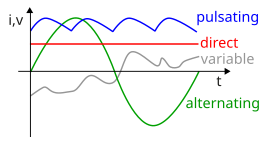
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal that typically contains information to be transmitted. Most radio systems in the 20th century used frequency modulation (FM) or amplitude modulation (AM) to make the carrier carry the radio broadcast.
In general telecommunications, modulation is a process of conveying message signal, for example, a digital bit stream or an analog audio signal, inside another signal that can be physically transmitted. Modulation of a sine waveform transforms a narrow frequency range baseband message signal into a moderate to high frequency range passband signal, one that can pass through a filter.
A modulator is a device that performs modulation. A demodulator (sometimes detector or demod) is a device that performs demodulation, the inverse of modulation. A modem (from modulator–demodulator) can perform both operations.
The aim of analog modulation is to transfer an analog baseband (or lowpass) signal, for example an audio signal or TV signal, over an analog bandpass channel at a different frequency, for example over a limited radio frequency band or a cable TV network channel.
The aim of digital modulation is to transfer a digital bit stream over an analog communication channel, for example over the public switched telephone network (where a bandpass filter limits the frequency range to 300–3400 Hz) or over a limited radio frequency band.
Analog and digital modulation facilitate frequency division multiplexing (FDM), where several low pass information signals are transferred simultaneously over the same shared physical medium, using separate passband channels (several different carrier frequencies).
The aim of digital baseband modulation methods, also known as line coding, is to transfer a digital bit stream over a baseband channel, typically a non-filtered copper wire such as a serial bus or a wired local area network.
The aim of pulse modulation methods is to transfer a narrowband analog signal, for example, a phone call over a wideband baseband channel or, in some of the schemes, as a bit stream over another digital transmission system.
In music synthesizers, modulation may be used to synthesize waveforms with an extensive overtone spectrum using a small number of oscillators. In this case, the carrier frequency is typically in the same order or much lower than the modulating waveform (see frequency modulation synthesis or ring modulation synthesis).
In general telecommunications, modulation is a process of conveying message signal, for example, a digital bit stream or an analog audio signal, inside another signal that can be physically transmitted. Modulation of a sine waveform transforms a narrow frequency range baseband message signal into a moderate to high frequency range passband signal, one that can pass through a filter.
A modulator is a device that performs modulation. A demodulator (sometimes detector or demod) is a device that performs demodulation, the inverse of modulation. A modem (from modulator–demodulator) can perform both operations.
The aim of analog modulation is to transfer an analog baseband (or lowpass) signal, for example an audio signal or TV signal, over an analog bandpass channel at a different frequency, for example over a limited radio frequency band or a cable TV network channel.
The aim of digital modulation is to transfer a digital bit stream over an analog communication channel, for example over the public switched telephone network (where a bandpass filter limits the frequency range to 300–3400 Hz) or over a limited radio frequency band.
Analog and digital modulation facilitate frequency division multiplexing (FDM), where several low pass information signals are transferred simultaneously over the same shared physical medium, using separate passband channels (several different carrier frequencies).
The aim of digital baseband modulation methods, also known as line coding, is to transfer a digital bit stream over a baseband channel, typically a non-filtered copper wire such as a serial bus or a wired local area network.
The aim of pulse modulation methods is to transfer a narrowband analog signal, for example, a phone call over a wideband baseband channel or, in some of the schemes, as a bit stream over another digital transmission system.
In music synthesizers, modulation may be used to synthesize waveforms with an extensive overtone spectrum using a small number of oscillators. In this case, the carrier frequency is typically in the same order or much lower than the modulating waveform (see frequency modulation synthesis or ring modulation synthesis).
Analog modulation methods
A low-frequency message signal (top) may be carried by an AM or FM radio wave.
Waterfall plot
of a 146.52 MHZ radio carrier, with amplitude modulation by a 1,000 hz
sinusoid. Two strong sidebands at + and - 1Khz from the carrier
frequency are shown.
A carrier, frequency modulated by a 1,000 hz sinusoid. The modulation index
has been adjusted to around 2.4, so the carrier frequency has small
amplitude. Several strong sidebands are apparent; in principle an
infinite number are produced in FM but the higher-order sidebands are of
negligible magnitude.
In analog modulation, the modulation is applied continuously in response to the analog information signal. Common analog modulation techniques are include:
- Amplitude modulation
(AM) (here the amplitude of the carrier signal is varied in accordance
with the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal)
- Double-sideband modulation (DSB)
- Double-sideband modulation with carrier (DSB-WC) (used on the AM radio broadcasting band)
- Double-sideband suppressed-carrier transmission (DSB-SC)
- Double-sideband reduced carrier transmission (DSB-RC)
- Single-sideband modulation (SSB, or SSB-AM)
- Single-sideband modulation with carrier (SSB-WC)
- Single-sideband modulation suppressed carrier modulation (SSB-SC)
- Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB, or VSB-AM)
- Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM)
- Double-sideband modulation (DSB)
- Angle modulation, which is approximately constant envelope
- Frequency modulation (FM) (here the frequency of the carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal)
- Phase modulation (PM) (here the phase shift of the carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal)
- Transpositional Modulation (TM), in which the waveform inflection is modified resulting in a signal where each quarter cycle is transposed in the modulation process. TM is a pseudo-analog modulation (AM). Where an AM carrier also carries a phase variable phase f(ǿ). TM is f(AM,ǿ)
Digital modulation methods
In digital modulation, an analog carrier signal is modulated by a discrete signal. Digital modulation methods can be considered as digital-to-analog conversion and the corresponding demodulation or detection as analog-to-digital conversion. The changes in the carrier signal are chosen from a finite number of M alternative symbols (the modulation alphabet).
Schematic of 4 baud (8 bit/s) data link containing arbitrarily chosen values.
A simple example: A telephone line is designed for transferring audible sounds, for example, tones, and not digital bits (zeros and ones). Computers may, however, communicate over a telephone line by means of modems, which are representing the digital bits by tones, called symbols. If there are four alternative symbols (corresponding to a musical instrument that can generate four different tones, one at a time), the first symbol may represent the bit sequence 00, the second 01, the third 10 and the fourth 11. If the modem plays a melody consisting of 1000 tones per second, the symbol rate is 1000 symbols/second, or baud. Since each tone (i.e., symbol) represents a message consisting of two digital bits in this example, the bit rate is twice the symbol rate, i.e. 2000 bits per second. This is similar to the technique used by dial-up modems as opposed to DSL modems.
According to one definition of digital signal, the modulated signal is a digital signal. According to another definition, the modulation is a form of digital-to-analog conversion. Most textbooks would consider digital modulation schemes as a form of digital transmission, synonymous to data transmission; very few would consider it as analog transmission.
Fundamental digital modulation methods
The most fundamental digital modulation techniques are based on keying:- PSK (phase-shift keying): a finite number of phases are used.
- FSK (frequency-shift keying): a finite number of frequencies are used.
- ASK (amplitude-shift keying): a finite number of amplitudes are used.
- QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation): a finite number of at least two phases and at least two amplitudes are used.
In all of the above methods, each of these phases, frequencies or amplitudes are assigned a unique pattern of binary bits. Usually, each phase, frequency or amplitude encodes an equal number of bits. This number of bits comprises the symbol that is represented by the particular phase, frequency or amplitude.
If the alphabet consists of alternative symbols, each symbol represents a message consisting of N bits. If the symbol rate (also known as the baud rate) is symbols/second (or baud), the data rate is bit/second.
For example, with an alphabet consisting of 16 alternative symbols, each symbol represents 4 bits. Thus, the data rate is four times the baud rate.
In the case of PSK, ASK or QAM, where the carrier frequency of the modulated signal is constant, the modulation alphabet is often conveniently represented on a constellation diagram, showing the amplitude of the I signal at the x-axis, and the amplitude of the Q signal at the y-axis, for each symbol.
Modulator and detector principles of operation
PSK and ASK, and sometimes also FSK, are often generated and detected using the principle of QAM. The I and Q signals can be combined into a complex-valued signal I+jQ (where j is the imaginary unit). The resulting so called equivalent lowpass signal or equivalent baseband signal is a complex-valued representation of the real-valued modulated physical signal (the so-called passband signal or RF signal).These are the general steps used by the modulator to transmit data:
- Group the incoming data bits into codewords, one for each symbol that will be transmitted.
- Map the codewords to attributes, for example, amplitudes of the I and Q signals (the equivalent low pass signal), or frequency or phase values.
- Adapt pulse shaping or some other filtering to limit the bandwidth and form the spectrum of the equivalent low pass signal, typically using digital signal processing.
- Perform digital to analog conversion (DAC) of the I and Q signals (since today all of the above is normally achieved using digital signal processing, DSP).
- Generate a high-frequency sine carrier waveform, and perhaps also a cosine quadrature component. Carry out the modulation, for example by multiplying the sine and cosine waveform with the I and Q signals, resulting in the equivalent low pass signal being frequency shifted to the modulated passband signal or RF signal. Sometimes this is achieved using DSP technology, for example direct digital synthesis using a waveform table, instead of analog signal processing. In that case, the above DAC step should be done after this step.
- Amplification and analog bandpass filtering to avoid harmonic distortion and periodic spectrum.
- Bandpass filtering.
- Automatic gain control, AGC (to compensate for attenuation, for example fading).
- Frequency shifting of the RF signal to the equivalent baseband I and Q signals, or to an intermediate frequency (IF) signal, by multiplying the RF signal with a local oscillator sine wave and cosine wave frequency (see the superheterodyne receiver principle).
- Sampling and analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) (sometimes before or instead of the above point, for example by means of undersampling).
- Equalization filtering, for example, a matched filter, compensation for multipath propagation, time spreading, phase distortion and frequency selective fading, to avoid intersymbol interference and symbol distortion.
- Detection of the amplitudes of the I and Q signals, or the frequency or phase of the IF signal.
- Quantization of the amplitudes, frequencies or phases to the nearest allowed symbol values.
- Mapping of the quantized amplitudes, frequencies or phases to codewords (bit groups).
- Parallel-to-serial conversion of the codewords into a bit stream.
- Pass the resultant bit stream on for further processing such as removal of any error-correcting codes.
Non-coherent modulation methods do not require a receiver reference clock signal that is phase synchronized with the sender carrier signal. In this case, modulation symbols (rather than bits, characters, or data packets) are asynchronously transferred. The opposite is coherent modulation.
List of common digital modulation techniques
The most common digital modulation techniques are:- Phase-shift keying (PSK)
- Binary PSK (BPSK), using M=2 symbols
- Quadrature PSK (QPSK), using M=4 symbols
- 8PSK, using M=8 symbols
- 16PSK, using M=16 symbols
- Differential PSK (DPSK)
- Differential QPSK (DQPSK)
- Offset QPSK (OQPSK)
- π/4–QPSK
- Frequency-shift keying (FSK)
- Audio frequency-shift keying (AFSK)
- Multi-frequency shift keying (M-ary FSK or MFSK)
- Dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF)
- Amplitude-shift keying (ASK)
- On-off keying (OOK), the most common ASK form
- M-ary vestigial sideband modulation, for example 8VSB
- Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM), a combination of PSK and ASK
- Polar modulation like QAM a combination of PSK and ASK[citation needed]
- Continuous phase modulation (CPM) methods
- Minimum-shift keying (MSK)
- Gaussian minimum-shift keying (GMSK)
- Continuous-phase frequency-shift keying (CPFSK)
- Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation
- Discrete multitone (DMT), including adaptive modulation and bit-loading
- Wavelet modulation
- Trellis coded modulation (TCM), also known as Trellis modulation
- Spread-spectrum techniques
- Direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS)
- Chirp spread spectrum (CSS) according to IEEE 802.15.4a CSS uses pseudo-stochastic coding
- Frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) applies a special scheme for channel release
OFDM is based on the idea of frequency-division multiplexing (FDM), but the multiplexed streams are all parts of a single original stream. The bit stream is split into several parallel data streams, each transferred over its own sub-carrier using some conventional digital modulation scheme. The modulated sub-carriers are summed to form an OFDM signal. This dividing and recombining help with handling channel impairments. OFDM is considered as a modulation technique rather than a multiplex technique since it transfers one bit stream over one communication channel using one sequence of so-called OFDM symbols. OFDM can be extended to multi-user channel access method in the orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) and multi-carrier code division multiple access (MC-CDMA) schemes, allowing several users to share the same physical medium by giving different sub-carriers or spreading codes to different users.
Of the two kinds of RF power amplifier, switching amplifiers (Class D amplifiers) cost less and use less battery power than linear amplifiers of the same output power. However, they only work with relatively constant-amplitude-modulation signals such as angle modulation (FSK or PSK) and CDMA, but not with QAM and OFDM. Nevertheless, even though switching amplifiers are completely unsuitable for normal QAM constellations, often the QAM modulation principle are used to drive switching amplifiers with these FM and other waveforms, and sometimes QAM demodulators are used to receive the signals put out by these switching amplifiers.
Automatic digital modulation recognition (ADMR)
Automatic digital modulation recognition in intelligent communication systems is one of the most important issues in software defined radio and cognitive radio. According to incremental expanse of intelligent receivers, automatic modulation recognition becomes a challenging topic in telecommunication systems and computer engineering. Such systems have many civil and military applications. Moreover, blind recognition of modulation type is an important problem in commercial systems, especially in software defined radio. Usually in such systems, there are some extra information for system configuration, but considering blind approaches in intelligent receivers, we can reduce information overload and increase transmission performance. Obviously, with no knowledge of the transmitted data and many unknown parameters at the receiver, such as the signal power, carrier frequency and phase offsets, timing information, etc., blind identification of the modulation is made fairly difficult. This becomes even more challenging in real-world scenarios with multipath fading, frequency-selective and time-varying channels.There are two main approaches to automatic modulation recognition. The first approach uses likelihood-based methods to assign an input signal to a proper class. Another recent approach is based on feature extraction.
Digital baseband modulation or line coding
The term digital baseband modulation (or digital baseband transmission) is synonymous to line codes. These are methods to transfer a digital bit stream over an analog baseband channel (a.k.a. lowpass channel) using a pulse train, i.e. a discrete number of signal levels, by directly modulating the voltage or current on a cable or serial bus. Common examples are unipolar, non-return-to-zero (NRZ), Manchester and alternate mark inversion (AMI) codings.Pulse modulation methods
Pulse modulation schemes aim at transferring a narrowband analog signal over an analog baseband channel as a two-level signal by modulating a pulse wave. Some pulse modulation schemes also allow the narrowband analog signal to be transferred as a digital signal (i.e., as a quantized discrete-time signal) with a fixed bit rate, which can be transferred over an underlying digital transmission system, for example, some line code. These are not modulation schemes in the conventional sense since they are not channel coding schemes, but should be considered as source coding schemes, and in some cases analog-to-digital conversion techniques.Analog-over-analog methods
- Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM)
- Pulse-width modulation (PWM) and Pulse-depth modulation (PDM)
- Pulse-position modulation (PPM)
- Pulse-code modulation (PCM)
- Differential PCM (DPCM)
- Adaptive DPCM (ADPCM)
- Delta modulation (DM or Δ-modulation)
- Delta-sigma modulation (∑Δ)
- Continuously variable slope delta modulation (CVSDM), also called Adaptive-delta modulation (ADM)
- Pulse-density modulation (PDM)
Miscellaneous modulation techniques
- The use of on-off keying to transmit Morse code at radio frequencies is known as continuous wave (CW) operation.
- Adaptive modulation
- Space modulation is a method whereby signals are modulated within airspace such as that used in instrument landing systems.














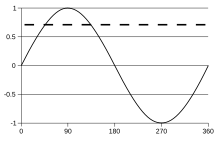






















![V_{\mathrm {rms} }={\sqrt {{\frac {1}{T}}\int _{0}^{T}{[v(t)]^{2}dt}}}.](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fcbde5a08727ac8afb4ae9825d92f5aa7c20f1cf)
![{\begin{aligned}V_{\mathrm {rms} }&={\sqrt {{\frac {1}{T}}\int _{0}^{T}[{V_{pk}\sin(\omega t+\phi )]^{2}dt}}}\\&=V_{pk}{\sqrt {{\frac {1}{2T}}\int _{0}^{T}[{1-\cos(2\omega t+2\phi )]dt}}}\\&=V_{pk}{\sqrt {{\frac {1}{2T}}\int _{0}^{T}{dt}}}\\&={\frac {V_{pk}}{\sqrt {2}}}\end{aligned}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4af299ef918adbd3daeb95e32f24c27e18211fcf)










