https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_bot
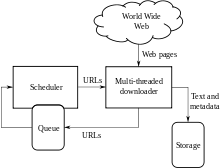
An Internet bot, also known as a web robot, robot or simply bot, is a software application that runs automated tasks (scripts) over the Internet. Typically, bots perform tasks that are both simple and structurally repetitive, at a much higher rate than would be possible for a human alone. The largest use of bots is in web spidering (web crawler), in which an automated script fetches, analyzes and files information from web servers at many times the speed of a human. More than half of all web traffic is made up of bots.
Efforts by servers hosting websites to counteract bots vary. Servers may choose to outline rules on the behaviour of internet bots by implementing a
An Internet bot, also known as a web robot, robot or simply bot, is a software application that runs automated tasks (scripts) over the Internet. Typically, bots perform tasks that are both simple and structurally repetitive, at a much higher rate than would be possible for a human alone. The largest use of bots is in web spidering (web crawler), in which an automated script fetches, analyzes and files information from web servers at many times the speed of a human. More than half of all web traffic is made up of bots.
Efforts by servers hosting websites to counteract bots vary. Servers may choose to outline rules on the behaviour of internet bots by implementing a
robots.txt
file: this file is simply text stating the rules governing a bot's
behaviour on that server. Any bot that does not follow these rules when
interacting with (or 'spidering') any server should, in theory, be
denied access to, or removed from, the affected website. If the only
rule implementation by a server is a posted text file with no associated
program/software/app, then adhering to those rules is entirely
voluntary – in reality there is no way to enforce those rules, or even
to ensure that a bot's creator or implementer acknowledges, or even
reads, the robots.txt file contents. Some bots are "good" – e.g. search
engine spiders – while others can be used to launch malicious and harsh
attacks, most notably, in political campaigns.IM and IRC
Some bots communicate with other users of Internet-based services, via instant messaging (IM), Internet Relay Chat (IRC), or another web interface such as Facebook Bots and Twitterbots. These chatterbots
may allow people to ask questions in plain English and then formulate a
proper response. These bots can often handle many tasks, including
reporting weather, zip-code information, sports scores, converting
currency or other units, etc. Others are used for entertainment, such as SmarterChild on AOL Instant Messenger and MSN Messenger.
An additional role of IRC bots
may be to lurk in the background of a conversation channel, commenting
on certain phrases uttered by the participants (based on pattern matching). This is sometimes used as a help service for new users, or for censorship of profanity.
Social bots
Social networking bots are sets of algorithms that take on the duties
of repetitive sets of instructions in order to establish a service or
connection among social networking users. Various designs of networking
bots vary from chat bots,
algorithms designed to converse with a human user, to social bots,
algorithms designed to mimic human behaviors to converse with behavioral
patterns similar to that of a human user. The history of social botting
can be traced back to Alan Turing in the 1950s and his vision of designing sets of instructional code that passes the Turing test. From 1964 to 1966, ELIZA, a natural language processing computer program created by Joseph Weizenbaum,
is an early indicator of artificial intelligence algorithms that
inspired computer programmers to design tasked programs that can match
behavior patterns to their sets of instruction. As a result, natural
language processing has become an influencing factor to the development
of artificial intelligence and social bots as innovative technological
advancements are made alongside the progression of the mass spreading of
information and thought on social media websites.
Reports of political interferences in recent elections, including the 2016 US and 2017 UK general elections,
have set the notion of botting being more prevalent because of the
ethics that is challenged between the bot's design and the bot's
designer. According to Emilio Ferrara, a computer scientist from the
University of Southern California reporting on Communications of the
ACM,
the lack of resources available to implement fact-checking and
information verification results in the large volumes of false reports
and claims made on these bots in social media platforms. In the case of
Twitter, most of these bots are programmed with searching filter
capabilities that target key words and phrases that reflect in favor and
against political agendas and retweet them. While the attention of bots
is programmed to spread unverified information throughout the social
media platform,
it is a challenge that programmers face in the wake of a hostile
political climate. Binary functions are designated to the programs and
using an Application Program interface embedded in the social media
website executes the functions tasked. The Bot Effect is what Ferrera
reports as when the socialization of bots and human users creates a
vulnerability to the leaking of personal information and polarizing
influences outside the ethics of the bot's code. According to Guillory
Kramer in his study, he observes the behavior of emotionally volatile
users and the impact the bots have on the users, altering the perception
of reality.
Commercial bots
There has been a great deal of controversy about the use of bots in an automated trading function. Auction website eBay
has been to court in an attempt to suppress a third-party company from
using bots to traverse their site looking for bargains; this approach
backfired on eBay and attracted the attention of further bots. The
United Kingdom-based bet exchange Betfair
saw such a large amount of traffic coming from bots that it launched a
WebService API aimed at bot programmers, through which it can actively
manage bot interactions.
Bot farms are known to be used in online app stores, like the Apple App Store and Google Play, to manipulate positions or to increase positive ratings/reviews.
A rapidly growing, benign, form of internet bot is the chatbot.
From 2016, when Facebook Messenger allowed developers to place chatbots
on their platform, there has been an exponential growth of their use on
that forum alone. 30,000 bots were created for Messenger in the first
six months, rising to 100,000 by September 2017.
Avi Ben Ezra, CTO of SnatchBot, told Forbes that evidence from the use
of their chatbot building platform pointed to a near future saving of
millions of hours of human labour as 'live chat' on websites was
replaced with bots.
Companies use internet bots to increase online engagement and
streamline communication. Companies often use bots to cut down on cost,
instead of employing people to communicate with consumers, companies
have developed new ways to be efficient. These chatbots are used to
answer customers' questions. For example, Domino's has developed a chatbot that can take orders via Facebook Messenger. Chatbots allow companies to allocate their employees' time to more important things.
Malicious bots
A malicious use of bots is the coordination and operation of an automated attack on networked computers, such as a denial-of-service attack by a botnet. Internet bots can also be used to commit click fraud and more recently have seen usage around MMORPG games as computer game bots. Now a days such kind of bots are also being used in video games such as PUBG. PUBG mobile bots are also related to the family of malicious bots. A spambot is an internet bot that attempts to spam
large amounts of content on the Internet, usually adding advertising
links. More than 94.2% of websites have experienced a bot attack.
- There are malicious bots (and botnets) of the following types:
- Spambots that harvest email addresses from contact or guestbook pages
- Downloader programs that suck bandwidth by downloading entire websites
- Website scrapers that grab the content of websites and re-use it without permission on automatically generated doorway pages
- Registration bots which sign up a specific email address to numerous services in order to have the confirmation messages flood the email inbox and distract from important messages indicating a security breach.[12]
- Viruses and worms
- DDoS attacks
- Botnets, zombie computers, etc.
- Spambots that try to redirect people onto a malicious website, sometimes found in comment sections or forums of various websites.
- Bots are also used to buy up good seats for concerts, particularly by ticket brokers who resell the tickets. Bots are employed against entertainment event-ticketing sites. The bots are used by ticket brokers to unfairly obtain the best seats for themselves while depriving the general public of also having a chance to obtain the good seats. The bot runs through the purchase process and obtains better seats by pulling as many seats back as it can.
- Bots are often used in Massively Multiplayer Online Roleplaying Games to farm for resources that would otherwise take significant time or effort to obtain; this is a concern for most online in-game economies.
- Bots are also used to increase views for YouTube videos.
- Bots are used to increase traffic counts on analytics reporting to extract money from advertisers. A study by comScore found that 54 percent of display ads shown in thousands of campaigns between May 2012 and February 2013 never appeared in front of a human being.
- in 2012, reporter Percy von Lipinski reported that he discovered millions of bot or botted or pinged views at CNN iReport. CNN iReport quietly removed millions of views from the account of so-called superstar iReporter Chris Morrow. It is not known if the ad revenue received by CNN from the fake views was ever returned to the advertisers.
- Bots may be used on internet forums to automatically post inflammatory or nonsensical posts to disrupt the forum and anger users.
The most widely used anti-bot technique is the use of CAPTCHA, which is a form of Turing test
used to distinguish between a human user and a less-sophisticated
AI-powered bot, by the use of graphically-encoded human-readable text.
Examples of providers include Recaptcha, and commercial companies such as Minteye, Solve Media, and NuCaptcha. Captchas, however, are not foolproof in preventing bots as they can often be circumvented by computer character recognition, security holes, and even by outsourcing captcha solving to cheap laborers.
Helpful bots
Companies
and customers can benefit from internet bots. Internet bots are
allowing customers to communicate with companies without having to
communicate with a person. KLM Royal Dutch Airlines
has produced a chatbot that allows customers to receive boarding
passes, check in reminders, and other information that is needed for a
flight.
Companies have made chatbots that can benefit customers. Customer
engagement has grown since these chatbots have been developed.
Chat bots are used on a daily basis. Google Assistant and Siri
are considered forms of chat bots. Google Assistant and Siri allow
people to ask questions and get a response using an AI system. These
technological advances are positively benefiting people's daily lives.