From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Environmental assessment (
EA) is the assessment of the
environmental consequences
(positive and negative) of a plan, policy, program, or actual projects
prior to the decision to move forward with the proposed action. In this
context, the term "
environmental impact assessment" (
EIA) is usually used when applied to actual projects by individuals or companies and the term "
strategic environmental assessment" (SEA) applies to policies, plans and programmes most often proposed by organs of state. Environmental assessments may be governed by rules of
administrative procedure regarding public participation and documentation of decision making, and may be subject to judicial review.
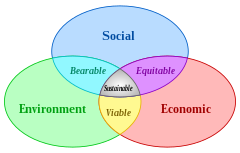
The purpose of the assessment is to ensure that decision makers
consider the environmental impacts when deciding whether or not to
proceed with a project. The International Association for Impact
Assessment (IAIA) defines an environmental impact assessment as "the
process of identifying, predicting, evaluating and mitigating the
biophysical, social, and other relevant effects of development proposals prior to major decisions being taken and commitments made".
EIAs are unique in that they do not require adherence to a
predetermined environmental outcome, but rather they require decision
makers to
account for environmental values
in their decisions and to justify those decisions in light of detailed
environmental studies and public comments on the potential environmental
impacts.
History
Environmental impact assessments commenced in the 1960s, as part of increasing
environmental awareness.
EIAs involved a technical evaluation intended to contribute to more
objective decision making. In the United States, environmental impact
assessments obtained formal status in 1969, with enactment of the
National Environmental Policy Act.
EIAs have been used increasingly around the world. The number of
"Environmental Assessments" filed every year "has vastly overtaken the
number of more rigorous
Environmental Impact Statements (EIS)."
An Environmental Assessment is a "mini-EIS designed to provide
sufficient information to allow the agency to decide whether the
preparation of a full-blown Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) is
necessary."
EIA is an activity that is done to find out the impact that would be done before development will occur.
Methods
General and industry specific assessment methods are available including:
- Industrial products – Product environmental life cycle analysis
(LCA) is used for identifying and measuring the impact of industrial
products on the environment. These EIAs consider activities related to
extraction of raw materials, ancillary materials, equipment; production,
use, disposal and ancillary equipment.
- Genetically modified plants – Specific methods available to perform EIAs of genetically modified organisms include GMP-RAM and INOVA.
- Fuzzy logic
– EIA methods need measurement data to estimate values of impact
indicators. However, many of the environment impacts cannot be
quantified, e.g. landscape quality, lifestyle quality and social
acceptance. Instead information from similar EIAs, expert judgment and
community sentiment are employed. Approximate reasoning methods known as
fuzzy logic can be used. A fuzzy arithmetic approach has also been proposed and implemented using a software tool (TDEIA).
Follow-up
At
the end of the project, an audit evaluates the accuracy of the EIA by
comparing actual to predicted impacts. The objective is to make future
EIAs more valid and effective. Two primary considerations are:
- Scientific – to examine the accuracy of predictions and explain errors
- Management – to assess the success of mitigation in reducing impacts
Audits can be performed either as a rigorous assessment of the
null hypothesis or with a simpler approach comparing what actually occurred against the predictions in the EIA document.
Around the world
Australia
The history of EIA in Australia could be linked to the enactment of the
U.S. National Environment Policy Act
(NEPA) in 1970, which made the preparation of environmental impact
statements a requirement. In Australia, one might say that the EIA
procedures were introduced at a State Level prior to that of the
Commonwealth (Federal), with a majority of the states having divergent
views to the Commonwealth. One of the pioneering states was New South
Wales, whose State Pollution Control Commission issued EIA guidelines in
1974. At a Commonwealth (i.e. Federal) level, this was followed by
passing of the
Environment Protection (Impact of Proposals) Act 1974 (Cth) in 1974. The
Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (Cth) (EPBC Act) superseded the
Environment Protection (Impact of Proposals) Act 1974
(Cth) and is the current central piece for EIA in Australia on a
Commonwealth (i.e. Federal) level. An important point to note is that
this federal legislation does not override the validity of the States or
Territories environmental and development assessments and approvals;
rather the EPBC Act runs as a parallel to the State/Territory Systems.
Overlap between federal and state requirements is addressed via
bilateral agreements or one-off accreditation of state processes, as
provided for in the EPBC Act.
The Commonwealth Level
The
EPBC Act provides a legal framework to protect and manage nationally
and internationally important flora, fauna, ecological communities and
heritage places-defined in the EPBC Act as matters of ‘National
Environmental Significance’. Following are the nine matters of ‘National
Environmental Significance’ to which the EPBC Act applies:
- World Heritage properties;
- National Heritage places;
- Wetlands of international importance (listed under the Ramsar Convention);
- Listed threatened species and ecological communities;
- Migratory species protected under international agreements;
- Commonwealth marine areas;
- the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park;
- Nuclear actions (including uranium mining); and
- Water resources, in relation with coal seam gas development and large coal mining development.
In addition to this, the EPBC Act aims at providing a streamlined
national assessment and approval process for activities. These
activities could be by the Commonwealth, or its agents, anywhere in the
world or activities on Commonwealth land; and activities that are listed
as having a ‘significant impact’ on matters of ‘national environment
significance'.
The EPBC Act comes into play when a person (a ‘proponent') wants
an action (often called a ‘proposal’ or ‘project’) assessed for
environmental impacts under the EPBC Act, he or she must refer the
project to the Department of the Environment and Energy (Commonwealth).
This ‘referral’ is then released to the public, as well as relevant
state, territory and Commonwealth ministers, for comment on whether the
project is likely to have a significant impact on matters of national
environmental significance.
The Department of the Environment and Energy assess the process and
makes recommendation to the minister or the delegate for the
feasibility. The final discretion on the decision remains of the
minister, which is not solely based on matters of ‘national
environmental significance’ but also the consideration of social and
economic impact of the project.
The Australian Government Minister for the Environment and Energy
cannot intervene in a proposal if it has no significant impact on one
of the eight matters of ‘national environmental significance’ despite
the fact that there may be other undesirable environmental impacts.
This is primarily due to the division of powers between the States and
the Federal government and due to which the Australian Government
environment minister cannot overturn a state decision.
There are strict civil and criminal penalties for the breach of
EPBC Act. Depending on the kind of breach, civil penalty (maximum) may
go up to $550,000 for an individual and $5.5 million for a body
corporate, or for criminal penalty (maximum) of seven years imprisonment
and/or penalty of $46,200.
The State and Territory Level
Australian Capital Territory (ACT)
EIA provisions within Ministerial Authorities in the ACT are found in the Chapters 7 and 8 of the Planning and Development Act 2007
(ACT). EIA in ACT was previously administered with the help of Part 4
of the Land (Planning and Environment) Act 1991 (Land Act) and Territory
Plan (plan for land-use).
Note that some EIA may occur in the ACT on Commonwealth land under the EPBC Act (Cth). Further provisions of the Australian Capital Territory (Planning and Land Management) Act 1988 (Cth) may also be applicable particularly to national land and "designated areas".
New South Wales (NSW)
In New South Wales, the Environment Planning and Assessment Act 1979
(EP&A Act) establishes two pathways for EIA. The first is under
Division 5.2 of the EP&A Act, which provides for EIA of 'State
Significant Infrastructure' projects (from June 2011, this Part replaced
the previous Part 3A, which previously covered EIA of major projects).
The second is under Part 4 of the EP&A Act dealing with development
assessments for local, regional, and State Significant Developments
(other than State Significant Infrastructure).
Northern Territory (NT)
The EIA process in Northern Territory is chiefly administered under the Environmental Assessment Act (EAA).
Although EAA is the primary tool for EIA in Northern Territory, there
are further provisions for proposals in the Inquiries Act 1985 (NT).
Queensland (QLD)
There are four main EIA processes in Queensland.
Firstly, under the Integrated Planning Act 1997 (IPA) for development
projects other than mining. Secondly, under the Chapter 3 of the Environmental Protection Act 1994 (Qld) (EP Act) for some mining and petroleum activities. Thirdly, under the State Development and Public Works Organisation Act 1971 (Qld) (State Development Act) for ‘significant projects’. Finally, under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (Cth) for ‘controlled actions’.
South Australia (SA)
The local governing tool for EIA in South Australia is the Development Act 1993
(SA). There are three levels of assessment possible under the Act in
the form of an environment impact statement (EIS), a public
environmental report (PER) or a Development Report (DR).
Tasmania (TAS)
In
Tasmania, an integrated system of legislation is used to govern
development and approval process, this system is a mixture of the Environmental Management and Pollution Control Act 1994 (Tas) (EMPC Act), Land Use Planning and Approvals Act 1993 (Tas) (LUPA Act), State Policies and Projects Act 1993 (Tas) (SPPA), and Resource Management and Planning Appeals Tribunal Act 1993 (Tas).
Victoria (VIC)
The EIA process in Victoria is intertwined with the
Environment Effects Act 1978 (Vic) and the Ministerial Guidelines for Assessment of Environmental Effects (made under the s 10 of the EE Act).
Western Australia (WA)
Part 4 of the Environmental Protection Act 1986 (WA) provides the legislative framework for the EIA process in Western Australia. The EPA Act oversees the planning and development proposals and assesses their likely impacts on the environment.
Canada
In
Friends of the Oldman River Society v. Canada (Minister of Transportation),(
SCC 1992)
La Forest J of the
Supreme Court of Canada
described environmental impact assessment in terms of the proper scope
of federal jurisdiction with respect to environments matters,
Environmental
impact assessment is, in its simplest form, a planning tool that is now
generally regarded as an integral component of sound decision-making.
Supreme Court Justice La Forest cited (
Cotton, Emond & 1981 245),
"The basic concepts behind environmental assessment are simply stated:
(1) early identification and evaluation of all potential environmental
consequences of a proposed undertaking; (2) decision making that both
guarantees the adequacy of this process and reconciles, to the greatest
extent possible, the proponent’s development desires with environmental
protection and preservation."
La Forest referred to (
Jeffrey 1989, 1.2,1.4) and (
Emond 1978,
p. 5) who described "...environmental assessments as a planning tool
with both an information-gathering and a decision-making component" that
provide "...an objective basis for granting or denying approval for a
proposed development."
Justice La Forest addressed his concerns about the implications
of Bill C-45 regarding public navigation rights on lakes and rivers that
would contradict previous cases.(
La Forest, 1973 & 178-80)
The
Canadian Environmental Assessment Act 2012 (CEAA 2012)
"and its regulations establish the legislative basis for the federal
practice of environmental assessment in most regions of Canada." CEAA 2012 came into force July 6, 2012 and replaces the former
Canadian Environmental Assessment Act
(1995). EA is defined as a planning tool to identify, understand,
assess and mitigate, where possible, the environmental effects of a
project.
"The purposes of this Act are:
(a) to protect the components of the environment that are within the
legislative authority of Parliament from significant adverse
environmental effects caused by a designated project;
(b) to ensure that designated projects that require the exercise of a
power or performance of a duty or function by a federal authority under
any Act of Parliament other than this Act to be carried out, are
considered in a careful and precautionary manner to avoid significant
adverse environmental effects;
(c) to promote cooperation and coordinated action between federal and
provincial governments with respect to environmental assessments;
(d) to promote communication and cooperation with aboriginal peoples
with respect to environmental assessments;
(e) to ensure that opportunities are provided for meaningful public
participation during an environmental assessment;
(f) to ensure that an environmental assessment is completed in a timely
manner;
(g) to ensure that projects, as defined in section 66, that are to be
carried out on federal lands, or those that are outside Canada and that
are to be carried out or financially supported by a federal authority,
are considered in a careful and precautionary manner to avoid
significant adverse environmental effects;
(h) to encourage federal authorities to take actions that promote
sustainable development in order to achieve or maintain a healthy
environment and a healthy economy; and (i) to encourage the study of the cumulative effects of physical
activities in a region and the consideration of those study results in
environmental assessments."
Canadian Environmental Assessment Act
Opposition
Environmental
Lawyer Dianne Saxe argued that the CEAA 2012 "allows the federal
government to create mandatory timelines for assessments of even the
largest and most important projects, regardless of public opposition." (
Saxe 2012)
Now that federal
environmental assessments are gone, the federal government will only
assess very large, very important projects. But it’s going to do them in
a hurry."--Dianne Saxe
On 22 April 2013, Official Opposition Environment critic
Megan Leslie issued a statement claiming that the federal government's recent changes to "fish habitat protection, the
Navigable Waters Protection Act
and the Canadian Environmental Assessment Act", along with gutting
existing laws and making cuts to science and research, "will be
disastrous, not only for the environment, but also for Canadians’ health
and economic prosperity."
On 26 September 2012, Leslie argued that with the changes to the
Canadian Environmental Assessment Act that came into effect 6 July 2012,
"seismic testing, dams, wind farms and power plants" no longer required
any federal environmental assessment. She also claimed that because the
CEAA 2012—which she claimed was rushed through Parliament—dismantled
the CEAA 1995, the Oshawa ethanol plant project would no longer have a
full federal environmental assessment.
Mr. Peter Kent (Minister of the Environment) explained that the CEAA
2012 "provides for the Government of Canada and the Environmental
Assessment Agency to focus on the large and most significant projects
that are being proposed across the country." The 2,000 to 3,000-plus
smaller screenings that were in effect under CEAA 1995 became the
"responsibility of lower levels of government but are still subject to
the same strict federal environmental laws."
Anne Minh-Thu Quach, MP for Beauharnois—Salaberry, QC, argued that the
mammoth budget bill dismantled 50 years of environmental protection
without consulting Canadians about the "colossal changes they are making
to environmental assessments." She claimed that the federal government
is entering into "limited consultations, by invitation only, months
after the damage was done."
China
The
Environmental Impact Assessment Law (EIA Law) requires that an
environmental impact assessment be completed prior to project
construction. However, if a developer completely ignores this
requirement and builds a project without submitting an environmental
impact statement, the only penalty is that the environmental protection
bureau (EPB) may require the developer to do a make-up environmental
assessment. If the developer does not complete this make-up assessment
within the designated time, only then is the EPB authorized to fine the
developer. Even so, the possible fine is capped at a maximum of about
US$25,000, a fraction of the overall cost of most major projects. The
lack of more stringent enforcement mechanisms has resulted in a
significant percentage of projects not completing legally required
environmental impact assessments prior to construction.
China's
State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) used the legislation to halt 30 projects in 2004, including three hydro-power plants under the
Three Gorges
Project Company. Although one month later (Note as a point of
reference, that the typical EIA for a major project in the USA takes one
to two years.), most of the 30 halted projects resumed their
construction, reportedly having passed the environmental assessment, the
fact that these key projects' construction was ever suspended was
notable.
A joint investigation by SEPA and the Ministry of Land and
Resources in 2004 showed that 30–40% of the mining construction projects
went through the procedure of environment impact assessment as
required, while in some areas only 6–7% did so. This partly explains why
China has witnessed so many mining accidents in recent years.
SEPA alone cannot guarantee the full enforcement of environmental laws and regulations, observed Professor
Wang Canfa, director of the centre to help environmental victims at
China University of Political Science and Law.
In fact, according to Wang, the rate of China's environmental laws and
regulations that are actually enforced is estimated at barely 10%.
Egypt
Environmental
Impact Assessment (EIA)
EIA is implemented in Egypt under the umbrella of the Ministry of state
for environmental affairs. The Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency
(EEAA) is responsible for the EIA services.
In June 1997, the responsibility of Egypt's first full-time
Minister of State for Environmental Affairs was assigned as stated in
the Presidential Decree no.275/1997. From thereon, the new ministry has
focused, in close collaboration with the national and international
development partners, on defining environmental policies, setting
priorities and implementing initiatives within a context of sustainable
development.
According to the Law 4/1994 for the Protection of the
Environment, the Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency (EEAA) was
restructured with the new mandate to substitute the institution
initially established in 1982. At the central level, EEAA represents the
executive arm of the Ministry.
The purpose of EIA is to ensure the protection and conservation
of the environment and natural resources including human health aspects
against uncontrolled development. The long-term objective is to ensure a
sustainable economic development that meets present needs without
compromising future generations ability to meet their own needs. EIA is
an important tool in the integrated environmental management approach.
EIA must be performed for new establishments or projects and for
expansions or renovations of existing establishments according to the
Law for the Environment.
EU
A wide range of instruments exist in the
Environmental policy of the European Union. Among them the
European Union has established a mix of mandatory and discretionary procedures to assess environmental impacts.
European Union Directive (85/337/EEC) on Environmental Impact Assessments (known as the
EIA Directive)
was first introduced in 1985 and was amended in 1997. The directive was
amended again in 2003, following EU signature of the 1998
Aarhus Convention,
and once more in 2009. The initial Directive of 1985 and its three
amendments have been codified in Directive 2011/92/EU of 13 December
2011.
In 2001, the issue was enlarged to the assessment of plans and programmes by the so-called
Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) Directive (2001/42/EC), which is now in force.
Under the EU directive, an EIA must provide certain information to comply. There are seven key areas that are required:
- Description of the project
- Description of actual project and site description
- Break the project down into its key components, i.e. construction, operations, decommissioning
- For each component list all of the sources of environmental disturbance
- For each component all the inputs and outputs must be listed, e.g., air pollution, noise, hydrology
- Alternatives that have been considered
- Examine alternatives that have been considered
- Example: in a biomass power station, will the fuel be sourced locally or nationally?
- Description of the environment
- List of all aspects of the environment that may be affected by the development
- Example: populations, fauna, flora, air, soil, water, humans, landscape, cultural heritage
- This section is best carried out with the help of local experts, e.g. the RSPB in the UK
- Description of the significant effects on the environment
- The word significant is crucial here as the definition can vary
- 'Significant' must be defined
- The most frequent method used here is use of the Leopold matrix
- The matrix is a tool used in the systematic examination of potential interactions
- Example: in a windfarm development a significant impact may be collisions with birds
- Mitigation
- This is where EIA is most useful
- Once section 4 is complete, it is obvious where impacts are greatest
- Using this information ways to avoid negative impacts should be developed
- Best working with the developer with this section as they know the project best
- Using the windfarm example again, construction could be out of bird
nesting seasons. Or removal of hardstanding on a potentially
contaminated land site, out of the rainy season.
- Non-technical summary (EIS)
- The EIA is in the public domain and be used in the decision making process
- It is important that the information is available to the public
- This section is a summary that does not include jargon or complicated diagrams
- It should be understood by the informed lay-person
- Lack of know-how/technical difficulties
- This section is to advise any areas of weakness in knowledge
- It can be used to focus areas of future research
- Some developers see the EIA as a starting block for poor environmental management
Annexed projects
All
projects are either classified as Annex 1 or Annex 2 projects. Those
lying in Annex 1 are large scale developments such as motorways,
chemical works, bridges, power stations etc. These always require an EIA
under the Environmental Impact Assessment Directive (85,337,EEC as
amended). Annex 2 projects are smaller in scale than those referred to
in Annex 1. Member States must determine whether these project shall be
made subject to an assessment subject to a set of criteria set out in
Annex 3 of codified Directive 2011/92/EU.
The Netherlands
EIA
was implemented in Dutch legislation on September 1, 1987. The
categories of projects that require an EIA are summarized in Dutch
legislation, the Wet milieubeheer. The use of thresholds for activities
makes sure that EIA is obligatory for those activities that may have
considerable impacts on the environment.
For projects and plans that fit these criteria, an EIA report is
required. The EIA report defines a.o. the proposed initiative, it makes
clear the impact of that initiative on the environment and compares this
with the impact of possible alternatives with less a negative impact.
Hong Kong
EIA in Hong Kong, since 1998, is regulated by the Environmental Impact Assessment Ordinance 1997.
The original proposal to construct the
Lok Ma Chau Spur Line overground across the
Long Valley failed to get through EIA, and the
Kowloon–Canton Railway Corporation had to change its plan and build the railway underground. In April 2011, the EIA of the Hong Kong section of the
Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge
was found to have breached the ordinance, and was declared unlawful.
The appeal by the government was allowed in September 2011. However, it
was estimated that this EIA court case had increased the construction
cost of the Hong Kong section of the bridge by HK$6.5 billion in
money-of-the-day prices.
Iraq
Ministry of
Environment of the federal government of Iraq is in charge of issuing
Environmental compliance certificate based on an EIA report prepared by
professional consultant and thoroughly reviewed by MOE. Any project or
activity prior to its establishment or even already existing project has
to be approved and obtain such certificate from the MOE. Projects are
classified into 3 categories; “A”, “B” and “C”. EIA report is usually
obligatory for those projects and activities falling under categories
“A” (large-scale) and “B” (small-scale) that may have considerable
impacts on environment.
An example of “A” category activities such as: dams and reservoirs,
forestry production projects, industrial plants, irrigation, drainage
and flood control, land clearance and leveling, port and harbor
development, river basin development, thermal power and hydro-power
development, manufacture, transportation and use of pesticides or other
hazardous materials, hazardous waste management and disposal....etc. An
example of “B” category activities such as: agro-industries, electrical
transmission, renewable energy, rural electrification, tourism,
rehabilitation or maintenance of highway or rural roads, rehabilitation
or modification of existing industrial facilities...etc. preparation of
EIA report is usually exempt for projects falling under category “C”
that may have low to no impact on environment, and example of “C”
category activities: small fish breeding pond, institutional
development, most human resources projects...etc.
The main environmental legislations in Iraq are: Law No.64 for
cities and land use (1965), Law No.21 for noise prevention (1966), Law
No.25 for system of rivers and other water resources protection (1967),
Law No.99 for ionized radiation (1980), Law No.89 for public health
(drinking water provision, sanitation and environmental monitoring
(1981), Law No.79 for protection and improvement of environment (1986),
Environmental criteria for agricultural, industrial and public service
projects (1990), Law No.3 for protection and improvement of environment
(1997), Law No.2 for water systems protection (2001), Law No.44 for
creation of Ministry of Environment instead of the council of protection
and improvement of environment (2003), Law No.27 for environmental
protection and improvement (2009), Law No.4 for protection of ambient air system (2012).
Meanwhile, Environmental Protection and Improvement Board in the
regional government of Kurdistan in the northern Iraq (Erbil, Duhok,
Sulaimany and Garmyan) is responsible of issuing Environmental
compliance certificate, the board was established according to law No.3
Environmental protection and improvement board in Iraqi Kurdistan Region
(2010).
The board is responsible of issuing such certificate for all projects
and activities except of petroleum operation which EIA process is
organized and implemented by the Ministry of Natural Resources of
Kurdistan Regional government.
The same Iraqi Environmental Legislations mentioned are adopted but the
procedure of EIA in Iraqi-Kurdistan region government may differ from
the one in the Federal government of Iraq.
India
The
Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change
(MoEFCC) of India has been in a great effort in Environmental Impact
Assessment in India. The main laws in action are the Water Act(1974),
the Indian
Wildlife (Protection) Act (1972),
the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act (1981) and the
Environment (Protection) Act (1986),Biological Diversity Act(2002).
The responsible body for this is the Central Pollution Control Board.
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) studies need a significant amount
of primary and secondary environmental data. Primary data are those
collected in the field to define the status of the environment (like air
quality data, water quality data etc.). Secondary data are those
collected over the years that can be used to understand the existing
environmental scenario of the study area. The environmental impact
assessment (EIA) studies are conducted over a short period of time and
therefore the understanding of the environmental trends, based on a few
months of primary data, has limitations. Ideally, the primary data must
be considered along with the secondary data for complete understanding
of the existing environmental status of the area. In many EIA studies,
the secondary data needs could be as high as 80% of the total data
requirement. EIC is the repository of one stop secondary data source for
environmental impact assessment in India.
The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) experience in India
indicates that the lack of timely availability of reliable and authentic
environmental data has been a major bottle neck in achieving the full
benefits of EIA. The environment being a multi-disciplinary subject, a
multitude of agencies are involved in collection of environmental data.
However, no single organization in India tracks available data from
these agencies and makes it available in one place in a form required by
environmental impact assessment practitioners. Further, environmental
data is not available in enhanced forms that improve the quality of the
EIA. This makes it harder and more time-consuming to generate
environmental impact assessments and receive timely environmental
clearances from regulators. With this background, the Environmental
Information Centre (EIC) has been set up to serve as a professionally
managed clearing house of environmental information that can be used by
MoEF, project proponents, consultants, NGOs and other stakeholders
involved in the process of environmental impact assessment in India. EIC
caters to the need of creating and disseminating of organized
environmental data for various developmental initiatives all over the
country.
EIC stores data in GIS format and makes it available to all
environmental impact assessment studies and to EIA stakeholders in a
cost effective and timely manner. So that we can manage that in
different proportions such as remedy measures etc.,
Malaysia
In Malaysia, Section 34A, Environmental Quality Act, 1974
requires developments that have significant impact to the environment
are required to conduct the Environmental impact assessment.
Nepal
In Nepal,
EIA has been integrated in major development projects since the early
1980s. In the planning history of Nepal, the sixth plan (1980–85), for
the first time, recognized the need for EIA with the establishment of
Environmental Impact Study Project (EISP) under the Department of Soil
Conservation in 1982 to develop necessary instruments for integration of
EIA in infrastructure
development projects. However, the government of Nepal enunciated
environment conservation related
policies in the seventh plan (NPC, 1985–1990). To enforce this policy
and make necessary arrangements, a series of guidelines were developed,
thereby incorporating the elements of environmental factors right from
the project formulation stage of the development plans
and projects and to avoid or minimize adverse effects on the ecological
system. In addition, it has also emphasized that EIAs of industry,
tourism, water resources, transportation, urbanization, agriculture,
forest and other developmental projects be conducted.
In Nepal, the government's Environmental Impact Assessment
Guideline of 1993 inspired the enactment of the Environment Protection
Act (EPA) of 1997 and the Environment Protection Rules (EPR) of 1997
(EPA and EPR have been enforced since 24 and 26 June 1997 respectively
in Nepal) to internalizing the environmental assessment system. The
process institutionalized the EIA process in development proposals and
enactment, which makes the integration of IEE and EIA legally binding to
the prescribed projects. The projects, requiring EIA or IEE, are
included in Schedules 1 and 2 of the EPR, 1997
(GoN/MoLJPA 1997).
New Zealand
In New Zealand, EIA is usually referred to as
Assessment of Environmental Effects
(AEE). The first use of EIA's dates back to a Cabinet minute passed in
1974 called Environmental Protection and Enhancement Procedures. This
had no legal force and only related to the activities of government
departments. When the
Resource Management Act
was passed in 1991, an EIA was required as part of a resource consent
application. Section 88 of the Act specifies that the AEE must include
"such detail as corresponds with the scale and significance of the
effects that the activity may have on the environment". While there is
no duty to consult any person when making a resource consent application
(Sections 36A and Schedule 4), proof of consultation is almost certain
required by local councils when they decide whether or not to publicly
notify the consent application under Section 93.
Russian Federation
As
of 2004, the state authority responsible for conducting the State EIA
in Russia has been split between two Federal bodies: 1) Federal service
for monitoring the use of natural resources – a part of the Russian
Ministry for Natural Resources and Environment and 2) Federal Service
for Ecological, Technological and Nuclear Control. The two main pieces
of environmental legislation in Russia are: The Federal Law ‘On
Ecological Expertise, 1995 and the ‘Regulations on Assessment of Impact
from Intended Business and Other Activity on Environment in the Russian
Federation, 2000.
Federal Service for monitoring the use of natural resources
In
2006, the parliament committee on ecology in conjunction with the
Ministry for Natural Resources and Environment, created a working group
to prepare a number of amendments to existing legislation to cover such
topics as stringent project documentation for building of potentially
environmentally damaging objects as well as building of projects on the
territory of protected areas.
There has been some success in this area, as evidenced from abandonment
of plans to construct a gas pipe-line through the only remaining habitat
of the critically endangered Amur leopard in the Russian Far East.
Federal Service for Ecological, Technological and Nuclear Control
The
government's decision to hand over control over several important
procedures, including state EIA in the field of all types of energy
projects, to the Federal Service for Ecological, Technological and
Nuclear Control had caused a major controversy and criticism from
environmental groups that blamed the government for giving nuclear power
industry control over the state EIA.
Not surprisingly the main problem concerning State EIA in Russia
is the clear differentiation of jurisdiction between the two
above-mentioned Federal bodies.
Sri Lanka
The
National Environmental Act, 1998 requires environmental impact
assessment for large scale projects in sensitive areas. It is enforced
by the Central Environmental Authority.
Ukraine
The new
law of Ukraine on evaluation of impact on surroundings prescribes the
requirements of environmental safety, rational use of national
resources, minimizing of harmful impact on surroundings in the process
of making managerial decisions about planned activity. The designing of
the conclusion of evaluation of impact is a result of its conducting.
The key moment of the law on evaluation of impact on surroundings is a
substitution of conclusion of state environmental experize on the
conclusion of evaluation of impact on surroundings. Business entity is
forbidden to conduct or to start its planned activity without the
conclusion of impact on surroundings.
United States
The
National Environmental Policy Act
of 1969 (NEPA), enacted in 1970, established a policy of environmental
impact assessment for federal agency actions, federally funded
activities or federally permitted/licensed activities that in the U. S.
is termed "environmental review" or simply "the NEPA process." The law also created the
Council on Environmental Quality, which promulgated regulations to codify the law's requirements. Under
United States environmental law an Environmental Assessment (EA) is compiled to determine the need for an
Environmental Impact Statement
(EIS). Federal or federalized actions expected to subject or be
subject to significant environmental impacts will publish a Notice of
Intent to Prepare an EIS as soon as significance is known. Certain
actions of
federal agencies
must be preceded by the NEPA process. Contrary to a widespread
misconception, NEPA does not prohibit the federal government or its
licensees/permittees from harming the environment, nor does it specify
any penalty if an environmental impact assessment turns out to be
inaccurate, intentionally or otherwise. NEPA requires that plausible
statements as to the prospective impacts be disclosed in advance. The
purpose of NEPA process is to ensure that the decision maker is fully
informed of the environmental aspects and consequences prior to making
the final decision.
Environmental assessment
An
environmental assessment
(EA) is an environmental analysis prepared pursuant to the National
Environmental Policy Act to determine whether a federal action would
significantly affect the environment and thus require a more detailed
Environmental Impact Statement (EIS). The certified release of an Environmental Assessment results in either a
Finding of No Significant Impact (FONSI) or an
EIS.
The
Council on Environmental Quality
(CEQ), which oversees the administration of NEPA, issued regulations
for implementing the NEPA in 1979. Eccleston reports that the NEPA
regulations barely mention preparation of EAs. This is because the EA
was originally intended to be a simple document used in relatively rare
instances where an agency was not sure if the potential significance of
an action would be sufficient to trigger preparation of an EIS. But
today, because EISs are so much longer and complicated to prepare,
federal agencies are going to great effort to avoid preparing EISs by
using EAs, even in cases where the use of EAs may be inappropriate. The
ratio of EAs that are being issued compared to EISs is about 100 to 1.
Likewise, even the preparation of an accurate EA is viewed today
as an onerous burden by many entities responsible for the environmental
review of a proposal. Federal agencies have responded by streamlining
their regulations that implement NEPA environmental review, by defining
categories of projects that by their well understood nature may be
safely excluded from review under NEPA, and by drawing up lists of
project types that have negligible material impact upon the environment
and can thus be exempted.
Content
The Environmental Assessment is a concise public document prepared by the federal action agency that serves to:
- Briefly provide sufficient evidence and analysis for determining
whether to prepare an EIS or a Finding of No Significant Impact (FONSI)
- Demonstrate compliance with the act when no EIS is required
- facilitate the preparation of an EIS when a FONSI cannot be demonstrated
The Environmental Assessment includes a brief discussion of the
purpose and need of the proposal and of its alternatives as required by
NEPA 102(2)(E), and of the human environmental impacts resulting from
and occurring to the proposed actions and alternatives considered
practicable, plus a listing of studies conducted and agencies and
stakeholders consulted to reach these conclusions. The action agency
must approve an EA before it is made available to the public. The EA is
made public through notices of availability by local, state, or regional
clearing houses, often triggered by the purchase of a public notice
advertisement in a newspaper of general circulation in the proposed
activity area.
Structure
The structure of a generic Environmental Assessment is as follows:
- Summary
- Introduction
- Background
- Purpose and Need for Action
- Proposed Action
- Decision Framework
- Public Involvement
- Issues
- Alternatives, including the Proposed Action
- Alternatives
- Mitigation Common to All Alternatives
- Comparison of Alternatives
- Environmental Consequences
- Consultation and Coordination
Procedure
The
EA becomes a draft public document when notice of it is published,
usually in a newspaper of general circulation in the area affected by
the proposal. There is a 15-day review period required for an
Environmental Assessment (30 days if exceptional circumstances) while
the document is made available for public commentary, and a similar time
for any objection to improper process. Commenting on the Draft EA is
typically done in writing or email, submitted to the lead action agency
as published in the notice of availability. An EA does not require a
public hearing for verbal comments. Following the mandated public
comment period, the lead action agency responds to any comments, and
certifies either a FONSI or a Notice of Intent (NOI) to prepare an EIS
in its public environmental review record. The preparation of an EIS
then generates a similar but more lengthy, involved and expensive
process.
Environmental impact statement
This variety of state requirements produces voluminous data not
just upon impacts of individual projects, but also in insufficiently
researched scientific domains. For example, in a seemingly routine
Environmental Impact Report for the city of
Monterey, California, information came to light that led to the official federal endangered species listing of
Hickman's potentilla, a rare coastal
wildflower.
Transboundary application
Environmental
threats do not respect national borders. International pollution can
have detrimental effects on the atmosphere, oceans, rivers,
aquifers, farmland, the weather and biodiversity. Global climate change is transnational. Specific pollution threats include
acid rain,
radioactive contamination,
debris in outer space,
stratospheric ozone depletion and toxic
oil spills. The
Chernobyl disaster, precipitated by a
nuclear accident on April 26, 1986, is a stark reminder of the devastating effects of transboundary nuclear pollution.
However, as there is no universal legislature or administration
with a comprehensive mandate, most international treaties exist parallel
to one another and are further developed without the benefit of
consideration being given to potential conflicts with other agreements.
There is also the issue of international enforcement.
This has led to duplications and failures, in part due to an inability
to enforce agreements. An example is the failure of many international
fisheries regimes to restrict harvesting practises.
Application shall be achieved by the willing of counties authorities.
Criticism
As per Jay et al.,
EIA is used as a decision aiding tool rather than decision making tool.
There is growing dissent about them as their influence on decisions is
limited. Improved training for practitioners, guidance on bestpractice
and continuing research have all been proposed.
EIAs have been criticized for excessively limiting their scope in
space and time. No accepted procedure exists for determining such
boundaries. The boundary refers to ‘the spatial and temporal boundary of
the proposal’s effects’. This boundary is determined by the applicant
and the lead assessor, but in practice, almost all EIAs address only
direct and immediate on-site effects.
Development causes both direct and indirect effects. Consumption
of goods and services, production, use and disposal of building
materials and machinery, additional land use for activities of
manufacturing and services, mining and refining, etc., all have
environmental impacts. The indirect effects of development can be much
higher than the direct effects examined by an EIA. Proposals such as
airports or
shipyards cause wide-ranging national and international effects, which should be covered in EIAs.
Broadening the scope of EIA can benefit the conservation of
threatened species. Instead of concentrating on the project site, some
EIAs employed a
habitat-based
approach that focused on much broader relationships among humans and
the environment. As a result, alternatives that reduce the negative
effects to the population of whole species, rather than local
subpopulations, can be assessed.
Thissen and Agusdinata
have argued that little attention is given to the systematic
identification and assessment of uncertainties in environmental studies
which is critical in situations where uncertainty cannot be easily
reduced by doing more research. In line with this, Maier et al.
have concluded on the need to consider uncertainty at all stages of the
decision-making process. In such a way decisions can be made with
confidence or known uncertainty. These proposals are justified on data
that shows that environmental assessments fail to predict accurately the
impacts observed. Tenney et al. and Wood et al.
have reported evidence of the intrinsic uncertainty attached to EIAs
predictions from a number of case studies worldwide. The gathered
evidence consisted of comparisons between predictions in EIAs and the
impacts measured during, or following project implementation. In
explaining this trend, Tenney et al.
have highlighted major causes such as project changes, modelling
errors, errors in data and assumptions taken and bias introduced by
people in the projects analyzed.