A fish parasite, the isopod Cymothoa exigua, replacing the tongue of a Lithognathus
In evolutionary biology, parasitism is a relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or in another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophically transmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation.
Like predation, parasitism is a type of consumer-resource interaction, but unlike predators,
parasites, with the exception of parasitoids, are typically much
smaller than their hosts, do not kill them, and often live in or on
their hosts for an extended period. Parasites of animals are highly specialised, and reproduce at a faster rate than their hosts. Classic examples include interactions between vertebrate hosts and tapeworms, flukes, the malaria-causing Plasmodium species, and fleas.
Parasites reduce host fitness by general or specialised pathology,
from parasitic castration to modification of host behaviour. Parasites
increase their own fitness by exploiting hosts for resources necessary
for their survival, in particular by feeding on them and by using
intermediate (secondary) hosts to assist in their transmission
from one definitive (primary) host to another. Although parasitism is
often unambiguous, it is part of a spectrum of interactions between species, grading via parasitoidism into predation, through evolution into mutualism, and in some fungi, shading into being saprophytic.
People have known about parasites such as roundworms and tapeworms since ancient Egypt, Greece, and Rome. In Early Modern times, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek observed Giardia lamblia in his microscope in 1681, while Francesco Redi described internal and external parasites including sheep liver fluke and ticks. Modern parasitology developed in the 19th century. In human culture, parasitism has negative connotations. These were exploited to satirical effect in Jonathan Swift's 1733 poem "On Poetry: A Rhapsody", comparing poets to hyperparasitical "vermin". In fiction, Bram Stoker's 1897 Gothic horror novel Dracula and its many later adaptations featured a blood-drinking parasite. Ridley Scott's 1979 film Alien was one of many works of science fiction to feature a terrifying parasitic alien species.
Etymology
Firt used in English in 1539, the word parasite comes from the Medieval French parasite, from the Latin parasitus, the latinisation of the Greek παράσιτος (parasitos), "one who eats at the table of another" and that from παρά (para), "beside, by" + σῖτος (sitos), "wheat", hence "food". The related term parasitism appears in English from 1611.
Evolutionary strategies
Basic concepts
Parasitism is a kind of symbiosis, a close and persistent long-term biological interaction between the parasite and its host. Unlike commensalism and mutualism,
the parasitic relationship harms the host, either feeding on it or, as
in the case of intestinal parasites, consuming some of its food. Because parasites interact with other species, they are well placed to act as vectors of pathogens, microscopic parasites that cause disease. Predation is not generally considered a symbiosis as the interaction is brief, but the entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one".
Within that scope are many possible ways of life. Parasites are
classified in a variety of different but overlapping schemes, based on
their interactions with their hosts and on their life cycles, which are sometimes very complex. An obligate parasite is totally dependent on the host to complete its life cycle, while a facultative parasite
is not. Parasite life cycles involving only one host are called direct;
those with a definitive host, where the parasite reproduces sexually,
and at least one intermediate host are called indirect. An endoparasite is one that lives inside the host's body; an ectoparasite lives outside, on the host's surface. Mesoparasites like some copepods enter an opening in the host's body and remain partly embedded there.
It is possible for parasites to be generalists, feeding on a wide range
of hosts, but many parasites, and the majority of protozoans and helminths that parasitise animals, are specialists and extremely host-specific. An early basic, functional division of parasites was that of microparasites and macroparasites. These each had a mathematical model assigned in order to analyse the population movements of the host–parasite groupings.
The microorganisms and viruses that can reproduce and complete their
life cycle within the host are known as microparasites. Macroparasites
are the multicellular organisms that reproduce and complete their life
cycle outside of the host or on the host's body.
Much of the thinking on types of parasitism has focussed on
terrestrial animal parasites of animals, such as helminths. Those in
other environments and with other hosts often have analogous strategies.
For example, the snubnosed eel is probably a facultative endoparasite that opportunistically burrows into and eats sick and dying fish. Plant-eating insects such as scale insects, aphids, and caterpillars are much like ectoparasites, attacking much larger plants; they serve as vectors of bacteria, fungi and viruses which cause plant diseases. As female scale insects are unable to move, they are obligate parasites, permanently attached to their hosts.
Major strategies
There are six major parasitic strategies, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism, trophically transmitted parasitism, vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. These apply to parasites whose hosts are plants as well as animals. These strategies represent adaptive peaks; intermediate strategies are possible, but organisms in many different groups have consistently converged on these six, which are evolutionarily stable.
A perspective on the evolutionary options can be gained by considering
four questions: the effect on the fitness of a parasite's hosts; the
number of hosts they have per life stage; whether the host is prevented
from reproducing; and whether the effect depends on intensity (number of
parasites per host). From this analysis, the major evolutionary
strategies of parasitism emerge, alongside predation.
| Host fitness | Single host, stays alive | Single host, dies | Multiple hosts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Able to reproduce (fitness > 0) |
Conventional parasite Pathogen |
Trophically transmitted parasite Trophically transmitted pathogen |
Micropredator Micropredator |
| Unable to reproduce (fitness = 0) |
----- Parasitic castrator |
Trophically transmitted parasitic castrator Parasitoid |
Social predator Solitary predator |
The parasitic castrator Sacculina carcini (highlighted) attached to its crab host
Parasitic castrators
Parasitic castrators
partly or completely destroy their host's ability to reproduce,
diverting the energy that would have gone into reproduction into host
and parasite growth, sometimes causing gigantism in the host. The host's
other systems are left intact, allowing it to survive and sustain the
parasite. Parasitic crustaceans such as those in the specialised barnacle genus Sacculina specifically cause damage to the gonads of their many species of host crabs. In the case of Sacculina, the testes of over two-thirds of their crab hosts degenerate sufficiently for these male crabs to have gained female secondary sex characteristics such as broader abdomens, smaller claws
and egg-grasping appendages. Various species of helminth castrate their
hosts (such as insects and snails). This may be directly, whether
mechanically by feeding on their gonads, or by secreting a chemical that
destroys reproductive cells; or indirectly, whether by secreting a
hormone or by diverting nutrients. For example, the trematode Zoogonus lasius, whose sporocysts lack mouths, castrates the intertidal marine snail Tritia obsoleta chemically, developing in its gonad and killing its reproductive cells.
Human head lice are directly-transmitted obligate ectoparasites.
Directly transmitted
Directly
transmitted parasites, not requiring a vector to reach their hosts,
include parasites of terrestrial vertebrates such as lice and mites;
marine parasites such as copepods and cyamid amphipods; monogeneans;
and many species of nematodes, fungi, protozoans, bacteria, and
viruses. Whether endoparasites or ectoparasites, each has a single host
species. Within that species, most individuals are free or almost free
of parasites, while a minority carry a large number of parasites; this
highly uneven distribution is described as aggregated.
Trophically transmitted
Clonorchis sinensis, the Chinese liver fluke, is trophically transmitted.
Trophically transmitted parasites are transmitted by being eaten by a host. They include trematodes (all except schistosomes), cestodes, acanthocephalans, pentastomids, many round worms, and many protozoa such as Toxoplasma. They have complex life cycles involving hosts of two or more species. In their juvenile stages, they infect and often encyst
in the intermediate host. When this animal is eaten by a predator, the
definitive host, the parasite survives the digestion process and matures
into an adult; some live as intestinal parasites. Many trophically transmitted parasites modify the behaviour
of their intermediate hosts, increasing their chances of being eaten by
a predator. Like directly transmitted parasites, the distribution of
trophically transmitted parasites among host individuals is aggregated. Coinfection by multiple parasites is common. Autoinfection, where (by exception) the whole of the parasite's life cycle takes place in a single primary host, can sometimes occur in helminths such as Strongyloides stercoralis.
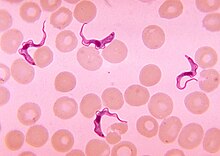
Vector-transmitted
The vector-transmitted protozoan endoparasite Trypanosoma among human red blood cells
Vector-transmitted parasites rely on a third party, an intermediate host, where the parasite does not reproduce sexually to carry them from one definitive host to another. These parasites are microorganisms, namely protozoa, bacteria, or viruses, often intracellular pathogens (causing disease). Their vectors are mostly hematophagic arthropods such as fleas, lice, ticks, and mosquitoes. For example, the deer tick Ixodes scapularis acts as a vector for diseases including Lyme disease, babesiosis, and anaplasmosis. Protozoan endoparasites, such as the malarial parasites in the genus Plasmodium and sleeping sickness parasites in the genus Trypanosoma, infective stages in the host's blood are transported to new hosts by biting insects.
Parasitoids
Parasitoids are insects which sooner or later kill their hosts, placing their relationship close to predation. Most parasitoids are hymenopterans, parasitoid wasps; others include dipterans such as phorid flies. They can be divided into two groups, idiobionts and koinobionts, differing in their treatment of their hosts.
Idiobiont
parasitoids sting their often large prey on capture, either killing
them outright or paralysing them immediately. The immobilised prey is
then carried to a nest, sometimes alongside other prey if it is not
large enough to support a parasitoid throughout its development. An egg is laid on top of the prey, and the nest is then sealed. The parasitoid develops rapidly through its larval and pupal stages, feeding on the provisions left for it.
Koinobiont parasitoids, which include flies
as well as wasps, lay their eggs inside young hosts, usually larvae.
These are allowed to go on growing, so the host and parasitoid develop
together for an extended period, ending when the parasitoids emerge as
adults, leaving the prey dead, eaten from inside. Some koinobionts
regulate their host's development, for example preventing it from pupating or making it moult whenever the parasitoid is ready to moult. They may do this by producing hormones that mimic the host's moulting hormones (ecdysteroids), or by regulating the host's endocrine system.
- Idiobiont parasitoid wasps immediately paralyse their hosts for their larvae (Pimplinae, pictured) to eat.
- Koinobiont parasitoid wasps like this braconid lay their eggs inside their hosts, which continue to grow and moult.
- Phorid fly (centre left) is laying eggs in the abdomen of a worker honey bee, altering its behaviour.
Micropredators
Mosquitoes are micropredators, and important vectors of disease.
A micropredator attacks more than one host, reducing each host's
fitness at least a small amount, and is only in contact with any one
host intermittently. This makes them suitable as vectors as they can
pass smaller parasites from one host to another. Most micropredators are hematophagic, feeding on blood. They include annelids such as leeches, crustaceans such as branchiurans and gnathiid isopods, various dipterans such as mosquitoes and tsetse flies, other arthropods such as fleas and ticks, vertebrates such as lampreys, and mammals such as vampire bats.
Transmission strategies
Life cycle of Entamoeba histolytica, an anaerobic parasitic protozoan transmitted by the fecal–oral route
Parasites use a variety of methods to infect animal hosts, including physical contact, the fecal–oral route, free-living infectious stages, and vectors, suiting their differing hosts, life cycles, and ecological contexts.
Variations
Among the many variations on parasitic strategies are hyperparasitism, social parasitism, brood parasitism, kleptoparasitism, sexual parasitism, and adelphoparasitism.
Hyperparasitism
Hyperparasites feed on another parasite, as exemplified by protozoa living in helminth parasites, or facultative or obligate parasitoids whose hosts are either conventional parasites or parasitoids. Levels of parasitism beyond secondary also occur, especially among facultative parasitoids. In oak gall systems, there can be up to five levels of parasitism.
Hyperparasites can control their hosts' populations, and are used for this purpose in agriculture and to some extent in medicine. The controlling effects can be seen in the way that the CHV1 virus helps to control the damage that chestnut blight, Cryphonectria parasitica, does to American chestnut trees, and in the way that bacteriophages
can limit bacterial infections. It is likely, though little researched,
that most pathogenic microparasites have hyperparasites which may prove
widely useful in both agriculture and medicine.
Social parasitism
Social parasites take advantage of interspecific interactions between members of social animals such as ants, termites, and bumblebees. Examples include the large blue butterfly, Phengaris arion, its larvae employing ant mimicry to parasitise certain ants, Bombus bohemicus,
a bumblebee which invades the hives of other bees and takes over
reproduction while their young are raised by host workers, and Melipona scutellaris, a eusocial bee whose virgin queens escape killer workers and invade another colony without a queen. An extreme example of interspecific social parasitism is found in the ant Tetramorium inquilinum, an obligate parasite which lives exclusively on the backs of other Tetramorium ants. Emery's rule notes that social parasites tend to be closely related to their hosts, often being in the same genus.
Intraspecific social parasitism occurs in parasitic nursing, where some individual young take milk from unrelated females. In wedge-capped capuchins, higher ranking females sometimes take milk from low ranking females without any reciprocation.
Brood parasitism
In brood parasitism, the hosts act as parents as they raise the young as their own. Brood parasites include birds in different families such as cowbirds, whydahs, cuckoos, and black-headed ducks. These do not build nests of their own, but leave their eggs in nests of other species. The eggs of some brood parasites mimic
those of their hosts, while some cowbird eggs have tough shells, making
them hard for the hosts to kill by piercing, both mechanisms implying
selection by the hosts against parasitic eggs. The adult female European cuckoo further mimics a predator, the European sparrowhawk, giving her time to lay her eggs in the host's nest unobserved.
Kleptoparasitism
In kleptoparasitism (from Greek κλέπτης (kleptēs),
"thief"), parasites steal food gathered by the host. The parasitism is
often on close relatives, whether within the same species or between
species in the same genus or family. For instance, the many lineages of cuckoo bees lay their eggs in the nest cells of other bees in the same family. Kleptoparasitism is uncommon generally but conspicuous in birds; some such as skuas are specialised in pirating food from other seabirds, relentlessly chasing them down until they disgorge their catch.
Sexual parasitism
A unique approach is seen in some species of anglerfish, such as Ceratias holboelli, where the males are reduced to tiny sexual parasites,
wholly dependent on females of their own species for survival,
permanently attached below the female's body, and unable to fend for
themselves. The female nourishes the male and protects him from
predators, while the male gives nothing back except the sperm that the
female needs to produce the next generation.
Adelphoparasitism
Adelphoparasitism, (from Greek ἀδελφός (adelphós), brother),
also known as sibling-parasitism, occurs where the host species is
closely related to the parasite, often in the same family or genus. In the citrus blackfly parasitoid, Encarsia perplexa, unmated females of which may lay haploid eggs in the fully developed larvae of their own species, producing male offspring, while the marine worm Bonellia viridis has a similar reproductive strategy, although the larvae are planktonic.
Illustrations
Examples of the major variant strategies are illustrated.
- In brood parasitism, the host raises the young of another species, here a cowbird's egg, that has been laid in its nest.
- The great skua is a powerful kleptoparasite, relentlessly pursuing other seabirds until they disgorge their catches of food.
- The male anglerfish Ceratias holboelli lives as a tiny sexual parasite permanently attached below the female's body.
- Encarsia perplexa (centre), a parasitoid of citrus blackfly (lower left), is also an adelphoparasite, laying eggs in larvae of its own species
Taxonomic range
Head (scolex) of tapeworm Taenia solium, an intestinal parasite, has hooks and suckers to attach to its host.
A wide range of organisms is parasitic, from animals, plants, and fungi to protozoans, bacteria, and viruses.
Animals
Parasitism is widespread in the animal kingdom, and has evolved independently from free-living forms hundreds of times. Many types of helminth including flukes and cestodes have complex life cycles involving two or more hosts. By far the largest group is the parasitoid wasps in the Hymenoptera. The phyla and classes
with the largest numbers of parasitic species are listed in the table.
Numbers are conservative minimum estimates. The columns for Endo- and
Ecto-parasitism refer to the definitive host, as documented in the
Vertebrate and Invertebrate columns.
Plants
Cuscuta (a dodder), a stem holoparasite, on an acacia tree
A hemiparasite or partial parasite, such as mistletoe derives some of its nutrients from another living plant, and a holoparasite such as dodder derives all of its nutrients from another plant. Parasitic plants make up about one per cent of angiosperms and are in almost every biome in the world. All these plants have modified roots, haustoria, which penetrate the host plants, connecting them to the conductive system – either the xylem, the phloem,
or both. This provides them with the ability to extract water and
nutrients from the host. A parasitic plant is classified depending on
where it latches onto the host, either the stem or the root, and the
amount of nutrients it requires. Since holoparasites have no chlorophyll and therefore cannot make food for themselves by photosynthesis, they are always obligate parasites, deriving all their food from their hosts. Some parasitic plants can locate their host plants by detecting chemicals in the air or soil given off by host shoots or roots, respectively. About 4,500 species of parasitic plant in approximately 20 families of flowering plants are known.
Species within Orobanchaceae (broomrapes) are some of the most economically destructive of all plants. Species of Striga
(witchweeds) are estimated to cost billions of dollars a year in crop
yield loss, infesting over 50 million hectares of cultivated land within
Sub-Saharan Africa alone. Striga infects both grasses and grains, including corn, rice and sorghum, undoubtedly some of the most important food crops. Orobanche also threatens a wide range of other important crops, including peas, chickpeas, tomatoes, carrots, and varieties of cabbage. Yield loss from Orobanche can be total; despite extensive research, no method of control has been entirely successful.
Many plants and fungi exchange carbon and nutrients in mutualistic mycorrhizal relationships. Some 400 species of myco-heterotrophic plants, mostly in the tropics, however effectively cheat
by taking carbon from a fungus rather than exchanging it for minerals.
They have much reduced roots, as they do not need to absorb water from
the soil; their stems are slender with few vascular bundles,
and their leaves are reduced to small scales, as they do not
photosynthesize. Their seeds are very small and numerous, so they appear
to rely on being infected by a suitable fungus soon after germinating.
The honey fungus, Armillaria mellea, is a parasite of trees, and a saprophyte feeding on the trees it has killed.
Fungi
Parasitic fungi derive some or all of their nutritional requirements from plants, other fungi, or animals. Unlike mycorrhizal fungi which have a mutualistic relationship with their host plants, they are pathogenic. For example, the honey fungi in the genus Armillaria grow in the roots of a wide variety of trees, and eventually kill them. They then continue to live in the dead wood, feeding saprophytically.
Fungal infection (mycosis) is widespread in animals including humans; it kills some 1.6 million people each year. Microsporidia
are obligate intracellular parasitic fungi that can also be
hyperparasites. They largely affect insects, but some affect vertebrates
including humans, where they can cause the intestinal infection microsporidiosis.
Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes Lyme disease, is transmitted by Ixodes ticks.
Protozoa
Protozoa such as Plasmodium, Trypanosoma, and Entamoeba,
are endoparasitic. They cause serious diseases in vertebrates including
humans – in these examples, malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery – and have complex life cycles.
Bacteria
Many bacteria are parasitic, though they are more generally thought of as pathogens causing disease. Parasitic bacteria are extremely diverse, and infect their hosts by a variety of routes. To give a few examples, Bacillus anthracis, the cause of anthrax, is spread by contact with infected domestic animals; its spores, which can survive for years outside the body, can enter a host through an abrasion or may be inhaled. Borrelia, the cause of Lyme disease and relapsing fever, is transmitted by a vector, ticks of the genus Ixodes, from the diseases' reservoirs in animals such as deer. Campylobacter jejuni, a cause of gastroenteritis, is spread by the fecal–oral route from animals, or by eating insufficiently cooked poultry, or by contaminated water. Haemophilus influenzae, an agent of bacterial meningitis and respiratory tract infections such as influenza and bronchitis, is transmitted by droplet contact. Treponema pallidum, the cause of syphilis, is spread by sexual activity.
Enterobacteria phage T4 is a bacteriophage virus. It infects its host, Escherichia coli, by injecting its DNA through its tail, which attaches to the bacterium's surface.
Viruses
Viruses
are obligate intracellular parasites, characterised by extremely
limited biological function, to the point where, while they are
evidently able to infect all other organisms from bacteria and archaea to animals, plants and fungi, it is unclear whether they can themselves be described as living. Viruses can be either RNA or DNA viruses consisting of a single or double strand of genetic material (RNA or DNA respectively), covered in a protein coat and sometimes a lipid envelope. They thus lack all the usual machinery of the cell such as enzymes, relying entirely on the host cell's ability to replicate DNA and synthesise proteins. Most viruses are bacteriophages, infecting bacteria.
Evolutionary ecology
Restoration of a Tyrannosaurus with holes possibly caused by a Trichomonas-like parasite
Parasitism is a major aspect of evolutionary ecology; for example,
almost all free-living animals are host to at least one species of
parasite. Vertebrates, the best-studied group, are hosts to between
75,000 and 300,000 species of helminths and an uncounted number of
parasitic microorganisms. On average, a mammal species hosts four
species of nematode, two of trematodes, and two of cestodes. Humans have 342 species of helminth parasites, and 70 species of protozoan parasites. Some three-quarters of the links in food webs include a parasite, important in regulating host numbers. Perhaps 40 percent of described species are parasitic. This is harder to demonstrate from the fossil record, but for example holes in the mandibles of several specimens of Tyrannosaurus may have been caused by Trichomonas-like parasites.
Coevolution
As hosts and parasites evolve together, their relationships often
change. When a parasite is in a sole relationship with a host, selection
drives the relationship to become more benign, even mutualistic, as the
parasite can reproduce for longer if its host lives longer.
But where parasites are competing, selection favours the parasite that
reproduces fastest, leading to increased virulence. There are thus
varied possibilities in host–parasite coevolution.
Coevolution favouring mutualism
Wolbachia bacteria within an insect cell
Long-term coevolution sometimes leads to a relatively stable relationship tending to commensalism or mutualism,
as, all else being equal, it is in the evolutionary interest of the
parasite that its host thrives. A parasite may evolve to become less
harmful for its host or a host may evolve to cope with the unavoidable
presence of a parasite—to the point that the parasite's absence causes
the host harm. For example, although animals parasitised by worms are often clearly harmed, such infections may also reduce the prevalence and effects of autoimmune disorders in animal hosts, including humans. In a more extreme example, some nematode worms cannot reproduce, or even survive, without infection by Wolbachia bacteria.
Lynn Margulis and others have argued, following Peter Kropotkin's 1902 Mutual Aid: A Factor of Evolution,
that natural selection drives relationships from parasitism to
mutualism when resources are limited. This process may have been
involved in the symbiogenesis which formed the eukaryotes from an intracellular relationship between archaea and bacteria, though the sequence of events remains largely undefined.
Competition favoring virulence
Competition between parasites can be expected to favour faster reproducing and therefore more virulent parasites, by natural selection.
Parasites whose life cycle involves the death of the host, in order to
leave it and to sometimes enter the next host, evolve to be more
virulent, and may alter the behavior or other properties of the host to
make it more vulnerable to predators. Conversely, parasites whose reproduction is largely tied to their host's reproductive success tend to become less virulent or mutualist, so that their hosts reproduce more effectively.
Biologists long suspected cospeciation of flamingos and ducks with their parasitic lice, which were similar in the two families. Cospeciation did occur, but it led to flamingos and grebes, with a later host switch of flamingo lice to ducks.
Among competing parasitic insect-killing bacteria of the genera Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus, virulence depended on the relative potency of the antimicrobial toxins (bacteriocins)
produced by the two strains involved. When only one bacterium could
kill the other, the other strain was excluded by the competition. But
when caterpillars
were infected with bacteria both of which had toxins able to kill the
other strain, neither strain was excluded, and their virulence was less
than when the insect was infected by a single strain.
Cospeciation
A parasite sometimes undergoes cospeciation with its host, resulting in the pattern described in Fahrenholz's rule, that the phylogenies of the host and parasite come to mirror each other.
An example is between the simian foamy virus (SFV) and its primate hosts. The phylogenies of SFV polymerase and the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit II
from African and Asian primates were found to be closely congruent in
branching order and divergence times, implying that the simian foamy
viruses cospeciated with Old World primates for at least 30 million
years.
The presumption of a shared evolutionary history between
parasites and hosts can help elucidate how host taxa are related. For
instance, there has been a dispute about whether flamingos are more closely related to storks or ducks.
The fact that flamingos share parasites with ducks and geese was
initially taken as evidence that these groups were more closely related
to each other than either is to storks. However, evolutionary events
such as the duplication, or the extinction of parasite species (without
similar events on the host phylogeny) often erode similarities between
host and parasite phylogenies. In the case of flamingos, they have
similar lice to those of grebes. Flamingos and grebes do have a common ancestor, implying cospeciation of birds and lice in these groups. Flamingo lice then switched hosts to ducks, creating the situation which had confused biologists.
The protozoan Toxoplasma gondii facilitates its transmission by inducing behavioral changes in rats through infection of neurons in their central nervous system.
Parasites infect sympatric hosts (those within their same geographical area) more effectively, as has been shown with digenetic trematodes infecting lake snails. This is in line with the Red Queen hypothesis,
which states that interactions between species lead to constant natural
selection for coadaptation. Parasites track the locally common hosts'
phenotypes, so the parasites are less infective to allopatric hosts, those from different geographical regions.
Modifying host behaviour
Some parasites modify host behaviour in order to increase their transmission between hosts, often in relation to predator and prey (parasite increased trophic transmission). For example, in the California coastal salt marsh, the fluke Euhaplorchis californiensis reduces the ability of its killifish host to avoid predators. This parasite matures in egrets, which are more likely to feed on infected killifish than on uninfected fish. Another example is the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii, a parasite that matures in cats but can be carried by many other mammals. Uninfected rats avoid cat odors, but rats infected with T. gondii are drawn to this scent, which may increase transmission to feline hosts.
The malaria parasite modifies the skin odour of its human hosts,
increasing their attractiveness to mosquitoes and hence improving the
chance that the parasite will be transmitted.
Trait loss: bed bug, Cimex lectularius, is flightless, like many insect ectoparasites.
Trait loss
Parasites
can exploit their hosts to carry out a number of functions that they
would otherwise have to carry out for themselves. Parasites which lose
those functions then have a selective advantage, as they can divert
resources to reproduction. Many insect ectoparasites including bedbugs, batbugs, lice and fleas have lost their ability to fly, relying instead on their hosts for transport. Trait loss more generally is widespread among parasites.
Host defences
Hosts
have evolved a variety of defensive measures against their parasites,
including physical barriers like the skin of vertebrates, the immune system of mammals, insects actively removing parasites, and defensive chemicals in plants.
The evolutionary biologist W. D. Hamilton suggested that sexual reproduction could have evolved to help to defeat multiple parasites by enabling genetic recombination,
the shuffling of genes to create varied combinations. Hamilton showed
by mathematical modelling that sexual reproduction would be
evolutionarily stable in different situations, and that the theory's
predictions matched the actual ecology of sexual reproduction. However, there may be a trade-off between immunocompetence and breeding male vertebrate hosts' secondary sex characteristics, such as the plumage of peacocks and the manes of lions. This is because the male hormone testosterone encourages the growth of secondary sex characteristics, favouring such males in sexual selection, at the price of reducing their immune defences.
Vertebrates
The dry skin of vertebrates such as the short-horned lizard prevents the entry of many parasites.
The physical barrier of the tough and often dry and waterproof skin of reptiles, birds and mammals keeps invading microorganisms from entering the body. Human skin also secretes sebum, which is toxic to most microorganisms. On the other hand, larger parasites such as trematodes detect chemicals produced by the skin to locate their hosts when they enter the water. Vertebrate saliva and tears contain lysozyme, an enzyme which breaks down the cell walls of invading bacteria. Should the organism pass the mouth, the stomach with its hydrochloric acid, toxic to most microorganisms, is the next line of defence.
Some intestinal parasites have a thick, tough outer coating which is
digested slowly or not at all, allowing the parasite to pass through the
stomach alive, at which point they enter the intestine and begin the
next stage of their life. Once inside the body, parasites must overcome
the immune system's serum proteins and pattern recognition receptors, intracellular and cellular, that trigger the adaptive immune system's lymphocytes such as T cells and antibody-producing B cells. These have receptors that recognise parasites.
Insects
Insects often adapt their nests to reduce parasitism. For example, one of the key reasons why the wasp Polistes canadensis nests across multiple combs, rather than building a single comb like much of the rest of its genus, is to avoid infestation by tineid moths.
The tineid moth lays its eggs within the wasps' nests and then these
eggs hatch into larvae that can burrow from cell to cell and prey on
wasp pupae. Adult wasps attempt to remove and kill moth eggs and larvae
by chewing down the edges of cells, coating the cells with an oral
secretion that gives the nest a dark brownish appearance.
Plants
Plants respond to parasite attack with a series of chemical defences, such as polyphenol oxidase, under the control of the jasmonic acid-insensitive (JA) and salicylic acid (SA) signalling pathways.
The different biochemical pathways are activated by different attacks,
and the two pathways can interact positively or negatively. In general,
plants can either initiate a specific or a non-specific response.
Specific responses involve recognition of a parasite by the plant's
cellular receptors, leading to a strong but localised response:
defensive chemicals are produced around the area where the parasite was
detected, blocking its spread, and avoiding wasting defensive production
where it is not needed.
Nonspecific defensive responses are systemic, meaning that the
responses are not confined to an area of the plant, but spread
throughout the plant, making them costly in energy. These are effective
against a wide range of parasites. When damaged, such as by lepidopteran caterpillars, leaves of plants including maize and cotton release increased amounts of volatile chemicals such as terpenes that signal they are being attacked; one effect of this is to attract parasitoid wasps, which in turn attack the caterpillars.
Biology and conservation
Ecology and parasitology
Parasitism and parasite evolution were until the twentyfirst century studied by parasitologists, in a science dominated by medicine, rather than by ecologists or evolutionary biologists.
Even though parasite–host interactions were plainly ecological and
important in evolution, the history of parasitology caused what the
evolutionary ecologist Robert Poulin called a "takeover of parasitism by
parasitologists", leading ecologists to ignore the area. This was in
his opinion "unfortunate", as parasites are "omnipresent agents of
natural selection" and significant forces in evolution and ecology.
In his view, the long-standing split between the sciences limited the
exchange of ideas, with separate conferences and separate journals. The
technical languages of ecology and parasitology sometimes involved
different meanings for the same words. There were philosophical
differences, too: Poulin notes that, influenced by medicine, "many
parasitologists accepted that evolution led to a decrease in parasite
virulence, whereas modern evolutionary theory would have predicted a
greater range of outcomes".
The rescuing from extinction of the California condor was a successful if very expensive project, but its ectoparasite, the louse Colpocephalum californici, became extinct.
Their complex relationships make parasites difficult to place in food
webs: a trematode with multiple hosts for its various life cycle stages
would occupy many positions in a food web simultaneously, and would set
up loops of energy flow, confusing the analysis. Further, since nearly
every animal has (multiple) parasites, parasites would occupy the top
levels of every food web.
Rationale for conservation
Although parasites are widely considered to be harmful, the
eradication of all parasites would not be beneficial. Parasites account
for at least half of life's diversity; they perform important ecological
roles; and without parasites, organisms might tend to asexual
reproduction, diminishing the diversity of traits brought about by
sexual reproduction. Parasites provide an opportunity for the transfer of genetic material between species, facilitating evolutionary change.
Many parasites require multiple hosts of the different species to
complete their life cycles and rely on predator–prey or other stable
ecological interactions to get from one host to another. The presence of
parasites thus indicates that an ecosystem is healthy.
A well-known case was that of an ectoparasite, the California condor louse, Colpocephalum californici. Any lice found were "deliberately killed" during the major and very costly captive breeding program to rescue its host, the Californian condor.
The result was that one species, the condor, was saved and returned to
the wild, while another species, the parasite, became extinct.
Although parasites are often omitted in depictions of food webs, they usually occupy the top position. Parasites can function like keystone species, reducing the dominance of superior competitors and allowing competing species to co-exist.
Parasites are distributed very unevenly
among their hosts, most hosts having no parasites, and a few hosts
harbouring most of the parasite population. This distribution makes
sampling difficult and requires careful use of statistics.
Quantitative ecology
A single parasite species usually has an aggregated distribution
across host animals, which means that most hosts carry few parasites,
while a few hosts carry the vast majority of parasite individuals. This
poses considerable problems for students of parasite ecology, as it
renders parametric statistics as commonly used by biologists invalid. Log-transformation of data before the application of parametric test, or the use of non-parametric statistics
is recommended by several authors, but this can give rise to further
problems, so quantitative parasitology is based on more advanced
biostatistical methods.
History
Ancient
Human parasites including roundworms, the Guinea worm, threadworms and tapeworms are mentioned in Egyptian papyrus records from 3000 BC onwards; the Ebers papyrus describes hookworm. In ancient Greece, parasites including the bladder worm are described in the Hippocratic Corpus, while the comic playwright Aristophanes called tapeworms "hailstones". The Roman physicians Celsus and Galen documented the roundworms Ascaris lumbricoides and Enterobius vermicularis.
Medieval
A plate from Francesco Redi's Osservazioni intorno agli animali viventi che si trovano negli animali viventi (Observations on living animals found inside living animals), 1684
In his Canon of Medicine, completed in 1025, the Persian physician Avicenna recorded human and animal parasites including roundworms, threadworms, the Guinea worm and tapeworms.
In his 1397 book Traité de l'état, science et pratique de l'art de la Bergerie (Account of the state, science and practice of the art of shepherding), Jehan de Brie wrote the first description of a trematode endoparasite, the sheep liver fluke Fasciola hepatica.
Early Modern
In the Early Modern period, Francesco Redi's 1668 book Esperienze Intorno alla Generazione degl'Insetti (Experiences of the Generation of Insects), explicitly described ecto- and endoparasites, illustrating ticks, the larvae of nasal flies of deer, and sheep liver fluke. Redi noted that parasites develop from eggs, contradicting the theory of spontaneous generation. In his 1684 book Osservazioni intorno agli animali viventi che si trovano negli animali viventi (Observations on Living Animals found in Living Animals), Redi described and illustrated over 100 parasites including the large roundworm in humans that causes ascariasis. Redi was the first to name the cysts of Echinococcus granulosus seen in dogs and sheep as parasitic; a century later, in 1760, Peter Simon Pallas correctly suggested that these were the larvae of tapeworms.
In 1681, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek observed and illustrated the protozoan parasite Giardia lamblia, and linked it to "his own loose stools". This was the first protozoan parasite of humans to be seen under a microscope. A few years later, in 1687, the Italian biologists Giovanni Cosimo Bonomo and Diacinto Cestoni described scabies as caused by the parasitic mite Sarcoptes scabiei, marking it as the first disease of humans with a known microscopic causative agent.
Ronald Ross won the 1902 Nobel Prize for showing that the malaria parasite is transmitted by mosquitoes. This 1897 notebook page records his first observations of the parasite in mosquitoes.
Parasitology
Modern parasitology developed in the 19th century with accurate observations and experiments by many researchers and clinicians; the term was first used in 1870. In 1828, James Annersley described amoebiasis, protozoal infections of the intestines and the liver, though the pathogen, Entamoeba histolytica, was not discovered until 1873 by Friedrich Lösch. James Paget discovered the intestinal nematode Trichinella spiralis in humans in 1835. James McConnell described the human liver fluke, Clonorchis sinensis, in 1875. Algernon Thomas and Rudolf Leuckart independently made the first discovery of the life cycle of a trematode, the sheep liver fluke, by experiment in 1881–1883. In 1877 Patrick Manson discovered the life cycle of the filarial worms, that cause elephantiatis transmitted by mosquitoes. Manson further predicted that the malaria parasite, Plasmodium, had a mosquito vector, and persuaded Ronald Ross to investigate. Ross confirmed that the prediction was correct in 1897–1898. At the same time, Giovanni Battista Grassi and others described the malaria parasite's life cycle stages in Anopheles mosquitoes. Ross was controversially awarded the 1902 Nobel prize for his work, while Grassi was not. In 1903, David Bruce identified the protozoan parasite and the tsetse fly vector of African trypanosomiasis.
Vaccine
Given the importance of malaria, with some 220 million people
infected annually, many attempts have been made to interrupt its
transmission. Various methods of malaria prophylaxis have been tried including the use of antimalarial drugs to kill off the parasites in the blood, the eradication of its mosquito vectors with organochlorine and other insecticides, and the development of a malaria vaccine. All of these have proven problematic, with drug resistance, insecticide resistance among mosquitoes, and repeated failure of vaccines as the parasite mutates. The first and as of 2015 the only licensed vaccine for any parasitic disease of humans is RTS,S for Plasmodium falciparum malaria.
Resistance
Poulin observes that the widespread prophylactic use of anthelmintic drugs in domestic sheep and cattle constitutes a worldwide uncontrolled experiment
in the life-history evolution of their parasites. The outcomes depend
on whether the drugs decrease the chance of a helminth larva reaching
adulthood. If so, natural selection can be expected to favour the
production of eggs at an earlier age. If on the other hand the drugs
mainly affects adult parasitic worms, selection could cause delayed
maturity and increased virulence. Such changes appear to be under way: the nematode Teladorsagia circumcincta is changing its adult size and reproductive rate in response to drugs.
Cultural significance
"An Old Parasite in a New Form": an 1881 Punch cartoon by Edward Linley Sambourne compares a crinoletta bustle to a parasitic insect's exoskeleton
Classical times
In the classical era, the concept of the parasite was not strictly pejorative: the parasitus was an accepted role in Roman society,
in which a person could live off the hospitality of others, in return
for "flattery, simple services, and a willingness to endure
humiliation".
Society
Parasitism has a derogatory sense in popular usage. According to the immunologist John Playfair,
In everyday speech, the term 'parasite' is loaded with derogatory meaning. A parasite is a sponger, a lazy profiteer, a drain on society.
The satirical cleric Jonathan Swift
refers to hyperparasitism in his 1733 poem "On Poetry: A Rhapsody",
comparing poets to "vermin" who "teaze and pinch their foes":
The vermin only teaze and pinch
Their foes superior by an inch.
So nat'ralists observe, a flea
Hath smaller fleas that on him prey;
And these have smaller fleas to bite 'em.
And so proceeds ad infinitum.
Thus every poet, in his kind,
Is bit by him that comes behind:
Fiction
Parasites by Katrin Alvarez. Oil on canvas, 2011
In Bram Stoker's 1897 Gothic horror novel Dracula, and its many film adaptations, the eponymous Count Dracula is a blood-drinking parasite. The critic Laura Otis
argues that as a "thief, seducer, creator, and mimic, Dracula is the
ultimate parasite. The whole point of vampirism is sucking other
people's blood—living at other people's expense."
Disgusting and terrifying parasitic alien species are widespread in science fiction, as for instance in Ridley Scott's 1979 film Alien. In one scene, a Xenomorph bursts out of the chest of a dead man, with blood squirting out under high pressure assisted by explosive squibs. Animal organs
were used to reinforce the shock effect. The scene was filmed in a
single take, and the startled reaction of the actors was genuine.