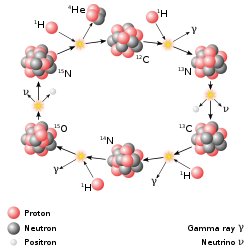The Sun is a main-sequence star, and thus generates its energy by nuclear fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium. In its core, the Sun fuses 500 million metric tons of hydrogen each second.
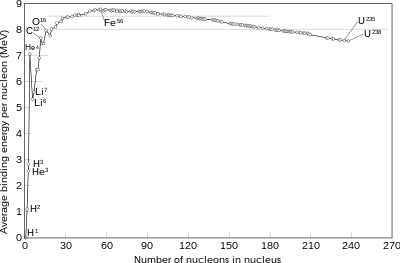
The nuclear binding energy curve. The formation of nuclei with masses up to iron-56 releases energy, as illustrated above.
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles (neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises due to the difference in atomic "binding energy" between the atomic nuclei before and after the reaction. Fusion is the process that powers active or "main sequence" stars, or other high magnitude stars.
A fusion process that produces nuclei lighter than iron-56 or nickel-62 will generally release energy. These elements have relatively small mass per nucleon and large binding energy per nucleon. Fusion of nuclei lighter than these releases energy (an exothermic process), while fusion of heavier nuclei results in energy retained by the product nucleons, and the resulting reaction is endothermic. The opposite is true for the reverse process, nuclear fission. This means that the lighter elements, such as hydrogen and helium, are in general more fusible; while the heavier elements, such as uranium, thorium and plutonium, are more fissionable. The extreme astrophysical event of a supernova can produce enough energy to fuse nuclei into elements heavier than iron.
In 1920, Arthur Eddington suggested hydrogen-helium fusion could be the primary source of stellar energy. Quantum tunneling was discovered by Friedrich Hund in 1929, and shortly afterwards Robert Atkinson and Fritz Houtermans
used the measured masses of light elements to show that large amounts
of energy could be released by fusing small nuclei. Building on the
early experiments in nuclear transmutation by Ernest Rutherford, laboratory fusion of hydrogen isotopes was accomplished by Mark Oliphant in 1932. In the remainder of that decade, the theory of the main cycle of nuclear fusion in stars was worked out by Hans Bethe. Research into fusion for military purposes began in the early 1940s as part of the Manhattan Project. Fusion was accomplished in 1951 with the Greenhouse Item nuclear test. Nuclear fusion on a large scale in an explosion was first carried out on 1 November 1952, in the Ivy Mike hydrogen bomb test.
Research into developing controlled fusion inside fusion reactors has been ongoing since the 1940s, but the technology is still in its development phase.
Process
The release of energy with the fusion of light elements is due to the interplay of two opposing forces: the nuclear force, which combines together protons and neutrons, and the Coulomb force,
which causes protons to repel each other. Protons are positively
charged and repel each other by the Coulomb force, but they can
nonetheless stick together, demonstrating the existence of another,
short-range, force referred to as nuclear attraction.
Light nuclei (or nuclei smaller than iron and nickel) are sufficiently
small and proton-poor allowing the nuclear force to overcome repulsion.
This is because the nucleus is sufficiently small that all nucleons feel
the short-range attractive force at least as strongly as they feel the
infinite-range Coulomb repulsion. Building up nuclei from lighter nuclei
by fusion releases the extra energy from the net attraction of
particles. For larger nuclei,
however, no energy is released, since the nuclear force is short-range
and cannot continue to act across longer nuclear length scales. Thus,
energy is not released with the fusion of such nuclei; instead, energy
is required as input for such processes.
Fusion powers stars and produces virtually all elements in a process called nucleosynthesis.
The Sun is a main-sequence star, and, as such, generates its energy by
nuclear fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium. In its core, the Sun
fuses 620 million metric tons of hydrogen and makes 606 million metric
tons of helium each second. The fusion of lighter elements in stars
releases energy and the mass that always accompanies it. For example, in
the fusion of two hydrogen nuclei to form helium, 0.7% of the mass is
carried away in the form of kinetic energy of an alpha particle or other forms of energy, such as electromagnetic radiation.
It takes considerable energy to force nuclei to fuse, even those of the lightest element, hydrogen.
When accelerated to high enough speeds, nuclei can overcome this
electrostatic repulsion and be brought close enough such that the
attractive nuclear force is greater than the repulsive Coulomb force. The strong force
grows rapidly once the nuclei are close enough, and the fusing nucleons
can essentially "fall" into each other and the result is fusion and net
energy produced. The fusion of lighter nuclei, which creates a heavier
nucleus and often a free neutron or proton, generally releases more energy than it takes to force the nuclei together; this is an exothermic process that can produce self-sustaining reactions.
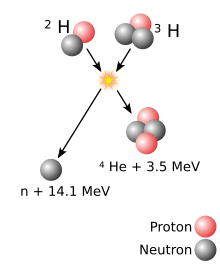
Energy released in most nuclear reactions is much larger than in chemical reactions, because the binding energy that holds a nucleus together is greater than the energy that holds electrons to a nucleus. For example, the ionization energy gained by adding an electron to a hydrogen nucleus is 13.6 eV—less than one-millionth of the 17.6 MeV released in the deuterium–tritium (D–T) reaction shown in the adjacent diagram. Fusion reactions have an energy density many times greater than nuclear fission; the reactions produce far greater energy per unit of mass even though individual fission reactions are generally much more energetic than individual fusion ones, which are themselves millions of times more energetic than chemical reactions. Only direct conversion of mass into energy, such as that caused by the annihilatory collision of matter and antimatter, is more energetic per unit of mass than nuclear fusion. (The complete conversion of one gram of matter would release 9×1013 joules of energy.)
Research into using fusion
for the production of electricity has been pursued for over 60 years.
Successful accomplishment of controlled fusion has been stymied by
scientific and technological difficulties; nonetheless, important
progress has been made. At present, controlled fusion reactions have
been unable to produce break-even (self-sustaining) controlled fusion. The two most advanced approaches for it are magnetic confinement (toroid designs) and inertial confinement (laser designs).
Workable designs for a toroidal reactor that theoretically will
deliver ten times more fusion energy than the amount needed to heat
plasma to the required temperatures are in development (see ITER).
The ITER facility is expected to finish its construction phase in 2025.
It will start commissioning the reactor that same year and initiate
plasma experiments in 2025, but is not expected to begin full
deuterium-tritium fusion until 2035.
Similarly, Canadian-based General Fusion, which is developing a magnetized target fusion nuclear energy system, aims to build its demonstration plant by 2025.
The US National Ignition Facility, which uses laser-driven inertial confinement fusion, was designed with a goal of break-even
fusion; the first large-scale laser target experiments were performed
in June 2009 and ignition experiments began in early 2011.
Nuclear fusion in stars
The proton-proton chain reaction, branch I, dominates in stars the size of the Sun or smaller.
The CNO cycle dominates in stars heavier than the Sun.
An important fusion process is the stellar nucleosynthesis that powers stars,
including the Sun. In the 20th century, it was recognized that the
energy released from nuclear fusion reactions accounted for the
longevity of stellar heat and light. The fusion of nuclei in a star,
starting from its initial hydrogen and helium abundance, provides that
energy and synthesizes new nuclei as a byproduct of the fusion process.
Different reaction chains are involved, depending on the mass of the
star (and therefore the pressure and temperature in its core).
Around 1920, Arthur Eddington anticipated the discovery and mechanism of nuclear fusion processes in stars, in his paper The Internal Constitution of the Stars.
At that time, the source of stellar energy was a complete mystery;
Eddington correctly speculated that the source was fusion of hydrogen
into helium, liberating enormous energy according to Einstein's equation E = mc2.
This was a particularly remarkable development since at that time
fusion and thermonuclear energy, and even that stars are largely
composed of hydrogen (see metallicity), had not yet been discovered. Eddington's paper, based on knowledge at the time, reasoned that:
- The leading theory of stellar energy, the contraction hypothesis, should cause stars' rotation to visibly speed up due to conservation of angular momentum. But observations of Cepheid variable stars showed this was not happening.
- The only other known plausible source of energy was conversion of matter to energy; Einstein had shown some years earlier that a small amount of matter was equivalent to a large amount of energy.
- Francis Aston had also recently shown that the mass of a helium atom was about 0.8% less than the mass of the four hydrogen atoms which would, combined, form a helium atom, suggesting that if such a combination could happen, it would release considerable energy as a byproduct.
- If a star contained just 5% of fusible hydrogen, it would suffice to explain how stars got their energy. (We now know that most 'ordinary' stars contain far more than 5% hydrogen)
- Further elements might also be fused, and other scientists had speculated that stars were the "crucible" in which light elements combined to create heavy elements, but without more accurate measurements of their atomic masses nothing more could be said at the time.
All of these speculations were proven correct in the following decades.
The primary source of solar energy, and similar size stars, is the fusion of hydrogen to form helium (the proton-proton chain reaction), which occurs at a solar-core temperature of 14 million kelvin. The net result is the fusion of four protons into one alpha particle, with the release of two positrons and two neutrinos (which changes two of the protons into neutrons), and energy. In heavier stars, the CNO cycle
and other processes are more important. As a star uses up a substantial
fraction of its hydrogen, it begins to synthesize heavier elements. The
heaviest elements are synthesized by fusion that occurs as a more
massive star undergoes a violent supernova at the end of its life, a process known as supernova nucleosynthesis.
Requirements
A
substantial energy barrier of electrostatic forces must be overcome
before fusion can occur. At large distances, two naked nuclei repel one
another because of the repulsive electrostatic force between their positively charged
protons. If two nuclei can be brought close enough together, however,
the electrostatic repulsion can be overcome by the quantum effect in
which nuclei can tunnel through coulomb forces.
When a nucleon such as a proton or neutron
is added to a nucleus, the nuclear force attracts it to all the other
nucleons of the nucleus (if the atom is small enough), but primarily to
its immediate neighbours due to the short range of the force. The
nucleons in the interior of a nucleus have more neighboring nucleons
than those on the surface. Since smaller nuclei have a larger surface
area-to-volume ratio, the binding energy per nucleon due to the nuclear force
generally increases with the size of the nucleus but approaches a
limiting value corresponding to that of a nucleus with a diameter of
about four nucleons. It is important to keep in mind that nucleons are quantum objects.
So, for example, since two neutrons in a nucleus are identical to each
other, the goal of distinguishing one from the other, such as which one
is in the interior and which is on the surface, is in fact meaningless,
and the inclusion of quantum mechanics is therefore necessary for proper
calculations.
The electrostatic force, on the other hand, is an inverse-square force, so a proton added to a nucleus will feel an electrostatic repulsion from all
the other protons in the nucleus. The electrostatic energy per nucleon
due to the electrostatic force thus increases without limit as nuclei
atomic number grows.
The electrostatic force
between the positively charged nuclei is repulsive, but when the
separation is small enough, the quantum effect will tunnel through the
wall. Therefore, the prerequisite for fusion is that the two nuclei be
brought close enough together for a long enough time for quantum
tunnelling to act.
The net result of the opposing electrostatic and strong nuclear
forces is that the binding energy per nucleon generally increases with
increasing size, up to the elements iron and nickel, and then decreases for heavier nuclei. Eventually, the binding energy
becomes negative and very heavy nuclei (all with more than 208
nucleons, corresponding to a diameter of about 6 nucleons) are not
stable. The four most tightly bound nuclei, in decreasing order of binding energy per nucleon, are 62Ni
, 58Fe
, 56Fe
, and 60Ni
. Even though the nickel isotope, 62Ni
, is more stable, the iron isotope 56Fe
is an order of magnitude more common. This is due to the fact that there is no easy way for stars to create 62Ni
through the alpha process.
, 58Fe
, 56Fe
, and 60Ni
. Even though the nickel isotope, 62Ni
, is more stable, the iron isotope 56Fe
is an order of magnitude more common. This is due to the fact that there is no easy way for stars to create 62Ni
through the alpha process.
An exception to this general trend is the helium-4 nucleus, whose binding energy is higher than that of lithium, the next heaviest element. This is because protons and neutrons are fermions, which according to the Pauli exclusion principle
cannot exist in the same nucleus in exactly the same state. Each proton
or neutron's energy state in a nucleus can accommodate both a spin up
particle and a spin down particle. Helium-4 has an anomalously large
binding energy because its nucleus consists of two protons and two
neutrons (it is a doubly magic
nucleus), so all four of its nucleons can be in the ground state. Any
additional nucleons would have to go into higher energy states. Indeed,
the helium-4 nucleus is so tightly bound that it is commonly treated as
a single quantum mechanical particle in nuclear physics, namely, the alpha particle.
The situation is similar if two nuclei are brought together. As
they approach each other, all the protons in one nucleus repel all the
protons in the other. Not until the two nuclei actually come close
enough for long enough so the strong nuclear force
can take over (by way of tunneling) is the repulsive electrostatic
force overcome. Consequently, even when the final energy state is lower,
there is a large energy barrier that must first be overcome. It is
called the Coulomb barrier.
The Coulomb barrier is smallest for isotopes of hydrogen, as their nuclei contain only a single positive charge. A diproton
is not stable, so neutrons must also be involved, ideally in such a way
that a helium nucleus, with its extremely tight binding, is one of the
products.
Using deuterium–tritium fuel, the resulting energy barrier is about 0.1 MeV. In comparison, the energy needed to remove an electron from hydrogen is 13.6 eV, about 7500 times less energy. The (intermediate) result of the fusion is an unstable 5He nucleus, which immediately ejects a neutron with 14.1 MeV. The recoil energy of the remaining 4He
nucleus is 3.5 MeV, so the total energy liberated is 17.6 MeV. This is
many times more than what was needed to overcome the energy barrier.
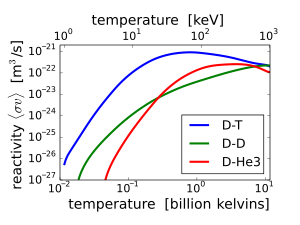
The
fusion reaction rate increases rapidly with temperature until it
maximizes and then gradually drops off. The DT rate peaks at a lower
temperature (about 70 keV, or 800 million kelvin) and at a higher value
than other reactions commonly considered for fusion energy.
The reaction cross section
(σ) is a measure of the probability of a fusion reaction as a function
of the relative velocity of the two reactant nuclei. If the reactants
have a distribution of velocities, e.g. a thermal distribution, then it
is useful to perform an average over the distributions of the product of
cross section and velocity. This average is called the 'reactivity',
denoted <σv>. The reaction rate (fusions per volume per time) is
<σv> times the product of the reactant number densities:
If a species of nuclei is reacting with a nucleus like itself, such as the DD reaction, then the product must be replaced by .
increases from virtually zero at room temperatures up to meaningful magnitudes at temperatures of 10–100 keV. At these temperatures, well above typical ionization energies (13.6 eV in the hydrogen case), the fusion reactants exist in a plasma state.
The significance of as a function of temperature in a device with a particular energy confinement time is found by considering the Lawson criterion.
This is an extremely challenging barrier to overcome on Earth, which
explains why fusion research has taken many years to reach the current
advanced technical state.
Artificial fusion
Thermonuclear fusion
If matter is sufficiently heated (hence being plasma)
and confined, fusion reactions may occur due to collisions with extreme
thermal kinetic energies of the particles. Thermonuclear weapons
produce what amounts to an uncontrolled release of fusion energy. Controlled thermonuclear fusion concepts use magnetic fields to confine the plasma.
Inertial confinement fusion
Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) is a method aimed at releasing fusion energy by heating and compressing a fuel target, typically a pellet containing deuterium and tritium.
Inertial electrostatic confinement
Inertial electrostatic confinement is a set of devices that use an electric field to heat ions to fusion conditions. The most well known is the fusor. Starting in 1999, a number of amateurs have been able to do amateur fusion using these homemade devices. Other IEC devices include: the Polywell, MIX POPS and Marble concepts.
Beam-beam or beam-target fusion
If the energy to initiate the reaction comes from accelerating one of the nuclei, the process is called beam-target fusion; if both nuclei are accelerated, it is beam-beam fusion.
Accelerator-based light-ion fusion is a technique using particle
accelerators to achieve particle kinetic energies sufficient to induce
light-ion fusion reactions. Accelerating light ions is relatively easy,
and can be done in an efficient manner—requiring only a vacuum tube, a
pair of electrodes, and a high-voltage transformer; fusion can be
observed with as little as 10 kV between the electrodes. The key problem
with accelerator-based fusion (and with cold targets in general) is
that fusion cross sections are many orders of magnitude lower than
Coulomb interaction cross sections. Therefore, the vast majority of ions
expend their energy emitting bremsstrahlung radiation and the ionization of atoms of the target. Devices referred to as sealed-tube neutron generators
are particularly relevant to this discussion. These small devices are
miniature particle accelerators filled with deuterium and tritium gas in
an arrangement that allows ions of those nuclei to be accelerated
against hydride targets, also containing deuterium and tritium, where
fusion takes place, releasing a flux of neutrons. Hundreds of neutron
generators are produced annually for use in the petroleum industry where
they are used in measurement equipment for locating and mapping oil
reserves.
To overcome the problem of bremsstrahlung radiation in
Beam-target fusion, a combinatorial approach has been suggested by
Tri-Alpha and Helion energy companies, this method is based on
interpenetration of two oppositely directed plasmoids.
Theoretical works represent that by creating and warming two
accelerated head-on colliding plasmoids up to some kilo electron volts
thermal energy which is low in comparison with that of required for
thermonuclear fusion, net fusion gain is possible even with aneutronic
fuels such as p-11B.
In order to attain the necessary conditions of break-even by this
method the accelerated plasmoids must have enough colliding velocities
of the order of some thousands of kilometers per second (106 m/s) depending on the kind of fusion fuel. In addition, the plasmoids density must be between the inertial and magnetic fusion criteria.
Muon-catalyzed fusion
Muon-catalyzed fusion is a fusion process that occurs at ordinary temperatures. It was studied in detail by Steven Jones
in the early 1980s. Net energy production from this reaction has been
unsuccessful because of the high energy required to create muons, their short 2.2 µs half-life, and the high chance that a muon will bind to the new alpha particle and thus stop catalyzing fusion.
Other principles
The Tokamak à configuration variable, research fusion reactor, at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (Switzerland).
Some other confinement principles have been investigated.
- Antimatter-initialized fusion uses small amounts of antimatter to trigger a tiny fusion explosion. This has been studied primarily in the context of making nuclear pulse propulsion, and pure fusion bombs feasible. This is not near becoming a practical power source, due to the cost of manufacturing antimatter alone.
- Pyroelectric fusion was reported in April 2005 by a team at UCLA. The scientists used a pyroelectric crystal heated from −34 to 7 °C (−29 to 45 °F), combined with a tungsten needle to produce an electric field of about 25 gigavolts per meter to ionize and accelerate deuterium nuclei into an erbium deuteride target. At the estimated energy levels, the D-D fusion reaction may occur, producing helium-3 and a 2.45 MeV neutron. Although it makes a useful neutron generator, the apparatus is not intended for power generation since it requires far more energy than it produces.
- Hybrid nuclear fusion-fission (hybrid nuclear power) is a proposed means of generating power by use of a combination of nuclear fusion and fission processes. The concept dates to the 1950s, and was briefly advocated by Hans Bethe during the 1970s, but largely remained unexplored until a revival of interest in 2009, due to the delays in the realization of pure fusion.
- Project PACER, carried out at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in the mid-1970s, explored the possibility of a fusion power system that would involve exploding small hydrogen bombs (fusion bombs) inside an underground cavity. As an energy source, the system is the only fusion power system that could be demonstrated to work using existing technology. However it would also require a large, continuous supply of nuclear bombs, making the economics of such a system rather questionable.
- Bubble fusion (Debunked) also called sonofusion was a proposed mechanism for achieving fusion via sonic cavitation which rose to prominence in the early 2000s. Subsequent attempts at replication failed and the principal investigator, Rusi Taleyarkhan, was judged guilty of research misconduct in 2008.
Important reactions
Stellar reaction chains
At
the temperatures and densities in stellar cores the rates of fusion
reactions are notoriously slow. For example, at solar core temperature (T ≈ 15 MK) and density (160 g/cm3), the energy release rate is only 276 μW/cm3—about a quarter of the volumetric rate at which a resting human body generates heat.
Thus, reproduction of stellar core conditions in a lab for nuclear
fusion power production is completely impractical. Because nuclear
reaction rates depend on density as well as temperature and most fusion
schemes operate at relatively low densities, those methods are strongly
dependent on higher temperatures. The fusion rate as a function of
temperature (exp(−E/kT)), leads to the need to achieve
temperatures in terrestrial reactors 10–100 times higher temperatures
than in stellar interiors: T ≈ 0.1–1.0×109 K.
Criteria and candidates for terrestrial reactions
In artificial fusion, the primary fuel is not constrained to be
protons and higher temperatures can be used, so reactions with larger
cross-sections are chosen. Another concern is the production of
neutrons, which activate the reactor structure radiologically, but also
have the advantages of allowing volumetric extraction of the fusion
energy and tritium breeding. Reactions that release no neutrons are referred to as aneutronic.
To be a useful energy source, a fusion reaction must satisfy several criteria. It must:
- Be exothermic
- This limits the reactants to the low Z (number of protons) side of the curve of binding energy. It also makes helium 4He
the most common product because of its extraordinarily tight binding, although 3He
and 3H
also show up. - Involve low atomic number (Z) nuclei
- This is because the electrostatic repulsion that must be overcome before the nuclei are close enough to fuse is directly related to the number of protons it contains - its atomic number.
- Have two reactants
- At anything less than stellar densities, three body collisions are too improbable. In inertial confinement, both stellar densities and temperatures are exceeded to compensate for the shortcomings of the third parameter of the Lawson criterion, ICF's very short confinement time.
- Have two or more products
- This allows simultaneous conservation of energy and momentum without relying on the electromagnetic force.
- Conserve both protons and neutrons
- The cross sections for the weak interaction are too small.
Few reactions meet these criteria.
For reactions with two products, the energy is divided between them
in inverse proportion to their masses, as shown. In most reactions with
three products, the distribution of energy varies. For reactions that
can result in more than one set of products, the branching ratios are
given.
Some reaction candidates can be eliminated at once. The D-6Li reaction has no advantage compared to p+-11
5B
because it is roughly as difficult to burn but produces substantially more neutrons through 2
1D
-2
1D
side reactions. There is also a p+-7
3Li
reaction, but the cross section is far too low, except possibly when Ti > 1 MeV, but at such high temperatures an endothermic, direct neutron-producing reaction also becomes very significant. Finally there is also a p+-9
4Be
reaction, which is not only difficult to burn, but 9
4Be
can be easily induced to split into two alpha particles and a neutron.
5B
because it is roughly as difficult to burn but produces substantially more neutrons through 2
1D
-2
1D
side reactions. There is also a p+-7
3Li
reaction, but the cross section is far too low, except possibly when Ti > 1 MeV, but at such high temperatures an endothermic, direct neutron-producing reaction also becomes very significant. Finally there is also a p+-9
4Be
reaction, which is not only difficult to burn, but 9
4Be
can be easily induced to split into two alpha particles and a neutron.
In addition to the fusion reactions, the following reactions with
neutrons are important in order to "breed" tritium in "dry" fusion
bombs and some proposed fusion reactors:
The latter of the two equations was unknown when the U.S. conducted the Castle Bravo
fusion bomb test in 1954. Being just the second fusion bomb ever tested
(and the first to use lithium), the designers of the Castle Bravo
"Shrimp" had understood the usefulness of 6Li in tritium production, but had failed to recognize that 7Li fission would greatly increase the yield of the bomb. While 7Li has a small neutron cross-section for low neutron energies, it has a higher cross section above 5 MeV. The 15 Mt yield was 150% greater than the predicted 6 Mt and caused unexpected exposure to fallout.
To evaluate the usefulness of these reactions, in addition to the
reactants, the products, and the energy released, one needs to know
something about the nuclear cross section.
Any given fusion device has a maximum plasma pressure it can sustain,
and an economical device would always operate near this maximum. Given
this pressure, the largest fusion output is obtained when the
temperature is chosen so that <σv>/T2 is a maximum. This is also the temperature at which the value of the triple product nTτ required for ignition is a minimum, since that required value is inversely proportional to <σv>/T2 (see Lawson criterion).
(A plasma is "ignited" if the fusion reactions produce enough power to
maintain the temperature without external heating.) This optimum
temperature and the value of <σv>/T2 at that temperature is given for a few of these reactions in the following table.
| fuel | T [keV] | <σv>/T2 [m3/s/keV2] |
|---|---|---|
| 2 1D -3 1T |
13.6 | 1.24×10−24 |
| 2 1D -2 1D |
15 | 1.28×10−26 |
| 2 1D -3 2He |
58 | 2.24×10−26 |
| p+-6 3Li |
66 | 1.46×10−27 |
| p+-11 5B |
123 | 3.01×10−27 |
Note that many of the reactions form chains. For instance, a reactor fueled with 3
1T
and 3
2He
creates some 2
1D
, which is then possible to use in the 2
1D
-3
2He
reaction if the energies are "right". An elegant idea is to combine the reactions (8) and (9). The 3
2He
from reaction (8) can react with 6
3Li
in reaction (9) before completely thermalizing. This produces an energetic proton, which in turn undergoes reaction (8) before thermalizing. Detailed analysis shows that this idea would not work well, but it is a good example of a case where the usual assumption of a Maxwellian plasma is not appropriate.
1T
and 3
2He
creates some 2
1D
, which is then possible to use in the 2
1D
-3
2He
reaction if the energies are "right". An elegant idea is to combine the reactions (8) and (9). The 3
2He
from reaction (8) can react with 6
3Li
in reaction (9) before completely thermalizing. This produces an energetic proton, which in turn undergoes reaction (8) before thermalizing. Detailed analysis shows that this idea would not work well, but it is a good example of a case where the usual assumption of a Maxwellian plasma is not appropriate.
Neutronicity, confinement requirement, and power density
Any of the reactions above can in principle be the basis of fusion power
production. In addition to the temperature and cross section discussed
above, we must consider the total energy of the fusion products Efus, the energy of the charged fusion products Ech, and the atomic number Z of the non-hydrogenic reactant.
Specification of the 2
1D
-2
1D
reaction entails some difficulties, though. To begin with, one must average over the two branches (2i) and (2ii). More difficult is to decide how to treat the 3
1T
and 3
2He
products. 3
1T
burns so well in a deuterium plasma that it is almost impossible to extract from the plasma. The 2
1D
-3
2He
reaction is optimized at a much higher temperature, so the burnup at the optimum 2
1D
-2
1D
temperature may be low. Therefore, it seems reasonable to assume the 3
1T
but not the 3
2He
gets burned up and adds its energy to the net reaction, which means the total reaction would be the sum of (2i), (2ii), and (1):
1D
-2
1D
reaction entails some difficulties, though. To begin with, one must average over the two branches (2i) and (2ii). More difficult is to decide how to treat the 3
1T
and 3
2He
products. 3
1T
burns so well in a deuterium plasma that it is almost impossible to extract from the plasma. The 2
1D
-3
2He
reaction is optimized at a much higher temperature, so the burnup at the optimum 2
1D
-2
1D
temperature may be low. Therefore, it seems reasonable to assume the 3
1T
but not the 3
2He
gets burned up and adds its energy to the net reaction, which means the total reaction would be the sum of (2i), (2ii), and (1):
For calculating the power of a reactor (in which the reaction rate is determined by the D-D step), we count the 2
1D
-2
1D
fusion energy per D-D reaction as Efus = (4.03 MeV + 17.6 MeV)×50% + (3.27 MeV)×50% = 12.5 MeV and the energy in charged particles as Ech = (4.03 MeV + 3.5 MeV)×50% + (0.82 MeV)×50% = 4.2 MeV. (Note: if the tritium ion reacts with a deuteron while it still has a large kinetic energy, then the kinetic energy of the helium-4 produced may be quite different from 3.5 MeV, so this calculation of energy in charged particles is only an approximation of the average.) The amount of energy per deuteron consumed is 2/5 of this, or 5.0 MeV (a specific energy of about 225 million MJ per kilogram of deuterium).
1D
-2
1D
fusion energy per D-D reaction as Efus = (4.03 MeV + 17.6 MeV)×50% + (3.27 MeV)×50% = 12.5 MeV and the energy in charged particles as Ech = (4.03 MeV + 3.5 MeV)×50% + (0.82 MeV)×50% = 4.2 MeV. (Note: if the tritium ion reacts with a deuteron while it still has a large kinetic energy, then the kinetic energy of the helium-4 produced may be quite different from 3.5 MeV, so this calculation of energy in charged particles is only an approximation of the average.) The amount of energy per deuteron consumed is 2/5 of this, or 5.0 MeV (a specific energy of about 225 million MJ per kilogram of deuterium).
Another unique aspect of the 2
1D
-2
1D
reaction is that there is only one reactant, which must be taken into account when calculating the reaction rate.
1D
-2
1D
reaction is that there is only one reactant, which must be taken into account when calculating the reaction rate.
With this choice, we tabulate parameters for four of the most important reactions
| fuel | Z | Efus [MeV] | Ech [MeV] | neutronicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 1D -3 1T |
1 | 17.6 | 3.5 | 0.80 |
| 2 1D -2 1D |
1 | 12.5 | 4.2 | 0.66 |
| 2 1D -3 2He |
2 | 18.3 | 18.3 | ≈0.05 |
| p+-11 5B |
5 | 8.7 | 8.7 | ≈0.001 |
The last column is the neutronicity
of the reaction, the fraction of the fusion energy released as
neutrons. This is an important indicator of the magnitude of the
problems associated with neutrons like radiation damage, biological
shielding, remote handling, and safety. For the first two reactions it
is calculated as (Efus-Ech)/Efus.
For the last two reactions, where this calculation would give zero, the
values quoted are rough estimates based on side reactions that produce
neutrons in a plasma in thermal equilibrium.
Of course, the reactants should also be mixed in the optimal
proportions. This is the case when each reactant ion plus its associated
electrons accounts for half the pressure. Assuming that the total
pressure is fixed, this means that particle density of the
non-hydrogenic ion is smaller than that of the hydrogenic ion by a
factor 2/(Z+1). Therefore, the rate for these reactions is
reduced by the same factor, on top of any differences in the values of
<σv>/T2. On the other hand, because the 2
1D
-2
1D
reaction has only one reactant, its rate is twice as high as when the fuel is divided between two different hydrogenic species, thus creating a more efficient reaction.
1D
-2
1D
reaction has only one reactant, its rate is twice as high as when the fuel is divided between two different hydrogenic species, thus creating a more efficient reaction.
Thus there is a "penalty" of (2/(Z+1)) for non-hydrogenic fuels
arising from the fact that they require more electrons, which take up
pressure without participating in the fusion reaction. (It is usually a
good assumption that the electron temperature will be nearly equal to
the ion temperature. Some authors, however discuss the possibility that
the electrons could be maintained substantially colder than the ions. In
such a case, known as a "hot ion mode", the "penalty" would not apply.)
There is at the same time a "bonus" of a factor 2 for 2
1D
-2
1D
because each ion can react with any of the other ions, not just a fraction of them.
1D
-2
1D
because each ion can react with any of the other ions, not just a fraction of them.
We can now compare these reactions in the following table:
| fuel | <σv>/T2 | penalty/bonus | inverse reactivity | Lawson criterion | power density (W/m3/kPa2) | inverse ratio of power density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 1D -3 1T |
1.24×10−24 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 34 | 1 |
| 2 1D -2 1D |
1.28×10−26 | 2 | 48 | 30 | 0.5 | 68 |
| 2 1D -3 2He |
2.24×10−26 | 2/3 | 83 | 16 | 0.43 | 80 |
| p+-6 3Li |
1.46×10−27 | 1/2 | 1700 | 0.005 | 6800 | |
| p+-11 5B |
3.01×10−27 | 1/3 | 1240 | 500 | 0.014 | 2500 |
The maximum value of <σv>/T2 is taken from a
previous table. The "penalty/bonus" factor is that related to a
non-hydrogenic reactant or a single-species reaction. The values in the
column "inverse reactivity" are found by dividing 1.24×10−24
by the product of the second and third columns. It indicates the factor
by which the other reactions occur more slowly than the 2
1D
-3
1T
reaction under comparable conditions. The column "Lawson criterion" weights these results with Ech and gives an indication of how much more difficult it is to achieve ignition with these reactions, relative to the difficulty for the 2
1D
-3
1T
reaction. The next-to-last column is labeled "power density" and weights the practical reactivity by Efus. The final column indicates how much lower the fusion power density of the other reactions is compared to the 2
1D
-3
1T
reaction and can be considered a measure of the economic potential.
1D
-3
1T
reaction under comparable conditions. The column "Lawson criterion" weights these results with Ech and gives an indication of how much more difficult it is to achieve ignition with these reactions, relative to the difficulty for the 2
1D
-3
1T
reaction. The next-to-last column is labeled "power density" and weights the practical reactivity by Efus. The final column indicates how much lower the fusion power density of the other reactions is compared to the 2
1D
-3
1T
reaction and can be considered a measure of the economic potential.
Bremsstrahlung losses in quasineutral, isotropic plasmas
The ions undergoing fusion in many systems will essentially never occur alone but will be mixed with electrons that in aggregate neutralize the ions' bulk electrical charge and form a plasma.
The electrons will generally have a temperature comparable to or
greater than that of the ions, so they will collide with the ions and
emit x-ray radiation of 10–30 keV energy, a process known as Bremsstrahlung.
The huge size of the Sun and stars means that the x-rays produced
in this process will not escape and will deposit their energy back into
the plasma. They are said to be opaque to x-rays. But any terrestrial fusion reactor will be optically thin
for x-rays of this energy range. X-rays are difficult to reflect but
they are effectively absorbed (and converted into heat) in less than mm
thickness of stainless steel (which is part of a reactor's shield). This
means the bremsstrahlung process is carrying energy out of the plasma,
cooling it.
The ratio of fusion power produced to x-ray radiation lost to
walls is an important figure of merit. This ratio is generally maximized
at a much higher temperature than that which maximizes the power
density (see the previous subsection). The following table shows
estimates of the optimum temperature and the power ratio at that
temperature for several reactions:
| fuel | Ti (keV) | Pfusion/PBremsstrahlung |
|---|---|---|
| 2 1D -3 1T |
50 | 140 |
| 2 1D -2 1D |
500 | 2.9 |
| 2 1D -3 2He |
100 | 5.3 |
| 3 2He -3 2He |
1000 | 0.72 |
| p+-6 3Li |
800 | 0.21 |
| p+-11 5B |
300 | 0.57 |
The actual ratios of fusion to Bremsstrahlung power will likely be
significantly lower for several reasons. For one, the calculation
assumes that the energy of the fusion products is transmitted completely
to the fuel ions, which then lose energy to the electrons by
collisions, which in turn lose energy by Bremsstrahlung. However,
because the fusion products move much faster than the fuel ions, they
will give up a significant fraction of their energy directly to the
electrons. Secondly, the ions in the plasma are assumed to be purely
fuel ions. In practice, there will be a significant proportion of
impurity ions, which will then lower the ratio. In particular, the
fusion products themselves must remain in the plasma until they have given up their energy, and will
remain some time after that in any proposed confinement scheme.
Finally, all channels of energy loss other than Bremsstrahlung have been
neglected. The last two factors are related. On theoretical and
experimental grounds, particle and energy confinement seem to be closely
related. In a confinement scheme that does a good job of retaining
energy, fusion products will build up. If the fusion products are
efficiently ejected, then energy confinement will be poor, too.
The temperatures maximizing the fusion power compared to the
Bremsstrahlung are in every case higher than the temperature that
maximizes the power density and minimizes the required value of the fusion triple product. This will not change the optimum operating point for 2
1D
-3
1T
very much because the Bremsstrahlung fraction is low, but it will push the other fuels into regimes where the power density relative to 2
1D
-3
1T
is even lower and the required confinement even more difficult to achieve. For 2
1D
-2
1D
and 2
1D
-3
2He
, Bremsstrahlung losses will be a serious, possibly prohibitive problem. For 3
2He
-3
2He
, p+-6
3Li
and p+-11
5B
the Bremsstrahlung losses appear to make a fusion reactor using these fuels with a quasineutral, isotropic plasma impossible. Some ways out of this dilemma are considered—and rejected—in fundamental limitations on plasma fusion systems not in thermodynamic equilibrium. This limitation does not apply to non-neutral and anisotropic plasmas; however, these have their own challenges to contend with.
1D
-3
1T
very much because the Bremsstrahlung fraction is low, but it will push the other fuels into regimes where the power density relative to 2
1D
-3
1T
is even lower and the required confinement even more difficult to achieve. For 2
1D
-2
1D
and 2
1D
-3
2He
, Bremsstrahlung losses will be a serious, possibly prohibitive problem. For 3
2He
-3
2He
, p+-6
3Li
and p+-11
5B
the Bremsstrahlung losses appear to make a fusion reactor using these fuels with a quasineutral, isotropic plasma impossible. Some ways out of this dilemma are considered—and rejected—in fundamental limitations on plasma fusion systems not in thermodynamic equilibrium. This limitation does not apply to non-neutral and anisotropic plasmas; however, these have their own challenges to contend with.
Mathematical description of cross section
Fusion under classical physics
In
a classical picture, nuclei can be understood as hard spheres that
repel each other through the Coulomb force but fuse once the two spheres
come close enough for contact. Estimating the radius of an atomic
nuclei as about one femtometer, the energy needed for fusion of two
hydrogen is:
This would imply that for the core of the sun, which has a Boltzmann distribution with a temperature of around 1.4 keV, the probability hydrogen would reach the threshold is , that is, fusion would never occur. However, fusion in the sun does occur due to quantum mechanics.
Parameterization of cross section
The
probability that fusion occurs is greatly increased compared to the
classical picture, thanks to the smearing of the effective radius as the
DeBroglie wavelength as well as quantum tunnelling through the potential barrier. To determine the rate of fusion reactions, the value of most interest is the cross section,
which describes the probability that particle will fuse by giving a
characteristic area of interaction. An estimation of the fusion cross
sectional area is often broken into three pieces:
Where is the geometric cross section, T is the barrier transparency and R is the reaction characteristics of the reaction.
is of the order of the square of the de-Broglie wavelength where is the reduced mass of the system and is the center of mass energy of the system.
T can be approximated by the Gamow transparency, which has the form: where is the Gamow factor and comes from estimating the quantum tunneling probability through the potential barrier.
R
contains all the nuclear physics of the specific reaction and takes very
different values depending on the nature of the interaction. However,
for most reactions, the variation of is small compared to the variation from the Gamow factor and so is approximated by a function called the Astrophysical S-factor, ,
which is weakly varying in energy. Putting these dependencies together,
one approximation for the fusion cross section as a function of energy
takes the form:
More detailed forms of the cross section can be derived through nuclear physics based models and R-matrix theory.
Formulas of fusion cross sections
The Naval Research Lab's plasma physics formulary gives the total cross section in barns as a function of the energy (in keV) of the incident particle towards a target ion at rest fit by the formula:
with the following coefficient values:
| DT(1) | DD(2i) | DD(2ii) | DHe3(3) | TT(4) | THe3(6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 45.95 | 46.097 | 47.88 | 89.27 | 38.39 | 123.1 |
| A2 | 50200 | 372 | 482 | 25900 | 448 | 11250 |
| A3 | 1.368e-2 | 4.36e-4 | 3.08e-4 | 3.98e-3 | 1.02e-3 | 0 |
| A4 | 1.076 | 1.22 | 1.177 | 1.297 | 2.09 | 0 |
| A5 | 409 | 0 | 0 | 647 | 0 | 0 |
Bosch-Hale also reports a R-matrix calculated cross sections fitting observation data with Padé rational approximating coefficients. With energy in units of keV and cross sections in units of millibarn, the factor has the form:
, with the coefficient values:
|
|
DT(1) | DD(2ii) | DHe3(3) | THe4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.3970 | 68.7508 | 31.3970 | 34.3827 | |
| A1 | 5.5576e4 | 5.7501e6 | 5.3701e4 | 6.927e4 |
| A2 | 2.1054e2 | 2.5226e3 | 3.3027e2 | 7.454e8 |
| A3 | -3.2638e-2 | 4.5566e1 | -1.2706e-1 | 2.050e6 |
| A4 | 1.4987e-6 | 0 | 2.9327e-5 | 5.2002e4 |
| A5 | 1.8181e-10 | 0 | -2.5151e-9 | 0 |
| B1 | 0 | -3.1995e-3 | 0 | 6.38e1 |
| B2 | 0 | -8.5530e-6 | 0 | -9.95e-1 |
| B3 | 0 | 5.9014e-8 | 0 | 6.981e-5 |
| B4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.728e-4 |
| Applicable Energy Range [keV] | 0.5-5000 | 0.3-900 | 0.5-4900 | 0.5-550 |
| 2.0 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 1.9 |
Maxwell averaged nuclear cross sections
In fusions systems that are in thermal equilibrium the particles are in a Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution,
meaning the particles have a range of energies centered around the
plasma temperature. The sun, magnetically confined plasmas and inertial
confinement fusion systems are well modeled to be in a thermal
equilibrium. In these cases, the value of interest is the fusion cross
section averaged across the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. The Naval
Research Lab's plasma physics formulary tabulates Maxwell averaged
fusion cross sections reactivities in .
| Temperature [keV] | DT(1) | DD(2ii) | DHe3(3) | TT(4) | THe3(6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.5e-21 | 1.5e-22 | 1.0e-26 | 3.3e-22 | 1.0e-28 |
| 2 | 2.6e-19 | 5.4e-21 | 1.4e-23 | 7.1e-21 | 1.0e-25 |
| 5 | 1.3e-17 | 1.8e-19 | 6.7e-21 | 1.4e-19 | 2.1e-22 |
| 10 | 1.1e-16 | 1.2e-18 | 2.3e-19 | 7.2e-19 | 1.2e-20 |
| 20 | 4.2e-16 | 5.2e-18 | 3.8e-18 | 2.5e-18 | 2.6e-19 |
| 50 | 8.7e-16 | 2.1e-17 | 5.4e-17 | 8.7e-18 | 5.3e-18 |
| 100 | 8.5e-16 | 4.5e-17 | 1.6e-16 | 1.9e-17 | 2.7e-17 |
| 200 | 6.3e-16 | 8.8e-17 | 2.4e-16 | 4.2e-17 | 9.2e-17 |
| 500 | 3.7e-16 | 1.8e-16 | 2.3e-16 | 8.4e-17 | 2.9e-16 |
| 1000 | 2.7e-16 | 2.2e-16 | 1.8e-16 | 8.0e-17 | 5.2e-16 |
For energies the data can be represented by: