| Artificial cardiac pacemaker | |
|---|---|

St Jude Medical pacemaker with ruler
|
A cardiac pacemaker (or artificial pacemaker, so as not to be confused with the natural pacemaker of the heart), is a medical device that generates electrical impulses delivered by electrodes to cause the heart muscle chambers (the upper, or atria and/or the lower, or ventricles) to contract and therefore pump blood; by doing so this device replaces and/or regulates the function of the electrical conduction system of the heart.
The primary purpose of a pacemaker is to maintain an adequate heart rate, either because the heart's natural pacemaker is not fast enough, or because there is a block in the heart's electrical conduction system. Modern pacemakers are externally programmable and allow a cardiologist, particularly a cardiac electrophysiologist to select the optimal pacing modes for individual patients. A specific type of pacemakers called defibrillator combines pacemaker and defibrillator functions in a single implantable device, which should be called only defibrillator, for clarity. Others, called biventricular pacemakers have multiple electrodes stimulating differing positions within the lower heart chambers to improve synchronization of the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart.
Methods of pacing
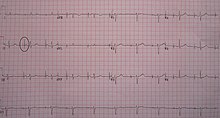
An ECG in a person with an atrial pacemaker. Note the circle around one of the sharp electrical spikes in the position where one would expect the P wave.
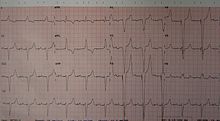
An ECG of a person with a dual chamber pacemaker
Percussive pacing
Percussive
pacing, also known as transthoracic mechanical pacing, is the use of
the closed fist, usually on the left lower edge of the sternum over the right ventricle in the vena cava, striking from a distance of 20 – 30 cm to induce a ventricular beat (the British Journal of Anaesthesia
suggests this must be done to raise the ventricular pressure to
10–15 mmHg to induce electrical activity). This is an old procedure used
only as a life saving means until an electrical pacemaker is brought to
the patient.
Transcutaneous pacing
Transcutaneous pacing (TCP), also called external pacing, is
recommended for the initial stabilization of hemodynamically significant
bradycardias
of all types. The procedure is performed by placing two pacing pads on
the patient's chest, either in the anterior/lateral position or the
anterior/posterior position. The rescuer selects the pacing rate, and
gradually increases the pacing current (measured in mA) until electrical
capture (characterized by a wide QRS complex with a tall, broad T wave on the ECG)
is achieved, with a corresponding pulse. Pacing artifact on the ECG and
severe muscle twitching may make this determination difficult. External
pacing should not be relied upon for an extended period of time. It is
an emergency procedure that acts as a bridge until transvenous pacing or
other therapies can be applied.
Epicardial pacing (temporary)
ECG
rhythm strip of a threshold determination in a patient with a temporary
(epicardial) ventricular pacemaker. The epicardial pacemaker leads were
placed after the patient collapsed during aortic valve surgery. In the first half of the tracing, pacemaker stimuli at 60 beats per minute result in a wide QRS complex with a right bundle branch block pattern. Progressively weaker pacing stimuli are administered, which results in asystole
in the second half of the tracing. At the end of the tracing,
distortion results from muscle contractions due to a (short) hypoxic seizure. Because decreased pacemaker stimuli do not result in a ventricular escape rhythm, the patient can be said to be pacemaker-dependent and needs a definitive pacemaker.
Temporary epicardial pacing is used during open heart surgery should
the surgical procedure create atrio-ventricular block. The electrodes
are placed in contact with the outer wall of the ventricle (epicardium)
to maintain satisfactory cardiac output until a temporary transvenous
electrode has been inserted.
Transvenous pacing (temporary)
Transvenous pacing, when used for temporary pacing, is an alternative
to transcutaneous pacing. A pacemaker wire is placed into a vein, under
sterile conditions, and then passed into either the right atrium or
right ventricle. The pacing wire is then connected to an external
pacemaker outside the body. Transvenous pacing is often used as a bridge
to permanent pacemaker placement. It can be kept in place until a
permanent pacemaker is implanted or until there is no longer a need for a
pacemaker and then it is removed.
Right
atrial and right ventricular leads as visualized under x-ray during a
pacemaker implant procedure. The atrial lead is the curved one making a U
shape in the upper left part of the figure.
Permanent transvenous pacing
Permanent
pacing with an implantable pacemaker involves transvenous placement of
one or more pacing electrodes within a chamber, or chambers, of the
heart, while the pacemaker is implanted inside the skin under the
clavicle. The procedure is performed by incision of a suitable vein into
which the electrode lead
is inserted and passed along the vein, through the valve of the heart,
until positioned in the chamber. The procedure is facilitated by fluoroscopy
which enables the physician to view the passage of the electrode lead.
After satisfactory lodgement of the electrode is confirmed, the opposite
end of the electrode lead is connected to the pacemaker generator.
There are three basic types of permanent pacemakers, classified according to the number of chambers involved and their basic operating mechanism:
- Single-chamber pacemaker. In this type, only one pacing lead is placed into a chamber of the heart, either the atrium or the ventricle.
- Dual-chamber pacemaker. Here, wires are placed in two chambers of the heart. One lead paces the atrium and one paces the ventricle. This type more closely resembles the natural pacing of the heart by assisting the heart in coordinating the function between the atria and ventricles.
- Biventricular pacemaker. This pacemaker has three wires placed in three chambers of the heart. One in the atrium and two in either ventricle. It is more complicated to implant.
- Rate-responsive pacemaker. This pacemaker has sensors that detect changes in the patient's physical activity and automatically adjust the pacing rate to fulfill the body's metabolic needs.
The pacemaker generator is a hermetically sealed device containing a power source, usually a lithium battery,
a sensing amplifier which processes the electrical manifestation of
naturally occurring heart beats as sensed by the heart electrodes, the computer logic for the pacemaker and the output circuitry which delivers the pacing impulse to the electrodes.
Most commonly, the generator is placed below the subcutaneous fat
of the chest wall, above the muscles and bones of the chest. However,
the placement may vary on a case by case basis.
The outer casing of pacemakers is so designed that it will rarely be rejected by the body's immune system. It is usually made of titanium, which is inert in the body.
Leadless pacing
Leadless
pacemakers are devices that are small enough to allow the generator to
be placed within the heart, therefore avoiding the need for pacing
leads.
As pacemaker leads can fail over time, a pacing system that avoids
these components offers theoretical advantages. Leadless pacemakers can
be implanted into the heart using a steerable catheter fed into the femoral vein via an incision in the groin.
Basic function
Modern
pacemakers usually have multiple functions. The most basic form
monitors the heart's native electrical rhythm. When the pacemaker wire
or 'lead" does not detect heart electrical activity in the chamber -
atrium or ventricle - within a normal beat-to-beat time period - most
commonly one thousand milliseconds = a second - it will stimulate
respectively the atrium or the ventricle of the heart with a short low
voltage pulse. If it does sense electrical activity, it will hold off
stimulating. This sensing and stimulating activity continues on a beat
by beat basis and is called 'demand pacing". In the case of a dual
chamber device, when the upper chambers have a spontaneous or stimulated
activation, the device starts a countdown to ensure that in an
acceptable - and programmable - interval, there is an activation of the
ventricle, otherwise again an impulse will be delivered.
The more complex forms include the ability to sense and/or stimulate both the atrial and ventricular chambers.
| I | II | III | IV | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chamber(s) paced | Chamber(s) sensed | Response to sensing | Rate modulation | Multisite pacing |
| O = None | O = None | O = None | O = None | O = None |
| A = Atrium | A = Atrium | T = Triggered | R = Rate modulation | A = Atrium |
| V = Ventricle | V = Ventricle | I = Inhibited | V = Ventricle | |
| D = Dual (A+V) | D = Dual (A+V) | D = Dual (T+I) | D = Dual (A+V) |
From this the basic ventricular "on demand" pacing mode is VVI or
with automatic rate adjustment for exercise VVIR – this mode is suitable
when no synchronization with the atrial beat is required, as in atrial
fibrillation. The equivalent atrial pacing mode is AAI or AAIR which is
the mode of choice when atrioventricular conduction is intact but the
natural pacemaker the sinoatrial node is unreliable – sinus node disease (SND) or sick sinus syndrome. Where the problem is atrioventricular block
(AVB) the pacemaker is required to detect (sense) the atrial beat and
after a normal delay (0.1–0.2 seconds) trigger a ventricular beat,
unless it has already happened – this is VDD mode and can be achieved
with a single pacing lead with electrodes in the right atrium (to sense)
and ventricle (to sense and pace). These modes AAIR and VDD are unusual
in the US but widely used in Latin America and Europe.
The DDDR mode is most commonly used as it covers all the options though
the pacemakers require separate atrial and ventricular leads and are
more complex, requiring careful programming of their functions for
optimal results.
Biventricular pacing
Three
leads can be seen in this example of a cardiac resynchronization
device: a right atrial lead (solid black arrow), a right ventricular
lead (dashed black arrow), and a coronary sinus lead (red arrow). The
coronary sinus lead wraps around the outside of the left ventricle,
enabling pacing of the left ventricle. Note that the right ventricular
lead in this case has 2 thickened aspects that represent conduction
coils and that the generator is larger than typical pacemaker
generators, demonstrating that this device is both a pacemaker and a
cardioverter-defibrillator, capable of delivering electrical shocks for
dangerously fast abnormal ventricular rhythms.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is used for people with heart failure in whom the left and right ventricles do not contract simultaneously (ventricular dyssynchrony),
which occurs in approximately 25–50% of heart failure patients. To
achieve CRT, a biventricular pacemaker (BVP) is used, which can pace
both the septal and lateral walls of the left ventricle. By pacing both sides of the left ventricle, the pacemaker can resynchronize the ventricular contractions.
CRT devices have at least two leads, one passing through the vena cava and the right atrium into the right ventricle to stimulate the septum, and another passing through the vena cava and the right atrium and inserted through the coronary sinus
to pace the epicardial wall of the left ventricle. Often, for patients
in normal sinus rhythm, there is also a lead in the right atrium to
facilitate synchrony with the atrial contraction. Thus, timing between
the atrial and ventricular contractions, as well as between the septal
and lateral walls of the left ventricle can be adjusted to achieve
optimal cardiac function.
CRT devices have been shown to reduce mortality and improve
quality of life in patients with heart failure symptoms; a LV ejection
fraction less than or equal to 35% and QRS duration on EKG of 120 ms or
greater.
Biventricular pacing alone is referred to as CRT-P (for pacing).
For selected patients at risk of arrhythmias, CRT can be combined with
an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
(ICD): such devices, known as CRT-D (for defibrillation), also provide
effective protection against life-threatening arrhythmias.
His Bundle Pacing
Conventional placement of ventricular leads in or around the tip or apex
of the right ventricle, or RV apical pacing, can have negative effects
on heart function. Indeed, it has been associated with increased risk of
atrial fibrillation, heart failure, weakening of the heart muscle and potentially shorter life expectancy. His bundle pacing
(HBP) leads to a more natural or perfectly natural ventricular
activation and has generated strong research and clinical interest. By
stimulating the His–Purkinje
fiber network directly with a special lead and placement technique, HBP
causes a synchronized and therefore more effective ventricular
activation and avoid long term heart muscle disease. HBP in some cases
can also correct bundle branch block patterns.
Advancements in function
Posteroanterior and lateral chest radiographs
of a pacemaker with normally located leads in the right atrium (white
arrow) and right ventricle (black arrowhead), respectively.
A major step forward in pacemaker function has been to attempt to
mimic nature by utilizing various inputs to produce a rate-responsive
pacemaker using parameters such as the QT interval, pO2 – pCO2 (dissolved oxygen or carbon dioxide levels) in the arterial-venous system, physical activity as determined by an accelerometer, body temperature, ATP levels, adrenaline,
etc.
Instead of producing a static, predetermined heart rate, or intermittent
control, such a pacemaker, a 'Dynamic Pacemaker', could compensate for
both actual respiratory loading and potentially anticipated respiratory
loading. The first dynamic pacemaker was invented by Anthony Rickards of
the National Heart Hospital, London, UK, in 1982.
Dynamic pacemaking technology could also be applied to future artificial hearts.
Advances in transitional tissue welding would support this and other
artificial organ/joint/tissue replacement efforts. Stem cells may be of
interest in transitional tissue welding.
Many advancements have been made to improve the control of the
pacemaker once implanted. Many of these have been made possible by the
transition to microprocessor controlled pacemakers. Pacemakers that control not only the ventricles but the atria
as well have become common. Pacemakers that control both the atria and
ventricles are called dual-chamber pacemakers. Although these
dual-chamber models are usually more expensive, timing the contractions
of the atria to precede that of the ventricles improves the pumping
efficiency of the heart and can be useful in congestive heart failure.
Rate responsive pacing allows the device to sense the physical
activity of the patient and respond appropriately by increasing or
decreasing the base pacing rate via rate response algorithms.
The DAVID trials have shown that unnecessary pacing of the right ventricle can exacerbate heart failure
and increases the incidence of atrial fibrillation. The newer dual
chamber devices can keep the amount of right ventricle pacing to a
minimum and thus prevent worsening of the heart disease.
Considerations
Insertion
A pacemaker is typically inserted into the patient through a simple surgery using either local anesthetic or a general anesthetic.
The patient may be given a drug for relaxation before the surgery as
well. An antibiotic is typically administered to prevent infection.
In most cases, the pacemaker is inserted in the left shoulder area,
where an incision is made below the collar bone, creating a small pocket
where the pacemaker is actually housed in the patient's body. The lead or leads (the number of leads varies depending on the type of pacemaker) are fed into the heart through a large vein using a fluoroscope
to monitor the progress of lead insertion. The right ventricular lead
would be positioned away from the apex (tip) of the right ventricle and
up on the interventricular septum, below the outflow tract, to prevent
deterioration of the strength of the heart. The actual surgery typically
lasts 30 to 90 minutes.
Following surgery, the patient should exercise reasonable care
with the wound as it heals. There is a follow-up session during which
the pacemaker is checked using a "programmer" that can communicate with
the device and allows a health care professional to evaluate the
system's integrity and determine the settings such as pacing voltage
output. The patient should have the strength of his or her heart
analyzed frequently with echocardiography, every 1 or 2 years, to make
sure that placement of the right ventricular lead has not led to a
weakening of the left ventricle.
The patient may want to consider some basic preparation before
the surgery. The most basic preparation is that people who have body
hair on the chest may want to remove the hair by clipping just prior to
surgery or using a depilatory
agent (preoperative shaving has been on the decline since it can cause
skin breakage and increase infection risk of any surgical procedure)
since the surgery will involve bandages and monitoring equipment to be
affixed to the body.
Since a pacemaker uses batteries, the device itself will need
replacement as the batteries lose power. Device replacement is usually a
simpler procedure than the original insertion since it does not
normally require leads to be implanted. The typical replacement requires
a surgery in which an incision is made to remove the existing device,
the leads are disconnected from the existing device, the leads are then
attached to the new device, and the new device is inserted into the
patient's body, replacing the previous device.
Periodic pacemaker checkups
Two types of remote monitoring devices used by pacemaker patients
Once the pacemaker is implanted, it is periodically checked to ensure
the device is operational and performing appropriately. Depending on
the frequency set by the following physician, the device can be checked
as often as is necessary. Routine pacemaker checks are typically done
in-office every six (6) months, though will vary depending upon
patient/device status and remote monitoring availability. Newer
pacemaker models can also be interrogated remotely, with the patient
transmitting their pacemaker data using an at-home transmitter connected
to their geographical cellular network. This data can then be accessed
by the technician through the device manufacturer's web portal.
At the time of in-office follow-up, the device will be interrogated to perform diagnostic testing. These tests include:
- Sensing: the ability of the device to "see" intrinsic cardiac activity (Atrial and ventricular depolarization).
- Impedance: A test to measure lead integrity. Large and/or sudden increases in impedance can be indicative of a lead fracture while large and/or sudden decreases in impedance can signify a breach in lead insulation.
- Threshold amplitude: The minimum amount of energy (generally in hundredths of volts) required in order to pace the atrium or ventricle connected to the lead.
- Threshold duration: The amount of time that the device requires at the preset amplitude to reliably pace the atrium or ventricle connected to the lead.
- Percentage of pacing: Defines how dependent the patient is on the device, the percentage of time that the pacemaker has been actively pacing since the previous device interrogation.
- Estimated battery life at current rate: As modern pacemakers are "on-demand", meaning that they only pace when necessary, device longevity is affected by how much it is utilized. Other factors affecting device longevity include programmed output and algorithms (features) causing a higher level of current drain from the battery.
- Any events that were stored since the last follow-up, in particular arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. These are typically stored based on specific criteria set by the physician and specific to the patient. Some devices have the availability to display intracardiac electrograms of the onset of the event as well as the event itself. This is especially helpful in diagnosing the cause or origin of the event and making any necessary programming changes.
Magnetic fields, MRIs, and other lifestyle issues
A
patient's lifestyle is usually not modified to any great degree after
insertion of a pacemaker. There are a few activities that are unwise
such as full contact sports and activities that involve intense magnetic
fields.
The pacemaker patient may find that some types of everyday
actions need to be modified. For instance, the shoulder harness of a
vehicle seatbelt may be uncomfortable if the harness should fall across the pacemaker insertion site.
Any kind of an activity that involves intense electro-magnetic fields should be avoided. This includes activities such as arc welding possibly, with certain types of equipment, or maintaining heavy equipment that may generate intense magnetic fields (such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine).
However, in February 2011 the FDA approved a new pacemaker device from Medtronic called the Revo MRI SureScan which was the first to be labeled as conditional for MRI use.
There are several limitations to its use including certain patients'
qualifications and scan settings. An MRI conditional device has to be
reprogrammed right before and right after MRI scanning. All the 5 most
common cardiac pacing device manufacturers (covering more than 99% of
the US market) now have FDA-approved MR-conditional pacemakers.
A 2008 US study has found
that the magnetic field created by some headphones included with
portable music players or cell phones, when placed within inches of
pacemakers, may cause interference.
In addition, according to the American Heart Association,
some home devices have a remote potential to cause interference by
occasionally inhibiting a single beat. Cellphones available in the
United States (less than 3 watts) do not seem to damage pulse generators
or affect how the pacemaker works.
Having a pacemaker does not imply that a patient requires the use of antibiotics to be administered before procedures such as dental work.
The patient should inform all medical personnel that he or she has a
pacemaker. The use of MRI may be ruled out by the patient having a
pacemaker manufactured before MRI conditional devices became common, or
by the patient having old pacing wires abandoned inside the heart, no
longer connected to their pacemaker.
Turning off the pacemaker
A panel of The Heart Rhythm Society,
a specialist organization based in Washington, DC found that it was
legal and ethical to honor requests by patients, or by those with legal
authority to make decisions for patients, to deactivate implanted
cardiac devices. Lawyers say that the legal situation is similar to
removing a feeding tube, though there is currently no legal precedent
involving pacemakers in the United States of America. A patient in the
United States is thought to have a right to refuse or discontinue
treatment, including a pacemaker that keeps him or her alive. Physicians
have a right to refuse to turn it off, but are advised by the HRS panel
that they should refer the patient to a physician who will.
Some patients believe that hopeless, debilitating conditions, like
those brought on by severe strokes or late-stage dementia, can cause so
much suffering that they would prefer not to prolong their lives with
supportive measures, such as cardiac devices.
Privacy and security
Security
and privacy concerns have been raised with pacemakers that allow
wireless communication. Unauthorized third parties may be able to read
patient records contained in the pacemaker, or reprogram the devices, as
has been demonstrated by a team of researchers.
The demonstration worked at short range; they did not attempt to
develop a long range antenna. The proof of concept exploit helps
demonstrate the need for better security and patient alerting measures
in remotely accessible medical implants.
In response to this threat, Purdue University and Princeton University
researchers have developed a prototype firewall device, called MedMon,
which is designed to protect wireless medical devices such as pacemakers
and insulin pumps from attackers.
Complications
Ultrasound showing non capture of a pacemaker
Complications from having surgery to implant a pacemaker
are uncommon ( each 1-3 % approximately ), but could include: infection
where the pacemaker is implanted or in the bloodstream; allergic reaction to the dye or anesthesia
used during the procedure; swelling, bruising or bleeding at the
generator site, or around the heart, especially if the patient is taking
blood thinners, elderly, of thin frame or otherwise on chronic steroids use.
A possible complication of dual-chamber artificial pacemakers is
'pacemaker-mediated tachycardia' (PMT), a form of reentrant tachycardia.
In PMT, the artificial pacemaker forms the anterograde (atrium to
ventricle) limb of the circuit and the atrioventricular (AV) node forms
the retrograde limb (ventricle to atrium) of the circuit. Treatment of PMT typically involves reprogramming the pacemaker.
Another possible complication is "pacemaker-tracked tachycardia," where a supraventricular tachycardia such as atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter
is tracked by the pacemaker and produces beats from a ventricular lead.
This is becoming exceedingly rare as newer devices are often programmed
to recognize supraventricular tachycardias and switch to non-tracking
modes.
Sometimes the leads, which are small diameter wires, from the
pacemaker to the implantation site in the heart muscle will need to be
removed. The most common reason for lead removal is infection, however
over time leads can degrade due to a number of reasons such as lead
flexing.
Changes to programming of the pacemaker may overcome lead degradation
to some extent. However, a patient who has several pacemaker
replacements over a decade or two in which the leads were reused may
require a lead replacement surgery.
Lead replacement may be done in one of two ways. Insert a new set
of leads without removing the current leads (not recommended as it
provides additional obstruction to blood flow and heart valve function)
or remove the current leads and then insert replacements. The lead
removal technique will vary depending on the surgeon's estimation of the
probability that simple traction will suffice to more complex
procedures. Leads can normally be disconnected from the pacemaker easily
which is why device replacement usually entails simple surgery to
access the device and replace it by simply unhooking the leads from the
device to replace and hooking the leads to the new device. The possible
complications, such as perforation of the heart wall, come from removing
the lead{s} from the patient's body.
The other end of a pacemaker lead is actually implanted into the
heart muscle with a miniature screw or anchored with small plastic hooks
called tines. In addition, the longer the leads have been implanted
starting from a year or two, the more likely that they will have
attachments to the patient's body at various places in the pathway from
device to heart muscle, since the human body tends to incorporate
foreign devices into tissue. In some cases, for a lead that has been
inserted for a short amount of time, removal may involve simple traction
to pull the lead from the body. Removal in other cases is typically
done with a laser or cutting device which threads like a cannula with a
cutting edge over the lead and is moved down the lead to remove any
organic attachments with tiny cutting lasers or similar device.
Pacemaker lead malposition in various locations has been
described in the literature. Depending on the location of the pacer lead
and symptoms treatment varies.
Another possible complication called twiddler's syndrome
occurs when a patient manipulates the pacemaker and causes the leads to
be removed from their intended location and causes possible stimulation
of other nerves.
Other devices
Sometimes devices resembling pacemakers, called implantable cardioverter-defibrillators
(ICDs) are implanted. These devices are often used in the treatment of
patients at risk from sudden cardiac death. An ICD has the ability to
treat many types of heart rhythm disturbances by means of pacing, cardioversion, or defibrillation. Some ICD devices can distinguish between ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia
(VT), and may try to pace the heart faster than its intrinsic rate in
the case of VT, to try to break the tachycardia before it progresses to
ventricular fibrillation. This is known as fast-pacing, overdrive pacing, or anti-tachycardia pacing
(ATP). ATP is only effective if the underlying rhythm is ventricular
tachycardia, and is never effective if the rhythm is ventricular
fibrillation.
| I | II | III | IV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shock chamber | Antitachycardia pacing chamber | Tachycardia detection | Antibradycardia pacing chamber |
| O = None | O = None | E = Electrogram | O = None |
| A = Atrium | A = Atrium | H = Hemodynamic | A = Atrium |
| V = Ventricle | V = Ventricle | V = Ventricle | |
| D = Dual (A+V) | D = Dual (A+V) | D = Dual (A+V) |
| ICD-S | ICD with shock capability only |
| ICD-B | ICD with bradycardia pacing as well as shock |
| ICD-T | ICD with tachycardia (and bradycardia) pacing as well as shock |
History
In 1958, Arne Larsson
(1915–2001) became the first to receive an implantable pacemaker. He
had 26 devices during his life and campaigned for other patients needing
pacemakers.
Origin
In 1889, John Alexander MacWilliam reported in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) of his experiments in which application of an electrical impulse to the human heart in asystole caused a ventricular
contraction and that a heart rhythm of 60–70 beats per minute could be
evoked by impulses applied at spacings equal to 60–70/minute.
In 1926, Mark C Lidwill of the Royal Prince Alfred Hospital of Sydney, supported by physicist Edgar H. Booth of the University of Sydney,
devised a portable apparatus which "plugged into a lighting point" and
in which "One pole was applied to a skin pad soaked in strong salt
solution" while the other pole "consisted of a needle insulated except
at its point, and was plunged into the appropriate cardiac chamber".
"The pacemaker rate was variable from about 80 to 120 pulses per minute,
and likewise the voltage variable from 1.5 to 120 volts". In 1928, the
apparatus was used to revive a stillborn infant at Crown Street Women's Hospital, Sydney whose heart continued "to beat on its own accord", "at the end of 10 minutes" of stimulation.
In 1932, American physiologist Albert Hyman,
with the help of his brother, described an electro-mechanical
instrument of his own, powered by a spring-wound hand-cranked motor.
Hyman himself referred to his invention as an "artificial pacemaker",
the term continuing in use to this day.
An apparent hiatus in publication of research conducted between the early 1930s and World War II
may be attributed to the public perception of interfering with nature
by "reviving the dead". For example, "Hyman did not publish data on the
use of his pacemaker in humans because of adverse publicity, both among
his fellow physicians, and due to newspaper reporting at the time.
Lidwell may have been aware of this and did not proceed with his
experiments in humans".
Transcutaneous
In 1950, Canadian electrical engineer John Hopps designed and built the first external pacemaker based upon observations by cardio-thoracic surgeons Wilfred Gordon Bigelow and John Callaghan at Toronto General Hospital, although the device was first tested at the University of Toronto's Banting Institute on a dog. A substantial external device using vacuum tube technology to provide transcutaneous pacing,
it was somewhat crude and painful to the patient in use and, being
powered from an AC wall socket, carried a potential hazard of electrocution of the patient and inducing ventricular fibrillation.
A number of innovators, including Paul Zoll, made smaller but still bulky transcutaneous pacing devices from 1952 using a large rechargeable battery as the power supply.
In 1957, William L. Weirich published the results of research performed at the University of Minnesota.
These studies demonstrated the restoration of heart rate, cardiac
output and mean aortic pressures in animal subjects with complete heart block through the use of a myocardial electrode.
In 1958 Colombian doctor Alberto Vejarano Laverde and Colombian electrical engineer Jorge Reynolds Pombo constructed an external pacemaker, similar to those of Hopps and Zoll, weighing 45 kg and powered by a 12 volt car lead–acid battery,
but connected to electrodes attached to the heart. This apparatus was
successfully used to sustain a 70-year-old priest, Gerardo Florez.
The development of the silicon transistor
and its first commercial availability in 1956 was the pivotal event
that led to rapid development of practical cardiac pacemaking.
Wearable
In 1958, engineer Earl Bakken of Minneapolis, Minnesota, produced the first wearable external pacemaker for a patient of C. Walton Lillehei.
This transistorized pacemaker, housed in a small plastic box, had
controls to permit adjustment of pacing heart rate and output voltage
and was connected to electrode leads which passed through the skin of the patient to terminate in electrodes attached to the surface of the myocardium of the heart.
One of the earliest patients to receive this Lucas pacemaker
device was a woman in her early 30s in an operation carried out in 1964
at the Radcliffe Infirmary in Oxford by cardiac surgeon Alf Gunning from South Africa and later Professor Gunning who was a student of Christiaan Barnard. This pioneering operation was carried out under the guidance of cardiac consultant Peter Sleight
at the Radcliffe Infirmary in Oxford and his cardiac research team at
St George's Hospital in London. Sleight later became Professor of
Cardiovascular Medicine at Oxford University.
Implantable
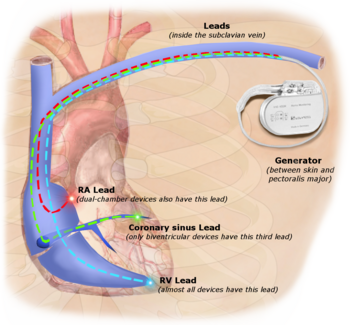
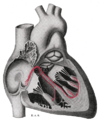
Illustration of implanted cardiac pacemaker showing locations of cardiac pacemaker leads
The first clinical implantation into a human of a fully implantable pacemaker was in 1958 at the Karolinska Institute in Solna, Sweden, using a pacemaker designed by inventor Rune Elmqvist and surgeon Åke Senning (in collaboration with Elema-Schönander AB, later Siemens-Elema AB), connected to electrodes attached to the myocardium of the heart by thoracotomy.
The device failed after three hours. A second device was then implanted
which lasted for two days. The world's first implantable pacemaker
patient, Arne Larsson, went on to receive 26 different pacemakers during
his lifetime. He died in 2001, at the age of 86, outliving the inventor
as well as the surgeon.
In 1959, temporary transvenous pacing was first demonstrated by Seymour Furman and John Schwedel, whereby the catheter electrode was inserted via the patient's basilic vein.
In February 1960, an improved version of the Swedish Elmqvist design was implanted in Montevideo, Uruguay in the Casmu 1 Hospital by Doctors Orestes Fiandra
and Roberto Rubio. That device lasted until the patient died of other
ailments, nine months later. The early Swedish-designed devices used
rechargeable batteries, which were charged by an induction coil from the
outside. It was the first pacemaker implanted in America.
Implantable pacemakers constructed by engineer Wilson Greatbatch entered use in humans from April 1960 following extensive animal testing. The Greatbatch innovation varied from the earlier Swedish devices in using primary cells (mercury battery) as the energy source. The first patient lived for a further 18 months.
The first use of transvenous pacing in conjunction with an implanted pacemaker was by Parsonnet in the United States, Lagergren in Sweden and Jean-Jacques Welti in France in 1962–63.
The transvenous, or pervenous, procedure involved incision of a vein into which was inserted the catheter electrode lead under fluoroscopic guidance, until it was lodged within the trabeculae of the right ventricle. This method was to become the method of choice by the mid-1960s.
Cardiothoracic Surgeon Leon Abrams, and Medical Engineer Ray Lightwood, developed and implanted the first patient-controlled variable-rate heart pacemaker in 1960 at Birmingham University.
The first implant took place in March 1960, with two further implants
the following month. These three patients made good recoveries and
returned to a high quality of life. By 1966, 56 patients had undergone
implantation with one surviving for over 5 1⁄2 years.
Lithium battery
The first lithium-iodide cell powered pacemaker. Cardiac Pacemakers Inc. 1972
The preceding implantable devices all suffered from the unreliability
and short lifetime of the available primary cell technology which was
mainly that of the mercury battery. In the late 1960s, several companies, including ARCO in the USA, developed isotope-powered pacemakers, but this development was overtaken by the development in 1971 of the lithium iodide cell battery by Wilson Greatbatch. Lithium-iodide or lithium anode cells became the standard for future pacemaker designs.
A further impediment to reliability of the early devices was the diffusion of water vapour from the body fluids through the epoxy
resin encapsulation affecting the electronic circuitry. This phenomenon
was overcome by encasing the pacemaker generator in a hermetically
sealed metal case, initially by Telectronics of Australia in 1969 followed by Cardiac Pacemakers Inc of Minneapolis in 1972. This technology, using titanium as the encasing metal, became the standard by the mid-1970s.
On July 9, 1974, Manuel A. Villafaña and Anthony Adducci founders of Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. (Guidant)
in St. Paul, Minnesota, manufactured the world's first pacemaker with a
lithium anode and a lithium-iodide electrolyte solid-state battery.
Intra-cardial
In
2013, multiple firms announced devices that could be inserted via a leg
catheter rather than invasive surgery. The devices are roughly the size
and shape of a pill, much smaller than the size of a traditional
pacemaker. Once implanted, the device's prongs contact the muscle and
stabilize heartbeats. Engineers and scientists are currently working on
this type of device.
In November 2014 a patient, Bill Pike of Fairbanks, Alaska, received a
Medtronic Micra pacemaker in Providence St Vincent Hospital in Portland
Oregon. D. Randolph Jones was the EP doctor. In 2014 also St. Jude
Medical Inc. announced the first enrollments in the company’s leadless
Pacemaker Observational Study evaluating the Nanostim leadless pacing
technology. The Nanostim pacemaker received CE marking in 2013. The
post-approval implants have occurred in Europe.
The European study was recently stopped, after there were reports of
six perforations that led to two patient deaths. After investigations St
Jude Medical restarted the study. But in the United States this therapy is still not approved by the FDA.
While the St Jude Nanostim and the Medtronic Micra are just
single-chamber pacemakers it is anticipated that leadless dual-chamber
pacing for patients with atrioventricular block will become possible
with further development.
Reusable Pacemakers
Thousands
of pacemakers are removed by funeral home personnel each year all over
the world. They have to be removed postmortem from bodies that are going
to be cremated to avoid explosions. It is a fairly simple procedure
that can be carried out by a mortician. Pacemakers with significant
battery life are potentially life-saving devices for people in low and
middle income countries (LMICs). The Institute of Medicine, a United States non-governmental organization,
has reported that inadequate access to advanced cardiovascular
technologies is one of the major contributors to cardiovascular disease
morbidity and mortality in LMICs. Ever since the 1970s, multiple studies
all over the world have reported on the safety and efficacy of
pacemaker reuse. As of 2016, widely acceptable standards for safe
pacemaker and ICD reuse have not been developed, and there continue to
be legal and regulatory barriers to widespread adoption of medical
device reuse.