The Athabasca oil sands in Alberta, Canada, are a very large source of bitumen, which can be upgraded to synthetic crude oil.
Tar sandstone from California, United States
Oil sands, also known as tar sands or crude bitumen, or more technically bituminous sands, are a type of unconventional petroleum deposit. Oil sands are either loose sands or partially consolidated sandstone containing a naturally occurring mixture of sand, clay, and water, saturated with a dense and extremely viscous form of petroleum technically referred to as bitumen (or colloquially as tar due to its superficially similar appearance).
Natural bitumen deposits are reported in many countries, but in particular are found in extremely large quantities in Canada. Other large reserves are located in Kazakhstan, Russia, and Venezuela. The estimated worldwide deposits of oil are more than 2 trillion barrels (320 billion cubic metres);
the estimates include deposits that have not been discovered. Proven
reserves of bitumen contain approximately 100 billion barrels, and total natural bitumen reserves are estimated at 249.67 Gbbl (39.694×109 m3) worldwide, of which 176.8 Gbbl (28.11×109 m3), or 70.8%, are in Alberta, Canada.
The crude bitumen contained in the Canadian oil sands is described by the National Energy Board of Canada as "a highly viscous mixture of hydrocarbons heavier than pentanes which, in its natural state, is not usually recoverable at a commercial rate through a well because it is too thick to flow."
Crude bitumen is a thick, sticky form of crude oil, so heavy and
viscous (thick) that it will not flow unless heated or diluted with
lighter hydrocarbons such as light crude oil or natural-gas condensate. At room temperature, it is much like cold molasses. The World Energy Council (WEC) defines natural bitumen as "oil having a viscosity greater than 10,000 centipoise under reservoir conditions and an API gravity of less than 10° API". The Orinoco Belt in Venezuela is sometimes described as oil sands, but these deposits are non-bituminous, falling instead into the category of heavy or extra-heavy oil due to their lower viscosity.
Natural bitumen and extra-heavy oil differ in the degree by which they
have been degraded from the original conventional oils by bacteria.
According to the WEC, extra-heavy oil has "a gravity of less than 10°
API and a reservoir viscosity of no more than 10,000 centipoise".
Oil sands have only recently been considered to be part of the world's oil reserves,
as historically high oil prices and new technology enabled profitable
extraction and processing. Together with other so-called unconventional oil extraction practices, oil sands are implicated in the unburnable carbon debate but also contribute to energy security and counteract the international price cartel OPEC. According to a study ordered by the Government of Alberta, Canada, conducted by Jacobs Engineering Group, carbon emissions from oil-sand crude are 12% higher than from conventional oil.
History
The exploitation of bituminous deposits and seeps dates back to Paleolithic times. The earliest known use of bitumen was by Neanderthals, some 40,000 years ago. Bitumen has been found adhering to stone tools used by Neanderthals at sites in Syria. After the arrival of Homo sapiens, humans used bitumen for construction of buildings and waterproofing of reed boats, among other uses. In ancient Egypt, the use of bitumen was important in preparing mummies.
In ancient times, bitumen was primarily a Mesopotamian commodity used by the Sumerians and Babylonians, although it was also found in the Levant and Persia. The area along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers
was littered with hundreds of pure bitumen seepages. The Mesopotamians
used the bitumen for waterproofing boats and buildings. In Europe, they
were extensively mined near the French city of Pechelbronn, where the vapour separation process was in use in 1742.
Nomenclature
The name tar sands was applied to bituminous sands in the late 19th and early 20th century.
People who saw the bituminous sands during this period were familiar
with the large amounts of tar residue produced in urban areas as a by-product of the manufacture of coal gas for urban heating and lighting. The word "tar" to describe these natural bitumen deposits is really a misnomer, since, chemically speaking, tar is a human-made substance produced by the destructive distillation of organic material, usually coal.
Since then, coal gas has almost completely been replaced by natural gas as a fuel, and coal tar as a material for paving roads has been replaced by the petroleum product asphalt. Naturally occurring bitumen is chemically more similar to asphalt than to coal tar, and the term oil sands (or oilsands) is more commonly used by industry in the producing areas than tar sands because synthetic oil is manufactured from the bitumen, and due to the feeling that the terminology of tar sands is less politically acceptable to the public. Oil sands are now an alternative to conventional crude oil.
Early explorers
In Canada, the First Nation peoples had used bitumen from seeps along the Athabasca and Clearwater Rivers to waterproof their birch bark canoes from early prehistoric times. The Canadian oil sands first became known to Europeans in 1719 when a Cree native named Wa-Pa-Su brought a sample to Hudsons Bay Company fur trader Henry Kelsey,
who commented on it in his journals. Fur trader Peter Pond paddled down
the Clearwater River to Athabasca in 1778, saw the deposits and wrote
of "springs of bitumen that flow along the ground." In 1787, fur trader
and explorer Alexander MacKenzie
on his way to the Arctic Ocean saw the Athabasca oil sands, and
commented, "At about 24 miles from the fork (of the Athabasca and
Clearwater Rivers) are some bituminous fountains into which a pole of 20
feet long may be inserted without the least resistance."
Pioneers
The commercial possibilities of Canada's vast oil sands were realized early by Canadian government researchers. In 1884, Robert Bell of the Geological Survey of Canada
commented, "The banks of the Athabasca would furnish an inexhaustible
supply of fuel... the material occurs in such enormous quantities that a
profitable means of extracting oil...may be found". In 1915, Sidney
Ells of the Federal Mines Branch experimented with separation techniques
and used the material to pave 600 ft (200 m) of road in Edmonton as
well as in other places. In 1920, chemist Karl Clark of the Alberta Research Council
began experimenting with methods to extract bitumen from the oil sands
and in 1928 he patented the first commercial hot water separation
process.
Commercial development began in 1923 when businessman Robert Fitzsimmons began drilling oil wells at Bitumount, north of Fort McMurray
but obtained disappointing results with conventional drilling. In 1927
he formed the International Bitumen Company and in 1930 built a small
hot-water separation plant based on Clark's design. He produced about
300 bbl (50 m3) of bitumen in 1930 and shipped it by barge
and rail to Edmonton. The bitumen from the mine had numerous uses but
most of it was used to waterproof roofs. Costs were too high and
Fitzsimmons went bankrupt. In 1941 the company was renamed Oil Sands
Limited and attempted to iron out technical problems but was never very
successful. It went through several changes of ownership and in 1958
closed down permanently. In 1974 Bitumount became an Alberta Provincial
Historic Site.
In 1930 businessman Max Ball formed Canadian Oil Sand Product,
Ltd, which later became Abasand Oils. He built a separation plant
capable of handling 250 tons of oil sands per day which opened in 1936
and produced an average of 200 bbl/d (30 m3/d) of oil. The
plant burned down in late 1941 but was rebuilt in 1942 with even larger
capacity. In 1943 the Canadian government took control of the Abasand
plant under the War Measures Act and planned to expand it further.
However in 1945 the plant burned down again and in 1946 the Canadian
government abandoned the project because the need for fuel had
diminished with the end of the war. The Abasand site is also an Alberta
Historic Site.
Geology
The world's largest deposits of oil sands are in Venezuela and
Canada. The geology of the deposits in the two countries is generally
rather similar. They are vast heavy oil, extra-heavy oil, and/or bitumen deposits with oil heavier than 20°API, found largely in unconsolidated sandstones
with similar properties. "Unconsolidated" in this context means that
the sands have high porosity, no significant cohesion, and a tensile
strength close to zero. The sands are saturated with oil which has
prevented them from consolidating into hard sandstone.
Size of resources
The magnitude of the resources in the two countries is on the order
of 3.5 to 4 trillion barrels (550 to 650 billion cubic metres) of
original oil in place (OOIP). Oil in place is not necessarily oil reserves, and the amount that can be produced depends on technological evolution. Rapid technological developments in Canada in the 1985–2000 period resulted in techniques such as steam-assisted gravity drainage (SAGD) that can recover a much greater percentage of the OOIP
than conventional methods. The Alberta government estimates that with
current technology, 10% of its bitumen and heavy oil can be recovered,
which would give it about 200 billion barrels (32 billion m3) of recoverable oil reserves. Venezuela estimates its recoverable oil at 267 billion barrels (42 billion m3). This places Canada and Venezuela in the same league as Saudi Arabia, having the three largest oil reserves in the world.
Major deposits
There are numerous deposits of oil sands in the world, but the biggest and most important are in Canada and Venezuela, with lesser deposits in Kazakhstan and Russia.
The total volume of non-conventional oil in the oil sands of these
countries exceeds the reserves of conventional oil in all other
countries combined. Vast deposits of bitumen – over 350 billion cubic
metres (2.2 trillion barrels) of oil in place – exist in the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. If only 30% of this oil could be extracted, it could supply the entire needs of North America
for over 100 years at 2002 consumption levels. These deposits represent
plentiful oil, but not cheap oil. They require advanced technology to extract the oil and transport it to oil refineries.
Canada
The oil sands of the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin (WCSB) are a result of the formation of the Canadian Rocky Mountains by the Pacific Plate overthrusting the North American Plate as it pushed in from the west, carrying the formerly large island chains which now comprise most of British Columbia. The collision compressed the Alberta plains and raised the Rockies above the plains, forming mountain ranges. This mountain building process buried the sedimentary rock layers which underlie most of Alberta to a great depth, creating high subsurface temperatures, and producing a giant pressure cooker effect that converted the kerogen in the deeply buried organic-rich shales to light oil and natural gas. These source rocks were similar to the American so-called oil shales, except the latter have never been buried deep enough to convert the kerogen in them into liquid oil.
This overthrusting also tilted the pre-Cretaceous sedimentary rock formations underlying most of the sub-surface of Alberta, depressing
the rock formations in southwest Alberta up to 8 km (5 mi) deep near
the Rockies, but to zero depth in the northeast, where they pinched out
against the igneous rocks of the Canadian Shield,
which outcrop on the surface. This tilting is not apparent on the
surface because the resulting trench has been filled in by eroded
material from the mountains. The light oil migrated up-dip through
hydro-dynamic transport from the Rockies in the southwest toward the Canadian Shield in the northeast following a complex pre-Cretaceous unconformity
that exists in the formations under Alberta. The total distance of oil
migration southwest to northeast was about 500 to 700 km (300 to
400 mi). At the shallow depths of sedimentary formations in the
northeast, massive microbial biodegradation as the oil approached the surface caused the oil to become highly viscous
and immobile. Almost all of the remaining oil is found in the far north
of Alberta, in Middle Cretaceous (115 million-year old) sand-silt-shale deposits
overlain by thick shales, although large amounts of heavy oil lighter
than bitumen are found in the Heavy Oil Belt along the
Alberta-Saskatchewan border, extending into Saskatchewan and approaching
the Montana border. Note that, although adjacent to Alberta,
Saskatchewan has no massive deposits of bitumen, only large reservoirs
of heavy oil >10°API.
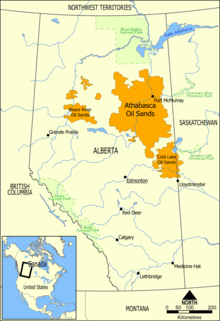
Most of the Canadian oil sands are in three major deposits in northern Alberta. They are the Athabasca-Wabiskaw oil sands of north northeastern Alberta, the Cold Lake deposits of east northeastern Alberta, and the Peace River deposits of northwestern Alberta. Between them, they cover over 140,000 square kilometres (54,000 sq mi)—an area larger than England—and contain approximately 1.75 Tbbl (280×109 m3) of crude bitumen in them. About 10% of the oil in place, or 173 Gbbl (27.5×109 m3), is estimated by the government of Alberta
to be recoverable at current prices, using current technology, which
amounts to 97% of Canadian oil reserves and 75% of total North American
petroleum reserves.
Although the Athabasca deposit is the only one in the world which has
areas shallow enough to mine from the surface, all three Alberta areas
are suitable for production using in-situ methods, such as cyclic steam stimulation (CSS) and steam assisted gravity drainage (SAGD).
The largest Canadian oil sands deposit, the Athabasca oil sands is in the McMurray Formation, centered on the city of Fort McMurray, Alberta.
It outcrops on the surface (zero burial depth) about 50 km (30 mi)
north of Fort McMurray, where enormous oil sands mines have been
established, but is 400 m (1,300 ft) deep southeast of Fort McMurray.
Only 3% of the oil sands area containing about 20% of the recoverable
oil can be produced by surface mining, so the remaining 80% will have to be produced using in-situ wells. The other Canadian deposits are between 350 to 900 m (1,000 to 3,000 ft) deep and will require in-situ production.
Athabasca
The City of Fort McMurray on the banks of the Athabasca River
The Athabasca oil sands lie along the Athabasca River
and are the largest natural bitumen deposit in the world, containing
about 80% of the Alberta total, and the only one suitable for surface mining. With modern unconventional oil production technology, at least 10% of these deposits, or about 170 Gbbl (27×109 m3) are considered to be economically recoverable, making Canada's total proven reserves the third largest in the world, after Saudi Arabia's conventional oil and Venezuela's Orinoco oil sands.
The Athabasca oil sands are more or less centered around the remote northern city of Fort McMurray.
They are by far the largest deposit of bitumen in Canada, probably
containing over 150 billion cubic metres (900 billion barrels) of oil in place. The bitumen is highly viscous and is often denser than water (10°API or 1000 kg/m3).
The oil saturated sands range from 15 to 65 metres (49 to 213 ft) thick
in places, and the oil saturation in the oil-rich zones is on the order
of 90% bitumen by weight.
The Athabasca River cuts through the heart of the deposit, and
traces of the heavy oil are readily observed as black stains on the
river banks. Since portions of the Athabasca sands are shallow enough to
be surface-mineable, they were the earliest ones to see development. Historically, the bitumen was used by the indigenous Cree and Dene Aboriginal peoples to waterproof their canoes. The Athabasca oil sands first came to the attention of European fur traders in 1719 when Wa-pa-su, a Cree trader, brought a sample of bituminous sands to the Hudson's Bay Company post at York Factory on Hudson Bay.
Oil sands on the banks of the Athabasca River, c. 1900
In 1778, Peter Pond, a fur trader for the rival North West Company, was the first European to see the Athabasca deposits. In 1788, fur trader and explorer Alexander Mackenzie from the Hudson Bay Company, who later discovered the Mackenzie River
and routes to both the Arctic and Pacific Oceans, described the oil
sands in great detail. He said, "At about 24 miles (39 km) from the fork
(of the Athabasca and Clearwater Rivers) are some bituminous fountains
into which a pole of 20 feet (6.1 m) long may be inserted without the
least resistance. The bitumen is in a fluid state and when mixed with
gum, the resinous substance collected from the spruce fir, it serves to gum the Indians' canoes."
In 1883, G.C. Hoffman of the Geological Survey of Canada tried separating the bitumen from oil sand with the use of water and reported that it separated readily. In 1888, Robert Bell
of the Geological Survey of Canada reported to a Senate Committee that
"The evidence ... points to the existence in the Athabasca and Mackenzie
valleys of the most extensive petroleum field in America, if not the
world." In 1926, Karl Clark
of the University of Alberta patented a hot water separation process
which was the forerunner of today's thermal extraction processes.
However, it was 1967 before the first large scale commercial operation
began with the opening of the Great Canadian Oil Sands mine by the Sun Oil Company of Ohio.
Today its successor company, Suncor Energy (no longer affiliated with Sun Oil), is the largest oil company in Canada. In addition, other companies such as Royal Dutch Shell, ExxonMobil,
and various national oil companies are developing the Athabasca oil
sands. As a result, Canada is now by far the largest exporter of oil to
the United States.
The smaller Wabasca (or Wabiskaw) oil sands lie
above the western edge of the Athabasca oil sands and overlap them. They
probably contain over 15 billion cubic metres (90 billion barrels) of
oil in place. The deposit is buried from 100 to 700 metres (330 to
2,300 ft) deep and ranges from 0 to 10 metres (0 to 33 ft) thick. In
many regions the oil-rich Wabasca formation overlies the similarly
oil-rich McMurray formation, and as a result the two overlapping oil
sands are often treated as one oil sands deposit. However, the two
deposits are invariable separated by a minimum of 6 metres (20 ft) of
clay shale and silt. The bitumen in the Wabasca is as highly viscous as
that in the Athabasca, but lies too deep to be surface-mined, so in-situ
production methods must be used to produce the crude bitumen.
Cold Lake
Cold Lake viewed from Meadow Lake Provincial Park, Saskatchewan.
The Cold Lake oil sands are northeast of Alberta's capital, Edmonton, near the border with Saskatchewan.
A small portion of the Cold Lake deposit lies in Saskatchewan. Although
smaller than the Athabasca oil sands, the Cold Lake oil sands are
important because some of the oil is fluid enough to be extracted by conventional methods. The Cold Lake bitumen contains more alkanes and less asphaltenes than the other major Alberta oil sands and the oil is more fluid. As a result, cyclic steam stimulation (CSS) is commonly used for production.
The Cold Lake oil sands are of a roughly circular shape, centered around Bonnyville, Alberta.
They probably contain over 60 billion cubic metres (370 billion
barrels) of extra-heavy oil-in-place. The oil is highly viscous, but
considerably less so than the Athabasca oil sands, and is somewhat less sulfurous. The depth of the deposits is 400 to 600 metres (1,300 to 2,000 ft) and they are from 15 to 35 metres (49 to 115 ft) thick. They are too deep to surface mine.
Much of the oil sands are on Canadian Forces Base Cold Lake. CFB Cold Lake's CF-18 Hornet
jet fighters defend the western half of Canadian air space and cover
Canada's Arctic territory. Cold Lake Air Weapons Range (CLAWR) is one of
the largest live-drop bombing ranges in the world, including testing of
cruise missiles. As oil sands production continues to grow, various
sectors vie for access to airspace, land, and resources, and this
complicates oil well drilling and production significantly.
Peace River
Peace River
The Peace River oil sands located in northwest-central Alberta are
the smallest of the three major oil sands deposits in Alberta. The Peace
River oil sands lie generally in the watershed of the Peace River,
the largest river in Alberta. The Peace and Athabasca rivers, which are
by far the largest rivers in Alberta, flow through their respective oil
sands and merge at Lake Athabasca to form the Slave River, which flows into the MacKenzie River, one of the largest rivers in the world. All of the water from these rivers flow into the Arctic Ocean.
The Peace River oil sands probably contain over 30 billion cubic
metres (200 billion barrels) of oil-in-place. The thickness of the
deposit ranges from 5 to 25 metres (16 to 82 ft) and it is buried about
500 to 700 metres (1,600 to 2,300 ft) deep.
Whereas the Athabasca oil sands lie close enough to the surface that the bitumen can be excavated in open-pit mines, the smaller Peace River deposits are too deep, and must be exploited using in situ methods such as steam-assisted gravity drainage and Cold Heavy Oil Production with Sand (CHOPS).
Venezuela
The Eastern Venezuelan Basin
has a structure similar to the WCSB, but on a shorter scale. The
distance the oil has migrated up-dip from the Sierra Orientale mountain
front to the Orinoco oil sands where it pinches out against the igneous rocks of the Guyana Shield is only about 200 to 300 km (100 to 200 mi). The hydrodynamic conditions of oil transport were similar, source rocks
buried deep by the rise of the mountains of the Sierra Orientale
produced light oil that moved up-dip toward the south until it was
gradually immobilized by the viscosity increase caused by biodgradation
near the surface. The Orinoco deposits are early Tertiary (50 to 60 million years old) sand-silt-shale sequences overlain by continuous thick shales, much like the Canadian deposits.
In Venezuela, the Orinoco Belt
oil sands range from 350 to 1,000 m (1,000 to 3,000 ft) deep and no
surface outcrops exist. The deposit is about 500 km (300 mi) long
east-to-west and 50 to 60 km (30 to 40 mi) wide north-to-south, much
less than the combined area covered by the Canadian deposits. In
general, the Canadian deposits are found over a much wider area, have a
broader range of properties, and have a broader range of reservoir types
than the Venezuelan ones, but the geological structures and mechanisms
involved are similar. The main differences is that the oil in the sands
in Venezuela is less viscous than in Canada, allowing some of it to be
produced by conventional drilling techniques, but none of it approaches
the surface as in Canada, meaning none of it can be produced using
surface mining. The Canadian deposits will almost all have to be
produced by mining or using new non-conventional techniques.
Orinoco
Panorama of the Orinoco River.
The Orinoco Belt is a territory in the southern strip of the eastern Orinoco River Basin in Venezuela
which overlies one of the world's largest deposits of petroleum. The
Orinoco Belt follows the line of the river. It is approximately 600
kilometres (370 mi) from east to west, and 70 kilometres (43 mi) from
north to south, with an area about 55,314 square kilometres
(21,357 sq mi).
The oil sands consist of large deposits of extra heavy crude. Venezuela's heavy oil deposits of about 1,200 Gbbl (190×109 m3) of oil in place are estimated to approximately equal the world's reserves of lighter oil. Petróleos de Venezuela S.A.
(PDVSA), Venezuela's national oil company, has estimated that the
producible reserves of the Orinoco Belt are up to 235 Gbbl (37.4×109 m3) which would make it the largest petroleum reserve in the world.
In 2009, the US Geological Survey (USGS) increased its estimates of the reserves to 513 Gbbl (81.6×109 m3)
of oil which is "technically recoverable (producible using currently
available technology and industry practices)." No estimate of how much
of the oil is economically recoverable was made.
Other deposits
Location of Melville Island
In addition to the three major Canadian oil sands in Alberta, there is a fourth major oil sands deposit in Canada, the Melville Island oil sands in the Canadian Arctic islands, which are too remote to expect commercial production in the foreseeable future.
Apart from the megagiant
oil sands deposits in Canada and Venezuela, numerous other countries
hold smaller oil sands deposits. In the United States, there are
supergiant oil sands resources primarily concentrated in Eastern Utah, with a total of 32 Gbbl (5.1×109 m3) of oil (known and potential) in eight major deposits in Carbon, Garfield, Grand, Uintah, and Wayne counties.
In addition to being much smaller than the Canadian oil sands deposits,
the US oil sands are hydrocarbon-wet, whereas the Canadian oil sands
are water-wet. This requires somewhat different extraction techniques for the Utah oil sands than those used for the Alberta oil sands.
Russia holds oil sands in two main regions. Large resources are present in the Tunguska Basin, East Siberia, with the largest deposits being Olenek and Siligir. Other deposits are located in the Timan-Pechora and Volga-Urals basins (in and around Tatarstan),
which is an important but very mature province in terms of conventional
oil, holds large amounts of oil sands in a shallow Permian formation. In Kazakhstan, large bitumen deposits are located in the North Caspian Basin.
In Madagascar, Tsimiroro and Bemolanga are two heavy oil sands deposits, with a pilot well already producing small amounts of oil in Tsimiroro. and larger scale exploitation in the early planning phase. In the Republic of the Congo reserves are estimated between 0.5 and 2.5 Gbbl (79×106 and 397×106 m3).
Production
Bituminous
sands are a major source of unconventional oil, although only Canada
has a large-scale commercial oil sands industry. In 2006, bitumen
production in Canada averaged 1.25 Mbbl/d (200,000 m3/d) through 81 oil sands projects. 44% of Canadian oil production in 2007 was from oil sands.
This proportion was (as of 2008) expected to increase in coming decades
as bitumen production grows while conventional oil production declines,
although due to the 2008 economic downturn work on new projects has
been deferred. Petroleum is not produced from oil sands on a significant level in other countries.
Canada
The Alberta oil sands have been in commercial production since the original Great Canadian Oil Sands (now Suncor Energy)
mine began operation in 1967. Despite the increasing levels of
production, the process of extraction and processing of oil sands can
still be considered to be in its infancy; with new technologies and
stakeholders oversight providing an ever-lower environmental footprint. A second mine, operated by the Syncrude
consortium, began operation in 1978 and is the biggest mine of any type
in the world. The third mine in the Athabasca Oil Sands, the Albian Sands consortium of Shell Canada, Chevron Corporation, and Western Oil Sands Inc. [purchased by Marathon Oil Corporation in 2007] began operation in 2003. Petro-Canada was also developing a $33 billion Fort Hills Project, in partnership with UTS Energy Corporation and Teck Cominco, which lost momentum after the 2009 merger of Petro-Canada into Suncor.
By 2013 there were nine oil sands mining projects in the
Athabasca oil sands deposit: Suncor Energy Inc. (Suncor), Syncrude
Canada Limited (Syncrude)'s Mildred Lake and Aurora North, Shell Canada
Limited (Shell)'s Muskeg River and Jackpine, Canadian Natural Resources
Limited (CNRL), Horizon, Imperial Oil Resources Ventures Limited
(Imperial), Kearl Oil Sands Project (KOSP), Total E&P Canada Ltd.
Joslyn North Mine and Fort Hills Energy Corporation (FHEC). In 2011 alone they produced over 52 million cubic metres of bitumen.
Venezuela
No significant development of Venezuela's extra-heavy oil deposits
was undertaken before 2000, except for the BITOR operation which
produced somewhat less than 100,000 barrels of oil per day (16,000 m3/d) of 9°API oil by primary production. This was mostly shipped as an emulsion (Orimulsion) of 70% oil and 30% water with similar characteristics as heavy fuel oil for burning in thermal power plants. However, when a major strike hit the Venezuelan state oil company PDVSA, most of the engineers were fired as punishment.
Orimulsion had been the pride of the PDVSA engineers, so Orimulsion
fell out of favor with the key political leaders. As a result, the
government has been trying to "Wind Down" the Orimulsion program.
Despite the fact that the Orinoco oil sands contain extra-heavy
oil which is easier to produce than Canada's similarly-sized reserves of
bitumen, Venezuela's oil production has been declining in recent years
because of the country's political and economic problems, while Canada's
has been increasing. As a result, Canadian heavy oil and bitumen
exports have been backing Venezuelan heavy and extra-heavy oil out of
the US market, and Canada's total exports of oil to the US have become
several times as great as Venezuela's.
By 2016, with the economy of Venezuela
in a tailspin and the country experiencing widespread shortages of
food, rolling power blackouts, rioting, and anti-government protests, it
was unclear how much new oil sands production would occur in the near
future.
Other countries
In May 2008, the Italian oil company Eni announced a project to develop a small oil sands deposit in the Republic of the Congo. Production is scheduled to commence in 2014 and is estimated to eventually yield a total of 40,000 bbl/d (6,400 m3/d).
Methods of extraction
Except
for a fraction of the extra-heavy oil or bitumen which can be extracted
by conventional oil well technology, oil sands must be produced by strip mining or the oil made to flow into wells using sophisticated in-situ
techniques. These methods usually use more water and require larger
amounts of energy than conventional oil extraction. While much of
Canada's oil sands are being produced using open-pit mining, approximately 90% of Canadian oil sands and all of Venezuela's oil sands are too far below the surface to use surface mining.
Primary production
Conventional crude oil is normally extracted from the ground by drilling oil wells into a petroleum reservoir, allowing oil to flow into them under natural reservoir pressures, although artificial lift and techniques such as horizontal drilling, water flooding
and gas injection are often required to maintain production. When
primary production is used in the Venezuelan oil sands, where the
extra-heavy oil is about 50 degrees Celsius,
the typical oil recovery rates are about 8–12%. Canadian oil sands are
much colder and more biodegraded, so bitumen recovery rates are usually
only about 5–6%. Historically, primary recovery was used in the more
fluid areas of Canadian oil sands. However, it recovered only a small
fraction of the oil in place, so it is not often used today.
Surface mining
Mining operations in the Athabasca oil sands. NASA Earth Observatory image, 2009.
The Athabasca oil sands
are the only major oil sands deposits which are shallow enough to
surface mine. In the Athabasca sands there are very large amounts of bitumen covered by little overburden, making surface mining the most efficient method of extracting it. The overburden consists of water-laden muskeg
(peat bog) over top of clay and barren sand. The oil sands themselves
are typically 40 to 60 metres (130 to 200 ft) thick deposits of crude
bitumen embedded in unconsolidated sandstone, sitting on top of flat limestone rock. Since Great Canadian Oil Sands (now Suncor Energy)
started operation of the first large-scale oil sands mine in 1967,
bitumen has been extracted on a commercial scale and the volume has
grown at a steady rate ever since.
A large number of oil sands mines are currently in operation and more are in the stages of approval or development. The Syncrude Canada mine was the second to open in 1978, Shell Canada opened its Muskeg River mine (Albian Sands) in 2003 and Canadian Natural Resources Ltd (CNRL) opened its Horizon Oil Sands project in 2009. Newer mines include Shell Canada's Jackpine mine, Imperial Oil's Kearl Oil Sands Project, the Synenco Energy (now owned by Total S.A.) Northern Lights mine, and Suncor's Fort Hills mine.
Oil sands tailings ponds
Syncrude's Mildred Lake site, plant and tailings ponds Fort McMurray, Alberta
Oil sands tailings ponds are engineered dam and dyke systems that
contain salts, suspended solids and other dissolvable chemical compounds
such as naphthenic acids, benzene, hydrocarbons residual bitumen, fine silts (mature fine tails MFT), and water.
Large volumes of tailings are a byproduct of surface mining of the oil
sands and managing these tailings is one of the most difficult
environmental challenges facing the oil sands industry.
The Government of Alberta reported in 2013 that tailings ponds in the
Alberta oil sands covered an area of about 77 square kilometres
(30 sq mi). The Syncrude Tailings Dam or Mildred Lake Settling Basin (MLSB) is an embankment dam that is, by volume of construction material, the largest earth structure in the world in 2001.
Cold Heavy Oil Production with Sand (CHOPS)
Some years ago Canadian oil companies discovered that if they removed the sand
filters from heavy oil wells and produced as much sand as possible with
the oil, production rates improved significantly. This technique became
known as Cold Heavy Oil Production with Sand (CHOPS). Further research
disclosed that pumping out sand opened "wormholes" in the sand formation
which allowed more oil to reach the wellbore.
The advantage of this method is better production rates and recovery
(around 10% versus 5–6% with sand filters in place) and the disadvantage
that disposing of the produced sand is a problem. A novel way to do this was spreading it on rural roads, which rural governments liked because the oily sand reduced dust and the oil companies did their road maintenance for them. However, governments have become concerned about the large volume and composition of oil spread on roads. so in recent years disposing of oily sand in underground salt caverns has become more common.
Cyclic Steam Stimulation (CSS)
The use of steam
injection to recover heavy oil has been in use in the oil fields of
California since the 1950s. The cyclic steam stimulation (CSS)
"huff-and-puff" method is now widely used in heavy oil production
worldwide due to its quick early production rates; however recovery
factors are relatively low (10–40% of oil in place) compared to SAGD
(60–70% of OIP).
CSS has been in use by Imperial Oil at Cold Lake since 1985 and is also used by Canadian Natural Resources at Primrose and Wolf Lake and by Shell Canada
at Peace River. In this method, the well is put through cycles of steam
injection, soak, and oil production. First, steam is injected into a
well at a temperature of 300 to 340 degrees Celsius
for a period of weeks to months; then, the well is allowed to sit for
days to weeks to allow heat to soak into the formation; and, later, the
hot oil is pumped out of the well for a period of weeks or months. Once
the production rate falls off, the well is put through another cycle of
injection, soak and production. This process is repeated until the cost
of injecting steam becomes higher than the money made from producing
oil.
Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage (SAGD)
Steam assisted gravity drainage was developed in the 1980s by the Alberta Oil Sands Technology and Research Authority and fortuitously coincided with improvements in directional drilling
technology that made it quick and inexpensive to do by the mid 1990s.
In SAGD, two horizontal wells are drilled in the oil sands, one at the
bottom of the formation and another about 5 metres above it. These wells
are typically drilled
in groups off central pads and can extend for miles in all directions.
In each well pair, steam is injected into the upper well, the heat melts
the bitumen, which allows it to flow into the lower well, where it is
pumped to the surface.
SAGD has proved to be a major breakthrough
in production technology since it is cheaper than CSS, allows very high
oil production rates, and recovers up to 60% of the oil in place.
Because of its economic feasibility and applicability to a vast area of oil sands, this method alone quadrupled North American oil reserves
and allowed Canada to move to second place in world oil reserves after
Saudi Arabia. Most major Canadian oil companies now have SAGD projects
in production or under construction in Alberta's oil sands areas and in
Wyoming. Examples include Japan Canada Oil Sands Ltd's (JACOS) project, Suncor's Firebag project, Nexen's Long Lake project, Suncor's (formerly Petro-Canada's) MacKay River project, Husky Energy's Tucker Lake and Sunrise projects, Shell Canada's Peace River project, Cenovus Energy's Foster Creek and Christina Lake developments, ConocoPhillips' Surmont project, Devon Canada's
Jackfish project, and Derek Oil & Gas's LAK Ranch project.
Alberta's OSUM Corp has combined proven underground mining technology
with SAGD to enable higher recovery rates by running wells underground
from within the oil sands deposit, thus also reducing energy
requirements compared to traditional SAGD. This particular technology
application is in its testing phase.
Vapor Extraction (VAPEX)
Several
methods use solvents, instead of steam, to separate bitumen from sand.
Some solvent extraction methods may work better in in situ production and other in mining. Solvent can be beneficial if it produces more oil while requiring less energy to produce steam.
Vapor Extraction Process (VAPEX) is an in situ technology,
similar to SAGD. Instead of steam, hydrocarbon solvents are injected
into an upper well to dilute bitumen and enables the diluted bitumen to
flow into a lower well. It has the advantage of much better energy
efficiency over steam injection, and it does some partial upgrading of
bitumen to oil right in the formation. The process has attracted
attention from oil companies, who are experimenting with it.
The above methods are not mutually exclusive. It is becoming
common for wells to be put through one CSS injection-soak-production
cycle to condition the formation prior to going to SAGD production, and
companies are experimenting with combining VAPEX with SAGD to improve
recovery rates and lower energy costs.
Toe to Heel Air Injection (THAI)
This
is a very new and experimental method that combines a vertical air
injection well with a horizontal production well. The process ignites
oil in the reservoir and creates a vertical wall of fire moving from the
"toe" of the horizontal well toward the "heel", which burns the heavier
oil components and upgrades some of the heavy bitumen into lighter oil
right in the formation. Historically fireflood projects have not worked
out well because of difficulty in controlling the flame front and a
propensity to set the producing wells on fire. However, some oil
companies feel the THAI method will be more controllable and practical,
and have the advantage of not requiring energy to create steam.
Advocates of this method of extraction state that it uses less freshwater, produces 50% less greenhouse gases, and has a smaller footprint than other production techniques.
Petrobank Energy and Resources has reported encouraging results from their test wells in Alberta, with production rates of up to 400 bbl/d (64 m3/d) per well, and the oil upgraded from 8 to 12 API degrees.
The company hopes to get a further 7-degree upgrade from its CAPRI (controlled atmospheric pressure resin infusion) system, which pulls the oil through a catalyst lining the lower pipe.
After several years of production in situ, it has become clear
that current THAI methods do not work as planned. Amid steady drops in
production from their THAI wells at Kerrobert, Petrobank has written
down the value of their THAI patents and the reserves at the facility to
zero. They have plans to experiment with a new configuration they call
"multi-THAI," involving adding more air injection wells.
Combustion Overhead Gravity Drainage (COGD)
This
is an experimental method that employs a number of vertical air
injection wells above a horizontal production well located at the base
of the bitumen pay zone. An initial Steam Cycle similar to CSS is used
to prepare the bitumen for ignition and mobility. Following that cycle,
air is injected into the vertical wells, igniting the upper bitumen and
mobilizing (through heating) the lower bitumen to flow into the
production well. It is expected that COGD will result in water savings
of 80% compared to SAGD.
Energy balance
Approximately 1.0–1.25 gigajoules (280–350 kWh) of energy is needed
to extract a barrel of bitumen and upgrade it to synthetic crude. As of
2006, most of this is produced by burning natural gas. Since a barrel of oil equivalent is about 6.117 gigajoules (1,699 kWh), its EROEI
is 5–6. That means this extracts about 5 or 6 times as much energy as
is consumed. Energy efficiency is expected to improve to an average of
900 cubic feet (25 m3) of natural gas or 0.945 gigajoules (262 kWh) of energy per barrel by 2015, giving an EROEI of about 6.5.
Alternatives to natural gas exist and are available in the oil
sands area. Bitumen can itself be used as the fuel, consuming about
30–35% of the raw bitumen per produced unit of synthetic crude. Nexen's
Long Lake project will use a proprietary deasphalting technology to
upgrade the bitumen, using asphaltene residue fed to a gasifier whose syngas will be used by a cogeneration turbine and a hydrogen producing unit, providing all the energy needs of the project: steam, hydrogen, and electricity. Thus, it will produce syncrude without consuming natural gas, but the capital cost is very high.
Shortages of natural gas for project fuel were forecast to be a
problem for Canadian oil sands production a few years ago, but recent
increases in US shale gas production have eliminated much of the problem for North America. With the increasing use of hydraulic fracturing making US largely self-sufficient in natural gas and exporting more natural gas to Eastern Canada to replace Alberta gas, the Alberta government is using its powers under the NAFTA and the Canadian Constitution
to reduce shipments of natural gas to the US and Eastern Canada, and
divert the gas to domestic Alberta use, particularly for oil sands fuel.
The natural gas pipelines to the east and south are being converted to
carry increasing oil sands production to these destinations instead of
gas. Canada also has huge undeveloped shale gas deposits
in addition to those of the US, so natural gas for future oil sands
production does not seem to be a serious problem. The low price of
natural gas as the result of new production has considerably improved
the economics of oil sands production.
Upgrading and/or blending
The extra-heavy crude oil or crude bitumen extracted from oil sands is a very viscous
semisolid form of oil that does not easily flow at normal temperatures,
making it difficult to transport to market by pipeline. To flow through
oil pipelines, it must either be upgraded to lighter synthetic crude oil (SCO), blended with diluents to form dilbit, or heated to reduce its vicosity.
Canada
In the
Canadian oil sands, bitumen produced by surface mining is generally
upgraded on-site and delivered as synthetic crude oil. This makes
delivery of oil to market through conventional oil pipelines quite easy.
On the other hand, bitumen produced by the in-situ projects is
generally not upgraded but delivered to market in raw form. If the agent
used to upgrade the bitumen to synthetic crude is not produced on site,
it must be sourced elsewhere and transported to the site of upgrading.
If the upgraded crude is being transported from the site by pipeline,
and additional pipeline will be required to bring in sufficient
upgrading agent. The costs of production of the upgrading agent, the
pipeline to transport it and the cost to operate the pipeline must be
calculated into the production cost of the synthetic crude.
Upon reaching a refinery,
the synthetic crude is processed and a significant portion of the
upgrading agent will be removed during the refining process. It may be
used for other fuel fractions, but the end result is that liquid fuel
has to be piped to the upgrading facility simply to make the bitumen
transportable by pipeline. If all costs are considered, synthetic crude
production and transfer using bitumen and an upgrading agent may prove
economically unsustainable.
When the first oil sands plants were built over 50 years ago,
most oil refineries in their market area were designed to handle light
or medium crude oil with lower sulfur content than the 4–7% that is
typically found in bitumen. The original oil sands upgraders were
designed to produce a high-quality synthetic crude oil (SCO) with lower
density and lower sulfur content. These are large, expensive plants
which are much like heavy oil refineries. Research is currently being
done on designing simpler upgraders which do not produce SCO but simply
treat the bitumen to reduce its viscosity, allowing to be transported
unblended like conventional heavy oil.
Western Canadian Select, launched in 2004 as a new heavy oil stream, blended at the Husky Energy terminal in Hardisty, Alberta,
is the largest crude oil stream coming from the Canadian oil sands and the benchmark for emerging heavy, high TAN (acidic) crudes.
WCS is traded at Cushing, Oklahoma,
a major oil supply hub connecting oil suppliers to the Gulf Coast,
which has become the most significant trading hub for crude oil in North
America. While its major component is bitumen, it also contains a
combination of sweet synthetic and condensate diluents, and 25 existing streams of both conventional and unconventional oil making it a syndilbit— both a dilbit and a synbit.
The first step in upgrading is vacuum distillation to separate the lighter fractions. After that, de-asphalting is used to separate the asphalt from the feedstock. Cracking
is used to break the heavier hydrocarbon molecules down into simpler
ones. Since cracking produces products which are rich in sulfur, desulfurization must be done to get the sulfur content below 0.5% and create sweet, light synthetic crude oil.
In 2012, Alberta produced about 1,900,000 bbl/d (300,000 m3/d) of crude bitumen from its three major oil sands deposits, of which about 1,044,000 bbl/d (166,000 m3/d)
was upgraded to lighter products and the rest sold as raw bitumen. The
volume of both upgraded and non-upgraded bitumen is increasing yearly.
Alberta has five oil sands upgraders producing a variety of products.
These include:
- Suncor Energy can upgrade 440,000 bbl/d (70,000 m3/d) of bitumen to light sweet and medium sour synthetic crude oil (SCO), plus produce diesel fuel for its oil sands operations at the upgrader.
- Syncrude can upgrade 407,000 bbl/d (64,700 m3/d) of bitumen to sweet light SCO.
- Canadian Natural Resources Limited (CNRL) can upgrade 141,000 bbl/d (22,400 m3/d) of bitumen to sweet light SCO.
- Nexen, since 2013 wholly owned by China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC), can upgrade 72,000 bbl/d (11,400 m3/d) of bitumen to sweet light SCO.
- Shell Canada operates its Scotford Upgrader in combination with an oil refinery and chemical plant at Scotford, Alberta, near Edmonton. The complex can upgrade 255,000 bbl/d (40,500 m3/d) of bitumen to sweet and heavy SCO as well as a range of refinery and chemical products.
Modernized and new large refineries such as are found in the Midwestern United States and on the Gulf Coast of the United States, as well as many in China,
can handle upgrading heavy oil themselves, so their demand is for
non-upgraded bitumen and extra-heavy oil rather than SCO. The main
problem is that the feedstock would be too viscous to flow through
pipelines, so unless it is delivered by tanker or rail car, it must be
blended with diluent to enable it to flow. This requires mixing the
crude bitumen with a lighter hydrocarbon diluent such as condensate from
gas wells, pentanes
and other light products from oil refineries or gas plants, or
synthetic crude oil from oil sands upgraders to allow it to flow through
pipelines to market.
Typically, blended bitumen contains about 30% natural gas condensate or other diluents and 70% bitumen. Alternatively, bitumen can also be delivered to market by specially designed railway tank cars, tank trucks, liquid cargo barges, or ocean-going oil tankers.
These do not necessarily require the bitumen be blended with diluent
since the tanks can be heated to allow the oil to be pumped out.
The demand for condensate for oil sands diluent is expected to be more than 750,000 bbl/d (119,000 m3/d) by 2020, double 2012 volumes. Since Western Canada only produces about 150,000 bbl/d (24,000 m3/d)
of condensate, the supply was expected to become a major constraint on
bitumen transport. However, the recent huge increase in US tight oil
production has largely solved this problem, because much of the
production is too light for US refinery use but ideal for diluting
bitumen. The surplus American condensate and light oil is being exported
to Canada and blended with bitumen, and then re-imported to the US as
feedstock for refineries. Since the diluent is simply exported and then
immediately re-imported, it is not subject to the US ban on exports of
crude oil. Once it is back in the US, refineries separate the diluent
and re-export it to Canada, which again bypasses US crude oil export
laws since it is now a refinery product. To aid in this process, Kinder Morgan Energy Partners is reversing its Cochin Pipeline, which used to carry propane from Edmonton to Chicago, to transport 95,000 bbl/d (15,100 m3/d) of condensate from Chicago to Edmonton by mid-2014; and Enbridge is considering the expansion of its Southern Lights pipeline, which currently ships 180,000 bbl/d (29,000 m3/d) of diluent from the Chicago area to Edmonton, by adding another 100,000 bbl/d (16,000 m3/d).
Venezuela
Although
Venezuelan extra-heavy oil is less viscous than Canadian bitumen, much
of the difference is due to temperature. Once the oil comes out of the
ground and cools, it has the same difficulty in that it is too viscous
to flow through pipelines. Venezuela is now producing more extra heavy
crude in the Orinoco oil sands than its four upgraders, which were built
by foreign oil companies over a decade ago, can handle. The upgraders
have a combined capacity of 630,000 bbl/d (100,000 m3/d), which is only half of its production of extra-heavy oil. In addition Venezuela produces insufficient volumes of naphtha to use as diluent to move extra-heavy oil to market. Unlike Canada, Venezuela does not produce much natural gas condensate from its own gas wells, and unlike Canada, it does not have easy access to condensate from new US shale gas
production. Since Venezuela also has insufficient refinery capacity to
supply its domestic market, supplies of naptha are insufficient to use
as pipeline diluent, and it is having to import naptha to fill the gap.
Since Venezuela also has financial problems – as a result of the
country's economic crisis -, and political disagreements with the US government and oil companies, the situation remains unresolved.
Transportation
A network of gathering and feeder pipelines collects crude bitumen
and SCO from Alberta's northern oil sands deposits (primarily Athabasca,
Cold Lake, and Peace River), and feeds them into two main collection
points for southbound deliveries: Edmonton, Alberta and Hardisty, Alberta.
Most of the feeder pipelines move blended bitumen or SCO southbound and
diluent northbound, but a few move product laterally within the oil
sands region. In 2012, the capacity of the southbound feeder lines was
over 300,000 m³/d (2 million bbl/d) and more capacity was being added.
The building of new oil sands feeder pipelines requires only the
approval of the Alberta Energy Regulator, an agency that deals with
matters entirely within Alberta and is likely to give little
consideration to interference from political and environmental interest
from outside Alberta.
Existing pipelines
From
Edmonton and Hardisty, main transmission pipelines move blended bitumen
and SCO, as well as conventional crude oil and various oil and natural
productions to market destinations across North America. The main
transmission systems include:
- Enbridge has a complex existing system of pipelines that takes crude oil from Edmonton and Hardisty east to Montreal and south as far as the Gulf Coast of the United States, with a total capacity of 2.5×106 bbl/d (400,000 m3/d). It also has a northbound pipeline that takes diluent from refineries in Illinois and other Midwestern states to Edmonton with a capacity of 160,000 bbl/d (25,000 m3/d) of light hydrocarbons.
- Kinder Morgan has the Trans Mountain Pipeline that takes crude oil from Edmonton over the Rocky Mountains to the west coasts of British Columbia and Washington State, with an existing capacity of 300,000 bbl/d (48,000 m3/d). It has plans to add an additional 450,000 bbl/d (72,000 m3/d) of capacity to this pipeline within the existing pipeline easement.
- Spectra Energy has a system of pipelines that takes crude oil from Hardisty south to Casper, Wyoming and then east to Wood River, Illinois. The first segment has a capacity of 280,000 bbl/d (45,000 m3/d) and the second segment 160,000 bbl/d (25,000 m3/d).
- TransCanada Corporation has the Keystone Pipeline system. Phase 1 currently takes crude oil from Hardisty south to Steele City, Nebraska and then east to Wood River, Illinois. The existing Phase 2 moves crude oil from Steele City to the main US oil marketing hub at Cushing, Oklahoma. Phases 1 and 2 have a combined capacity of 590,000 bbl/d (94,000 m3/d).
Overall, the total pipeline capacity for the movement of crude oil
from Edmonton and Hardisty to the rest of North America is about 3.5×106 bbl/d (560,000 m3/d).
However, other substances such as conventional crude oil and refined
petroleum products also share this pipeline network. The rapidly
increasing tight oil production from the Bakken formation of North Dakota
also competes for space on the Canadian export pipeline system. North
Dakota oil producers are using the Canadian pipelines to deliver their
oil to US refineries.
In 2012, the Canadian export pipeline system began to become
overloaded with new oil production. As a result, Enbridge implemented pipeline apportionment
on its southbound lines, and Kinder Morgan on its westbound line. This
rationed pipeline space by reducing the monthly allocation of each
shipper to a certain percentage of its requirements. The Chevron Corporation Burnaby Refinery,
the last remaining oil refinery on Canada's west coast, applied to the
NEB for preferential access to Canadian oil since American refineries in
Washington and California were outbidding it for pipeline space, but
was denied because it would violate NAFTA equal access to energy rules. Similarly, new North Dakota tight oil production began to block new Canadian production from using the Enbridge, Kinder Morgan, and TransCanada southbound systems.
In addition, the US oil marketing hub at Cushing was flooded with
new oil because most new North American production from Canada, North
Dakota, and Texas converged at that point, and there was insufficient
capacity to take it from there to refineries on the Gulf Coast, where
half of US oil refinery capacity is located. The American pipeline
system is designed to take imported oil from the Gulf Coast and Texas to
the refineries in the northern US, and the new oil was flowing in the
opposite direction, toward the Gulf Coast. The price of West Texas Intermediate delivered at Cushing, which is the main benchmark for US oil prices, fell to unprecedented low levels below other international benchmark oils such as Brent Crude and Dubai Crude. Since the price of WTI at Cushing is usually quoted by US media as the price of oil,
this gave many Americans a distorted view of world oil prices as being
lower than they were, and the supply being better than it was
internationally. Canada used to be in a similar position to the US in
that offshore oil was cheaper than domestic oil, so the oil pipelines
used to run westward from the east coast to Central Canada, now they are
being reversed to carry cheaper domestic oil sands production from
Alberta to the east coast.
New pipelines
Lack
of access to markets, limited export capacity, and oversupply in the US
market have been a problem for oil sands producers in recent years.
They have caused lower prices to Canadian oil sands producers and
reduced royalty and tax revenues to Canadian governments. The pipeline
companies have moved forward with a number of solutions to the
transportation problems:
- Enbridge's line from Sarnia, Ontario to Westover, Ontario near the head of Lake Erie has been reversed. This line used to take offshore oil to refineries in the Sarnia area. Now it takes Alberta SCO and blended bitumen to most refineries in Ontario.
- Enbridge has applied to reverse its line from Westover to Montreal, Quebec. This line used to take offshore oil to refineries in southern Ontario. After reversal, it will take Alberta SCO and bitumen to Montreal. Since Suncor Energy owns a very large oil sands mine and upgrader in Alberta and also owns a large oil refinery in Montreal, it finds this project appealing. The alternative is closing the refinery since it is noncompetitive using offshore oil.
- TransCanada is evaluating converting part of its mainline natural gas transmission system from western Canada to eastern North America to transport oil. Eastern North America is well supplied with natural gas as a result of the recent increases in US shale gas production, but has problems with oil supply since most of their oil comes from offshore.
- Enbridge's Seaway Pipeline which used to take oil from the US Gulf Coast to the oil trading hub at Cushing was reversed in 2012 to take oil from Cushing to the Coast, helping to alleviate the bottleneck at Cushing. It has a capacity of 400,000 bbl/d (64,000 m3/d) but Enbridge is twinning the pipeline to add an additional 400,000 bbl/d (64,000 m3/d).
- Following the denial of a US regulatory permit for its Keystone XL pipeline, TransCanada went ahead with the southern leg of the Keystone project. This will deliver 830,000 bbl/d (132,000 m3/d) from Cushing to the Coast. Since it is entirely within the states of Oklahoma and Texas, it does not require US federal government approval.
Future pipelines
With
the main constraint on Canadian oil sands development becoming the
availability of export pipeline capacity, pipeline companies have
proposed a number of major new transmission pipelines. Many of these
became stalled in government regulatory processes, both by the Canadian
and American governments. Another factor is competition for pipeline
space from rapidly increasing tight oil production from North Dakota, which under NAFTA trade rules has equal access to Canadian pipelines.
- Enbridge has announced its intention to expand its Alberta Clipper line from 450,000 bbl/d (72,000 m3/d) to 570,000 bbl/d (91,000 m3/d) and its Southern Access line from 400,000 bbl/d (64,000 m3/d) to 560,000 bbl/d (89,000 m3/d). It is also proposing to build a Flanagan South line with an initial capacity of 585,000 bbl/d (93,000 m3/d) expandable to 800,000 bbl/d (130,000 m3/d).
- Enbridge is proposing to build the Northern Gateway Pipeline from Bruderheim, near Edmonton, Alberta to the port of Kitimat, BC for loading on supertankers with an initial capacity of 525,000 bbl/d (83,500 m3/d) with a reverse flow condensate pipeline to take diluent from tankers at Kitimat to Alberta. This was approved by the Canadian federal cabinet on June 17, 2014, subject to 209 conditions. After this point, the company has to satisfy most of the conditions to National Energy Board satisfaction before construction can start. Satisfying the conditions is expected to take a year or more. The leaders of both main opposition parties promised to reverse the decision if they form the government in the 2015 election. This in fact occurred, as the Liberal party under Justin Trudeau won a majority government.
- Kinder Morgan is proposing to increase the capacity of its Trans Mountain pipeline through British Columbia to 900,000 bbl/d (140,000 m3/d) by 2017. Kinder Morgan is also proposing to build the Trans Mountain Expansion pipeline which will add 550,000 bbl/d (87,000 m3/d) of capacity to the West Coast of Canada and the US.
- TransCanada has proposed the construction of the Keystone XL extension to its Keystone Pipeline which would add 700,000 bbl/d (110,000 m3/d) of capacity from Alberta to the US Gulf Coast. On November 6, 2015, American president Barack Obama announced that the State Department had rejected the proposed expansion.
- TransCanada has also proposed to build the 4,600 km (2,900 mi) Energy East Pipeline, which would carry 1.1×106 bbl/d (170,000 m3/d) of oil from Alberta to refineries in Eastern Canada, including Quebec and New Brunswick. It would also have marine facilities that would enable Alberta production to be delivered to Atlantic markets by oil tanker. The Irving Oil Refinery in New Brunswick, which is the largest oil refinery in Canada, is especially interested in it since its traditional sources such as North Sea oil are shrinking and international oil is more expensive than Alberta oil delivered to the Atlantic coast.
In addition, there are a large number of new pipelines proposed for
Alberta. These will likely be approved rapidly by the Alberta Energy
Regulator, so there are likely to be few capacity problems within
Alberta.
Rail
The movement of crude oil by rail is far from new, but it is now a rapidly growing market for North American railroads.
The growth is driven by several factors. One is that the transmission
pipelines from Alberta are operating at or near capacity and companies
who cannot get pipeline space have to move oil by rail instead. Another
is that many refineries on the east, west, and Gulf coasts of North
America are under-served by pipelines since they assumed that they would
obtain their oil by ocean tanker. Producers of new oil in Alberta,
North Dakota, and West Texas are now shipping oil by rail to coastal
refiners who are having difficulty obtaining international oil at prices
competitive with those in the interior of North America. In addition,
crude bitumen can be loaded directly into tank cars equipped with steam
heating coils, avoiding the need for blending it with expensive
condensate in order to ship it to market. Tank cars can also be built to
transport condensate on the back-haul from refineries to the oil sands
to make additional revenue rather than returning empty.
A single-track rail line carrying 10 trains per day, each with 120 tank cars, can move 630,000 bbl/d (100,000 m3/d) to 780,000 bbl/d (124,000 m3/d),
which is the capacity of a large transmission pipeline. This would
require 300 locomotives and 18,000 tank cars, which is a small part of
the fleet of a Class 1 railroad. By comparison, the two Canadian Class 1
railways, Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) and Canadian National Railway
(CN), have 2,400 locomotives and 65,000 freight cars between them, and
CP moves 30–35 trains per day on its main line to Vancouver. Two US
Class 1 railways, Union Pacific Railroad (UP) and BNSF Railway handle more than 100 trains per day on their western corridors. CN Rail has said that it could move 1,500,000 bbl/d (240,000 m3/d) of bitumen from Edmonton to the deepwater port of Prince Rupert, BC if the Northern Gateway Pipeline from Edmonton to the port of Kitimat, BC was not approved.
With many of their lines being underused, railroads find
transporting crude oil an attractive source of revenue. With enough new
tank cars they could carry all the new oil being produced in North
America, albeit at higher prices than pipelines. In the short term, the
use of rail will probably continue to grow as producers try to bypass
short-term pipeline bottlenecks to take advantage of higher prices in
areas with refineries capable of handling heavier crudes. In the long
term the growth in rail transport will largely depend on the continued
pipeline bottlenecks due to increased production in North America and
regulatory delays for new pipelines. At present rail moves over
90,000 bbl/d (14,000 m3/d) of crude oil, and with continued
growth in oil production and building of new terminals, rail movements
will probably continue to grow into the foreseeable future.
By 2013, exports of oil from Canada to the US by rail had increased 9-fold in less than two years, from 16,000 bbl/d (2,500 m3/d) in early 2012 to 146,000 bbl/d (23,200 m3/d)
in late 2013, mainly because new export pipelines had been held up by
regulatory delays. As a result, Canadian farmers suffered an acute
shortage of rail capacity to export their grains because so much of
Canada's rail capacity was tied up by oil products. The safety of rail
transport of oil was being called into question after several
derailments, especially after a train with 74 tank cars of oil derailed
and caught fire in Lac Megantic, Quebec.
The ensuing explosion and firestorm burned down 40 buildings in the
town center and killed 47 people. The cleanup of the derailment area
could take 5 years, and another 160 buildings may need to be demolished.
Ironically, the oil was not Canadian bitumen being exported to the
United States but Bakken formation light crude oil being imported into Canada from North Dakota to the Irving Oil Refinery in New Brunswick. Although near a huge oil import port
on the Atlantic Ocean, the Irving refinery is importing US Bakken oil
by rail because oil from outside North America is too expensive to be
economic, and there are no pipelines to deliver heavier but cheaper
Western Canadian oil to New Brunswick. It was subsequently pointed out
that the Bakken light oil was much more flammable than Alberta bitumen,
and the rail cars were mislabeled by the North Dakota producers as to
their flammability.
By 2014, the movement of crude by rail had become very profitable to oil companies. Suncor Energy,
Canada's largest oil company declared record profits and attributed
much of it to transporting oil to market by rail. It was moving about
70,000 bbl/d (11,000 m3/d) to Cushing, Oklahoma,
and putting it into TransCanada's new Gulf Coast pipeline – which was
originally going to be the southern leg of the Keystone XL pipeline,
before the northern leg across the border from Canada was stalled by US
federal government delays.
Suncor has also been moving 20,000 bbl/d (3,200 m3/d) of Alberta bitumen and North Dakota tight oil by rail to its Montreal Refinery with plans to increase it to 35,000 bbl/d (5,600 m3/d).
Suncor claimed this saved about $10/bbl off the price of buying
offshore oil. However, it was also anticipating the reversal of Enbridge's Line 9 from southwestern Ontario to Montreal to deliver 300,000 bbl/d (48,000 m3/d)
oil even cheaper. Suncor has been considering adding a coker to its
Montreal refinery to upgrade heavy oil sands bitumen, which would be
cheaper than adding another upgrader to its oil sands operation. It was
also shipping marine cargoes on an "opportunistic basis" from Texas and
Louisiana "at significant discounts to the international crudes we would
typically run in Montreal", thereby taking advantage of the recent US tight oil glut in addition to increased supplies of cheap Canadian oil sands bitumen.
Refining
Heavy crude oil feedstock#crude feedstock
needs pre-processing before it is fit for conventional refineries,
although heavy oil and bitumen refineries can do the pre-processing
themselves. This pre-processing is called 'upgrading', the key
components of which are as follows:
- removal of water, sand, physical waste, and lighter products
- catalytic purification by hydrodemetallisation (HDM), hydrodesulfurization (HDS) and hydrodenitrogenation (HDN)
- hydrogenation through carbon rejection or catalytic hydrocracking (HCR)
As carbon rejection is very inefficient and wasteful in most cases, catalytic hydrocracking
is preferred in most cases. All these processes take large amounts of
energy and water, while emitting more carbon dioxide than conventional
oil.
Catalytic purification and hydrocracking are together known as hydroprocessing.
The big challenge in hydroprocessing is to deal with the impurities
found in heavy crude, as they poison the catalysts over time. Many
efforts have been made to deal with this to ensure high activity and
long life of a catalyst. Catalyst materials and pore size distributions
are key parameters that need to be optimized to deal with this challenge
and varies from place to place, depending on the kind of feedstock
present.
Alberta
There are four major oil refineries in Alberta which supply most of Western Canada with petroleum products, but as of 2012 these processed less than 1/4 of the approximately 1,900,000 bbl/d (300,000 m3/d)
of bitumen and SCO produced in Alberta. Some of the large oil sands
upgraders also produced diesel fuel as part of their operations. Some of
the oil sands bitumen and SCO went to refineries other provinces, but
most of it was exported to the United States. The four major Alberta
refineries are:
- Suncor Energy, the largest oil company in Canada, operates the Petro-Canada refinery near Edmonton, Alberta which can process 142,000 bbl/d (22,600 m3/d) of all types of oil and bitumen into all types of products.
- Imperial Oil, controlled by ExxonMobil, operates the Strathcona Refinery near Edmonton, which can process 187,200 bbl/d (29,760 m3/d) of SCO and conventional oil into all types of products.
- Shell Canada, a subsidiary of Royal Dutch Shell, operates the Scotford Refinery near Edmonton, which is integrated with the Scotford Upgrader, and which can process 100,000 bbl/d (16,000 m3/d) of all types of oil and bitumen into all types of products.
- Husky Energy, a Canadian company controlled by Hong Kong billionaire Li Ka-shing, operates the Husky Lloydminster Refinery in Lloydminster on the Alberta/Saskatchewan border, which can process 28,300 bbl/d (4,500 m3/d) of feedstock from the adjacent Husky Upgrader into asphalt and other products.
The $8.5-billion Sturgeon Refinery, a fifth major Alberta refinery, is under construction near Fort Saskatchewan with a completion date of 2017. The proponents are Alberta Petroleum Marketing Commission, Canadian Natural Resources Limited and North West Upgrading Inc. NWU, which was founded in 2004, is a private, Alberta-based company with headquarters in Calgary. Canadian Natural Resources Limited 50/50 entered into a joint venture partnership with NWU in February 2011
forming North West Redwater Partnership. This is the first oil refinery
to be constructed in Alberta in thirty years – the last was Shell’s
Scotford refinery which was completed in 1984. The Sturgeon Refinery is the "first new refinery to be built with a carbon capture and storage system." The plant is designed to convert up to 150,000 bbl/d (24,000 m3/d) of crude bitumen directly to diesel fuel.
"In addition to producing ultra low-sulphur diesel and naphtha, the
project will capture carbon dioxide which will be sold to Enhance
Energy’s Alberta Carbon Trunk Line for use in enhanced oil recovery."
The refinery will process bitumen into diesel fuel not SCO so it is
more of an upgrader than a refinery. A petroleum coker is required to
upgrade the raw product before it can be made into diesel."
By June 2014 the estimated cost of construction had increased from $5.7 billion to $8.5 billion – or $170,000 per barrel of new capacity.
The Alberta government has guaranteed NWU's loans and signed a
firm contract for feedstock deliveries because of some economic issues.
Alberta levies royalties
on bitumen at "before payout" (2%) and "after payout" (25%) rates, and
accepts payments "in kind" rather than "in cash." (BRIK), Alberta will
receive 300,000 bpd of bitumen under this BRIK program. With bitumen
production expected to reach 5,000,000 bbl/d (790,000 m3/d) by 2035, it means that after the projects pay out, the Alberta government will have 1,250,000 bbl/d (200,000 m3/d)
of bitumen to sell. Since Alberta has a chronic shortage of diesel
fuel, the government would prefer to sell diesel fuel rather than
bitumen to Alberta and international oil companies.
British Columbia
The Pacific Future Energy
project proposes a new refinery in British Columbia that would bring in
Western Canadian bitumen and process it into fuels for Asian and
Canadian markets. Pacific Future Energy proposes to transport near-solid
bitumen to the refinery using railway tank cars.
Rest of Canada
Canadian oil exports have increased tenfold since 1980, mostly as the
result of new oil sands bitumen and heavy oil output, but at the same
time Canadian oil consumption and refining capacity has hardly grown at
all. Since the 1970s, the number of oil refineries in Canada has
declined from 40 to 19. There hasn't been a new oil refinery (other than
oil sands upgraders) built in Canada since 1984.
Most of the Canadian oil refining industry is foreign-owned, and
except for Alberta, international companies preferred to build refining
capacity elsewhere than in Canada. The result is a serious imbalance
between Canadian oil production versus Canadian oil refining. Although
Canada produces much more oil than it refines, and exports more oil and
refined products than it consumes, most of the new production is heavier
than traditional oil and concentrated in the landlocked
provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. Canadian refineries have
pipeline access to and can process only about 25% of the oil produced in
Canada. The remainder of Canadian oil production is exported, almost
all of it to the US. At the same time Canada imports 700,000 bbl/d
(110,000 m3/d) of crude oil from other countries and exports much of the oil products to other countries, most of it to the US.
Canadian refineries, outside of the major oil producing provinces
of Alberta and Saskatchewan, were originally built on the assumption
that light and medium crude oil would continue to be cheap in the long
term, and that imported oil would be cheaper than oil sands production.
With new oil sands production coming on production at lower prices than
international oil, market price imbalances have ruined the economics of
refineries which could not process it. Most of the Canadian oil
refineries which closed were in the oil deficient regions of Quebec, the Atlantic Provinces, and British Columbia
where they had no access to cheaper domestic Canadian production. They
also were not designed to refine the heavier grades which comprised most
new Canadian production. These refinery closures were part of an
international trend, since about a dozen refineries in Europe, the
Caribbean and along the US east coast have shut down recent years due to
sharp increases in the cost of imported oil and declining domestic
demand for fuel.
United States
Prior to 2013, when China surpassed it, the United States was the largest oil importer in the world.
Unlike Canada, the US has hundreds of oil refineries, many of which
have been modified to process heavy oil as US production of light and
medium oil declined. The main market for Canadian bitumen as well as
Venezuelan extra-heavy oil was assumed to be the US. The United States
has historically been Canada’s largest customer for crude oil and
products, particularly in recent years. American imports of oil and
products from Canada grew from 450,000 bbl/d (72,000 m3/d) in 1981 to 3,120,000 bbl/d (496,000 m3/d)
in 2013 as Canada's oil sands produced more and more oil, while in the
US, domestic production and imports from other countries declined.
However, this relationship is becoming strained due to physical,
economic and political influences. Export pipeline capacity is
approaching its limits; Canadian oil is selling at a discount to world
market prices; and US demand for crude oil and product imports has
declined because of US economic problems.
For the benefit of oil marketers, in 2004 Western Canadian producers created a new benchmark crude oil called Western Canadian Select,
(WCS), a bitumen-derived heavy crude oil blend that is similar in its
transportation and refining characteristics to California, Mexico Maya,
or Venezuela heavy crude oils. This heavy oil has an API gravity of
19–21 and despite containing large amounts of bitumen and synthetic
crude oil, flows through pipelines well and is classified as
"conventional heavy oil" by governments. There are several hundred
thousand barrels per day of this blend being imported into the US, in
addition to larger amounts of crude bitumen and synthetic crude oil
(SCO) from the oil sands.
The demand from US refineries is increasingly for non-upgraded bitumen rather than SCO. The Canadian National Energy Board (NEB) expects SCO volumes to double to around 1,900,000 bbl/d (300,000 m3/d)
by 2035, but not keep pace with the total increase in bitumen
production. It projects that the portion of oil sands production that is
upgraded to SCO to decline from 49% in 2010 to 37% in 2035. This
implies that over 3,200,000 bbl/d (510,000 m3/d) of bitumen will have to be blended with diluent for delivery to market.
Asia
Demand for oil in Asia has been growing much faster than in North
America or Europe. In 2013, China replaced the United States as the
world's largest importer of crude oil, and its demand continues to grow
much faster than its production. The main impediment to Canadian exports
to Asia is pipeline capacity – The only pipeline capable of delivering
oil sands production to Canada's Pacific Coast is the Trans Mountain
Pipeline from Edmonton to Vancouver, which is now operating at its
capacity of 300,000 bbl/d (48,000 m3/d) supplying refineries
in B.C. and Washington State. However, once complete, the Northern
Gateway pipeline and the Trans Mountain expansion currently undergoing
government review are expected to deliver an additional 500,000 bbl/d
(79,000 m3/d) to 1,100,000 bbl/d (170,000 m3/d) to
tankers on the Pacific coast, from where they could deliver it anywhere
in the world. There is sufficient heavy oil refinery capacity in China
and India to refine the additional Canadian volume, possibly with some
modifications to the refineries. In recent years, Chinese oil companies such as China Petrochemical Corporation (Sinopec), China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC), and PetroChina
have bought over $30 billion in assets in Canadian oil sands projects,
so they would probably like to export some of their newly acquired oil
to China.
Economics
The world's largest deposits of bitumen are in Canada, although Venezuela's deposits of extra-heavy crude oil
are even bigger. Canada has vast energy resources of all types and its
oil and natural gas resource base would be large enough to meet Canadian
needs for generations if demand was sustained. Abundant hydroelectric
resources account for the majority of Canada's electricity production
and very little electricity is produced from oil. In a scenario with oil
prices above US$100, Canada would have more than enough energy to meet
its growing needs, with the excess oil production from its oil sands
probably going to export. The major importing country would probably
continue to be the United States, although before the developments in
2014, there was increasing demand for oil, particularly heavy oil, from
Asian countries such as China and India.
Canada has abundant resources of bitumen and crude oil, with an
estimated remaining ultimate resource potential of 54 billion cubic
metres (340 billion barrels). Of this, oil sands bitumen accounts for 90
per cent. Alberta currently accounts for all of Canada’s bitumen
resources. Resources become reserves only after it is
proven that economic recovery can be achieved. At 2013 prices using
current technology, Canada had remaining oil reserves of 27 billion m3 (170 billion bbls), with 98% of this attributed to oil sands bitumen. This put its reserves in third place in the world behind Venezuela and Saudi Arabia. At the much lower prices of 2015, the reserves are much smaller.
Costs
The costs
of production and transportation of saleable petroleum from oil sands is
typically significantly higher than from conventional global sources. Hence the economic viability of oil sands production is more vulnerable to the price of oil. The price of benchmark West Texas Intermediate (WTI) oil at Cushing, Oklahoma
above US$100/bbl that prevailed until late 2014 was sufficient to
promote active growth in oil sands production. Major Canadian oil
companies had announced expansion plans and foreign companies were
investing significant amounts of capital, in many cases forming
partnerships with Canadian companies. Investment had been shifting
towards in-situ steam assisted gravity drainage
(SAGD) projects and away from mining and upgrading projects, as oil
sands operators foresee better opportunities from selling bitumen and
heavy oil directly to refineries than from upgrading it to synthetic crude oil. Cost estimates for Canada include
the effects of the mining when the mines are returned to the
environment in "as good as or better than original condition". Cleanup
of the end products of consumption are the responsibility of the
consuming jurisdictions, which are mostly in provinces or countries
other than the producing one.
The Alberta government estimated that in 2012, the supply cost of
oil sands new mining operations was $70 to $85 per barrel, whereas the
cost of new SAGD projects was $50 to $80 per barrel.
These costs included capital and operating costs, royalties and taxes,
plus a reasonable profit to the investors. Since the price of WTI rose
to $100/bbl beginning in 2011,
production from oil sands was then expected to be highly profitable
assuming the product could be delivered to markets. The main market was
the huge refinery complexes on the US Gulf Coast, which are generally
capable of processing Canadian bitumen and Venezuelan extra-heavy oil
without upgrading.
The Canadian Energy Research Institute (CERI) performed an
analysis, estimating that in 2012 the average plant gate costs
(including 10% profit margin, but excluding blending and transport) of
primary recovery was $30.32/bbl, of SAGD was $47.57/bbl, of mining and
upgrading was $99.02/bbl, and of mining without upgrading was
$68.30/bbl.
Thus, all types of oil sands projects except new mining projects with
integrated upgraders were expected to be consistently profitable from
2011 onward, provided that global oil prices remained favourable. Since
the larger and more sophisticated refineries preferred to buy raw
bitumen and heavy oil rather than synthetic crude oil, new oil sands
projects avoided the costs of building new upgraders. Although primary
recovery such as is done in Venezuela is cheaper than SAGD, it only
recovers about 10% of the oil in place versus 60% or more for SAGD and
over 99% for mining. Canadian oil companies were in a more competitive
market and had access to more capital than in Venezuela, and preferred
to spend that extra money on SAGD or mining to recover more oil.
Then in late 2014 the dramatic rise in U.S. production from shale
formations, combined with a global economic malaise that reduced
demand, caused the price of WTI to drop below $50, where it remained as
of late 2015.
In 2015, the Canadian Energy Research Institute (CERI) re-estimated the
average plant gate costs (again including 10% profit margin) of SAGD to
be $58.65/bbl, and 70.18/bbl for mining without upgrading. Including
costs of blending and transportation, the WTI equivalent supply costs
for delivery to Cushing become US$80.06/bbl for SAGD projects, and
US$89.71/bbl for a standalone mine.
In this economic environment, plans for further development of production from oil sands have been slowed or deferred, or even abandoned during construction.
Production of synthetic crude from mining operations continue at a loss
because of the costs of shutdown and restart, as well as commitments to
supply contracts.
Production forecasts
Oil sands production forecasts released by the Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers (CAPP), the Alberta Energy Regulator (AER), and the Canadian Energy Research Institute (CERI) are comparable to National Energy Board
(NEB) projections, in terms of total bitumen production. None of these
forecasts take into account probable international constraints to be
imposed on combustion of all hydrocarbons in order to limit global
temperature rise, giving rise to a situation denoted by the term "carbon bubble".
Ignoring such constraints, and also assuming that the price of oil
recovers from its collapse in late 2014, the list of currently proposed
projects, many of which are in the early planning stages, would suggest
that by 2035 Canadian bitumen production could potentially reach as much
as 1.3 million m3/d (8.3 million barrels per day) if most
were to go ahead. Under the same assumptions, a more likely scenario is
that by 2035, Canadian oil sands bitumen production would reach 800,000 m3/d
(5.0 million barrels/day), 2.6 times the production for 2012. The
majority of the growth would likely occur in the in-situ category, as
in-situ projects usually have better economics than mining projects.
Also, 80% of Canada's oil sands reserves are well-suited to in-situ
extraction, versus 20% for mining methods.
An additional assumption is that there would be sufficient
pipeline infrastructure to deliver increased Canadian oil production to
export markets. If this were a limiting factor, there could be impacts
on Canadian crude oil prices, constraining future production growth.
Another assumption is that US markets will continue to absorb increased
Canadian exports. Rapid growth of tight oil production in the US, Canada's primary oil export market, has greatly reduced US reliance on imported crude.
The potential for Canadian oil exports to alternative markets such as
Asia is also uncertain. There are increasing political obstacles to
building any new pipelines to deliver oil in Canada and the US. In
November 2015, U.S. President Barack Obama rejected the proposal to build the Keystone XL pipeline from Alberta to Steele City, Nebraska.
In the absence of new pipeline capacity, companies are increasingly
shipping bitumen to US markets by railway, river barge, tanker, and
other transportation methods. Other than ocean tankers, these
alternatives are all more expensive than pipelines.
A shortage of skilled workers in the Canadian oil sands developed
during periods of rapid development of new projects. In the absence of
other constraints on further development, the oil and gas industry would
need to fill tens of thousands of job openings in the next few years as
a result of industry activity levels as well as age-related attrition.
In the longer term, under a scenario of higher oil and gas prices, the
labor shortages would continue to get worse. A potential labor shortage
can increase construction costs and slow the pace of oil sands
development.
The skilled worker shortage was much more severe in Venezuela because the government controlled oil company PDVSA fired most of its heavy oil experts after the Venezuelan general strike of 2002–03, and wound down the production of Orimulsion, which was the primary product from its oil sands. Following that, the government re-nationalized the Venezuelan oil industry
and increased taxes on it. The result was that foreign companies left
Venezuela, as did most of its elite heavy oil technical experts. In
recent years, Venezuela's heavy oil production has been falling, and it
has consistently been failing to meet its production targets.
As of late 2015, development of new oil sand projects were
deterred by the price of WTI below US$50, which is barely enough to
support production from existing operations. Demand recovery was suppressed by economic problems that may continue indefinitely to bedevil both the European Community and China. Low-cost production by OPEC
continued at maximum capacity, efficiency of production from U.S.
shales continued to improve, and Russian exports were mandated even
below cost of production, as their only source of hard currency.
There is also the possibility that there will emerge an international
agreement to introduce measures to constrain the combustion of
hydrocarbons in an effort to limit global temperature rise to the
nominal 2 °C that is consensually predicted to limit environmental harm
to tolerable levels. Rapid technological progress is being made to reduce the cost of competing renewable sources of energy. Hence there is no consensus about when, if ever, oil prices paid to producers may substantially recover.
A detailed academic study of the consequences for the producers
of the various hydrocarbon fuels concluded in early 2015 that a third of
global oil reserves, half of gas reserves and over 80% of current coal
reserves should remain underground from 2010 to 2050 in order to meet
the target of 2 °C. Hence continued exploration or development of
reserves would be extraneous to needs. To meet the 2 °C target, strong
measures would be needed to suppress demand, such as a substantial
carbon tax leaving a lower price for the producers from a smaller
market. The impact on producers in Canada would be far larger than in
the U.S. Open-pit mining of natural bitumen in Canada would soon drop to
negligible levels after 2020 in all scenarios considered because it is
considerably less economic than other methods of production.
Environmental issues

Satellite images show the growth of pit mines over Canada's oil sands between 1984 and 2011.
Demonstration of citizens against tar sands and the Keystone Pipeline.
In their 2011 commissioned report entitled "Prudent Development:
Realizing the Potential of North America’s Abundant Natural Gas and Oil
Resources," the National Petroleum Council,
an advisory committee to the U.S. Secretary of Energy, acknowledged
health and safety concerns regarding the oil sands which include
"volumes of water needed to generate issues of water sourcing; removal
of overburden for surface mining can fragment wildlife habitat and
increase the risk of soil erosion or surface run-off events to nearby
water systems; GHG and other air emissions from production."
Oil sands extraction can affect the land when the bitumen is
initially mined, water resources by its requirement for large quantities
of water during separation of the oil and sand, and the air due to the
release of carbon dioxide and other emissions. Heavy metals such as vanadium, nickel, lead, cobalt, mercury, chromium, cadmium, arsenic, selenium, copper, manganese, iron and zinc are naturally present in oil sands and may be concentrated by the extraction process. The environmental impact caused by oil sand extraction is frequently criticized by environmental groups such as Greenpeace, Climate Reality Project, Pembina Institute, 350.org, MoveOn.org, League of Conservation Voters, Patagonia, Sierra Club, and Energy Action Coalition. In particular, mercury contamination has been found around oil sands production in Alberta, Canada.
The European Union has indicated that it may vote to label oil sands
oil as "highly polluting". Although oil sands exports to Europe are
minimal, the issue has caused friction between the EU and Canada. According to the California-based Jacobs Consultancy,
the European Union used inaccurate and incomplete data in assigning a
high greenhouse gas rating to gasoline derived from Alberta’s oilsands.
Also, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Nigeria and Russia do not provide data on how
much natural gas is released via flaring or venting
in the oil extraction process. The Jacobs report pointed out that extra
carbon emissions from oil-sand crude are 12 percent higher than from
regular crude, although it was assigned a GHG rating 22% above the
conventional benchmark by EU.
In 2014 results of a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
showed that official reports on emissions were not high enough. Report
authors noted that, "emissions of organic substances with potential
toxicity to humans and the environment are a major concern surrounding
the rapid industrial development in the Athabasca oil sands region
(AOSR)." This study found that tailings ponds were an indirect pathway
transporting uncontrolled releases of evaporative emissions of three
representative polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH)s (phenanthrene, pyrene, and benzo(a)pyrene) and that these emissions had been previously unreported.
Air pollution management
The Alberta government computes an Air Quality Health Index (AQHI) from sensors in five communities in the oil sands region, operated by a "partner" called the Wood Buffalo
Environmental Association (WBEA). Each of their 17 continuously
monitoring stations measure 3 to 10 air quality parameters among carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen sulfide (H
2S), total reduced sulfur (TRS), Ammonia (NH
3), nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO
2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), ozone (O
3), particulate matter (PM2.5), sulfur dioxide (SO
2), total hydrocarbons (THC), and methane/non-methane hydrocarbons (CH
4/NMHC). These AQHI are said to indicate 'low risk"'air quality more than 95% of the time. Prior to 2012, air monitoring showed significant increases in exceedances of hydrogen sulfide (H
2S) both in the Fort McMurray area and near the oil sands upgraders. In 2007, the Alberta government issued an environmental protection order to Suncor in response to numerous occasions when ground level concentration for H
2S) exceeded standards.[130] The Alberta Ambient Air Data Management System (AAADMS) of the Clean Air Strategic Alliance[131] (aka CASA Data Warehouse) records that, during the year ending on 1 November 2015, there were 6 hourly reports of values exceeding the limit of 10 ppb for H
2S, and 4 in 2013, down from 11 in 2014, and 73 in 2012.
2S), total reduced sulfur (TRS), Ammonia (NH
3), nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO
2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), ozone (O
3), particulate matter (PM2.5), sulfur dioxide (SO
2), total hydrocarbons (THC), and methane/non-methane hydrocarbons (CH
4/NMHC). These AQHI are said to indicate 'low risk"'air quality more than 95% of the time. Prior to 2012, air monitoring showed significant increases in exceedances of hydrogen sulfide (H
2S) both in the Fort McMurray area and near the oil sands upgraders. In 2007, the Alberta government issued an environmental protection order to Suncor in response to numerous occasions when ground level concentration for H
2S) exceeded standards.[130] The Alberta Ambient Air Data Management System (AAADMS) of the Clean Air Strategic Alliance[131] (aka CASA Data Warehouse) records that, during the year ending on 1 November 2015, there were 6 hourly reports of values exceeding the limit of 10 ppb for H
2S, and 4 in 2013, down from 11 in 2014, and 73 in 2012.
In September 2015, the Pembina Institute
published a brief report about "a recent surge of odour and air quality
concerns in northern Alberta associated with the expansion of oilsands
development", contrasting the responses to these concerns in Peace River and Fort McKay.
In Fort McKay, air quality is actively addressed by stakeholders
represented in the WBEA, whereas the Peace River community must rely on
the response of the Alberta Energy Regulator.
In an effort to identify the sources of the noxious odours in the Fort
McKay community, a Fort McKay Air Quality Index was established,
extending the provincial Air Quality Health Index to include possible
contributors to the problem: SO
2, TRS, and THC. Despite these advantages, more progress was made in remediating the odour problems in the Peace River community, although only after some families had already abandoned their homes. The odour concerns in Fort McKay were reported to remain unresolved.
2, TRS, and THC. Despite these advantages, more progress was made in remediating the odour problems in the Peace River community, although only after some families had already abandoned their homes. The odour concerns in Fort McKay were reported to remain unresolved.
Land use and waste management
A large part of oil sands mining operations involves clearing trees and brush from a site and removing the overburden—topsoil, muskeg, sand, clay and gravel – that sits atop the oil sands deposit. Approximately 2.5 tons of oil sands are needed to produce one barrel of oil (roughly ⅛ of a ton).
As a condition of licensing, projects are required to implement a reclamation plan. The mining industry asserts that the boreal forest
will eventually colonize the reclaimed lands, but their operations are
massive and work on long-term timeframes. As of 2013, about 715 square
kilometres (276 sq mi) of land in the oil sands region have been
disturbed, and 72 km2 (28 sq mi) of that land is under reclamation.
In March 2008, Alberta issued the first-ever oil sands land
reclamation certificate to Syncrude for the 1.04 square kilometres
(0.40 sq mi) parcel of land known as Gateway Hill approximately 35
kilometres (22 mi) north of Fort McMurray. Several reclamation certificate applications for oil sands projects are expected within the next 10 years.
Water management
Between 2 and 4.5 volume units of water are used to produce each volume unit of synthetic crude oil in an ex-situ mining operation. According to Greenpeace, the Canadian oil sands operations use 349×106 m3/a (12.3×109 cu ft/a) of water, twice the amount of water used by the city of Calgary.
However, in SAGD operations, 90–95% of the water is recycled and only
about 0.2 volume units of water is used per volume unit of bitumen
produced.
For the Athabasca oil sand operations water is supplied from the Athabasca River, the ninth longest river in Canada. The average flow just downstream of Fort McMurray is 633 m3/s (22,400 cu ft/s) with its highest daily average measuring 1,200 m3/s (42,000 cu ft/s).
Oil sands industries water license allocations totals about 1.8% of
the Athabasca river flow. Actual use in 2006 was about 0.4%.
In addition, according to the Water Management Framework for the Lower
Athabasca River, during periods of low river flow water consumption
from the Athabasca River is limited to 1.3% of annual average flow.
In December 2010, the Oil Sands Advisory Panel, commissioned by
former environment minister Jim Prentice, found that the system in place
for monitoring water quality in the region, including work by the
Regional Aquatic Monitoring Program, the Alberta Water Research
Institute, the Cumulative Environmental Management Association and
others, was piecemeal and should become more comprehensive and
coordinated.
Greenhouse gas emissions
The
production of bitumen and synthetic crude oil emits more greenhouse
gases than the production of conventional crude oil. A 2009 study by the
consulting firm IHS CERA estimated that production from Canada's oil sands emits "about 5% to 15% more carbon dioxide, over the
"well-to-wheels" (WTW) lifetime analysis of the fuel, than average crude oil."
Author and investigative journalist David Strahan that same year stated
that IEA figures show that carbon dioxide emissions from the oil sands
are 20% higher than average emissions from the petroleum production.
A Stanford University study commissioned by the EU in 2011 found that oil sands crude was as much as 22% more carbon intensive than other fuels.
Greenpeace says the oil sands industry has been identified as the largest contributor to greenhouse gas emissions growth in Canada, as it accounts for 40 million tons of CO
2 emissions per year.
2 emissions per year.
According to the Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers and Environment Canada
the industrial activity undertaken to produce oil sands make up about
5% of Canada's greenhouse gas emissions, or 0.1% of global greenhouse
gas emissions. It predicts the oil sands will grow to make up 8% of
Canada's greenhouse gas emissions by 2015.
While the production industrial activity emissions per barrel of
bitumen produced decreased 26% over the decade 1992–2002, total
emissions from production activity were expected to increase due to
higher production levels.
As of 2006, to produce one barrel of oil from the oil sands released
almost 75 kilograms (165 lb) of greenhouse gases with total emissions
estimated to be 67 megatonnes (66,000,000 long tons; 74,000,000 short tons) per year by 2015.
A study by IHS CERA found that fuels made from Canadian oil sands
resulted in significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions than many
commonly cited estimates. A 2012 study by Swart and Weaver estimated that if only the economically viable reserve of 170 Gbbl (27×109 m3)
oil sands was burnt, the global mean temperature would increase by 0.02
to 0.05 °C. If the entire oil-in-place of 1.8 trillion barrels were to
be burnt, the predicted global mean temperature increase is 0.24 to
0.50 °C. Bergerson et al. found that while the WTW emissions can be higher than crude oil, the lower emitting oil sands cases can outperform higher emitting conventional crude cases.
To offset greenhouse gas emissions from the oil sands and
elsewhere in Alberta, sequestering carbon dioxide emissions inside
depleted oil and gas reservoirs has been proposed. This technology is
inherited from enhanced oil recovery methods.
In July 2008, the Alberta government announced a C$2 billion fund to
support sequestration projects in Alberta power plants and oil sands
extraction and upgrading facilities.
In November 2014, Fatih Birol, the chief economist of the International Energy Agency,
described additional greenhouse gas emissions from Canada's oil sands
as "extremely low". The IEA forecasts that in the next 25 years oil
sands production in Canada will increase by more than 3 million barrels
per day (480,000 m3/d), but Dr. Birol said "the emissions of this additional production is equal to only 23 hours of emissions of China
— not even one day." The IEA is charged with responsibility for
battling climate change, but Dr. Birol said he spends little time
worrying about carbon emissions from oil sands. "There is a lot of
discussion on oil sands projects in Canada and the United States and
other parts of the world, but to be frank, the additional CO2 emissions
coming from the oil sands is extremely low." Dr. Birol acknowledged that
there is tremendous difference of opinion on the course of action
regarding climate change, but added, "I hope all these reactions are
based on scientific facts and sound analysis."
In 2014, the U.S. Congressional Research Service published a report in preparation for the decision about permitting construction of the Keystone XL pipeline.
The report states in part: "Canadian oil sands crudes are generally
more GHG emission-intensive than other crudes they may displace in U.S.
refineries, and emit an estimated 17% more GHGs on a life-cycle basis
than the average barrel of crude oil refined in the United States".
Aquatic life deformities
There
is conflicting research on the effects of the oil sands development on
aquatic life. In 2007, Environment Canada completed a study that shows
high deformity rates in fish embryos exposed to the oil sands. David W. Schindler, a limnologist from the University of Alberta, co-authored a study on Alberta's oil sands' contribution of aromatic polycyclic compounds, some of which are known carcinogens, to the Athabasca River and its tributaries.
Scientists, local doctors, and residents supported a letter sent to
the Prime Minister in September 2010 calling for an independent study of
Lake Athabasca (which is downstream of the oil sands) to be initiated
due to the rise of deformities and tumors found in fish caught there.
The bulk of the research that defends the oil sands development
is done by the Regional Aquatics Monitoring Program (RAMP). RAMP studies
show that deformity rates are normal compared to historical data and
the deformity rates in rivers upstream of the oil sands.
Public health impacts
In
2007, it was suggested that wildlife has been negatively affected by
the oil sands; for instance, moose were found in a 2006 study to have as
high as 453 times the acceptable levels of arsenic
in their systems, though later studies lowered this to 17 to 33 times
the acceptable level (although below international thresholds for
consumption).
Concerns have been raised concerning the negative impacts that
the oil sands have on public health, including higher than normal rates
of cancer among residents of Fort Chipewyan.
However, John O'Connor, the doctor who initially reported the higher
cancer rates and linked them to the oil sands development, was
subsequently investigated by the Alberta College of Physicians and Surgeons. The College later reported that O'Connor's statements consisted of "mistruths, inaccuracies and unconfirmed information."
In 2010, the Royal Society of Canada
released a report stating that "there is currently no credible evidence
of environmental contaminant exposures from oil sands reaching Fort
Chipewyan at levels expected to cause elevated human cancer rates."
In August 2011, the Alberta government initiated a provincial
health study to examine whether a link exists between the higher rates
of cancer and the oil sands emissions.
In a report released in 2014, Alberta’s Chief Medical Officer of
Health, Dr. James Talbot, stated that "There isn’t strong evidence for
an association between any of these cancers and environmental exposure
[to tar sands]." Rather, Talbot suggested that the cancer rates at Fort Chipewyan,
which were slightly higher compared with the provincial average, were
likely due to a combination of factors such as high rates of smoking,
obesity, diabetes, and alcoholism as well as poor levels of
vaccination."