Climate change occurs when changes in Earth's climate system result in new weather
patterns that remain in place for an extended period of time. This
length of time can be as short as a few decades to as long as millions
of years. Scientists have identified many episodes of climate change
during Earth's geological history; more recently since the industrial revolution the climate has increasingly been affected by human activities driving global warming, and the terms are commonly used interchangeably in that context.
The climate system receives nearly all of its energy from the sun. The climate system also gives off energy to outer space. The balance of incoming and outgoing energy, and the passage of the energy through the climate system, determines Earth's energy budget. When the incoming energy is greater than the outgoing energy, earth's energy budget is positive and the climate system is warming. If more energy goes out, the energy budget is negative and earth experiences cooling.
The energy moving through Earth's climate system finds expression in weather, varying on geographic scales and time. Long-term averages of weather in a region constitute the region's climate. Climate change is a long-term, sustained trend of change in climate. Such changes can be the result of "internal variability", when natural processes inherent to the various parts of the climate system alter the distribution of energy. Examples include variability in ocean basins such as the Pacific decadal oscillation and Atlantic multidecadal oscillation. Climate change can also result from external forcing, when events outside of the climate system's components nonetheless produce changes within the system. Examples include changes in solar output and volcanism.
Climate change has various consequences for sea level changes, plant life, mass extinctions and also affects human societies.
The term "climate change" is often used to refer specifically to anthropogenic climate change (also known as global warming). Anthropogenic climate change is caused by human activity, as opposed to changes in climate that may have resulted as part of Earth's natural processes. In this sense, especially in the context of environmental policy, the term climate change has become synonymous with anthropogenic global warming. Within scientific journals, global warming refers to surface temperature increases while climate change includes global warming and everything else that increasing greenhouse gas levels affect.
A related term, "climatic change", was proposed by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 1966 to encompass all forms of climatic variability on time-scales longer than 10 years, but regardless of cause. During the 1970s, the term climate change replaced climatic change to focus on anthropogenic causes, as it became clear that human activities had a potential to drastically alter the climate. Climate change was incorporated in the title of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Climate change is now used as both a technical description of the process, as well as a noun used to describe the problem.
Factors that can shape climate are called climate forcings or "forcing mechanisms". These include processes such as variations in solar radiation, variations in the Earth's orbit, variations in the albedo or reflectivity of the continents, atmosphere, and oceans, mountain-building and continental drift and changes in greenhouse gas concentrations. There are a variety of climate change feedbacks that can either amplify or diminish the initial forcing. Some parts of the climate system, such as the oceans and ice caps, respond more slowly in reaction to climate forcings, while others respond more quickly. There are also key threshold factors which when exceeded can produce rapid change.
Climate change can either occur due to external forcing or due to internal processes. Internal unforced processes often involve changes in the distribution of energy in the ocean and atmosphere, for instance changes in the thermohaline circulation. External forcing mechanisms can be either anthropogenic (e.g. increased emissions of greenhouse gases and dust) or natural (e.g., changes in solar output, the earth's orbit, volcano eruptions).
The response of the climate system to a climate forcing might be fast (e.g., a sudden cooling due to airborne volcanic ash reflecting sunlight), slow (e.g. thermal expansion of warming ocean water), or a combination (e.g., sudden loss of albedo in the Arctic Ocean as sea ice melts, followed by more gradual thermal expansion of the water). Therefore, the climate system can respond abruptly, but the full response to forcing mechanisms might not be fully developed for centuries or even longer.
The climate system receives nearly all of its energy from the sun. The climate system also gives off energy to outer space. The balance of incoming and outgoing energy, and the passage of the energy through the climate system, determines Earth's energy budget. When the incoming energy is greater than the outgoing energy, earth's energy budget is positive and the climate system is warming. If more energy goes out, the energy budget is negative and earth experiences cooling.
The energy moving through Earth's climate system finds expression in weather, varying on geographic scales and time. Long-term averages of weather in a region constitute the region's climate. Climate change is a long-term, sustained trend of change in climate. Such changes can be the result of "internal variability", when natural processes inherent to the various parts of the climate system alter the distribution of energy. Examples include variability in ocean basins such as the Pacific decadal oscillation and Atlantic multidecadal oscillation. Climate change can also result from external forcing, when events outside of the climate system's components nonetheless produce changes within the system. Examples include changes in solar output and volcanism.
Climate change has various consequences for sea level changes, plant life, mass extinctions and also affects human societies.
Terminology
The most general definition of climate change is a change in the statistical properties (principally its mean and spread) of meteorological variables when considered over long periods of time, regardless of cause. Accordingly, fluctuations over periods shorter than a few decades, such as El Niño, do not represent climate change.The term "climate change" is often used to refer specifically to anthropogenic climate change (also known as global warming). Anthropogenic climate change is caused by human activity, as opposed to changes in climate that may have resulted as part of Earth's natural processes. In this sense, especially in the context of environmental policy, the term climate change has become synonymous with anthropogenic global warming. Within scientific journals, global warming refers to surface temperature increases while climate change includes global warming and everything else that increasing greenhouse gas levels affect.
A related term, "climatic change", was proposed by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 1966 to encompass all forms of climatic variability on time-scales longer than 10 years, but regardless of cause. During the 1970s, the term climate change replaced climatic change to focus on anthropogenic causes, as it became clear that human activities had a potential to drastically alter the climate. Climate change was incorporated in the title of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Climate change is now used as both a technical description of the process, as well as a noun used to describe the problem.
Causes
On the broadest scale, the rate at which energy is received from the Sun and the rate at which it is lost to space determine the equilibrium temperature and climate of Earth. This energy is distributed around the globe by winds, ocean currents, and other mechanisms to affect the climates of different regions.Factors that can shape climate are called climate forcings or "forcing mechanisms". These include processes such as variations in solar radiation, variations in the Earth's orbit, variations in the albedo or reflectivity of the continents, atmosphere, and oceans, mountain-building and continental drift and changes in greenhouse gas concentrations. There are a variety of climate change feedbacks that can either amplify or diminish the initial forcing. Some parts of the climate system, such as the oceans and ice caps, respond more slowly in reaction to climate forcings, while others respond more quickly. There are also key threshold factors which when exceeded can produce rapid change.
Climate change can either occur due to external forcing or due to internal processes. Internal unforced processes often involve changes in the distribution of energy in the ocean and atmosphere, for instance changes in the thermohaline circulation. External forcing mechanisms can be either anthropogenic (e.g. increased emissions of greenhouse gases and dust) or natural (e.g., changes in solar output, the earth's orbit, volcano eruptions).
The response of the climate system to a climate forcing might be fast (e.g., a sudden cooling due to airborne volcanic ash reflecting sunlight), slow (e.g. thermal expansion of warming ocean water), or a combination (e.g., sudden loss of albedo in the Arctic Ocean as sea ice melts, followed by more gradual thermal expansion of the water). Therefore, the climate system can respond abruptly, but the full response to forcing mechanisms might not be fully developed for centuries or even longer.
Internal variability
Pacific decadal oscillation 1925 to 2010
Scientists generally define the five components of earth's climate system to include atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere (restricted to the surface soils, rocks, and sediments), and biosphere. Natural changes in the climate system result in internal "climate variability". Examples include the type and distribution of species, and changes in ocean-atmosphere circulations.
Climate change due to internal variability sometimes occurs in
cycles or oscillations, for instance every 100 or 2000 years. For other
types of natural climatic change, we cannot predict when it happens; the
change is called random or stochastic. From a climate perspective, the weather can be considered as being random.
If there are little clouds in a particular year, there is an energy
imbalance and extra heat can be absorbed by the oceans. Due to climate inertia,
this signal can be 'stored' in the ocean and be expressed as
variability on longer time scales than the original weather
disturbances. If the weather disturbances are completely random, occurring as white noise,
the inertia of glaciers or oceans can transform this into climate
changes where longer-duration oscillations are also larger oscillations,
a phenomenon called red noise. Many climate changes have a random aspect and a cyclical aspect. This behavior is dubbed stochastic resonance.
Ocean-atmosphere variability
The ocean and atmosphere can work together to spontaneously generate
internal climate variability that can persist for years to decades at a
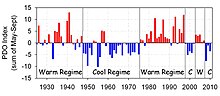
time. Examples of this type of variability include the El Niño–Southern Oscillation, the Pacific decadal oscillation, and the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation.
These variations can affect global average surface temperature by
redistributing heat between the deep ocean and the atmosphere and/or by altering the cloud/water vapor/sea ice distribution which can affect the total energy budget of the earth.
Ocean circulation
A schematic of modern thermohaline circulation.
Tens of millions of years ago, continental-plate movement formed a
land-free gap around Antarctica, allowing the formation of the ACC, which keeps warm waters away from Antarctica.
The oceanic aspects of climate variability can generate variability
on centennial timescales due to the ocean having hundreds of times more
mass than in the atmosphere, and thus very high thermal inertia.
For example, alterations to ocean processes such as thermohaline
circulation play a key role in redistributing heat in the world's
oceans.
Ocean currents transport a lot of energy from the warm tropical
regions to the colder polar regions. Changes occurring around the last
ice age (in technical terms, the last glacial) show that the circulation is the North Atlantic
can change suddenly and substantially, leading to global climate
changes, even though the total amount of energy coming into the climate
system didn't change much. These large changes may have come from so
called Heinrich events
where internal instability of ice sheets caused huge ice bergs to be
released into the ocean. When the ice sheet melts, the resulting water
is very low in salt and cold, driving changes in circulation. Another example of climate changes partially driven by internal variability are the regional changes driven by the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation.
Life
Life affects climate through its role in the carbon and water cycles and through such mechanisms as albedo, evapotranspiration, cloud formation, and weathering. Examples of how life may have affected past climate include:
- glaciation 2.3 billion years ago triggered by the evolution of oxygenic photosynthesis, which depleted the atmosphere of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide and introduced free oxygen
- another glaciation 300 million years ago ushered in by long-term burial of decomposition-resistant detritus of vascular land-plants (creating a carbon sink and forming coal)
- termination of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum 55 million years ago by flourishing marine phytoplankton
- reversal of global warming 49 million years ago by 800,000 years of arctic azolla blooms
- global cooling over the past 40 million years driven by the expansion of grass-grazer ecosystems
External climate forcing
Greenhouse gases
Increase in atmospheric CO
2 levels
2 levels
Whereas greenhouse gases released by the biosphere is often seen as a
feedback or internal climate process, greenhouse gases emitted from
volcanoes are typically classified as external by climatologists. Greenhouse gases, such as CO
2, methane and nitrous oxide, heat the climate system by trapping infrared light.
2, methane and nitrous oxide, heat the climate system by trapping infrared light.
The scientific consensus on climate change is "that climate is changing and that these changes are in large part caused by human activities",
and it "is largely irreversible". There has been multiple indications of how human activities affect global warming and continue to do so.
... there is a strong, credible body of evidence, based on multiple lines of research, documenting that climate is changing and that these changes are in large part caused by human activities. While much remains to be learned, the core phenomenon, scientific questions, and hypotheses have been examined thoroughly and have stood firm in the face of serious scientific debate and careful evaluation of alternative explanations.
— United States National Research Council, Advancing the Science of Climate Change
Human's main impact is by emitting CO2 from fossil fuel combustion, followed by aerosols (particulate matter in the atmosphere), and the CO2 released by cement manufacture. Other factors, including land use, ozone depletion, animal husbandry (ruminant animals such as cattle produce methane), and deforestation, are also play a role.
Volcanoes are also part of the extended carbon cycle.
Over very long (geological) time periods, they release carbon dioxide
from the Earth's crust and mantle, counteracting the uptake by
sedimentary rocks and other geological carbon dioxide sinks. The US Geological Survey
estimates are that volcanic emissions are at a much lower level than
the effects of current human activities, which generate 100–300 times
the amount of carbon dioxide emitted by volcanoes. The annual amount put out by human activities may be greater than the amount released by supereruptions, the most recent of which was the Toba eruption in Indonesia 74,000 years ago.
Orbital variations
Slight variations in Earth's motion lead to changes in the seasonal
distribution of sunlight reaching the Earth's surface and how it is
distributed across the globe. There is very little change to the
area-averaged annually averaged sunshine; but there can be strong
changes in the geographical and seasonal distribution. The three types
of kinematic change are variations in Earth's eccentricity, changes in the tilt angle of Earth's axis of rotation, and precession of Earth's axis. Combined together, these produce Milankovitch cycles which affect climate and are notable for their correlation to glacial and interglacial periods, their correlation with the advance and retreat of the Sahara, and for their appearance in the stratigraphic record.
During the glacial cycles, there was a high correlation between CO
2 concentrations and temperatures. Early studies indicated that CO
2 concentrations lagged temperatures, but it has become clear that this isn't always the case. When seawater temperatures increase, the solubility of CO
2 decreases so that it is released from the ocean. The exchange of CO
2 between the air and the ocean can also be impacted by further aspects of climatic change. These and other self-reinforcing processes allow small changes in Earth's motion to have a possibly large effect on climate.
2 concentrations and temperatures. Early studies indicated that CO
2 concentrations lagged temperatures, but it has become clear that this isn't always the case. When seawater temperatures increase, the solubility of CO
2 decreases so that it is released from the ocean. The exchange of CO
2 between the air and the ocean can also be impacted by further aspects of climatic change. These and other self-reinforcing processes allow small changes in Earth's motion to have a possibly large effect on climate.
Solar output
Variations in solar activity during the last several centuries based on observations of sunspots and beryllium isotopes. The period of extraordinarily few sunspots in the late 17th century was the Maunder minimum.
The Sun is the predominant source of energy input to the Earth's climate system. Other sources include geothermal
energy from the Earth's core, tidal energy from the Moon and heat from
the decay of radioactive compounds. Both long term variations in solar
intensity are known to affect global climate. Solar output varies on shorter time scales, including the 11-year solar cycle and longer-term modulations. Correlation between sunspots and climate and tenuous at best.
Three to four billion years ago, the Sun emitted only 75% as much power as it does today.
If the atmospheric composition had been the same as today, liquid water
should not have existed on the Earth's surface. However, there is
evidence for the presence of water on the early Earth, in the Hadean and Archean eons, leading to what is known as the faint young Sun paradox.
Hypothesized solutions to this paradox include a vastly different
atmosphere, with much higher concentrations of greenhouse gases than
currently exist.
Over the following approximately 4 billion years, the energy output of
the Sun increased. Over the next five billion years, the Sun's ultimate
death as it becomes a red giant and then a white dwarf will have large effects on climate, with the red giant phase possibly ending any life on Earth that survives until that time.
Volcanism
The eruptions
considered to be large enough to affect the Earth's climate on a scale
of more than 1 year are the ones that inject over 100,000 tons of SO2 into the stratosphere. This is due to the optical properties of SO2 and sulfate aerosols, which strongly absorb or scatter solar radiation, creating a global layer of sulfuric acid haze.
On average, such eruptions occur several times per century, and cause
cooling (by partially blocking the transmission of solar radiation to
the Earth's surface) for a period of several years. Although volcanoes
are technically part of the lithosphere, which itself is part of the
climate system, the IPCC explicitly defines volcanism as an external
forcing agent.
Notable eruptions in the historical records are the eruption of Mount Pinatubo in 1991 which lowered global temperatures by about 0.5 °C (0.9 °F) for up to three years, and the Mount Tambora eruption in 1815 causing the Year Without a Summer.
At a larger scale – a few times every 50 million to 100 million years – the eruption of large igneous provinces brings large quantities of igneous rock from the mantle and lithosphere to the Earth's surface. Carbon dioxide in the rock is then released into the atmosphere.
Small eruptions, with injections of less than 0.1 Mt of sulfur dioxide
into the stratosphere, affect the atmosphere only subtly, as temperature
changes are comparable with natural variability. However, because
smaller eruptions occur at a much higher frequency, they too
significantly affect Earth's atmosphere.
Plate tectonics
Over the course of millions of years, the motion of tectonic plates
reconfigures global land and ocean areas and generates topography. This
can affect both global and local patterns of climate and
atmosphere-ocean circulation.
The position of the continents determines the geometry of the
oceans and therefore influences patterns of ocean circulation. The
locations of the seas are important in controlling the transfer of heat
and moisture across the globe, and therefore, in determining global
climate. A recent example of tectonic control on ocean circulation is
the formation of the Isthmus of Panama about 5 million years ago, which shut off direct mixing between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This strongly affected the ocean dynamics of what is now the Gulf Stream and may have led to Northern Hemisphere ice cover. During the Carboniferous period, about 300 to 360 million years ago, plate tectonics may have triggered large-scale storage of carbon and increased glaciation. Geologic evidence points to a "megamonsoonal" circulation pattern during the time of the supercontinent Pangaea, and climate modeling suggests that the existence of the supercontinent was conducive to the establishment of monsoons.
The size of continents is also important. Because of the
stabilizing effect of the oceans on temperature, yearly temperature
variations are generally lower in coastal areas than they are inland. A
larger supercontinent will therefore have more area in which climate is
strongly seasonal than will several smaller continents or islands.
Other mechanisms
It has been postulated that ionized particles known as cosmic rays
could impact cloud cover and thereby the climate. As the sun shields
the earth from these particles, changes in solar activity were
hypothesized to influence climate indirectly as well. To test the
hypothesis, CERN designed the CLOUD experiment, which showed the effect of cosmic rays is too weak to influence climate noticeably.
Evidence exists that the Chicxulub asteroid impact
some 66 million years ago had severely affected the Earth's climate.
Large quantities of sulfate aerosols were kicked up into the atmosphere,
decreasing global temperatures by up to 26 °C and producing
sub-freezing temperatures for a period of 3–16 years. The recovery time
for this event took more than 30 years. The large-scale use of nuclear weapons
has also been investigated for its impact on the climate. The
hypothesis is that soot released by large-scale fires blocks a
significant fraction of sunlight for as much as a year, leading to a
sharp drop in temperatures for a few years. This possible event is
described as nuclear winter.
Human's use of land impact how much sunlight the surface reflects
and the concentration of dust. Cloud formation is not only influenced
by how much water is in the air and the temperature, but also by the
amount of aerosols in the air such as dust. Globally, more dust is available if there are many regions with dry soils, little vegetation and strong winds.
Evidence and measurement of climate changes
Evidence of past climate change and present climate change comes from a variety of sources. Paleoclimatology is the study of changes in climate taken on the scale of the entire history of Earth. It uses a variety of proxy methods from the Earth and life sciences to obtain data previously preserved within things such as rocks, sediments, ice sheets, tree rings, corals, shells, and microfossils. It then uses the records to determine the past states of the Earth's various climate regions and its atmospheric system. Direct measurements give a more complete overview of climate change.
Direct measurements
Climate changes that occurred after the widespread deployment of
measuring devices, can be observed directly. Reasonably complete global
records of surface temperature are available beginning from the mid-late
19th century. Further observations are done by satellite and derived indirectly from historical documents. Satellite cloud and precipitation data has been available since the 1970s. Historical climatology
is the study of historical changes in climate and their effect on human
history and development. The primary sources include written records
such as sagas, chronicles, maps and local history literature as well as pictorial representations such as paintings, drawings and even rock art.
Climate change in the recent past may be detected by corresponding changes in settlement and agricultural patterns. Archaeological evidence, oral history and historical documents can offer insights into past changes in the climate. Climate change effects have been linked to the rise and also the collapse of various civilizations.
Proxy measurements
Various archives of past climate are present in rocks, trees and
fossils. From these archive, indirect measures of climate, so-called
proxies, can be derived. Quantification of climatological variation of
precipitation in prior centuries and epochs is less complete but
approximated using proxies such as marine sediments, ice cores, cave
stalagmites, and tree rings.
Stress, too little precipitation or unsuitable temperatures, can alter
the growth rate of trees, which allows scientists to infer climate
trends by analyzing the growth rate of tree rings. This branch of
science studying this called dendroclimatology. Glaciers leave behind moraines
that contain a wealth of material—including organic matter, quartz, and
potassium that may be dated—recording the periods in which a glacier
advanced and retreated.
Analysis of ice in a core drilled from an ice sheet such as the Antarctic ice sheet,
can be used to show a link between temperature and global sea level
variations. The air trapped in bubbles in the ice can also reveal the CO2
variations of the atmosphere from the distant past, well before modern
environmental influences. The study of these ice cores has been a
significant indicator of the changes in CO2 over many
millennia, and continues to provide valuable information about the
differences between ancient and modern atmospheric conditions. The 18O/16O ratio in calcite and ice core samples used to deduce ocean temperature in the distant past is an example of a temperature proxy method, as are other climate metrics noted in subsequent categories.
The remnants of plants, and specifically pollen, are also used to
study climatic change. Plant distributions varies under different
climate conditions. Different groups of plants have pollen with
distinctive shapes and surface textures, and since the outer surface of
pollen is composed of a very resilient material, they resist decay.
Changes in the type of pollen found in different layers of sediment
indicate changes in plant communities. These changes are often a sign of
a changing climate. As an example, pollen studies have been used to track changing vegetation patterns throughout the Quaternary glaciations and especially since the last glacial maximum. Remains of beetles
are common in freshwater and land sediments. Different species of
beetles tend to be found under different climatic conditions. Given the
extensive lineage of beetles whose genetic makeup has not altered
significantly over the millennia, knowledge of the present climatic
range of the different species, and the age of the sediments in which
remains are found, past climatic conditions may be inferred.
Consequences of climate change
All elements of the climate system portray changes as a consequence of climate change.
Changes in the cryosphere
Glaciers and ice sheets
Glaciers are considered among the most sensitive indicators of climate change. Their size is determined by a mass balance
between snow input and melt output. As temperatures increase, glaciers
retreat unless snow precipitation increases to make up for the
additional melt. Glaciers grow and shrink due both to natural
variability and external forcings. Variability in temperature,
precipitation and hydrology can strongly determine the evolution of a
glacier in a particular season.
The most significant climate processes since the middle to late Pliocene (approximately 3 million years ago) are the glacial and interglacial cycles. The present interglacial period (the Holocene) has lasted about 11,700 years. Shaped by orbital variations, responses such as the rise and fall of continental ice sheets and significant sea-level changes helped create the climate. Other changes, including Heinrich events, Dansgaard–Oeschger events and the Younger Dryas, however, illustrate how glacial variations may also influence climate without the orbital forcing.
Sea level change
During the Last Glacial Maximum,
some 25,000 years ago, sea levels were roughly 130 m lower than today.
The deglaciation afterwards was characterized by rapid sea level change. The deglaciations at the end of The deglaciation that took place In the early Pliocene, global temperatures were 1–2˚C warmer than the present temperature, yet sea level was 15–25 meters higher than today.
Sea ice
Sea ice plays an important role in Earth's climate as it affects the
total amount of sunlight that is reflected away from the Earth.
In the past, the Earth's oceans have been almost entirely covered by
sea ice on a number of occasions, when the Earth was in a so-called Snowball Earth state, and completely ice-free in periods of warm climate. When there is a lot of sea ice present globally, especially in the tropics and subtropics, the climate is more sensitive to forcings as the ice–albedo feedback is very strong.
Flora and fauna
Top: Arid ice age climateMiddle: Atlantic Period, warm and wetBottom: Potential vegetation in climate now if not for human effects like agriculture.
Vegetation
A change in the type, distribution and coverage of vegetation may
occur given a change in the climate. Some changes in climate may result
in increased precipitation and warmth, resulting in improved plant
growth and the subsequent sequestration of airborne CO2. The effects are expected to affect the rate of many natural cycles like plant litter decomposition rates.
A gradual increase in warmth in a region will lead to earlier flowering
and fruiting times, driving a change in the timing of life cycles of
dependent organisms. Conversely, cold will cause plant bio-cycles to
lag.
Larger, faster or more radical changes, however, may result in vegetation stress, rapid plant loss and desertification in certain circumstances. An example of this occurred during the Carboniferous Rainforest Collapse
(CRC), an extinction event 300 million years ago. At this time vast
rainforests covered the equatorial region of Europe and America. Climate
change devastated these tropical rainforests, abruptly fragmenting the
habitat into isolated 'islands' and causing the extinction of many plant
and animal species.
Fauna
One of the most important ways animals can deal with climatic change is migration to warmer or colder regions. On a longer timescale, evolution makes ecosystems including animals better adapted to a new climate. Rapid or large climate change can cause mass extinctions when creatures are stretched too far to be able to adapt.
Past and modern climate change
Examples of past change
Climatological temperatures substantially affect cloud cover and
precipitation. At lower temperatures, air can hold less water vapour,
which can lead to decreased precipitation. For instance, during the Last Glacial Maximum of 18,000 years ago, thermal-driven evaporation from the oceans onto continental landmasses was low, causing large areas of extreme desert, including polar deserts (cold but with low rates of cloud cover and precipitation). In contrast, the world's climate was cloudier and wetter than today near the start of the warm Atlantic Period of 8000 years ago. Notable climate events known to paleoclimatology are provided in this list of periods and events in climate history.
Paleo-Eocene Thermal maximum
The Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) was a time period with
more than 5–8 °C global average temperature rise across the event. This climate event occurred at the time boundary of the Paleocene and Eocene geological epochs. During the event large amounts of methane was released, a potent greenhouse gas.
The PETM represents a "case study" for modern climate change as in the
greenhouse gases were released in a geologically relatively short amount
of time. During the PETM, a mass extinction of organisms in the deep ocean took place.
Modern climate change and global warming
As a consequence of humans emitting greenhouse gases, global surface temperatures have started rising (global warming).
Global warming is an aspect of modern climate change, a term that also
includes the observed changes in precipitation, storm tracks and
cloudiness. As a consequence, glaciers worldwide have been found to be shrinking significantly Data from NASA's Grace satellites show that the land ice sheets in both Antarctica (upper chart) and Greenland (lower) have been losing mass since 2002. Both ice sheets have seen an acceleration of ice mass loss since 2009.
Global sea levels have been rising as a consequence of thermal
expansion and ice melt. The decline in Arctic sea ice, both in extent
and thickness, over the last several decades is further evidence for
rapid climate change.