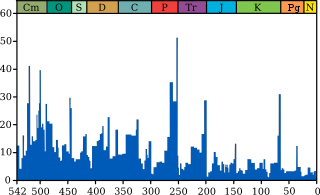
The blue graph shows the apparent
percentage (not the absolute number) of marine
animal genera becoming extinct during any given time interval. It does not represent all marine species, just those that are readily fossilized. The labels of the "Big Five" extinction events are clickable hyperlinks; see
Extinction event for more details.
(source and image info)
An
extinction (
level)
event (also known as a
mass extinction or
biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the amount of life on
Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp change in the diversity and abundance of macroscopic life. It occurs when the rate of
extinction increases with respect to the rate of
speciation. Because the majority of diversity and
biomass on Earth is
microbial, and thus difficult to measure, recorded extinction events affect the
easily observed, biologically complex component of the
biosphere rather than the
total diversity and abundance of life.
[1]
Although there are 10–14 million
species of
life currently on the Earth,
[2] more than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on the planet are estimated to be extinct.
[3][4][5]
Extinction occurs at an uneven rate. Based on the
fossil record, the
background rate of extinctions on Earth is about two to five
taxonomic families of marine
invertebrates and
vertebrates every million years. Marine fossils are mostly used to measure extinction rates because of their superior fossil record and stratigraphic range compared to land organisms.
Since life began on Earth, several major mass extinctions have significantly exceeded the background extinction rate. The most recent, the
Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, which occurred approximately 66 million years ago (Ma), was a large-scale mass extinction of animal and plant species in a geologically short period of time. In the past 540 million years there have been five major events when over 50% of animal species died. Mass extinctions seem to be a
Phanerozoic phenomenon, with extinction rates low before large complex organisms arose.
[6]
Estimates of the number of major mass extinctions in the last 540 million years range from as few as five to more than twenty. These differences stem from the threshold chosen for describing an extinction event as "major", and the data chosen to measure past diversity.
Major extinction events
In a landmark paper published in 1982,
Jack Sepkoski and
David M. Raup identified five mass extinctions. They were originally identified as outliers to a general trend of decreasing extinction rates during the Phanerozoic,
[7] but as more stringent statistical tests have been applied to the accumulating data, the "Big Five" cannot be so clearly defined, but rather appear to represent the largest (or some of the largest) of a relatively smooth continuum of extinction events.
[7]
- Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (End Cretaceous, K-T extinction, or K-Pg extinction): 66 Ma at the Cretaceous(Maastrichtian)-Paleogene(Danian) transition interval.[8] The K–T event is now officially called the Cretaceous–Paleogene (or K–Pg) extinction event in place of Cretaceous-Tertiary. About 17% of all families, 50% of all genera[9] and 75% of all species became extinct.[10] In the seas it reduced the percentage of sessile animals to about 33%. All non-avian dinosaurs became extinct during that time.[11] The boundary event was severe with a significant amount of variability in the rate of extinction between and among different clades. Mammals and birds emerged as dominant land vertebrates in the age of new life.
- Triassic–Jurassic extinction event (End Triassic): 201.3 Ma at the Triassic-Jurassic transition. About 23% of all families, 48% of all genera (20% of marine families and 55% of marine genera) and 70% to 75% of all species went extinct.[9] Most non-dinosaurian archosaurs, most therapsids, and most of the large amphibians were eliminated, leaving dinosaurs with little terrestrial competition. Non-dinosaurian archosaurs continued to dominate aquatic environments, while non-archosaurian diapsids continued to dominate marine environments. The Temnospondyl lineage of large amphibians also survived until the Cretaceous in Australia (e.g., Koolasuchus).
- Permian–Triassic extinction event (End Permian): 252 Ma at the Permian-Triassic transition. Earth's largest extinction killed 57% of all families, 83% of all genera and 90% to 96% of all species[9] (53% of marine families, 84% of marine genera, about 96% of all marine species and an estimated 70% of land species, including insects).[12] The evidence of plants is less clear, but new taxa became dominant after the extinction.[13] The "Great Dying" had enormous evolutionary significance: on land, it ended the primacy of mammal-like reptiles. The recovery of vertebrates took 30 million years,[14] but the vacant niches created the opportunity for archosaurs to become ascendant. In the seas, the percentage of animals that were sessile dropped from 67% to 50%. The whole late Permian was a difficult time for at least marine life, even before the "Great Dying".
- Late Devonian extinction: 375–360 Ma near the Devonian-Carboniferous transition. At the end of the Frasnian Age in the later part(s) of the Devonian Period, a prolonged series of extinctions eliminated about 19% of all families, 50% of all genera[9] and 70% of all species.[citation needed] This extinction event lasted perhaps as long as 20 Ma, and there is evidence for a series of extinction pulses within this period.
- Ordovician–Silurian extinction events (End Ordovician or O-S): 450–440 Ma at the Ordovician-Silurian transition. Two events occurred that killed off 27% of all families, 57% of all genera and 60% to 70% of all species.[9] Together they are ranked by many scientists as the second largest of the five major extinctions in Earth's history in terms of percentage of genera that went extinct.
Despite the popularization of these five events, there is no fine line separating them from other extinction events; using different methods of calculating an extinction's impact can lead to other events featuring in the top five.
[15]
The older the fossil record gets, the more difficult it is to read. This is because:
- Older fossils are harder to find as they are usually buried at a considerable depth.
- Dating older fossils is more difficult.
- Productive fossil beds are researched more than unproductive ones, therefore leaving certain periods unresearched.
- Prehistoric environmental can disturb the deposition process.
- The preservation of fossils varies on land, but marine fossils tend to be better preserved than their sought after land-based counterparts.[16]
It has been suggested that the apparent variations in marine biodiversity may actually be an artifact, with abundance estimates directly related to quantity of rock available for sampling from different time periods.
[17] However, statistical analysis shows that this can only account for 50% of the observed pattern,
[citation needed] and other evidence (such as fungal spikes)
[clarification needed] provides reassurance that most widely accepted extinction events are real. A quantification of the rock exposure of Western Europe indicates that many of the minor events for which a biological explanation has been sought are most readily explained by
sampling bias.
[18]
List of extinction events
This is a list of extinction events:
[19]
Evolutionary importance
Mass extinctions have sometimes accelerated the evolution of
life on Earth. When dominance of particular ecological niches passes from one group of organisms to another, it is rarely because the new dominant group is "superior" to the old and usually because an extinction event eliminates the old dominant group and makes way for the new one.
[22][23]
For example
mammaliformes ("almost mammals") and then
mammals existed throughout the reign of the
dinosaurs, but could not compete for the large terrestrial vertebrate niches which dinosaurs monopolized. The
end-Cretaceous mass extinction removed the non-avian dinosaurs and made it possible for mammals to expand into the large terrestrial vertebrate niches. Ironically, the dinosaurs themselves had been beneficiaries of a previous mass extinction, the
end-Triassic, which eliminated most of their chief rivals, the
crurotarsans.
Another point of view put forward in the
Escalation hypothesis predicts that species in ecological niches with more organism-to-organism conflict will be less likely to survive extinctions. This is because the very traits that keep a species numerous and viable under fairly static conditions become a burden once population levels fall among competing organisms during the dynamics of an extinction event.
Furthermore, many groups which survive mass extinctions do not recover in numbers or diversity, and many of these go into long-term decline, and these are often referred to as "
Dead Clades Walking".
[24] So analysing extinctions in terms of "what died and what survived" often fails to tell the full story.
Darwin was firmly of the opinion that biotic interactions, such as competition for food and space—the ‘struggle for existence’—were of considerably greater importance in promoting evolution and extinction than changes in the physical environment. He expressed this in The origin of species: “Species are produced and exterminated by slowly acting causes…and the most import of all causes of organic change is one which is almost independent of altered…physical conditions, namely the mutual relation of organism to organism-the improvement of one organism entailing the improvement or extermination of others”.
[25]
Patterns in frequency
"Well-defined" genera
Trend line
Other mass extinctions
Million years ago
Thousands of generaPhanerozoic biodiversity as shown by the fossil record
It has been suggested variously that extinction events occurred periodically, every 26 to 30 million years,
[26] or that diversity fluctuates episodically every ~62 million years.
[27] Various ideas attempt to explain the supposed pattern, including the presence of a
hypothetical companion star to the sun,
[28] [29] oscillations in the galactic plane, or passage through the Milky Way's spiral arms.
[30]
However, other authors have concluded the data on marine mass extinctions do not fit with the idea that mass extinctions are periodic, or that ecosystems gradually build up to a point at which a mass extinction is inevitable.
[7] Many of the proposed correlations have been argued to be spurious.
[31][32] Others have argued that there is strong evidence supporting periodicity in a variety of records,
[33] and additional evidence in the form of coincident periodic variation in nonbiological geochemical variables.
[34]
Mass extinctions are thought to result when a long-term stress is compounded by a short term shock.
[35] Over the course of the
Phanerozoic, individual taxa appear to be less likely to become extinct at any time,
[36] which may reflect more robust food webs as well as less extinction-prone species and other factors such as continental distribution.
[36] However, even after accounting for sampling bias, there does appear to be a gradual decrease in extinction and origination rates during the Phanerozoic.
[7] This may represent the fact that groups with higher turnover rates are more likely to become extinct by chance; or it may be an artefact of taxonomy: families tend to become more speciose, therefore less prone to extinction, over time;
[7] and larger taxonomic groups (by definition) appear earlier in geological time.
[37]
It has also been suggested that the oceans have gradually become more hospitable to life over the last 500 million years, and thus less vulnerable to mass extinctions,
[note 1][38][39] but susceptibility to extinction at a taxonomic level does not appear to make mass extinctions more or less probable.
[36]
There is still debate about the causes of all mass extinctions. In general, large extinctions may result when a biosphere under long-term stress undergoes a short-term shock.
[35] An underlying mechanism appears to be present in the correlation of extinction and origination rates to diversity. High diversity leads to a persistent increase in extinction rate; low diversity to a persistent increase in origination rate. These presumably ecologically controlled relationships likely amplify smaller perturbations (asteroid impacts, etc.) to produce the global effects observed.
[7]
Identifying causes of particular mass extinctions[edit]
A good theory for a particular mass extinction should: (i) explain all of the losses, not just focus on a few groups (such as dinosaurs); (ii) explain why particular groups of organisms died out and why others survived; (iii) provide mechanisms which are strong enough to cause a mass extinction but not a total extinction; (iv) be based on events or processes that can be shown to have happened, not just inferred from the extinction.
It may be necessary to consider combinations of causes. For example the marine aspect of the
end-Cretaceous extinction appears to have been caused by several processes which partially overlapped in time and may have had different levels of significance in different parts of the world.
[40]
Arens and West (2006) proposed a "press / pulse" model in which mass extinctions generally require two types of cause: long-term pressure on the eco-system ("press") and a sudden catastrophe ("pulse") towards the end of the period of pressure.
[41] Their statistical analysis of marine extinction rates throughout the
Phanerozoic suggested that neither long-term pressure alone nor a catastrophe alone was sufficient to cause a significant increase in the extinction rate.
Most widely supported explanations[edit]
Macleod (2001)
[42] summarized the relationship between mass extinctions and events which are most often cited as causes of mass extinctions, using data from Courtillot
et al. (1996),
[43] Hallam (1992)
[44] and Grieve
et al. (1996):
[45]
- Flood basalt events: 11 occurrences, all associated with significant extinctions[46][47] But Wignall (2001) concluded that only five of the major extinctions coincided with flood basalt eruptions and that the main phase of extinctions started before the eruptions.[48]
- Sea-level falls: 12, of which seven were associated with significant extinctions.[47]
- Asteroid impacts; One large impact associated with a mass extinction; there have been many smaller impacts but they are not associated with significant extinctions.[clarification needed]
The most commonly suggested causes of mass extinctions are listed below.
Flood basalt events
The formation of
large igneous provinces by flood basalt events could have:
Flood basalt events occur as pulses of activity punctuated by dormant periods. As a result they are likely to cause the climate to oscillate between cooling and warming, but with an overall trend towards warming as the carbon dioxide they emit can stay in the atmosphere for hundreds of years.
It is speculated that massive volcanism caused or contributed to the
End-Permian,
End-Triassic and
End-Cretaceous extinctions.
[49] The correlation between gigantic volcanic events expressed in the large igneous provinces and mass extinctions was shown for the last 260 Myr.
[50] [51] Recently such possible correlation was extended for the whole Phanerozoic Eon.
[52]
Sea-level falls
These are often clearly marked by worldwide sequences of contemporaneous sediments which show all or part of a transition from sea-bed to tidal zone to beach to dry land – and where there is no evidence that the rocks in the relevant areas were raised by geological processes such as
orogeny.
Sea-level falls could reduce the continental shelf area (the most productive part of the oceans) sufficiently to cause a marine mass extinction, and could disrupt weather patterns enough to cause extinctions on land. But sea-level falls are very probably the result of other events, such as sustained global cooling or the sinking of the
mid-ocean ridges.
Sea-level falls are associated with most of the mass extinctions, including all of the "Big Five"—
End-Ordovician,
Late Devonian,
End-Permian,
End-Triassic, and
End-Cretaceous.
A study, published in the journal Nature (online June 15, 2008) established a relationship between the speed of mass extinction events and changes in sea level and sediment.
[53] The study suggests changes in ocean environments related to sea level exert a driving influence on rates of extinction, and generally determine the composition of life in the oceans.
[54]
Impact events
The impact of a sufficiently large asteroid or comet could have caused
food chains to collapse both on land and at sea by producing dust and
particulate aerosols and thus inhibiting photosynthesis.
Impacts on
sulfur-rich rocks could have emitted sulfur oxides precipitating as poisonous
acid rain, contributing further to the collapse of food chains. Such impacts could also have caused
megatsunamis and/or global
forest fires.
Most paleontologists now agree that an asteroid did hit the Earth about 66 Ma, but there is an ongoing dispute whether the impact was the sole cause of the
Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.
[55][56] There is evidence that there was an interval of about 300 ka from the impact to the mass extinction.
[55] In 1997, paleontologist
Sankar Chatterjee drew attention to the proposed and much larger 600 km (370 mi)
Shiva crater and the possibility of a multiple-impact scenario.
In 2007, a hypothesis was put forth that argued the impactor that killed the dinosaurs 66 Ma years ago belonged to the
Baptistina family of asteroids.
[57] Concerns have been raised regarding the reputed link, in part because very few solid observational constraints exist of the asteroid or family.
[58] Indeed, it was discovered that 298 Baptistina does not share the same chemical signature as the source of the
K–Pg (Chicxulub) impact.
[59] Although this finding may make the link between the Baptistina family and K-T impactor more difficult to substantiate, it does not preclude the possibility.
[59]
In 2010, another hypothesis was offered which implicated the newly discovered asteroid
P/2010 A2, a member of the
Flora family of asteroids, as a possible remnant cohort of the K–Pg (Chicxulub) impact.
[60]
The
Shiva hypothesis proposes that periodic gravitational disturbances cause comets from the
Oort cloud to bombard earth every 26 to 30 million years.
[61]
Ocean asteroid impacts
Carbon Dioxide (CO
2) is soluble in sea water and is present in very large
quantities. It mostly reports as the bicarbonate radical (−HCO
3) which is only stable at temperatures below 50°C.
[62]
Sea surface temperatures are normally below 50°C, but can easily exceed that temperature when an asteroid strikes the ocean thereby inducing a large thermal shock. Under those circumstances very large quantities of CO
2 erupt from the ocean.
[63] As a heavy gas, the CO
2 can quickly spread around the world in concentrations sufficient to suffocate air breathing fauna, selectively at low altitudes.
Asteroid impacts with the ocean may not leave obvious signs, but these impacts have the potential to be far more devastating to life on earth than impacts with land.
Sustained and significant global cooling
Sustained global cooling could kill many
polar and
temperate species and force others to migrate towards the
equator; reduce the area available for
tropical species; often make the Earth's climate more arid on average, mainly by locking up more of the planet's water in ice and snow. The
glaciation cycles of the current
ice age are believed to have had only a very mild impact on biodiversity, so the mere existence of a significant cooling is not sufficient on its own to explain a mass extinction.
It has been suggested that global cooling caused or contributed to the
End-Ordovician,
Permian-Triassic,
Late Devonian extinctions, and possibly others. Sustained global cooling is distinguished from the temporary climatic effects of flood basalt events or impacts.
Sustained and significant global warming
This would have the opposite effects: expand the area available for
tropical species; kill
temperate species or force them to migrate towards the
poles; possibly cause severe extinctions of polar species; often make the Earth's climate wetter on average, mainly by melting ice and snow and thus increasing the volume of the
water cycle. It might also cause anoxic events in the oceans (see below).
Global warming as a cause of mass extinction is supported by several recent studies.
[64]
The most dramatic example of sustained warming is the
Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum, which was associated with one of the smaller mass extinctions. It has also been suggested to have caused the
Triassic-Jurassic extinction event, during which 20% of all marine families went extinct. Furthermore, the
Permian–Triassic extinction event has been suggested to have been caused by warming.
[65][66][67] Human-caused global warming is contributing to extinctions today.
Clathrate gun hypothesis
Clathrates are composites in which a lattice of one substance forms a cage around another.
Methane clathrates (in which water molecules are the cage) form on
continental shelves. These clathrates are likely to break up rapidly and release the methane if the temperature rises quickly or the pressure on them drops quickly—for example in response to sudden
global warming or a sudden drop in sea level or even
earthquakes. Methane is a much more powerful
greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide, so a methane eruption ("clathrate gun") could cause rapid global warming or make it much more severe if the eruption was itself caused by global warming.
The most likely signature of such a methane eruption would be a sudden decrease in the
ratio of carbon-13 to carbon-12 in sediments, since methane clathrates are low in carbon-13; but the change would have to be very large, as other events can also reduce the percentage of carbon-13.
[68]
It has been suggested that "clathrate gun" methane eruptions were involved in the
end-Permian extinction ("the Great Dying") and in the
Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum, which was associated with one of the smaller mass extinctions.
Anoxic events
Anoxic events are situations in which the middle and even the upper layers of the ocean become deficient or totally lacking in oxygen. Their causes are complex and controversial, but all known instances are associated with severe and sustained global warming, mostly caused by sustained massive volcanism.
It has been suggested that anoxic events caused or contributed to the
Ordovician–Silurian,
late Devonian,
Permian–Triassic and
Triassic–Jurassic extinctions, as well as a number of lesser extinctions (such as the
Ireviken,
Mulde,
Lau,
Toarcian and Cenomanian–Turonian events). On the other hand, there are widespread black shale beds from the mid-Cretaceous which indicate anoxic events but are not associated with mass extinctions.
Hydrogen sulfide emissions from the seas
Kump, Pavlov and Arthur (2005) have proposed that during the
Permian–Triassic extinction event the warming also upset the oceanic balance between
photosynthesising plankton and deep-water
sulfate-reducing bacteria, causing massive emissions of
hydrogen sulfide which poisoned life on both land and sea and severely weakened the
ozone layer, exposing much of the life that still remained to fatal levels of
UV radiation.
[69][70][71]
Oceanic overturn
Oceanic overturn is a disruption of
thermo-haline circulation which lets surface water (which is more saline than deep water because of evaporation) sink straight down, bringing anoxic deep water to the surface and therefore killing most of the oxygen-breathing organisms which inhabit the surface and middle depths. It may occur either at the beginning or the end of a
glaciation, although an overturn at the start of a glaciation is more dangerous because the preceding warm period will have created a larger volume of anoxic water.
[72]
Unlike other oceanic catastrophes such as regressions (sea-level falls) and anoxic events, overturns do not leave easily identified "signatures" in rocks and are theoretical consequences of researchers' conclusions about other climatic and marine events.
It has been suggested that oceanic overturn caused or contributed to the
late Devonian and
Permian–Triassic extinctions.
A nearby nova, supernova or gamma ray burst
A nearby
gamma ray burst (less than 6000
light years away) would be powerful enough to destroy the Earth's
ozone layer, leaving organisms vulnerable to
ultraviolet radiation from the
sun.
[73] Gamma ray bursts are fairly rare, occurring only a few times in a given galaxy per million years.
[74] It has been suggested that a supernova or gamma ray burst caused the
End-Ordovician extinction.
[33]
Geomagnetic reversal
One theory is that periods of increased
geomagnetic reversals will weaken
Earth's magnetic field long enough to expose the atmosphere to the
solar winds, causing oxygen ions to escape the atmosphere in a rate increased by 3-4 orders, resulting in a disastrous drop on oxygen.
[75]
Plate tectonics
Movement of the continents into some configurations can cause or contribute to extinctions in several ways: by initiating or ending
ice ages; by changing ocean and wind currents and thus altering climate; by opening seaways or land bridges which expose previously isolated species to competition for which they are poorly adapted (for example, the extinction of most of South America's
native ungulates and all of its
large metatherians after the
creation of a land bridge between North and South America). Occasionally continental drift creates a super-continent which includes the vast majority of Earth's land area, which in addition to the effects listed above is likely to reduce the total area of
continental shelf (the most species-rich part of the ocean) and produce a vast, arid continental interior which may have extreme seasonal variations.
Another theory is that the creation of the super-continent
Pangaea contributed to the
End-Permian mass extinction. Pangaea was almost fully formed at the transition from mid-Permian to late-Permian, and the "Marine genus diversity" diagram at the top of this article shows a level of extinction starting at that time which might have qualified for inclusion in the "Big Five" if it were not overshadowed by the "Great Dying" at the end of the Permian.
[76]
Other hypotheses
Many other hypotheses have been proposed, such as the spread of a new
disease, or simple out-competition following an especially successful biological innovation. But all have been rejected, usually for one of the following reasons: they require events or processes for which there is no evidence; they assume mechanisms which are contrary to the available evidence; they are based on other theories which have been rejected or superseded.
Supervolcanic events may also been potential causes of mass extinctions. While none of the extinction events in Earth's past have been caused by any supervolcanic eruptions, the
Toba supereruption may have reduced the first humans down to a few thousand individuals.
Scientists have been concerned that human activities could cause more plants and animals to become extinct than any point in the past. Along with man-made changes in climate (see above), some of these extinctions could be caused by overhunting, overfishing, invasive species, or habitat loss.
Future biosphere extinction
The eventual warming and expanding of the Sun, combined with the eventual decline of atmospheric carbon dioxide could actually cause an even greater mass extinction, having the potential to wipe out even microbes, where rising global temperatures caused by the expanding Sun will gradually increase the rate of weathering, which in turn removes more and more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When carbon dioxide levels get too low (perhaps at 50 ppm), all plant life will die out, although simpler plants like grasses and mosses can survive much longer, until CO2 levels drop to 10 ppm.
[77][78]
With all photosynthetic organisms gone, atmospheric oxygen can no longer be replenished, and is eventually removed by chemical reactions in the atmosphere, perhaps from volcanic eruptions. Eventually the loss of oxygen will cause all remaining aerobic life to die out via asphyxiation, leaving behind only simple anaerobic prokaryotes. When the Sun becomes 10% brighter
[77] Earth will suffer a moist greenhouse effect resulting in its oceans boiling away, while the Earth's liquid outer core freezes due to the inner core's expansion and causes the Earth's magnetic field to shut down. In the absence of a magnetic field, charged particles from the Sun will deplete the atmosphere and further increase the Earth's temperature to an average of ~420 K (147 °C, 296 °F), causing the last remaining life on Earth to die out. This is the most extreme instance of a climate-caused extinction event. Since this will only happen late in the Sun's life, such will cause the final mass extinction in Earth's history.
[77][78]
Effects and recovery
The impact of mass extinction events varied widely. After a major extinction event, usually only
weedy species survive due to their ability to live in diverse habitats.
[79] Later, species diversify and occupy empty niches. Generally,
biodiversity recovers 5 to 10 million years after the extinction event. In the most severe mass extinctions it may take 15 to 30 million years.
[79]
The worst event, the
Permian–Triassic extinction event, devastated life on earth and is estimated to have killed off over 90% of species. Life seemed to recover quickly after the P-T extinction, but this was mostly in the form of
disaster taxa, such as the hardy
Lystrosaurus. The most recent research indicates that the specialized animals that formed complex ecosystems, with high biodiversity, complex food webs and a variety of niches, took much longer to recover. It is thought that this long recovery was due to the successive waves of extinction which inhibited recovery, as well as to prolonged environmental stress to organisms which continued into the Early Triassic. Recent research indicates that recovery did not begin until the start of the mid-Triassic, 4M to 6M years after the extinction;
[80] and some writers estimate that the recovery was not complete until 30M years after the P-Tr extinction, i.e. in the late Triassic.
[81] Subsequent to the PT mass extinction, there was an increase in provincialization, with species occupying smaller ranges - perhaps removing incumbents from niches and setting the stage for an eventual rediversification.
[82]
The effects of mass extinctions on plants are somewhat harder to quantify, given the biases inherent in the plant fossil record. Some mass extinctions (such as the end-Permian) were equally catastrophic for plants, whereas others, such as the end-Devonian, did not affect the flora.
[83]