| |
| Age | 4.568 billion years |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| System mass | 1.0014 Solar masses |
| Nearest star |
|
| Nearest known planetary system | Proxima Centauri system (4.25 ly) |
| Planetary system | |
| Semi-major axis of outer known planet (Neptune) | 30.10 AU (4.503 billion km) |
| Distance to Kuiper cliff | 50 AU |
Populations
| |
| Stars | 1 (Sun) |
| Known planets | |
| Known dwarf planets | |
| Known natural satellites |
525
|
| Known minor planets | 778,897 (as of 2018-06-21) |
| Known comets | 4,017 (as of 2018-06-21) |
| Identified rounded satellites | 19 |
| Orbit about Galactic Center | |
| Invariable-to-galactic plane inclination | 60.19° (ecliptic) |
| Distance to Galactic Center | 27,000 ± 1,000 ly |
| Orbital speed | 220 km/s |
| Orbital period | 225–250 Myr |
| Star-related properties | |
| Spectral type | G2V |
| Frost line | ≈5 AU |
| Distance to heliopause | ≈120 AU |
| Hill sphere radius | ≈1–3 ly |
The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of the objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest are the eight planets, with the remainder being smaller objects, such as the five dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies. Of the objects that orbit the Sun indirectly—the moons—two are larger than the smallest planet, Mercury.
The Solar System formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun, with the majority of the remaining mass contained in Jupiter. The four smaller inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, are terrestrial planets, being primarily composed of rock and metal. The four outer planets are giant planets, being substantially more massive than the terrestrials. The two largest, Jupiter and Saturn, are gas giants, being composed mainly of hydrogen and helium; the two outermost planets, Uranus and Neptune, are ice giants, being composed mostly of substances with relatively high melting points compared with hydrogen and helium, called volatiles, such as water, ammonia and methane. All eight planets have almost circular orbits that lie within a nearly flat disc called the ecliptic.
The Solar System also contains smaller objects. The asteroid belt, which lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, mostly contains objects composed, like the terrestrial planets, of rock and metal. Beyond Neptune's orbit lie the Kuiper belt and scattered disc, which are populations of trans-Neptunian objects composed mostly of ices, and beyond them a newly discovered population of sednoids. Within these populations are several dozen to possibly tens of thousands of objects large enough that they have been rounded by their own gravity. Such objects are categorized as dwarf planets. Identified dwarf planets include the asteroid Ceres and the trans-Neptunian objects Pluto and Eris. In addition to these two regions, various other small-body populations, including comets, centaurs and interplanetary dust clouds, freely travel between regions. Six of the planets, at least four of the dwarf planets, and many of the smaller bodies are orbited by natural satellites, usually termed "moons" after the Moon. Each of the outer planets is encircled by planetary rings of dust and other small objects.
The solar wind, a stream of charged particles flowing outwards from the Sun, creates a bubble-like region in the interstellar medium known as the heliosphere. The heliopause is the point at which pressure from the solar wind is equal to the opposing pressure of the interstellar medium; it extends out to the edge of the scattered disc. The Oort cloud, which is thought to be the source for long-period comets, may also exist at a distance roughly a thousand times further than the heliosphere. The Solar System is located in the Orion Arm, 26,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
Discovery and exploration
Andreas Cellarius's illustration of the Copernican system, from the Harmonia Macrocosmica (1660)
For most of history, humanity did not recognize or understand the concept of the Solar System. Most people up to the Late Middle Ages–Renaissance believed Earth to be stationary at the centre of the universe and categorically different from the divine or ethereal objects that moved through the sky. Although the Greek philosopher Aristarchus of Samos had speculated on a heliocentric reordering of the cosmos, Nicolaus Copernicus was the first to develop a mathematically predictive heliocentric system.
In the 17th century, Galileo discovered that the Sun was marked with sunspots, and that Jupiter had four satellites in orbit around it. Christiaan Huygens followed on from Galileo's discoveries by discovering Saturn's moon Titan and the shape of the rings of Saturn. Edmond Halley realised in 1705 that repeated sightings of a comet
were recording the same object, returning regularly once every 75–76
years. This was the first evidence that anything other than the planets
orbited the Sun. Around this time (1704), the term "Solar System" first appeared in English. In 1838, Friedrich Bessel successfully measured a stellar parallax,
an apparent shift in the position of a star created by Earth's motion
around the Sun, providing the first direct, experimental proof of
heliocentrism. Improvements in observational astronomy and the use of unmanned spacecraft have since enabled the detailed investigation of other bodies orbiting the Sun.
Structure and composition
Comprehensive overview of the Solar System.
The Sun, planets, dwarf planets and moons are at scale for their
relative sizes, not for distances. A separate distance scale is at the
bottom. Moons are listed near their planets by proximity of their
orbits; only the largest moons are shown.
The principal component of the Solar System is the Sun, a G2 main-sequence star that contains 99.86% of the system's known mass and dominates it gravitationally. The Sun's four largest orbiting bodies, the giant planets,
account for 99% of the remaining mass, with Jupiter and Saturn together
comprising more than 90%. The remaining objects of the Solar System
(including the four terrestrial planets, the dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, and comets) together comprise less than 0.002% of the Solar System's total mass.
Most large objects in orbit around the Sun lie near the plane of Earth's orbit, known as the ecliptic. The planets are very close to the ecliptic, whereas comets and Kuiper belt objects are frequently at significantly greater angles to it.
All the planets, and most other objects, orbit the Sun in the same
direction that the Sun is rotating (counter-clockwise, as viewed from
above Earth's north pole). There are exceptions, such as Halley's Comet.
The overall structure of the charted regions of the Solar System
consists of the Sun, four relatively small inner planets surrounded by a
belt of mostly rocky asteroids, and four giant planets surrounded by
the Kuiper belt of mostly icy objects. Astronomers sometimes informally
divide this structure into separate regions. The inner Solar System
includes the four terrestrial planets and the asteroid belt. The outer
Solar System is beyond the asteroids, including the four giant planets.
Since the discovery of the Kuiper belt, the outermost parts of the
Solar System are considered a distinct region consisting of the objects
beyond Neptune.
Most of the planets in the Solar System have secondary systems of their own, being orbited by planetary objects called natural satellites, or moons (two of which, Titan and Ganymede, are larger than the planet Mercury), and, in the case of the four giant planets, by planetary rings, thin bands of tiny particles that orbit them in unison. Most of the largest natural satellites are in synchronous rotation, with one face permanently turned toward their parent.
All planets of the Solar System lie very close to the ecliptic. The closer they are to the Sun, the faster they travel.
Kepler's laws of planetary motion describe the orbits of objects about the Sun. Following Kepler's laws, each object travels along an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. Objects closer to the Sun (with smaller semi-major axes)
travel more quickly because they are more affected by the Sun's
gravity. On an elliptical orbit, a body's distance from the Sun varies
over the course of its year. A body's closest approach to the Sun is
called its perihelion, whereas its most distant point from the Sun is called its aphelion.
The orbits of the planets are nearly circular, but many comets,
asteroids, and Kuiper belt objects follow highly elliptical orbits. The
positions of the bodies in the Solar System can be predicted using numerical models.
Although the Sun dominates the system by mass, it accounts for only about 2% of the angular momentum.
The planets, dominated by Jupiter, account for most of the rest of the
angular momentum due to the combination of their mass, orbit, and
distance from the Sun, with a possibly significant contribution from
comets.
The Sun, which comprises nearly all the matter in the Solar System, is composed of roughly 98% hydrogen and helium. Jupiter and Saturn, which comprise nearly all the remaining matter, are also primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. A composition gradient exists in the Solar System, created by heat and light pressure
from the Sun; those objects closer to the Sun, which are more affected
by heat and light pressure, are composed of elements with high melting
points. Objects farther from the Sun are composed largely of materials
with lower melting points. The boundary in the Solar System beyond which those volatile substances could condense is known as the frost line, and it lies at roughly 5 AU from the Sun.
The objects of the inner Solar System are composed mostly of rock, the collective name for compounds with high melting points, such as silicates, iron or nickel, that remained solid under almost all conditions in the protoplanetary nebula.
Jupiter and Saturn are composed mainly of gases, the astronomical term
for materials with extremely low melting points and high vapour pressure, such as hydrogen, helium, and neon, which were always in the gaseous phase in the nebula. Ices, like water, methane, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and carbon dioxide, have melting points up to a few hundred kelvins.
They can be found as ices, liquids, or gases in various places in the
Solar System, whereas in the nebula they were either in the solid or
gaseous phase.
Icy substances comprise the majority of the satellites of the giant
planets, as well as most of Uranus and Neptune (the so-called "ice giants") and the numerous small objects that lie beyond Neptune's orbit. Together, gases and ices are referred to as volatiles.
Distances and scales
The distance from Earth to the Sun is 1 astronomical unit [AU] (150,000,000 km; 93,000,000 mi). For comparison, the radius of the Sun is 0.0047 AU (700,000 km). Thus, the Sun occupies 0.00001% (10−5 %) of the volume of a sphere with a radius the size of Earth's orbit, whereas Earth's volume is roughly one millionth (10−6)
that of the Sun. Jupiter, the largest planet, is 5.2 astronomical units
(780,000,000 km) from the Sun and has a radius of 71,000 km
(0.00047 AU), whereas the most distant planet, Neptune, is 30 AU (4.5×109 km) from the Sun.
With a few exceptions, the farther a planet or belt is from the
Sun, the larger the distance between its orbit and the orbit of the next
nearer object to the Sun. For example, Venus is approximately 0.33 AU
farther out from the Sun than Mercury, whereas Saturn is 4.3 AU out from
Jupiter, and Neptune lies 10.5 AU out from Uranus. Attempts have been
made to determine a relationship between these orbital distances (for
example, the Titius–Bode law),
but no such theory has been accepted. The images at the beginning of
this section show the orbits of the various constituents of the Solar
System on different scales.
Some Solar System models
attempt to convey the relative scales involved in the Solar System on
human terms. Some are small in scale (and may be mechanical—called orreries)—whereas others extend across cities or regional areas. The largest such scale model, the Sweden Solar System, uses the 110-metre (361 ft) Ericsson Globe in Stockholm as its substitute Sun, and, following the scale, Jupiter is a 7.5-metre (25-foot) sphere at Arlanda International Airport, 40 km (25 mi) away, whereas the farthest current object, Sedna, is a 10 cm (4 in) sphere in Luleå, 912 km (567 mi) away.
If the Sun–Neptune distance is scaled
to 100 metres, then the Sun would be about 3 cm in diameter (roughly
two-thirds the diameter of a golf ball), the giant planets would be all
smaller than about 3 mm, and Earth's diameter along with that of the
other terrestrial planets would be smaller than a flea (0.3 mm) at this
scale.

Distances of selected bodies of the Solar System from the Sun. The left and right edges of each bar correspond to the perihelion and aphelion of the body, respectively, hence long bars denote high orbital eccentricity. The radius of the Sun is 0.7 million km, and the radius of Jupiter (the largest planet) is 0.07 million km, both too small to resolve on this image.
Formation and evolution
The Solar System formed 4.568 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a region within a large molecular cloud. This initial cloud was likely several light-years across and probably birthed several stars.
As is typical of molecular clouds, this one consisted mostly of
hydrogen, with some helium, and small amounts of heavier elements fused
by previous generations of stars. As the region that would become the
Solar System, known as the pre-solar nebula, collapsed, conservation of angular momentum caused it to rotate faster. The centre, where most of the mass collected, became increasingly hotter than the surrounding disc. As the contracting nebula rotated faster, it began to flatten into a protoplanetary disc with a diameter of roughly 200 AU and a hot, dense protostar at the centre. The planets formed by accretion from this disc,
in which dust and gas gravitationally attracted each other, coalescing
to form ever larger bodies. Hundreds of protoplanets may have existed in
the early Solar System, but they either merged or were destroyed,
leaving the planets, dwarf planets, and leftover minor bodies.
Due to their higher boiling points, only metals and silicates
could exist in solid form in the warm inner Solar System close to the
Sun, and these would eventually form the rocky planets of Mercury,
Venus, Earth, and Mars. Because metallic elements only comprised a very
small fraction of the solar nebula, the terrestrial planets could not
grow very large. The giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and
Neptune) formed further out, beyond the frost line, the point between
the orbits of Mars and Jupiter where material is cool enough for
volatile icy compounds to remain solid. The ices that formed these
planets were more plentiful than the metals and silicates that formed
the terrestrial inner planets, allowing them to grow massive enough to
capture large atmospheres of hydrogen and helium, the lightest and most
abundant elements. Leftover debris that never became planets congregated
in regions such as the asteroid belt, Kuiper belt, and Oort cloud. The Nice model
is an explanation for the creation of these regions and how the outer
planets could have formed in different positions and migrated to their
current orbits through various gravitational interactions.
Within 50 million years, the pressure and density of hydrogen in the centre of the protostar became great enough for it to begin thermonuclear fusion. The temperature, reaction rate, pressure, and density increased until hydrostatic equilibrium was achieved: the thermal pressure equalled the force of gravity. At this point, the Sun became a main-sequence star.
The main-sequence phase, from beginning to end, will last about
10 billion years for the Sun compared to around two billion years for
all other phases of the Sun's pre-remnant life combined. Solar wind from the Sun created the heliosphere
and swept away the remaining gas and dust from the protoplanetary disc
into interstellar space, ending the planetary formation process. The Sun
is growing brighter; early in its main-sequence life its brightness was
70% that of what it is today.
The Solar System will remain roughly as we know it today until
the hydrogen in the core of the Sun has been entirely converted to
helium, which will occur roughly 5 billion years from now. This will
mark the end of the Sun's main-sequence life. At this time, the core of
the Sun will contract with hydrogen fusion occurring along a shell
surrounding the inert helium, and the energy output will be much greater
than at present. The outer layers of the Sun will expand to roughly 260
times its current diameter, and the Sun will become a red giant.
Because of its vastly increased surface area, the surface of the Sun
will be considerably cooler (2,600 K at its coolest) than it is on the
main sequence.
The expanding Sun is expected to vaporize Mercury and render Earth
uninhabitable. Eventually, the core will be hot enough for helium
fusion; the Sun will burn helium for a fraction of the time it burned
hydrogen in the core. The Sun is not massive enough to commence the
fusion of heavier elements, and nuclear reactions in the core will
dwindle. Its outer layers will move away into space, leaving a white dwarf, an extraordinarily dense object, half the original mass of the Sun but only the size of Earth. The ejected outer layers will form what is known as a planetary nebula, returning some of the material that formed the Sun—but now enriched with heavier elements like carbon—to the interstellar medium.
Sun
The Sun is the Solar System's star and by far its most massive component. Its large mass (332,900 Earth masses), which comprises 99.86% of all the mass in the Solar System, produces temperatures and densities in its core high enough to sustain nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium, making it a main-sequence star. This releases an enormous amount of energy, mostly radiated into space as electromagnetic radiation peaking in visible light.
The Sun is a G2-type main-sequence star. Hotter main-sequence stars are more luminous. The Sun's temperature is intermediate between that of the hottest stars
and that of the coolest stars. Stars brighter and hotter than the Sun
are rare, whereas substantially dimmer and cooler stars, known as red dwarfs, make up 85% of the stars in the Milky Way.
The Sun is a population I star; it has a higher abundance of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium ("metals" in astronomical parlance) than the older population II stars.
Elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were formed in the cores of
ancient and exploding stars, so the first generation of stars had to die
before the Universe could be enriched with these atoms. The oldest
stars contain few metals, whereas stars born later have more. This high
metallicity is thought to have been crucial to the Sun's development of a
planetary system because the planets form from the accretion of "metals".
Interplanetary medium
The vast majority of the Solar System consists of a near-vacuum known as the interplanetary medium. Along with light, the Sun radiates a continuous stream of charged particles (a plasma) known as the solar wind. This stream of particles spreads outwards at roughly 1.5 million kilometres per hour, creating a tenuous atmosphere that permeates the interplanetary medium out to at least 100 AU (see § Heliosphere). Activity on the Sun's surface, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, disturb the heliosphere, creating space weather and causing geomagnetic storms. The largest structure within the heliosphere is the heliospheric current sheet, a spiral form created by the actions of the Sun's rotating magnetic field on the interplanetary medium.
Earth's magnetic field stops its atmosphere from being stripped away by the solar wind.
Venus and Mars do not have magnetic fields, and as a result the solar
wind is causing their atmospheres to gradually bleed away into space. Coronal mass ejections
and similar events blow a magnetic field and huge quantities of
material from the surface of the Sun. The interaction of this magnetic
field and material with Earth's magnetic field funnels charged particles
into Earth's upper atmosphere, where its interactions create aurorae seen near the magnetic poles.
The heliosphere and planetary magnetic fields (for those planets
that have them) partially shield the Solar System from high-energy
interstellar particles called cosmic rays. The density of cosmic rays in the interstellar medium
and the strength of the Sun's magnetic field change on very long
timescales, so the level of cosmic-ray penetration in the Solar System
varies, though by how much is unknown.
The interplanetary medium is home to at least two disc-like regions of cosmic dust. The first, the zodiacal dust cloud, lies in the inner Solar System and causes the zodiacal light. It was likely formed by collisions within the asteroid belt brought on by gravitational interactions with the planets. The second dust cloud extends from about 10 AU to about 40 AU, and was probably created by similar collisions within the Kuiper belt.
Inner Solar System
The inner Solar System is the region comprising the terrestrial planets and the asteroid belt. Composed mainly of silicates
and metals, the objects of the inner Solar System are relatively close
to the Sun; the radius of this entire region is less than the distance
between the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn. This region is also within the
frost line, which is a little less than 5 AU (about 700 million km) from the Sun.
Inner planets
Orrery showing the motions of the inner four planets. The small spheres represent the position of each planet on every Julian day, beginning July 6 2018 (aphelion) and ending January 3 2019 (perihelion).
The four terrestrial or inner planets have dense, rocky compositions, few or no moons, and no ring systems. They are composed largely of refractory minerals, such as the silicates—which form their crusts and mantles—and metals, such as iron and nickel, which form their cores. Three of the four inner planets (Venus, Earth and Mars) have atmospheres substantial enough to generate weather; all have impact craters and tectonic surface features, such as rift valleys and volcanoes. The term inner planet should not be confused with inferior planet, which designates those planets that are closer to the Sun than Earth is (i.e. Mercury and Venus).
Mercury
- Mercury (0.4 AU from the Sun) is the closest planet to the Sun and the smallest planet in the Solar System (0.055 M⊕). Mercury has no natural satellites; besides impact craters, its only known geological features are lobed ridges or rupes that were probably produced by a period of contraction early in its history. Mercury's very tenuous atmosphere consists of atoms blasted off its surface by the solar wind. Its relatively large iron core and thin mantle have not yet been adequately explained. Hypotheses include that its outer layers were stripped off by a giant impact; or, that it was prevented from fully accreting by the young Sun's energy.
Venus
- Venus (0.7 AU from the Sun) is close in size to Earth (0.815 M⊕) and, like Earth, has a thick silicate mantle around an iron core, a substantial atmosphere, and evidence of internal geological activity. It is much drier than Earth, and its atmosphere is ninety times as dense. Venus has no natural satellites. It is the hottest planet, with surface temperatures over 400 °C (752 °F), most likely due to the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. No definitive evidence of current geological activity has been detected on Venus, but it has no magnetic field that would prevent depletion of its substantial atmosphere, which suggests that its atmosphere is being replenished by volcanic eruptions.
Earth
- Earth (1 AU from the Sun) is the largest and densest of the inner planets, the only one known to have current geological activity, and the only place where life is known to exist. Its liquid hydrosphere is unique among the terrestrial planets, and it is the only planet where plate tectonics has been observed. Earth's atmosphere is radically different from those of the other planets, having been altered by the presence of life to contain 21% free oxygen. It has one natural satellite, the Moon, the only large satellite of a terrestrial planet in the Solar System.
Mars
- Mars (1.5 AU from the Sun) is smaller than Earth and Venus (0.107 M⊕). It has an atmosphere of mostly carbon dioxide with a surface pressure of 6.1 millibars (roughly 0.6% of that of Earth). Its surface, peppered with vast volcanoes, such as Olympus Mons, and rift valleys, such as Valles Marineris, shows geological activity that may have persisted until as recently as 2 million years ago. Its red colour comes from iron oxide (rust) in its soil. Mars has two tiny natural satellites (Deimos and Phobos) thought to be either captured asteroids, or ejected debris from a massive impact early in Mars's history.
Asteroid belt
The donut-shaped asteroid belt is located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
| Sun Jupiter trojans Planetary orbit | Asteroid belt Hilda asteroids NEOs (selection) |
Asteroids except for the largest, Ceres, are classified as small Solar System bodies and are composed mainly of refractory rocky and metallic minerals, with some ice. They range from a few metres to hundreds of kilometres in size. Asteroids smaller than one meter are usually called meteoroids and micrometeoroids (grain-sized), depending on different, somewhat arbitrary definitions.
The asteroid belt occupies the orbit between Mars and Jupiter, between 2.3 and 3.3 AU
from the Sun. It is thought to be remnants from the Solar System's
formation that failed to coalesce because of the gravitational
interference of Jupiter. The asteroid belt contains tens of thousands, possibly millions, of objects over one kilometre in diameter. Despite this, the total mass of the asteroid belt is unlikely to be more than a thousandth of that of Earth. The asteroid belt is very sparsely populated; spacecraft routinely pass through without incident.
Ceres
Ceres – map of gravity fields: red is high; blue, low.
- Ceres (2.77 AU) is the largest asteroid, a protoplanet, and a dwarf planet. It has a diameter of slightly under 1000 km, and a mass large enough for its own gravity to pull it into a spherical shape. Ceres was considered a planet when it was discovered in 1801, and was reclassified to asteroid in the 1850s as further observations revealed additional asteroids. It was classified as a dwarf planet in 2006 when the definition of a planet was created.
Asteroid groups
- Asteroids in the asteroid belt are divided into asteroid groups and families based on their orbital characteristics. Asteroid moons are asteroids that orbit larger asteroids. They are not as clearly distinguished as planetary moons, sometimes being almost as large as their partners. The asteroid belt also contains main-belt comets, which may have been the source of Earth's water.
- Jupiter trojans are located in either of Jupiter's L4 or L5 points (gravitationally stable regions leading and trailing a planet in its orbit); the term trojan is also used for small bodies in any other planetary or satellite Lagrange point. Hilda asteroids are in a 2:3 resonance with Jupiter; that is, they go around the Sun three times for every two Jupiter orbits.
- The inner Solar System also contains near-Earth asteroids, many of which cross the orbits of the inner planets. Some of them are potentially hazardous objects.
Outer Solar System
The outer region of the Solar System is home to the giant planets and their large moons. The centaurs and many short-period comets
also orbit in this region. Due to their greater distance from the Sun,
the solid objects in the outer Solar System contain a higher proportion
of volatiles, such as water, ammonia, and methane than those of the
inner Solar System because the lower temperatures allow these compounds
to remain solid.
Outer planets
Orrery showing the motions of the outer four planets. The small spheres represent the position of each planet on every 100 Julian days, beginning January 21 2023 (Jovian perihelion) and ending December 2 2034 (Jovian perihelion).
The four outer planets, or giant planets (sometimes called Jovian
planets), collectively make up 99% of the mass known to orbit the Sun. Jupiter and Saturn are together more than 400 times the mass of Earth and consist overwhelmingly of hydrogen and helium. Uranus and Neptune are far less massive—less than 20 Earth masses (M⊕) each—and are composed primarily of ices. For these reasons, some astronomers suggest they belong in their own category, ice giants. All four giant planets have rings, although only Saturn's ring system is easily observed from Earth. The term superior planet designates planets outside Earth's orbit and thus includes both the outer planets and Mars.
Jupiter
- Jupiter (5.2 AU), at 318 M⊕, is 2.5 times the mass of all the other planets put together. It is composed largely of hydrogen and helium. Jupiter's strong internal heat creates semi-permanent features in its atmosphere, such as cloud bands and the Great Red Spot. Jupiter has 79 known satellites. The four largest, Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa, show similarities to the terrestrial planets, such as volcanism and internal heating. Ganymede, the largest satellite in the Solar System, is larger than Mercury.
Saturn
- Saturn (9.5 AU), distinguished by its extensive ring system, has several similarities to Jupiter, such as its atmospheric composition and magnetosphere. Although Saturn has 60% of Jupiter's volume, it is less than a third as massive, at 95 M⊕. Saturn is the only planet of the Solar System that is less dense than water. The rings of Saturn are made up of small ice and rock particles. Saturn has 62 confirmed satellites composed largely of ice. Two of these, Titan and Enceladus, show signs of geological activity. Titan, the second-largest moon in the Solar System, is larger than Mercury and the only satellite in the Solar System with a substantial atmosphere.
Uranus
- Uranus (19.2 AU), at 14 M⊕, is the lightest of the outer planets. Uniquely among the planets, it orbits the Sun on its side; its axial tilt is over ninety degrees to the ecliptic. It has a much colder core than the other giant planets and radiates very little heat into space. Uranus has 27 known satellites, the largest ones being Titania, Oberon, Umbriel, Ariel, and Miranda.
Neptune
- Neptune (30.1 AU), though slightly smaller than Uranus, is more massive (17 M⊕) and hence more dense. It radiates more internal heat, but not as much as Jupiter or Saturn. Neptune has 14 known satellites. The largest, Triton, is geologically active, with geysers of liquid nitrogen. Triton is the only large satellite with a retrograde orbit. Neptune is accompanied in its orbit by several minor planets, termed Neptune trojans, that are in 1:1 resonance with it.
Centaurs
The centaurs are icy comet-like bodies whose orbits have semi-major
axes greater than Jupiter's (5.5 AU) and less than Neptune's (30 AU).
The largest known centaur, 10199 Chariklo, has a diameter of about 250 km. The first centaur discovered, 2060 Chiron, has also been classified as comet (95P) because it develops a coma just as comets do when they approach the Sun.
Comets
Hale–Bopp seen in 1997
Comets are small Solar System bodies,
typically only a few kilometres across, composed largely of volatile
ices. They have highly eccentric orbits, generally a perihelion within
the orbits of the inner planets and an aphelion far beyond Pluto. When a
comet enters the inner Solar System, its proximity to the Sun causes
its icy surface to sublimate and ionise, creating a coma: a long tail of gas and dust often visible to the naked eye.
Short-period comets have orbits lasting less than two hundred
years. Long-period comets have orbits lasting thousands of years.
Short-period comets are thought to originate in the Kuiper belt, whereas
long-period comets, such as Hale–Bopp, are thought to originate in the Oort cloud. Many comet groups, such as the Kreutz Sungrazers, formed from the breakup of a single parent. Some comets with hyperbolic orbits may originate outside the Solar System, but determining their precise orbits is difficult. Old comets that have had most of their volatiles driven out by solar warming are often categorised as asteroids.
Trans-Neptunian region
Beyond the orbit of Neptune lies the area of the "trans-Neptunian region",
with the doughnut-shaped Kuiper belt, home of Pluto and several other
dwarf planets, and an overlapping disc of scattered objects, which is tilted toward the plane of the Solar System and reaches much further out than the Kuiper belt. The entire region is still largely unexplored.
It appears to consist overwhelmingly of many thousands of small
worlds—the largest having a diameter only a fifth that of Earth and a
mass far smaller than that of the Moon—composed mainly of rock and ice.
This region is sometimes described as the "third zone of the Solar
System", enclosing the inner and the outer Solar System.
Kuiper belt
Known objects in the Kuiper belt
| Sun Jupiter trojans Giant planets | Kuiper belt Scattered disc Neptune trojans |
The Kuiper belt is a great ring of debris similar to the asteroid
belt, but consisting mainly of objects composed primarily of ice.
It extends between 30 and 50 AU from the Sun. Though it is estimated to
contain anything from dozens to thousands of dwarf planets, it is
composed mainly of small Solar System bodies. Many of the larger Kuiper
belt objects, such as Quaoar, Varuna, and Orcus,
may prove to be dwarf planets with further data. There are estimated to
be over 100,000 Kuiper belt objects with a diameter greater than 50 km,
but the total mass of the Kuiper belt is thought to be only a tenth or
even a hundredth the mass of Earth. Many Kuiper belt objects have multiple satellites, and most have orbits that take them outside the plane of the ecliptic.
The Kuiper belt can be roughly divided into the "classical" belt and the resonances.
Resonances are orbits linked to that of Neptune (e.g. twice for every
three Neptune orbits, or once for every two). The first resonance begins
within the orbit of Neptune itself. The classical belt consists of
objects having no resonance with Neptune, and extends from roughly
39.4 AU to 47.7 AU. Members of the classical Kuiper belt are classified as cubewanos, after the first of their kind to be discovered, 15760 Albion (which previously had the provisional designation 1992 QB1), and are still in near primordial, low-eccentricity orbits.
Pluto and Charon
- The dwarf planet Pluto (39 AU average) is the largest known object in the Kuiper belt. When discovered in 1930, it was considered to be the ninth planet; this changed in 2006 with the adoption of a formal definition of planet. Pluto has a relatively eccentric orbit inclined 17 degrees to the ecliptic plane and ranging from 29.7 AU from the Sun at perihelion (within the orbit of Neptune) to 49.5 AU at aphelion. Pluto has a 3:2 resonance with Neptune, meaning that Pluto orbits twice round the Sun for every three Neptunian orbits. Kuiper belt objects whose orbits share this resonance are called plutinos.
- Charon, the largest of Pluto's moons, is sometimes described as part of a binary system with Pluto, as the two bodies orbit a barycentre of gravity above their surfaces (i.e. they appear to "orbit each other"). Beyond Charon, four much smaller moons, Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra, orbit within the system.
Eris
- Eris (minor-planet designation 136199 Eris) is the most massive and second-largest (by volume) dwarf planet in the known Solar System. Eris was discovered in January 2005 by a Palomar Observatory-based team led by Mike Brown, and its discovery was verified later that year. In September 2006 it was named after Eris, the Greek goddess of strife and discord. Eris is the ninth most massive object directly orbiting the Sun, and the 16th most massive overall, because seven moons are more massive than all known dwarf planets. It is also the largest which has not yet been visited by a spacecraft. Eris was measured to be 2,326 ± 12 kilometers (1,445.3 ± 7.5 mi) in diameter. Eris's mass is about 0.27% of the Earth mass, about 27% more than dwarf planet Pluto, although Pluto is slightly larger by volume.
Makemake and Haumea
- Makemake (45.79 AU average), although smaller than Pluto, is the largest known object in the classical Kuiper belt (that is, a Kuiper belt object not in a confirmed resonance with Neptune). Makemake is the brightest object in the Kuiper belt after Pluto. It was named and designated a dwarf planet in 2008. Its orbit is far more inclined than Pluto's, at 29°.
- Haumea (43.13 AU average) is in an orbit similar to Makemake except that it is in a 7:12 orbital resonance with Neptune. It is about the same size as Makemake and has two natural satellites. A rapid, 3.9-hour rotation gives it a flattened and elongated shape. It was named and designated a dwarf planet in 2008.
Scattered disc
The scattered disc, which overlaps the Kuiper belt but extends much
further outwards, is thought to be the source of short-period comets.
Scattered-disc objects are thought to have been ejected into erratic
orbits by the gravitational influence of Neptune's early outward migration.
Most scattered disc objects (SDOs) have perihelia within the Kuiper
belt but aphelia far beyond it (some more than 150 AU from the Sun).
SDOs' orbits are also highly inclined to the ecliptic plane and are
often almost perpendicular to it. Some astronomers consider the
scattered disc to be merely another region of the Kuiper belt and
describe scattered disc objects as "scattered Kuiper belt objects".
Some astronomers also classify centaurs as inward-scattered Kuiper belt
objects along with the outward-scattered residents of the scattered
disc.
Farthest regions
From the Sun to the nearest star: The Solar System on a logarithmic scale in astronomical units (AU)
The point at which the Solar System ends and interstellar space
begins is not precisely defined because its outer boundaries are shaped
by two separate forces: the solar wind and the Sun's gravity. The limit
of the solar wind's influence is roughly four times Pluto's distance
from the Sun; this heliopause, the outer boundary of the heliosphere, is considered the beginning of the interstellar medium. The Sun's Hill sphere,
the effective range of its gravitational dominance, is thought to
extend up to a thousand times farther and encompasses the theorized Oort cloud.
Heliosphere
The bubble-like heliosphere with its various transitional regions moving through the interstellar medium
The heliosphere is a stellar-wind bubble, a region of space dominated by the Sun, which radiates at roughly 400 km/s its solar wind, a stream of charged particles, until it collides with the wind of the interstellar medium.
The collision occurs at the termination shock, which is roughly 80–100 AU from the Sun upwind of the interstellar medium and roughly 200 AU from the Sun downwind. Here the wind slows dramatically, condenses and becomes more turbulent, forming a great oval structure known as the heliosheath.
This structure is thought to look and behave very much like a comet's
tail, extending outward for a further 40 AU on the upwind side but
tailing many times that distance downwind; evidence from Cassini and Interstellar Boundary Explorer spacecraft has suggested that it is forced into a bubble shape by the constraining action of the interstellar magnetic field.
The outer boundary of the heliosphere, the heliopause, is the point at which the solar wind finally terminates and is the beginning of interstellar space. Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 are reported to have passed the termination shock and entered the heliosheath, at 94 and 84 AU from the Sun, respectively. Voyager 1 is reported to have crossed the heliopause in August 2012.
The shape and form of the outer edge of the heliosphere is likely affected by the fluid dynamics of interactions with the interstellar medium as well as solar magnetic fields
prevailing to the south, e.g. it is bluntly shaped with the northern
hemisphere extending 9 AU farther than the southern hemisphere. Beyond the heliopause, at around 230 AU, lies the bow shock, a plasma "wake" left by the Sun as it travels through the Milky Way.
Zooming out the Solar System:
- inner Solar System and Jupiter
- outer Solar System and Pluto
- orbit of Sedna (detached object)
- inner part of the Oort Cloud
Due to a lack of data, conditions in local interstellar space are not known for certain. It is expected that NASA's Voyager spacecraft, as they pass the heliopause, will transmit valuable data on radiation levels and solar wind to Earth.
How well the heliosphere shields the Solar System from cosmic rays is
poorly understood. A NASA-funded team has developed a concept of a
"Vision Mission" dedicated to sending a probe to the heliosphere.
Detached objects
90377 Sedna
(520 AU average) is a large, reddish object with a gigantic, highly
elliptical orbit that takes it from about 76 AU at perihelion to 940 AU
at aphelion and takes 11,400 years to complete. Mike Brown, who discovered the object in 2003, asserts that it cannot be part of the scattered disc
or the Kuiper belt because its perihelion is too distant to have been
affected by Neptune's migration. He and other astronomers consider it to
be the first in an entirely new population, sometimes termed "distant
detached objects" (DDOs), which also may include the object 2000 CR105, which has a perihelion of 45 AU, an aphelion of 415 AU, and an orbital period of 3,420 years.
Brown terms this population the "inner Oort cloud" because it may have
formed through a similar process, although it is far closer to the Sun.
Sedna is very likely a dwarf planet, though its shape has yet to be
determined. The second unequivocally detached object, with a perihelion
farther than Sedna's at roughly 81 AU, is 2012 VP113, discovered in 2012. Its aphelion is only half that of Sedna's, at 400–500 AU.
Oort cloud
Schematic of the hypothetical Oort cloud, with a spherical outer cloud and a disc-shaped inner cloud
The Oort cloud is a hypothetical spherical cloud of up to a trillion
icy objects that is thought to be the source for all long-period comets
and to surround the Solar System at roughly 50,000 AU (around 1 light-year
(ly)), and possibly to as far as 100,000 AU (1.87 ly). It is thought to
be composed of comets that were ejected from the inner Solar System by
gravitational interactions with the outer planets. Oort cloud objects
move very slowly, and can be perturbed by infrequent events, such as
collisions, the gravitational effects of a passing star, or the galactic tide, the tidal force exerted by the Milky Way.
Boundaries
Much of the Solar System is still unknown. The Sun's gravitational field is estimated to dominate the gravitational forces of surrounding stars
out to about two light years (125,000 AU). Lower estimates for the
radius of the Oort cloud, by contrast, do not place it farther than
50,000 AU.
Despite discoveries such as Sedna, the region between the Kuiper belt
and the Oort cloud, an area tens of thousands of AU in radius, is still
virtually unmapped. There are also ongoing studies of the region between
Mercury and the Sun. Objects may yet be discovered in the Solar System's uncharted regions.
Currently, the furthest known objects, such as Comet West, have aphelia around 70,000 AU from the Sun, but as the Oort cloud becomes better known, this may change.
Galactic context
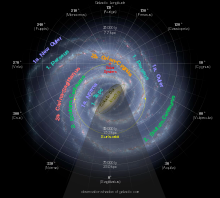
Diagram of the Milky Way with the position of the Solar System marked by a yellow arrow
The Solar System is located in the Milky Way, a barred spiral galaxy with a diameter of about 100,000 light-years containing about 100 billion stars. The Sun resides in one of the Milky Way's outer spiral arms, known as the Orion–Cygnus Arm or Local Spur. The Sun lies between 25,000 and 28,000 light-years from the Galactic Centre,
and its speed within the Milky Way is about 220 km/s, so that it
completes one revolution every 225–250 million years. This revolution is
known as the Solar System's galactic year. The solar apex, the direction of the Sun's path through interstellar space, is near the constellation Hercules in the direction of the current location of the bright star Vega. The plane of the ecliptic lies at an angle of about 60° to the galactic plane.
The Solar System's location in the Milky Way is a factor in the evolutionary history of life on Earth. Its orbit is close to circular, and orbits near the Sun are at roughly the same speed as that of the spiral arms. Therefore, the Sun passes through arms only rarely. Because spiral arms are home to a far larger concentration of supernovae,
gravitational instabilities, and radiation that could disrupt the Solar
System, this has given Earth long periods of stability for life to
evolve.
The Solar System also lies well outside the star-crowded environs of
the galactic centre. Near the centre, gravitational tugs from nearby
stars could perturb bodies in the Oort cloud
and send many comets into the inner Solar System, producing collisions
with potentially catastrophic implications for life on Earth. The
intense radiation of the galactic centre could also interfere with the
development of complex life.
Even at the Solar System's current location, some scientists have
speculated that recent supernovae may have adversely affected life in
the last 35,000 years, by flinging pieces of expelled stellar core
towards the Sun, as radioactive dust grains and larger, comet-like
bodies.
Neighborhood
Beyond
the heliosphere is the interstellar medium, consisting of various
clouds of gases. The Solar System currently moves through the Local Interstellar Cloud.
The Solar System is in the Local Interstellar Cloud or Local Fluff. It is thought to be near the neighbouring G-Cloud
but it is not known if the Solar System is embedded in the Local
Interstellar Cloud, or if it is in the region where the Local
Interstellar Cloud and G-Cloud are interacting. The Local Interstellar Cloud is an area of denser cloud in an otherwise sparse region known as the Local Bubble, an hourglass-shaped cavity in the interstellar medium
roughly 300 light-years (ly) across. The bubble is suffused with
high-temperature plasma, that suggests it is the product of several
recent supernovae.
There are relatively few stars within ten light-years of the Sun. The closest is the triple star system Alpha Centauri, which is about 4.4 light-years away. Alpha Centauri A and B are a closely tied pair of Sun-like stars, whereas the small red dwarf, Proxima Centauri, orbits the pair at a distance of 0.2 light-year. In 2016, a potentially habitable exoplanet was confirmed to be orbiting Proxima Centauri, called Proxima Centauri b, the closest confirmed exoplanet to the Sun. The stars next closest to the Sun are the red dwarfs Barnard's Star (at 5.9 ly), Wolf 359 (7.8 ly), and Lalande 21185 (8.3 ly).
The largest nearby star is Sirius, a bright main-sequence star roughly 8.6 light-years away and roughly twice the Sun's mass and that is orbited by a white dwarf, Sirius B. The nearest brown dwarfs are the binary Luhman 16 system at 6.6 light-years. Other systems within ten light-years are the binary red-dwarf system Luyten 726-8 (8.7 ly) and the solitary red dwarf Ross 154 (9.7 ly). The closest solitary Sun-like star to the Solar System is Tau Ceti at 11.9 light-years. It has roughly 80% of the Sun's mass but only 60% of its luminosity. The closest known free-floating planetary-mass object to the Sun is WISE 0855−0714, an object with a mass less than 10 Jupiter masses roughly 7 light-years away.
Comparison with extrasolar systems
Compared to many other planetary systems, the Solar System stands out in lacking planets interior to the orbit of Mercury. The known Solar System also lacks super-Earths (Planet Nine could be a super-Earth beyond the known Solar System).
Uncommonly, it has only small rocky planets and large gas giants;
elsewhere planets of intermediate size are typical—both rocky and gas—so
there is no "gap" as seen between the size of Earth and of Neptune
(with a radius 3.8 times as large). Also, these super-Earths have closer
orbits than Mercury.
This led to hypothesis that all planetary systems start with many
close-in planets, and that typically a sequence of their collisions
causes consolidation of mass into few larger planets, but in case of the
Solar System the collisions caused their destruction and ejection.
The orbits of Solar System planets are nearly circular. Compared to other systems, they have smaller orbital eccentricity.
Although there are attempts to explain it partly with a bias in the
radial-velocity detection method and partly with long interactions of a
quite high number of planets, the exact causes remain undetermined.