From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Fusion power is the energy generated by nuclear fusion processes. In the context of energy production, it signifies the production of net usable power from a fusion source, similar to the usage of the term "steam power". Fusion reactions are high energy reactions in which two lighter atomic nuclei fuse to form a heavier nucleus (in contrast with fission power where very heavy nuclei are split into lighter ones). In fusing, the nuclei release a comparatively large amount of energy arising from the binding energy due to the strong nuclear force, which manifests as an increase in temperature of the reactants and can be used to generate electricity. Fusion power is a primary area of research in plasma physics, where it is seen as a means of producing large scale cleaner energy.
In most large scale commercial proposals, heat from the fusion reaction is used to operate a steam turbine that drives electrical generators, as in existing fossil fuel and nuclear fission power stations. Smaller scale reactors often propose to use much simpler thermocouples - with no moving parts or hot liquids - to generate electricity from heat at a lower electrical efficiency, but with more safety and smaller size. Smaller fission reactors such as those on nuclear submarines have proven this approach, and research into materials suitable for fusion date back to at least 1981 [8]. Because of the variety of fusion reactions, the potential use of solid boron or liquid lithium fuel, a non-radioactive supply and minimally radioactive waste chain, smaller reactors may be deployed outside the military without these concerns, which have inhibited small uranium reactors.
There are two primary problems to be overcome in fusion power research: sustained confinement and choice of container materials. Confinement means confining the fusion reaction so it continues using its own energy. Fusion reactions are extremely delicate and will stop almost immediately if not very precisely maintained - this makes them safer in many important ways compared to existing fission reactors. They must also avoid losing energy in order to be sustainable. Leading designs for controlled fusion research use magnetic (tokamak design) or inertial (laser) confinement of a plasma. Both approaches are still under development and are years away from commercial operation. A few other models such as purely inertial confinement using centrifugal force are being explored for heavier fusion fuel such as liquid lithium, but these are not thought suitable for large scale power plants.
Materials research refers to researching suitable materials for construction purposes, which will not become brittle or excessively damaged by exposure to fast neutrons during fusion processes. If neutrons convey the energy released, then whatever medium absorbs the neutron scattering eventually becomes mildly radioactive and must also be disposed of, e.g. ordinary water becomes heavy water. In a fusion supply chain heavy water is actually useful again as a fuel, making a breeder reactor style of design more practical. However the overall complexity of this design has proven problematic in fission reactors such as the CANDU and may be uneconomic. It may be possible to retrofit turbines of existing fission reactors for thorium fission and for fusion-based neutron scatter. However, aneutronic fusion and minimal neutron energy reactions such as proton-boron have received more research attention in the 2010s, largely for their potential to create small clean portable energy sources without neutron pollution.
To fuse, nuclei must overcome the repulsive Coulomb force. This is a force caused by the nuclei containing positively charged protons that repel via the electromagnetic force. To overcome this "Coulomb barrier", the atoms must have a high kinetic energy. There are several ways of doing this, including heating or acceleration. Once an atom is heated above its ionization energy, its electrons are stripped away, leaving just the bare nucleus: the ion. Most fusion experiments use a hot cloud of ions and electrons. This cloud is known as a plasma. Most fusion reactions produce neutrons, which can be detected and degrade materials.
Theoretically, any atom could be fused, if enough pressure and temperature was applied.[2] Mankind has studied many high energy fusion reactions, using particles beams.[3] These are fired at a target. For a power plant, however, we are currently limited to only the light elements. Hydrogen is ideal: because of its small charge, it is the easiest atom to fuse. This reaction produces helium.
A reaction's cross section, (denoted σ) is the measure of how likely a fusion reaction will happen. It is a probability, and it depends on the velocity of the two nuclei when they strike one another. If the atoms move faster, fusion is more likely. If the atoms hit head on, fusion is more likely. Cross sections for many different fusion reactions were measured mainly in the 1970s using particle beams.[3] A beam of species A was fired at species B at different speeds, and the amount of neutrons coming off was measured. Neutrons are a key product of fusion reactions. These nuclei are flying around in a hot cloud, with some distribution of velocities. If the plasma is thermalized, then the distribution looks like a bell curve, or maxwellian distribution. In this case, it is useful to take the average cross section over the velocity distribution. This is entered into the volumetric fusion rate:[4]
(ntτ) as a metric of success, has hurt other considerations like cost, size, complexity and efficiency.[dubious ] This has led to larger, more complicated and more expensive machines like ITER and NIF.[citation needed]
Stellarator These are twisted rings of hot plasma. Stellarators are distinct from tokamak in that they are not azimuthally symmetric. Instead, they have a discrete rotational symmetry, often fivefold, like a regular pentagon. Stellarators were developed by Lyman Spitzer in 1950. There are four designs: Torsatron, Heliotron, Heliac and Helias.
Levitated Dipole Experiment (LDX) These use a solid superconducting torus. This is magnetically levitated inside the reactor chamber. The superconductor forms an axisymmetric magnetic field that contains the plasma. The LDX was developed between MIT and Columbia University after 2000 by Jay Kesner and Michael E. Mauel.[10]
Magnetic mirror Developed by Richard F. Post and teams at LLNL in the 1960s.[11] Magnetic mirrors reflected hot plasma back and forth in a line. Variations included the magnetic bottle and the biconic cusp.[12] A series of well-funded, large, mirror machines were built by the US government in the 1970s and 1980s.
Field-reversed configuration This device confines a plasma on closed magnetic field lines without a central penetration.[13]
Fast ignition This method uses two laser blasts. The first blast compresses the fusion fuel, while the second high energy pulse ignites it. Experiments have been conducted at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics using the Omega and Omega EP systems.
Indirect drive In this technique, lasers blasts a structure around the pellet of fuel. This structure is known as a Hohlraum. As it disintegrates the pellet is bathed in a more uniform x-ray light, creating better compression. The largest system using this method is the National Ignition Facility.
Magneto-inertial fusion This technique, combines laser pulses with the magnetic pinch to compress and confine an imploding plasma cloud.[15] The field traps heat within the core, which improves the fusion rates. A similar concept is the magnetized target fusion device, which uses a magnetic field in an external metal shell to achieve the same basic goals.
Theta-Pinch This method sends a current inside a plasma, in the theta direction.
Polywell This designs attempts to combine magnetic confinement with electrostatic fields, to avoid the conduction losses generated by the cage.[20] This research, however, is immature and under developed.
Uncontrolled Fusion has been initiated by man, using uncontrolled fission explosions. Early proposals for fusion power included using bombs to initiate reactions.
Beam fusion A beam of high energy particles can be fired at another beam or target and fusion will occur. This was used in the 1970s and 80's to study the cross sections of high energy fusion reactions.[3]
Bubble fusion This was a supposed fusion reaction that was supposed to occur inside extraordinarily large collapsing gas bubbles, created during acoustic liquid cavitation.[22]
Cold fusion This is a hypothetical type of nuclear reaction that would occur at, or near, room temperature. Cold fusion has gained a reputation as Pathological science.[23][24]
Muon-catalyzed fusion Muons allow atoms to get much closer and thus reduce the kinetic energy required to initiate fusion. Muons require more energy to produce than can be obtained from muon-catalysed fusion, making this approach impractical for the generation of power[25]
Pinch was first developed in the UK in the immediate post-war era. Starting in 1947 small experiments were carried out and plans were laid to build a much larger machine. Two teams were quickly formed and began a series of ever-larger experiments. When the Huemul results hit the news, James L. Tuck, a UK physicist working at Los Alamos, introduced the pinch concept in the US and produced a series of machines known as the Perhapsatron. In the Soviet Union, unbeknownst to the west, a series of similar machines were being built. All of these devices quickly demonstrated a series of instabilities when the pinch was applied, which broke up the plasma column long before it reached the densities and temperatures required for fusion. In 1953 Tuck and others suggested a number of solutions to these problems.
A major area of study in early fusion power research is the "pinch" concept. Pinch is based on the fact that plasmas are electrically conducting. By running a current through the plasma, a magnetic field will be generated around the plasma. This field will, according to Lenz's law, create an inward directed force that causes the plasma to collapse inward, raising its density. Denser plasmas generate denser magnetic fields, increasing the inward force, leading to a chain reaction. If the conditions are correct, this can lead to the densities and temperatures needed for fusion. The difficulty is getting the current into the plasma, which would normally melt any sort of mechanical electrode. A solution emerges again due to the conducting nature of the plasma; by placing the plasma in the middle of an electromagnet, induction can be used to generate the current.
The first successful man-made fusion device was the boosted fission weapon tested in 1951 in the Greenhouse Item test. This was followed by true fusion weapons in 1952's Ivy Mike, and the first practical examples in 1954's Castle Bravo. This was uncontrolled fusion. In these devices, the energy released by the fission explosion is used to compress and heat fusion fuel, starting a fusion reaction. Fusion releases neutrons. These neutrons hit the surrounding fission fuel, causing the atoms to split apart much faster than normal fission processes - almost instantly by comparison. This increases the effectiveness of bombs: normal fission weapons blow themselves apart before all their fuel is used; fusion/fission weapons do not have this practical upper limit.
In 1951, Lyman Spitzer began work on a stellarator under the code name Project Matterhorn. His work led to the creation of the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory. Spitzer planned an aggressive development project of four machines, A, B, C, and D. A and B were small research devices, C would be the prototype of a power-producing machine, and D would be the prototype of a commercial device. A worked without issue, but even by the time B was being used it was clear the stellarator was also suffering from instabilities and plasma leakage. Progress on C slowed as attempts were made to correct for these problems.
Around the same time, an expatriate German Ronald Richter proposed the Huemul Project in Argentina, announcing positive results in 1951. Although these results turned out to be false, it sparked off intense interest around the world. The UK pinch programs were greatly expanded, culminating in the ZETA and Sceptre devices. In the US, pinch experiments like those in the UK started at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. Similar devices were built in the USSR after data on the UK program was passed to them by Klaus Fuchs. At Princeton University a new approach developed as the stellarator, and the research establishment formed there continues to this day as the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory.
By the mid-1950s it was clear that the simple theoretical tools being used to calculate the performance of all fusion machines were simply not predicting their actual behavior. Machines invariably leaked their plasma from their confinement area at rates far higher than predicted.
In 1954, Edward Teller held a gathering of fusion researchers at the Princeton Gun Club, near the Project Matterhorn (now known as Project Sherwood) grounds. Teller started by pointing out the problems that everyone was having, and suggested that any system where the plasma was confined within concave fields was doomed to fail. Attendees remember him saying something to the effect that the fields were like rubber bands, and they would attempt to snap back to a straight configuration whenever the power was increased, ejecting the plasma. He went on to say that it appeared the only way to confine the plasma in a stable configuration would be to use convex fields, a "cusp" configuration.[27]
When the meeting concluded, most of the researchers quickly turned out papers saying why Teller's concerns did not apply to their particular device. The pinch machines did not use magnetic fields in this way at all, while the mirror and stellarator seemed to have various ways out. This was soon followed by a paper by Martin David Kruskal and Martin Schwarzschild discussing pinch machines, however, which demonstrated instabilities in those devices were inherent to the design.
The largest "classic" pinch device was the ZETA, including all of these suggested upgrades, starting operations in the UK in 1957. In early 1958, John Cockcroft announced that fusion had been achieved in the ZETA, an announcement that made headlines around the world. When physicists in the US expressed concerns about the claims they were initially dismissed. US experiments soon demonstrated the same neutrons, although temperature measurements suggested these could not be from fusion reactions. The neutrons seen in the UK were later demonstrated to be from different versions of the same instability processes that plagued earlier machines. Cockcroft was forced to retract the fusion claims, and the entire field was tainted for years. ZETA ended its experiments in 1968.
The first controlled fusion experiment was accomplished using Scylla I at the Los Alamos National Laboratory in 1958. This was a pinch machine, with a cylinder full of deuterium. Electric current shot down the sides of the cylinder. The current made magnetic fields that compressed the plasma to 15 million degrees Celsius, squeezed the gas, fused it and produced neutrons.[16][17]
In 1950–1951 I.E. Tamm and A.D. Sakharov in the Soviet Union, first discussed a tokamak-like approach. Experimental research on those designs began in 1956 at the Kurchatov Institute in Moscow by a group of Soviet scientists led by Lev Artsimovich. The tokamak essentially combined a low-power pinch device with a low-power simple stellarator. The key was to combine the fields in such a way that the particles orbited within the reactor a particular number of times, today known as the "safety factor". The combination of these fields dramatically improved confinement times and densities, resulting in huge improvements over existing devices.
Laser fusion was suggested in 1962 by scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, shortly after the invention of the laser itself in 1960. At the time, Lasers were low power machines, but low-level research began as early as 1965. Laser fusion, formally known as inertial confinement fusion, involves imploding a target by using laser beams. There are two ways to do this: indirect drive and direct drive. In direct drive, the laser blasts a pellet of fuel. In indirect drive, the lasers blast a structure around the fuel. This makes x-rays that squeeze the fuel. Both methods compress the fuel so that fusion can take place.
At the 1964 World's Fair, the public was given its first demonstration of nuclear fusion.[29] The device was a θ-pinch from General Electric. This was similar to the Scylla machine developed earlier at Los Alamos.
The magnetic mirror was first published in 1967 by Richard F. Post and many others at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory.[11] The mirror consisted of two large magnets arranged so they had strong fields within them, and a weaker, but connected, field between them. Plasma introduced in the area between the two magnets would "bounce back" from the stronger fields in the middle.
The A.D. Sakharov group constructed the first tokamaks, the most successful being the T-3 and its larger version T-4. T-4 was tested in 1968 in Novosibirsk, producing the world's first quasistationary fusion reaction.[30] When this were first announced, the international community was highly skeptical. A British team was invited to see T-3, however, and after measuring it in depth they released their results that confirmed the Soviet claims. A burst of activity followed as many planned devices were abandoned and new tokamaks were introduced in their place — the C model stellarator, then under construction after many redesigns, was quickly converted to the Symmetrical Tokamak.
In his work with vacuum tubes, Philo Farnsworth observed that electric charge would accumulate in regions of the tube. Today, this effect is known as the Multipactor effect.[31] Farnsworth reasoned that if ions were concentrated high enough they could collide and fuse. In 1962, he filed a patent on a design using a positive inner cage to concentrate plasma, in order to achieve nuclear fusion.[32] During this time, Robert L. Hirsch joined the Farnsworth Television labs and began work on what became the fusor. Hirsch patented the design in 1966[33] and published the design in 1967.[34]
In 1972, John Nuckolls outlined the idea of ignition.[14] This is a fusion chain reaction. Hot helium made during fusion reheats the fuel and starts more reactions. John argued that ignition would require lasers of about 1 kJ. This turned out to be wrong. Nuckolls's paper started a major development effort. Several laser systems were built at LLNL. These included the argus, the Cyclops, the Janus, the long path, the Shiva laser and the Nova in 1984. This prompted the UK to build the Central Laser Facility in 1976.[35]
During this time, great strides in understanding the tokamak system were made. A number of improvements to the design are now part of the "advanced tokamak" concept, which includes non-circular plasma, internal diverters and limiters, often superconducting magnets, and operate in the so-called "H-mode" island of increased stability. Two other designs have also become fairly well studied; the compact tokamak is wired with the magnets on the inside of the vacuum chamber, while the spherical tokamak reduces its cross section as much as possible.
In the mid-1970s, Project PACER, carried out at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) explored the possibility of a fusion power system that would involve exploding small hydrogen bombs (fusion bombs) inside an underground cavity.[36] As an energy source, the system is the only fusion power system that could be demonstrated to work using existing technology. It would also require a large, continuous supply of nuclear bombs, however, making the economics of such a system rather questionable.
In 1974 a study of the ZETA results demonstrated an interesting side-effect; after an experimental run ended, the plasma would enter a short period of stability. This led to the reversed field pinch concept, which has seen some level of development since.

As a result of advocacy, the cold war, and the 1970s energy crisis a massive magnetic mirror program was funded by the US federal government in the late 70's and early 80's. This program resulted in a series of large magnetic mirror devices including: 2X,[37] Baseball I, Baseball II, the Tandem Mirror Experiment, the Tandem mirror experiment upgrade, the Mirror Fusion Test Facility and the MFTF-B. These machines were built and tested at Livermore from the late 60's to the mid 80's.[38][39] A number of institutions collaborated on these machines, conducting experiments. These included the Institute for Advanced Study and the University of Wisconsin–Madison. The last machine, the Mirror Fusion Test Facility cost 372 million dollars and was, at that time, the most expensive project in Livermore history.[40] It opened on February 21, 1986 and was promptly shut down. The reason given was to balance the United States federal budget. This program was supported from within the Carter and early Reagan administrations by Edwin E. Kintner, a US Navy captain, under Alvin Trivelpiece.[41]
In Laser fusion, efforts focused on either fast delivery or beam smoothness. Both tried to deliver the energy uniformly to implode the target. One early problem was that the light in the infrared wavelength, lost lots of energy before hitting the fuel. Breakthroughs were also made at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics at the University of Rochester. Rochester scientists used frequency-tripling crystals to transform the infrared laser beams into ultraviolet beams. In 1985, Donna Strickland[42] and Gérard Mourou invented a method to amplify lasers pulses by "chirping". This method changes a single wavelength into a full spectrum. The system then amplifies the laser at each wavelength and then reconstitutes the beam into one color. Chirp pulsed amplification became instrumental in building the National Ignition Facility and the Omega EP system. Most research into ICF was towards weapons research, because the implosion is relevant to nuclear weapons.
During this time Los Alamos National Laboratory constructed a series of laser facilities.[43] This included Gemini (a two beam system), Helios (eight beams), Antares (24 beams) and Aurora (96 beams).[44][45] The program ended in the early nineties with a cost on the order of one billion dollars.[43]
In 1989, Pons and Fleischmann submitted papers to the Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry claiming that they had observed fusion in a room temperature device and disclosing their work in a press release.[46] Some scientists reported excess heat, neutrons, tritium, helium and other nuclear effects in so-called cold fusion systems, which for a time gained interest as showing promise. Hopes fell when replication failures were weighed in view of several reasons cold fusion is not likely to occur, the discovery of possible sources of experimental error, and finally the discovery that Fleischmann and Pons had not actually detected nuclear reaction byproducts.[47] By late 1989, most scientists considered cold fusion claims dead,[48] and cold fusion subsequently gained a reputation as pathological science.[49] However, a small community of researchers continues to investigate cold fusion[48][50][51][52] claiming to replicate Fleishmann and Pons' results including nuclear reaction byproducts.[53][54] Claims related to cold fusion are largely disbelieved in the mainstream scientific community.[55] In 1989, the majority of a review panel organized by the US Department of Energy (DOE) found that the evidence for the discovery of a new nuclear process was not persuasive. A second DOE review, convened in 2004 to look at new research, reached conclusions similar to the first.[56]
In 1991 the Preliminary Tritium Experiment at the Joint European Torus in England achieved the world’s first controlled release of fusion power.[57]
In 1992, a major article was published in physics today by Robert McCory at the Laboratory for laser energetics outlying the current state of ICF and advocating for a national ignition facility.[58] This was followed up by a major review article, from John Lindl in 1995,[59] advocating for NIF. During this time a number of ICF subsystems were developing, including target manufacturing, cryogenic handling systems, new laser designs (notably the NIKE laser at NRL) and improved diagnostics like time of flight analyzers and Thomson scattering. This work was done at the NOVA laser system, General Atomics, Laser Mégajoule and the GEKKO XII system in Japan. Through this work and lobbying by groups like the fusion power associates and John Sethian at NRL, a vote was made in congress, authorizing funding for the NIF project in the late nineties.
In the early nineties, theory and experimental work regarding fusors and polywells was published.[60][61] In response, Todd Rider at MIT developed general models of these devices.[62] Rider argued that all plasma systems at thermodynamic equilibrium were fundamentally limited. In 1995, William Nevins published a criticism [63] arguing that the particles inside fusors and polywells would build up angular momentum, causing the dense core to degrade.
In 1995, the University of Wisconsin–Madison built a large fusor, known as HOMER, which is still in operation.[64] Meanwhile, Dr George H. Miley at Illinois, built a small fusor that has produced neutrons using deuterium gas [65] and discovered the "star mode" of fusor operation.[66] The following year, the first "US-Japan Workshop on IEC Fusion", was conducted. At this time in Europe, an IEC device was developed as a commercial neutron source by Daimler-Chrysler and NSD Fusion.[67][68]
In 1996, the Z-machine was upgraded and opened to the public by the US Army in August 1998 in Scientific American.[69][70] The key attributes of Sandia’s Z machine[71] are its 18 million amperes and a discharge time of less than 100 nanoseconds. This generates a magnetic pulse, inside a large oil tank, this strikes an array of tungsten wires called a liner.[72] Firing the Z-machine has become a way to test very high energy, high temperature (2 billion degrees) conditions.[73]
In 1997, JET produced a peak of 16.1MW of fusion power (65% of input power), with fusion power of over 10MW sustained for over 0.5 sec. Its successor, the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), was officially announced as part of a seven-party consortium (six countries and the EU).[74] ITER is designed to produce ten times more fusion power than the power put into the plasma. ITER is currently under construction in Cadarache, France.
In the March 8, 2002 issue of the peer-reviewed journal Science, Rusi P. Taleyarkhan and colleagues at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) reported that acoustic cavitation experiments conducted with deuterated acetone (C3D6O) showed measurements of tritium and neutron output consistent with the occurrence of fusion.[80] Taleyarkhan was later found guilty of misconduct,[81] the Office of Naval Research debarred him for 28 months from receiving Federal Funding,[82][83] and his name was listed in the 'Excluded Parties List'.[82]
"Fast ignition" was developed in the late nineties, and was part of a push by the Laboratory for Laser Energetics for building the Omega EP system. This system was finished in 2008. Fast ignition showed such dramatic power savings that ICF appears to be a useful technique for energy production. There are even proposals to build an experimental facility dedicated to the fast ignition approach, known as HiPER.
In April 2005, a team from UCLA announced[84] it had devised a way of producing fusion using a machine that "fits on a lab bench", using lithium tantalate to generate enough voltage to smash deuterium atoms together. The process, however, does not generate net power (see Pyroelectric fusion). Such a device would be useful in the same sort of roles as the fusor.
In the early 2000s, Researchers at LANL reasoned that a plasma oscillating could be at local thermodynamic equilibrium. This prompted the POPS and Penning trap designs.[85][86] At this time, researchers at MIT became interested in fusors for space propulsion[87] and powering space vehicles.[88] Specifically, researchers developed fusors with multiple inner cages. Greg Piefer graduated from Madison and founded Phoenix Nuclear Labs, a company that developed the fusor into a neutron source for the mass production of medical isotopes.[89] Robert Bussard began speaking openly about the Polywell in 2006.[90] He attempted to generate interest [91] in the research, before his death.
In 2009, a high-energy laser system, the National Ignition Facility (NIF), was created in the US, which can heat hydrogen atoms to temperatures only existing in nature in the cores of stars. The new laser is expected to have the ability to produce, for the first time, more energy from controlled, inertially confined nuclear fusion than was required to initiate the reaction.[92]
In 2010, NIF researchers were conducting a series of "tuning" shots to determine the optimal target design and laser parameters for high-energy ignition experiments with fusion fuel in the following months.[93] Two firing tests were performed on 31 October 2010 and 2 November 2010. In early 2012, NIF director Mike Dunne expected the laser system to generate fusion with net energy gain by the end of 2012.[94] Nonetheless, it was not achieved by that date due to delays.
Inertial (laser) confinement is being developed at the United States National Ignition Facility (NIF) based at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California, the French Laser Mégajoule, and the planned European Union High Power laser Energy Research (HiPER) facility. NIF reached initial operational status in 2010 and has been in the process of increasing the power and energy of its "shots", with fusion ignition tests to follow.[95] A three year goal announced in 2009 to produce net energy from fusion by 2012 was missed; in September 2013, however, the facility announced a significant milestone from an August 2013 test that produced more energy from the fusion reaction than had been provided to the fuel pellet. This was reported as the first time this had been accomplished in fusion power research. The facility reported that their next step involved improving the system to prevent the hohlraum breaking up asymmetrically or too soon.[96][97][98]
A 2012 paper demonstrated that a dense plasma focus had achieved temperatures of 1.8 billion degrees C, sufficient for boron fusion, and that fusion reactions were occurring primarily within the contained plasmoid, a necessary condition for net power.[99] The focus consists of two coaxial cylindrical electrodes made from copper or beryllium and housed in a vacuum chamber containing a low-pressure fusible gas. An electrical pulse is applied across the electrodes, heating the gas into a plasma. The current forms into a minuscule vortex along the axis of the machine, which then kinks into a cage of current with an associated magnetic field. The cage of current and magnetic field entrapped plasma is called a plasmoid. The acceleration of the electrons about the magnetic field lines heats the nuclei within the plasmoid to fusion temperatures.
In September 2013 the NIF was widely acclaimed to have achieved a milestone in controlled fusion, by successfully initiating a reaction that resulted in the release of more energy than the fuel absorbed — even if only for a fraction of a second.[100] However, it was still far short of creating a self-sustaining reaction.[101] The process will need to be made more efficient to yield commercially viable amounts of energy.[102]
In 2014, Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works announced the development of a high beta fusion reactor they expect to yield a functioning 100 megawatt prototype by 2017 and to be ready for regular operation by 2022.[103][104][105] Deep space exploration as well as higher-velocity lower-cost space transport services in general would be enabled by this compact fusion reactor technology.[106]
In April 2014, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory ended the Laser Inertial Fusion Energy (LIFE) program and redirected their efforts towards NIF.[107] In August 2014, Phoenix Nuclear Labs announced the sale of a high yield neutron generator. Costing on the order of a millions, this device could sustain 5E+11 deuterium fusion reactions per second over a 24 hour period.[108]
In January 2015, the polywell was presented at Microsoft Research.[109]
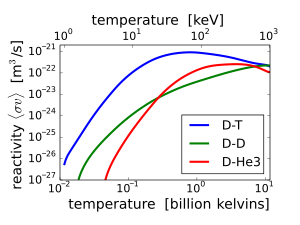
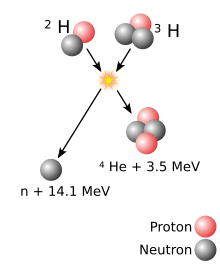
The easiest nuclear reaction, at the lowest energy, is:
Several drawbacks are commonly attributed to D-T fusion power:
In a production setting, the neutrons would be used to react with lithium in order to create more tritium. This also deposits the energy of the neutrons in the lithium, which would then be transferred to drive electrical production. The lithium neutron absorption reaction protects the outer portions of the reactor from the neutron flux. Newer designs, the advanced tokamak in particular, also use lithium inside the reactor core as a key element of the design. The plasma interacts directly with the lithium, preventing a problem known as "recycling". The advantage of this design was demonstrated in the Lithium Tokamak Experiment.
Assuming complete tritium burn-up, the reduction in the fraction of fusion energy carried by neutrons would be only about 18%, so that the primary advantage of the D-D fuel cycle is that tritium breeding would not be required. Other advantages are independence from scarce lithium resources and a somewhat softer neutron spectrum. The disadvantage of D-D compared to D-T is that the energy confinement time (at a given pressure) must be 30 times longer and the power produced (at a given pressure and volume) would be 68 times less[citation needed] .
Assuming complete removal of tritium and recycling of 3He, only 6% of the fusion energy is carried by neutrons. The tritium-suppressed D-D fusion requires an energy confinement that is 10 times longer compared to D-T and a plasma temperature that is twice as high.[116]
Since the confinement properties of conventional approaches to fusion such as the tokamak and laser pellet fusion are marginal, most proposals for aneutronic fusion are based on radically different confinement concepts, such as the Polywell and the Dense Plasma Focus. Results have been extremely promising:
Radiofrequency Heating A radio wave is applied to the plasma, causing it to oscillate.
Electrostatic Heating An electric field can do work on charged ions or electrons, heating them.
Neutral Beam Injection Gas is heated and injected into the fusion device. It may be heated using an electric field and then neutralized. After injection, it collides with particles the imparting energy.
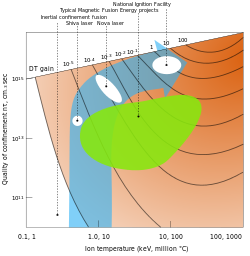
Inertial confinement produces plasmas with very high densities and temperatures making it suitable for weapons research, X-ray generation and perhaps in the distant future, spaceflight .[citation needed] ICF implosions require fuel pellets with close to a perfect shape in order to generate an symmetrical inward shock wave and to produce the high-density plasma. These are known as targets and, building them has presented its own technical challenges.
A recent development in ICF research is fast ignition. This is the use of two laser systems to heat a compressed targets. A conventional laser system compresses the pellet, after which a second ultrashort laser pulse heats the compressed plasma. This burst has many petawatts of power. Fast ignition implodes the pellet at exactly the moment of greatest density. Research into fast ignition has been carried out at the OMEGA EP petawatt and OMEGA lasers at the University of Rochester and at the GEKKO XII laser at the institute for laser engineering in Osaka Japan. If fruitful, it may have the effect of greatly reducing the cost of a laser fusion based power source.[citation needed]
The first is to use the magnetic mirror effect. If a particle follows the field line and enters a region of higher field strength, the particles can be reflected. There are several devices that try to use this effect. The most famous was the magnetic mirror machines, which was a series of large, expensive devices built at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory from the 1960s to mid 1980s.[124] Some other examples include the magnetic bottles and Biconic cusp.[125] Because the mirror machines were straight, they had some advantages over a ring shape. First, mirrors would easier to construct and maintain and second direct conversion energy capture, was easier to implement.[8] As the confinement achieved in experiments was poor, this approach has been essentially abandoned.[citation needed]
The second possibility to prevent end losses is to bend the field lines back on themselves, either in circles or more commonly in nested toroidal surfaces. The most highly developed system of this type is the tokamak, with the stellarator being next most advanced, followed by the Reversed field pinch. Compact toroids, especially the Field-Reversed Configuration and the spheromak, attempt to combine the advantages of toroidal magnetic surfaces with those of a simply connected (non-toroidal) machine, resulting in a mechanically simpler and smaller confinement area. Compact toroids still have some enthusiastic supporters but are not backed as readily by the majority of the fusion community.[citation needed]
If graphite is used, the gross erosion rates due to physical and chemical sputtering would be many meters per year, so one must rely on redeposition of the sputtered material. The location of the redeposition will not exactly coincide with the location of the sputtering, so one is still left with erosion rates that may be prohibitive. An even larger problem is the tritium co-deposited with the redeposited graphite. The tritium inventory in graphite layers and dust in a reactor could quickly build up to many kilograms, representing a waste of resources and a serious radiological hazard in case of an accident. The consensus of the fusion community seems to be that graphite, although a very attractive material for fusion experiments, cannot be the primary PFC material in a commercial reactor.
The sputtering rate of tungsten by the plasma fuel ions is orders of magnitude smaller than that of carbon, and tritium is much less incorporated into redeposited tungsten, making this a more attractive choice. On the other hand, tungsten impurities in a plasma are much more damaging than carbon impurities, and self-sputtering of tungsten can be high, so it will be necessary to ensure that the plasma in contact with the tungsten is not too hot (a few tens of eV rather than hundreds of eV). Tungsten also has disadvantages in terms of eddy currents and melting in off-normal events, as well as some radiological issues.
Neutron blankets Deuterium and tritium fusion generates neutrons. This varies by technique (NIF has a record of 3E14 neutrons per second[131] while a typical fusor produces 1E5 - 1E9 neutrons per second). It has been proposed to use these neutrons as a way to regenerate spent fission fuel [132] or as a way to breed tritium from a liquid lithium blanket.
Direct conversion This is a method where the kinetic energy of a particle is converted into voltage.[133] It was first suggested by Richard F. Post in conjunction with magnetic mirrors, in the late sixties. It has also been suggested for Field-Reversed Configurations. The process takes the plasma, expands it, and converts a large fraction of the random energy of the fusion products into directed motion. The particles are then collected on electrodes at various large electrical potentials. This method has demonstrated an experimental efficiency of 48 percent.[134]
Langmuir probe This is a metal object placed in a plasma. A potential is applied to it, giving it a positive or negative voltage against the surrounding plasma. The metal collects charged particles, drawing a current. As the voltage changes, the current changes. This makes a IV Curve. The IV-curve can be used to determine the local plasma density, potential and temperature.[137]
Geiger counter Deuterium or tritium fusion produces neutrons. Geiger counters record the rate of neutron production, so they are an essential tool for demonstrating success.
Therefore fusion reactors are considered extremely safe in this sense, making them favorable over fission reactors, which, in contrast, continue to generate heat through beta-decay for several months after reactor shut-down, meaning that melting of fuel rods is possible even after the reactor has been stopped due to continued accumulation of heat.[139]
There is also no risk of a runaway reaction in a fusion reactor. The plasma is burnt at optimal conditions, and any significant change will render it unable to react or to produce excess heat. In fusion reactors the reaction process is so delicate that this level of safety is inherent; no elaborate failsafe mechanism is required. Although the plasma in a fusion power plant will have a volume of 1000 cubic meters or more, the density of the plasma is extremely low, and the total amount of fusion fuel in the vessel is very small, typically a few grams.[139] If the fuel supply is closed, the reaction stops within seconds. In comparison, a fission reactor is typically loaded with enough fuel for several years, and no additional fuel is necessary to keep the reaction going.[140]
In the magnetic approach, strong fields are developed in coils that are held in place mechanically by the reactor structure. Failure of this structure could release this tension and allow the magnet to "explode" outward. The severity of this event would be similar to any other industrial accident or an MRI machine quench/explosion, and could be effectively stopped with a containment building similar to those used in existing (fission) nuclear generators. The laser-driven inertial approach is generally lower-stress. Although failure of the reaction chamber is possible, simply stopping fuel delivery would prevent any sort of catastrophic failure.
Most reactor designs rely on the use of liquid lithium as both a coolant and a method for converting stray neutrons from the reaction into tritium, which is fed back into the reactor as fuel. Lithium is highly flammable, and in the case of a fire it is possible that the lithium stored on-site could be burned up and escape. In this case, the tritium contents of the lithium would be released into the atmosphere, posing a radiation risk. Calculations suggest that at about 1 kg the total amount of tritium and other radioactive gases in a typical power plant would be so small that they would have diluted to legally acceptable limits by the time they blew as far as the plant's perimeter fence.[141]
The likelihood of small industrial accidents including the local release of radioactivity and injury to staff cannot be estimated yet. These would include accidental releases of lithium, tritium, or mis-handling of decommissioned radioactive components of the reactor itself.
Although tritium is volatile and biologically active the health risk posed by a release is much lower than that of most radioactive contaminants, due to tritium's short half-life (12.32 years), very low decay energy (~14.95 keV), and the fact that it does not bioaccumulate (instead being cycled out of the body as water, with a biological half-life of 7 to 14 days).[142] Current ITER designs are investigating total containment facilities for any tritium.
The half-life of the radioisotopes produced by fusion tends to be less than those from fission, so that the inventory decreases more rapidly. Unlike fission reactors, whose waste remains radioactive for thousands of years, most of the radioactive material in a fusion reactor would be the reactor core itself, which would be dangerous for about 50 years, and low-level waste another 100. Although this waste will be considerably more radioactive during those 50 years than fission waste, the very short half-life makes the process very attractive, as the waste management is fairly straightforward. By 500 years the material would have the same radiotoxidity as coal ash.[141]
Additionally, the choice of materials used in a fusion reactor is less constrained than in a fission design, where many materials are required for their specific neutron cross-sections. This allows a fusion reactor to be designed using materials that are selected specifically to be "low activation", materials that do not easily become radioactive. Vanadium, for example, would become much less radioactive than stainless steel. Carbon fiber materials are also low-activation, as well as being strong and light, and are a promising area of study for laser-inertial reactors where a magnetic field is not required.
In general terms, fusion reactors would create far less radioactive material than a fission reactor, the material it would create is less damaging biologically, and the radioactivity "burns off" within a time period that is well within existing engineering capabilities for safe long-term waste storage.
A study conducted 2011 assessed the risk of three scenarios:[143]
Fusion power commonly proposes the use of deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen, as fuel and in many current designs also use lithium. Assuming a fusion energy output equal to the 1995 global power output of about 100 EJ/yr (= 1 × 1020 J/yr) and that this does not increase in the future, which is unlikely, then the known current lithium reserves would last 3000 years. Lithium from sea water would last 60 million years, however, and a more complicated fusion process using only deuterium from sea water would have fuel for 150 billion years.[145] To put this in context, 150 billion years is close to 30 times the remaining lifespan of the sun,[146] and more than 10 times the estimated age of the universe.
It is estimated that up to the point of possible implementation of electricity generation by nuclear fusion, R&D will need further promotion totalling around €60–80 billion over a period of 50 years or so (of which €20–30 billion within the EU) based on a report from 2002.[147] Nuclear fusion research receives €750 million (excluding ITER funding) from the European Union, compared with €810 million for sustainable energy research,[148] putting research into fusion power well ahead of that of any single rivaling technology. Indeed, the size of the investments and time frame of the expected results mean that fusion research is almost exclusively publicly funded, while research in other forms of energy can be done by the private sector.
Despite being technically non-renewable, fusion power has many of the benefits of renewable energy sources (such as being a long-term energy supply and emitting no greenhouse gases) as well as some of the benefits of the resource-limited energy sources as hydrocarbons and nuclear fission (without reprocessing). Like these currently dominant energy sources, fusion could provide very high power-generation density and uninterrupted power delivery (due to the fact that it is not dependent on the weather, unlike wind and solar power).
Another aspect of fusion energy is that the cost of production does not suffer from diseconomies of scale. The cost of water and wind energy, for example, goes up as the optimal locations are developed first, while further generators must be sited in less ideal conditions. With fusion energy the production cost will not increase much even if large numbers of plants are built, because the raw resource (seawater) is abundant and widespread.
Some problems that are expected to be an issue in this century, such as fresh water shortages, can alternatively be regarded as problems of energy supply. For example, in desalination plants, seawater can be purified through distillation or reverse osmosis. Nonetheless, these processes are energy intensive. Even if the first fusion plants are not competitive with alternative sources, fusion could still become competitive if large-scale desalination requires more power than the alternatives are able to provide.
A scenario has been presented of the effect of the commercialization of fusion power on the future of human civilization.[153] ITER and later Demo are envisioned to bring online the first commercial nuclear fusion energy reactor by 2050. Using this as the starting point and the history of the uptake of nuclear fission reactors as a guide, the scenario depicts a rapid take up of nuclear fusion energy starting after the middle of this century.
Fusion power could be used in interstellar space, where solar energy is not available.
In most large scale commercial proposals, heat from the fusion reaction is used to operate a steam turbine that drives electrical generators, as in existing fossil fuel and nuclear fission power stations. Smaller scale reactors often propose to use much simpler thermocouples - with no moving parts or hot liquids - to generate electricity from heat at a lower electrical efficiency, but with more safety and smaller size. Smaller fission reactors such as those on nuclear submarines have proven this approach, and research into materials suitable for fusion date back to at least 1981 [8]. Because of the variety of fusion reactions, the potential use of solid boron or liquid lithium fuel, a non-radioactive supply and minimally radioactive waste chain, smaller reactors may be deployed outside the military without these concerns, which have inhibited small uranium reactors.
There are two primary problems to be overcome in fusion power research: sustained confinement and choice of container materials. Confinement means confining the fusion reaction so it continues using its own energy. Fusion reactions are extremely delicate and will stop almost immediately if not very precisely maintained - this makes them safer in many important ways compared to existing fission reactors. They must also avoid losing energy in order to be sustainable. Leading designs for controlled fusion research use magnetic (tokamak design) or inertial (laser) confinement of a plasma. Both approaches are still under development and are years away from commercial operation. A few other models such as purely inertial confinement using centrifugal force are being explored for heavier fusion fuel such as liquid lithium, but these are not thought suitable for large scale power plants.
Materials research refers to researching suitable materials for construction purposes, which will not become brittle or excessively damaged by exposure to fast neutrons during fusion processes. If neutrons convey the energy released, then whatever medium absorbs the neutron scattering eventually becomes mildly radioactive and must also be disposed of, e.g. ordinary water becomes heavy water. In a fusion supply chain heavy water is actually useful again as a fuel, making a breeder reactor style of design more practical. However the overall complexity of this design has proven problematic in fission reactors such as the CANDU and may be uneconomic. It may be possible to retrofit turbines of existing fission reactors for thorium fission and for fusion-based neutron scatter. However, aneutronic fusion and minimal neutron energy reactions such as proton-boron have received more research attention in the 2010s, largely for their potential to create small clean portable energy sources without neutron pollution.
Background

Mechanism
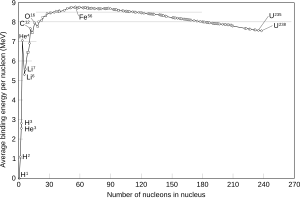
Fusion happens when two (or more) nuclei come close enough for the strong nuclear force to exceed the electrostatic force and pull them together. This process takes light nuclei and forms a heavier one, through a nuclear reaction. For nuclei lighter than iron-56 this is exothermic and releases energy. For nuclei heavier than iron-56 this is endothermic and requires an external source of energy.[1] Hence, nuclei smaller than iron-56 are more likely to fuse while those heavier than iron-56 are more likely to break apart.To fuse, nuclei must overcome the repulsive Coulomb force. This is a force caused by the nuclei containing positively charged protons that repel via the electromagnetic force. To overcome this "Coulomb barrier", the atoms must have a high kinetic energy. There are several ways of doing this, including heating or acceleration. Once an atom is heated above its ionization energy, its electrons are stripped away, leaving just the bare nucleus: the ion. Most fusion experiments use a hot cloud of ions and electrons. This cloud is known as a plasma. Most fusion reactions produce neutrons, which can be detected and degrade materials.
Theoretically, any atom could be fused, if enough pressure and temperature was applied.[2] Mankind has studied many high energy fusion reactions, using particles beams.[3] These are fired at a target. For a power plant, however, we are currently limited to only the light elements. Hydrogen is ideal: because of its small charge, it is the easiest atom to fuse. This reaction produces helium.
Cross section
A reaction's cross section, (denoted σ) is the measure of how likely a fusion reaction will happen. It is a probability, and it depends on the velocity of the two nuclei when they strike one another. If the atoms move faster, fusion is more likely. If the atoms hit head on, fusion is more likely. Cross sections for many different fusion reactions were measured mainly in the 1970s using particle beams.[3] A beam of species A was fired at species B at different speeds, and the amount of neutrons coming off was measured. Neutrons are a key product of fusion reactions. These nuclei are flying around in a hot cloud, with some distribution of velocities. If the plasma is thermalized, then the distribution looks like a bell curve, or maxwellian distribution. In this case, it is useful to take the average cross section over the velocity distribution. This is entered into the volumetric fusion rate:[4]
Pfusion=nAnB⟨σvA,B⟩Efusion
Pfusion is the energy made by fusion, per time and volume- n is the number density of species A or B, the particles in the volume
⟨σvA,B⟩ is the cross section of that reaction, average over all the velocities of the two species vEfusion is the energy released by that fusion reaction.
Lawson criterion
This equation shows that energy varies with the temperature, density, speed of collision, and fuel used. To reach net power, fusion reactions have to occur fast enough to make up for energy losses. Any power plant using fusion will hold in this hot cloud. Plasma clouds lose energy through conduction and radiation.[4] Conduction is when ions, electrons or neutrals hit a surface and transfer a portion of their kinetic energy to the atoms of the surface. Radiation is when energy leaves the cloud as light. Radiation increases as the temperature rises. To get net power from fusion, you must overcome these losses. This leads to an equation for power output.Pout=ηcapture(Pfusion−Pconduction−Pradiation)
- η, is the efficiency with which the plant captures energy
Density, temperature, time: ntτ
The Lawson criterion argues that a machine holding in a hot, thermalized and quasi-neutral plasma, has to meet basic criteria to overcome the radiation losses, conduction losses and a power plant efficiency of 30 percent.[4][5] This became known as the "triple product": the plasma density and temperature and how long it is held in.[6] For many years, work has been focused on reaching the highest triple product possible. This emphasis onEnergy capture
There are several proposals for energy capture. The simplest is using a heat cycle to heat a fluid with fusion reactions. It has been proposed to use the neutrons generated by fusion to re-generate a spent fission fuel.[7] In addition, direct energy conversion, has been developed (at LLNL in the 1980s) as a method to maintain a voltage using the products of a fusion reaction. This has demonstrated an energy capture efficiency of 48 percent.[8]Possible approaches
Magnetic confinement fusion
Tokamak The most well developed and well funded approach to fusion energy. As of January 2011 there were an estimated 177 tokamak experiments either planned, decommissioned or currently operating, worldwide.[9] This method races hot plasma around in a magnetically confined ring. When completed, ITER will be the world's largest Tokamak.Stellarator These are twisted rings of hot plasma. Stellarators are distinct from tokamak in that they are not azimuthally symmetric. Instead, they have a discrete rotational symmetry, often fivefold, like a regular pentagon. Stellarators were developed by Lyman Spitzer in 1950. There are four designs: Torsatron, Heliotron, Heliac and Helias.
Levitated Dipole Experiment (LDX) These use a solid superconducting torus. This is magnetically levitated inside the reactor chamber. The superconductor forms an axisymmetric magnetic field that contains the plasma. The LDX was developed between MIT and Columbia University after 2000 by Jay Kesner and Michael E. Mauel.[10]
Magnetic mirror Developed by Richard F. Post and teams at LLNL in the 1960s.[11] Magnetic mirrors reflected hot plasma back and forth in a line. Variations included the magnetic bottle and the biconic cusp.[12] A series of well-funded, large, mirror machines were built by the US government in the 1970s and 1980s.
Field-reversed configuration This device confines a plasma on closed magnetic field lines without a central penetration.[13]
Inertial confinement fusion
Direct drive In this technique, lasers directly blast a pellet of fuel. The goal is to start ignition, a fusion chain reaction. Ignition was first suggested by John Nuckolls, in 1972.[14] Notable direct drive experiments have been conducted at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics, Laser Mégajoule and the GEKKO XII facilities.Fast ignition This method uses two laser blasts. The first blast compresses the fusion fuel, while the second high energy pulse ignites it. Experiments have been conducted at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics using the Omega and Omega EP systems.
Indirect drive In this technique, lasers blasts a structure around the pellet of fuel. This structure is known as a Hohlraum. As it disintegrates the pellet is bathed in a more uniform x-ray light, creating better compression. The largest system using this method is the National Ignition Facility.
Magneto-inertial fusion This technique, combines laser pulses with the magnetic pinch to compress and confine an imploding plasma cloud.[15] The field traps heat within the core, which improves the fusion rates. A similar concept is the magnetized target fusion device, which uses a magnetic field in an external metal shell to achieve the same basic goals.
Magnetic pinches
Z-Pinch This method sends a strong current (in the z-direction) through the plasma. The current generates a magnetic field that squeezes the plasma to fusion conditions. Pinches were the first method for man-made controlled fusion.[16][17] Some examples include the Dense plasma focus and the Z machine at Sandia National Laboratories.Theta-Pinch This method sends a current inside a plasma, in the theta direction.
Inertial electrostatic confinement
Fusor This method uses an electric field to heat ions to fusion conditions. The machine typically uses two spherical cages, a cathode inside the anode, inside a vacuum. These machines are not considered a viable approach to net power due to their high conduction and radiation[18] losses. They are simple enough to build that amateurs have fused atoms using them.[19]Polywell This designs attempts to combine magnetic confinement with electrostatic fields, to avoid the conduction losses generated by the cage.[20] This research, however, is immature and under developed.
Other
Magnetized target fusionThis method confines hot plasma using a magnetic field and squeezes it using inertia. Examples include LANL FRX-L machine [21] and General Fusion device.Uncontrolled Fusion has been initiated by man, using uncontrolled fission explosions. Early proposals for fusion power included using bombs to initiate reactions.
Beam fusion A beam of high energy particles can be fired at another beam or target and fusion will occur. This was used in the 1970s and 80's to study the cross sections of high energy fusion reactions.[3]
Bubble fusion This was a supposed fusion reaction that was supposed to occur inside extraordinarily large collapsing gas bubbles, created during acoustic liquid cavitation.[22]
Cold fusion This is a hypothetical type of nuclear reaction that would occur at, or near, room temperature. Cold fusion has gained a reputation as Pathological science.[23][24]
Muon-catalyzed fusion Muons allow atoms to get much closer and thus reduce the kinetic energy required to initiate fusion. Muons require more energy to produce than can be obtained from muon-catalysed fusion, making this approach impractical for the generation of power[25]
History of research
1920s
Research into nuclear fusion started in the early part of the 20th century. In 1920 the British physicist Francis William Aston discovered that the total mass equivalent of four hydrogen atoms (two protons and two neutrons) are heavier than the total mass of one helium atom (He-4), which implied that net energy can be released by combining hydrogen atoms together to form helium, and provided the first hints of a mechanism by which stars could produce energy in the quantities being measured. Through the 1920s, Arthur Stanley Eddington became a major proponent of the proton–proton chain reaction (PP reaction) as the primary system running the Sun.1930s
A theory was verified by Hans Bethe in 1939 showing that beta decay and quantum tunneling in the Sun's core might convert one of the protons into a neutron and thereby producing deuterium rather than a diproton. The deuterium would then fuse through other reactions to further increase the energy output. For this work, Bethe won the Nobel Prize in Physics.1940s
In 1942, nuclear fusion research was subsumed into the Manhattan Project and the science became obscured by the secrecy surrounding the field. The first patent related to a fusion reactor was registered in 1946[26] by the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority, the inventors being Sir George Paget Thomson and Moses Blackman. This was the first detailed examination of the Z-pinch concept, and small efforts to experiment with it started at several sites in the UK.Pinch was first developed in the UK in the immediate post-war era. Starting in 1947 small experiments were carried out and plans were laid to build a much larger machine. Two teams were quickly formed and began a series of ever-larger experiments. When the Huemul results hit the news, James L. Tuck, a UK physicist working at Los Alamos, introduced the pinch concept in the US and produced a series of machines known as the Perhapsatron. In the Soviet Union, unbeknownst to the west, a series of similar machines were being built. All of these devices quickly demonstrated a series of instabilities when the pinch was applied, which broke up the plasma column long before it reached the densities and temperatures required for fusion. In 1953 Tuck and others suggested a number of solutions to these problems.
A major area of study in early fusion power research is the "pinch" concept. Pinch is based on the fact that plasmas are electrically conducting. By running a current through the plasma, a magnetic field will be generated around the plasma. This field will, according to Lenz's law, create an inward directed force that causes the plasma to collapse inward, raising its density. Denser plasmas generate denser magnetic fields, increasing the inward force, leading to a chain reaction. If the conditions are correct, this can lead to the densities and temperatures needed for fusion. The difficulty is getting the current into the plasma, which would normally melt any sort of mechanical electrode. A solution emerges again due to the conducting nature of the plasma; by placing the plasma in the middle of an electromagnet, induction can be used to generate the current.
1950s
The first successful man-made fusion device was the boosted fission weapon tested in 1951 in the Greenhouse Item test. This was followed by true fusion weapons in 1952's Ivy Mike, and the first practical examples in 1954's Castle Bravo. This was uncontrolled fusion. In these devices, the energy released by the fission explosion is used to compress and heat fusion fuel, starting a fusion reaction. Fusion releases neutrons. These neutrons hit the surrounding fission fuel, causing the atoms to split apart much faster than normal fission processes - almost instantly by comparison. This increases the effectiveness of bombs: normal fission weapons blow themselves apart before all their fuel is used; fusion/fission weapons do not have this practical upper limit.
In 1951, Lyman Spitzer began work on a stellarator under the code name Project Matterhorn. His work led to the creation of the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory. Spitzer planned an aggressive development project of four machines, A, B, C, and D. A and B were small research devices, C would be the prototype of a power-producing machine, and D would be the prototype of a commercial device. A worked without issue, but even by the time B was being used it was clear the stellarator was also suffering from instabilities and plasma leakage. Progress on C slowed as attempts were made to correct for these problems.
Around the same time, an expatriate German Ronald Richter proposed the Huemul Project in Argentina, announcing positive results in 1951. Although these results turned out to be false, it sparked off intense interest around the world. The UK pinch programs were greatly expanded, culminating in the ZETA and Sceptre devices. In the US, pinch experiments like those in the UK started at the Los Alamos National Laboratory. Similar devices were built in the USSR after data on the UK program was passed to them by Klaus Fuchs. At Princeton University a new approach developed as the stellarator, and the research establishment formed there continues to this day as the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory.
By the mid-1950s it was clear that the simple theoretical tools being used to calculate the performance of all fusion machines were simply not predicting their actual behavior. Machines invariably leaked their plasma from their confinement area at rates far higher than predicted.
In 1954, Edward Teller held a gathering of fusion researchers at the Princeton Gun Club, near the Project Matterhorn (now known as Project Sherwood) grounds. Teller started by pointing out the problems that everyone was having, and suggested that any system where the plasma was confined within concave fields was doomed to fail. Attendees remember him saying something to the effect that the fields were like rubber bands, and they would attempt to snap back to a straight configuration whenever the power was increased, ejecting the plasma. He went on to say that it appeared the only way to confine the plasma in a stable configuration would be to use convex fields, a "cusp" configuration.[27]
When the meeting concluded, most of the researchers quickly turned out papers saying why Teller's concerns did not apply to their particular device. The pinch machines did not use magnetic fields in this way at all, while the mirror and stellarator seemed to have various ways out. This was soon followed by a paper by Martin David Kruskal and Martin Schwarzschild discussing pinch machines, however, which demonstrated instabilities in those devices were inherent to the design.
The largest "classic" pinch device was the ZETA, including all of these suggested upgrades, starting operations in the UK in 1957. In early 1958, John Cockcroft announced that fusion had been achieved in the ZETA, an announcement that made headlines around the world. When physicists in the US expressed concerns about the claims they were initially dismissed. US experiments soon demonstrated the same neutrons, although temperature measurements suggested these could not be from fusion reactions. The neutrons seen in the UK were later demonstrated to be from different versions of the same instability processes that plagued earlier machines. Cockcroft was forced to retract the fusion claims, and the entire field was tainted for years. ZETA ended its experiments in 1968.
The first controlled fusion experiment was accomplished using Scylla I at the Los Alamos National Laboratory in 1958. This was a pinch machine, with a cylinder full of deuterium. Electric current shot down the sides of the cylinder. The current made magnetic fields that compressed the plasma to 15 million degrees Celsius, squeezed the gas, fused it and produced neutrons.[16][17]
In 1950–1951 I.E. Tamm and A.D. Sakharov in the Soviet Union, first discussed a tokamak-like approach. Experimental research on those designs began in 1956 at the Kurchatov Institute in Moscow by a group of Soviet scientists led by Lev Artsimovich. The tokamak essentially combined a low-power pinch device with a low-power simple stellarator. The key was to combine the fields in such a way that the particles orbited within the reactor a particular number of times, today known as the "safety factor". The combination of these fields dramatically improved confinement times and densities, resulting in huge improvements over existing devices.
1960s
A key plasma physics text was published by Lyman Spitzer at Princeton in 1963.[28] Spitzer took the ideal gas laws and adopted them to an ionized plasma, developing many of the fundamental equations used to model a plasma.Laser fusion was suggested in 1962 by scientists at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, shortly after the invention of the laser itself in 1960. At the time, Lasers were low power machines, but low-level research began as early as 1965. Laser fusion, formally known as inertial confinement fusion, involves imploding a target by using laser beams. There are two ways to do this: indirect drive and direct drive. In direct drive, the laser blasts a pellet of fuel. In indirect drive, the lasers blast a structure around the fuel. This makes x-rays that squeeze the fuel. Both methods compress the fuel so that fusion can take place.
At the 1964 World's Fair, the public was given its first demonstration of nuclear fusion.[29] The device was a θ-pinch from General Electric. This was similar to the Scylla machine developed earlier at Los Alamos.
The magnetic mirror was first published in 1967 by Richard F. Post and many others at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory.[11] The mirror consisted of two large magnets arranged so they had strong fields within them, and a weaker, but connected, field between them. Plasma introduced in the area between the two magnets would "bounce back" from the stronger fields in the middle.
The A.D. Sakharov group constructed the first tokamaks, the most successful being the T-3 and its larger version T-4. T-4 was tested in 1968 in Novosibirsk, producing the world's first quasistationary fusion reaction.[30] When this were first announced, the international community was highly skeptical. A British team was invited to see T-3, however, and after measuring it in depth they released their results that confirmed the Soviet claims. A burst of activity followed as many planned devices were abandoned and new tokamaks were introduced in their place — the C model stellarator, then under construction after many redesigns, was quickly converted to the Symmetrical Tokamak.
In his work with vacuum tubes, Philo Farnsworth observed that electric charge would accumulate in regions of the tube. Today, this effect is known as the Multipactor effect.[31] Farnsworth reasoned that if ions were concentrated high enough they could collide and fuse. In 1962, he filed a patent on a design using a positive inner cage to concentrate plasma, in order to achieve nuclear fusion.[32] During this time, Robert L. Hirsch joined the Farnsworth Television labs and began work on what became the fusor. Hirsch patented the design in 1966[33] and published the design in 1967.[34]
1970s
In 1972, John Nuckolls outlined the idea of ignition.[14] This is a fusion chain reaction. Hot helium made during fusion reheats the fuel and starts more reactions. John argued that ignition would require lasers of about 1 kJ. This turned out to be wrong. Nuckolls's paper started a major development effort. Several laser systems were built at LLNL. These included the argus, the Cyclops, the Janus, the long path, the Shiva laser and the Nova in 1984. This prompted the UK to build the Central Laser Facility in 1976.[35]
During this time, great strides in understanding the tokamak system were made. A number of improvements to the design are now part of the "advanced tokamak" concept, which includes non-circular plasma, internal diverters and limiters, often superconducting magnets, and operate in the so-called "H-mode" island of increased stability. Two other designs have also become fairly well studied; the compact tokamak is wired with the magnets on the inside of the vacuum chamber, while the spherical tokamak reduces its cross section as much as possible.
In the mid-1970s, Project PACER, carried out at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) explored the possibility of a fusion power system that would involve exploding small hydrogen bombs (fusion bombs) inside an underground cavity.[36] As an energy source, the system is the only fusion power system that could be demonstrated to work using existing technology. It would also require a large, continuous supply of nuclear bombs, however, making the economics of such a system rather questionable.
In 1974 a study of the ZETA results demonstrated an interesting side-effect; after an experimental run ended, the plasma would enter a short period of stability. This led to the reversed field pinch concept, which has seen some level of development since.
1980s

Inertial confinement fusion implosion on the Nova laser during the 80's was a key driver of fusion development.
As a result of advocacy, the cold war, and the 1970s energy crisis a massive magnetic mirror program was funded by the US federal government in the late 70's and early 80's. This program resulted in a series of large magnetic mirror devices including: 2X,[37] Baseball I, Baseball II, the Tandem Mirror Experiment, the Tandem mirror experiment upgrade, the Mirror Fusion Test Facility and the MFTF-B. These machines were built and tested at Livermore from the late 60's to the mid 80's.[38][39] A number of institutions collaborated on these machines, conducting experiments. These included the Institute for Advanced Study and the University of Wisconsin–Madison. The last machine, the Mirror Fusion Test Facility cost 372 million dollars and was, at that time, the most expensive project in Livermore history.[40] It opened on February 21, 1986 and was promptly shut down. The reason given was to balance the United States federal budget. This program was supported from within the Carter and early Reagan administrations by Edwin E. Kintner, a US Navy captain, under Alvin Trivelpiece.[41]
In Laser fusion, efforts focused on either fast delivery or beam smoothness. Both tried to deliver the energy uniformly to implode the target. One early problem was that the light in the infrared wavelength, lost lots of energy before hitting the fuel. Breakthroughs were also made at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics at the University of Rochester. Rochester scientists used frequency-tripling crystals to transform the infrared laser beams into ultraviolet beams. In 1985, Donna Strickland[42] and Gérard Mourou invented a method to amplify lasers pulses by "chirping". This method changes a single wavelength into a full spectrum. The system then amplifies the laser at each wavelength and then reconstitutes the beam into one color. Chirp pulsed amplification became instrumental in building the National Ignition Facility and the Omega EP system. Most research into ICF was towards weapons research, because the implosion is relevant to nuclear weapons.
During this time Los Alamos National Laboratory constructed a series of laser facilities.[43] This included Gemini (a two beam system), Helios (eight beams), Antares (24 beams) and Aurora (96 beams).[44][45] The program ended in the early nineties with a cost on the order of one billion dollars.[43]
In 1989, Pons and Fleischmann submitted papers to the Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry claiming that they had observed fusion in a room temperature device and disclosing their work in a press release.[46] Some scientists reported excess heat, neutrons, tritium, helium and other nuclear effects in so-called cold fusion systems, which for a time gained interest as showing promise. Hopes fell when replication failures were weighed in view of several reasons cold fusion is not likely to occur, the discovery of possible sources of experimental error, and finally the discovery that Fleischmann and Pons had not actually detected nuclear reaction byproducts.[47] By late 1989, most scientists considered cold fusion claims dead,[48] and cold fusion subsequently gained a reputation as pathological science.[49] However, a small community of researchers continues to investigate cold fusion[48][50][51][52] claiming to replicate Fleishmann and Pons' results including nuclear reaction byproducts.[53][54] Claims related to cold fusion are largely disbelieved in the mainstream scientific community.[55] In 1989, the majority of a review panel organized by the US Department of Energy (DOE) found that the evidence for the discovery of a new nuclear process was not persuasive. A second DOE review, convened in 2004 to look at new research, reached conclusions similar to the first.[56]
1990s
In 1991 the Preliminary Tritium Experiment at the Joint European Torus in England achieved the world’s first controlled release of fusion power.[57]
In 1992, a major article was published in physics today by Robert McCory at the Laboratory for laser energetics outlying the current state of ICF and advocating for a national ignition facility.[58] This was followed up by a major review article, from John Lindl in 1995,[59] advocating for NIF. During this time a number of ICF subsystems were developing, including target manufacturing, cryogenic handling systems, new laser designs (notably the NIKE laser at NRL) and improved diagnostics like time of flight analyzers and Thomson scattering. This work was done at the NOVA laser system, General Atomics, Laser Mégajoule and the GEKKO XII system in Japan. Through this work and lobbying by groups like the fusion power associates and John Sethian at NRL, a vote was made in congress, authorizing funding for the NIF project in the late nineties.
In the early nineties, theory and experimental work regarding fusors and polywells was published.[60][61] In response, Todd Rider at MIT developed general models of these devices.[62] Rider argued that all plasma systems at thermodynamic equilibrium were fundamentally limited. In 1995, William Nevins published a criticism [63] arguing that the particles inside fusors and polywells would build up angular momentum, causing the dense core to degrade.
In 1995, the University of Wisconsin–Madison built a large fusor, known as HOMER, which is still in operation.[64] Meanwhile, Dr George H. Miley at Illinois, built a small fusor that has produced neutrons using deuterium gas [65] and discovered the "star mode" of fusor operation.[66] The following year, the first "US-Japan Workshop on IEC Fusion", was conducted. At this time in Europe, an IEC device was developed as a commercial neutron source by Daimler-Chrysler and NSD Fusion.[67][68]
In 1996, the Z-machine was upgraded and opened to the public by the US Army in August 1998 in Scientific American.[69][70] The key attributes of Sandia’s Z machine[71] are its 18 million amperes and a discharge time of less than 100 nanoseconds. This generates a magnetic pulse, inside a large oil tank, this strikes an array of tungsten wires called a liner.[72] Firing the Z-machine has become a way to test very high energy, high temperature (2 billion degrees) conditions.[73]
In 1997, JET produced a peak of 16.1MW of fusion power (65% of input power), with fusion power of over 10MW sustained for over 0.5 sec. Its successor, the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), was officially announced as part of a seven-party consortium (six countries and the EU).[74] ITER is designed to produce ten times more fusion power than the power put into the plasma. ITER is currently under construction in Cadarache, France.
2000s
In the March 8, 2002 issue of the peer-reviewed journal Science, Rusi P. Taleyarkhan and colleagues at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) reported that acoustic cavitation experiments conducted with deuterated acetone (C3D6O) showed measurements of tritium and neutron output consistent with the occurrence of fusion.[80] Taleyarkhan was later found guilty of misconduct,[81] the Office of Naval Research debarred him for 28 months from receiving Federal Funding,[82][83] and his name was listed in the 'Excluded Parties List'.[82]
"Fast ignition" was developed in the late nineties, and was part of a push by the Laboratory for Laser Energetics for building the Omega EP system. This system was finished in 2008. Fast ignition showed such dramatic power savings that ICF appears to be a useful technique for energy production. There are even proposals to build an experimental facility dedicated to the fast ignition approach, known as HiPER.
In April 2005, a team from UCLA announced[84] it had devised a way of producing fusion using a machine that "fits on a lab bench", using lithium tantalate to generate enough voltage to smash deuterium atoms together. The process, however, does not generate net power (see Pyroelectric fusion). Such a device would be useful in the same sort of roles as the fusor.
In the early 2000s, Researchers at LANL reasoned that a plasma oscillating could be at local thermodynamic equilibrium. This prompted the POPS and Penning trap designs.[85][86] At this time, researchers at MIT became interested in fusors for space propulsion[87] and powering space vehicles.[88] Specifically, researchers developed fusors with multiple inner cages. Greg Piefer graduated from Madison and founded Phoenix Nuclear Labs, a company that developed the fusor into a neutron source for the mass production of medical isotopes.[89] Robert Bussard began speaking openly about the Polywell in 2006.[90] He attempted to generate interest [91] in the research, before his death.
In 2009, a high-energy laser system, the National Ignition Facility (NIF), was created in the US, which can heat hydrogen atoms to temperatures only existing in nature in the cores of stars. The new laser is expected to have the ability to produce, for the first time, more energy from controlled, inertially confined nuclear fusion than was required to initiate the reaction.[92]
2010s
In 2010, NIF researchers were conducting a series of "tuning" shots to determine the optimal target design and laser parameters for high-energy ignition experiments with fusion fuel in the following months.[93] Two firing tests were performed on 31 October 2010 and 2 November 2010. In early 2012, NIF director Mike Dunne expected the laser system to generate fusion with net energy gain by the end of 2012.[94] Nonetheless, it was not achieved by that date due to delays.
Inertial (laser) confinement is being developed at the United States National Ignition Facility (NIF) based at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California, the French Laser Mégajoule, and the planned European Union High Power laser Energy Research (HiPER) facility. NIF reached initial operational status in 2010 and has been in the process of increasing the power and energy of its "shots", with fusion ignition tests to follow.[95] A three year goal announced in 2009 to produce net energy from fusion by 2012 was missed; in September 2013, however, the facility announced a significant milestone from an August 2013 test that produced more energy from the fusion reaction than had been provided to the fuel pellet. This was reported as the first time this had been accomplished in fusion power research. The facility reported that their next step involved improving the system to prevent the hohlraum breaking up asymmetrically or too soon.[96][97][98]
A 2012 paper demonstrated that a dense plasma focus had achieved temperatures of 1.8 billion degrees C, sufficient for boron fusion, and that fusion reactions were occurring primarily within the contained plasmoid, a necessary condition for net power.[99] The focus consists of two coaxial cylindrical electrodes made from copper or beryllium and housed in a vacuum chamber containing a low-pressure fusible gas. An electrical pulse is applied across the electrodes, heating the gas into a plasma. The current forms into a minuscule vortex along the axis of the machine, which then kinks into a cage of current with an associated magnetic field. The cage of current and magnetic field entrapped plasma is called a plasmoid. The acceleration of the electrons about the magnetic field lines heats the nuclei within the plasmoid to fusion temperatures.
In September 2013 the NIF was widely acclaimed to have achieved a milestone in controlled fusion, by successfully initiating a reaction that resulted in the release of more energy than the fuel absorbed — even if only for a fraction of a second.[100] However, it was still far short of creating a self-sustaining reaction.[101] The process will need to be made more efficient to yield commercially viable amounts of energy.[102]
In 2014, Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works announced the development of a high beta fusion reactor they expect to yield a functioning 100 megawatt prototype by 2017 and to be ready for regular operation by 2022.[103][104][105] Deep space exploration as well as higher-velocity lower-cost space transport services in general would be enabled by this compact fusion reactor technology.[106]
In April 2014, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory ended the Laser Inertial Fusion Energy (LIFE) program and redirected their efforts towards NIF.[107] In August 2014, Phoenix Nuclear Labs announced the sale of a high yield neutron generator. Costing on the order of a millions, this device could sustain 5E+11 deuterium fusion reactions per second over a 24 hour period.[108]
In January 2015, the polywell was presented at Microsoft Research.[109]
Fuels
By firing particle beams at targets, many fusion reactions have been tested, while the fuels considered for power have all been light elements like the isotopes of hydrogen—deuterium and tritium.[3] Other reactions like the deuterium and Helium3 reaction or the Helium3 and Helium3 reactions, would require a supply of Helium3. This can either come from other nuclear reactions or from extraterrestrial sources. Finally, researchers hope to do the p-11B reaction, because it does not directly produce neutrons, though side reactions can.[110]Deuterium, tritium
The easiest nuclear reaction, at the lowest energy, is:
- 2
1D + 3
1T → 4
2He + 1
0n
- 1
0n + 6
3Li → 3
1T + 4
2He - 1
0n + 7
3Li → 3
1T + 4
2He + 1
0n
Several drawbacks are commonly attributed to D-T fusion power:
- It produces substantial amounts of neutrons that result in the neutron activation of the reactor materials.[111]
- Only about 20% of the fusion energy yield appears in the form of charged particles with the remainder carried off by neutrons, which limits the extent to which direct energy conversion techniques might be applied.[112]
- It requires the handling of the radioisotope tritium. Similar to hydrogen, tritium is difficult to contain and may leak from reactors in some quantity. Some estimates suggest that this would represent a fairly large environmental release of radioactivity.[113]
In a production setting, the neutrons would be used to react with lithium in order to create more tritium. This also deposits the energy of the neutrons in the lithium, which would then be transferred to drive electrical production. The lithium neutron absorption reaction protects the outer portions of the reactor from the neutron flux. Newer designs, the advanced tokamak in particular, also use lithium inside the reactor core as a key element of the design. The plasma interacts directly with the lithium, preventing a problem known as "recycling". The advantage of this design was demonstrated in the Lithium Tokamak Experiment.
Deuterium, deuterium
This fuel is commonly used by amateurs who fuse. This is second easiest fusion reaction, fusing of deuterium with itself. This reaction has two branches that occur with nearly equal probability:D + D → T + 1H D + D → 3He + n
Assuming complete tritium burn-up, the reduction in the fraction of fusion energy carried by neutrons would be only about 18%, so that the primary advantage of the D-D fuel cycle is that tritium breeding would not be required. Other advantages are independence from scarce lithium resources and a somewhat softer neutron spectrum. The disadvantage of D-D compared to D-T is that the energy confinement time (at a given pressure) must be 30 times longer and the power produced (at a given pressure and volume) would be 68 times less[citation needed] .
Assuming complete removal of tritium and recycling of 3He, only 6% of the fusion energy is carried by neutrons. The tritium-suppressed D-D fusion requires an energy confinement that is 10 times longer compared to D-T and a plasma temperature that is twice as high.[116]
Deuterium, helium 3
A second-generation approach to controlled fusion power involves combining helium-3 (3He) and deuterium (2H):D + 3He → 4He + 1H
Proton, boron 11
If aneutronic fusion is the goal, then the most promising candidate may be the Hydrogen-1 (proton)/boron reaction, which releases alpha (helium) particles, but does not rely on neutron scattering for energy transfer.- 1H + 11B → 3 4He
Since the confinement properties of conventional approaches to fusion such as the tokamak and laser pellet fusion are marginal, most proposals for aneutronic fusion are based on radically different confinement concepts, such as the Polywell and the Dense Plasma Focus. Results have been extremely promising:
- "In the October 2013 edition of Nature Communications,[118] a research team led by Christine Labaune at Ecole Polytechnique in Palaiseau, France, reported a new record fusion rate: an estimated 80 million fusion reactions during the 1.5 nanoseconds that the laser fired, which is at least 100 times more than any previous proton-boron experiment. " [9]
Heating
Gas must be first heated to form a plasma. This then needs to be hot enough to start fusion reactions. A number of heating schemes have been explored:[119]Radiofrequency Heating A radio wave is applied to the plasma, causing it to oscillate.
Electrostatic Heating An electric field can do work on charged ions or electrons, heating them.
Neutral Beam Injection Gas is heated and injected into the fusion device. It may be heated using an electric field and then neutralized. After injection, it collides with particles the imparting energy.
Confinement

Parameter space occupied by inertial fusion energy and magnetic fusion energy devices as of the mid 1990s. The regime allowing thermonuclear ignition with high gain lies near the upper right corner of the plot.
Unconfined
The first human-made, large-scale fusion reaction was the test of the hydrogen bomb, Ivy Mike, in 1952. As part of the PACER project, it was once proposed to use hydrogen bombs as a source of power by detonating them in underground caverns and then generating electricity from the heat produced, but such a power plant is unlikely ever to be constructed.[citation needed]General confinement principles
Confinement refers to all the conditions necessary to keep a plasma dense and hot long enough to undergo fusion:- Equilibrium: The forces acting on the plasma must be balanced so that it will not rapidly disassemble. The exception, of course, is inertial confinement, where the relevant physics must occur faster than the disassembly time.
- Stability: The plasma must be so constructed that small deviations are restored to the initial state, otherwise some unavoidable disturbance will occur and grow exponentially until the plasma is destroyed.
- Transport: The loss of particles and heat in all channels must be sufficiently slow. The word "confinement" is often used in the restricted sense of "energy confinement".
Inertial confinement
Inertial confinement is the use of rapidly imploding shell to heat and confine plasma. The shell is imploded using a direct laser blast (direct drive) or a secondary x-ray blast (indirect drive). Theoretically, fusion using lasers would be done using tiny pellets of fuel that explode several times a second. To induce the explosion, the pellet must be compressed to about 30 times solid density with energetic beams. If direct drive is used - the beams are focused directly on the pellet - it can in principle be very efficient, but in practice is difficult to obtain the needed uniformity.[122] The alternative approach, indirect drive, uses beams to heat a shell, and then the shell radiates x-rays, which then implode the pellet. The beams are commonly laser beams, but heavy and light ion beams and electron beams have all been investigated.[123]Inertial confinement produces plasmas with very high densities and temperatures making it suitable for weapons research, X-ray generation and perhaps in the distant future, spaceflight .[citation needed] ICF implosions require fuel pellets with close to a perfect shape in order to generate an symmetrical inward shock wave and to produce the high-density plasma. These are known as targets and, building them has presented its own technical challenges.
A recent development in ICF research is fast ignition. This is the use of two laser systems to heat a compressed targets. A conventional laser system compresses the pellet, after which a second ultrashort laser pulse heats the compressed plasma. This burst has many petawatts of power. Fast ignition implodes the pellet at exactly the moment of greatest density. Research into fast ignition has been carried out at the OMEGA EP petawatt and OMEGA lasers at the University of Rochester and at the GEKKO XII laser at the institute for laser engineering in Osaka Japan. If fruitful, it may have the effect of greatly reducing the cost of a laser fusion based power source.[citation needed]
Magnetic confinement
At the temperatures required for fusion, the fuel is heated to a plasma state. In this state it has a very good electrical conductivity. This opens the possibility of confining the plasma with magnetic fields, an idea known as magnetic confinement. This puts a Lorentz force on the plasma. The force works perpendicular to the magnetic fields, so one problem in magnetic confinement is preventing the plasma from leaking out the ends of the field lines. These ends are known as magnetic cusps. There are basically two solutions.[citation needed]The first is to use the magnetic mirror effect. If a particle follows the field line and enters a region of higher field strength, the particles can be reflected. There are several devices that try to use this effect. The most famous was the magnetic mirror machines, which was a series of large, expensive devices built at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory from the 1960s to mid 1980s.[124] Some other examples include the magnetic bottles and Biconic cusp.[125] Because the mirror machines were straight, they had some advantages over a ring shape. First, mirrors would easier to construct and maintain and second direct conversion energy capture, was easier to implement.[8] As the confinement achieved in experiments was poor, this approach has been essentially abandoned.[citation needed]
The second possibility to prevent end losses is to bend the field lines back on themselves, either in circles or more commonly in nested toroidal surfaces. The most highly developed system of this type is the tokamak, with the stellarator being next most advanced, followed by the Reversed field pinch. Compact toroids, especially the Field-Reversed Configuration and the spheromak, attempt to combine the advantages of toroidal magnetic surfaces with those of a simply connected (non-toroidal) machine, resulting in a mechanically simpler and smaller confinement area. Compact toroids still have some enthusiastic supporters but are not backed as readily by the majority of the fusion community.[citation needed]
Electrostatic confinement
There are also electrostatic confinement fusion devices. These devices heat and confine ions using electrostatic fields. The best known is the Fusor. This device has an cathode inside an anode wire cage. Positive ions fly towards the negative inner cage, and are heated by the electric field in the process. If they miss the inner cage they can collide and fuse. Ions typically hit the cathode, however, creating prohibitory high conduction losses. Also, fusion rates in fusors are very low due to competing physical effects, such as energy loss in the form of light radiation.[126] Designs have been proposed to avoid the problems associated with the cage, by generating the field using a non-neutral cloud. These include a plasma oscillating device,[127] a penning trap and the polywell.[128] The technology is relatively immature, however, and many scientific and engineering questions remain.Material selection
Considerations
Any power plant using hot plasma, is going to have plasma facing walls. In even the simplest plasma approaches, the material will get blasted with matter and energy. This leads to a minimum list of considerations, including dealing with:- A heating and cooling cycle, up to a 10 MW/m² thermal load[citation needed].
- Neutron radiation, which over time leads to neutron activation and embrittlement.
- High energy ions leaving at tens to hundreds of electronvolts.
- Alpha particles leaving at millions of electronvolts.
- Electrons leaving at high energy.
- Light radiation (IR, visible, UV, X-ray).
Durability
For long term use, each atom in the wall is expected to be hit by a neutron and displaced about a hundred times before the material is replaced. High-energy neutrons will produce hydrogen and helium by way of various nuclear reactions that tends to form bubbles at grain boundaries and result in swelling, blistering or embrittlement.[129]Selection
One can choose either a low-Z material, such as graphite or beryllium, or a high-Z material, usually tungsten with molybdenum as a second choice. Use of liquid metals (lithium, gallium, tin) has also been proposed, e.g., by injection of 1–5 mm thick streams flowing at 10 m/s on solid substrates[citation needed].If graphite is used, the gross erosion rates due to physical and chemical sputtering would be many meters per year, so one must rely on redeposition of the sputtered material. The location of the redeposition will not exactly coincide with the location of the sputtering, so one is still left with erosion rates that may be prohibitive. An even larger problem is the tritium co-deposited with the redeposited graphite. The tritium inventory in graphite layers and dust in a reactor could quickly build up to many kilograms, representing a waste of resources and a serious radiological hazard in case of an accident. The consensus of the fusion community seems to be that graphite, although a very attractive material for fusion experiments, cannot be the primary PFC material in a commercial reactor.
The sputtering rate of tungsten by the plasma fuel ions is orders of magnitude smaller than that of carbon, and tritium is much less incorporated into redeposited tungsten, making this a more attractive choice. On the other hand, tungsten impurities in a plasma are much more damaging than carbon impurities, and self-sputtering of tungsten can be high, so it will be necessary to ensure that the plasma in contact with the tungsten is not too hot (a few tens of eV rather than hundreds of eV). Tungsten also has disadvantages in terms of eddy currents and melting in off-normal events, as well as some radiological issues.
Plant design
Nuclear island
A fusion power plant may be designed with a nuclear island and the balance of plant. This is common in typical fission reactors. The nuclear island has a plasma chamber with an associated vacuum system, surrounded by plasma-facing components (first wall and divertor) maintaining the vacuum and absorbing the heat coming from the plasma. If magnetic confinement is used, a magnet system made from superconducting magnets will be needed, as well as systems for heating and refueling the plasma. If inertial confinement is used, it will require a driver (laser or accelerator) and a focusing system, as well as place to manufacture and position the target. The balance of plant converts heat into electricity via steam turbines.Energy extraction
Steam turbines It has been proposed [130] that steam turbines be used to convert the heat from the fusion chamber into electricity. The heat is transferred into a working fluid that turns into steam, driving electric generators.Neutron blankets Deuterium and tritium fusion generates neutrons. This varies by technique (NIF has a record of 3E14 neutrons per second[131] while a typical fusor produces 1E5 - 1E9 neutrons per second). It has been proposed to use these neutrons as a way to regenerate spent fission fuel [132] or as a way to breed tritium from a liquid lithium blanket.
Direct conversion This is a method where the kinetic energy of a particle is converted into voltage.[133] It was first suggested by Richard F. Post in conjunction with magnetic mirrors, in the late sixties. It has also been suggested for Field-Reversed Configurations. The process takes the plasma, expands it, and converts a large fraction of the random energy of the fusion products into directed motion. The particles are then collected on electrodes at various large electrical potentials. This method has demonstrated an experimental efficiency of 48 percent.[134]
Diagnostics
Thomson Scattering Certain wavelengths of light will scatter off a plasma. This light can be detected and used to reconstruct the plasmas' behavior. This technique can be used to find its' density and temperature. It is common in Inertial confinement fusion,[135] Tokamaks[136] and fusors. In ICF systems, this can be done by firing a second beam into a gold foil adjacent to the target. This makes x-rays that scatter or traverse the plasma. In Tokamaks, this can be done using mirrors and detectors to reflect light across a plane (two dimensions) or in a line (one dimension).Langmuir probe This is a metal object placed in a plasma. A potential is applied to it, giving it a positive or negative voltage against the surrounding plasma. The metal collects charged particles, drawing a current. As the voltage changes, the current changes. This makes a IV Curve. The IV-curve can be used to determine the local plasma density, potential and temperature.[137]
Geiger counter Deuterium or tritium fusion produces neutrons. Geiger counters record the rate of neutron production, so they are an essential tool for demonstrating success.
Safety and the environment
Accident potential
There is no possibility of a catastrophic accident in a fusion reactor resulting in major release of radioactivity to the environment or injury to non-staff, unlike modern fission reactors. The primary reason is that the requirements for nuclear fusion differ greatly from nuclear fission: fusion requires extremely precise and controlled temperature, pressure, and magnetic field parameters for any net energy to be produced, and a far smaller amount of fuel. If the reactor suffered damage or lost even a small degree of required control, fusion reactions and heat generation would rapidly cease.[138]Therefore fusion reactors are considered extremely safe in this sense, making them favorable over fission reactors, which, in contrast, continue to generate heat through beta-decay for several months after reactor shut-down, meaning that melting of fuel rods is possible even after the reactor has been stopped due to continued accumulation of heat.[139]
There is also no risk of a runaway reaction in a fusion reactor. The plasma is burnt at optimal conditions, and any significant change will render it unable to react or to produce excess heat. In fusion reactors the reaction process is so delicate that this level of safety is inherent; no elaborate failsafe mechanism is required. Although the plasma in a fusion power plant will have a volume of 1000 cubic meters or more, the density of the plasma is extremely low, and the total amount of fusion fuel in the vessel is very small, typically a few grams.[139] If the fuel supply is closed, the reaction stops within seconds. In comparison, a fission reactor is typically loaded with enough fuel for several years, and no additional fuel is necessary to keep the reaction going.[140]
In the magnetic approach, strong fields are developed in coils that are held in place mechanically by the reactor structure. Failure of this structure could release this tension and allow the magnet to "explode" outward. The severity of this event would be similar to any other industrial accident or an MRI machine quench/explosion, and could be effectively stopped with a containment building similar to those used in existing (fission) nuclear generators. The laser-driven inertial approach is generally lower-stress. Although failure of the reaction chamber is possible, simply stopping fuel delivery would prevent any sort of catastrophic failure.
Most reactor designs rely on the use of liquid lithium as both a coolant and a method for converting stray neutrons from the reaction into tritium, which is fed back into the reactor as fuel. Lithium is highly flammable, and in the case of a fire it is possible that the lithium stored on-site could be burned up and escape. In this case, the tritium contents of the lithium would be released into the atmosphere, posing a radiation risk. Calculations suggest that at about 1 kg the total amount of tritium and other radioactive gases in a typical power plant would be so small that they would have diluted to legally acceptable limits by the time they blew as far as the plant's perimeter fence.[141]
The likelihood of small industrial accidents including the local release of radioactivity and injury to staff cannot be estimated yet. These would include accidental releases of lithium, tritium, or mis-handling of decommissioned radioactive components of the reactor itself.
Effluents during normal operation
The natural product of the fusion reaction is a small amount of helium, which is completely harmless to life. Of more concern is tritium, which, like other isotopes of hydrogen, is difficult to retain completely. During normal operation, some amount of tritium will be continually released. There would be no acute danger, but the cumulative effect on the world's population from a fusion economy could be a matter of concern.[citation needed]Although tritium is volatile and biologically active the health risk posed by a release is much lower than that of most radioactive contaminants, due to tritium's short half-life (12.32 years), very low decay energy (~14.95 keV), and the fact that it does not bioaccumulate (instead being cycled out of the body as water, with a biological half-life of 7 to 14 days).[142] Current ITER designs are investigating total containment facilities for any tritium.
Waste management
The large flux of high-energy neutrons in a reactor will make the structural materials radioactive. The radioactive inventory at shut-down may be comparable to that of a fission reactor, but there are important differences.The half-life of the radioisotopes produced by fusion tends to be less than those from fission, so that the inventory decreases more rapidly. Unlike fission reactors, whose waste remains radioactive for thousands of years, most of the radioactive material in a fusion reactor would be the reactor core itself, which would be dangerous for about 50 years, and low-level waste another 100. Although this waste will be considerably more radioactive during those 50 years than fission waste, the very short half-life makes the process very attractive, as the waste management is fairly straightforward. By 500 years the material would have the same radiotoxidity as coal ash.[141]
Additionally, the choice of materials used in a fusion reactor is less constrained than in a fission design, where many materials are required for their specific neutron cross-sections. This allows a fusion reactor to be designed using materials that are selected specifically to be "low activation", materials that do not easily become radioactive. Vanadium, for example, would become much less radioactive than stainless steel. Carbon fiber materials are also low-activation, as well as being strong and light, and are a promising area of study for laser-inertial reactors where a magnetic field is not required.
In general terms, fusion reactors would create far less radioactive material than a fission reactor, the material it would create is less damaging biologically, and the radioactivity "burns off" within a time period that is well within existing engineering capabilities for safe long-term waste storage.
Nuclear proliferation
Although fusion power uses nuclear technology, the overlap with nuclear weapons would be limited. A huge amount of tritium could be produced by a fusion power plant. Tritium is used in the trigger of hydrogen bombs and in a modern boosted fission weapon. But tritium can be also produced by nuclear fission. The energetic neutrons from a fusion reactor could be used to breed weapons-grade plutonium or uranium for an atomic bomb (for example by transmutation of U238 to Pu239, or Th232 to U233).A study conducted 2011 assessed the risk of three scenarios:[143]
- Use in small-scale fusion plant: Due to much higher power consumption, heat dissipation and a more unique design compared to enrichment gas centrifuges this choice would be much easier to detect and therefore implausible.[143]
- Modifications to produce weapon-usable material in a commercial facility: The production potential is significant. But no fertile or fissile substances necessary for the production of weapon-usable materials needs to be present at a civil fusion system at all. If not shielded, a detection of these materials can be done by their characteristic gamma radiation. The underlying redesign could be detected by regular design information verifications. In the (technically more feasible) case of solid breeder blanket modules, it would be necessary for incoming components to be inspected for the presence of fertile material,[143] otherwise plutonium for several weapons could be produced each year.[144]
- Prioritizing a fast production of weapon-grade material regardless of secrecy: The fastest way to produce weapon usable material was seen in modifying a prior civil fusion power plant. Unlike in some nuclear power plants, there is no weapon compatible material during civil use. Even without the need for covert action this modification would still take about 2 months to start the production and at least an additional week to generate a significant amount for weapon production. This was seen as enough time to detect a military use and to react with diplomatic or military means. To stop the production, a military destruction of inevitable parts of the facility leaving out the reactor itself would be sufficient. This, together with the intrinsic safety of fusion power would only bear a low risk of radioactive contamination.[143]
As a sustainable energy source
Large-scale reactors using neutronic fuels (e.g. ITER) and thermal power production (turbine based) are most comparable to fission power from an engineering and economics viewpoint. Both fission and fusion power plants involve a relatively compact heat source powering a conventional steam turbine-based power plant, while producing enough neutron radiation to make activation of the plant materials problematic. The main distinction is that fusion power produces no high-level radioactive waste (though activated plant materials still need to be disposed of). There are some power plant ideas that may significantly lower the cost or size of such plants; however, research in these areas is nowhere near as advanced as in tokamaks.[citation needed]Fusion power commonly proposes the use of deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen, as fuel and in many current designs also use lithium. Assuming a fusion energy output equal to the 1995 global power output of about 100 EJ/yr (= 1 × 1020 J/yr) and that this does not increase in the future, which is unlikely, then the known current lithium reserves would last 3000 years. Lithium from sea water would last 60 million years, however, and a more complicated fusion process using only deuterium from sea water would have fuel for 150 billion years.[145] To put this in context, 150 billion years is close to 30 times the remaining lifespan of the sun,[146] and more than 10 times the estimated age of the universe.
Economics
While fusion power is still in early stages of development, substantial sums have been and continue to be invested in research. In the EU almost €10 billion was spent on fusion research up to the end of the 1990s, and the new ITER reactor alone is budgeted at €10 billion.It is estimated that up to the point of possible implementation of electricity generation by nuclear fusion, R&D will need further promotion totalling around €60–80 billion over a period of 50 years or so (of which €20–30 billion within the EU) based on a report from 2002.[147] Nuclear fusion research receives €750 million (excluding ITER funding) from the European Union, compared with €810 million for sustainable energy research,[148] putting research into fusion power well ahead of that of any single rivaling technology. Indeed, the size of the investments and time frame of the expected results mean that fusion research is almost exclusively publicly funded, while research in other forms of energy can be done by the private sector.
Advantages
Fusion power would provide more energy for a given weight of fuel than any fuel-consuming energy source currently in use,[149] and the fuel itself (primarily deuterium) exists abundantly in the Earth's ocean: about 1 in 6500 hydrogen atoms in seawater is deuterium.[150] Although this may seem a low proportion (about 0.015%), because nuclear fusion reactions are so much more energetic than chemical combustion and seawater is easier to access and more plentiful than fossil fuels, fusion could potentially supply the world's energy needs for millions of years.[151][152]Despite being technically non-renewable, fusion power has many of the benefits of renewable energy sources (such as being a long-term energy supply and emitting no greenhouse gases) as well as some of the benefits of the resource-limited energy sources as hydrocarbons and nuclear fission (without reprocessing). Like these currently dominant energy sources, fusion could provide very high power-generation density and uninterrupted power delivery (due to the fact that it is not dependent on the weather, unlike wind and solar power).
Another aspect of fusion energy is that the cost of production does not suffer from diseconomies of scale. The cost of water and wind energy, for example, goes up as the optimal locations are developed first, while further generators must be sited in less ideal conditions. With fusion energy the production cost will not increase much even if large numbers of plants are built, because the raw resource (seawater) is abundant and widespread.
Some problems that are expected to be an issue in this century, such as fresh water shortages, can alternatively be regarded as problems of energy supply. For example, in desalination plants, seawater can be purified through distillation or reverse osmosis. Nonetheless, these processes are energy intensive. Even if the first fusion plants are not competitive with alternative sources, fusion could still become competitive if large-scale desalination requires more power than the alternatives are able to provide.
A scenario has been presented of the effect of the commercialization of fusion power on the future of human civilization.[153] ITER and later Demo are envisioned to bring online the first commercial nuclear fusion energy reactor by 2050. Using this as the starting point and the history of the uptake of nuclear fission reactors as a guide, the scenario depicts a rapid take up of nuclear fusion energy starting after the middle of this century.
Fusion power could be used in interstellar space, where solar energy is not available.