The financial crisis of 2007–2008, also known as the global financial crisis (GFC), was a severe worldwide economic crisis. Prior to the COVID-19 recession in 2020, it was considered by many economists to have been the most serious financial crisis since the Great Depression. Predatory lending targeting low-income homebuyers, excessive risk-taking by global financial institutions, and the bursting of the United States housing bubble culminated in a "perfect storm". Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) tied to American real estate, as well as a vast web of derivatives linked to those MBS, collapsed in value. Financial institutions worldwide suffered severe damage, reaching a climax with the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers on September 15, 2008 and a subsequent international banking crisis.
The preconditions for the financial crisis were complex and multi-causal. Almost two decades prior, the U.S. Congress had passed legislation encouraging financing for affordable housing. In 1999, the Glass-Steagall legislation was repealed, permitting financial institutions to cross-pollinate their commercial (risk-averse) and proprietary trading (risk-seeking) operations. Arguably the largest contributor to the conditions necessary for financial collapse was the rapid development in predatory financial products which targeted low-income, low-information homebuyers who largely belonged to racial minorities. This market development went unattended by regulators and thus caught the U.S. government by surprise.
After the onset of the crisis, governments deployed massive bail-outs of financial institutions and other palliative monetary and fiscal policies to prevent a collapse of the global financial system. The crisis sparked the Great Recession which resulted in increases in unemployment and suicide and decreases in institutional trust and fertility, among other metrics. The recession was a significant precondition for the European debt crisis.
In 2010, the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act was enacted in the US as a response to the crisis to "promote the financial stability of the United States". The Basel III capital and liquidity standards were also adopted by countries around the world.
Background
The crisis sparked the Great Recession, which, at the time, was the most severe global recession since the Great Depression. It was also followed by the European debt crisis, which began with a deficit in Greece in late 2009, and the 2008–2011 Icelandic financial crisis, which involved the bank failure of all three of the major banks in Iceland and, relative to the size of its economy, was the largest economic collapse suffered by any country in history. It was among the five worst financial crises the world had experienced and led to a loss of more than $2 trillion from the global economy. U.S. home mortgage debt relative to GDP increased from an average of 46% during the 1990s to 73% during 2008, reaching $10.5 trillion. The increase in cash out refinancings, as home values rose, fueled an increase in consumption that could no longer be sustained when home prices declined. Many financial institutions owned investments whose value was based on home mortgages such as mortgage-backed securities, or credit derivatives used to insure them against failure, which declined in value significantly. The International Monetary Fund estimated that large U.S. and European banks lost more than $1 trillion on toxic assets and from bad loans from January 2007 to September 2009.
Lack of investor confidence in bank solvency and declines in credit availability led to plummeting stock and commodity prices in late 2008 and early 2009. The crisis rapidly spread into a global economic shock, resulting in several bank failures. Economies worldwide slowed during this period since credit tightened and international trade declined. Housing markets suffered and unemployment soared, resulting in evictions and foreclosures. Several businesses failed. From its peak in the second quarter of 2007 at $64.4 trillion, household wealth in the United States fell $14 trillion, to $50.4 trillion by the end of the first quarter of 2009, resulting in a decline in consumption, then a decline in business investment. In the fourth quarter of 2008, the quarter-over-quarter decline in real GDP in the U.S. was 8.4%. The U.S. unemployment rate peaked at 10.0% in October 2009, the highest rate since 1983 and roughly twice the pre-crisis rate. The average hours per work week declined to 33, the lowest level since the government began collecting the data in 1964.
The economic crisis started in the U.S. but spread to the rest of the world. U.S. consumption accounted for more than a third of the growth in global consumption between 2000 and 2007 and the rest of the world depended on the U.S. consumer as a source of demand. Toxic securities were owned by corporate and institutional investors globally. Derivatives such as credit default swaps also increased the linkage between large financial institutions. The de-leveraging of financial institutions, as assets were sold to pay back obligations that could not be refinanced in frozen credit markets, further accelerated the solvency crisis and caused a decrease in international trade. Reductions in the growth rates of developing countries were due to falls in trade, commodity prices, investment and remittances sent from migrant workers (example: Armenia). States with fragile political systems feared that investors from Western states would withdraw their money because of the crisis.
As part of national fiscal policy response to the Great Recession, governments and central banks, including the Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank and the Bank of England, provided then-unprecedented trillions of dollars in bailouts and stimulus, including expansive fiscal policy and monetary policy to offset the decline in consumption and lending capacity, avoid a further collapse, encourage lending, restore faith in the integral commercial paper markets, avoid the risk of a deflationary spiral, and provide banks with enough funds to allow customers to make withdrawals. In effect, the central banks went from being the "lender of last resort" to the "lender of only resort" for a significant portion of the economy. In some cases the Fed was considered the "buyer of last resort". During the fourth quarter of 2008, these central banks purchased US$2.5 trillion of government debt and troubled private assets from banks. This was the largest liquidity injection into the credit market, and the largest monetary policy action in world history. Following a model initiated by the 2008 United Kingdom bank rescue package, the governments of European nations and the United States guaranteed the debt issued by their banks and raised the capital of their national banking systems, ultimately purchasing $1.5 trillion newly issued preferred stock in major banks. The Federal Reserve created then-significant amounts of new currency as a method to combat the liquidity trap.
Bailouts came in the form of trillions of dollars of loans, asset purchases, guarantees, and direct spending. Significant controversy accompanied the bailouts, such as in the case of the AIG bonus payments controversy, leading to the development of a variety of "decision making frameworks", to help balance competing policy interests during times of financial crisis. Alistair Darling, the U.K.'s Chancellor of the Exchequer at the time of the crisis, stated in 2018 that Britain came within hours of "a breakdown of law and order" the day that Royal Bank of Scotland was bailed-out.
Instead of financing more domestic loans, some banks instead spent some of the stimulus money in more profitable areas such as investing in emerging markets and foreign currencies.
In July 2010, the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act was enacted in the United States to "promote the financial stability of the United States". The Basel III capital and liquidity standards were adopted worldwide. Since the 2008 financial crisis, consumer regulators in America have more closely supervised sellers of credit cards and home mortgages in order to deter anticompetitive practices that led to the crisis.
At least two major reports on the causes of the crisis were produced by the U.S. Congress: the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission report, released January 2011, and a report by the United States Senate Homeland Security Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations entitled Wall Street and the Financial Crisis: Anatomy of a Financial Collapse, released April 2011.
In total, 47 bankers served jail time as a result of the crisis, over half of which were from Iceland, where the crisis was the most severe and led to the collapse of all 3 of the major Icelandic banks. In April 2012, Geir Haarde of Iceland became the only politician to be convicted as a result of the crisis. Only one banker in the United States served jail time as a result of the crisis, Kareem Serageldin, a banker at Credit Suisse who was sentenced to 30 months in jail and returned $25.6 million in compensation for manipulating bond prices to hide $1 billion of losses. No individuals in the United Kingdom were convicted as a result of the crisis. Goldman Sachs paid $550 million to settle fraud charges after allegedly anticipating the crisis and selling toxic investments to its clients.
With fewer resources to risk in creative destruction, the number of patent applications was flat, compared to exponential increases in patent application in prior years.
Typical American families did not fare well, nor did the "wealthy-but-not-wealthiest" families just beneath the pyramid's top. However, half of the poorest families in the United States did not have wealth declines at all during the crisis because they generally did not own financial investments whose value can fluctuate. The Federal Reserve surveyed 4,000 households between 2007 and 2009, and found that the total wealth of 63% of all Americans declined in that period and 77% of the richest families had a decrease in total wealth, while only 50% of those on the bottom of the pyramid suffered a decrease.
History
Timeline
Following is a timeline of major events during the financial crisis, including government responses, and the subsequent economic recovery:
- May 19, 2005: Fund manager Michael Burry closed a Credit Default Swap against subprime mortgage bonds with Deutsche Bank valued at $60 million – the first such CDS. He projected they would become volatile within two years of the low "teaser rate" of the mortgages expiring.
- 2006: After years of above-average price increases, housing prices peaked and mortgage loan delinquency rose, leading to the United States housing bubble. Due to increasingly lax underwriting standards—which were inevitable in light of government mandates that required 30–55% of all mortgages sold to Fannie and Freddie to be subprime—one-third of all mortgages in 2006 were such loans, which comprised 17–20% of loan originations.
- February 27, 2007: Stock prices in China and the U.S. fell by the most since 2003 as reports of a decline in home prices and durable goods orders stoked growth fears, with Alan Greenspan predicting a recession. Due to increased delinquency rates in subprime lending, Freddie Mac said that it would stop investing in certain subprime loans.
- April 2, 2007: New Century, an American real estate investment trust specializing in Subprime lending and securitization, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. This propagated the subprime mortgage crisis.
- June 20, 2007: After receiving margin calls, Bear Stearns bailed out two of its hedge funds with $20 billion of exposure to collateralized debt obligations including subprime mortgages. Bear Stearns said that the problem was contained.
- July 31, 2007: Bear Stearns liquidated the two hedge funds.
- August 6, 2007: American Home Mortgage filed bankruptcy.
- August 9, 2007: BNP Paribas blocked withdrawals from three of its hedge funds with a total of $2.2 billion in assets under management, due to "a complete evaporation of liquidity", making valuation of the funds impossible – a clear sign that banks were refusing to do business with each other.
- September 14, 2007: Northern Rock, a medium-sized and highly leveraged British bank, received support from the Bank of England. This led to investor panic and a bank run.
- September 18, 2007: The Federal Open Market Committee began reducing the federal funds rate from its peak of 5.25% in response to worries about liquidity and confidence.
- September 28, 2007: NetBank suffered from bank failure and filed bankruptcy due to exposure to home loans.
- October 9, 2007: The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) hit its peak closing price of 14,164.53.
- October 15, 2007: Citigroup, Bank of America, and JPMorgan Chase announced plans for the $80 billion Master Liquidity Enhancement Conduit to provide liquidity to structured investment vehicles. The plan was abandoned in December.
- December 17, 2007: Delta Financial Corporation filed bankruptcy after failing to securitize subprime loans.
- December 12, 2007: The Federal Reserve instituted the Term auction facility to supply short-term credit to banks with sub-prime mortgages.
- January 11, 2008: Bank of America agreed to buy Countrywide Financial for $4 billion in stock.
- January 18, 2008: Stock markets fell to a yearly low as the credit rating of Ambac, a bond insurance company was downgraded.
- January 2008: U.S. stocks had the worst January since 2000 over concerns about the exposure of companies that issue bond insurance.
- February 13, 2008: The Economic Stimulus Act of 2008 was enacted, which included a tax rebate.
- February 22, 2008: The nationalisation of Northern Rock was completed.
- March 5, 2008: The Carlyle Group received margin calls on its mortgage bond fund.
- March 17, 2008: Bear Stearns, with $46 billion of mortgage assets that had not been written down and $10 trillion in total assets, faced bankruptcy; instead, in its first emergency meeting in 30 years, the Federal Reserve agreed to guarantee its bad loans to facilitate its acquisition by JPMorgan Chase for $2/share. A week earlier, the stock was trading at $60/share and a year earlier it traded for $178/share. The buyout price was increased to $10/share the following week.
- March 18, 2008: In a contentious meeting, the Federal Reserve cut the federal funds rate by 75 basis points, its 6th cut in 6 months. It also allowed Fannie Mae & Freddie Mac to buy $200 billion in subprime mortgages from banks. Officials thought this would contain the possible crisis. The U.S. dollar weakened and commodity prices soared.
- Late June 2008: Despite the U.S. stock market falling to a 20% drop off its highs, commodity-related stocks soared as oil traded above $140/barrel for the first time and steel prices rose above $1,000 per ton. Worries about inflation combined with strong demand from China encouraged people to invest in commodities during the 2000s commodities boom.
- July 11, 2008: IndyMac failed.
- July 30, 2008: The Housing and Economic Recovery Act of 2008 was enacted.
- September 7, 2008: The Federal takeover of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac was implemented.
- September 15, 2008: After the Federal Reserve declined to guarantee its loans as it did for Bear Stearns, the Bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers led to a 504-point drop in the DJIA, its worst decline in seven years. To avoid bankruptcy, Merrill Lynch was acquired by Bank of America for $50 billion in a transaction facilitated by the government. Lehman had been in talks to be sold to either Bank of America or Barclays but neither bank wanted to acquire the entire company.
- September 16, 2008: The Federal Reserve took over American International Group with $85 billion in debt and equity funding. The Reserve Primary Fund "broke the buck" as a result its exposure to Lehman Brothers securities.
- September 17, 2008: Investors withdrew $144 billion from U.S. money market funds, the equivalent of a bank run on money market funds, which frequently invest in commercial paper issued by corporations to fund their operations and payrolls, causing the short-term lending market to freeze. The withdrawal compared to $7.1 billion in withdrawals the week prior. This interrupted the ability of corporations to rollover their short-term debt. The U.S. government extended insurance for money market accounts analogous to bank deposit insurance via a temporary guarantee and with Federal Reserve programs to purchase commercial paper.
- September 18, 2008: In a dramatic meeting, United States Secretary of the Treasury Henry Paulson and Chair of the Federal Reserve Ben Bernanke met with Speaker of the United States House of Representatives Nancy Pelosi and warned that the credit markets were close to a complete meltdown. Bernanke requested a $700 billion fund to acquire toxic mortgages and reportedly told them: "If we don't do this, we may not have an economy on Monday."
- September 19, 2008: The Federal Reserve created the Asset Backed Commercial Paper Money Market Mutual Fund Liquidity Facility to temporarily insure money market funds and allow the credit markets to continue operating.
- September 20, 2008: Paulson requested the U.S. Congress authorize a $700 billion fund to acquire toxic mortgages, telling Congress "If it doesn't pass, then heaven help us all."
- September 21, 2008: Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley converted from investment banks to bank holding companies to increase their protection by the Federal Reserve.
- September 22, 2008: MUFG Bank acquired 20% of Morgan Stanley.
- September 23, 2008: Berkshire Hathaway made a $5 billion investment in Goldman Sachs.
- September 26, 2008: Washington Mutual went bankrupt and was seized by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation after a bank run in which panicked depositors withdrew $16.7 billion in 10 days.
- September 29, 2008: By a vote of 225–208, with most Democrats in support and Republicans against, the House of Representatives rejected the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008, which included the $700 billion Troubled Asset Relief Program. In response, the DJIA dropped 777.68 points, or 7%, its largest point drop in history. The S&P 500 Index fell 8.8% and the Nasdaq Composite fell 9.1%. Several stock market indices worldwide fell 10%. Gold prices soared to $900/ounce. The Federal Reserve doubled its credit swaps with foreign central banks as they all needed to provide liquidity. Wachovia reached a deal to sell itself to Citigroup; however, the deal would have made shares worthless and required government funding.
- September 30, 2008: President George W. Bush addressed the country, saying "Congress must act. ...Our economy is depending on decisive action from the government. The sooner we address the problem, the sooner we can get back on the path of growth and job creation." The DJIA rebounded 4.7%.
- October 1, 2008: The U.S. Senate passed the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008.
- October 2, 2008: Stock market indices fell 4% as investors were nervous ahead of a vote in the U.S. House of Representatives on the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008.
- October 3, 2008: The House of Representatives passed the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008. Bush signed the legislation that same day. Wachovia reached a deal to be acquired by Wells Fargo in a deal that did not require government funding.
- October 6–10, 2008: From October 6–10, 2008, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) closed lower in all five sessions. Volume levels were record-breaking. The DJIA fell over 1,874 points, or 18%, in its worst weekly decline ever on both a points and percentage basis. The S&P 500 fell more than 20%.
- October 7, 2008: In the U.S., per the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation increased deposit insurance coverage to $250,000 per depositor.
- October 8, 2008: The Indonesian stock market halted trading after a 10% drop in one day.
- October 11, 2008: The head of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) warned that the world financial system was teetering on the "brink of systemic meltdown".
- October 14, 2008: Having been suspended for three successive trading days (October 9, 10, and 13), the Icelandic stock market reopened on October 14, with the main index, the OMX Iceland 15, closing at 678.4, which was about 77% lower than the 3,004.6 at the close on October 8, after the value of the three big banks, which had formed 73.2% of the value of the OMX Iceland 15, had been set to zero, leading to the 2008–2011 Icelandic financial crisis. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation created the Temporary Liquidity Guarantee Program to guarantee the senior debt of all FDIC-insured institutions through June 30, 2009.
- October 16, 2008: A rescue plan was unveiled for Swiss banks UBS AG and Credit Suisse.
- October 24, 2008: Many of the world's stock exchanges experienced the worst declines in their history, with drops of around 10% in most indices. In the U.S., the DJIA fell 3.6%, although not as much as other markets. The United States dollar and Japanese yen and the Swiss franc soared against other major currencies, particularly the British pound and Canadian dollar, as world investors sought safe havens. A currency crisis developed, with investors transferring vast capital resources into stronger currencies, leading many governments of emerging economies to seek aid from the International Monetary Fund. Later that day, the deputy governor of the Bank of England, Charlie Bean, suggested that "This is a once in a lifetime crisis, and possibly the largest financial crisis of its kind in human history." In a transaction pushed by regulators, PNC Financial Services agreed to acquire National City Corp.
- November 6, 2008: The IMF predicted a worldwide recession of −0.3% for 2009. On the same day, the Bank of England and the European Central Bank, respectively, reduced their interest rates from 4.5% to 3%, and from 3.75% to 3.25%.
- November 10, 2008: American Express converted to a bank holding company.
- November 20, 2008: Iceland obtained an emergency loan from the International Monetary Fund after the failure of banks in Iceland resulted in a devaluation of the Icelandic króna and threatened the government with bankruptcy.
- November 25, 2008: The Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility was announced.
- November 29, 2008: Economist Dean Baker observed:
There is a really good reason for tighter credit. Tens of millions of homeowners who had substantial equity in their homes two years ago have little or nothing today. Businesses are facing the worst downturn since the Great Depression. This matters for credit decisions. A homeowner with equity in her home is very unlikely to default on a car loan or credit card debt. They will draw on this equity rather than lose their car and/or have a default placed on their credit record. On the other hand, a homeowner who has no equity is a serious default risk. In the case of businesses, their creditworthiness depends on their future profits. Profit prospects look much worse in November 2008 than they did in November 2007... While many banks are obviously at the brink, consumers and businesses would be facing a much harder time getting credit right now even if the financial system were rock solid. The problem with the economy is the loss of close to $6 trillion in housing wealth and an even larger amount of stock wealth.
- December 6, 2008: The 2008 Greek riots began, sparked in part by economic conditions in the country.
- December 16, 2008: The federal funds rate was lowered to zero percent.
- December 20, 2008: Financing under the Troubled Asset Relief Program was made available to General Motors and Chrysler.
- January 6, 2009: Citi argued Singapore in 2009 would experience "the most severe recession in Singapore’s history". In the end the economy grew in 2009 by 3.1% and in 2010
- January 20–26, 2009: The 2009 Icelandic financial crisis protests intensified and the Icelandic government collapsed.
- February 13, 2009: Congress approved the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, a $787 billion economic stimulus package. President Barack Obama signed it the same day.
- February 20, 2009: The DJIA closed at a 6-year low amidst worries that the largest banks in the United States would have to be nationalized.
- February 27, 2009: The DJIA closed its lowest value since 1997 as the U.S. government increased its stake in Citigroup to 36%, raising further fears of nationalization and a report showed that GDP shrank at the sharpest pace in 26 years.
- Early March 2009: The drop in stock prices was compared to that of the Great Depression.
- March 3, 2009: Obama stated that "Buying stocks is a potentially good deal if you've got a long-term perspective on it".
- March 6, 2009: The Dow Jones hit its lowest level of 6,443.27, a drop of 54% from its peak of 14,164 on October 9, 2007, over a span of 17 months, before beginning to recover.
- March 10, 2009: Shares of Citigroup rose 38% after the CEO said that the company was profitable in the first two months of the year and expressed optimism about its capital position going forward. Major stock market indices rose 5-7%, marking the bottom of the stock market decline.
- March 12, 2009: Stock market indices in the U.S. rose another 4% after Bank of America said it was profitable in January and February and would likely not need more government funding. Bernie Madoff was convicted.
- First quarter of 2009: For the first quarter of 2009, the annualized rate of decline in GDP was 14.4% in Germany, 15.2% in Japan, 7.4% in the UK, 18% in Latvia, 9.8% in the Euro area and 21.5% for Mexico.
- April 2, 2009: Unrest over economic policy and bonuses paid to bankers resulted in the 2009 G-20 London summit protests.
- April 10, 2009: Time magazine declared "More Quickly Than It Began, The Banking Crisis Is Over."
- April 29, 2009: The Federal Reserve projected GDP growth of 2.5–3% in 2010; an unemployment plateau in 2009 and 2010 around 10% with moderation in 2011; and inflation rates around 1–2%.
- May 1, 2009: People protested economic conditions globally during the 2009 May Day protests.
- May 20, 2009: President Obama signed the Fraud Enforcement and Recovery Act of 2009.
- June 2009: The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) declared June 2009 as the end date of the U.S. recession. The Federal Open Market Committee release in June 2009 stated:
...the pace of economic contraction is slowing. Conditions in financial markets have generally improved in recent months. Household spending has shown further signs of stabilizing but remains constrained by ongoing job losses, lower housing wealth, and tight credit. Businesses are cutting back on fixed investment and staffing but appear to be making progress in bringing inventory stocks into better alignment with sales. Although economic activity is likely to remain weak for a time, the Committee continues to anticipate that policy actions to stabilize financial markets and institutions, fiscal and monetary stimulus, and market forces will contribute to a gradual resumption of sustainable economic growth in a context of price stability.
- June 17, 2009: Barack Obama and key advisers introduced a series of regulatory proposals that addressed consumer protection, executive pay, bank capital requirements, expanded regulation of the shadow banking system and derivatives, and enhanced authority for the Federal Reserve to safely wind-down systemically important institutions.
- December 11, 2009: United States House of Representatives passed bill H.R.4173, a precursor to what became the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act.
- January 22, 2010: President Obama introduced "The Volcker Rule" limiting the ability of banks to engage in proprietary trading, named after Paul Volcker, who publicly argued for the proposed changes. Obama also proposed a Financial Crisis Responsibility Fee on large banks.
- January 27, 2010: President Obama declared on "the markets are now stabilized, and we've recovered most of the money we spent on the banks."
- First quarter 2010: Delinquency rates in the United States peaked at 11.54%.
- April 15, 2010: U.S. Senate introduced bill S.3217, Restoring American Financial Stability Act of 2010.
- May 2010: The U.S. Senate passed the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. The Volcker Rule against proprietary trading was not part of the legislation.
- July 21, 2010: Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act enacted.
- September 12, 2010: European regulators introduced Basel III regulations for banks, which increased capital ratios, limits on leverage, narrowed the definition of capital to exclude subordinated debt, limited counter-party risk, and added liquidity requirements. Critics argued that Basel III didn't address the problem of faulty risk-weightings. Major banks suffered losses from AAA-rated created by financial engineering (which creates apparently risk-free assets out of high risk collateral) that required less capital according to Basel II. Lending to AA-rated sovereigns has a risk-weight of zero, thus increasing lending to governments and leading to the next crisis. Johan Norberg argued that regulations (Basel III among others) have indeed led to excessive lending to risky governments (see European sovereign-debt crisis) and the European Central Bank pursues even more lending as the solution.
- November 3, 2010: To improve economic growth, the Federal Reserve announced another round of quantitative easing, dubbed QE2, which included the purchase of $600 billion in long-term Treasuries over the following eight months.
- March 2011: Two years after the nadir of the crisis, many stock market indices were 75% above their lows set in March 2009. Nevertheless, the lack of fundamental changes in banking and financial markets worried many market participants, including the International Monetary Fund.
- 2011: Median household wealth fell 35% in the U.S., from $106,591 to $68,839 between 2005 and 2011.
- July 26, 2012: During the European debt crisis, President of the European Central Bank Mario Draghi announced that "The ECB is ready to do whatever it takes to preserve the euro."
- August 2012: In the United States, many homeowners still faced foreclosure and could not refinance or modify their mortgages. Foreclosure rates remained high.
- September 13, 2012: To improve lower interest rates, support mortgage markets, and make financial conditions more accommodative, the Federal Reserve announced another round of quantitative easing, dubbed QE3, which included the purchase of $40 billion in long-term Treasuries each month.
- 2014: A report showed that the distribution of household incomes in the United States became more unequal during the post-2008 economic recovery, a first for the United States but in line with the trend over the last ten economic recoveries since 1949. Income inequality in the United States grew from 2005 to 2012 in more than 2 out of 3 metropolitan areas.
- June 2015: A study commissioned by the ACLU found that white home-owning households recovered from the financial crisis faster than black home-owning households, widening the racial wealth gap in the U.S.
- 2017: Per the International Monetary Fund, from 2007 to 2017, "advanced" economies accounted for only 26.5% of global GDP (PPP) growth while emerging and developing economies accounted for 73.5% of global GDP (PPP) growth.
In the table, the names of emerging and developing economies are shown in boldface type, while the names of developed economies are in Roman (regular) type.
| Economy | Incremental GDP (billions in USD)
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (01) |
14,147
| ||||||||
| (02) |
5,348
| ||||||||
| (03) |
4,913
| ||||||||
| (—) |
4,457
| ||||||||
| (04) |
1,632
| ||||||||
| (05) |
1,024
| ||||||||
| (06) |
1,003
| ||||||||
| (07) |
984
| ||||||||
| (08) |
934
| ||||||||
| (09) |
919
| ||||||||
| (10) |
744
| ||||||||
| (11) |
733
| ||||||||
| (12) |
700
| ||||||||
| (13) |
671
| ||||||||
| (14) |
566
| ||||||||
| (15) |
523
| ||||||||
| (16) |
505
| ||||||||
| (17) |
482
| ||||||||
| (18) |
462
| ||||||||
| (19) |
447
| ||||||||
| (20) |
440
| ||||||||
|
The twenty largest economies contributing to global GDP (PPP) growth (2007–2017) | |||||||||
Causes
While the causes of the bubble are disputed, the precipitating factor for the Financial Crisis of 2007–2008 was the bursting of the United States housing bubble and the subsequent subprime mortgage crisis, which occurred due to a high default rate and resulting foreclosures of mortgage loans, particularly adjustable-rate mortgages. Some or all of the following factors contributed to the crisis:
- Government mandates forced banks to extend loans to borrowers previously considered uncreditworthy, leading to increasingly lax underwriting standards and high mortgage approval rates. These, in turn, led to an increase in the number of homebuyers, which drove up housing prices. This appreciation in value led many homeowners to borrow against the equity in their homes as an apparent windfall, leading to over-leveraging.
- The high delinquency and default rates by homeowners, particularly those with subprime credit, led to a rapid devaluation of mortgage-backed securities including bundled loan portfolios, derivatives and credit default swaps. As the value of these assets plummeted, buyers for these securities evaporated and banks who were heavily invested in these assets began to experience a liquidity crisis.
- Securitization allowed for shifting of risk and lax underwriting standards: Many mortgages were bundled together and formed into new financial instruments called mortgage-backed securities, in a process known as securitization. These bundles could be sold as (ostensibly) low-risk securities partly because they were often backed by credit default swaps insurance. Because mortgage lenders could pass these mortgages (and the associated risks) on in this way, they could and did adopt loose underwriting criteria.
- Lax regulation allowed predatory lending in the private sector, especially after the federal government overrode anti-predatory state laws in 2004.
- The Community Reinvestment Act (CRA), a 1977 U.S. federal law designed to help low- and moderate-income Americans get mortgage loans required banks to grant mortgages to higher risk families.
- Reckless lending by lenders such as Bank of America's Countrywide Financial unit was increasingly incentivized and even mandated by government regulation. This may have caused Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to lose market share and to respond by lowering their own standards.
- Mortgage guarantees by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, quasi-government agencies, which purchased many subprime loan securitizations. The implicit guarantee by the U.S. federal government created a moral hazard and contributed to a glut of risky lending.
- Government policies that encouraged home ownership, providing easier access to loans for subprime borrowers; overvaluation of bundled subprime mortgages based on the theory that housing prices would continue to escalate; questionable trading practices on behalf of both buyers and sellers; compensation structures by banks and mortgage originators that prioritize short-term deal flow over long-term value creation; and a lack of adequate capital holdings from banks and insurance companies to back the financial commitments they were making.
- The Wall Street and the Financial Crisis: Anatomy of a Financial Collapse (Levin–Coburn Report) by the United States Senate concluded that the crisis was the result of "high risk, complex financial products; undisclosed conflicts of interest; the failure of regulators, the credit rating agencies, and the market itself to rein in the excesses of Wall Street".
- In its January 2011 report, the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission (FCIC, a committee of U.S. congressmen) concluded that the financial crisis was avoidable and was caused by:
- "widespread failures in financial regulation and supervision", including the Federal Reserve's failure to stem the tide of Toxic assets;
- "dramatic failures of corporate governance and risk management at many systemically important financial institutions" including too many financial firms acting recklessly and taking on too much risk;
- "a combination of excessive borrowing, risky investments, and lack of transparency" by financial institutions and by households that put the financial system on a collision course with crisis;
- ill preparation and inconsistent action by government and key policy makers lacking a full understanding of the financial system they oversaw that "added to the uncertainty and panic"
- a "systemic breakdown in accountability and ethics" at all levels.
- "collapsing mortgage-lending standards and the mortgage securitization pipeline"
- deregulation of over-the-counter derivatives, especially credit default swaps
- "the failures of credit rating agencies" to correctly price risk
- The 1999 Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, which partially repealed the Glass-Steagall Act effectively removed the separation between investment banks and depository banks in the United States and increased speculation on the part of depository banks.
- Credit rating agencies and investors failed to accurately price the financial risk involved with mortgage loan-related financial products, and governments did not adjust their regulatory practices to address changes in financial markets.
- Variations in the cost of borrowing.
- Fair value accounting was issued as U.S. accounting standard SFAS 157 in 2006 by the privately run Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)—delegated by the SEC with the task of establishing financial reporting standards. This required that tradable assets such as mortgage securities be valued according to their current market value rather than their historic cost or some future expected value. When the market for such securities became volatile and collapsed, the resulting loss of value had a major financial effect upon the institutions holding them even if they had no immediate plans to sell them.
- Easy availability of credit in the US, fueled by large inflows of foreign funds after the 1998 Russian financial crisis and 1997 Asian financial crisis of the 1997–1998 period, led to a housing construction boom and facilitated debt-financed consumer spending. As banks began to give out more loans to potential home owners, housing prices began to rise. Lax lending standards and rising real estate prices also contributed to the real estate bubble. Loans of various types (e.g., mortgage, credit card, and auto) were easy to obtain and consumers assumed an unprecedented debt load.
- As part of the housing and credit booms, the number of mortgage-backed securities (MBS) and collateralized debt obligations (CDO), which derived their value from mortgage payments and housing prices, greatly increased. Such financial innovation enabled institutions and investors to invest in the U.S. housing market. As housing prices declined, these investors reported significant losses.
- Falling prices also resulted in homes worth less than the mortgage loans, providing borrowers with a financial incentive to enter foreclosure. Foreclosure levels were elevated until early 2014. drained significant wealth from consumers, losing up to $4.2 trillion Defaults and losses on other loan types also increased significantly as the crisis expanded from the housing market to other parts of the economy. Total losses were estimated in the trillions of U.S. dollars globally.
- Financialization - the increased use of leverage in the financial system.
- Financial institutions such as investment banks and hedge funds, as well as certain, differently regulated banks, assumed significant debt burdens while providing the loans described above and did not have a financial cushion sufficient to absorb large loan defaults or losses. These losses affected the ability of financial institutions to lend, slowing economic activity.
Subprime lending
The relaxing of credit lending standards by investment banks and commercial banks allowed for a significant increase in subprime lending. Subprime had not become less risky; Wall Street just accepted this higher risk.
Due to competition between mortgage lenders for revenue and market share, and when the supply of creditworthy borrowers was limited, mortgage lenders relaxed underwriting standards and originated riskier mortgages to less creditworthy borrowers. In the view of some analysts, the relatively conservative government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) policed mortgage originators and maintained relatively high underwriting standards prior to 2003. However, as market power shifted from securitizers to originators, and as intense competition from private securitizers undermined GSE power, mortgage standards declined and risky loans proliferated. The riskiest loans were originated in 2004–2007, the years of the most intense competition between securitizers and the lowest market share for the GSEs. The GSEs eventually relaxed their standards to try to catch up with the private banks.
A contrarian view is that Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac led the way to relaxed underwriting standards, starting in 1995, by advocating the use of easy-to-qualify automated underwriting and appraisal systems, by designing no-down-payment products issued by lenders, by the promotion of thousands of small mortgage brokers, and by their close relationship to subprime loan aggregators such as Countrywide.
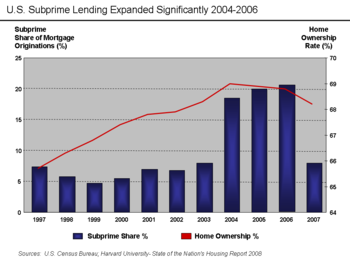
Depending on how "subprime" mortgages are defined, they remained below 10% of all mortgage originations until 2004, when they rose to nearly 20% and remained there through the 2005–2006 peak of the United States housing bubble.
Role of affordable housing programs
The majority report of the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission, written by the six Democratic appointees, the minority report, written by three of the four Republican appointees, studies by Federal Reserve economists, and the work of several independent scholars generally contend that government affordable housing policy was not the primary cause of the financial crisis. Although they concede that governmental policies had some role in causing the crisis, they contend that GSE loans performed better than loans securitized by private investment banks, and performed better than some loans originated by institutions that held loans in their own portfolios.
In his dissent to the majority report of the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission, conservative American Enterprise Institute fellow Peter J. Wallison stated his belief that the roots of the financial crisis can be traced directly and primarily to affordable housing policies initiated by the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) in the 1990s and to massive risky loan purchases by government-sponsored entities Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. Based upon information in the SEC's December 2011 securities fraud case against six former executives of Fannie and Freddie, Peter Wallison and Edward Pinto estimated that, in 2008, Fannie and Freddie held 13 million substandard loans totaling over $2 trillion.
In the early and mid-2000s, the Bush administration called numerous times for investigations into the safety and soundness of the GSEs and their swelling portfolio of subprime mortgages. On September 10, 2003, the United States House Committee on Financial Services held a hearing, at the urging of the administration, to assess safety and soundness issues and to review a recent report by the Office of Federal Housing Enterprise Oversight (OFHEO) that had uncovered accounting discrepancies within the two entities. The hearings never resulted in new legislation or formal investigation of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, as many of the committee members refused to accept the report and instead rebuked OFHEO for their attempt at regulation. Some, such as Wallison, believe this was an early warning to the systemic risk that the growing market in subprime mortgages posed to the U.S. financial system that went unheeded.
A 2000 United States Department of the Treasury study of lending trends for 305 cities from 1993 to 1998 showed that $467 billion of mortgage lending was made by Community Reinvestment Act (CRA)-covered lenders into low and mid level income (LMI) borrowers and neighborhoods, representing 10% of all U.S. mortgage lending during the period. The majority of these were prime loans. Sub-prime loans made by CRA-covered institutions constituted a 3% market share of LMI loans in 1998, but in the run-up to the crisis, fully 25% of all subprime lending occurred at CRA-covered institutions and another 25% of subprime loans had some connection with CRA. However, most sub-prime loans were not made to the LMI borrowers targeted by the CRA, especially in the years 2005–2006 leading up to the crisis, nor did it find any evidence that lending under the CRA rules increased delinquency rates or that the CRA indirectly influenced independent mortgage lenders to ramp up sub-prime lending.
To other analysts the delay between CRA rule changes in 1995 and the explosion of subprime lending is not surprising, and does not exonerate the CRA. They contend that there were two, connected causes to the crisis: the relaxation of underwriting standards in 1995 and the ultra-low interest rates initiated by the Federal Reserve after the terrorist attack on September 11, 2001. Both causes had to be in place before the crisis could take place. Critics also point out that publicly announced CRA loan commitments were massive, totaling $4.5 trillion in the years between 1994 and 2007. They also argue that the Federal Reserve's classification of CRA loans as "prime" is based on the faulty and self-serving assumption that high-interest-rate loans (3 percentage points over average) equal "subprime" loans.
Others have pointed out that there were not enough of these loans made to cause a crisis of this magnitude. In an article in Portfolio Magazine, Michael Lewis spoke with one trader who noted that "There weren't enough Americans with [bad] credit taking out [bad loans] to satisfy investors' appetite for the end product." Essentially, investment banks and hedge funds used financial innovation to enable large wagers to be made, far beyond the actual value of the underlying mortgage loans, using derivatives called credit default swaps, collateralized debt obligations and synthetic CDOs.
By March 2011, the FDIC had paid out $9 billion to cover losses on bad loans at 165 failed financial institutions. The Congressional Budget Office estimated, in June 2011, that the bailout to Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac exceeds $300 billion (calculated by adding the fair value deficits of the entities to the direct bailout funds at the time).
Economist Paul Krugman argued in January 2010 that the simultaneous growth of the residential and commercial real estate pricing bubbles and the global nature of the crisis undermines the case made by those who argue that Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, CRA, or predatory lending were primary causes of the crisis. In other words, bubbles in both markets developed even though only the residential market was affected by these potential causes.
Countering Krugman, Wallison wrote: "It is not true that every bubble—even a large bubble—has the potential to cause a financial crisis when it deflates." Wallison notes that other developed countries had "large bubbles during the 1997–2007 period" but "the losses associated with mortgage delinquencies and defaults when these bubbles deflated were far lower than the losses suffered in the United States when the 1997–2007 [bubble] deflated." According to Wallison, the reason the U.S. residential housing bubble (as opposed to other types of bubbles) led to financial crisis was that it was supported by a huge number of substandard loans—generally with low or no downpayments.
Krugman's contention (that the growth of a commercial real estate bubble indicates that U.S. housing policy was not the cause of the crisis) is challenged by additional analysis. After researching the default of commercial loans during the financial crisis, Xudong An and Anthony B. Sanders reported (in December 2010): "We find limited evidence that substantial deterioration in CMBS [commercial mortgage-backed securities] loan underwriting occurred prior to the crisis." Other analysts support the contention that the crisis in commercial real estate and related lending took place after the crisis in residential real estate. Business journalist Kimberly Amadeo reported: "The first signs of decline in residential real estate occurred in 2006. Three years later, commercial real estate started feeling the effects. Denice A. Gierach, a real estate attorney and CPA, wrote:
... most of the commercial real estate loans were good loans destroyed by a really bad economy. In other words, the borrowers did not cause the loans to go bad-it was the economy.
Growth of the housing bubble
Between 1998 and 2006, the price of the typical American house increased by 124%. During the 1980s and 1990s, the national median home price ranged from 2.9 to 3.1 times median household income. By contrast, this ratio increased to 4.0 in 2004, and 4.6 in 2006. This housing bubble resulted in many homeowners refinancing their homes at lower interest rates, or financing consumer spending by taking out second mortgages secured by the price appreciation.
In a Peabody Award winning program, NPR correspondents argued that a "Giant Pool of Money" (represented by $70 trillion in worldwide fixed income investments) sought higher yields than those offered by U.S. Treasury bonds early in the decade. This pool of money had roughly doubled in size from 2000 to 2007, yet the supply of relatively safe, income generating investments had not grown as fast. Investment banks on Wall Street answered this demand with products such as the mortgage-backed security and the collateralized debt obligation that were assigned safe ratings by the credit rating agencies.
In effect, Wall Street connected this pool of money to the mortgage market in the US, with enormous fees accruing to those throughout the mortgage supply chain, from the mortgage broker selling the loans to small banks that funded the brokers and the large investment banks behind them. By approximately 2003, the supply of mortgages originated at traditional lending standards had been exhausted, and continued strong demand began to drive down lending standards.
The collateralized debt obligation in particular enabled financial institutions to obtain investor funds to finance subprime and other lending, extending or increasing the housing bubble and generating large fees. This essentially places cash payments from multiple mortgages or other debt obligations into a single pool from which specific securities draw in a specific sequence of priority. Those securities first in line received investment-grade ratings from rating agencies. Securities with lower priority had lower credit ratings but theoretically a higher rate of return on the amount invested.
By September 2008, average U.S. housing prices had declined by over 20% from their mid-2006 peak. As prices declined, borrowers with adjustable-rate mortgages could not refinance to avoid the higher payments associated with rising interest rates and began to default. During 2007, lenders began foreclosure proceedings on nearly 1.3 million properties, a 79% increase over 2006. This increased to 2.3 million in 2008, an 81% increase vs. 2007. By August 2008, approximately 9% of all U.S. mortgages outstanding were either delinquent or in foreclosure. By September 2009, this had risen to 14.4%.
After the bubble burst, Australian economist John Quiggin wrote, "And, unlike the Great Depression, this crisis was entirely the product of financial markets. There was nothing like the postwar turmoil of the 1920s, the struggles over gold convertibility and reparations, or the Smoot-Hawley tariff, all of which have shared the blame for the Great Depression." Instead, Quiggin lays the blame for the 2008 near-meltdown on financial markets, on political decisions to lightly regulate them, and on rating agencies which had self-interested incentives to give good ratings.
Easy credit conditions
Lower interest rates encouraged borrowing. From 2000 to 2003, the Federal Reserve lowered the federal funds rate target from 6.5% to 1.0%. This was done to soften the effects of the collapse of the dot-com bubble and the September 11 attacks, as well as to combat a perceived risk of deflation. As early as 2002, it was apparent that credit was fueling housing instead of business investment as some economists went so far as to advocate that the Fed "needs to create a housing bubble to replace the Nasdaq bubble". Moreover, empirical studies using data from advanced countries show that excessive credit growth contributed greatly to the severity of the crisis.
Additional downward pressure on interest rates was created by the high and rising U.S. current account deficit, which peaked along with the housing bubble in 2006. Federal Reserve chairman Ben Bernanke explained how trade deficits required the U.S. to borrow money from abroad, in the process bidding up bond prices and lowering interest rates.
Bernanke explained that between 1996 and 2004, the U.S. current account deficit increased by $650 billion, from 1.5% to 5.8% of GDP. Financing these deficits required the country to borrow large sums from abroad, much of it from countries running trade surpluses. These were mainly the emerging economies in Asia and oil-exporting nations. The balance of payments identity requires that a country (such as the US) running a current account deficit also have a capital account (investment) surplus of the same amount. Hence large and growing amounts of foreign funds (capital) flowed into the U.S. to finance its imports.
All of this created demand for various types of financial assets, raising the prices of those assets while lowering interest rates. Foreign investors had these funds to lend either because they had very high personal savings rates (as high as 40% in China) or because of high oil prices. Ben Bernanke referred to this as a "saving glut".
A flood of funds (capital or liquidity) reached the U.S. financial markets. Foreign governments supplied funds by purchasing Treasury bonds and thus avoided much of the direct effect of the crisis. U.S. households, used funds borrowed from foreigners to finance consumption or to bid up the prices of housing and financial assets. Financial institutions invested foreign funds in mortgage-backed securities.
The Fed then raised the Fed funds rate significantly between July 2004 and July 2006. This contributed to an increase in 1-year and 5-year adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) rates, making ARM interest rate resets more expensive for homeowners. This may have also contributed to the deflating of the housing bubble, as asset prices generally move inversely to interest rates, and it became riskier to speculate in housing. U.S. housing and financial assets dramatically declined in value after the housing bubble burst.
Weak and fraudulent underwriting practices
Subprime lending standards declined in the U.S.: in early 2000, a subprime borrower had a FICO score of 660 or less. By 2005, many lenders dropped the required FICO score to 620, making it much easier to qualify for prime loans and making subprime lending a riskier business. Proof of income and assets were de-emphasized. Loans at first required full documentation, then low documentation, then no documentation. One subprime mortgage product that gained wide acceptance was the no income, no job, no asset verification required (NINJA) mortgage. Informally, these loans were aptly referred to as "liar loans" because they encouraged borrowers to be less than honest in the loan application process. Testimony given to the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission by whistleblower Richard M. Bowen III, on events during his tenure as the Business Chief Underwriter for Correspondent Lending in the Consumer Lending Group for Citigroup, where he was responsible for over 220 professional underwriters, suggests that by 2006 and 2007, the collapse of mortgage underwriting standards was endemic. His testimony stated that by 2006, 60% of mortgages purchased by Citigroup from some 1,600 mortgage companies were "defective" (were not underwritten to policy, or did not contain all policy-required documents)—this, despite the fact that each of these 1,600 originators was contractually responsible (certified via representations and warrantees) that its mortgage originations met Citigroup standards. Moreover, during 2007, "defective mortgages (from mortgage originators contractually bound to perform underwriting to Citi's standards) increased ... to over 80% of production".
In separate testimony to the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission, officers of Clayton Holdings, the largest residential loan due diligence and securitization surveillance company in the United States and Europe, testified that Clayton's review of over 900,000 mortgages issued from January 2006 to June 2007 revealed that scarcely 54% of the loans met their originators' underwriting standards. The analysis (conducted on behalf of 23 investment and commercial banks, including 7 "too big to fail" banks) additionally showed that 28% of the sampled loans did not meet the minimal standards of any issuer. Clayton's analysis further showed that 39% of these loans (i.e. those not meeting any issuer's minimal underwriting standards) were subsequently securitized and sold to investors.
Predatory lending
Predatory lending refers to the practice of unscrupulous lenders, enticing borrowers to enter into "unsafe" or "unsound" secured loans for inappropriate purposes.
In June 2008, Countrywide Financial was sued by then California Attorney General Jerry Brown for "unfair business practices" and "false advertising", alleging that Countrywide used "deceptive tactics to push homeowners into complicated, risky, and expensive loans so that the company could sell as many loans as possible to third-party investors". In May 2009, Bank of America modified 64,000 Countrywide loans as a result. When housing prices decreased, homeowners in ARMs then had little incentive to pay their monthly payments, since their home equity had disappeared. This caused Countrywide's financial condition to deteriorate, ultimately resulting in a decision by the Office of Thrift Supervision to seize the lender. One Countrywide employee—who would later plead guilty to two counts of wire fraud and spent 18 months in prison—stated that, "If you had a pulse, we gave you a loan."
Former employees from Ameriquest, which was United States' leading wholesale lender, described a system in which they were pushed to falsify mortgage documents and then sell the mortgages to Wall Street banks eager to make fast profits. There is growing evidence that such mortgage frauds may be a cause of the crisis.
Deregulation and lack of regulation
According to Barry Eichengreen, the roots of the financial crisis lay in the deregulation of financial markets. A 2012 OECD study suggest that bank regulation based on the Basel accords encourage unconventional business practices and contributed to or even reinforced the financial crisis. In other cases, laws were changed or enforcement weakened in parts of the financial system. Key examples include:
- Jimmy Carter's Depository Institutions Deregulation and Monetary Control Act of 1980 (DIDMCA) phased out several restrictions on banks' financial practices, broadened their lending powers, allowed credit unions and savings and loans to offer checkable deposits, and raised the deposit insurance limit from $40,000 to $100,000 (thereby potentially lessening depositor scrutiny of lenders' risk management policies).
- In October 1982, U.S. President Ronald Reagan signed into law the Garn–St. Germain Depository Institutions Act, which provided for adjustable-rate mortgage loans, began the process of banking deregulation, and contributed to the savings and loan crisis of the late 1980s/early 1990s.
- In November 1999, U.S. President Bill Clinton signed into law the Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act, which repealed provisions of the Glass-Steagall Act that prohibited a bank holding company from owning other financial companies. The repeal effectively removed the separation that previously existed between Wall Street investment banks and depository banks, providing a government stamp of approval for a universal risk-taking banking model. Investment banks such as Lehman became competitors with commercial banks. Some analysts say that this repeal directly contributed to the severity of the crisis, while others downplay its impact since the institutions that were greatly affected did not fall under the jurisdiction of the act itself.
- In 2004, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission relaxed the net capital rule, which enabled investment banks to substantially increase the level of debt they were taking on, fueling the growth in mortgage-backed securities supporting subprime mortgages. The SEC conceded that self-regulation of investment banks contributed to the crisis.
- Financial institutions in the shadow banking system are not subject to the same regulation as depository banks, allowing them to assume additional debt obligations relative to their financial cushion or capital base. This was the case despite the Long-Term Capital Management debacle in 1998, in which a highly leveraged shadow institution failed with systemic implications and was bailed out.
- Regulators and accounting standard-setters allowed depository banks such as Citigroup to move significant amounts of assets and liabilities off-balance sheet into complex legal entities called structured investment vehicles, masking the weakness of the capital base of the firm or degree of leverage or risk taken. Bloomberg News estimated that the top four U.S. banks will have to return between $500 billion and $1 trillion to their balance sheets during 2009. This increased uncertainty during the crisis regarding the financial position of the major banks. Off-balance sheet entities were also used in the Enron scandal, which brought down Enron in 2001.
- As early as 1997, Federal Reserve chairman Alan Greenspan fought to keep the derivatives market unregulated. With the advice of the Working Group on Financial Markets, the U.S. Congress and President Bill Clinton allowed the self-regulation of the over-the-counter derivatives market when they enacted the Commodity Futures Modernization Act of 2000. Written by Congress with lobbying from the financial industry, it banned the further regulation of the derivatives market. Derivatives such as credit default swaps (CDS) can be used to hedge or speculate against particular credit risks without necessarily owning the underlying debt instruments. The volume of CDS outstanding increased 100-fold from 1998 to 2008, with estimates of the debt covered by CDS contracts, as of November 2008, ranging from US$33 to $47 trillion. Total over-the-counter (OTC) derivative notional value rose to $683 trillion by June 2008. Warren Buffett famously referred to derivatives as "financial weapons of mass destruction" in early 2003.
A 2011 paper suggested that Canada's avoidance of a banking crisis in 2008 (as well as in prior eras) could be attributed to Canada possessing a single, powerful, overarching regulator, while the United States had a weak, crisis prone and fragmented banking system with multiple competing regulatory bodies.
Increased debt burden or overleveraging
Prior to the crisis, financial institutions became highly leveraged, increasing their appetite for risky investments and reducing their resilience in case of losses. Much of this leverage was achieved using complex financial instruments such as off-balance sheet securitization and derivatives, which made it difficult for creditors and regulators to monitor and try to reduce financial institution risk levels.
U.S. households and financial institutions became increasingly indebted or overleveraged during the years preceding the crisis. This increased their vulnerability to the collapse of the housing bubble and worsened the ensuing economic downturn. Key statistics include:
Free cash used by consumers from home equity extraction doubled from $627 billion in 2001 to $1,428 billion in 2005 as the housing bubble built, a total of nearly $5 trillion over the period, contributing to economic growth worldwide. home mortgage debt relative to GDP increased from an average of 46% during the 1990s to 73% during 2008, reaching $10.5 trillion.
U.S. household debt as a percentage of annual disposable personal income was 127% at the end of 2007, versus 77% in 1990. In 1981, U.S. private debt was 123% of GDP; by the third quarter of 2008, it was 290%.
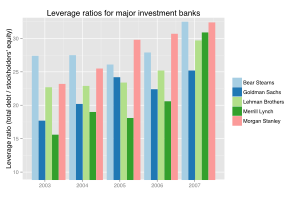
From 2004 to 2007, the top five U.S. investment banks each significantly increased their financial leverage, which increased their vulnerability to a financial shock. Changes in capital requirements, intended to keep U.S. banks competitive with their European counterparts, allowed lower risk weightings for AAA-rated securities. The shift from first-loss tranches to AAA-rated tranches was seen by regulators as a risk reduction that compensated the higher leverage. These five institutions reported over $4.1 trillion in debt for fiscal year 2007, about 30% of U.S. nominal GDP for 2007. Lehman Brothers went bankrupt and was liquidated, Bear Stearns and Merrill Lynch were sold at fire-sale prices, and Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley became commercial banks, subjecting themselves to more stringent regulation. With the exception of Lehman, these companies required or received government support.
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, two U.S. government-sponsored enterprises, owned or guaranteed nearly $5trillion in mortgage obligations at the time they were placed into conservatorship by the U.S. government in September 2008.
These seven entities were highly leveraged and had $9 trillion in debt or guarantee obligations; yet they were not subject to the same regulation as depository banks.
Behavior that may be optimal for an individual such as saving more during adverse economic conditions, can be detrimental if too many individuals pursue the same behavior, as ultimately one person's consumption is another person's income. Too many consumers attempting to save or pay down debt simultaneously is called the paradox of thrift and can cause or deepen a recession. Economist Hyman Minsky also described a "paradox of deleveraging" as financial institutions that have too much leverage (debt relative to equity) cannot all de-leverage simultaneously without significant declines in the value of their assets.
In April 2009, Federal Reserve vice-chair Janet Yellen discussed these paradoxes:
Once this massive credit crunch hit, it didn't take long before we were in a recession. The recession, in turn, deepened the credit crunch as demand and employment fell, and credit losses of financial institutions surged. Indeed, we have been in the grips of precisely this adverse feedback loop for more than a year. A process of balance sheet deleveraging has spread to nearly every corner of the economy. Consumers are pulling back on purchases, especially on durable goods, to build their savings. Businesses are cancelling planned investments and laying off workers to preserve cash. And, financial institutions are shrinking assets to bolster capital and improve their chances of weathering the current storm. Once again, Minsky understood this dynamic. He spoke of the paradox of deleveraging, in which precautions that may be smart for individuals and firms—and indeed essential to return the economy to a normal state—nevertheless magnify the distress of the economy as a whole.
Financial innovation and complexity
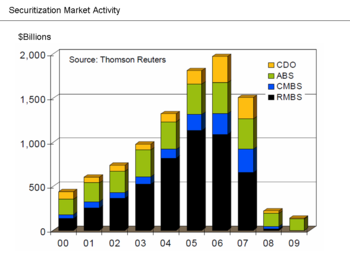
The term financial innovation refers to the ongoing development of financial products designed to achieve particular client objectives, such as offsetting a particular risk exposure (such as the default of a borrower) or to assist with obtaining financing. Examples pertinent to this crisis included: the adjustable-rate mortgage; the bundling of subprime mortgages into mortgage-backed securities (MBS) or collateralized debt obligations (CDO) for sale to investors, a type of securitization; and a form of credit insurance called credit default swaps (CDS). The usage of these products expanded dramatically in the years leading up to the crisis. These products vary in complexity and the ease with which they can be valued on the books of financial institutions.
CDO issuance grew from an estimated $20 billion in Q1 2004 to its
peak of over $180 billion by Q1 2007, then declined back under $20
billion by Q1 2008. Further, the credit quality of CDO's declined from
2000 to 2007, as the level of subprime and other non-prime mortgage debt
increased from 5% to 36% of CDO assets. As described in the section on
subprime lending, the CDS and portfolio of CDS called synthetic CDO
enabled a theoretically infinite amount to be wagered on the finite
value of housing loans outstanding, provided that buyers and sellers of
the derivatives could be found. For example, buying a CDS to insure a
CDO ended up giving the seller the same risk as if they owned the CDO,
when those CDO's became worthless.
This boom in innovative financial products went hand in hand with more complexity. It multiplied the number of actors connected to a single mortgage (including mortgage brokers, specialized originators, the securitizers and their due diligence firms, managing agents and trading desks, and finally investors, insurances and providers of repo funding). With increasing distance from the underlying asset these actors relied more and more on indirect information (including FICO scores on creditworthiness, appraisals and due diligence checks by third party organizations, and most importantly the computer models of rating agencies and risk management desks). Instead of spreading risk this provided the ground for fraudulent acts, misjudgments and finally market collapse. Economists have studied the crisis as an instance of cascades in financial networks, where institutions' instability destabilized other institutions and led to knock-on effects.
Martin Wolf, chief economics commentator at the Financial Times, wrote in June 2009 that certain financial innovations enabled firms to circumvent regulations, such as off-balance sheet financing that affects the leverage or capital cushion reported by major banks, stating: "... an enormous part of what banks did in the early part of this decade—the off-balance-sheet vehicles, the derivatives and the 'shadow banking system' itself—was to find a way round regulation."
Incorrect pricing of risk
Mortgage risks were underestimated by almost all institutions in the chain from originator to investor by underweighting the possibility of falling housing prices based on historical trends of the past 50 years. Limitations of default and prepayment models, the heart of pricing models, led to overvaluation of mortgage and asset-backed products and their derivatives by originators, securitizers, broker-dealers, rating-agencies, insurance underwriters and the vast majority of investors (with the exception of certain hedge funds). While financial derivatives and structured products helped partition and shift risk between financial participants, it was the underestimation of falling housing prices and the resultant losses that led to aggregate risk.
The pricing of risk refers to the risk premium required by investors for taking on additional risk, which may be measured by higher interest rates or fees. Several scholars have argued that a lack of transparency about banks' risk exposures prevented markets from correctly pricing risk before the crisis, enabled the mortgage market to grow larger than it otherwise would have, and made the financial crisis far more disruptive than it would have been if risk levels had been disclosed in a straightforward, readily understandable format.
For a variety of reasons, market participants did not accurately measure the risk inherent with financial innovation such as MBS and CDOs or understand its effect on the overall stability of the financial system. The pricing model for CDOs clearly did not reflect the level of risk they introduced into the system. Banks estimated that $450 billion of CDO were sold between "late 2005 to the middle of 2007"; among the $102 billion of those that had been liquidated, JPMorgan estimated that the average recovery rate for "high quality" CDOs was approximately 32 cents on the dollar, while the recovery rate for mezzanine capital CDO was approximately five cents for every dollar.
AIG insured obligations of various financial institutions through the usage of credit default swaps. The basic CDS transaction involved AIG receiving a premium in exchange for a promise to pay money to party A in the event party B defaulted. However, AIG did not have the financial strength to support its many CDS commitments as the crisis progressed and was taken over by the government in September 2008. U.S. taxpayers provided over $180 billion in government loans and investments in AIG during 2008 and early 2009, through which the money flowed to various counterparties to CDS transactions, including many large global financial institutions.
The Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission (FCIC) made the major government study of the crisis. It concluded in January 2011:
The Commission concludes AIG failed and was rescued by the government primarily because its enormous sales of credit default swaps were made without putting up the initial collateral, setting aside capital reserves, or hedging its exposure—a profound failure in corporate governance, particularly its risk management practices. AIG's failure was possible because of the sweeping deregulation of over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives, including credit default swaps, which effectively eliminated federal and state regulation of these products, including capital and margin requirements that would have lessened the likelihood of AIG's failure.
The limitations of a widely used financial model also were not properly understood. This formula assumed that the price of CDS was correlated with and could predict the correct price of mortgage-backed securities. Because it was highly tractable, it rapidly came to be used by a huge percentage of CDO and CDS investors, issuers, and rating agencies. According to one wired.com article:
Then the model fell apart. Cracks started appearing early on, when financial markets began behaving in ways that users of Li's formula hadn't expected. The cracks became full-fledged canyons in 2008—when ruptures in the financial system's foundation swallowed up trillions of dollars and put the survival of the global banking system in serious peril... Li's Gaussian copula formula will go down in history as instrumental in causing the unfathomable losses that brought the world financial system to its knees.
As financial assets became more complex and harder to value, investors were reassured by the fact that the international bond rating agencies and bank regulators accepted as valid some complex mathematical models that showed the risks were much smaller than they actually were. George Soros commented that "The super-boom got out of hand when the new products became so complicated that the authorities could no longer calculate the risks and started relying on the risk management methods of the banks themselves. Similarly, the rating agencies relied on the information provided by the originators of synthetic products. It was a shocking abdication of responsibility."
A conflict of interest between investment management professional and institutional investors, combined with a global glut in investment capital, led to bad investments by asset managers in over-priced credit assets. Professional investment managers generally are compensated based on the volume of client assets under management. There is, therefore, an incentive for asset managers to expand their assets under management in order to maximize their compensation. As the glut in global investment capital caused the yields on credit assets to decline, asset managers were faced with the choice of either investing in assets where returns did not reflect true credit risk or returning funds to clients. Many asset managers continued to invest client funds in over-priced (under-yielding) investments, to the detriment of their clients, so they could maintain their assets under management. They supported this choice with a "plausible deniability" of the risks associated with subprime-based credit assets because the loss experience with early "vintages" of subprime loans was so low.
Despite the dominance of the above formula, there are documented attempts of the financial industry, occurring before the crisis, to address the formula limitations, specifically the lack of dependence dynamics and the poor representation of extreme events. The volume "Credit Correlation: Life After Copulas", published in 2007 by World Scientific, summarizes a 2006 conference held by Merrill Lynch in London where several practitioners attempted to propose models rectifying some of the copula limitations. See also the article by Donnelly and Embrechts and the book by Brigo, Pallavicini and Torresetti, that reports relevant warnings and research on CDOs appeared in 2006.
Boom and collapse of the shadow banking system
There is strong evidence that the riskiest, worst performing mortgages were funded through the "shadow banking system" and that competition from the shadow banking system may have pressured more traditional institutions to lower their underwriting standards and originate riskier loans.
In a June 2008 speech, President and CEO of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York Timothy Geithner—who in 2009 became United States Secretary of the Treasury—placed significant blame for the freezing of credit markets on a "run" on the entities in the "parallel" banking system, also called the shadow banking system. These entities became critical to the credit markets underpinning the financial system, but were not subject to the same regulatory controls. Further, these entities were vulnerable because of Asset–liability mismatch, meaning that they borrowed short-term in liquid markets to purchase long-term, illiquid and risky assets. This meant that disruptions in credit markets would force them to engage in rapid deleveraging, selling their long-term assets at depressed prices. He described the significance of these entities:
In early 2007, asset-backed commercial paper conduits, in structured investment vehicles, in auction-rate preferred securities, tender option bonds and variable rate demand notes, had a combined asset size of roughly $2.2 trillion. Assets financed overnight in tri-party repo grew to $2.5 trillion. Assets held in hedge funds grew to roughly $1.8 trillion. The combined balance sheets of the five largest investment banks totaled $4 trillion. In comparison, the total assets of the top five bank holding companies in the United States at that point were just over $6 trillion, and total assets of the entire banking system were about $10 trillion. The combined effect of these factors was a financial system vulnerable to self-reinforcing asset price and credit cycles.
Economist Paul Krugman, laureate of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, described the run on the shadow banking system as the "core of what happened" to cause the crisis. He referred to this lack of controls as "malign neglect" and argued that regulation should have been imposed on all banking-like activity. Without the ability to obtain investor funds in exchange for most types of mortgage-backed securities or asset-backed commercial paper, investment banks and other entities in the shadow banking system could not provide funds to mortgage firms and other corporations.
This meant that nearly one-third of the U.S. lending mechanism was frozen and continued to be frozen into June 2009. According to the Brookings Institution, at that time the traditional banking system did not have the capital to close this gap: "It would take a number of years of strong profits to generate sufficient capital to support that additional lending volume." The authors also indicate that some forms of securitization were "likely to vanish forever, having been an artifact of excessively loose credit conditions". While traditional banks raised their lending standards, it was the collapse of the shadow banking system that was the primary cause of the reduction in funds available for borrowing.
The securitization markets supported by the shadow banking system started to close down in the spring of 2007 and nearly shut-down in the fall of 2008. More than a third of the private credit markets thus became unavailable as a source of funds. According to the Brookings Institution in June 2009, the traditional banking system did not have the capital to close this gap: "It would take a number of years of strong profits to generate sufficient capital to support that additional lending volume" and some forms of securitization are "likely to vanish forever, having been an artifact of excessively loose credit conditions".
Commodity price inflation
Rapid increases in several commodity prices followed the collapse in the housing bubble. The price of oil nearly tripled from $50 to $147 from early 2007 to 2008, before plunging as the financial crisis began to take hold in late 2008. Experts debate the causes, with some attributing it to speculative flow of money from housing and other investments into commodities, some to monetary policy, and some to the increasing feeling of raw materials scarcity in a fast-growing world, leading to long positions taken on those markets, such as Chinese increasing presence in Africa. An increase in oil prices tends to divert a larger share of consumer spending into gasoline, which creates downward pressure on economic growth in oil importing countries, as wealth flows to oil-producing states. There was a pattern of spiking instability in the price of oil over the decade leading up to the price high of 2008. The destabilizing effects of this price variance was proposed as a contributory factor in the financial crisis.
Copper prices increased at the same time as oil prices. Copper traded at about $2,500 per ton from 1990 until 1999, when it fell to about $1,600. The price slump lasted until 2004, when a price surge pushed copper to $7,040 per ton in 2008.
Nickel prices boomed in the late 1990s, then declined from around $51,000 /£36,700 per metric ton in May 2007 to about $11,550/£8,300 per metric ton in January 2009. Prices were only just starting to recover as of January 2010, but most of Australia's nickel mines had gone bankrupt by then. As the price for high grade nickel sulphate ore recovered in 2010, so did the Australian nickel mining industry.
Coincidentally with these price fluctuations, long-only commodity index funds became popular—by one estimate investment increased from $90 billion in 2006 to $200 billion at the end of 2007, while commodity prices increased 71% – which raised concern as to whether these index funds caused the commodity bubble. The empirical research has been mixed.
Systemic crisis of capitalism
In a 1998 book, John McMurtry suggested that a financial crisis is a systemic crisis of capitalism itself.
In his 1978 book, The Downfall of Capitalism and Communism, Ravi Batra suggests that growing inequality of financial capitalism produces speculative bubbles that burst and result in depression and major political changes. He also suggested that a "demand gap" related to differing wage and productivity growth explains deficit and debt dynamics important to stock market developments.
John Bellamy Foster, a political economy analyst and editor of the Monthly Review, believed that the decrease in GDP growth rates since the early 1970s is due to increasing market saturation.
Marxian economics followers Andrew Kliman, Michael Roberts, and Guglielmo Carchedi, in contradistinction to the Monthly Review school represented by Foster, pointed to capitalism's long-term tendency of the rate of profit to fall as the underlying cause of crises generally. From this point of view, the problem was the inability of capital to grow or accumulate at sufficient rates through productive investment alone. Low rates of profit in productive sectors led to speculative investment in riskier assets, where there was potential for greater return on investment. The speculative frenzy of the late 90s and 2000s was, in this view, a consequence of a rising organic composition of capital, expressed through the fall in the rate of profit. According to Michael Roberts, the fall in the rate of profit "eventually triggered the credit crunch of 2007 when credit could no longer support profits".
In 2005 book, The Battle for the Soul of Capitalism, John C. Bogle wrote that "Corporate America went astray largely because the power of managers went virtually unchecked by our gatekeepers for far too long". Echoing the central thesis of James Burnham's 1941 seminal book, The Managerial Revolution, Bogle cites issues, including:
- that "Manager's capitalism" replaced "owner's capitalism", meaning management runs the firm for its benefit rather than for the shareholders, a variation on the principal–agent problem;
- the burgeoning executive compensation;
- the management of earnings, mainly a focus on share price rather than the creation of genuine value; and
- the failure of gatekeepers, including auditors, boards of directors, Wall Street analysts, and career politicians.
In his book The Big Mo, Mark Roeder, a former executive at the Swiss-based UBS Bank, suggested that large-scale momentum, or The Big Mo "played a pivotal role" in the financial crisis. Roeder suggested that "recent technological advances, such as computer-driven trading programs, together with the increasingly interconnected nature of markets, has magnified the momentum effect. This has made the financial sector inherently unstable."
Robert Reich attributed the economic downturn to the stagnation of wages in the United States, particularly those of the hourly workers who comprise 80% of the workforce. This stagnation forced the population to borrow to meet the cost of living.
Economists Ailsa McKay and Margunn Bjørnholt argued that the financial crisis and the response to it revealed a crisis of ideas in mainstream economics and within the economics profession, and call for a reshaping of both the economy, economic theory and the economics profession.
Wrong banking model: resilience of credit unions
A report by the International Labour Organization concluded that cooperative banking institutions were less likely to fail than their competitors during the crisis. The cooperative banking sector had 20% market share of the European banking sector, but accounted for only 7% of all the write-downs and losses between the third quarter of 2007 and first quarter of 2011. In 2008, in the U.S., the rate of commercial bank failures was almost triple that of credit unions, and almost five times the credit union rate in 2010. Credit unions increased their lending to small- and medium-sized businesses while overall lending to those businesses decreased.
Economists who predicted the crisis
Economists, particularly followers of mainstream economics, mostly failed to predict the crisis. The Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania's online business journal examined why economists failed to predict a major global financial crisis and concluded that economists used mathematical models that failed to account for the critical roles that banks and other financial institutions, as opposed to producers and consumers of goods and services, play in the economy.
Popular articles published in the mass media have led the general public to believe that the majority of economists have failed in their obligation to predict the financial crisis. For example, an article in The New York Times noted that economist Nouriel Roubini warned of such crisis as early as September 2006, and stated that the profession of economics is bad at predicting recessions. According to The Guardian, Roubini was ridiculed for predicting a collapse of the housing market and worldwide recession, while The New York Times labelled him "Dr. Doom".
Within mainstream financial economics, most believe that financial crises are simply unpredictable, following Eugene Fama's efficient-market hypothesis and the related random-walk hypothesis, which state respectively that markets contain all information about possible future movements, and that the movements of financial prices are random and unpredictable. Recent research casts doubt on the accuracy of "early warning" systems of potential crises, which must also predict their timing.
The Austrian School regarded the crisis as a vindication and classic example of a predictable credit-fueled bubble caused by laxity in monetary supply.
Several followers of heterodox economics predicted the crisis, with varying arguments. Dirk Bezemer credits 12 economists with predicting the crisis: Dean Baker (US), Wynne Godley (UK), Fred Harrison (UK), Michael Hudson (US), Eric Janszen (US), Steve Keen (Australia), Jakob Broechner Madsen & Jens Kjaer Sørensen (Denmark), Med Jones (US) Kurt Richebächer (US), Nouriel Roubini (US), Peter Schiff (US), and Robert Shiller (US).
Shiller, a founder of the Case-Shiller index that measures home prices, wrote an article a year before the collapse of Lehman Brothers in which he predicted that a slowing U.S. housing market would cause the housing bubble to burst, leading to financial collapse. Schiff regularly appeared on television in the years before the crisis and warned of the impending real estate collapse.
Karim Abadir, based on his work with Gabriel Talmain, predicted the timing of the recession whose trigger had already started manifesting itself in the real economy from early 2007.
There were other economists that did warn of a pending crisis.
The former Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, Raghuram Rajan, had predicted the crisis in 2005 when he became chief economist at the International Monetary Fund. In 2005, at a celebration honoring Alan Greenspan, who was about to retire as chairman of the US Federal Reserve, Rajan delivered a controversial paper that was critical of the financial sector. In that paper, Rajan "argued that disaster might loom". Rajan argued that financial sector managers were encouraged to "take risks that generate severe adverse consequences with small probability but, in return, offer generous compensation the rest of the time. These risks are known as tail risks. But perhaps the most important concern is whether banks will be able to provide liquidity to financial markets so that if the tail risk does materialize, financial positions can be unwound and losses allocated so that the consequences to the real economy are minimized."
Stock trader and financial risk engineer Nassim Nicholas Taleb, author of the 2007 book The Black Swan, spent years warning against the breakdown of the banking system in particular and the economy in general owing to their use of and reliance on bad risk models and reliance on forecasting, and framed the problem as part of "robustness and fragility". He also took action against the establishment view by making a big financial bet on banking stocks and making a fortune from the crisis ("They didn't listen, so I took their money"). According to David Brooks from The New York Times, "Taleb not only has an explanation for what's happening, he saw it coming."
IndyMac
The first visible institution to run into trouble in the United States was the Southern California–based IndyMac, a spin-off of Countrywide Financial. Before its failure, IndyMac Bank was the largest savings and loan association in the Los Angeles market and the seventh largest mortgage loan originator in the United States. The failure of IndyMac Bank on July 11, 2008, was the fourth largest bank failure in United States history up until the crisis precipitated even larger failures, and the second largest failure of a regulated thrift. IndyMac Bank's parent corporation was IndyMac Bancorp until the FDIC seized IndyMac Bank. IndyMac Bancorp filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy in July 2008.
IndyMac Bank was founded as Countrywide Mortgage Investment in 1985 by David S. Loeb and Angelo Mozilo as a means of collateralizing Countrywide Financial loans too big to be sold to Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae. In 1997, Countrywide spun off IndyMac as an independent company run by Mike Perry, who remained its CEO until the downfall of the bank in July 2008.
The primary causes of its failure were largely associated with its business strategy of originating and securitizing Alt-A loans on a large scale. This strategy resulted in rapid growth and a high concentration of risky assets. From its inception as a savings association in 2000, IndyMac grew to the seventh largest savings and loan and ninth largest originator of mortgage loans in the United States. During 2006, IndyMac originated over $90 billion of mortgages.
IndyMac's aggressive growth strategy, use of Alt-A and other nontraditional loan products, insufficient underwriting, credit concentrations in residential real estate in the California and Florida markets—states, alongside Nevada and Arizona, where the housing bubble was most pronounced—and heavy reliance on costly funds borrowed from a Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) and from brokered deposits, led to its demise when the mortgage market declined in 2007.
IndyMac often made loans without verification of the borrower's income or assets, and to borrowers with poor credit histories. Appraisals obtained by IndyMac on underlying collateral were often questionable as well. As an Alt-A lender, IndyMac's business model was to offer loan products to fit the borrower's needs, using an extensive array of risky option-adjustable-rate mortgages (option ARMs), subprime loans, 80/20 loans, and other nontraditional products. Ultimately, loans were made to many borrowers who simply could not afford to make their payments. The thrift remained profitable only as long as it was able to sell those loans in the secondary mortgage market. IndyMac resisted efforts to regulate its involvement in those loans or tighten their issuing criteria: see the comment by Ruthann Melbourne, Chief Risk Officer, to the regulating agencies.
On May 12, 2008, in the "Capital" section of its last 10-Q, IndyMac revealed that it may not be well capitalized in the future.
IndyMac reported that during April 2008, Moody's and Standard & Poor's downgraded the ratings on a significant number of Mortgage-backed security (MBS) bonds—including $160 million issued by IndyMac that the bank retained in its MBS portfolio. IndyMac concluded that these downgrades would have harmed its risk-based capital ratio as of June 30, 2008. Had these lowered ratings been in effect at March 31, 2008, IndyMac concluded that the bank's capital ratio would have been 9.27% total risk-based. IndyMac warned that if its regulators found its capital position to have fallen below "well capitalized" (minimum 10% risk-based capital ratio) to "adequately capitalized" (8–10% risk-based capital ratio) the bank might no longer be able to use brokered deposits as a source of funds.
Senator Charles Schumer (D-NY) later pointed out that brokered deposits made up more than 37% of IndyMac's total deposits, and ask the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) whether it had considered ordering IndyMac to reduce its reliance on these deposits. With $18.9 billion in total deposits reported on March 31, Senator Schumer would have been referring to a little over $7 billion in brokered deposits. While the breakout of maturities of these deposits is not known exactly, a simple averaging would have put the threat of brokered deposits loss to IndyMac at $500 million a month, had the regulator disallowed IndyMac from acquiring new brokered deposits on June 30.
IndyMac was taking new measures to preserve capital, such as deferring interest payments on some preferred securities. Dividends on common shares had already been suspended for the first quarter of 2008, after being cut in half the previous quarter. The company still had not secured a significant capital infusion nor found a ready buyer.
IndyMac reported that the bank's risk-based capital was only $47 million above the minimum required for this 10% mark. But it did not reveal some of that $47 million capital it claimed it had, as of March 31, 2008, was fabricated.
When home prices declined in the latter half of 2007 and the secondary mortgage market collapsed, IndyMac was forced to hold $10.7 billion of loans it could not sell in the secondary market. Its reduced liquidity was further exacerbated in late June 2008 when account holders withdrew $1.55 billion or about 7.5% of IndyMac's deposits. This bank run on the thrift followed the public release of a letter from Senator Charles Schumer to the FDIC and OTS. The letter outlined the Senator's concerns with IndyMac. While the run was a contributing factor in the timing of IndyMac's demise, the underlying cause of the failure was the unsafe and unsound way it was operated.
On June 26, 2008, Senator Charles Schumer (D-NY), a member of the Senate Banking Committee, chairman of Congress' Joint Economic Committee and the third-ranking Democrat in the Senate, released several letters he had sent to regulators, in which he was"concerned that IndyMac's financial deterioration poses significant risks to both taxpayers and borrowers." Some worried depositors began to withdraw money.
On July 7, 2008, IndyMac announced on the company blog that it:
- Had failed to raise capital since its May 12, 2008 quarterly earnings report;
- Had been notified by bank and thrift regulators that IndyMac Bank was no longer deemed "well-capitalized";
IndyMac announced the closure of both its retail lending and wholesale divisions, halted new loan submissions, and cut 3,800 jobs.
On July 11, 2008, citing liquidity concerns, the FDIC put IndyMac Bank into conservatorship. A bridge bank, IndyMac Federal Bank, FSB, was established to assume control of IndyMac Bank's assets, its secured liabilities, and its insured deposit accounts. The FDIC announced plans to open IndyMac Federal Bank, FSB on July 14, 2008. Until then, depositors would have access their insured deposits through ATMs, their existing checks, and their existing debit cards. Telephone and Internet account access was restored when the bank reopened. The FDIC guarantees the funds of all insured accounts up to US$100,000, and declared a special advance dividend to the roughly 10,000 depositors with funds in excess of the insured amount, guaranteeing 50% of any amounts in excess of $100,000. Yet, even with the pending sale of Indymac to IMB Management Holdings, an estimated 10,000 uninsured depositors of Indymac are still at a loss of over $270 million.
With $32 billion in assets, IndyMac Bank was one of the largest bank failures in American history.
IndyMac Bancorp filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy on July 31, 2008.
Initially the companies affected were those directly involved in home construction and mortgage lending such as Northern Rock and Countrywide Financial, as they could no longer obtain financing through the credit markets. Over 100 mortgage lenders went bankrupt during 2007 and 2008. Concerns that investment bank Bear Stearns would collapse in March 2008 resulted in its fire-sale to JP Morgan Chase. The financial institution crisis hit its peak in September and October 2008. Several major institutions either failed, were acquired under duress, or were subject to government takeover. These included Lehman Brothers, Merrill Lynch, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, Washington Mutual, Wachovia, Citigroup, and AIG. On October 6, 2008, three weeks after Lehman Brothers filed the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history, Lehman's former CEO Richard S. Fuld Jr. found himself before Representative Henry A. Waxman, the California Democrat who chaired the House Committee on Oversight and Government Reform. Fuld said he was a victim of the collapse, blaming a "crisis of confidence" in the markets for dooming his firm.
Notable books and movies
- In 2006, Peter Schiff authored a book titled Crash Proof: How to Profit From the Coming Economic Collapse, which was published in February 2007 by Wiley. The book describes various features of the economy and housing market that led to the United States housing bubble, and warns of the impending decline. After many of the predictions came to pass, a second edition titled Crash Proof 2.0 was published in 2009, which included a "2009 update" addendum at the end of each chapter. It was featured on The New York Times Best Seller list.
- Meltdown: A Free-Market Look at Why the Stock Market Collapsed, the Economy Tanked, and the Government Bailout Will Make Things Worse, by Thomas Woods, was published in February 2009 by Regnery Publishing. It was featured on The New York Times Best Seller list for 10 weeks
- A 2010 documentary film, Overdose: A Film about the Next Financial Crisis, describes how the financial crisis came about and how the solutions that have been applied by many governments are setting the stage for the next crisis. The film is based on the book Financial Fiasco by Johan Norberg and features Alan Greenspan, with funding from the libertarian think tank Cato Institute.
- In October 2010, a documentary film about the crisis, Inside Job directed by Charles Ferguson, was released by Sony Pictures Classics. In 2011, it was awarded the Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature at the 83rd Academy Awards.
- Michael Lewis authored a best-selling non-fiction book about the crisis, entitled The Big Short. In 2015, it was adapted into a film of the same name, which won the Academy Award for Best Adapted Screenplay. One point raised is to what extent those outside of the markets themselves (i.e., not working for a mainstream investment bank) could forecast the events and be generally less myopic.
- Set on the night before the crisis broke, Margin Call is a movie that follows traders through a sleepless 24 hours as they try to contain the damage after an analyst discovers information that is likely to ruin their firm, and possibly the whole economy.
- The US documentary program Frontline produced several episodes investigating various aspects of the crisis:
- "Inside the Meltdown" (Season 2009: Episode 8)
- "Ten Trillion and Counting" (Season 2009: Episode 9)
- "Breaking the Bank" (Season 2009: Episode 15)
- "The Warning" (Season 2009: Episode 2)
See also
- Banking (Special Provisions) Act 2008 (United Kingdom)
- 2008–2011 bank failures in the United States
- 2008–2009 Keynesian resurgence
- 2010 United States foreclosure crisis
- 2012 May Day protests
- Crisis (Marxian)
- Europeans for Financial Reform
- Kondratiev wave
- List of banks acquired or bankrupted during the Great Recession
- List of acquired or bankrupt United States banks in the late 2000s financial crisis
- List of acronyms: European sovereign-debt crisis
- List of economic crises
- List of entities involved in 2007–2008 financial crises
- List of largest U.S. bank failures
- Low-Income Countries Under Stress
- Mark-to-market accounting
- Neoliberalism
- Occupy movement
- Pessimism porn
- PIGS (economics)
- Private equity in the 2000s
- Subprime crisis impact timeline
- The Chicago Plan Revisited