foundation.
Priestley continued the educational projects that had always been
important to him, helping to establish the "Northumberland Academy" and
donating his library to the fledgling institution. He exchanged letters
regarding the proper structure of a university with Thomas Jefferson, who used this advice when founding the University of Virginia. Jefferson and Priestley became close, and when he had completed his General History of the Christian Church,
he dedicated it to President Jefferson, writing that "it is now only
that I can say I see nothing to fear from the hand of power, the
government under which I live being for the first time truly favourable
to me."
Priestley tried to continue his scientific investigations in America with the support of the American Philosophical Society.
He was hampered by lack of news from Europe; unaware of the latest
scientific developments, Priestley was no longer on the forefront of
discovery. Although the majority of his publications focused on
defending phlogiston theory, he also did some original work on spontaneous generation and dreams. Despite Priestley's reduced scientific output, his presence stimulated American interest in chemistry.
By 1801, Priestley had become so ill that he could no longer write or experiment. He died on the morning of 6 February 1804, aged seventy and was buried at Riverview Cemetery in Northumberland, Pennsylvania.
Priestley's epitaph reads:
Return unto thy rest, O my soul, for the
Lord hath dealt bountifully with thee.
I will lay me down in peace and sleep till
I awake in the morning of the resurrection.
Legacy
By the time he died in 1804, Priestley had been made a member of
every major scientific society in the Western world and he had
discovered numerous substances. The 19th-century French naturalist George Cuvier,
in his eulogy of Priestley, praised his discoveries while at the same
time lamenting his refusal to abandon phlogiston theory, calling him
"the father of modern chemistry [who] never acknowledged his daughter".
Priestley published more than 150 works on topics ranging from
political philosophy to education to theology to natural philosophy. He led and inspired British radicals during the 1790s, paved the way for utilitarianism, and helped found Unitarianism. A wide variety of philosophers, scientists, and poets became associationists as a result of his redaction of David Hartley's Observations on Man, including Erasmus Darwin, Coleridge, William Wordsworth, John Stuart Mill, Alexander Bain, and Herbert Spencer. Immanuel Kant praised Priestley in his Critique of Pure Reason (1781), writing that he "knew how to combine his paradoxical teaching with the interests of religion".
Indeed, it was Priestley's aim to "put the most 'advanced'
Enlightenment ideas into the service of a rationalized though heterodox
Christianity, under the guidance of the basic principles of scientific
method".
Considering the extent of Priestley's influence, relatively
little scholarship has been devoted to him. In the early 20th century,
Priestley was most often described as a conservative and dogmatic
scientist who was nevertheless a political and religious reformer. In a historiographic review essay, historian of science Simon Schaffer
describes the two dominant portraits of Priestley: the first depicts
him as "a playful innocent" who stumbled across his discoveries; the
second portrays him as innocent as well as "warped" for not
understanding their implications better. Assessing Priestley's works as a
whole has been difficult for scholars because of his wide-ranging
interests. His scientific discoveries have usually been divorced from
his theological and metaphysical publications to make an analysis of his
life and writings easier, but this approach has been challenged
recently by scholars such as John McEvoy and Robert Schofield. Although
early Priestley scholarship claimed that his theological and
metaphysical works were "distractions" and "obstacles" to his scientific
work, scholarship published in the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s maintained
that Priestley's works constituted a unified theory. However, as
Schaffer explains, no convincing synthesis of his work has yet been
expounded.
More recently, in 2001, historian of science Dan Eshet has argued that
efforts to create a "synoptic view" have resulted only in a
rationalisation of the contradictions in Priestley's thought, because
they have been "organized around philosophical categories" and have
"separate[d] the producers of scientific ideas from any social
conflict".
A blue plaque from the Royal Society of Chemistry commemorates Priestley at New Meeting Street, Birmingham
Priestley has been remembered by the towns in which he served as a
reforming educator and minister and by the scientific organisations he
influenced. Two educational institutions have been named in his honour—Priestley College in Warrington and Joseph Priestley College in Leeds (now part of Leeds City College)—and an asteroid, 5577 Priestley, discovered in 1986 by Duncan Waldron. In Birstall, the Leeds City Square, and in Birmingham, he is memorialised through statues, and plaques commemorating him have been posted in Birmingham, Calne and Warrington. Also, since 1952 Dickinson College,
Pennsylvania, has presented the Priestley Award to a scientist who
makes "discoveries which contribute to the welfare of mankind". The main undergraduate chemistry laboratories at the University of Leeds
were refurbished as part of a £4m refurbishment plan in 2006 and
renamed as the Priestley Laboratories in his honour as a prominent
chemist from Leeds. In 2016 the University of Huddersfield
renamed the building housing its Applied Sciences department as the
Joseph Priestley Building, as part of an exercise to rename all campus
buildings after prominent local figures.
Additional recognition for Priestley's work is marked by a National Historic Chemical Landmark designation for his discovery of oxygen, made on 1 August 1994, at the Priestley House in Northumberland, Penn., by the American Chemical Society. Similar recognition was made on 7 August 2000, at Bowood House in Wiltshire, England. The ACS also awards their highest honour, the Priestley Medal, in his name.
Selected works
- The Rudiments of English Grammar (1761)
- A Chart of Biography (1765)
- Essay on a Course of Liberal Education for Civil and Active Life (1765)
- The History and Present State of Electricity (1767)
- Essay on the First Principles of Government (1768)
- A New Chart of History (1769)
- Institutes of Natural and Revealed Religion (1772–74)
- Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air (1774–77)
- Disquisitions relating to Matter and Spirit (1777)
- The Doctrine of Philosophical Necessity Illustrated (1777)
- Letters to a Philosophical Unbeliever (1780)
- An History of the Corruptions of Christianity (1782)
- Lectures on History and General Policy (1788)
- Theological Repository (1770–73, 1784–88)