| Gastrointestinal tract | |
|---|---|
 Diagram of the gastrointestinal tract in the average human | |
| Details | |
| System | Digestive system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus digestorius (mouth to anus), canalis alimentarius (esophagus to large intestine), canalis gastrointestinales stomach to large intestine) |
| MeSH | D041981 |
 |
| Major parts of the |
| Gastrointestinal tract |
|---|
|
|
|
|
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as faeces. Gastrointestinal is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines.
Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion.
The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is divided into the upper and lower gastrointestinal tracts. The GI tract includes all structures between the mouth and the anus, forming a continuous passageway that includes the main organs of digestion, namely, the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The complete human digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver and gallbladder). The tract may also be divided into foregut, midgut, and hindgut, reflecting the embryological origin of each segment. The whole human GI tract is about nine meters (30 feet) long at autopsy. It is considerably shorter in the living body because the intestines, which are tubes of smooth muscle tissue, maintain constant muscle tone in a halfway-tense state but can relax in spots to allow for local distention and peristalsis.
The gastrointestinal tract contains the gut microbiota, with some 1,000 different strains of bacteria having diverse roles in the maintenance of immune health and metabolism, and many other microorganisms. Cells of the GI tract release hormones to help regulate the digestive process. These digestive hormones, including gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, and ghrelin, are mediated through either intracrine or autocrine mechanisms, indicating that the cells releasing these hormones are conserved structures throughout evolution.
Human gastrointestinal tract
Structure

The structure and function can be described both as gross anatomy and as microscopic anatomy or histology. The tract itself is divided into upper and lower tracts, and the intestines small and large parts.
Upper gastrointestinal tract
The upper gastrointestinal tract consists of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The exact demarcation between the upper and lower tracts is the suspensory muscle of the duodenum. This differentiates the embryonic borders between the foregut and midgut, and is also the division commonly used by clinicians to describe gastrointestinal bleeding as being of either "upper" or "lower" origin. Upon dissection, the duodenum may appear to be a unified organ, but it is divided into four segments based on function, location, and internal anatomy. The four segments of the duodenum are as follows (starting at the stomach, and moving toward the jejunum): bulb, descending, horizontal, and ascending. The suspensory muscle attaches the superior border of the ascending duodenum to the jejunum.
The suspensory muscle is an important anatomical landmark that shows the formal division between the duodenum and the jejunum, the first and second parts of the small intestine, respectively. This is a thin muscle which is derived from the embryonic mesoderm.
Lower gastrointestinal tract
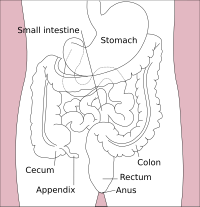
The lower gastrointestinal tract includes most of the small intestine and all of the large intestine. In human anatomy, the intestine (bowel or gut; Greek: éntera) is the segment of the gastrointestinal tract extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the anus and as in other mammals, consists of two segments: the small intestine and the large intestine. In humans, the small intestine is further subdivided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum while the large intestine is subdivided into the cecum, ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon, rectum, and anal canal.
Small intestine
The small intestine begins at the duodenum and is a tubular structure, usually between 6 and 7 m long. Its mucosal area in an adult human is about 30 m2 (320 sq ft). The combination of the circular folds, the villi, and the microvilli increases the absorptive area of the mucosa about 600-fold, making a total area of about 250 m2 (2,700 sq ft) for the entire small intestine. Its main function is to absorb the products of digestion (including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and vitamins) into the bloodstream. There are three major divisions:
- Duodenum: A short structure (about 20–25 cm long) that receives chyme from the stomach, together with pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes and bile from the gall bladder. The digestive enzymes break down proteins, and bile emulsifies fats into micelles. The duodenum contains Brunner's glands which produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion containing bicarbonate. These secretions, in combination with bicarbonate from the pancreas, neutralize the stomach acids contained in the chyme.
- Jejunum: This is the midsection of the small intestine, connecting the duodenum to the ileum. It is about 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long and contains the circular folds also known as plicae circulares and villi that increase its surface area. Products of digestion (sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids) are absorbed into the bloodstream here.
- Ileum: The final section of the small intestine. It is about 3 m long, and contains villi similar to the jejunum. It absorbs mainly vitamin B12 and bile acids, as well as any other remaining nutrients.
Large intestine
The large intestine, also called the colon, forms an arch starting at the cecum and ending at the rectum and anal canal. It also includes the appendix, which is attached to the cecum. Its length is about 1.5 m, and the area of the mucosa in an adult human is about 2 m2 (22 sq ft). Its main function is to absorb water and salts. The colon is further divided into:
- Cecum (first portion of the colon) and appendix
- Ascending colon (ascending in the back wall of the abdomen)
- Right colic flexure (flexed portion of the ascending and transverse colon apparent to the liver)
- Transverse colon (passing below the diaphragm)
- Left colic flexure (flexed portion of the transverse and descending colon apparent to the spleen)
- Descending colon (descending down the left side of the abdomen)
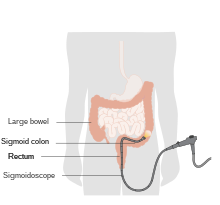
- Sigmoid colon (a loop of the colon closest to the rectum)
- Rectum
- Anal canal
Development
The gut is an endoderm-derived structure. At approximately the sixteenth day of human development, the embryo begins to fold ventrally (with the embryo's ventral surface becoming concave) in two directions: the sides of the embryo fold in on each other and the head and tail fold toward one another. The result is that a piece of the yolk sac, an endoderm-lined structure in contact with the ventral aspect of the embryo, begins to be pinched off to become the primitive gut. The yolk sac remains connected to the gut tube via the vitelline duct. Usually, this structure regresses during development; in cases where it does not, it is known as Meckel's diverticulum.
During fetal life, the primitive gut is gradually patterned into three segments: foregut, midgut, and hindgut. Although these terms are often used in reference to segments of the primitive gut, they are also used regularly to describe regions of the definitive gut as well.
Each segment of the gut is further specified and gives rise to specific gut and gut-related structures in later development. Components derived from the gut proper, including the stomach and colon, develop as swellings or dilatations in the cells of the primitive gut. In contrast, gut-related derivatives — that is, those structures that derive from the primitive gut but are not part of the gut proper, in general, develop as out-pouchings of the primitive gut. The blood vessels supplying these structures remain constant throughout development.
| Part | Part in adult | Gives rise to | Arterial supply |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foregut | esophagus to first 2 sections of the duodenum | Esophagus, stomach, duodenum (1st and 2nd parts), liver, gallbladder, pancreas, superior portion of pancreas (Though the spleen is supplied by the celiac trunk, it is derived from dorsal mesentery and therefore not a foregut derivative) |
celiac trunk |
| Midgut | lower duodenum, to the first two-thirds of the transverse colon | lower duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, appendix, ascending colon, and first two-thirds of the transverse colon | branches of the superior mesenteric artery |
| Hindgut | last third of the transverse colon, to the upper part of the anal canal | last third of the transverse colon, descending colon, rectum, and upper part of the anal canal | branches of the inferior mesenteric artery |
Histology

The gastrointestinal tract has a form of general histology with some differences that reflect the specialization in functional anatomy. The GI tract can be divided into four concentric layers in the following order:
Mucosa
The mucosa is the innermost layer of the gastrointestinal tract. The mucosa surrounds the lumen, or open space within the tube. This layer comes in direct contact with digested food (chyme). The mucosa is made up of:
- Epithelium – innermost layer. Responsible for most digestive, absorptive and secretory processes.
- Lamina propria – a layer of connective tissue. Unusually cellular compared to most connective tissue
- Muscularis mucosae – a thin layer of smooth muscle that aids the passing of material and enhances the interaction between the epithelial layer and the contents of the lumen by agitation and peristalsis
The mucosae are highly specialized in each organ of the gastrointestinal tract to deal with the different conditions. The most variation is seen in the epithelium.
Submucosa
The submucosa consists of a dense irregular layer of connective tissue with large blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves branching into the mucosa and muscularis externa. It contains the submucosal plexus, an enteric nervous plexus, situated on the inner surface of the muscularis externa.
Muscular layer
The muscular layer consists of an inner circular layer and a longitudinal outer layer. The circular layer prevents food from traveling backward and the longitudinal layer shortens the tract. The layers are not truly longitudinal or circular, rather the layers of muscle are helical with different pitches. The inner circular is helical with a steep pitch and the outer longitudinal is helical with a much shallower pitch. Whilst the muscularis externa is similar throughout the entire gastrointestinal tract, an exception is the stomach which has an additional inner oblique muscular layer to aid with grinding and mixing of food. The muscularis externa of the stomach is composed of the inner oblique layer, middle circular layer, and the outer longitudinal layer.
Between the circular and longitudinal muscle layers is the myenteric plexus. This controls peristalsis. Activity is initiated by the pacemaker cells, (myenteric interstitial cells of Cajal). The gut has intrinsic peristaltic activity (basal electrical rhythm) due to its self-contained enteric nervous system. The rate can be modulated by the rest of the autonomic nervous system.
The coordinated contractions of these layers is called peristalsis and propels the food through the tract. Food in the GI tract is called a bolus (ball of food) from the mouth down to the stomach. After the stomach, the food is partially digested and semi-liquid, and is referred to as chyme. In the large intestine, the remaining semi-solid substance is referred to as faeces.
Adventitia and serosa
The outermost layer of the gastrointestinal tract consists of several layers of connective tissue.
Intraperitoneal parts of the GI tract are covered with serosa. These include most of the stomach, first part of the duodenum, all of the small intestine, caecum and appendix, transverse colon, sigmoid colon and rectum. In these sections of the gut, there is a clear boundary between the gut and the surrounding tissue. These parts of the tract have a mesentery.
Retroperitoneal parts are covered with adventitia. They blend into the surrounding tissue and are fixed in position. For example, the retroperitoneal section of the duodenum usually passes through the transpyloric plane. These include the esophagus, pylorus of the stomach, distal duodenum, ascending colon, descending colon and anal canal. In addition, the oral cavity has adventitia.
Gene and protein expression
Approximately 20,000 protein coding genes are expressed in human cells and 75% of these genes are expressed in at least one of the different parts of the digestive organ system. Over 600 of these genes are more specifically expressed in one or more parts of the GI tract and the corresponding proteins have functions related to digestion of food and uptake of nutrients. Examples of specific proteins with such functions are pepsinogen PGC and the lipase LIPF, expressed in chief cells, and gastric ATPase ATP4A and gastric intrinsic factor GIF, expressed in parietal cells of the stomach mucosa. Specific proteins expressed in the stomach and duodenum involved in defence include mucin proteins, such as mucin 6 and intelectin-1.
Transit time
The time taken for food to transit through the gastrointestinal tract varies on multiple factors, including age, ethnicity, and gender. Several techniques have been used to measure transit time, including radiography following a barium-labeled meal, breath hydrogen analysis, scintigraphic analysis following a radiolabeled meal, and simple ingestion and spotting of corn kernels. It takes 2.5 to 3 hours for 50% of the contents to leave the stomach. The rate of digestion is also dependent of the material being digested, as food composition from the same meal may leave the stomach at different rates. Total emptying of the stomach takes around 4–5 hours, and transit through the colon takes 30 to 50 hours.
Immune function
The gastrointestinal tract forms an important part of the immune system.
Immune barrier
The surface area of the digestive tract is estimated to be about 32 square meters, or about half a badminton court. With such a large exposure (more than three times larger than the exposed surface of the skin), these immune components function to prevent pathogens from entering the blood and lymph circulatory systems. Fundamental components of this protection are provided by the intestinal mucosal barrier, which is composed of physical, biochemical, and immune elements elaborated by the intestinal mucosa. Microorganisms also are kept at bay by an extensive immune system comprising the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)
There are additional factors contributing to protection from pathogen invasion. For example, low pH (ranging from 1 to 4) of the stomach is fatal for many microorganisms that enter it. Similarly, mucus (containing IgA antibodies) neutralizes many pathogenic microorganisms. Other factors in the GI tract contribution to immune function include enzymes secreted in the saliva and bile.
Immune system homeostasis
Beneficial bacteria also can contribute to the homeostasis of the gastrointestinal immune system. For example, Clostridia, one of the most predominant bacterial groups in the GI tract, play an important role in influencing the dynamics of the gut's immune system. It has been demonstrated that the intake of a high fiber diet could be responsible for the induction of T-regulatory cells (Tregs). This is due to the production of short-chain fatty acids during the fermentation of plant-derived nutrients such as butyrate and propionate. Basically, the butyrate induces the differentiation of Treg cells by enhancing histone H3 acetylation in the promoter and conserved non-coding sequence regions of the FOXP3 locus, thus regulating the T cells, resulting in the reduction of the inflammatory response and allergies.
Intestinal microbiota
The large intestine contains multiple types of bacteria that can break down molecules the human body cannot process alone, demonstrating a symbiotic relationship. These bacteria are responsible for gas production at host–pathogen interface, which is released as flatulence. However, the primary function of the large intestine is water absorption from digested material (regulated by the hypothalamus) and the reabsorption of sodium and nutrients.
Beneficial intestinal bacteria compete with potentially harmful bacteria for space and "food", as the intestinal tract has limited resources. A ratio of 80–85% beneficial to 15–20% potentially harmful bacteria is proposed for maintaining homeostasis. An imbalanced ratio results in dysbiosis.
Detoxification and drug metabolism
Enzymes such as CYP3A4, along with the antiporter activities, are also instrumental in the intestine's role of drug metabolism in the detoxification of antigens and xenobiotics.
Other animals
In most vertebrates, including fishes, amphibians, birds, reptiles, and egg-laying mammals, the gastrointestinal tract ends in a cloaca and not an anus. In the cloaca, the urinary system is fused with the genito-anal pore. Therians (all mammals that do not lay eggs, including humans) possess separate anal and uro-genital openings. The females of the subgroup Placentalia have even separate urinary and genital openings.
During early development, the asymmetric position of the bowels and inner organs is initiated (see also axial twist theory).
Ruminants show many specializations for digesting and fermenting tough plant material, consisting of additional stomach compartments.
Many birds and other animals have a specialised stomach in the digestive tract called a gizzard used for grinding up food.
Another feature found in a range of animals is the crop. In birds this is found as a pouch alongside the esophagus.
In 2020, the oldest known fossil digestive tract, of an extinct wormlike organism in the Cloudinidae was discovered; it lived during the late Ediacaran period about 550 million years ago.
A through-gut (one with both mouth and anus) is thought to have evolved within the nephrozoan clade of Bilateria, after their ancestral ventral orifice (single, as in cnidarians and acoels; re-evolved in nephrozoans like flatworms) stretched antero-posteriorly, before the middle part of the stretch would get narrower and closed fully, leaving an anterior orifice (mouth) and a posterior orifice (anus plus genital opening). A stretched gut without the middle part closed is present in another branch of bilaterians, the extinct proarticulates. This and the amphistomic development (when both mouth and anus develop from the gut stretch in the embryo) present in some nephrozoans (e.g. roundworms) are considered to support this hypothesis.
Clinical significance
Diseases
There are many diseases and conditions that can affect the gastrointestinal system, including infections, inflammation and cancer.
Various pathogens, such as bacteria that cause foodborne illnesses, can induce gastroenteritis which results from inflammation of the stomach and small intestine. Antibiotics to treat such bacterial infections can decrease the microbiome diversity of the gastrointestinal tract, and further enable inflammatory mediators. Gastroenteritis is the most common disease of the GI tract.
- Gastrointestinal cancer may occur at any point in the gastrointestinal tract, and includes mouth cancer, tongue cancer, oesophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and colorectal cancer.
- Inflammatory conditions. Ileitis is an inflammation of the ileum, colitis is an inflammation of the large intestine.
- Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix located at the caecum. This is a potentially fatal condition if left untreated; most cases of appendicitis require surgical intervention.
Diverticular disease is a condition that is very common in older people in industrialized countries. It usually affects the large intestine but has been known to affect the small intestine as well. Diverticulosis occurs when pouches form on the intestinal wall. Once the pouches become inflamed it is known as diverticulitis.
Inflammatory bowel disease is an inflammatory condition affecting the bowel walls, and includes the subtypes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. While Crohn's can affect the entire gastrointestinal tract, ulcerative colitis is limited to the large intestine. Crohn's disease is widely regarded as an autoimmune disease. Although ulcerative colitis is often treated as though it were an autoimmune disease, there is no consensus that it actually is such.
Functional gastrointestinal disorders the most common of which is irritable bowel syndrome. Functional constipation and chronic functional abdominal pain are other functional disorders of the intestine that have physiological causes but do not have identifiable structural, chemical, or infectious pathologies.
Symptoms
Several symptoms can indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract, including:
- Vomiting, which may include regurgitation of food or the vomiting of blood
- Diarrhea, or the passage of liquid or more frequent stools
- Constipation, which refers to the passage of fewer and hardened stools
- Blood in stool, which includes fresh red blood, maroon-coloured blood, and tarry-coloured blood
Treatment
Gastrointestinal surgery can often be performed in the outpatient setting. In the United States in 2012, operations on the digestive system accounted for 3 of the 25 most common ambulatory surgery procedures and constituted 9.1 percent of all outpatient ambulatory surgeries.
Imaging
Various methods of imaging the gastrointestinal tract include the upper and lower gastrointestinal series:
- Radioopaque dyes may be swallowed to produce a barium swallow
- Parts of the tract may be visualised by camera. This is known as endoscopy if examining the upper gastrointestinal tract and colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy if examining the lower gastrointestinal tract. Capsule endoscopy is where a capsule containing a camera is swallowed in order to examine the tract. Biopsies may also be taken when examined.
- An abdominal x-ray may be used to examine the lower gastrointestinal tract.
Other related diseases
- Cholera
- Enteric duplication cyst
- Giardiasis
- Pancreatitis
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Yellow fever
- Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative spiral bacterium. Over half the world's population is infected with it, mainly during childhood; it is not certain how the disease is transmitted. It colonizes the gastrointestinal system, predominantly the stomach. The bacterium has specific survival conditions that are specific to the human gastric microenvironment: it is both capnophilic and microaerophilic. Helicobacter also exhibits a tropism for gastric epithelial lining and the gastric mucosal layer about it. Gastric colonization of this bacterium triggers a robust immune response leading to moderate to severe inflammation, known as gastritis. Signs and symptoms of infection are gastritis, burning abdominal pain, weight loss, loss of appetite, bloating, burping, nausea, bloody vomit, and black tarry stools. Infection can be detected in a number of ways: GI X-rays, endoscopy, blood tests for anti-Helicobacter antibodies, a stool test, and a urease breath test (which is a by-product of the bacteria). If caught soon enough, it can be treated with three doses of different proton pump inhibitors as well as two antibiotics, taking about a week to cure. If not caught soon enough, surgery may be required.
- Intestinal pseudo-obstruction is a syndrome caused by a malformation of the digestive system, characterized by a severe impairment in the ability of the intestines to push and assimilate. Symptoms include daily abdominal and stomach pain, nausea, severe distension, vomiting, heartburn, dysphagia, diarrhea, constipation, dehydration and malnutrition. There is no cure for intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Different types of surgery and treatment managing life-threatening complications such as ileus and volvulus, intestinal stasis which lead to bacterial overgrowth, and resection of affected or dead parts of the gut may be needed. Many patients require parenteral nutrition.
- Ileus is a blockage of the intestines.
- Coeliac disease is a common form of malabsorption, affecting up to 1% of people of northern European descent. An autoimmune response is triggered in intestinal cells by digestion of gluten proteins. Ingestion of proteins found in wheat, barley and rye, causes villous atrophy in the small intestine. Lifelong dietary avoidance of these foodstuffs in a gluten-free diet is the only treatment.
- Enteroviruses are named by their transmission-route through the intestine (enteric meaning intestinal), but their symptoms are not mainly associated with the intestine.
- Endometriosis can affect the intestines, with similar symptoms to IBS.
- Bowel twist (or similarly, bowel strangulation) is a comparatively rare event (usually developing sometime after major bowel surgery). It is, however, hard to diagnose correctly, and if left uncorrected can lead to bowel infarction and death. (The singer Maurice Gibb is understood to have died from this.)
- Angiodysplasia of the colon
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Hirschsprung's disease (aganglionosis)
- Intussusception
- Polyp (medicine) (see also colorectal polyp)
- Pseudomembranous colitis
- Toxic megacolon usually a complication of ulcerative colitis
Uses of animal guts
Intestines from animals other than humans are used in a number of ways. From each species of livestock that is a source of milk, a corresponding rennet is obtained from the intestines of milk-fed calves. Pig and calf intestines are eaten, and pig intestines are used as sausage casings. Calf intestines supply calf-intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIP), and are used to make goldbeater's skin. Other uses are:
- The use of animal gut strings by musicians can be traced back to the third dynasty of Egypt. In the recent past, strings were made out of lamb gut. With the advent of the modern era, musicians have tended to use strings made of silk, or synthetic materials such as nylon or steel. Some instrumentalists, however, still use gut strings in order to evoke the older tone quality. Although such strings were commonly referred to as "catgut" strings, cats were never used as a source for gut strings.
- Sheep gut was the original source for natural gut string used in racquets, such as for tennis. Today, synthetic strings are much more common, but the best gut strings are now made out of cow gut.
- Gut cord has also been used to produce strings for the snares that provide a snare drum's characteristic buzzing timbre. While the modern snare drum almost always uses metal wire rather than gut cord, the North African bendir frame drum still uses gut for this purpose.
- "Natural" sausage hulls, or casings, are made of animal gut, especially hog, beef, and lamb.
- The wrapping of kokoretsi, gardoubakia, and torcinello is made of lamb (or goat) gut.
- Haggis is traditionally boiled in, and served in, a sheep stomach.
- Chitterlings, a kind of food, consist of thoroughly washed pig's gut.
- Animal gut was used to make the cord lines in longcase clocks and for fusee movements in bracket clocks, but may be replaced by metal wire.
- The oldest known condoms, from 1640 AD, were made from animal intestine.