| A version of the Windows NT operating system | |
 | |
 Screenshot showing the new Start menu and centered taskbar | |
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Written in |
|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing | June 24, 2021 |
| General availability | October 5, 2021 |
| Latest release | 21H2 (10.0.22000.856) (August 9, 2022) |
| Latest preview |
22H2 (10.0.22621.457) (August 23, 2022)
22H2 (10.0.22622.586) (August 24, 2022)
|
| Marketing target | Personal computing, tablets |
| Available in | 110 languages |
| Update method | |
|---|---|
| Package manager | .exe, APPX, appxbundle and APK-based |
| Platforms | x86-64, ARMv8 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Userland | Native API Windows API .NET Framework Universal Windows Platform Windows Subsystem for Android Windows Subsystem for Linux |
| Default user interface | Windows shell (graphical) |
| Preceded by | Windows 10 (2015) |
| Official website | www |
| Support status | |
| See § Versions for details. | |
| Part of a series of articles on |
| Windows 11 |
|---|
| Related |
Windows 11 is the latest major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system, released in October 2021. It is a free upgrade to its predecessor, Windows 10 (2015), available for any Windows 10 devices that meet the new Windows 11 system requirements.
Windows 11 features major changes to the Windows shell influenced by the canceled Windows 10X, including a redesigned Start menu, the replacement of its "live tiles" with a separate "Widgets" panel on the taskbar, the ability to create tiled sets of windows that can be minimized and restored from the taskbar as a group, and new gaming technologies inherited from Xbox Series X and Series S such as Auto HDR and DirectStorage on compatible hardware. Internet Explorer (IE) has been replaced by the Chromium-based Microsoft Edge as the default web browser like its predecessor, Windows 10, and Microsoft Teams is integrated into the Windows shell. Microsoft also announced plans to allow more flexibility in software that can be distributed via Microsoft Store, and to support Android apps on Windows 11 (including a partnership with Amazon to make its app store available for the function).
Citing security considerations, the system requirements for Windows 11 were increased over Windows 10. Microsoft only officially supports the operating system on devices using an eighth-generation Intel Core CPU or newer (with some minor exceptions), AMD Ryzen CPU based on Zen+ microarchitecture or newer, or a Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 ARM system-on-chip or newer, with UEFI secure boot and Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 supported and enabled (although Microsoft may provide exceptions to the TPM 2.0 requirement for OEMs). While the OS can be installed on unsupported processors, Microsoft does not guarantee the availability of updates. Windows 11 removed support for 32-bit x86 CPUs and devices which use BIOS firmware.
Windows 11 has received a mixed reception. Pre-release coverage of the operating system focused on its stricter hardware requirements, with discussions over whether they were legitimately intended to improve the security of Windows or as a ploy to upsell users to newer devices, and over e-waste associated with the changes. Upon release, it was praised for its improved visual design, window management, and a stronger focus on security, but was criticized for various modifications to aspects of its user interface which were seen as worse than its predecessor.
As of August 2022, Windows 11, at 13% (and up to 16%, in the US, or more in some countries), is the 2nd most popular Windows edition on Windows PC, while Windows 10 is still by far most popular with 6× the market share of its successor (and also 6× the share of Windows 7). Windows 11 was 3rd on monthly statistics for July (and in some countries 4th) after Windows 7, that stands at 72% globally, and 77% in the United States. Across all platforms Windows 11 runs on a share of 3.3% of PCs.
Development
At the 2015 Ignite conference, Microsoft employee Jerry Nixon stated that Windows 10 would be the "last version of Windows", a statement that Microsoft confirmed was "reflective" of its view. The operating system was considered to be a service, with new builds and updates to be released over time.
In October 2019, Microsoft announced "Windows 10X", a future edition of Windows 10 designed exclusively for dual-touchscreen devices such as the then-upcoming Surface Neo. It featured a modified user interface designed around context-sensitive "postures" for different screen configurations and usage scenarios, and changes such as a centered taskbar and updated Start menu without Windows 10's "live tiles". Legacy Windows applications would also be required to run in "containers" to ensure performance and power optimization. Microsoft stated that it planned to release Windows 10X devices by the end of 2020.
In May 2020, amid the COVID-19 pandemic, chief product officer for Microsoft Windows and Office Panos Panay stated that "as we continue to put customers' needs at the forefront, we need to focus on meeting customers where they are now", and therefore announced that Windows 10X would only launch on single-screen devices at first, and that Microsoft would "continue to look for the right moment, in conjunction with our OEM partners, to bring dual-screen devices to market".
In January 2021, it was reported that a job listing referring to a "sweeping visual rejuvenation of Windows" had been posted by Microsoft. A visual refresh for Windows, developed under the codename "Sun Valley", was reportedly set to re-design the system's user interface. It was rumored to be released as a Windows 10 feature update as version 21H2. However, this would later be spun off into Windows 11. Microsoft began to implement and announce some of these visual changes and other new features on Windows 10 Insider Preview builds, such as new system icons (which also included the replacement of shell resources dating back as far as Windows 95), improvements to Task View to allow changing the wallpaper on each virtual desktop, emulation of x64 applications on ARM, and adding the Auto HDR feature from Xbox Series X.
On May 18, 2021, Head of Windows Servicing and Delivery John Cable stated that Windows 10X had been canceled and that Microsoft would be "accelerating the integration of key foundational 10X technology into other parts of Windows and products at the company".
Announcement
At the Microsoft Build 2021 developer conference, CEO and chairman Satya Nadella teased about the existence of the next generation of Windows during his keynote speech. According to Nadella, he had been self-hosting it for several months. He also teased that an official announcement would come very soon. Just a week after Nadella's keynote, Microsoft started sending invitations for a dedicated Windows media event at 11 am ET on June 24, 2021. Microsoft also posted an 11-minute video of Windows start-up sounds to YouTube on June 10, 2021, with many people speculating both the time of the Microsoft event and the duration of the Windows start-up sound video to be a reference to the name of the operating system as Windows 11.
On June 24, 2021, Windows 11 was officially announced at a virtual event hosted by Chief Product Officer Panos Panay. According to Nadella, Windows 11 is "a re-imagining of the operating system". Further details for developers such as updates to the Microsoft Store, the new Windows App SDK (code-named "Project Reunion"), new Fluent Design guidelines, and more were discussed during another developer-focused event on the same day.
Release
The Windows 11 name was accidentally released in an official Microsoft support document in June 2021. Leaked images of a purported beta build of Windows 11's desktop surfaced online later on June 15, 2021, which were followed by a leak of the aforementioned build on the same day. The screenshots and leaked build show an interface resembling that of the canceled Windows 10X, alongside a redesigned out-of-box experience (OOBE) and Windows 11 branding. Microsoft would later confirm the authenticity of the leaked beta, with Panay stating that it was an "early weird build".
At the June 24 media event, Microsoft also announced that Windows 11 would be released in "Holiday 2021". Its release will be accompanied by a free upgrade for compatible Windows 10 devices through Windows Update. On June 28, Microsoft announced the release of the first preview build and SDK of Windows 11 to Windows Insiders.
On August 31, 2021, Microsoft announced that Windows 11 was to be released on October 5, 2021. The release would be phased, with newer eligible devices to be offered the upgrade first. Since its predecessor Windows 10 was released on July 29, 2015, more than six years earlier, this is the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows operating systems, beating the time between Windows XP (released on October 25, 2001) and Windows Vista (released on January 30, 2007).
Microsoft officially released Windows 11 on October 4, 2021, at 2:00 p.m. PT, which was October 5 in parts of the world. It can be obtained as an in-place upgrade via either the Windows 11 Installation Assistant application (the successor to the Media Creation Tool from Windows 10, which can also generate an ISO image or USB install media), or via Windows Update on eligible devices. On May 9, 2022, Microsoft released Windows 11 on physical media in the form of a boxed USB drive and product key. These boxed copies were made available on Amazon and Best Buy's online storefronts.
Upgrades through Windows Update are a phased rollout, and are distributed on an opt-in basis: Microsoft stated that they "expect all eligible Windows 10 devices to be offered the upgrade to Windows 11 by mid-2022." Eligible devices also may present an option to download Windows 11 during the Windows 10 out-of-box experience (OOBE) on a new installation.
In launch they partnered up with Mikey Likes It Ice Cream in NYC to make a flavor named "Bloomberry" based on the default "Bloom" wallpaper to promote Windows 11. The ice cream is blueberry with blueberry pie filling, pound cake & candy chocolate pieces. The Burj Khalifa was also lighted up to promote the operating system. The ice cream could be compared to Windows 7's launch using a partnership with Burger King to create a 7-patty whopper and Windows 10's launch with a limited "10-scoop upgrade" for an ice cream parlor called Daily Chico that originally did 8-scoop ice cream.
Features
Windows 11, the first major Windows release since 2015, builds upon its predecessor by revamping the user interface to follow Microsoft's new Fluent Design guidelines. The redesign, which focuses on ease of use and flexibility, comes alongside new productivity and social features and updates to security and accessibility, addressing some of the deficiencies of Windows 10.
The Microsoft Store, which serves as a unified storefront for apps and other content, is also redesigned in Windows 11. Microsoft now allows developers to distribute Win32, progressive web applications, and other packaging technologies in the Microsoft Store, alongside Universal Windows Platform apps. Microsoft also announced plans to allow third-party application stores (such as Epic Games Store) to distribute their clients on Microsoft Store. Windows 11 supports x86-64 software emulation on ARM-based platforms.
The collaboration platform Microsoft Teams is integrated into the Windows 11 user interface, and is accessible via the taskbar. Skype will no longer be bundled with the OS by default.
Microsoft claims performance improvements such as smaller update sizes, faster web browsing in "any browser", faster wake time from sleep mode, and faster Windows Hello authentication.
Windows 11 ships with the Chromium-based Microsoft Edge web browser (for compatibility with Google Chrome web browser), and does not include or support Internet Explorer. Its rendering engine MSHTML (Trident) is still included with the operating system for backwards compatibility reasons, and Edge can be configured with Group Policy to render whitelisted websites in "IE Mode" (which still uses IE's rendering engine MSHTML, instead of Blink layout engine). Windows 11 is the first version of Windows since the original retail release of Windows 95 to not ship with Internet Explorer.
The updated Xbox app, along with the Auto HDR and DirectStorage technologies introduced by the Xbox Series X and Series S, will be integrated into Windows 11; the latter requiring a graphics card supporting DirectX 12 and an NVMe solid-state drive.
User interface
A redesigned user interface is present frequently throughout the operating system, building upon Fluent Design System; translucency, shadows, a new color palette, and rounded geometry are prevalent throughout the UI. A prevalent aspect of the design is an appearance known as "Mica", described as an "opaque, dynamic material that incorporates theme and desktop wallpaper to paint the background of long-lived windows such as apps and settings". Much of the interface and start menu takes heavy inspiration from the now-canceled Windows 10X. The Segoe UI font used since Windows Vista has been updated to a variable version, improving its ability to scale between different display resolutions.
The taskbar's buttons are center-aligned by default, and it is permanently pinned to the bottom edge of the screen; it cannot be moved to the top, left, or right edges of the screen as in previous versions of Windows without manual changes to the registry. The notifications sidebar is now accessed by clicking the date and time, with other Quick Actions toggles, as well as volume, brightness, and media playback controls, moved to a new settings pop-up displayed by clicking on the system tray. The "Widgets" button on the taskbar displays a panel with Microsoft Start, a news aggregator with personalized stories and content (expanding upon the "news and interests" panel introduced in later builds of Windows 10). Microsoft Teams is similarly integrated with the taskbar, with a pop-up showing a list of recent conversations.
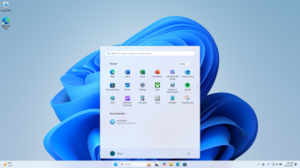
The Start menu has been significantly redesigned, replacing the "live tiles" used by Windows 8.x and 10 with a grid of "pinned" applications, and a list of recent applications and documents. File Explorer was updated to replace its ribbon toolbar with a more traditional toolbar, while its context menus have been redesigned to move some tasks (such as copy and paste) to a toolbar along the top of the menu, and hide other operations under an overflow menu.
Task View, a feature introduced in Windows 10, features a refreshed design, and supports giving separate wallpapers to each virtual desktop. The window snapping functionality has been enhanced with two additional features; hovering over a window's maximize button displays pre-determined "Snap Layouts" for tiling multiple windows onto a display, and tiled arrangement of windows can be minimized and restored from the taskbar as a "snap group". When a display is disconnected in a multi-monitor configuration, the windows that were previously on that display will be minimized rather than automatically moved to the main display. If the same display is reconnected, the windows are restored to their prior location.
Windows Subsystem for Android
On October 21, 2021, Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA) became available to Beta channel builds of Windows 11 for users in the United States, which allows users to install and run Android apps on their devices. Users can install Android apps through any source using the APK file format. An Amazon Appstore client for Microsoft Store is also available. The Windows Subsystem for Android and Amazon Appstore became available to Release channel users in the United States on February 15, 2022, in Windows 11 Release build 22000.527 released that same day.
WSA is based on the Intel Bridge runtime compiler; Intel stated that the technology is not dependent on its CPUs, and will also be supported on x86-64 and ARM CPUs from other vendors.
System security
As part of the minimum system requirements, Windows 11 only runs on devices with a Trusted Platform Module 2.0 security coprocessor. According to Microsoft, the TPM 2.0 coprocessor is a "critical building block" for protection against firmware and hardware attacks. In addition, Microsoft now requires devices with Windows 11 to include virtualization-based security (VBS), hypervisor-protected code integrity (HVCI), and Secure Boot built-in and enabled by default. The operating system also features hardware-enforced stack protection for supported Intel and AMD processors for protection against zero-day exploits.
Like its predecessor, Windows 11 also supports multi-factor authentication and biometric authentication through Windows Hello.
Versions
Windows 11 is available in two main editions; the Home edition, which is intended for consumer users, and the Pro edition, which contains additional networking and security features (such as BitLocker), as well as the ability to join a domain. Windows 11 Home may be restricted by default to verified software obtained from Microsoft Store ("S Mode"). Windows 11 Home requires an internet connection and a Microsoft account in order to complete first-time setup. In February 2022, it was announced that this restriction will also apply to Windows 11 Pro in the future.
Windows 11 SE was announced on November 9, 2021, as an edition exclusively for low-end devices sold in the education market, and a successor to Windows 10 S. It is designed to be managed via Microsoft Intune, and has changed based on feedback from educators to simplify the user interface and reduce "distractions", such as Snap Layouts not containing layouts for more than two applications at once, all applications opening maximized by default, Widgets being completely removed, and Microsoft Edge is configured by default to allow extensions from the Chrome Web Store (primarily to target those migrating from Chrome OS). It is bundled with applications such as Microsoft Office for Microsoft 365, Minecraft Education Edition, and Flipgrid, while OneDrive is used to save files by default. Windows 11 SE does not include Microsoft Store; third-party software is provisioned or installed by administrators.
The Windows Insider program carries over from Windows 10, with pre-release builds divided into "Dev" (unstable builds used to test features for future feature updates), "Beta" (test builds for the next feature update; relatively stable in comparison to Dev channel), and "Release Preview" (pre-release builds for final testing of upcoming feature updates) channels.
| Version | Marketing name | Build | Release date | Supported until (and support status by color) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||
| 21H2 | — | 22000 | October 4, 2021 | October 10, 2023 | October 8, 2024 | ||
| 22H2 | TBA | 22621 | TBA | 24 months | 36 months | ||
| Legend: Old version, not maintained Older version, still maintained Current stable version | |||||||
Supported languages
Before the launch of Windows 11, OEMs (as well as mobile operators) and businesses were offered two options for device imaging: Component-Based Servicing lp.cab files (for the languages to be preloaded on the first boot) and Local Experience Pack .appx files (for the languages available for download on supported PCs). The 38 fully-localized Language Pack (LP) languages were available as both lp.cab and .appx packages, while the remaining 72 partially-localized Language Interface Pack (LIP) languages were only available as .appx packages.
With Windows 11, that process has changed. Five new LP languages were added — Catalan, Basque, Galician, Indonesian, and Vietnamese — bringing the total number of LP languages to 43. Furthermore, these 43 languages can only be imaged using lp.cab packages. This is to ensure a fully supported language-imaging and cumulative update experience.
The remaining 67 LIP languages that are LXP-based will move to a self-service model, and can only be added by Windows users themselves via the Microsoft Store and Windows Settings apps, not during the Windows imaging process. Any user, not just admins, can now add both the display language and its features, which can help users in business environments, but these exact options for languages (both LP and LIP) still depend on the OEM and mobile operator.
Available languages
These languages are either preloaded or available for download, depending on the OEM, region of purchase, and mobile operator.
For each of the manufacturers listed, Yes is displayed if the language is supported or available for download in at least one region, and No is displayed if it is not supported in any region.
| Language/region | English translation | Surface | Samsung | HP | Lenovo | Asus | Acer | Dell | LG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Català | Catalan | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Čeština | Czech | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Dansk | Danish | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Deutsch | German | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Eesti | Estonian | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| English (Australia) | English (Australia) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| English (Canada) | English (Canada) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| English (United Kingdom) | English (United Kingdom) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| English (United States) | English (United States) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Español (España) | Spanish (Spain) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Español (México) | Spanish (Mexico) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Euskara | Basque | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Français (Canada) | French (Canada) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Français (France) | French (France) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Galego | Galician | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Hrvatski | Croatian | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Indonesia | Indonesian | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Italiano | Italian | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Latviešu | Latvian | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Lietuvių | Lithuanian | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Magyar | Hungarian | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Nederlands | Dutch | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Norsk bokmål | Norwegian Bokmål | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Polski | Polish | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Português (Brasil) | Portuguese (Brazil) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Português (Portugal) | Portuguese (Portugal) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Română | Romanian | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Slovenčina | Slovak | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Slovenščina | Slovenian | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Srpski | Serbian | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Suomi | Finnish | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Svenska | Swedish | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Tiếng Việt | Vietnamese | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Türkçe | Turkish | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ελληνικά | Greek | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Български | Bulgarian | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Русский | Russian | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Українська | Ukrainian | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| עברית | Hebrew | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| العربية | Arabic | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ไทย | Thai | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 한국어 | Korean | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 中文 (简体) | Chinese (Simplified) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 中文 (繁體) | Chinese (Traditional) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 中文 (香港) | Chinese (Hong Kong) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 日本語 | Japanese | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
The following languages are available for download on all 2021 and newer Surface devices regardless of the region:
- Danish
- German
- English (Australia)
- English (Canada)
- English (United Kingdom)
- English (United States)
- Spanish (Spain)
- Spanish (Mexico)
- French (Canada)
- French (France)
- Italian
- Dutch
- Norwegian
- Polish
- Finnish
- Swedish
- Japanese
These additional languages are available for download exclusively in their respective markets, in addition to the above languages:
- Americas: Portuguese (Brazil)
- EMEA: Czech, Estonian, Croatian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Hungarian, Portuguese (Portugal), Romanian, Slovak, Slovenian, Turkish, Greek, Bulgarian, Arabic
- Asia Pacific: Thai, Korean, Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), Chinese (Hong Kong)
System requirements
| Component | Minimum |
|---|---|
| Processor | A compatible 64-bit processor (x86-64 or ARM64) with at least 1 GHz clock rate and at least 2 processor cores |
| Memory (RAM) | At least 4 GB |
| Storage space | At least 64 GB |
| System firmware | Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) |
| Security | Secure Boot, enabled by default |
| Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0 | |
| Graphics card | Compatible with DirectX 12 or later with WDDM 2.0 driver |
| Display | High definition (720p) display that is greater than 9" diagonally, 8 bits per color channel |
| Internet connection and Microsoft accounts | Internet connection and Microsoft account required to complete first-time setup on Windows 11 Home (and soon, also on Windows 11 Pro) |
| Feature | Requirements |
|---|---|
| 5G support | 5G capable modem |
| Auto HDR | HDR capable monitor |
| Biometric authentication and Windows Hello | Illuminated infrared camera or fingerprint reader |
| BitLocker to Go | USB flash drive (available in Windows 11 Pro and higher editions) |
| Hyper-V | Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) |
| DirectStorage | NVMe Solid-state drive |
| DirectX 12 Ultimate | Available with supported games and graphics cards |
| Spatial sound | Supporting hardware and software |
| Two-factor authentication | Use of PIN, biometric authentication, or a phone with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth capabilities |
| Speech recognition | Microphone |
| Wi-Fi 6E support | New WLAN IHV hardware and driver, Wi-Fi 6E capable AP/router |
| Windows Projection | Wi-Fi adapter that supports Wi-Fi Direct, WDDM 2.0 |
| Windows Subsystem for Android (public preview) | A supported processor and a solid-state drive At least 8 GB of RAM (minimum) At least 16 GB of RAM (recommended) |
The basic system requirements of Windows 11 differ significantly from Windows 10. Windows 11 only supports 64-bit systems such as those using an x86-64 or ARM64 processor; IA-32 processors are no longer supported. Thus, Windows 11 is the first consumer version of Windows not to support 32-bit processors (although Windows Server 2008 R2 was the first version of Windows NT to not support them). The minimum RAM and storage requirements were also increased; Windows 11 now requires at least 4GB of RAM and 64GB of storage. S mode is only supported for the Home edition of Windows 11. As of August 2021, the officially supported list of processors includes Intel Coffee Lake (eighth generation Intel Core) CPUs and later, AMD Zen+ CPUs/APUs and later (which include the "AF" revisions of Ryzen 1000 CPUs, which are underclocked Zen+ CPUs that supplant Ryzen 1000 parts that could no longer be manufactured due to a change in process), and Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 and later. The compatibility list includes the Intel Core i7-7820HQ, a seventh-generation processor used by the Surface Studio 2, although only on devices that shipped with DCH-based drivers.
Legacy BIOS is no longer supported; a UEFI system with Secure Boot and a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 security coprocessor is now required. The TPM requirement in particular has led to confusion as many motherboards do not have TPM support, or require a compatible TPM to be physically installed onto the motherboard. Many newer CPUs also include a TPM implemented at the CPU level (with AMD referring to this "fTPM", and Intel referring to it as "Platform Trust Technology" [PTT]), which might be disabled by default and require changing settings in the computer's UEFI firmware, or an UEFI firmware update that is configured to automatically enable the firmware TPM upon installation.
Original equipment manufacturers can still ship computers without a TPM 2.0 coprocessor upon Microsoft's approval. Devices with unsupported processors are not blocked from installing or running Windows 11; however, a clean install or upgrade using ISO installation media must be performed as Windows Update will not offer an upgrade from Windows 10. Additionally, users must also accept an on-screen disclaimer stating that they will not be entitled to receive updates, and that damage caused by using Windows 11 on an unsupported configuration are not covered by the manufacturer's warranty. Some third-party software may refuse to run on "unsupported" configurations of Windows 11.
Reception
Pre-release
Reception of Windows 11 upon its reveal was positive, with critics praising the new design and productivity features. However, Microsoft was criticized for creating confusion over the minimum system requirements for Windows 11. The increased system requirements (compared to those of Windows 10) initially published by Microsoft meant that up to 60 percent of existing Windows 10 PCs were unable to upgrade to Windows 11, which has faced concerns that this will make the devices electronic waste.
Microsoft has not specifically acknowledged this when discussing the cutoff, it was also acknowledged that the sixth and seventh generation of Intel Core processors were prominently afflicted by CPU-level security vulnerabilities such as Meltdown and Spectre, and that newer CPUs manufactured since then had increased mitigations against the flaws.
Speaking to IT news outlet CRN, a dozen independent solution providers all felt that they “believe Windows 11 will be a meaningful step up in security, and they agree with Microsoft’s strategy of putting security first.”
Research Vice President of Gartner Stephen Kleynhans felt that Microsoft was "looking at the entire stack from the hardware up through the applications and the user experience and trying to make the entire stack work better and more securely.
Launch
Andrew Cunningham of Ars Technica praised the improvements to its visual design (describing the new "Mica" appearance as reminiscent of the visual appearance of iOS and macOS, and arguing that Microsoft had "[made] a serious effort" at making the user-facing aspects of Windows 11 more consistent visually), window management, performance (assessed as being equivalent to if not better than Windows 10), other "beneficial tweaks", and its system requirements having brought greater public attention to hardware security features present on modern PCs. Criticism was raised towards Widgets' lack of support for third-party content (thus limiting it to Microsoft services only), regressions in taskbar functionality and customization, the inability to easily select default applications for common tasks such as web browsing (now requiring the user to select the browser application for each file type individually), and Microsoft's unclear justification for its processor compatibility criteria. Cunningham concluded that "as I've dug into [Windows 11] and learned its ins and outs for this review, I've warmed to it more", but argued that the OS was facing similar "public perception" issues to Windows Vista and Windows 8. However, he noted that 11 did not have as many performance issues or bugs as Vista had upon its release, nor was as "disjointed" as 8, and recommended that users who were unsure about the upgrade should stay on Windows 10 in anticipation of future updates to 11.
Tom Warren of The Verge described Windows 11 as being akin to a house in the middle of renovations, but that "actually using Windows 11 for the past few months hasn't felt as controversial as I had expected"—praising its updated user interface as being more modern and reminiscent of iOS and Chrome OS, the new start menu for feeling less cluttered than the Windows 10 iteration, updates to some of its stock applications, and Snap Assist. Warren noted that he rarely used the Widgets panel or Microsoft Teams, citing that he preferred the weather display that later versions of Windows 10 offered, and didn't use Teams to communicate with his friends and family. He also acknowledged the expansion of Microsoft Store to include more "traditional" desktop applications. However, he felt that Windows 11 still felt like a work in progress, noting UI inconsistencies (such as dark mode and new context menu designs not being uniform across all dialogues and applications, and the modern Settings app still falling back upon legacy Control Panel applets for certain settings), regressions to the taskbar (including the inability to move it, drag files onto taskbar buttons to focus the corresponding application, and the clock only shown on the primary display in multi-monitor configurations), and promised features (such as dynamic refresh rate support and a universal microphone mute button) not being present on the initial release. Overall, he concluded that "I wouldn't rush out to upgrade to Windows 11, but I also wouldn't avoid it. After all, Windows 11 still feels familiar and underneath all the UI changes, it's the same Windows we've had for decades."
PC World was more critical, arguing that Windows 11 "sacrifices productivity for personality, but without cohesion", commenting upon changes such as the inability to use local "offline" accounts on Windows 11 Home, regressions to the taskbar, a "functionally worse" start menu, Microsoft Teams integration having privacy implications and being a ploy to coerce users into switching to the service, File Explorer obscuring common functions under unclear icons, using "terribly sleazy" behaviors to discourage changing the default web browser from Microsoft Edge, and that the OS "anecdotally feels less responsive, slower, and heavier than Windows 10." It was concluded that Windows 11 "feels practical and productive, but less so than its predecessor in many aspects", while its best features were either "hidden deeper within", required specific hardware (DirectStorage, Auto HDR) or were not available on launch (Android app support).
