From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A high-ranking male
mandrill advertises his status with bright facial coloration.
In biology, a dominance hierarchy (formerly and colloquially called a pecking order) is a type of social hierarchy that arises when members of animal social groups interact, creating a ranking system. A dominant higher-ranking individual is sometimes called an alpha, and the submissive lower-ranking individual a beta.
Different types of interactions can result in dominance depending on
the species, including ritualized displays of aggression or direct
physical violence. In social living groups, members are likely to compete for access to limited resources and mating opportunities.
Rather than fighting each time they meet, relative rank is established
between individuals of the same sex, with higher-ranking individuals
often gaining more access to resources and mates. Based on repetitive
interactions, a social order is created that is subject to change each
time a dominant animal is challenged by a subordinate one.
Definitions
Dominance
is an individual's preferential access to resources over another based
on coercive capacity based on strength, threat, and intimidation,
compared to prestige (persuasive capacity based on skills, abilities,
and knowledge). A dominant animal is one whose sexual,
feeding, aggressive, and other behaviour patterns subsequently occur
with relatively little influence from other group members. Subordinate animals are opposite; their behaviour is submissive, and can be relatively easily influenced or inhibited by other group members.
Dominance

For many animal societies, an individual's position in the dominance
hierarchy corresponds with their opportunities to reproduce.
In hierarchically social animals, dominant individuals may exert
control over others. For example, in a herd of feral goats it is a large
male that is dominant and maintains discipline and coherence of the
flock. He leads the group but shares leadership on a foraging expedition
with a mature she-goat who will normally outlast a succession of
dominant males. However, earlier work showed that leadership orders in goats were not related to age or dominance.
In sheep, position in a moving flock is highly correlated with social
dominance, but there is no definite study to show consistent voluntary
leadership by an individual.
In birds, dominant individuals preferentially select higher perches to
put themselves in the best position to detect and avoid predators, as
well as to display their dominance to other members of their own
species. It has been suggested that decision-taking about the actions of the group is commonly dissociated from social dominance.
When individuals seek high rank
Given
the benefits and costs of possessing a high rank within a hierarchical
group, there are certain characteristics of individuals, groups, and
environments that determine whether an individual will benefit from a
high rank. These include whether or not high rank gives them access to
valuable resources such as mates and food. Age, intelligence,
experience, and physical fitness can influence whether or not an
individual deems it worthwhile to pursue a higher ranking in the
hierarchy, which often comes at the expense of conflict. Hierarchy
results from interactions, group dynamics, and sharing of resources, so
group size and composition affect the dominance decisions of
high-ranking individuals. For example, in a large group with many males,
it may be difficult for the highest-ranking male to dominate all the
mating opportunities, so some mate sharing probably exists. These
opportunities available to subordinates reduce the likelihood of a
challenge to the dominant male: mating is no longer an all-or-nothing
game and the sharing is enough to placate most subordinates. Another
aspect that can determine dominance hierarchies is the environment. In
populations of Kenyan vervet monkeys,
high-ranking females have higher foraging success when the food
resources are clumped, but when food is distributed throughout an area
they lose their advantage, because subordinate females can acquire food
with less risk of encountering a dominant female.
Benefits
Foraging success
A benefit to high-ranking individuals is increased foraging
success and access to food resources. During times of water shortage
the highest-ranking vervet females have greater access than subordinates
females to water in tree holes. In chacma baboons,
the high-ranking males have the first access to vertebrate prey that
has been caught by the group, and in yellow baboons the dominant males
feed for longer without being interrupted.
In many bird species, the dominant individuals have higher rates of food intake. Such species include dark-eyed juncos and oystercatchers.
The dominant individuals in these groups fill themselves up first and
fill up more quickly, so they spend less time foraging, which reduces
the risk of predation. Thus they have increased survival because of
increased nutrition and decreased predation.
Reproductive success
In primates, a well-studied group, high rank brings reproductive success, as seen in a 1991 meta-analysis of 32 studies.
A 2016 study determined that higher status increased reproductive
success amongst men, and that this did not vary by type of subsistence
(foraging, horticulture, pastoralism, agriculture). This contradicts the
"egalitarian hypothesis", which predicts that status would affect
reproductive success more amongst foragers than amongst nonforagers.
High-ranking bonnet macaque
males have more access to fertile females and consequently partake in
most of the matings within the group; in one population, three males
were responsible for over 75% of matings. In this population, males
often vary in rank. As their rank improves, they gain more exclusive
time with fertile females; when their rank decreases, they get less
time. In many primates, including bonnet macaques and rhesus monkeys,
the offspring of high-ranking individuals have better fitness and thus
an increased rate of survival. This is most likely a function of two
factors: The first is that high-ranking males mate with high-ranking
females. Assuming their high rank is correlated with higher fitness and
fighting ability, this trait will be conferred to their offspring. The
second factor is that higher-ranking parents probably provide better
protection to their offspring and thus ensure higher survival rates.
Amongst rhesus macaques, higher-ranking males sired more offspring,
though the alpha male was never the one to sire the most offspring, with
that instead being a high-ranking but not top male. The complex
relationship between rank and reproduction in this species is likely
explained by the fact that rhesus macaques queue, rather than fight, for
dominance, meaning that the alpha male is not necessarily the strongest
or most attractive male.
In rodents, the highest-ranking male frequently sires the most
offspring. The same pattern is found in most carnivores, such as the dwarf mongoose.
The dwarf mongoose lives in a social system with one dominant pair. The
dominant female produces all or almost all of the offspring in the
living group, and the dominant male has first access to her during her
oestrus period. In red deer, the males who experienced winter dominance,
resulting from greater access to preferred foraging sites, had higher
ability to get and maintain larger harems during the mating season.
In many monogamous bird species, the dominant pairs tend to get
the best territories, which in turn promote offspring survival and adult
health. In dunnocks, a species of bird that experiences many mating
systems, sometimes individuals will form a group that will have one
dominant male who achieves all of the mating in the group.
In the monogynous bee species Melipona subnitida,
the queen seeks to maintain reproductive success by preventing workers
from caring for their cells, pushing or hitting them using her antennae.
Workers display aggression towards males, claiming priority over the
cells when males try to use them to place eggs.
Costs of being dominant
There
are costs to being of a high rank in a hierarchical group which offset
the benefits. The most common costs to high-ranking individuals are
higher metabolic rates and higher levels of stress hormones. In great tits and pied flycatchers,
high-ranking individuals experience higher resting metabolic rates and
therefore need to consume more food in order to maintain fitness and
activity levels compared to subordinates in their groups. The energetic
costs of defending territory, mates, and other resources can be very
consuming and cause high-ranking individuals, who spend more time in
these activities, to lose body mass over long periods of dominance.
Therefore, their physical condition decreases the longer they spend
partaking in these high-energy activities, and they lose rank as a
function of age.
In wild male baboons, the highest-ranking male, also known as the
alpha, experiences high levels of both testosterone and glucocorticoid,
which indicates that high-ranking males undergo higher levels of stress
which reduces fitness. Reduced health and longevity occurs because
these two hormones have immunosuppressant activity, which reduces
survival and presents opportunities for parasitic infestation and other
health risks. This reduced fitness due to the alpha position results in
individuals maintaining high rank for shorter periods of time and having
an overall reduced health and longevity from the physical strain and
costs of the position.
Interpersonal complementarity hypothesis
The interpersonal complementarity hypothesis suggests that obedience
and authority are reciprocal, complementary processes. That is, it
predicts that one group member's behaviours will elicit a predictable
set of actions from other group members. Friendly behaviours are
predicted to be met with friendly behaviours, and hostile behaviours are
predicted to be reciprocated with similar, hostile behaviours. When an
individual acts in a dominant, authoritative manner in a group, this
behaviour tends to prompt submissive responses from other group members.
Similarly, when group members display submissive behaviour, others feel
inclined to display dominant behaviours in return. Tiedens and Fragale
(2003) found that hierarchical differentiation plays a significant role
in liking behaviour in groups. Individuals prefer to interact with other
group members whose power, or status behaviour complements their own.
That is to say, group members who behave submissively when talking to
someone who appears to be in control are better liked, and similarly
individuals who display dominant behaviours (e.g., taking charge,
issuing orders) are more liked when interacting with docile, subservient
individuals.
Subordinance
Benefits
Being
subordinate offers a number of benefits. Subordination is beneficial in
agonistic conflicts where rank predicts the outcome of a fight. Less
injury will occur if subordinate individuals avoid fighting with
higher-ranking individuals who would win a large percentage of the time —
knowledge of the pecking order keeps both parties from incurring the
costs of a prolonged fight. In hens, it has been observed that both
dominants and subordinates benefit from a stable hierarchical
environment, because fewer challenges means more resources can be
dedicated to laying eggs. In groups of highly related individuals, kin
selection may influence the stability of hierarchical dominance. A
subordinate individual closely related to the dominant individual may
benefit more genetically by assisting the dominant individual to pass on
their genes.
Alpha male savanna baboons have high levels of testosterone
and stress; over a long period of time, this can lead to decreased
fitness. The lowest-ranking males also had high stress levels,
suggesting that it is the beta males that gain the most fitness,
avoiding stress but receiving some of the benefits of moderate rank.
The mating tactics of savanna baboons are correlated with their age.
Older, subordinate males form alliances to combat higher-ranking males
and get access to females.
Fighting with dominant males is a risky behavior that may result in defeat, injury or even death. In bighorn sheep,
however, subordinates occasionally win a fight for a female, and they
father 44% of the lambs born in the population. These sheep live in
large flocks, and dominance hierarchies are often restructured each
breeding season.
Burying beetles,
which have a social order involving one dominant male controlling most
access to mates, display a behavior known as sneak copulation. While one
male at a carcass has a 5:1 mating advantage, subordinate males will
tempt females away from the carcass with pheromones and attempt to copulate before the dominant male can drive them forcefully away. In flat lizards,
young males take advantage of their underdeveloped secondary sex
characteristics to engage in sneak copulations. These young males mimic
all the visual signs of a female lizard in order to successfully
approach a female and copulate without detection by the dominant male.
This strategy does not work at close range because the chemical signals
given off by the sneaky males reveal their true nature, and they are
chased out by the dominant.
Costs to subordinates
Subordinate
individuals suffer a range of costs from dominance hierarchies, one of
the most notable being reduced access to food sources. When a resource
is obtained, dominant individuals are first to feed as well as taking
the longest time. Subordinates also lose out in shelter and nesting
sites. Brown hyenas,
which display defined linear dominance in both sexes, allow subordinate
males and females decreased time of feeding at a carcass. In toque monkeys
subordinates are often displaced from feeding sites by dominant males.
Additionally, they are excluded from sleeping sites, and they suffer
reduced growth and increased mortality.
Subordinate individuals often demonstrate a huge reproductive
disadvantage in dominance hierarchies. Among brown hyenas, subordinate
females have less opportunity to rear young in the communal den, and
thus had decreased survival of offspring when compared to high-ranking
individuals. Subordinate males have far less copulations with females
compared to the high-ranking males. In African wild dogs
which live in social packs separated into male and female hierarchies,
top-ranking alpha females have been observed to produce 76–81% of all
litters.
Mitigating the costs
Subordinate
animals engage in a number of behaviors in order to outweigh the costs
of low rank. Dispersal is often associated with increased mortality and
subordination may decrease the potential benefits of leaving the group.
In the red fox
it has been shown that subordinate individuals, given the opportunity
to desert, often do not due to the risk of death and the low possibility
that they would establish themselves as dominant members in a new
group.
Conflict over dominance
Animal
decisions regarding involvement in conflict are defined by the
interplay between the costs and benefits of agonistic behaviors. When
initially developed, game theory,
the study of optimal strategies during pair-wise conflict, was grounded
in the false assumption that animals engaged in conflict were of equal
fighting ability. Modifications, however, have provided increased focus
on the differences between the fighting capabilities of animals and
raised questions about their evolutionary development. These differences
are believed to determine the outcomes of fights, their intensity, and
animal decisions to submit or continue fighting. The influence of
aggression, threats, and fighting on the strategies of individuals
engaged in conflict has proven integral to establishing social
hierarchies reflective of dominant-subordinate interactions.
The asymmetries between individuals have been categorized into three types of interactions:
- Resource-holding potential: Animals that are better able to defend resources often win without much physical contact.
- Resource value: Animals more invested in a resource are likely to
invest more in the fight despite potential for incurring higher costs.
- Intruder retreats: When participants are of equal fighting ability and competing for a certain territory,
the resident of the territory is likely to end as the victor because he
values the territory more. This can be explained further by looking at
the example of the common shrews.
If one participant believes he is the resident of the territory, he
will win when the opponent is weaker or food is scarce. However, if both
shrews believe they are the true territory holder, the one with the
greater need for food, and therefore, the one that values the resource
more, is most likely to win.
As expected, the individual who emerges triumphant is rewarded with
the dominant status, having demonstrated their physical superiority.
However, the costs incurred to the defeated, which include loss of
reproductive opportunities and quality food, can hinder the individual's
fitness. In order to minimize these losses, animals generally retreat
from fighting or displaying fighting ability unless there are obvious
cues indicating victory. These often involve characteristics that
provide an advantage during agonistic behavior, such as size of body,
displays, etc. Red stags, for example, engage in exhausting roaring contests to exhibit their strength.
However, such an activity would impose more costs than benefits for
unfit stags, and compel them to retreat from the contest. Larger stags
have also been known to make lower-frequency threat signals, acting as
indicators of body size, strength, and dominance.
Engaging in agonistic behavior can be very costly and thus there
are many examples in nature of animals who achieve dominance in more
passive ways. In some, the dominance status of an individual is clearly
visible, eliminating the need for agonistic behavior. In wintering bird
flocks, white-crowned sparrows
display a unique white plumage; the higher the percentage of the crown
that consists of white feathers, the higher the status of the
individual.
For other animals, the time spent in the group serves as a determinant
of dominance status. Rank may also be acquired from maternal dominance
rank. In rhesus monkeys,
offspring gain dominance status based on the rank of the mother—the
higher ranked the mother, the higher ranked the offspring will be
(Yahner). Similarly, the status of a male Canada goose
is determined by the rank of his family. Although dominance is
determined differently in each case, it is influenced by the
relationships between members of social groups.
Regulation mechanisms
Individuals with greater hierarchical status tend to displace those ranked lower from access to space, to food and to mating opportunities. Thus, individuals with higher social status tend to have greater reproductive success by mating more often and having more resources to invest in the survival of offspring.
Hence, hierarchy serves as an intrinsic factor for population control,
ensuring adequate resources for the dominant individuals and thus
preventing widespread starvation. Territorial behavior enhances this effect.
In eusocial animals
The suppression of reproduction by dominant individuals is the most common mechanism that maintains the hierarchy. In eusocial mammals
this is mainly achieved by aggressive interactions between the
potential reproductive females. In eusocial insects, aggressive
interactions are common determinants of reproductive status, such as in
the bumblebee Bombus bifarius, the paper wasp Polistes annularis and in the ants Dinoponera australis and D. quadriceps.
In general, aggressive interactions are ritualistic and involve
antennation (drumming), abdomen curling and very rarely mandible bouts
and stinging. The winner of the interaction may walk over the
subordinated, that in turn assumes a prostrated posture. To be
effective, these regulatory mechanisms must include traits that make an
individual rank position readily recognizable by its nestmates. The
composition of the lipid layer on the cuticle
of social insects is the clue used by nestmates to recognize each other
in the colony, and to discover each insect's reproductive status (and
rank). Visual cues may also transmit the same information. Paper wasps Polistes dominulus
have individual "facial badges" that permit them to recognize each
other and to identify the status of each individual. Individuals whose
badges were modified by painting were aggressively treated by their
nestmates; this makes advertising a false ranking status costly, and may
help to suppress such advertising.
Other behaviors are involved in maintaining reproductive status in social insects. The removal of a thoracic sclerite in Diacamma
ants inhibits ovary development; the only reproductive individual of
this naturally queenless genus is the one that retains its sclerite
intact. This individual is called a gamergate, and is responsible for mutilating all the newly emerged females, to maintain its social status. Gamergates of Harpegnathos saltator arise from aggressive interactions, forming a hierarchy of potential reproductives.
In the honey bee Apis mellifera, a pheromone produced by the queen mandibular glands is responsible for inhibiting ovary development in the worker caste. "Worker policing" is an additional mechanism that prevents reproduction by workers, found in bees and ants. Policing may involve oophagy and immobilization of workers who lay eggs. In some ant species such as the carpenter ant Camponotus floridanus,
eggs from queens have a peculiar chemical profile that workers can
distinguish from worker laid eggs. When worker-laid eggs are found, they
are eaten. In some species, such as Pachycondyla obscuricornis, workers may try to escape policing by shuffling their eggs within the egg pile laid by the queen.
Hormonal control
Modulation of hormone levels after hibernation may be associated with dominance hierarchies in the social order of the paper wasp (Polistes dominulus).
This depends on the queen (or foundress), possibly involving specific
hormones. Laboratory experiments have shown that when foundresses are
injected with juvenile hormone,
responsible for regulating growth and development in insects including
wasps, the foundresses exhibit an increase in dominance. Further, foundresses with larger corpora allata,
a region of the female wasp brain responsible for the synthesis and
secretion of juvenile hormone, are naturally more dominant.
A follow-up experiment utilized 20-hydroxyecdysone, an ecdysone known to enhance maturation and size of oocytes. The size of the oocytes plays a significant role in establishing dominance in the paper wasp.
Foundresses treated with 20-hydroxyecdysone showed increased dominance
compared to those treated with juvenile hormone, so 20-hydroxyecdysone
may play a larger role in establishing dominance (Roseler et al.,
1984). Subsequent research however, suggests that juvenile hormone is
implicated, though only on certain individuals. When injected with
juvenile hormone, larger foundresses showed more mounting behaviors than
smaller ones, and more oocytes in their ovaries.
Naked mole-rats (Heterocephalus glaber)
similarly have a dominance hierarchy dependent on the highest ranking
female (queen) and her ability to suppress critically important
reproductive hormones in male and female sub-dominants. In sub-dominant
males, it appears that luteinizing hormone and testosterone are suppressed, while in females it appears that the suppression involves the entire suppression of the ovarian cycle. This suppression reduces sexual virility and behavior and thus redirects the sub-dominant's behavior into helping the queen with her offspring, though the mechanisms of how this is accomplished are debated. Former research suggests that primer pheromones
secreted by the queen cause direct suppression of these vital
reproductive hormones and functions however current evidence suggests
that it is not the secretion of pheromones which act to suppress
reproductive function but rather the queen's extremely high levels of
circulating testosterone, which cause her to exert intense dominance and
aggressiveness on the colony and thus "scare" the other mole-rats into submission.
Research has shown that removal of the queen from the colony allows the
reestablishment of reproductive function in sub-dominant individuals.
To see if a priming pheromone secreted by the queen was indeed causing
reproductive suppression, researchers removed the queen from the colony
but did not remove her bedding. They reasoned that if a primer
pheromones were on the bedding then the sub-dominant's reproductive
function should continue to be suppressed. Instead however, they found
that the sub-dominants quickly regained reproductive function even in
the presence of the queen's bedding and thus it was concluded that
primer pheromones do not seem to play a role in suppressing reproductive
function.
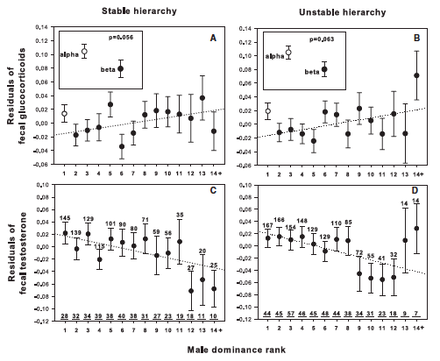
Glucocorticoids, signaling molecules which stimulate the fight or flight response,
may be implicated in dominance hierarchies. Higher ranking individuals
tend to have much higher levels of circulating glucocorticoids than subdominant individuals, the opposite of what had been expected. Two core hypotheses attempt to explain this.
The first suggests that higher ranking individuals exert more energy and thus need higher levels of glucocorticoids to mobilize glycogen for energy use. This is supported by the fact that when food availability is low, cortisol levels increase within the dominant male. The second suggests that elevated stress hormones
are a result of social factors, particularly when the hierarchy is in
transition, perhaps resulting in increased aggression and confrontation.
As a result, the dominant individual fights more and has elevated
glucocorticoids during this period. Field studies of olive baboons in Kenya
seem to support this, as dominant individuals had lower cortisol levels
in a stable hierarchy than did subdominant individuals, but the reverse
was true at unstable times.
Brain pathways and hierarchy
Several
areas of the brain contribute to hierarchical behavior in animals. One
of the areas that has been linked with this behavior is the prefrontal cortex,
a region involved with decision making and social behavior. High social
rank in a hierarchical group of mice has been associated with increased
excitability in the medial prefrontal cortex of pyramidal neurons, the primary excitatory cell type of the brain. High ranking macaques have a larger rostral prefrontal cortex in large social groups. Neuroimaging studies with computer stimulated hierarchal conditions showed increased activity in the ventral and dorsolateral
prefrontal cortex, one processing judgment cues and the other
processing status of an individual. Other studies have determined that
lesions to the prefrontal cortex (when the area is severed to disrupt
functioning to observe its role in behavior) led to deficits in
processing social hierarchy cues, suggesting this area is important in
regulating this information.
Although the prefrontal cortex has been implicated, there are other
downstream targets of the prefrontal cortex that have also been linked
in maintaining this behavior. This includes the amygdala
through lesion studies in rats and primates which led to disruption in
hierarchy, and can affect the individual negatively or positively
depending on the subnuclei that is targeted. Additionally, the dorsal
medial PFC-medial dorsal thalamus connection has been linked with maintenance of rank in mice. Another area that has been associated is the dorsal raphe nucleus, the primary serotonergic
nuclei (a neurotransmitter involved with many behaviors including
reward and learning). In manipulation studies of this region, there were
changes in fighting and affiliative behavior in primates and
crustaceans.
In specific groups
Female dominance in mammals
The
bonobo is one of the few mammals with female-biased dominance.
Female-biased dominance occurs rarely in mammals. It occurs when all
adult males exhibit submissive behavior to adult females in social
settings. These social settings are usually related to feeding,
grooming, and sleeping site priority. It is observed consistently in hyenas, lemurs and the bonobo. The ring-tailed lemur is observed to be the most prominent model of female dominance.
There are three basic proposals for the evolution of female dominance:
- The Energy Conservation Hypothesis: males subordinate to females
to conserve energy for intense male-male competition experienced during
very short breeding seasons
- Female behavioral strategy: dominance helps females deal with the
unusually high reproductive demands; they prevail in more social
conflicts because they have more at stake in terms of fitness.
- Male behavioral strategy: males defer as a parental investment
because it ensures more resources in a harsh unpredictable climate for
the female, and thus, the male's future offspring.
In lemurs, no single hypothesis fully explains female social dominance at this time and all three are likely to play a role. Adult female lemurs have increased concentrations of androgens when they transition from non-breeding to breeding seasons, increasing female aggression.
Androgens are greater in pregnant female lemurs, which suggests that
organizational androgens might influence the developing offspring. Organizational androgens play a role in "explaining female social dominance" in ring-tailed lemurs, as androgens are associated with aggressive behavior in young females.
Females that were "exposed to greater concentrations of maternal
[androstenedione] late in fetal development were less likely to be
aggressed against postnatally, whereas females that were...exposed to
greater concentrations of maternal [testosterone]...were more likely to
receive aggression postnatally." Dominance rank in female chimpanzees is correlated with reproductive success. Although a high rank is an advantage for females, clear linear hierarchies in female chimpanzees have not been detected. In "masculinized" female mammals like the spotted hyena (Crocuta crocuta),
androgens (i.e. specifically, androstenedione and testosterone) are
"implicated in the organization and activation of...nonreproductive
behavioral traits, including aggression, social dominance,
rough-and-tumble play, and scent marking" For aggressively dominant female meerkats (Suricata suricatta), they have "exceptionally high concentrations" of androgens, "particularly during gestation".
Birds
Bottom-rank
chicken showing feather damage from pecking by other hens
The concept of dominance, originally called "pecking order", was described in birds by Thorleif Schjelderup-Ebbe in 1921 under the German terms Hackordnung or Hackliste and introduced into English in 1927. In his 1924 German-language article, he noted that "defense and aggression in the hen is accomplished with the beak".
This emphasis on pecking led many subsequent studies on fowl behaviour
to use it as a primary observation; however, it has been noted that roosters tend to leap and use their claws in conflicts.
Wild and feral chickens form relatively small groups, usually
including no more than 10 to 20 individuals. It has been shown that in
larger groups, which is common in farming, the dominance hierarchy
becomes less stable and aggression increases.
Dominance hierarchies are found in many species of bird. For example, the blue-footed booby
brood of two chicks always has a dominance hierarchy due to the
asynchronous hatching of the eggs. One egg is laid four days before the
other, and incubation starts immediately after laying, so the elder
chick is hatched four days before the younger chick and has a four-day
head start on growth. The elder, stronger chick almost always becomes
the dominant chick. During times of food shortage, the dominant chick
often kills the subordinate chick by either repeatedly pecking or by
ousting the younger chick from the nest. The brood hierarchy makes it
easier for the subordinate chick to die quietly in times of food
scarcity, which provides an efficient system for booby parents to
maximize their investment.
Eusocial insects
In insect societies,
only one to few individuals members of a colony can reproduce, whereas
the other colony members have their reproductive capabilities
suppressed. This conflict over reproduction in some cases results in a
dominance hierarchy. Dominant individuals in this case are known as
queens and have the obvious advantage of performing reproduction and
benefiting from all the tasks performed by their subordinates, the
worker caste (foraging, nest maintenance, nest defense, brood care and
thermal regulation). According to Hamilton's rule,
the reproduction costs of the worker caste are compensated by the
contribution of workers to the queen's reproductive success, with which
they share genes. This is true not only for the popular social insects (ants, termites, some bees and wasps), but also for the naked mole-rat Heterocephalus glaber. In a laboratory experiment, Clarke and Faulkes (1997) demonstrated that reproductive status in a colony of H. glaber
was correlated with the individual's ranking position within a
dominance hierarchy, but aggression between potential reproductives only
started after the queen was removed.
The social insects mentioned above, excluding termites, are haplodiploid. Queen and workers are diploid, but males develop from haploid genotypes. In some species, suppression of ovary development is not totally achieved in the worker caste, which opens the possibility of reproduction by workers. Since nuptial flights are seasonal and workers are wingless, workers are almost always non-breeders, and (as gamergate ants or laying worker bees)
can only lay unfertilised eggs. These eggs are in general viable,
developing into males. A worker that performs reproduction is considered
a "cheater" within the colony, because its success in leaving
descendants becomes disproportionally larger, compared to its sisters
and mother. The advantage of remaining functionally sterile is only
accomplished if every worker assume this "compromise". When one or more
workers start reproducing, the "social contract" is destroyed and the
colony cohesion is dissolved. Aggressive behavior derived from this
conflict may result in the formation of hierarchies, and attempts of
reproduction by workers are actively suppressed. In some wasps, such as Polistes fuscatus,
instead of not laying eggs, the female workers begin being able to
reproduce, but once being under the presence of dominant females, the
subordinate female workers can no longer reproduce.
In some wasp species such as Liostenogaster flavolineata
there are many possible queens that inhabit a nest, but only one can be
queen at a time. When a queen dies the next queen is selected by an
age-based dominance hierarchy. This is also true in the species Polistes instabilis, where the next queen is selected based on age rather than size. Polistes exclamans also exhibits this type of hierarchy. Within the dominance hierarchies of the Polistes versicolor,
however, the dominant-subordinate context in the yellow paper wasps is
directly related to the exchange of food. Future foundresses within the
nest compete over the shared resources of nourishment, such as protein.
Unequal nourishment is often what leads to the size differences that
result in dominant-subordinate position rankings. Therefore, if during
the winter aggregate, the female is able to obtain greater access to
food, the female could thus reach a dominant position.
In some species, especially in ants, more than one queen can be found in the same colony, a condition called polygyny.
In this case, another advantage of maintaining a hierarchy is to
prolong the colony lifespan. The top ranked individuals may die or lose
fertility and "extra queens" may benefit from starting a colony in the
same site or nest. This advantage is critical in some ecological
contexts, such as in situations where nesting sites are limited or
dispersal of individuals is risky due to high rates of predation. This
polygynous behavior has also been observed in some eusocial bees such as
Schwarziana quadripunctata. In this species, multiple queens of varying sizes are present. The larger, physogastric, queens typically control the nest, though a "dwarf" queen will take its place in the case of a premature death.
Variations
Spectrum of social systems
Dominance hierarchies emerge as a result of intersexual and intrasexual
selection within groups, where competition between individuals results
in differential access to resources and mating opportunities. This can
be mapped across a spectrum of social organization ranging from
egalitarian to despotic, varying across multiple dimensions of
cooperation and competition in between.
Conflict can be resolved in multiple ways, including aggression,
tolerance, and avoidance. These are produced by social decision-making,
described in the "relational model" created by the zoologist Frans De Waal.
In systems where competition between and within the sexes is low,
social behaviour gravitates towards tolerance and egalitarianism, such
as that found in woolley spider monkeys. In despotic systems where competition is high, one or two members are
dominant while all other members of the living group are equally
submissive, as seen in Japanese and rhesus macaques, leopard geckos, dwarf hamsters, gorillas, the cichlid Neolamprologus pulcher, and African wild dog.
Linear ranking systems, or "pecking orders", which tend to fall in
between egalitarianism and despotism, follow a structure where every
member of the group is recognized as either dominant or submissive
relative to every other member. This results in a linear distribution of
rank, as seen in spotted hyenas and brown hyenas.
Context dependency
Eringer cattle competing for dominance.
Dominance and its organisation can be highly variable depending on the context or individuals involved. In European badgers,
dominance relationships may vary with time as individuals age, gain or
lose social status, or change their reproductive condition. Dominance may also vary across space in territorial
animals as territory owners are often dominant over all others in their
own territory but submissive elsewhere, or dependent on the resource.
Even with these factors held constant, perfect dominance hierarchies are
rarely found in groups of any great size, at least in the wild.
Dominance hierarchies in small herds of domestic horses are generally
linear hierarchies whereas in large herds the relationships are
triangular. Dominance hierarchies can be formed at a very early age. Domestic piglets are highly precocious
and, within minutes of being born, or sometimes seconds, will attempt
to suckle. The piglets are born with sharp teeth and fight to develop a
teat order as the anterior teats produce a greater quantity of milk. Once established, this teat order remains stable with each piglet tending to feed from a particular teat or group of teats. Dominance–subordination relationships can vary markedly between breeds of the same species. Studies on Merinos and Border Leicesters
sheep revealed an almost linear hierarchy in the Merinos but a less
rigid structure in the Border Leicesters when a competitive feeding
situation was created.
Species with egalitarian/non-linear hierarchies
Although
many group-living animal species have a hierarchy of some form, some
species have more fluid and flexible social groupings, where rank does
not need to be rigidly enforced, and low-ranking group members may enjoy
a wider degree of social flexibility. Some animal societies are
"democratic", with low-ranking group members being able to influence
which group member is leader and which one is not. Sometimes dominant
animals must maintain alliances with subordinates and grant them favours
to receive their support in order to retain their dominant rank. In
chimpanzees, the alpha male may need to tolerate lower-ranking group
members hovering near fertile females or taking portions of his meals.
Other examples can include Muriqui monkeys. Within their groups, there
is abundant food and females will mate promiscuously. Because of this,
males gain very little in fighting over females, who are, in turn, too
large and strong for males to monopolize or control, so males do not
appear to form especially prominent ranks between them, with several
males mating with the same female in view of each other. This type of mating style is also present in manatees, removing their need to engage in serious fighting.
Among female elephants, leadership roles are not acquired by sheer
brute force, but instead through seniority, and other females can
collectively show preferences for where the herd can travel. In hamadryas baboons, several high-ranking males will share a similar rank, with no single male being an absolute leader. Female bats also have a somewhat fluid social structure, in which rank is not strongly enforced.
Bonobos are matriarchal, yet their social groups are also generally
quite flexible, and serious aggression is quite rare between them.
In olive baboons, certain animals are dominant in certain contexts, but
not in others. Prime age male olive baboons claim feeding priority, yet
baboons of any age or sex can initiate and govern the group's
collective movements.