First
edition of the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht between Great Britain and Spain
in Spanish (left) and a later edition in Latin and English. | |
| Context |
|
|---|---|
| Signed | 1713–1715 |
| Location | Utrecht, Dutch Republic |
| Signatories | |
| Languages | |
| Full text at | |
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne of Spain, and involved much of Europe for over a decade. The main action saw France as the defender of Spain against a multinational coalition. The war was very expensive and bloody and finally stalemated. Essentially, the treaties allowed Philip V (grandson of King Louis XIV of France) to keep the Spanish throne in return for permanently renouncing his claim to the French throne, along with other necessary guarantees that would ensure that France and Spain should not merge, thus preserving the balance of power in Europe.
The treaties between several European states, including Spain, Great Britain, France, Portugal, Savoy and the Dutch Republic, helped end the war. The treaties were concluded between the representatives of Louis XIV of France and of his grandson Philip on one hand, and representatives of Queen Anne of Great Britain, King Victor Amadeus II of Sardinia, King John V of Portugal and the United Provinces of the Netherlands on the other. Though the king of France ensured the Spanish crown for his dynasty, the treaties marked the end of French ambitions of hegemony in Europe expressed in the continuous wars of Louis XIV, and paved the way to the European system based on the balance of power. British historian G. M. Trevelyan argued that:
That Treaty, which ushered in the stable and characteristic period of Eighteenth-Century civilization, marked the end of danger to Europe from the old French monarchy, and it marked a change of no less significance to the world at large, — the maritime, commercial and financial supremacy of Great Britain.
Another enduring result was the creation of the Spanish Bourbon dynasty, which still reigns over Spain up to the present day whilst the French branch of the House of Bourbon has long since been dethroned.
Negotiations
The War of the Spanish Succession was occasioned by the failure of the Habsburg king, Charles II of Spain, to produce an heir. Dispute followed the death of Charles II in 1700, and fourteen years of war were the result.
The pro-French Electorate of Bavaria was knocked out of the war early on by the Battle of Blenheim (13 August 1704), forcing it to sign the Treaty of Ilbesheim (7 November 1704) and accept Austrian occupation until the end of the war.
On 2 January 1710, king Louis XIV of France agreed to commence peace negotiations in Geertruidenberg.
France and Great Britain had come to terms in October 1711, when the preliminaries of peace had been signed in London. The preliminaries were based on a tacit acceptance of the partition of Spain's European possessions. Following this, the Congress of Utrecht opened on 29 January 1712, with the British representatives being John Robinson, Bishop of Bristol, and Thomas Wentworth, Lord Strafford. Reluctantly the United Provinces accepted the preliminaries and sent representatives, but Emperor Charles VI refused to do so until he was assured that the preliminaries were not binding. This assurance was given, and so in February the Imperial representatives made their appearance. As Philip was not yet recognized as its king, Spain did not at first send plenipotentiaries, but the Duke of Savoy sent one, and the Kingdom of Portugal was represented by Luís da Cunha. One of the first questions discussed was the nature of the guarantees to be given by France and Spain that their crowns would be kept separate, and little progress was made until 10 July 1712, when Philip signed a renunciation.
With Great Britain, France and Spain having agreed to a "suspension of arms" (armistice) covering Spain on 19 August in Paris, the pace of negotiation quickened. The first treaty signed at Utrecht was the truce between France and Portugal on 7 November, followed by the truce between France and Savoy on 14 March 1714. That same day, Spain, Great Britain, France and the Empire agreed to the evacuation of Catalonia and an armistice in Italy. The main treaties of peace followed on 11 April 1713. These were five separate treaties between France and Great Britain, the Netherlands, Savoy, Prussia and Portugal. Spain under Philip V signed separate peace treaties with Savoy and Great Britain at Utrecht on 13 July. Negotiations at Utrecht dragged on into the next year, for the peace treaty between Spain and the Netherlands was only signed on 26 June 1714 and that between Spain and Portugal on 6 February 1715.
Several other treaties came out of the congress of Utrecht. France signed treaties of commerce and navigation with Great Britain and the Netherlands (11 April 1713). Great Britain signed a like treaty with Spain (9 December 1713).
Treaties
| Peace and friendship treaties of Utrecht and elsewhere | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date (New Style / (Old Style)) | Treaty name | Anti-French side | French side | Texts | |
| 14 March 1713 | Convention for the Evacuation of Catalonia and the Armistice in Italy (Utrecht) |
Holy Roman Empire Great Britain |
France Bourbon Spain |
Spanish, French/German | |
| 11 April 1713 (31 March 1713) | Peace and Friendship Treaty of Utrecht | Great Britain | France | English, French/German | |
| 11 April 1713 | Peace Treaty of Utrecht | Dutch Republic | France | Dutch, French, French/German | |
| 11 April 1713 | Peace Treaty of Utrecht | Portugal | France | French/German,French (Art. 8) | |
| 11 April 1713 | Peace Treaty of Utrecht | Prussia | France | French/German | |
| 11 April 1713 | Peace Treaty of Utrecht | Savoy | France | French/German | |
| 13 July 1713 (2 July 1713) | Peace and Friendship Treaty of Utrecht | Great Britain | Bourbon Spain | English, Spanish, Spanish/Latin/English, French/German | |
| 13 July 1713 | Peace, Alliance and Friendship Treaty of Utrecht | Savoy | Bourbon Spain | Spanish, Spanish/German | |
| 6 March 1714 | Peace Treaty of Rastatt | Habsburg Austria | France | French/German | |
| 26 June 1714 | Adjusted Peace and Friendship Treaty of Utrecht | Dutch Republic | Bourbon Spain | Spanish | |
| 7 September 1714 | Peace Treaty of Baden | Holy Roman Empire | France | Latin/German | |
| 6 February 1715 | Adjusted Peace and Friendship Treaty of Utrecht | Portugal | Bourbon Spain | Portuguese, Spanish | |
| Navigation, commerce and other treaties of Utrecht and elsewhere | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date (New Style / (Old Style)) | Treaty name | Side | Side | Texts | |
| 30 January 1713 (19 January 1713) | Second Barrier Treaty (Utrecht) | Dutch Republic | Great Britain | Latin | |
| 2 April 1713 | Guelders Treaty of Utrecht | Holy Roman Empire | Prussia | German (p. 91–96) | |
| 11 April 1713 | Navigation and Commerce Treaty of Utrecht | Dutch Republic | France | French/German | |
| 11 April 1713 (31 March 1713) | Navigation and Commerce Treaty of Utrecht | France | Great Britain | French/German | |
| 13 July 1713 | Preliminary Commerce Treaty of Madrid | Bourbon Spain | Great Britain | Spanish | |
| 9 December 1713 (28 November 1713) | Adjusted Commerce and Friendship Treaty of Utrecht | Bourbon Spain | Great Britain | Spanish, Latin/German | |
| 15 November 1715 | Third Barrier Treaty (Antwerp) | Dutch Republic Great Britain |
Holy Roman Empire | French/German | |
| 14 December 1715 | Explanatory Peace and Commerce Treaty of Madrid | Bourbon Spain | Great Britain | Spanish | |
Principal provisions
The Peace confirmed the Bourbon candidate as Philip V of Spain to remain as king. In return, Philip renounced the French throne, both for himself and his descendants, with reciprocal renunciations by French Bourbons to the Spanish throne, including Louis XIV's nephew Philippe of Orléans. These became increasingly important after a series of deaths between 1712 and 1714 left the five year old Louis XV as his great-grandfather's heir.
Great Britain was the main beneficiary; Utrecht marked the point at which it became the primary European commercial power. In Article X, Spain ceded the strategic ports of Gibraltar and Minorca.
In a major coup for the British delegation, the British government emerged from the treaty with the Asiento de Negros, which referred to the monopoly contract granted by the Spanish government to other European nations to supply slaves to Spain's colonies in the Americas. The Asiento de Negros had come about due to the fact that the Spanish Empire rarely engaged in the transatlantic slave trade itself, preferring to outsource this to foreign merchants. Bourbon France had previously held the Asiento de Negros, allowing French slave traders to supply 5,000 slaves to the Spanish Empire each year; France had gained control over this contract after Philip V had become King of Spain. After the British government gained access to the Asiento de Negros, the economic prominence held by Dutch Sephardic Jewish slaveowners began to fade, while the South Sea Company was established in hopes of gaining exclusive access to the contract. The British government sought to reduce its debt by increasing the volume of trade it had with Spain, which required gaining access to the Asiento de Negros; as historian G.M. Trevelyan noted: "The finances of the country were based in May 1711 on the assumption that the Asiento, or monopoly of the slave trade with Spanish America, would be wrested from France as an integral part of the terms of peace". Following the passage of the treaty, the British government gained a thirty-year access to the Asiento de Negros.
The importance placed by British negotiators on commercial interests was demonstrated by their demand for France to "level the fortifications of Dunkirk, block up the port and demolish the sluices that scour the harbour, [which] shall never be reconstructed". This was because Dunkirk was the primary base for French privateers, as it was possible to reach the North Sea in a single tide and escape British patrols in the English Channel. This ultimately proved unenforceable.
Under Article XIII, Spain agreed to a British demand to preserve Catalan historical rights, in return for Catalan support for the Allies during the war. Spanish territories in Italy and Flanders were divided, with Savoy receiving Sicily and parts of the Duchy of Milan. The former Spanish Netherlands, the Kingdom of Naples, Sardinia, and the bulk of the Duchy of Milan went to Emperor Charles VI. In South America, Spain returned Colónia do Sacramento in modern Uruguay to Portugal and recognised Portuguese sovereignty over the lands between the Amazon and Oyapock rivers, now in Brazil.
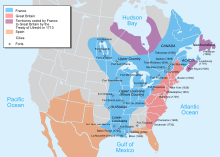
In North America, France recognised British suzerainty over the Iroquois, and ceded Nova Scotia and its claims to Newfoundland and territories in Rupert's Land. The French portion of Saint Kitts in the West Indies was also ceded in its entirety to Britain. France retained its other pre-war North American possessions, including Cape Breton Island, where it built the Fortress of Louisbourg, then the most expensive military installation in North America.
The successful French Rhineland campaign of 1713 finally induced Charles to sign the 1714 treaties of Rastatt and Baden, although terms were not agreed with Spain until the 1720 Treaty of The Hague.
Responses to the treaties
The treaty's territorial provisions did not go as far as the Whigs in Britain would have liked, considering that the French had made overtures for peace in 1706 and again in 1709. The Whigs considered themselves the heirs of the staunch anti-French policies of William III and the Duke of Marlborough. The now Whigs were now a minority in the house, but still pushing their anti-peace agenda. The whigs opposed peace every step of the way. The Whigs even called the treaty a sellout for letting the duke of Anjou stay on the Spanish throne. However, in the Parliament of 1710 the Tories had gained control of the House of Commons, and they wished for an end to Great Britain's participation in a European war. Queen Anne and her advisors had also come to agree.
The party in the administration of Robert Harley (created Earl of Oxford and Mortimer on 23 May 1711) and the Viscount Bolingbroke proved more flexible at the bargaining table and were characterized by the Whigs as "pro-French"; Oxford and Bolingbroke persuaded the Queen to create twelve new "Tory peers" to ensure ratification of the treaty in the House of Lords. The opponents of the treaty tried to rally support under the slogan of No Peace Without Spain.
Although the fate of the Spanish Netherlands in particular was of interest to the United Provinces, Dutch influence on the outcome of the negotiations was fairly insignificant, even though the talks were held on their territory. The French negotiator Melchior de Polignac taunted the Dutch with the scathing remark de vous, chez vous, sans vous, meaning that negotiations would be held "about you, around you, without you". The fact that Bolingbroke had secretly ordered the British commander, the Duke of Ormonde, to withdraw from the Allied forces before the Battle of Denain (informing the French but not the Allies), and the fact that they secretly arrived at separate peace with France was a fait accompli, made the objections of the Allies pointless. In any case, the Dutch achieved their condominium in the Austrian Netherlands with the Austro-Dutch Barrier Treaty of 1715.
Aftermath
The Treaty stipulated that "because of the great danger which threatened the liberty and safety of all Europe, from the too close conjunction of the kingdoms of Spain and France, ... one and the same person should never become King of both kingdoms". Some historians argue this makes it a significant milestone in the evolution of the modern nation state and concept of a balance of power.
First mentioned in 1701 by Charles Davenant in his Essays on the Balance of Power, it was widely publicised in Britain by author and Tory satirist Daniel Defoe in his 1709 article A Review of the Affairs of France. The idea was reflected in the wording of the treaties and resurfaced after the defeat of Napoleon in the 1815 Concert of Europe that dominated Europe in the 19th century.
For the individual signatories, Britain established naval superiority over its competitors, commercial access to Spain and America, and control of Menorca and Gibraltar; it retains the latter territory to this day. France accepted the Protestant succession on the British throne, ensuring a smooth transition when Anne died in August 1714, and ended its support for the Stuarts under the 1716 Anglo-French Treaty. While the war left all participants with unprecedented levels of government debt, only Great Britain successfully financed it.
Spain retained the majority of its Empire and recovered remarkably quickly; the recapture of Naples and Sicily in 1718 was only prevented by British naval power and a second attempt was successful in 1734. The 1707, 1715 and 1716 Nueva Planta decrees abolished regional political structures in the kingdoms of Aragon, Valencia, Majorca and the Principality of Catalonia, although Catalonia and Aragon retained some of these rights until 1767.
Despite failure in Spain, Austria secured its position in Italy and Hungary, allowing it to continue expansion into areas of South-East Europe previously held by the Ottoman Empire. Even after paying expenses associated with the Dutch Barrier, increased tax revenues from the Austrian Netherlands funded a significant upgrade of the Austrian military. However, these gains were diminished by various factors, chiefly the disruption of the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713 caused by Charles disinheriting his nieces in favour of his daughter Maria Theresa.
Attempts to ensure its succession involved Austria in wars of little strategic value; much of the fighting in the 1733–1735 War of the Polish Succession taking place in its maritime provinces in Italy. Austria had traditionally relied on naval support from the Dutch, whose own capability had been severely degraded; Britain prevented the loss of Sicily and Naples in 1718 but refused to do so again in 1734. The dispute continued to loosen Habsburg control over the Empire; Bavaria, Hanover, Prussia and Saxony increasingly acted as independent powers and in 1742, Charles of Bavaria became the first non-Habsburg Emperor in over 300 years.
The Dutch Republic ended the war effectively bankrupt, while the damage suffered by the Dutch merchant navy permanently affected their commercial and political strength and it was superseded by Britain as the pre-eminent European mercantile power. The acquisition of the Barrier Fortresses however became an important asset of Dutch foreign policy and enlarged their sphere of influence. Although judged favourably by contemporaries, it was later argued that the barrier proved to be largely illusory when put to the test during the War of Austrian Succession. The Dutch had in any case successfully defended their positions in the Southern Netherlands and their troops were central in the alliance which halted French territorial expansion in Europe until a new cycle began in 1792.
While the final settlement at Utrecht was far more favourable to France than the Allied offer of 1709 had been, it gained little that had not already been achieved through diplomacy by February 1701. Though France remained a great power, concern at its relative decline in military and economic terms compared to Britain was an underlying cause of the War of the Austrian Succession in 1740.