From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Sexual orientation is an enduring pattern of romantic or sexual attraction (or a combination of these) to persons of the opposite sex or gender, the same sex or gender, or to both sexes or more than one gender. These attractions are generally subsumed under heterosexuality, homosexuality, and bisexuality, while asexuality (the lack of sexual attraction to others) is sometimes identified as the fourth category.
These categories are aspects of the more nuanced nature of sexual identity and terminology. For example, people may use other labels, such as pansexual or polysexual, or none at all. According to the American Psychological Association,
sexual orientation "also refers to a person's sense of identity based
on those attractions, related behaviors, and membership in a community
of others who share those attractions". Androphilia and gynephilia are terms used in behavioral science to describe sexual orientation as an alternative to a gender binary conceptualization. Androphilia describes sexual attraction to masculinity; gynephilia describes the sexual attraction to femininity. The term sexual preference largely overlaps with sexual orientation, but is generally distinguished in psychological research. A person who identifies as bisexual, for example, may sexually prefer one sex over the other. Sexual preference may also suggest a degree of voluntary choice, whereas sexual orientation is not a choice.
Scientists do not know the exact cause of sexual orientation, but they theorize that it is caused by a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, and environmental influences. Although no single theory on the cause of sexual orientation has yet gained widespread support, scientists favor biologically based theories.
There is considerably more evidence supporting nonsocial, biological
causes of sexual orientation than social ones, especially for males.
There is no substantive evidence which suggests parenting or early
childhood experiences play a role with regard to sexual orientation. Across cultures, most people are heterosexual, with a minority of people having a homosexual or bisexual orientation. A person's sexual orientation can be anywhere on a continuum, from exclusive attraction to the opposite sex to exclusive attraction to the same sex.
Sexual orientation is studied primarily within biology, anthropology, and psychology (including sexology), but it is also a subject area in sociology, history (including social constructionist perspectives), and law.
Definitions and distinguishing from sexual identity and behavior
General
Sexual orientation is traditionally defined as including heterosexuality, bisexuality, and homosexuality, while asexuality
is considered the fourth category of sexual orientation by some
researchers and has been defined as the absence of a traditional sexual
orientation. An asexual has little to no sexual attraction to people. It may be considered a lack of a sexual orientation, and there is significant debate over whether or not it is a sexual orientation.
Most definitions of sexual orientation include a psychological
component, such as the direction of an individual's erotic desires, or a
behavioral component, which focuses on the sex of the individual's
sexual partner/s. Some people prefer simply to follow an individual's
self-definition or identity.
Scientific and professional understanding is that "the core attractions
that form the basis for adult sexual orientation typically emerge
between middle childhood and early adolescence".
Sexual orientation differs from sexual identity in that it encompasses
relationships with others, while sexual identity is a concept of self.
The American Psychological Association
states that "[s]exual orientation refers to an enduring pattern of
emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions to men, women, or both
sexes" and that "[t]his range of behaviors and attractions has been
described in various cultures and nations throughout the world. Many
cultures use identity labels to describe people who express these
attractions. In the United States, the most frequent labels are lesbians (women attracted to women), gay men
(men attracted to men), and bisexual people (men or women attracted to
both sexes). However, some people may use different labels or none at
all". They additionally state that sexual orientation "is distinct from
other components of sex and gender, including biological sex (the
anatomical, physiological, and genetic characteristics associated with
being male or female), gender identity (the psychological sense of being
male or female), and social gender role (the cultural norms that define
feminine and masculine behavior)".
Sexual identity and sexual behavior
are closely related to sexual orientation, but they are distinguished,
with sexual identity referring to an individual's conception of
themselves, behavior referring to actual sexual acts performed by the
individual, and orientation referring to "fantasies, attachments and
longings." Individuals may or may not express their sexual orientation in their behaviors. People who have a non-heterosexual sexual orientation that does not align with their sexual identity are sometimes referred to as 'closeted'.
The term may, however, reflect a certain cultural context and
particular stage of transition in societies which are gradually dealing
with integrating sexual minorities. In studies related to sexual
orientation, when dealing with the degree to which a person's sexual attractions, behaviors and identity match, scientists usually use the terms concordance or discordance.
Thus, a woman who is attracted to other women, but calls herself
heterosexual and only has sexual relations with men, can be said to
experience discordance between her sexual orientation (homosexual or
lesbian) and her sexual identity and behaviors (heterosexual).
Sexual identity may also be used to describe a person's perception of their own sex, rather than sexual orientation. The term sexual preference has a similar meaning to sexual orientation, and the two terms are often used interchangeably, but the American Psychological Association states sexual preference suggests a degree of voluntary choice.
The term has been listed by the American Psychological Association's
Committee on Gay and Lesbian Concerns as a wording that advances a
"heterosexual bias". The term sexual orientation was introduced by sexologist John Money in place of sexual preference, arguing that attraction is not necessarily a matter of free choice.
Androphilia, gynephilia, and other terms
Androphilia and gynephilia (or gynecophilia) are
terms used in behavioral science to describe sexual attraction, as an
alternative to a homosexual and heterosexual conceptualization. They are
used for identifying a subject's object of attraction without
attributing a sex assignment or gender identity to the subject. Related terms such as pansexual and polysexual do not make any such assignations to the subject. People may also use terms such as queer, pansensual, polyfidelitous, ambisexual, or personalized identities such as byke or biphilic.
Using androphilia and gynephilia can avoid confusion and
offense when describing people in non-western cultures, as well as when
describing intersex and transgender people. Psychiatrist Anil Aggrawal explains that androphilia, along with gynephilia,
is
needed to overcome immense difficulties in characterizing the sexual
orientation of trans men and trans women. For instance, it is difficult
to decide whether a trans man erotically attracted to males is a
heterosexual female or a homosexual male; or a trans woman erotically
attracted to females is a heterosexual male or a lesbian female. Any
attempt to classify them may not only cause confusion but arouse offense
among the affected subjects. In such cases, while defining sexual
attraction, it is best to focus on the object of their attraction rather
than on the sex or gender of the subject.
Sexologist Milton Diamond
writes, "The terms heterosexual, homosexual, and bisexual are better
used as adjectives, not nouns, and are better applied to behaviors, not
people. This usage is particularly advantageous when discussing the
partners of transsexual or intersexed individuals. These newer terms
also do not carry the social weight of the former ones."
Some researchers advocate use of the terminology to avoid bias inherent in Western conceptualizations of human sexuality. Writing about the Samoan fa'afafine demographic, sociologist Johanna Schmidt writes that in cultures where a third gender is recognized, a term like "homosexual transsexual" does not align with cultural categories.
Same gender loving, or SGL, is a term adopted by some African-Americans, meant as a culturally affirming homosexual identity.
Some researchers, such as Bruce Bagemihl,
have criticized certain ways the labels "heterosexual" and "homosexual"
have been used for transgender people, writing, "...the point of
reference for 'heterosexual' or 'homosexual' orientation in this
nomenclature is solely the individual's genetic sex prior to
reassignment (see for example, Blanchard et al. 1987, Coleman and
Bockting, 1988, Blanchard, 1989). These labels thereby ignore the
individual's personal sense of gender identity taking precedence over
biological sex, rather than the other way around." Bagemihl goes on to
take issue with the way this terminology makes it easy to claim
transsexuals are really homosexual males seeking to escape from stigma.
Terms have been proposed for sexual attraction to a person born male with a feminine gender expression, including gynandromorphophilia (adjective: gynandromorphophilic) and gynemimetophilia (adj.: gynemimetophilic).
Gender, transgender, cisgender, and conformance
The earliest writers on sexual orientation usually understood it to
be intrinsically linked to the subject's own sex. For example, it was
thought that a typical female-bodied person who is attracted to
female-bodied persons would have masculine attributes, and vice versa.
This understanding was shared by most of the significant theorists of
sexual orientation from the mid nineteenth to early twentieth century,
such as Karl Heinrich Ulrichs, Richard von Krafft-Ebing, Magnus Hirschfeld, Havelock Ellis, Carl Jung, and Sigmund Freud,
as well as many gender-variant homosexual people themselves. However,
this understanding of homosexuality as sexual inversion was disputed at
the time, and, through the second half of the twentieth century, gender identity came to be increasingly seen as a phenomenon distinct from sexual orientation. Transgender and cisgender
people may be attracted to men, women, or both, although the prevalence
of different sexual orientations is quite different in these two
populations. An individual homosexual, heterosexual, or bisexual person
may be masculine, feminine, or androgynous. Nevertheless, an analysis by J. Michael Bailey and Kenneth Zucker found a majority of the gay men and lesbians sampled in multiple studies reported "substantially more" cross-sex-typed behavior in childhood than heterosexual subjects.
Sexual orientation sees greater intricacy when non-binary understandings of both sex and gender are considered. Sociologist Paula Rodriguez Rust (2000) argues for a more multifaceted definition of sexual orientation:
Most alternative models of sexuality... define sexual orientation in terms of dichotomous
biological sex or gender... Most theorists would not eliminate the
reference to sex or gender, but instead advocate incorporating more
complex nonbinary concepts of sex or gender, more complex relationships
between sex, gender, and sexuality, and/or additional nongendered
dimensions into models of sexuality.
Relationships outside of orientation
Gay
and lesbian people can have sexual relationships with someone of the
opposite sex for a variety of reasons, including the desire for a
perceived traditional family and concerns of discrimination and
religious ostracism. While some LGBT
people hide their respective orientations from their spouses, others
develop positive gay and lesbian identities while maintaining successful
heterosexual marriages. Coming out
of the closet to oneself, a spouse of the opposite sex, and children
can present challenges that are not faced by gay and lesbian people who
are not married to people of the opposite sex or do not have children.
Fluidity
Often, sexual orientation and sexual orientation identity
are not distinguished, which can impact accurately assessing sexual
identity and whether or not sexual orientation is able to change; sexual
orientation identity can change throughout an individual's life, and
may or may not align with biological sex, sexual behavior, or actual
sexual orientation.
Sexual orientation is stable and unchanging for the vast majority of
people, but some research indicates that some people may experience
change in their sexual orientation, and this is more likely for women
than for men.
A recent evolutionary theory of female sexual fluidity suggests that
women may not have a sexual orientation in the same sense as men, and
that women's apparent sexual orientation may instead be a byproduct of
their sociosexual orientation. Compared to males, father absence
increases female same-sex sexual behavior in adulthood more
significantly.
The American Psychological Association distinguishes between sexual
orientation (an innate attraction) and sexual orientation identity
(which may change at any point in a person's life).
Causes
The
exact causes for the development of a particular sexual orientation have
yet to be established. To date, much research has been conducted to
determine the influence of genetics, hormonal action, development
dynamics, social and cultural influences—which has led many to think
that biology and environment factors play a complex role in forming it.
Biology
Research has identified several biological factors which may be related to the development of sexual orientation, including genes, prenatal hormones, and brain structure. No single controlling cause has been identified, and research is continuing in this area.
Although researchers generally believe that sexual orientation is
not determined by any one factor but by a combination of genetic,
hormonal, and environmental influences, with biological factors involving a complex interplay of genetic factors and the early uterine environment, they favor biological models for the cause.
There is considerably more evidence supporting nonsocial, biological
causes of sexual orientation than social ones, especially for males. Scientists do not believe that sexual orientation is a choice, and some of them believe that it is established at conception.
Current scientific investigation usually seeks to find biological
explanations for the adoption of a particular sexual orientation. Scientific studies have found a number of statistical biological differences between gay people and heterosexuals, which may result from the same underlying cause as sexual orientation itself.
Genetic factors
Genes may be related to the development of sexual orientation. A twin study from 2001 appears to exclude genes as a major factor, while a twin study from 2010 found that homosexuality was explained by both genes and environmental factors. However, experimental design of the available twin studies has made their interpretation difficult.
In 2012, a large, comprehensive genome-wide linkage study of male sexual orientation was conducted by several independent groups of researchers. Significant linkage to homosexuality was found with genes on chromosome Xq28
and chromosome 8 in the pericentromeric region. The authors concluded
that "our findings, taken in context with previous work, suggest that
genetic variation in each of these regions contributes to development of
the important psychological trait of male sexual orientation." It was
the largest study of the genetic basis of homosexuality to date and was
published online in November 2014.
However, in August 2019, a genome-wide association study
of 493,001 individuals concluded that hundreds or thousands of genetic
variants underlie homosexual behavior in both sexes, with 5 variants in
particular being significantly associated. They stated that in contrast
to linkage studies that found substantial association of sexual
orientation with variants on the X-chromosome, they found no excess of
signal (and no individual genome-wide significant variants) on Xq28 or
the rest of the X chromosome.
Hormones
The hormonal theory of sexuality holds that just as exposure to certain hormones plays a role in fetal sex differentiation,
hormonal exposure also influences the sexual orientation that emerges
later in the adult. Fetal hormones may be seen as either the primary
influence upon adult sexual orientation or as a co-factor interacting
with genes or environmental and social conditions.
For humans, the norm is that females possess two X sex
chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y. The default developmental
pathway for a human fetus being female, the Y chromosome is what
induces the changes necessary to shift to the male developmental
pathway. This differentiation process is driven by androgen hormones, mainly testosterone and dihydrotestosterone
(DHT). The newly formed testicles in the fetus are responsible for the
secretion of androgens, which will cooperate in driving the sexual
differentiation of the developing fetus, including its brain. This
results in sexual differences between males and females.
This fact has led some scientists to test in various ways the result of
modifying androgen exposure levels in mammals during fetus and early
life.
Birth order
A significant volume of research has demonstrated that the
probability of a male growing up to be gay increases with each older
brother he has from the same mother. Known as the fraternal birth order (FBO) effect, scientists attribute this to a prenatal
biological mechanism – specifically a maternal immune response to male
fetuses – since the effect is only present in men with older biological
brothers, and not present among men with older step-brothers and
adoptive brothers. This process, known as the maternal immunization hypothesis
(MIH), would begin when cells from a male fetus enter the mother's
circulation during pregnancy. These cells carry Y-proteins, which are
thought to play a role in brain masculinisation (sex-differentiation)
during fetal development. The mothers immune system builds antibodies to
these Y-proteins. These antibodies are later released on future male
fetuses and interfere with the masculinization role of Y-proteins,
leaving regions of the brain responsible for sexual orientation in the
'default' female-typical arrangement, causing the exposed son to be more
attracted to men over women. Biochemical evidence for this hypothesis
was identified in 2017, finding that mothers with a gay son, especially
those with older brothers, had significantly higher levels of
anti-bodies to the NLGN4Y Y-protein than mothers with heterosexual sons.
The effect becomes stronger with each successive male pregnancy,
meaning the odds of the next son being gay increase by 38–48%. This does
not mean that all or most sons will be gay after several male
pregnancies, but rather, the odds of having a gay son increase from
approximately 2% for the first born son, to 4% for the second, 6% for
the third and so on.
Scientists have estimated between 15% and 29% of gay men may owe their
sexual orientation to this effect, but the number may be higher, as
prior miscarriages and terminations of male pregnancies may have exposed
their mothers to Y-linked antigens. The fraternal birth order effect
would not likely apply to first born gay sons; instead, scientists say
they may owe their orientation to genes, prenatal hormones and other
maternal immune responses which also influence brain development. This effect is nullified if the man is left-handed. Ray Blanchard and Anthony Bogaert are credited with discovering the effect in the 1990s. J. Michael Bailey and Jacques Balthazart
say the FBO effect demonstrates that sexual orientation is heavily
influenced by prenatal biological mechanisms rather than unidentified
factors in socialization.
Environmental factors
In the field of genetics, any factor which is non-genetic is considered an environmental influence.
However, environmental influence does not automatically imply that the
social environment influences or contributes to the development of
sexual orientation. There is a vast non-social environment that is
non-genetic yet still biological, such as prenatal development, that likely helps shape sexual orientation.
Social factors
There
is no substantive evidence to support the suggestion that early
childhood experiences, parenting, sexual abuse, or other adverse life
events influence sexual orientation. Hypotheses for the impact of the
post-natal social environment on sexual orientation are weak, especially
for males. Parental attitudes may affect whether or not children openly identify with their sexual orientation.
Though it has since been found to be based on prejudice and
misinformation, it was once thought that homosexuality was the result of
faulty psychological development, resulting from childhood experiences
and troubled relationships, including childhood sexual abuse. Such hypotheses "have been associated with highly charged political,
moral and theological grounds for wanting to believe that it can".
Influences: professional organizations' statements
The American Academy of Pediatrics in 2004 stated:
The mechanisms for the development
of a particular sexual orientation remain unclear, but the current
literature and most scholars in the field state that one's sexual
orientation is not a choice; that is, individuals do not choose to be
homosexual or heterosexual. A variety of theories about the influences
on sexual orientation have been proposed. Sexual orientation probably is
not determined by any one factor but by a combination of genetic,
hormonal, and environmental influences. In recent decades, biologically
based theories have been favored by experts. Although there continues to
be controversy and uncertainty as to the genesis of the variety of
human sexual orientations, there is no scientific evidence that abnormal
parenting, sexual abuse, or other adverse life events influence sexual
orientation. Current knowledge suggests that sexual orientation is
usually established during early childhood.
The American Psychological Association, the American Psychiatric Association, and the National Association of Social Workers in 2006 stated:
Currently, there is no scientific
consensus about the specific factors that cause an individual to become
heterosexual, homosexual, or bisexual – including possible biological,
psychological, or social effects of the parents' sexual orientation.
However, the available evidence indicates that the vast majority of
lesbian and gay adults were raised by heterosexual parents and the vast
majority of children raised by lesbian and gay parents eventually grow
up to be heterosexual.
The Royal College of Psychiatrists in 2007 stated:
Despite almost a century of
psychoanalytic and psychological speculation, there is no substantive
evidence to support the suggestion that the nature of parenting or early
childhood experiences play any role in the formation of a person's
fundamental heterosexual or homosexual orientation. It would appear that
sexual orientation is biological in nature, determined by a complex
interplay of genetic factors and the early uterine environment. Sexual
orientation is therefore not a choice, though sexual behaviour clearly
is.
The American Psychiatric Association stated in 2011:
No one knows what causes
heterosexuality, homosexuality, or bisexuality. Homosexuality was once
thought to be the result of troubled family dynamics or faulty
psychological development. Those assumptions are now understood to have
been based on misinformation and prejudice.
A legal brief dated September 26, 2007, and presented on behalf of
the American Psychological Association, California Psychological
Association, American Psychiatric Association, National Association of
Social Workers, and National Association of Social Workers, California
Chapter, stated:
Although much research has examined
the possible genetic, hormonal, developmental, social, and cultural
influences on sexual orientation, no findings have emerged that permit
scientists to conclude that sexual orientation – heterosexuality,
homosexuality, or bisexuality – is determined by any particular factor
or factors. The evaluation of amici is that, although some of
this research may be promising in facilitating greater understanding of
the development of sexual orientation, it does not permit a conclusion
based in sound science at the present time as to the cause or causes of
sexual orientation, whether homosexual, bisexual, or heterosexual.
Efforts to change sexual orientation
Sexual orientation change efforts are methods that aim to change a
same-sex sexual orientation. They may include behavioral techniques, cognitive behavioral therapy, reparative therapy, psychoanalytic techniques, medical approaches, and religious and spiritual approaches.
No major mental health professional organization sanctions
efforts to change sexual orientation and virtually all of them have
adopted policy statements cautioning the profession and the public about
treatments that purport to change sexual orientation. These include the
American Psychiatric Association, American Psychological Association,
American Counseling Association, National Association of Social Workers
in the US, the Royal College of Psychiatrists, and the Australian Psychological Society.
In 2009, the American Psychological Association Task Force on
Appropriate Therapeutic Responses to Sexual Orientation conducted a
systematic review of the peer-reviewed journal literature on sexual
orientation change efforts (SOCE) and concluded:
Efforts to change sexual orientation are unlikely to be
successful and involve some risk of harm, contrary to the claims of SOCE
practitioners and advocates. Even though the research and clinical
literature demonstrate that same-sex sexual and romantic attractions,
feelings, and behaviors are normal and positive variations of human
sexuality, regardless of sexual orientation identity,
the task force concluded that the population that undergoes SOCE tends
to have strongly conservative religious views that lead them to seek to
change their sexual orientation. Thus, the appropriate application of
affirmative therapeutic interventions for those who seek SOCE involves
therapist acceptance, support, and understanding of clients and the
facilitation of clients' active coping, social support, and identity
exploration and development, without imposing a specific sexual
orientation identity outcome.
In 2012, the Pan American Health Organization (the North and South American branch of the World Health Organization)
released a statement cautioning against services that purport to "cure"
people with non-heterosexual sexual orientations as they lack medical
justification and represent a serious threat to the health and
well-being of affected people, and noted that the global scientific and
professional consensus is that homosexuality is a normal and natural
variation of human sexuality
and cannot be regarded as a pathological condition. The Pan American
Health Organization further called on governments, academic
institutions, professional associations and the media to expose these
practices and to promote respect for diversity. The World Health
Organization affiliate further noted that gay minors have sometimes been
forced to attend these "therapies" involuntarily, being deprived of
their liberty and sometimes kept in isolation for several months, and
that these findings were reported by several United Nations
bodies. Additionally, the Pan American Health Organization recommended
that such malpractices be denounced and subject to sanctions and
penalties under national legislation, as they constitute a violation of
the ethical principles of health care and violate human rights that are protected by international and regional agreements.
The National Association for Research & Therapy of Homosexuality
(NARTH), which described itself as a "professional, scientific
organization that offers hope to those who struggle with unwanted
homosexuality," disagreed with the mainstream mental health community's
position on conversion therapy, both on its effectiveness and by
describing sexual orientation not as a binary immutable quality, or as a
disease, but as a continuum of intensities of sexual attractions and
emotional affect. The American Psychological Association and the Royal College of Psychiatrists
expressed concerns that the positions espoused by NARTH are not
supported by the science and create an environment in which prejudice
and discrimination can flourish.
Assessment and measurement
Varying definitions and strong social norms about sexuality can make sexual orientation difficult to quantify.
Early classification schemes
One of the earliest sexual orientation classification schemes was proposed in the 1860s by Karl Heinrich Ulrichs in a series of pamphlets he published privately. The classification scheme, which was meant only to describe males, separated them into three basic categories: dionings, urnings and uranodionings. An urning can be further categorized by degree of effeminacy. These categories directly correspond with the categories of sexual orientation used today: heterosexual, homosexual, and bisexual. In the series of pamphlets, Ulrichs outlined a set of questions to determine if a man was an urning. The definitions of each category of Ulrichs' classification scheme are as follows:
- Dioning – Comparable to the modern term "heterosexual"
- Urning – Comparable to the modern term "homosexual"
- Mannling – A manly urning
- Weibling – An effeminate urning
- Zwischen – A somewhat manly and somewhat effeminate urning
- Virilised – An urning that sexually behaves like a dioning
- Urano-Dioning – Comparable to the modern term "bisexual"
From at least the late nineteenth century in Europe, there was
speculation that the range of human sexual response looked more like a
continuum than two or three discrete categories. Berlin sexologist Magnus Hirschfeld
published a scheme in 1896 that measured the strength of an
individual's sexual desire on two independent 10-point scales, A
(homosexual) and B (heterosexual).
A heterosexual individual may be A0, B5; a homosexual individual may be
A5, B0; an asexual would be A0, B0; and someone with an intense
attraction to both sexes would be A9, B9.
Kinsey scale
The Kinsey scale, also called the Heterosexual-Homosexual Rating Scale, was first published in Sexual Behavior in the Human Male (1948) by Alfred Kinsey, Wardell Pomeroy, and Clyde Martin and also featured in Sexual Behavior in the Human Female (1953).
The scale was developed to combat the assumption at the time that
people are either heterosexual or homosexual and that these two types
represent antitheses in the sexual world.
Recognizing that a significant portion of the population is not
completely heterosexual or homosexual and that such people can
experience both heterosexual and homosexual behavior and psychic
responses, Kinsey et al., stated:
Males do not represent two discrete
populations, heterosexual and homosexual. The world is not to be
divided into sheep and goats. Not all things are black nor all things
white... The living world is a continuum in each and every one of its
aspects. The sooner we learn this concerning human sexual behavior, the
sooner we shall reach a sound understanding of the realities of sex.
— Kinsey et al. (1948) p. 639.
The Kinsey scale provides a classification of sexual orientation
based on the relative amounts of heterosexual and homosexual experience
or psychic response in one's history at a given time.
The classification scheme works such that individuals in the same
category show the same balance between the heterosexual and homosexual
elements in their histories. The position on the scale is based on the
relation of heterosexuality to homosexuality in one's history, rather
than the actual amount of overt experience or psychic response. An
individual can be assigned a position on the scale in accordance with
the following definitions of the points of the scale:
| Rating |
Description
|
| 0 |
Exclusively heterosexual. Individuals make no physical
contact which results in erotic arousal or orgasm and make no psychic
responses to individuals of their own sex.
|
| 1 |
Predominantly heterosexual/incidentally homosexual.
Individuals have only incidental homosexual contacts which have involved
physical or psychic response or incidental psychic response without
physical contact.
|
| 2 |
Predominantly heterosexual but more than incidentally homosexual. Individuals have more than incidental homosexual experience or respond rather definitely to homosexual stimuli.
|
| 3 |
Equally heterosexual and homosexual. Individuals are about equally homosexual and heterosexual in their experiences or psychic reactions.
|
| 4 |
Predominantly homosexual but more than incidentally heterosexual.
Individuals have more overt activity or psychic reactions in the
homosexual while still maintaining a fair amount of heterosexual
activity or responding rather definitively to heterosexual contact.
|
| 5 |
Predominantly homosexual/only incidentally heterosexual. Individuals are almost entirely homosexual in their activities or reactions.
|
| 6 |
Exclusively homosexual. Individuals who are exclusively homosexual, both in regard to their overt experience and in regard to their psychic reactions.
|
The Kinsey scale has been praised for dismissing the dichotomous
classification of sexual orientation and allowing for a new perspective
on human sexuality. Despite seven categories being able to provide a
more accurate description of sexual orientation than a dichotomous
scale, it is still difficult to determine which category individuals
should be assigned to. In a major study comparing sexual response in
homosexual males and females, Masters and Johnson discuss the difficulty of assigning the Kinsey ratings to participants.
Particularly, they found it difficult to determine the relative amount
heterosexual and homosexual experience and response in a person's
history when using the scale. They report finding it difficult to assign
ratings 2–4 for individuals with a large number of heterosexual and
homosexual experiences. When there are a substantial number of
heterosexual and homosexual experiences in one's history, it becomes
difficult for that individual to be fully objective in assessing the
relative amount of each.
Weinrich et al. (1993) and Weinberg et al. (1994) criticized the
scale for lumping individuals who are different based on different
dimensions of sexuality into the same categories.
When applying the scale, Kinsey considered two dimensions of sexual
orientation: overt sexual experience and psychosexual reactions.
Valuable information was lost by collapsing the two values into one
final score. A person who has only predominantly same sex reactions is
different from someone with relatively little reaction but much same sex
experience. It would have been quite simple for Kinsey to have measured
the two dimensions separately and report scores independently to avoid
loss of information. Furthermore, there are more than two dimensions of
sexuality to be considered. Beyond behavior and reactions, one could
also assess attraction, identification, lifestyle, etc. This is
addressed by the Klein Sexual Orientation Grid.
A third concern with the Kinsey scale is that it inappropriately
measures heterosexuality and homosexuality on the same scale, making one
a tradeoff of the other.
Research in the 1970s on masculinity and femininity found that concepts
of masculinity and femininity are more appropriately measured as
independent concepts on a separate scale rather than as a single
continuum, with each end representing opposite extremes.
When compared on the same scale, they act as tradeoffs such, whereby
to be more feminine one had to be less masculine and vice versa.
However, if they are considered as separate dimensions one can be
simultaneously very masculine and very feminine. Similarly, considering
heterosexuality and homosexuality on separate scales would allow one to
be both very heterosexual and very homosexual or not very much of
either. When they are measured independently, the degree of
heterosexual and homosexual can be independently determined, rather than
the balance between heterosexual and homosexual as determined using the
Kinsey Scale.
Klein Sexual Orientation Grid
In response to the criticism of the Kinsey scale only measuring two dimensions of sexual orientation, Fritz Klein
developed the Klein sexual orientation grid (KSOG), a multidimensional
scale for describing sexual orientation. Introduced in Klein's book The Bisexual Option
(1978), the KSOG uses a 7-point scale to assess seven different
dimensions of sexuality at three different points in an individual's
life: past (from early adolescence up to one year ago), present (within
the last 12 months), and ideal (what the individual would choose if it
were completely their choice).
The Sell Assessment of Sexual Orientation
The
Sell Assessment of Sexual Orientation (SASO) was developed to address
the major concerns with the Kinsey Scale and Klein Sexual Orientation
Grid and as such, measures sexual orientation on a continuum, considers
various dimensions of sexual orientation, and considers homosexuality
and heterosexuality separately. Rather than providing a final solution
to the question of how to best measure sexual orientation, the SASO is
meant to provoke discussion and debate about measurements of sexual
orientation.
The SASO consists of 12 questions. Six of these questions assess
sexual attraction, four assess sexual behavior, and two assess sexual
orientation identity. For each question on the scale that measures
homosexuality there is a corresponding question that measures
heterosexuality giving six matching pairs of questions. Taken all
together, the six pairs of questions and responses provide a profile of
an individual's sexual orientation. However, results can be further
simplified into four summaries that look specifically at responses that
correspond to either homosexuality, heterosexuality, bisexuality or
asexuality.
Of all the questions on the scale, Sell considered those
assessing sexual attraction to be the most important as sexual
attraction is a better reflection of the concept of sexual orientation
which he defined as "extent of sexual attractions toward members of the
other, same, both sexes or neither" than either sexual identity or
sexual behavior. Identity and behavior are measured as supplemental
information because they are both closely tied to sexual attraction and
sexual orientation. Major criticisms of the SASO have not been
established, but a concern is that the reliability and validity remains
largely unexamined.
Difficulties with assessment
Research
focusing on sexual orientation uses scales of assessment to identify
who belongs in which sexual population group. It is assumed that these
scales will be able to reliably identify and categorize people by their
sexual orientation. However, it is difficult to determine an
individual's sexual orientation through scales of assessment, due to
ambiguity regarding the definition of sexual orientation. Generally,
there are three components of sexual orientation used in assessment.
Their definitions and examples of how they may be assessed are as
follows:
| Component |
Definition |
Questions
|
| Sexual attraction |
Attraction toward one sex or the desire to have sexual relations or
to be in a primary loving, sexual relationship with one or both sexes |
"Have you ever had a romantic attraction to a male? Have you ever had a romantic attraction to a female?"
|
| Sexual behavior |
"Any mutually voluntary activity with another person that involves
genital contact and sexual excitement or arousal, that is, feeling
really turned on, even if intercourse or orgasm did not occur" |
"Have you ever had a relationship with someone of your own sex which resulted in sexual orgasm?"
|
| Sexual identity |
Personally selected, socially and historically bound labels attached
to the perceptions and meaning individuals have about their sexual
identity. |
"Pick from these six option: gay or lesbian; bisexual, but mostly
gay or lesbian; bisexual equally gay/lesbian and heterosexual; bisexual
but mostly heterosexual; heterosexual; and uncertain, don't know for
sure."
|
Though sexual attraction, behavior, and identity are all components
of sexual orientation, if a person defined by one of these dimensions
were congruent with those defined by another dimension it would not
matter which was used in assessing orientation, but this is not the
case. There is "little coherent relationship between the amount and mix
of homosexual and heterosexual behavior in a person's biography and that
person's choice to label himself or herself as bisexual, homosexual, or
heterosexual".
Individuals typically experience diverse attractions and behaviors
that may reflect curiosity, experimentation, social pressure and is not
necessarily indicative of an underlying sexual orientation. For example,
a woman may have fantasies or thoughts about sex with other women but
never act on these thoughts and only have sex with opposite gender
partners. If sexual orientation was being assessed based on one's sexual
attraction then this individual would be considered homosexual, but her
behavior indicates heterosexuality.
As there is no research indicating which of the three components
is essential in defining sexual orientation, all three are used
independently and provide different conclusions regarding sexual
orientation. Savin Williams (2006) discusses this issue and notes that
by basing findings regarding sexual orientation on a single component,
researchers may not actually capture the intended population. For
example, if homosexual is defined by same sex behavior, gay virgins are
omitted, heterosexuals engaging in same sex behavior for other reasons
than preferred sexual arousal are miscounted, and those with same sex
attraction who only have opposite-sex relations are excluded.
Because of the limited populations that each component captures,
consumers of research should be cautious in generalizing these findings.
One of the uses for scales that assess sexual orientation is
determining what the prevalence of different sexual orientations are
within a population. Depending on subject's age, culture and sex, the
prevalence rates of homosexuality vary depending on which component of
sexual orientation is being assessed: sexual attraction, sexual
behavior, or sexual identity. Assessing sexual attraction will yield the
greatest prevalence of homosexuality in a population whereby the
proportion of individuals indicating they are same sex attracted is two
to three times greater than the proportion reporting same sex behavior
or identify as gay, lesbian, or bisexual. Furthermore, reports of same
sex behavior usually exceed those of gay, lesbian, or bisexual
identification.
The following chart demonstrates how widely the prevalence of
homosexuality can vary depending on what age, location and component of
sexual orientation is being assessed:
Prevalence of homosexuality
|
Attraction |
Behaviour |
Identity
|
| Country: Age group |
Female
|
Male |
Female
|
Male |
Female
|
Male
|
- US: Youth
|
6%
|
3% |
11%
|
5% |
8%
|
3%
|
- US: Young adults
|
13%
|
5% |
4%
|
3% |
4%
|
3%
|
- US: Adults
|
8%
|
8% |
4%
|
9% |
1%
|
2%
|
| Australia: Adults |
17%
|
15% |
8%
|
16% |
4%
|
7%
|
| Turkey: Young adults |
7%
|
6% |
4%
|
5% |
2%
|
2%
|
| Norway: Adolescents |
21%
|
9% |
7%
|
6% |
5%
|
5%
|
The variance in prevalence rates is reflected in people's
inconsistent responses to the different components of sexual orientation
within a study and the instability of their responses over time.
Laumann et al. (1994) found that among U.S. adults 20% of those who
would be considered homosexual on one component of orientation were
homosexual on the other two dimensions and 70% responded in a way that
was consistent with homosexuality on only one of the three dimensions.
Furthermore, sexuality may be fluid; for example, a person's sexual
orientation identity is not necessarily stable or consistent over time
but is subject to change throughout life. Diamond (2003) found that over
seven years, two-thirds of the women changed their sexual identity at
least once, with many reporting that the label was not adequate in
capturing the diversity of their sexual or romantic feelings.
Furthermore, women who relinquished bisexual and lesbian identification
did not relinquish same sex sexuality and acknowledged the possibility
for future same sex attractions or behaviour. One woman stated "I'm
mainly straight but I'm one of those people who, if the right
circumstance came along, would change my viewpoint".
Therefore, individuals classified as homosexual in one study might not
be identified the same way in another depending on which components are
assessed and when the assessment is made making it difficult to pin
point who is homosexual and who is not and what the overall prevalence
within a population may be.
Implications
Depending
on which component of sexual orientation is being assessed and
referenced, different conclusions can be drawn about the prevalence rate
of homosexuality which has real world consequences. Knowing how much of
the population is made up of homosexual individuals influences how this
population may be seen or treated by the public and government bodies.
For example, if homosexual individuals constitute only 1% of the general
population they are politically easier to ignore or than if they are
known to be a constituency that surpasses most ethnic and minority
groups. If the number is relatively minor then it is difficult to argue
for community based same sex programs and services, mass media
inclusion of gay role models, or Gay/Straight Alliances in schools. For
this reason, in the 1970s Bruce Voeller, the chair of the National Gay and Lesbian Task Force
perpetuated a common myth that the prevalence of homosexuality is 10%
for the whole population by averaging a 13% number for men and a 7%
number for women. Voeller generalized this finding and used it as part
of the modern gay rights movement to convince politicians and the public
that "we [gays and lesbians] are everywhere".
Proposed solutions
In the paper "Who's Gay? Does It Matter?", psychologist Ritch Savin-Williams
proposes two different approaches to assessing sexual orientation until
well positioned and psychometrically sound and tested definitions are
developed that would allow research to reliably identify the prevalence,
causes, and consequences of homosexuality.
He first suggests that greater priority should be given to sexual
arousal and attraction over behaviour and identity because it is less
prone to self- and other-deception, social conditions and variable
meanings. To measure attraction and arousal he proposed that biological
measures should be developed and used. There are numerous
biological/physiological measures that exist that can measure sexual
orientation such as sexual arousal, brain scans, eye tracking, body odour preference, and anatomical variations such as digit-length ratio
and right or left-handedness.
Secondly, Savin-Williams suggests that researchers should forsake the
general notion of sexual orientation altogether and assess only those
components that are relevant to the research question being
investigated. For example:
- To assess STIs or HIV transmission, measure sexual behaviour
- To assess interpersonal attachments, measure sexual/romantic attraction
- To assess political ideology, measure sexual identity
Means of assessment
Means typically used include surveys, interviews, cross-cultural studies, physical arousal measurements sexual behavior, sexual fantasy, or a pattern of erotic arousal. The most common is verbal self-reporting or self-labeling, which depend on respondents being accurate about themselves.
Sexual arousal
Studying human sexual arousal
has proved a fruitful way of understanding how men and women differ as
genders and in terms of sexual orientation. A clinical measurement may
use penile or vaginal photoplethysmography, where genital engorgement with blood is measured in response to exposure to different erotic material.
Some researchers who study sexual orientation argue that the
concept may apply differently for men and women. A study of sexual
arousal patterns
found that women, when viewing erotic films which show female-female,
male-male and male-female sexual activity (oral sex or penetration),
have patterns of arousal which do not match their declared sexual
orientations as well as men's. That is, heterosexual and lesbian
women's sexual arousal to erotic films do not differ significantly by
the genders of the participants (male or female) or by the type of
sexual activity (heterosexual or homosexual). Men's sexual arousal
patterns tend to be more in line with their stated orientations, with
heterosexual men showing more penis arousal to female-female sexual
activity and less arousal to female-male and male-male sexual stimuli,
and homosexual and bisexual men being more aroused by films depicting
male-male intercourse and less aroused by other stimuli.
Another study on men and women's patterns of sexual arousal confirmed
that men and women have different patterns of arousal, independent of
their sexual orientations. The study found that women's genitals become
aroused to both human and nonhuman stimuli from movies showing humans
of both genders having sex (heterosexual and homosexual) and from videos
showing non-human primates
(bonobos) having sex. Men did not show any sexual arousal to non-human
visual stimuli, their arousal patterns being in line with their
specific sexual interest (women for heterosexual men and men for
homosexual men).
These studies suggest that men and women are different in terms
of sexual arousal patterns and that this is also reflected in how their
genitals react to sexual stimuli of both genders or even to non-human
stimuli. Sexual orientation has many dimensions (attractions, behavior, identity),
of which sexual arousal is the only product of sexual attractions which
can be measured at present with some degree of physical precision.
Thus, the fact that women are aroused by seeing non-human primates
having sex does not mean that women's sexual orientation includes this
type of sexual interest. Some researchers argue that women's sexual
orientation depends less on their patterns of sexual arousal than men's
and that other components of sexual orientation (like emotional
attachment) must be taken into account when describing women's sexual
orientations. In contrast, men's sexual orientations tend to be
primarily focused on the physical component of attractions and, thus,
their sexual feelings are more exclusively oriented according to sex.
More recently, scientists have started to focus on measuring changes in brain activity related to sexual arousal, by using brain-scanning techniques. A study on how heterosexual and homosexual men's brains react to seeing pictures of naked men and women has found
that both hetero- and homosexual men react positively to seeing their
preferred sex, using the same brain regions. The only significant group
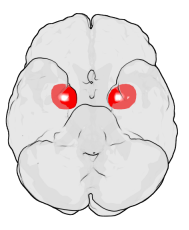
difference between these orientations was found in the amygdala, a brain region known to be involved in regulating fear.
Culture
Research suggests that sexual orientation is independent of cultural
and other social influences, but that open identification of one's
sexual orientation may be hindered by homophobic/heterosexist
settings. Social systems such as religion, language and ethnic
traditions can have a powerful impact on realization of sexual
orientation. Influences of culture may complicate the process of measuring sexual orientation.
The majority of empirical and clinical research on LGBT populations are
done with largely white, middle-class, well-educated samples; however,
there are pockets of research that document various other cultural
groups, although these are frequently limited in diversity of gender and
sexual orientation of the subjects.
Integration of sexual orientation with sociocultural identity may be a
challenge for LGBT individuals. Individuals may or may not consider
their sexual orientation to define their sexual identity, as they may experience various degrees of fluidity of sexuality,
or may simply identify more strongly with another aspect of their
identity such as family role. American culture puts a great emphasis on
individual attributes, and views the self as unchangeable and constant.
In contrast, East Asian cultures put a great emphasis on a person's
social role within social hierarchies, and view the self as fluid and
malleable.
These differing cultural perspectives have many implications on
cognition of the self, including perception of sexual orientation.
Language
Translation
is a major obstacle when comparing different cultures. Many English
terms lack equivalents in other languages, while concepts and words from
other languages fail to be reflected in the English language. Translation and vocabulary obstacles are not limited to the English language.
Language can force individuals to identify with a label that may or
may not accurately reflect their true sexual orientation. Language can
also be used to signal sexual orientation to others.
The meaning of words referencing categories of sexual orientation are
negotiated in the mass media in relation to social organization.
New words may be brought into use to describe new terms or better
describe complex interpretations of sexual orientation. Other words may
pick up new layers or meaning. For example, the heterosexual Spanish
terms marido and mujer for "husband" and "wife", respectively, have recently been replaced in Spain by the gender-neutral terms cónyuges or consortes meaning "spouses".
Perceptions
One person may presume knowledge of another person's sexual
orientation based upon perceived characteristics, such as appearance,
clothing, voice (c.f. Gay male speech),
and accompaniment by and behavior with other people. The attempt to
detect sexual orientation in social situations is sometimes colloquially
known as gaydar; some studies have found that guesses based on face photos perform better than chance. 2015 research suggests that "gaydar" is an alternate label for using LGBT stereotypes to infer orientation, and that face-shape is not an accurate indication of orientation.
Perceived sexual orientation may affect how a person is treated. For instance, in the United States, the FBI reported that 15.6% of hate crimes reported to police in 2004 were "because of a sexual-orientation bias". Under the UK Employment Equality (Sexual Orientation) Regulations 2003, as explained by Advisory, Conciliation and Arbitration Service,
"workers or job applicants must not be treated less favourably because
of their sexual orientation, their perceived sexual orientation or
because they associate with someone of a particular sexual orientation".
In Euro-American cultures, norms, values, traditions and laws facilitate heterosexuality, including constructs of marriage and family. Efforts are being made to change prejudiced attitudes, and legislation is being passed to promote equality.
Some other cultures do not recognize a
homosexual/heterosexual/bisexual distinction. It is common to
distinguish a person's sexuality according to their sexual role
(active/passive; insertive/penetrated). In this distinction, the passive
role is typically associated with femininity or inferiority, while the
active role is typically associated with masculinity or superiority.
For example, an investigation of a small Brazilian fishing village
revealed three sexual categories for men: men who have sex only with men
(consistently in a passive role), men who have sex only with women, and
men who have sex with women and men (consistently in an active role).
While men who consistently occupied the passive role were recognized as a
distinct group by locals, men who have sex with only women, and men who
have sex with women and men, were not differentiated. Little is known about same-sex attracted females, or sexual behavior between females in these cultures.
Racism and ethnically relevant support
In the United States, non-Caucasian LGBT individuals may find
themselves in a double minority, where they are neither fully accepted
or understood by mainly Caucasian LGBT communities, nor are they
accepted by their own ethnic group.
Many people experience racism in the dominant LGBT community where
racial stereotypes merge with gender stereotypes, such that
Asian-American LGBTs are viewed as more passive and feminine, while
African-American LGBTs are viewed as more masculine and aggressive.
There are a number of culturally specific support networks for LGBT
individuals active in the United States. For example, "Ô-Môi" for
Vietnamese American queer females.
Religion
Sexuality in the context of religion is often a controversial
subject, especially that of sexual orientation. In the past, various
sects have viewed homosexuality from a negative point of view and had
punishments for same-sex relationships. In modern times, an increasing
number of religions and religious denominations accept homosexuality. It
is possible to integrate sexual identity and religious identity,
depending on the interpretation of religious texts.
Some religious organizations object to the concept of sexual
orientation entirely. In the 2014 revision of the code of ethics of the
American Association of Christian Counselors, members are forbidden to
"describe or reduce human identity and nature to sexual orientation or
reference," even while counselors must acknowledge the client's
fundamental right to self-determination.
Internet and media
The Internet has influenced sexual orientation in two ways: it is a
common mode of discourse on the subject of sexual orientation and sexual
identity, and therefore shapes popular conceptions;
and it allows anonymous attainment of sexual partners, as well as
facilitates communication and connection between greater numbers of
people.
Demographics
Modern scientific surveys find that, across cultures, most people report a heterosexual orientation. Bisexuality comes in varying degrees of relative attraction to the same or opposite sex.
Men are more likely to be exclusively homosexual than to be equally
attracted to both sexes, while the opposite is true for women.
Surveys in Western cultures find, on average, that about 93% of
men and 87% of women identify as completely heterosexual, 4% of men and
10% of women as mostly heterosexual, 0.5% of men and 1% of women as
evenly bisexual, 0.5% of men and 0.5% of women as mostly homosexual, and
2% of men and 0.5% of women as completely homosexual.
An analysis of 67 studies found that the lifetime prevalence of sex
between men (regardless of orientation) was 3-5% for East Asia, 6-12%
for South and South East Asia, 6-15% for Eastern Europe, and 6-20% for
Latin America. The International HIV/AIDS Alliance estimates a worldwide prevalence of men who have sex with men between 3 and 16%.
The relative percentage of the population that reports a
homosexual or bisexual orientation can vary with different methodologies
and selection criteria. A 1998 report stated that these statistical
findings are in the range of 2.8 to 9% for males, and 1 to 5% for
females for the United States – this figure can be as high as 12% for some large cities and as low as 1% for rural areas.
A small percentage of people are not sexually attracted to anyone (asexuality). A study in 2004 placed the prevalence of asexuality at 1%.
Kinsey data
In Sexual Behavior in the Human Male (1948) and Sexual Behavior in the Human Female (1953), by Alfred C. Kinsey et al., people were asked to rate themselves on a scale
from completely heterosexual to completely homosexual. Kinsey reported
that when the individuals' behavior, as well as their identity, are
analyzed, a significant number of people appeared to be at least
somewhat bisexual – i.e., they have some attraction to either sex,
although usually one sex is preferred. Kinsey's methods have been
criticized as flawed, particularly with regard to the randomness of his
sample population, which included prison inmates, male prostitutes and
those who willingly participated in discussion of previously taboo
sexual topics. Nevertheless, Paul Gebhard, subsequent director of the Kinsey Institute for Sex Research, reexamined the data in the Kinsey Reports and concluded that removing the prison inmates and prostitutes barely affected the results.
More recent researchers believe that Kinsey overestimated the rate of
same-sex attraction because of flaws in his sampling methods.
Social constructionism
Because sexual orientation is complex, some academics and researchers, especially in queer studies, have argued that it is a historical and social construction. In 1976, philosopher and historian Michel Foucault argued in The History of Sexuality
that homosexuality as an identity did not exist in the eighteenth
century; that people instead spoke of "sodomy," which referred to sexual
acts. Sodomy was a crime that was often ignored, but sometimes punished
severely under sodomy laws. He wrote, "'Sexuality' is an invention of the modern state, the industrial revolution, and capitalism." Other scholars argue that there are significant continuities between ancient and modern homosexuality. The philosopher of science Michael Ruse
has stated that the social constructionist approach, which is
influenced by Foucault, is based on a selective reading of the
historical record that confuses the existence of homosexual people with
the way in which they are labelled or treated.
In much of the modern world, sexual identity
is defined based on the sex of one's partner. In some parts of the
world, however, sexuality is often socially defined based on sexual
roles, whether one is a penetrator or is penetrated.
In Western cultures, people speak meaningfully of gay, lesbian, and
bisexual identities and communities. In some other cultures,
homosexuality and heterosexual labels do not emphasize an entire social
identity or indicate community affiliation based on sexual orientation.
Some historians and researchers
argue that the emotional and affectionate activities associated with
sexual-orientation terms such as "gay" and "heterosexual" change
significantly over time and across cultural boundaries. For example, in
many English-speaking nations, it is assumed that same-sex kissing,
particularly between men, is a sign of homosexuality, whereas various
types of same-sex kissing are common expressions of friendship in other
nations. Also, many modern and historic cultures have formal ceremonies
expressing long-term commitment between same-sex friends, even though
homosexuality itself is taboo within the cultures.
Law, politics and theology
Professor
Michael King stated, "The conclusion reached by scientists who have
investigated the origins and stability of sexual orientation is that it
is a human characteristic that is formed early in life, and is resistant
to change. Scientific evidence on the origins of homosexuality is
considered relevant to theological and social debate because it
undermines suggestions that sexual orientation is a choice."
In 1999, law professor David Cruz wrote that "sexual orientation
(and the related concept homosexuality) might plausibly refer to a
variety of different attributes, singly or in combination. What is not
immediately clear is whether one conception is most suited to all
social, legal, and constitutional purposes."