Regenerative design is a process-oriented whole systems approach to design. The term "regenerative" describes processes that restore, renew or revitalize their own sources of energy and materials. Regenerative design uses whole systems thinking to create resilient and equitable systems that integrate the needs of society with the integrity of nature.
Designers use systems thinking, applied permaculture design principles, and community development processes to design human and ecological systems. The development of regenerative design has been influenced by approaches found in the biomimicry, biophilic design, ecological economics, circular economics. As well as social movements such as permaculture, transition and the new economy. Regenerative design can also refer to process of designing systems such as restorative justice, rewilding and regenerative agriculture.
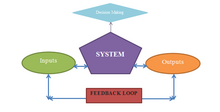
Feedback loop used in regenerative design
A new generation of designers are applying ecologically inspired design to agriculture, architecture, community planning, cities, enterprises, economics and ecosystem regeneration. Many designers use the resilient models observed in systems ecology in their design process and recognize that ecosystems are resilient largely because they operate in closed loop systems. Using this model regenerative design seeks feedback at every stage of the design process. Feedback loops are an integral to regenerative systems as understood by processes used in restorative practice and community development.
Regenerative design is interconnected with the approaches of systems thinking and with New Economy movement. The 'new economy' considers that the current economic system needs to be restructured.
The theory is based on the assumption that people and the planet should
come first, and that it is human well-being, not economic growth, which
should be prioritized.
Whereas the highest aim of sustainable development is to satisfy fundamental human needs
today without compromising the possibility of future generations to
satisfy theirs, the goal of regenerative design is to develop
restorative systems that are dynamic and emergent, and are beneficial
for humans and other species. This regeneration process is
participatory, iterative and individual to the community and environment
it is applied to. This process intends to revitalize communities, human
and natural resources, and for some, society as a whole.
In recent years regenerative design is made possible on a larger
scale using open source socio- technical platforms and technological
systems as used in SMART cities. It is an includes community and city development processes like gathering feedback, participatory governance, sortition and participatory budgeting.
History
Permaculture
The term permaculture was developed and coined by David Holmgren, then a graduate student at the Tasmanian College of Advanced Education's Department of Environmental Design, and Bill Mollison, senior lecturer in Environmental Psychology at University of Tasmania, in 1978. The word permaculture originally referred to "permanent agriculture",
but was expanded to stand also for "permanent culture", as it was
understood that social aspects were integral to a truly sustainable
system as inspired by Masanobu Fukuoka’s natural farming philosophy. Regenerative design is integral to permaculture design.
In 1974 David Holmgren and Bill Mollison first started working together to develop the theory and practice of permaculture.
They met when Mollison spoke at a seminar at the Department of
Environmental Design and began to work together. During their first
three years together Mollison worked at applying their ideas, and
Holmgren wrote the manuscript for what would become Permaculture One: a perennial agricultural system for human settlements
as he completed his Environmental Design studies, and submitted it as
the major reference for his thesis. He then handed the manuscript to
Mollison for editing and additions, before it was published in 1978.
Regenerative organic agriculture
Robert Rodale, son of American organic pioneer and Rodale Institute founder J.I. Rodale, coined the term ‘regenerative organic agriculture.’
The term distinguished a kind of farming that goes beyond simply
‘sustainable.’ Regenerative organic agriculture “takes advantage of the
natural tendencies of ecosystems to regenerate when disturbed. In that
primary sense it is distinguished from other types of agriculture that
either oppose or ignore the value of those natural tendencies.”
This type of farming is marked by "tendencies towards closed nutrient
loops, greater diversity in the biological community, fewer annuals and
more perennials, and greater reliance on internal rather than external
resources."
John T. Lyle (1934–1998), a landscape architecture professor saw the connection between concepts developed by Bob Rodale for regenerative agriculture
and the opportunity to develop regenerative systems for all other
aspects of the world. While regenerative agriculture focused solely on
agriculture, Lyle expanded its concepts and use to all systems. Lyle
understood that when developing for other types of systems, more
complicated ideas such as entropy and emergy must be taken into consideration.
Regenerative design in the built environment
In 1976, Lyle challenged his landscape architecture graduate students at California State Polytechnic University, Pomona to "envision a community in which daily activities were based on the value of living within the limits of available renewable resources without environmental degradation."
Over the next few decades an eclectic group of students, professors and
experts from around the world and crossing many disciplines developed
designs for an institute to be built at Cal Poly Pomona. In 1994, the Lyle Center for Regenerative Studies opened after two years of construction. In that same year Lyle's book Regenerative Design for Sustainable Development was published by Wiley. In 1995 Lyle worked with William McDonough at Oberlin College on the design of the Adam Joseph Lewis Center for Environmental Studies completed in 2000. In 2002 McDonough's book, the more popular and successful, Cradle to Cradle: Remaking the Way We Make Things was published reiterating the concepts developed by Lyle. Swiss architect Walter R. Stahel developed approaches entirely similar to Lyle's also in the late 1970s but instead coined the term cradle-to-cradle design made popular by McDonough and Michael Braungart.
Sim Van Der Ryn is an architect, author, and educator with more
than 40 years of experience integrating ecological principles into the
built environment. Author of eight publications, one of his most influential books titled Ecological Design,
published in 1996, provides a framework for integrating human design
with living systems. The book challenges designers to push beyond "green
building" to create buildings, infrastructure and landscapes that truly
restore and regenerative of the surrounding ecosystems.
Green vs. sustainable vs. regenerative
There
is an important distinction that should be made between the words
‘green’, ‘sustainable’, and ‘regenerative’ and how they influence
design.
Green Design
In the article Transitioning from green to regenerative design,
Raymond J. Cole explores the concept of regenerative design and what it
means in relation to ‘green’ and ‘sustainable’ design. Cole identifies
eight key attributes of green buildings:
- Reduces damage to natural or sensitive sites
- Reduces the need for new infrastructure
- Reduces the impacts on natural feature and site ecology during construction
- Reduces the potential environmental damage from emissions and outflows
- Reduces the contributions to global environmental damage
- Reduces resource use – energy, water, materials
- Minimizes the discomfort of building occupants
- Minimizes harmful substances and irritants within building interiors
By these eight key attributes, ‘green’ design is accomplished by
reducing the harmful, damaging and negative impacts to both the
environment and humans that result from the construction of the built
environment. Another characteristic that separates ‘green’ design is
that it is aimed at broad market transformation and therefore green
building assessment frameworks and tools are typically generic in
nature.
Sustainable Design
Sustainable design lies within a balance of economical, environmental and social responsibilities
‘Sustainable’ and ‘green’ are for the most part used interchangeably
however, there is a slight distinction between then. ‘Green’ design is
centralized around specifically decreasing environmental impacts from
human development whereas sustainability can be viewed for an
environmental, economic or social lens. The implication is that
sustainability can be incorporated to all three aspects of the Triple Bottom Line: people, planet, profit.
The definition of sustainable or sustainability
has been widely accepted as the ability to meet the needs of the
current generation without depleting the resources needed to meet the
needs of future generations. It “promotes a bio-centric view that places
the human presence within a larger natural context, and focuses on
constraints and on fundamental values and behavioral change.” David Orr defines two approaches to sustainability in his book Ecological Literacy: “technological sustainability” and “ecological sustainability.”
“Technological sustainability” emphasizes the anthropocentric view by
focusing on making technological and engineering processes more
efficient whereas “ecological sustainability" emphasizes the bio-centric
view and focuses on enabling and maintaining the essential and natural
functions of ecosystems.
The sustainability movement has gained momentum over the last two
decades, with interest from all sectors increasing rapidly each year.
In the book Regenerative Development and Design: A Framework for Evolving Sustainability, the Regenesis Group
asserts that the sustainability “debate is shifting from whether we
should work on sustainability to how we’re going to get it done.”
Sustainability was first viewed as a “steady state of equilibrium” in
which there was a balance between inputs and outputs with the idea that
sustainable practices meant future resources were not compromised by
current processes. As this idea of sustainability and sustainable
building has become more widely accepted and adopted, the idea of “net-zero”
and even “net-positive” have become topics of interest. These
relatively newer concepts focus on positively impacting the surrounding
environment of a building rather than simply reducing the negative
impacts.
Regenerative Design
J.T.
Gibberd argued “a building is an element set within wider human
endeavors and is necessarily dependent on this context. Thus, a building
can support sustainable patterns of living, but in and of itself cannot
be sustainable” Regenerative design goes a step further than sustainable design. In a regenerative system, feedback loops allow for adaptability, dynamism and emergence
to create and develop resilient and flourishing eco-systems. Cole
highlights a key distinction of regenerative design is the recognition
and emphasis of the “co-evolutionary, partnered relationship between
human and natural systems” and thus importance of project location and
place.
Bruno Duarte Dias asserts that regenerative design goes beyond the
traditional weighing and measuring of various environmental, social and
economic impacts of sustainable design and instead focuses on mapping
relationships. Dias is in agreement with Cole stating three fundamental
aspects of regenerative design which include: understanding place and
it’s unique patterns, designing for harmony within place, and
co-evolution.
Fundamental aspects of regenerative design
Co-evolution of humans & nature
Regenerative
design is built on the idea that humans and the built environment exist
within natural systems and thus, the built environment should be
designed to co-evolve with the surrounding natural environment. Dias
asserts that a building should serve as a “catalyst for positive
change.” The project does not end with the completion of construction
and certificate of occupancy, instead the building serves to enhance the
relationships between people, the built environment and the surrounding
natural systems over a long period of time.
Designing in context of place
Understanding
the location of the project, the unique dynamics of the site and the
relationship of the project to the living natural systems is a
fundamental concept in the regenerative design process. In their article
Designing from place: a regenerative framework and methodology,
Pamela Mang and Bill Reed define place as a "unique, multilayered
network of living systems within a geographic region that results from
the complex interactions, through time, of the natural ecology (climate,
mineral and other deposits, soil, vegetation, water and wildlife, etc.)
and culture (distinctive customs, expressions of values, economic
activities, forms of association, ideas for education, traditions,
etc.)" A systems-based approach to design in which the design team looks at the building within the larger system is crucial.
The Gardener Analogy
Beatrice
Benne and Pamela Mang emphasize the importance of the distinction
between working with a place rather than working on a place within the
regenerative design process. They use an analogy of a gardener to
re-define the role of a designer in the building process. “A gardener
does not ‘make’ a garden. Instead, a skilled gardener is one who has
developed an understanding of the key processes operating in the garden”
and thus the gardener “makes judicious decisions on how and where to
intervene to reestablish the flows of energy that are vital to the
health of the garden.”
In the same way a designer does not create a thriving ecosystem rather
they make decisions that indirectly influence whether the ecosystem
degrades or flourishes over time. This requires designers to push beyond
the prescriptive and narrow way of thinking they have been taught and
use complex systems thinking that will be ambiguous and overwhelming at
times. This includes accepting that the solutions do not exclusively lie
in technological advancements and are instead a combination of
sustainable technologies and an understanding of the natural flow of
resources and underlying ecological processes. Benne and Mang identify
these challenges and state the most difficult of these will be shifting
from a mechanistic to an ecological worldview. The tendency is to view
building as the physical processes of the structure rather than the
complex network of relationships the building has with the surrounding
environment including the natural systems and the human community.
Conservation vs. preservation
Regenerative
design places more importance on conservation and biodiversity rather
than on preservation. It is recognized in regenerative design that
humans are a part of natural ecosystems. To exclude people is to create
dense areas that destroy pockets of existing ecosystems while preserving
pockets of ecosystems without allowing them to change naturally over
time.
Regenerative design frameworks
There
are a few regenerative design frameworks that have been developed in
recent years. Unlike many green building rating systems, these
frameworks are not prescriptive checklists. Instead they are conceptual
and meant to guide dialogue throughout the design process. They should
not be used exclusively rather in conjunction with existing green
building rating systems such as LEED, BREEAM or Living Building Challenge.
SPeAR
Sustainable
Project Appraisal Routine (SPeAR) is a decision-making tool developed
by software and sustainability experts at Arup. The framework
incorporates key categories including transportation, biodiversity,
culture, employment and skills.
REGEN
The
regenerative design framework REGEN was proposed by Berkebile Nelson
Immenschuh McDowell (BNIM), a US architectural firm, for the US Green
Building Council (USGBC). The tool was was intended to be a web-based, data-rich framework to
guide dialogue between professionals in the design and development
process as well as "address the gap in information and integration of
information." The framework has three components:
- Framework - the framework encourages systems thinking and collaboration as well as linking individual strategies to the goals of the project as a whole
- Resources - the framework includes place-based data and information for project teams to use
- Projects - the framework includes examples of successful projects that have incorporated regenerative ideas into the design as models for project teams
LENSES
Living
Environments in Natural, Social and Economic Systems (LENSES) was
created by Colorado State University's Institute for the Built
Environment. The framework is intended to be process-based rather than
product-based. The goals of the framework include:
- to direct the development of eco-regional guiding principles for living built environments
- to illustrate connections and relationships between sustainability issues
- to guide collaborative dialogue
- to present complex concepts quickly and effectively to development teams and decision-makers
The framework consists of three "lenses": Foundational Lens, Aspects
of Place Lens and Flows Lens. The lenses work together to guide the
design process, emphasizing the guiding principles and core values,
understanding the delicate relationship between building and place and
how elements flow through the natural and human systems.
Perkins+Will
Perkins+Will
is a global architecture and design firm with a strong focus on
sustainability - by September of 2012 the firm had completed over 150
LEED-certified projects.
It was at te 2008 Healthcare Center for Excellence meeting in
Vancouver, British Columbia that the decision was made to develop a
regenerative design framework in an effort to generate broader
conversation and inspirational ideas.
Later that year, a regenerative design framework that could be used by
all market sectors including healthcare, education, commercial and
residential was developed by Perkins+Will in conjunction with the
University of British Columbia. The framework had four primary
objectives:
- to initiate a different and expanded dialogue between the design team members and with the client and users, moving beyond the immediate building and site boundaries
- to emphasize the opportunities of developed sites and buildings to relate to, maintain, and enhance the health of the ecological and human systems in the place in which they are situated
- to highlight the ecological and human benefits that accrue from regenerative approaches
- to facilitate the broader integration of allied design professionals - urban planners, landscape architects and engineers, together with other disciplines (ecologists, botanists, hydrologists, etc.) typically not involved in buildings - in an interdisciplinary design process
The structure of the framework consists of four primary themes:
- Representation of human and natural systems - the framework is representative of the interactions between humans and the natural environment and is built on the notion that human systems exist only within natural systems. Human needs are further categorized into four categories: individual human health and well-being, social connectivity and local community, cultural vitality and sense of place, and healthy community.
- Representation of resource flows - the framework recognizes that human systems and natural systems are impacted through the way building relates to the land and engages resource flows. These resource flows include energy, water and materials.
- Resource cycles - within the framework, resource flows illustrate how resources flow in and out of human and natural cycles whereas resource cycles focus on how resources move through human systems. The four sub-cycles included in the framework are produce, use, recycle and replenish.
- Direct and indirect engagement with flows - the framework distinguishes between the direct and indirect ways a building engages with resource flows. Direct engagement includes approaches and strategies that occur within the bounds of the project site. Indirect engagement extends beyond the boundaries of the project site and can thus be implemented on a much larger scale such as purchasing renewable energy credits.
Case study - Van Dusen Botanical Garden
The
Visitor Center at the Van Dusen Botanical Garden in Vancouver, British
Columbia was designed in parallel with the regenerative design framework
developed by Perkins+Will. The site of the new visitor center was
17,575 m2 and the building itself 1,784 m2.
A four stage process was identified and included: education and project
aspirations, goal setting, strategies and synergies, and whole systems
approaches. Each stage raises important questions that require the
design team to define place and look at the project in a much larger
context, identify key resources flows and understand the complex
holistic systems, determine synergistic relationships and identify
approaches that provoke the coevolution of both humans and ecological
systems.
The visitor centre was the first project that Perkins+Will worked on in
collaboration with an ecologist. Incorporating an ecologist on the
project team allowed the team to focus on the project from a larger
scale and understand how the building and its specific design would
interact with the surrounding ecosystem through its energy, water and
environmental performance.
Regenerative design for retrofitting existing buildings
Importance and implications
It is said that the majority of buildings estimated to exist in the year 2050 have already been built. Additionally, current buildings account for roughly 40 percent of the total energy consumption within the United States. This means that in order to meet climate change goals - such as the Paris Agreement on Climate Change
- and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, existing buildings need to be
updated to reflect sustainable and regenerative design strategies.
Strategies
Craft
et al. attempted to create a regenerative design model that could be
applied to retrofitting existing buildings. This model was prompted by
the large number of currently existing buildings projected to be present
in 2050. The model presented in this article for building retrofits
follows a ‘Levels of Work’ framework consisting of four levels that are
said to be pertinent in increasing the “vitality, viability and capacity
for evolution” which require a deep understanding of place and how the
building interacts with the natural systems. These four levels are
classified as either proactive or reactive and include regenerate,
improve, maintain and operate.
Case Study
University of New South Wales
Craft
et al. present a case study in which the chemical science building at
the University of New South Wales was retrofitted to incorporate these
regenerative design principles. The strategy uses biophilia
to improve occupants health and wellbeing by strengthening their
connection to nature. The facade acts as a “vertical ecosystem” by
providing habitats for indigenous wildlife to increase biodiversity.
This included the addition of balconies to increase the connection
between humans and nature.
Regenerative agriculture
Regenerative farming or 'regenerative agriculture'
calls for the creation of demand on agricultural systems to produce
food in a way that is beneficial to the production and the ecology of
the environment. It uses the science of systems ecology, and the design and application through permaculture. As understanding of its benefits to human biology and ecological systems that sustain us is increased as has the demand for organic food. Organic food grown using regenerative and permaculture design increases the biodiversity
and is used to develop business models that regenerate communities.
Whereas some foods are organic some are not strictly regenerative
because it is not clearly seeking to maximize biodiversity and the
resilience of the environment and the workforce. Regenerative
agriculture grows organic produce through ethical supply chains, zero waste policies, fair wages, staff development and wellbeing, and in some cases cooperative and social enterprise models. It seeks to benefit the staff along the supply chain, customers, and ecosystems with the outcome of human and ecological restoration and regeneration.
Size of regenerative systems
The size of the regenerative system effects the complexity of the design process. The smaller a system
is designed the more likely it is to be resilient and regenerative.
Multiple small regenerative systems that are put together to create
larger regenerative systems help to create supplies for multiple
human-inclusive-ecological systems.