| RNA silencing suppressor p19 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
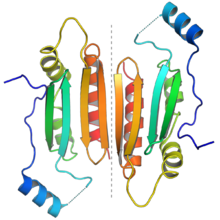 The protein dimer formed by two p19 molecules. Each monomer is colored from N-terminus (blue) to C-terminus
(red) to illustrate the end-to-end orientation of the dimer. The dotted
gray line in the center highlights the dimer interface. From PDB: 1R9F. | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| Symbol | Tombus_p19 | ||
| Pfam | PF03220 | ||
| InterPro | IPR004905 | ||
|
RNA silencing suppressor p19 (also known as Tombusvirus P19 core protein and 19 kDa symptom severity modulator) is a protein expressed from the ORF4 gene in the genome of tombusviruses. These viruses are positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses that infect plant cells, in which RNA silencing forms a widespread and robust antiviral defense system. The p19 protein serves as a counter-defense strategy, specifically binding the 19- to 21-nucleotide double-stranded RNAs that function as small interfering RNA (siRNA) in the RNA silencing system. By sequestering siRNA, p19 suppresses RNA silencing and promotes viral proliferation. The p19 protein is considered a significant virulence factor and a component of an evolutionary arms race between plants and their pathogens.
Structure
The p19 protein received its name from its size, being approximately 19 kilodaltons. It forms a functional homodimer. The crystal structures are available of p19 proteins from the tomato bushy stunt virus and Carnation Italian ringspot virus; the protein consists of a novel protein fold and exemplifies a previously unknown mechanism for binding RNA, using a binding surface formed by a beta sheet and flanked by alpha helices to interact with double-stranded RNAs of around 21 nucleotides in length in a non-sequence-specific manner.
Function
The p19 protein binds to double-stranded RNAs that function as short interfering RNA (siRNA) and is specialized for the 21-nucleotide product of the enzyme DCL4 (a member of a family of plant enzymes with homology to Dicer). By binding to siRNA, p19 sequesters these species and prevents them from interacting with the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), a protein complex that mediates the antiviral RNA silencing mechanism in the cell.
The p19 protein is also capable of binding to microRNA molecules that are endogenous to the host cell, as well as the siRNAs that are ultimately derived from the virus's own genome. Notably, an exception to this pattern is p19's inefficiency in interacting with the microRNA miR-168, a regulatory non-coding RNA that represses expression of argonaute-1 (AGO1). The AGO1 protein is required for RNA silencing, thus selectively sparing its repressor from p19's general sequestration of miRNA has the effect of reducing cellular AGO1 levels and is an additional mechanism by which p19 inhibits silencing. The two mechanisms are independent of one another and can be selectively abrogated by mutations.
Evolution
The gene encoding the p19 protein is an example of an overprinted gene, a genomic arrangement common in viruses in which multiple genes are encoded by the same portion of the genome read in alternate reading frames. The open reading frame ORF4, which encodes p19, is completely contained within the open reading frame of another gene, which is designated ORF3 and encodes the movement protein p22. Both genes, and their relative positions, are conserved within the tombusvirus family. P19 is thought to have originated de novo in this lineage.
Sequestration of dsRNA is a common viral counter-defense strategy against RNA silencing, evolved in a form of evolutionary arms race between virus and host. The p19 protein is not unique in this role; in an example of convergent evolution, this strategy appears to have evolved at least three times in distinct viral lineages using proteins with distinct structures and physical means of binding RNA.
History
The tomato bushy stunt virus, which is the type species of the tombusvirus family, is a long-standing model system for the study of plant viruses. The open reading frame encoding p19 was originally discovered in the late 1980s when the virus's genome was sequenced; it was subsequently demonstrated that the predicted protein was indeed expressed from the gene, although its role in promoting virulence and infectivity was initially underappreciated. Following the elucidation of its role as a suppressor of RNA silencing, p19 has also been used as a tool in molecular biology research on RNA silencing, RNA interference, and related processes.

