The nuclear power debate is a long-running controversy about the risks and benefits of using nuclear reactors to generate electricity for civilian purposes. The debate about nuclear power peaked during the 1970s and 1980s, as more and more reactors were built and came online, and "reached an intensity unprecedented in the history of technology controversies" in some countries.
In the 2010s, with growing public awareness about climate change and the critical role that carbon dioxide and methane emissions plays in causing the heating of the earth's atmosphere, there was a resurgence in the intensity of the nuclear power debate. Nuclear power advocates point to nuclear power's reliable, emission-free, high-density energy, alongside a generation of young physicists and engineers working to bring a new generation of nuclear technology into existence to replace fossil fuels. On the other hand, skeptics point to nuclear accidents such as the death of Louis Slotin, the Windscale fire, the Three Mile Island accident, the Chernobyl disaster, and the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, combined with escalating acts of global terrorism, to argue against continuing use of the technology.
Proponents of nuclear energy argue that nuclear power is the only consistently reliable clean and sustainable energy source which provides huge amounts of uninterrupted energy without polluting the atmosphere or emitting the carbon emissions that cause global warming. They argue that use of nuclear power provides plentiful, well-paying jobs, energy security, reduces a dependence on imported fuels and exposure to price risks associated with resource speculation and Middle East politics. Proponents advance the notion that nuclear power produces virtually no air pollution, in contrast to the massive amount of pollution and carbon emission generated from burning fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. Proponents also believe that nuclear power is the only viable course for a country to achieve energy independence while also meeting their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) to reduce carbon emissions in accordance with the Paris Agreement signed by 195 nations. They emphasize that the risks of storing waste are small and existing stockpiles can be reduced by using this waste to produce fuels for the latest technology in newer reactors. They contend that the operational safety record of nuclear power is much better than the other major kinds of power plants and by preventing pollution, actually saves lives every year.
Opponents say that nuclear power poses numerous threats to people and the environment and point to studies in the literature that question if it will ever be a sustainable energy source. These threats include health risks, accidents and environmental damage from uranium mining, processing and transport. They highlight the high cost and delays in the construction and maintenance of nuclear power plants, and the fears associated with nuclear weapons proliferation, nuclear power opponents fear sabotage by terrorists of nuclear plants, diversion and misuse of radioactive fuels or fuel waste, as well as naturally-occurring leakage from the unsolved and imperfect long-term storage process of radioactive nuclear waste. They also contend that reactors themselves are enormously complex machines where many things can and do go wrong, and there have been many serious nuclear accidents. Critics do not believe that these risks can be reduced through new technology. They further argue that when all the energy-intensive stages of the nuclear fuel chain are considered, from uranium mining to nuclear decommissioning, nuclear power is not a low-carbon electricity source.
History
At the 1963 ground-breaking for what would become the world's largest nuclear power plant, President John F. Kennedy declared that nuclear power was a "step on the long road to peace," and that by using "science and technology to achieve significant breakthroughs" that we could "conserve the resources" to leave the world in better shape. Yet he also acknowledged that the Atomic Age was a "dreadful age" and "when we broke the atom apart, we changed the history of the world." A decade later in Germany, the construction of a nuclear power plant in Wyhl was prevented by local protestors and anti-nuclear groups. The successful use of civil disobedience to prevent the building of this plant was a key moment in the anti-nuclear power movement as it sparked the creation of other groups not only in Germany, but also around the globe. The increase in anti-nuclear power sentiment was heightened after the Three Mile Island's partial meltdown and the Chernobyl Disaster, turning public sentiment even more against nuclear-power. Pro-nuclear power groups, however, have increasingly pointed towards the potential of Nuclear energy to reduce carbon emissions, it being a safer alternative to means of production such as coal, and the overall danger associated with nuclear power to be exaggerated through the media.
Electricity and energy supplied
Nuclear power output globally saw slow but steady increase till 2006 when it peaked at 2'791 TWh, and then dropped with the lowest level of generation in 2012, mostly as result of Japanese reactors being offline for a full year. The output has since continued to grow from newly connected reactors, returning to pre-Fukushima levels in 2019, when IEA described nuclear power as "historically one of the largest contributors of carbon-free electricity" with 452 reactors that in total produced 2'789 TWh electricity. In the same year, United States fleet of nuclear reactors produced 800 TWh low-carbon electricity with an average capacity factor of 92%.
Energy security
For many countries, nuclear power affords energy independence—for example, fossil fuel crisis in 1970's was the main driver behind France's Messmer plan. Nuclear power has been relatively unaffected by embargoes, and uranium is mined in countries willing to export, including Australia and Canada. Periods of low prices of fossil fuels and renewable energy typically reduced political interest towards nuclear power, while periods of expensive fossil fuels and underachieving renewable energy increased it. Increased interest in climate change mitigation, low-carbon energy and global energy crisis resulted in what was described as another "nuclear renaissance" in the early 2020's.
Sustainability
Nuclear power has been used since the 1950s as a low-carbon source of baseload electricity. Nuclear power plants in over 30 countries generate about 10% of global electricity. As of 2019, nuclear generated over a quarter of all low-carbon energy, making it the second largest source after hydropower.
Nuclear power's lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions—including the mining and processing of uranium—are similar to the emissions from renewable energy sources. Nuclear power uses little land per unit of energy produced, compared to the major renewables, and does not create local air pollution. Although the uranium ore used to fuel nuclear fission plants is a non-renewable resource, enough exists to provide a supply for hundreds to thousands of years. However, uranium resources that can be accessed in an economically feasible manner, at the present state, are limited and uranium production could hardly keep up during the expansion phase. Climate change mitigation pathways consistent with ambitious goals typically see an increase in power supply from nuclear.
There is controversy over whether nuclear power is sustainable, in part due to concerns around nuclear waste, nuclear weapon proliferation, and accidents. Radioactive nuclear waste must be managed for thousands of years and nuclear power plants create fissile material that can be used for weapons. For each unit of energy produced, nuclear energy has caused far fewer accidental and pollution-related deaths than fossil fuels, and the historic fatality rate of nuclear is comparable to renewable sources. Public opposition to nuclear energy often makes nuclear plants politically difficult to implement.
Reducing the time and the cost of building new nuclear plants have been goals for decades but costs remain high and timescales long. Various new forms of nuclear energy are in development, hoping to address the drawbacks of conventional plants. Fast breeder reactors are capable of recycling nuclear waste and therefore can significantly reduce the amount of waste that requires geological disposal, but have not yet been deployed on a large-scale commercial basis. Nuclear power based on thorium (rather than uranium) may be able to provide higher energy security for countries that do not have a large supply of uranium. Small modular reactors may have several advantages over current large reactors: It should be possible to build them faster and their modularization would allow for cost reductions via learning-by-doing.
Several countries are attempting to develop nuclear fusion reactors, which would generate small amounts of waste and no risk of explosions. Although fusion power has taken steps forward in the lab, the multi-decade timescale needed to bring it to commercialization and then scale means it won't contribute to a 2050 net zero goal for climate change mitigation.Reliability
The United States fleet of nuclear reactors produced 800 TWh zero-emissions electricity in 2019 with an average capacity factor of 92%.
In 2010, the worldwide average capacity factor was 80.1%. In 2005, the global average capacity factor was 86.8%, the number of SCRAMs per 7,000 hours critical was 0.6, and the unplanned capacity loss factor was 1.6%. Capacity factor is the net power produced divided by the maximum amount possible running at 100% all the time, thus this includes all scheduled maintenance/refueling outages as well as unplanned losses. The 7,000 hours is roughly representative of how long any given reactor will remain critical in a year, meaning that the scram rates translates into a sudden and unplanned shutdown about 0.6 times per year for any given reactor in the world. The unplanned capacity loss factor represents amount of power not produced due to unplanned scrams and postponed restarts.
Since nuclear power plants are fundamentally heat engines, waste heat disposal becomes an issue at high ambient temperature. Droughts and extended periods of high temperature can "cripple nuclear power generation, and it is often during these times when electricity demand is highest because of air-conditioning and refrigeration loads and diminished hydroelectric capacity". In such very hot weather a power reactor may have to operate at a reduced power level or even shut down. In 2009 in Germany, eight nuclear reactors had to be shut down simultaneously on hot summer days for reasons relating to the overheating of equipment or of rivers. Overheated discharge water has resulted in significant killing of fish in the past, harming livelihood and raising public concern. This issue applies equally to all thermal power plants including fossil-gas, coal, CSP and nuclear.
Economics
New nuclear plants
The economics of new nuclear power plants is a controversial subject, since there are diverging views on this topic, and multibillion-dollar investments ride on the choice of an energy source. Nuclear power plants typically have high capital costs for building the plant, but low direct fuel costs (with much of the costs of fuel extraction, processing, use and long-term storage externalized). Therefore, comparison with other power generation methods is strongly dependent on assumptions about construction timescales and capital financing for nuclear plants. Cost estimates also need to take into account plant decommissioning and nuclear waste storage costs. On the other hand, measures to mitigate global warming, such as a carbon tax or carbon emissions trading, may favor the economics of nuclear power.
In recent years there has been a slowdown of electricity demand growth and financing has become more difficult, which impairs large projects such as nuclear reactors, with very large upfront costs and long project cycles which carry a large variety of risks. In Eastern Europe, a number of long-established projects are struggling to find finance, notably Belene in Bulgaria and the additional reactors at Cernavoda in Romania, and some potential backers have pulled out. The reliable availability of cheap gas poses a major economic disincentive for nuclear projects.
Analysis of the economics of nuclear power must take into account who bears the risks of future uncertainties. To date all operating nuclear power plants were developed by state-owned or regulated utility monopolies where many of the risks associated with construction costs, operating performance, fuel price, and other factors were borne by consumers rather than suppliers. Many countries have now liberalized the electricity market where these risks, and the risk of cheaper competitors emerging before capital costs are recovered, are borne by plant suppliers and operators rather than consumers, which leads to a significantly different evaluation of the economics of new nuclear power plants.
Following the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, costs are likely to go up for currently operating and new nuclear power plants, due to increased requirements for on-site spent fuel management and elevated design basis threats.
New nuclear power plants require significant upfront investment which was so far mostly caused by highly customized designs of large plants but can be driven down by standardized, reusable designs (as did South Korea). While new nuclear power plants are more expensive than new renewable energy in upfront investment, the cost of the latter is expected to grow as the grid is saturated with intermittent sources and energy storage as well as land usage becomes a primary barrier to their expansion. A fleet of Small Modular Reactors can be also significantly cheaper than an equivalent single conventional size reactor due to standardized design and much smaller complexity.
In 2020 International Energy Agency called for creation of a global nuclear power licensing framework as in the existing legal situation each plant design needs to be licensed separately in each country.
Cost of decommissioning nuclear plants
The price of energy inputs and the environmental costs of every nuclear power plant continue long after the facility has finished generating its last useful electricity. Both nuclear reactors and uranium enrichment facilities must be decommissioned, returning the facility and its parts to a safe enough level to be entrusted for other uses. After a cooling-off period that may last as long as a century, reactors must be dismantled and cut into small pieces to be packed in containers for final disposal. The process is very expensive, time-consuming, potentially hazardous to the natural environment, and presents new opportunities for human error, accidents or sabotage. However, despite these risks, according to the World Nuclear Association, "In over 50 years of civil nuclear power experience, the management and disposal of civil nuclear waste has not caused any serious health or environmental problems, nor posed any real risk to the general public."
The total energy required for decommissioning can be as much as 50% more than the energy needed for the original construction. In most cases, the decommissioning process costs between US$300 million to US$5.6 billion. Decommissioning at nuclear sites which have experienced a serious accident are the most expensive and time-consuming. In the U.S. there are 13 reactors that have permanently shut down and are in some phase of decommissioning, and none of them have completed the process.
Current UK plants are expected to exceed £73 billion in decommissioning costs.
Subsidies
Critics of nuclear power claim that it is the beneficiary of inappropriately large economic subsidies, taking the form of research and development, financing support for building new reactors and decommissioning old reactors and waste, and that these subsidies are often overlooked when comparing the economics of nuclear against other forms of power generation.
Nuclear power proponents argue that competing energy sources also receive subsidies. Fossil fuels receive large direct and indirect subsidies, such as tax benefits and not having to pay for the greenhouse gases they emit, such as through a carbon tax. Renewable energy sources receive proportionately large direct production subsidies and tax breaks in many nations, although in absolute terms they are often less than subsidies received by non-renewable energy sources.
In Europe, the FP7 research program has more subsidies for nuclear power than for renewable and energy efficiency together; over 70% of this is directed at the ITER fusion project. In the US, public research money for nuclear fission declined from 2,179 to 35 million dollars between 1980 and 2000.
A 2010 report by Global Subsidies Initiative compared relative subsidies of most common energy sources. It found that nuclear energy receives 1.7 US cents per kilowatt hour (kWh) of energy it produces, compared to fossil fuels receiving 0.8 US cents per kWh, renewable energy receiving 5.0 US cents per kWh and biofuels receiving 5.1 US cents per kWh.
Carbon taxation is a significant positive driver in the economy of both nuclear plants and renewable energy sources, all of which are low emissions in their life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions.
In 2019 a heated debate happened in the European Union on creation of a "green finance taxonomy" list intended to create investment opportunities for zero-emission energy technologies. Initially the basic criterion for inclusion was life-cycle emissions at 100 gCO2eq/kWh or less which would include nuclear power which falls well under this threshold (12). Under lobbying from European Greens and Germany an additional "do no harm" criterion was introduced specifically to exclude nuclear power which in their intention should exclude nuclear power from the list.
In July 2020 W. Gyude Moore, former Liberia's Minister for Public Works, called international bodies to start (or restart) funding for nuclear projects in Africa, following the example of US Development Finance Corporation. Moore accused high-income countries like Germany and Australia of "hypocrisy" and "pulling up the ladder behind them", as they have built their strong economy over decades of cheap fossil or nuclear power, and now are effectively preventing African countries from using the only low-carbon and non-intermittent alternative, the nuclear power.
Also in July 2020 Hungary declared its nuclear power will be used as low-emission source of energy to produce hydrogen, while Czechia began the process of approval of public loan to CEZ nuclear power station.
Indirect nuclear insurance subsidy
Kristin Shrader-Frechette has said "if reactors were safe, nuclear industries would not demand government-guaranteed, accident-liability protection, as a condition for their generating electricity". No private insurance company or even consortium of insurance companies "would shoulder the fearsome liabilities arising from severe nuclear accidents".
The potential costs resulting from a nuclear accident (including one caused by a terrorist attack or a natural disaster) are great. The liability of owners of nuclear power plants in the U.S. is currently limited under the Price-Anderson Act (PAA). The Price-Anderson Act, introduced in 1957, was "an implicit admission that nuclear power provided risks that producers were unwilling to assume without federal backing". The Price-Anderson Act "shields nuclear utilities, vendors and suppliers against liability claims in the event of a catastrophic accident by imposing an upper limit on private sector liability". Without such protection, private companies were unwilling to be involved. No other technology in the history of American industry has enjoyed such continuing blanket protection.
The PAA was due to expire in 2002, and the former U.S. vice-president Dick Cheney said in 2001 that "nobody's going to invest in nuclear power plants" if the PAA is not renewed.
In 1983, U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (USNRC) concluded that the liability limits placed on nuclear insurance were significant enough to constitute a subsidy, but did not attempt to quantify the value of such a subsidy at that time. Shortly after this in 1990, Dubin and Rothwell were the first to estimate the value to the U.S. nuclear industry of the limitation on liability for nuclear power plants under the Price Anderson Act. Their underlying method was to extrapolate the premiums operators currently pay versus the full liability they would have to pay for full insurance in the absence of the PAA limits. The size of the estimated subsidy per reactor per year was $60 million prior to the 1982 amendments, and up to $22 million following the 1988 amendments. In a separate article in 2003, Anthony Heyes updates the 1988 estimate of $22 million per year to $33 million (2001 dollars).
In case of a nuclear accident, should claims exceed this primary liability, the PAA requires all licensees to additionally provide a maximum of $95.8 million into the accident pool—totaling roughly $10 billion if all reactors were required to pay the maximum. This is still not sufficient in the case of a serious accident, as the cost of damages could exceed $10 billion. According to the PAA, should the costs of accident damages exceed the $10 billion pool, the process for covering the remainder of the costs would be defined by Congress. In 1982, a Sandia National Laboratories study concluded that depending on the reactor size and 'unfavorable conditions' a serious nuclear accident could lead to property damages as high as $314 billion while fatalities could reach 50,000.
Environmental effects
Nuclear generation does not directly produce sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, mercury or other pollutants associated with the combustion of fossil fuels. Nuclear power has also very high surface power density, which means much less space is used to produce the same amount of energy (thousands times less when compared to wind or solar power).
The primary environmental effects of nuclear power come from uranium mining, radioactive effluent emissions, and waste heat. Nuclear industry, including all past nuclear weapon testing and nuclear accidents, contributes less than 1% of the overall background radiation globally.
A 2014 multi-criterion analysis of impact factors critical for biodiversity, economic and environmental sustainability indicated that nuclear and wind power have the best benefit-to-cost ratios and called environmental movements to reconsider their position on nuclear power and evidence-based policy making. In 2013 an open-letter with the same message signed by climate scientists Ken Caldeira, Kerry Emanuel, James Hansen, Tom Wigley and then co-signed by many others.
Resources usage in uranium mining is 840 m3 of water (up to 90% of the water is recycled) and 30 tonnes of CO2 per tonne of uranium mined. Energy return on investment (EROEI) for a PWR nuclear power plant ranges from 75 to 100 meaning total energy invested in the power plant is returned in 2 months. Median life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of nuclear power plant are 12 gCO2eq/kWh. Both indicators are one of the most competitive of all available energy sources. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) recognizes nuclear as one of the lowest lifecycle emissions energy sources available, lower than solar, and only bested by wind. The US National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL) also cites nuclear as a very low lifecycle emissions source.
In terms of life-cycle surface power density (land surface area used per power output), nuclear power has median density of 240 W/m2, which is 34x more than solar power (6.63 W/m2) and 130x more than wind power (1.84 W/m2) meaning than when the same power output is to be provided by nuclear or renewable sources, the latter are going to use tens to hundreds times more land surface for the same amount of power produced.
Greenpeace and some other environmental organizations have been criticized for distributing claims about CO2 emissions from nuclear power that are unsupported by the scientific data. Their influence has been attributed to "shocking" results of 2020 poll in France, where 69% of the respondents believed that nuclear power contributes to climate change. Greenpeace Australia for example claimed that "there’s no significant savings on carbon output" in nuclear power, which directly contradicts the IPCC life-cycle analysis. In 2018 Greenpeace Spain ignored conclusions from a report by University of Comillas report it procured, showing the lowest CO2 emissions in scenarios involving nuclear power, and instead supported an alternative scenario involving fossil fuels, with much higher emissions.
Life-cycle land usage by nuclear power (including mining and waste storage, direct and indirect) is 100 m2/GWh which is 1⁄2 of solar power and 1/10 of wind power. Land surface usage is the main reason for opposition against on-shore wind farms.
In June 2020 Zion Lights, spokesperson of Extinction Rebellion UK declared her support for nuclear energy as critical part of the energy mix along with renewable energy sources and called fellow environmentalists to accept that nuclear power is part of the "scientifically assessed solutions for addressing climate change".
In July 2020 Good Energy Collective, the first women-only pressure group advocating nuclear power as part of the climate change mitigation solutions was formed in the US. In March 2021, 46 environmental organizations from European Union wrote an open letter to the President of the European Commission calling to increase share of nuclear power as the most effective way of reducing EU's reliance on fossil fuels. The letter also condemned "multi-facetted misrepresentation" and "rigged information about nuclear, with opinion driven by fear" which results in shutting down of stable, low-carbon nuclear power plants.
A 2023 study calculated land surface usage of nuclear power at 0.15 km2/TWh, the lowest of all energy sources.
EU Taxonomy
A comprehensive debate on the role of nuclear power continued since 2020 as part of regulatory work on European Union Taxonomy of environmentally sustainable technologies. Low carbon intensity of nuclear power was not disputed, but opponents raised nuclear waste and thermal pollution as not sustainable element that should exclude it from the sustainable taxonomy. Detailed technical analysis was delegated to the European Commission Joint Research Centre (JRC) which looked at all potential issues of nuclear power from scientific, engineering and regulatory point of view and in March 2021 published a 387-page report which concluded:
The analyses did not reveal any science-based evidence that nuclear energy does more harm to human health or to the environment than other electricity production technologies already included in the Taxonomy as activities supporting climate change mitigation.
— Technical assessment of nuclear energy with respect to the ‘do no significant harm’ criteria of Regulation (EU) 2020/852 (‘Taxonomy Regulation’)
The EU tasked two further expert commissions to validate JRC findings—the Euratom Article 31 expert group on radiation protection and SCHEER (Scientific Committee on Health, Environmental and Emerging Risks). Both groups published their reports in July 2021, largely confirming JRC conclusions, with a number of topics that require further investigation.
The SCHEER is of the opinion that the findings and recommendations of the report with respect of the non-radiological impacts are in the main comprehensive. (...) The SCHEER broadly agrees with these statements, however, the SCHEER is of the view that dependence on an operational regulatory framework is not in itself sufficient to mitigate these impacts, e.g. in mining and milling where the burden of the impacts are felt outside Europe.
— SCHEER review of the JRC report on Technical assessment of nuclear energy with respect to the ‘do no significant harm’ criteria of Regulation (EU) 2020/852 (‘Taxonomy Regulation’)
SCHEER also pointed out that JRC conclusion that nuclear power "does less harm" as the other (e.g. renewable) technologies against which it was compared is not entirely equivalent to the "do no significant harm" criterion postulated by the taxonomy. The JRC analysis of thermal pollution doesn't fully take into account limited water mixing in shallow waters.
The Article 31 group confirmed JRC findings:
The conclusions of the JRC report are based on well-established results of scientific research, reviewed in detail by internationally recognised organisations and committees.
— Opinion of the Group of Experts referred to in Article 31 of the Euratom Treaty on the Joint Research Centre’s Report Technical assessment of nuclear energy with respect to the ‘do no significant harm’ criteria of Regulation (EU) 2020/852 (‘Taxonomy Regulation’)
Also in July 2021 a group of 87 members of European Parliament signed an open letter calling European Commission to include nuclear power in the sustainable taxonomy following favourable scientific reports, and warned against anti-nuclear coalitions that "ignore scientific conclusions and actively oppose nuclear power".
In February 2022 European Commission published the Complementary Climate Delegated Act to the taxonomy, that set specific criteria under which nuclear power may be included in sustainable energy funding schemes. Inclusion of nuclear power and fossil gas in the taxonomy was justified by scientific reports mentioned above and based primarily on very large potential of nuclear power to decarbonize electricity production. For nuclear power, the Taxonomy covers research and development of new Generation IV reactors, new nuclear power plants built with Generation III reactors and life-time extension of existing nuclear power plants. All projects must satisfy requirements as to the safety, thermal pollution and waste management.
Effect on greenhouse gas emissions
An average nuclear power plant prevents emission of 2,000,000 metric tons of CO2, 5,200 metric tons of SO2 and 2,200 metric tons of NOx in a year as compared to an average fossil fuel plant.
While nuclear power does not directly emit greenhouse gases, emissions occur, as with every source of energy, over a facility's life cycle: mining and fabrication of construction materials, plant construction, operation, uranium mining and milling, and plant decommissioning.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change found a median value of 12 g (0.42 oz) equivalent lifecycle carbon dioxide emissions per kilowatt hour (kWh) for nuclear power, being one of the lowest among all energy sources and comparable only with wind power.
Climate and energy scientists James Hansen, Ken Caldeira, Kerry Emanuel and Tom Wigley have released an open letter stating, in part, that
Renewables like wind and solar and biomass will certainly play roles in a future energy economy, but those energy sources cannot scale up fast enough to deliver cheap and reliable power at the scale the global economy requires. While it may be theoretically possible to stabilize the climate without nuclear power, in the real world there is no credible path to climate stabilization that does not include a substantial role for nuclear power.
The statement was widely discussed in the scientific community, with voices both against and in favor. It has been also recognized that the life-cycle CO2 emissions of nuclear power will eventually increase once high-grade uranium ore is used up and lower-grade uranium needs to be mined and milled using fossil fuels, although there is controversy over when this might occur.
As the nuclear power debate continues, greenhouse gas emissions are increasing. Predictions estimate that even with draconian emission reductions within the ten years, the world will still pass 650 ppm of carbon dioxide and a catastrophic 4 °C (7.2 °F) average rise in temperature. Public perception is that renewable energies such as wind, solar, biomass and geothermal are significantly affecting global warming. All of these sources combined only supplied 1.3% of global energy in 2013 as 8 billion tonnes (1.8×1013 lb) of coal was burned annually. This "too little, too late" effort may be a mass form of climate change denial, or an idealistic pursuit of green energy.
In 2015 an open letter from 65 leading biologists worldwide described nuclear power as one of the energy sources that are the most friendly to biodiversity due to its high energy density and low environmental footprint:
Much as leading climate scientists have recently advocated the development of safe, next-generation nuclear energy systems to combat climate change, we entreat the conservation and environmental community to weigh up the pros and cons of different energy sources using objective evidence and pragmatic trade-offs, rather than simply relying on idealistic perceptions of what is 'green'.
— Brave New Climate open letter
In response to 2016 Paris Agreement a number of countries explicitly listed nuclear power as part of their commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In June 2019, an open letter to "the leadership and people of Germany", written by almost 100 Polish environmentalists and scientist, urged Germany to "reconsider the decision on the final decommissioning of fully functional nuclear power plants" for the benefit of the fight against global warming.
In 2020 a group of European scientists published an open letter to the European Commission calling for inclusion of nuclear power as "element of stability in carbon-free Europe". Also in 2020 a coalition of 30 European nuclear industry companies and research bodies published an open letter highlighting that nuclear power remains the largest single source of zero-emissions energy in European Union.
In 2021 prime ministers of Hungary, France, Czech Republic, Romania, Slovak Republic, Poland and Slovenia, signed an open letter to European Commission calling for recognition of important role of nuclear power as the only non-intermittent low-carbon energy source currently available at industrial scale in Europe.
In 2021 UNECE described suggested pathways of building sustainable energy supply with increased role of low-carbon nuclear power. In April 2021 US President's Joe Biden Infrastructure Plan called for 100% of US electricity being generated from low-carbon sources of which nuclear power would be a significant component.
IEA "Net Zero by 2050" pathways published in 2021 assume growth of nuclear power capacity by 104% accompanied by 714% growth of renewable energy sources, mostly solar power. In June 2021 over 100 organisations published a position paper for the COP26 climate conference highlighting the fact that nuclear power is low-carbon dispatchable energy source that has been the most successful in reducing CO2 emissions from the energy sector.
In August 2021 United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) described nuclear power as important tool to mitigate climate change that has prevented 74 Gt of CO2 emissions over the last half century, that provides 20% of energy in Europe and 43% of low-carbon energy.
Faced with increasing fossil gas prices and reopening of new coal and gas power plants, a number of European leaders questioned the anti-nuclear policies of Belgium and Germany. European Commissioner for the Internal Market Thierry Breton described shutting down of operational nuclear power plants as depriving Europe of low-carbon energy capacity. Organizations such as Climate Bonds Initiative, Stand Up for Nuclear, Nuklearia and Mothers for Nuclear Germany-Austria-Switzerland are organizing periodic events in defense of the plants due to be closed.
High-level radioactive waste
The world's nuclear fleet creates about 10,000 metric tons (22,000,000 pounds) of high-level spent nuclear fuel each year. High-level radioactive waste management concerns management and disposal of highly radioactive materials created during production of nuclear power. This requires the use of "geological disposal", or burial, due to the extremely long periods of time that radioactive waste remain deadly to living organisms. Of particular concern are two long-lived fission products, technetium-99 (half-life 220,000 years) and iodine-129 (half-life 15.7 million years), which dominate spent nuclear fuel radioactivity after a few thousand years. The most troublesome transuranic elements in spent fuel are neptunium-237 (half-life two million years) and plutonium-239 (half-life 24,000 years). However, many nuclear power by-products are usable as nuclear fuel themselves; extracting the usable energy producing contents from nuclear waste is called "nuclear recycling". About 80% of the byproducts can be reprocessed and recycled back into nuclear fuel, negating this effect. The remaining high-level radioactive waste requires sophisticated treatment and management to successfully isolate it from the biosphere. This usually necessitates treatment, followed by a long-term management strategy involving permanent storage, disposal or transformation of the waste into a non-toxic form.
Governments around the world are considering a range of waste management and disposal options, usually involving deep-geologic placement, although there has been limited progress toward implementing long-term waste management solutions. This is partly because the timeframes in question when dealing with radioactive waste range from 10,000 to millions of years, according to studies based on the effect of estimated radiation doses.
Since the fraction of a radioisotope's atoms decaying per unit of time is inversely proportional to its half-life, the relative radioactivity of a quantity of buried human radioactive waste would diminish over time compared to natural radioisotopes (such as the decay chain of 120 trillion tons of thorium and 40 trillion tons of uranium which are at relatively trace concentrations of parts per million each over the crust's 3×1019 ton mass).
For instance, over a timeframe of thousands of years, after the most active short half-life radioisotopes decayed, burying U.S. nuclear waste would increase the radioactivity in the top 2,000 feet (610 m) of rock and soil in the United States (100 million km2 or 39 million sq mi) by approximately 0.1 parts per million over the cumulative amount of natural radioisotopes in such a volume, although the vicinity of the site would have a far higher concentration of artificial radioisotopes underground than such an average.
Nuclear waste disposal is one of the most controversial facets of the nuclear power debate. Presently, waste is mainly stored at individual reactor sites and there are over 430 locations around the world where radioactive material continues to accumulate. Experts agree that centralized underground repositories which are well-managed, guarded, and monitored, would be a vast improvement. There is an international consensus on the advisability of storing nuclear waste in deep underground repositories, but no country in the world has yet opened such a site as of 2009. There are dedicated waste storage sites at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant in New Mexico and two in German salt mines, the Morsleben Repository and the Schacht Asse II.
Public debate on the subject frequently focuses of nuclear waste only, ignoring the fact that existing deep geologic repositories globally (including Canada and Germany) already exist and store highly toxic waste such as arsenic, mercury and cyanide, which, unlike nuclear waste, does not lose toxicity over time. Numerous media reports about alleged "radioactive leaks" from nuclear storage sites in Germany also confused waste from nuclear plants with low-level medical waste (such as irradiated X-ray plates and devices).
European Commission Joint Research Centre report of 2021 (see above) concluded:
Management of radioactive waste and its safe and secure disposal is a necessary step in the lifecycle of all applications of nuclear science and technology (nuclear energy, research, industry, education, medical, and other). Radioactive waste is therefore generated in practically every country, the largest contribution coming from the nuclear energy lifecycle in countries operating nuclear power plants. Presently, there is broad scientific and technical consensus that disposal of high-level, long-lived radioactive waste in deep geologic formations is, at the state of today’s knowledge, considered as an appropriate and safe means of isolating it from the biosphere for very long time scales.
Prevented mortality
In March 2013, climate scientists Pushker Kharecha and James Hansen published a paper in Environmental Science & Technology, entitled Prevented mortality and greenhouse gas emissions from historical and projected nuclear power. It estimated an average of 1.8 million lives saved worldwide by the use of nuclear power instead of fossil fuels between 1971 and 2009. The paper examined mortality levels per unit of electrical energy produced from fossil fuels (coal and natural gas) as well as nuclear power. Kharecha and Hansen assert that their results are probably conservative, as they analyze only deaths and do not include a range of serious but non-fatal respiratory illnesses, cancers, hereditary effects and heart problems, nor do they include the fact that fossil fuel combustion in developing countries tends to have a higher carbon and air pollution footprint than in developed countries. The authors also conclude that the emission of some 64 billion tonnes (7.1×1010 tons) of carbon dioxide equivalent have been avoided by nuclear power between 1971 and 2009, and that between 2010 and 2050, nuclear power could additionally avoid up to 80–240 billion tonnes (8.8×1010–2.65×1011 tons).
A 2020 study on Energiewende found that if Germany had postponed the nuclear phase out and phased out coal first it could have saved 1,100 lives and $12 billion in social costs per year.
In 2020 the Vatican has praised "peaceful nuclear technologies" as significant factor to "alleviation of poverty and the ability of countries to meet their development goals in a sustainable way".
Accidents and safety
EU JRC study in 2021 compared actual and potential fatality rates for different energy generation technologies based on The Energy-Related Severe Accident Database (ENSAD). Due to the fact that actual nuclear accidents were very few as compared to technologies such as coal or fossil gas, there was an additional modelling applied using Probabilistic Safety Assessment (PSA) methodology to estimate and quantify the risk of hypothetical severe nuclear accidents in future. The analysis looked at Generation II reactors (PWR) and Generation III (EPR) reactors, and estimated two metrics—fatality rate per GWh (reflecting casualties related to normal operations), and a maximum credible number of casualties in a single hypothetical accident, reflecting general risk aversion. In respect to the fatality rate per GWh in Generation II reactors it made the following conclusion:
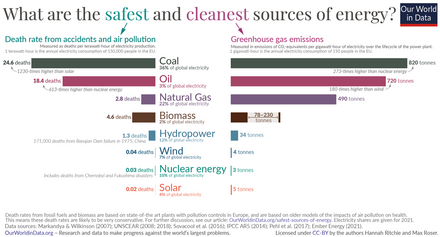
With regard to the first metric, fatality rates, the results indicate that current Generation II nuclear power plants have a very low fatality rate compared to all forms of fossil fuel energies and comparable with hydropower in OECD countries and wind power. Only Solar energy has significantly lower fatality rates. (...) Operating nuclear power plants are subject to continuous improvement. As a result of lessons learned from operating experience, the development of scientific knowledge, or as safety standards are updated, reasonably practicable safety improvements are implemented at existing nuclear power plants.
In respect to fatality rate per GWh Generation III (EPR) reactors:
Generation III nuclear power plants are designed fully in accordance with the latest international safety standards that have been continually updated to take account of advancement in knowledge and of the lessons learned from operating experience, including major events like the accidents at Three Mile Island, Chernobyl and Fukushima. The latest standards include extended requirements related to severe accident prevention and mitigation. The range of postulated initiating events taken into account in the design of the plant has been expanded to include, in a systematic way, multiple equipment failures and other very unlikely events, resulting in a very high level of prevention of accidents leading to melting of the fuel. Despite the high level of prevention of core melt accidents, the design must be such as to ensure the capability to mitigate the consequences of severe degradation of the reactor core. For this, it is necessary to postulate a representative set of core melt accident sequences that will be used to design mitigating features to be implemented in theplant design to ensure the protection of the containment function and avoid large or early radioactive releases into the environment. According to WENRA [3.5-3], the objective is to ensure that even in the worst case, the impact of any radioactive releases to the environment would be limited to within a few km of the site boundary. These latest requirements are reflected in the very low fatality rate for the Generation III European Pressurised-water Reactor (EPR) given in figure 3.5-1. The fatality rate associated with future nuclear energy are the lowest of all the technologies.
The second estimate, the maximum casualties in the worst-case scenario, is much higher, and likelihood of such accident is estimated at 10−10 per reactor year, or once in a ten billion years:
The maximum credible number of fatalities from a hypothetical nuclear accident at a Generation III NPP calculated by Hirschberg et al [3.5-1] is comparable with the corresponding number for hydroelectricity generation, which is in the region of 10,000 fatalities due to hypothetical dam failure. In this case, the fatalities are all or mostly immediate fatalities and are calculated to have a higher frequency of occurrence.
The JRC report notes that "such a number of fatalities, even if based on very pessimistic assumptions, has an impact on public perception due to disaster (or risk) aversion", explaining that general public attributes higher apparent importance to low-frequency events with higher number of casualties, while even much higher numbers of casualties but evenly spread over time are not perceived as equally important. In comparison, in the EU over 400'000 premature deaths per year are attributed to air pollution, and 480'000 premature deaths per year for smokers and 40'000 of non-smokers per year as result of tobacco in the US.
Benjamin K. Sovacool has reported that worldwide there have been 99 accidents at nuclear power plants. Fifty-seven accidents have occurred since the Chernobyl disaster, and 57% (56 out of 99) of all nuclear-related accidents have occurred in the US. Serious nuclear power plant accidents include the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster (2011), Chernobyl disaster (1986), Three Mile Island accident (1979), and the SL-1 accident (1961). Nuclear-powered submarine mishaps include the USS Thresher accident (1963), the K-19 reactor accident (1961), the K-27 reactor accident (1968), and the K-431 reactor accident (1985).
The effect of nuclear accidents has been a topic of debate practically since the first nuclear reactors were constructed. It has also been a key factor in public concern about nuclear facilities. Some technical measures to reduce the risk of accidents or to minimize the amount of radioactivity released to the environment have been adopted. As such, deaths caused by these accidents are minimal, to the point at which the Fukushima evacuation efforts caused an estimated 32 times the number of deaths caused by the accident itself, with 1,000 to 1,600 deaths from the evacuation, and 40 to 50 deaths coming from the accident itself. Despite the use of such safety measures, "there have been many accidents with varying effects as well near misses and incidents".
Nuclear power plants are a complex energy system and opponents of nuclear power have criticized the sophistication and complexity of the technology. Helen Caldicott has said: "... in essence, a nuclear reactor is just a very sophisticated and dangerous way to boil water—analogous to cutting a pound of butter with a chain saw." The 1979 Three Mile Island accident inspired Charles Perrow's book Normal Accidents, where a nuclear accident occurs, resulting from an unanticipated interaction of multiple failures in a complex system. TMI was an example of a normal accident because it was deemed "unexpected, incomprehensible, uncontrollable and unavoidable".
Perrow concluded that the failure at Three Mile Island was a consequence of the system's immense complexity. Such modern high-risk systems, he realized, were prone to failures however well they were managed. It was inevitable that they would eventually suffer what he termed a 'normal accident'. Therefore, he suggested, we might do better to contemplate a radical redesign, or if that was not possible, to abandon such technology entirely. These concerns have been addressed by modern passive safety systems, which require no human intervention to function.
Catastrophic scenarios involving terrorist attacks are also conceivable. An interdisciplinary team from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has estimated that given a three-fold increase in nuclear power from 2005 to 2055, and an unchanged accident frequency, four core damage accidents would be expected in that period.
Proponents of nuclear power argue that in comparison to other sources of power, nuclear power is (along with solar and wind energy) among the safest, accounting for all the risks from mining to production to storage, including the risks of spectacular nuclear accidents. Accidents in the nuclear industry have been less damaging than accidents in the hydroelectric power industry, and less damaging than the constant, incessant damage from air pollutants from fossil fuels. For instance, by running a 1000-MWe nuclear power plant including uranium mining, reactor operation and waste disposal, the radiation dose is 136 person-rem/year, while the dose is 490 person-rem/year for an equivalent coal-fired power plant. The World Nuclear Association provides a comparison of deaths from accidents in course of different forms of energy production. In their comparison, deaths per TW-yr of electricity produced from 1970 to 1992 are quoted as 885 for hydropower, 342 for coal, 85 for natural gas, and 8 for nuclear. Nuclear power plant accidents rank first in terms of their economic cost, accounting for 41 percent of all property damage attributed to energy accidents as of 2008.
In 2020 a Parliamentary inquiry in Australia found nuclear power to be one of the safest and cleanest among 140 specific technologies analyzed based on data provided by MIT.
European Commission Joint Research Centre report of 2021 (see above) concluded:
Severe accidents with core melt did happen in nuclear power plants and the public is well aware of the consequences of the three major accidents, namely Three Mile Island (1979, US), Chernobyl (1986, Soviet Union) and Fukushima (2011, Japan). The NPPs involved in these accidents were of various types (PWR, RBMK and BWR) and the circumstances leading to these events were also very different. Severe accidents are events with extremely low probability but with potentially serious consequences and they cannot be ruled out with 100% certainty. After the Chernobyl accident, international and national efforts focused on developing Gen III nuclear power plants designed according to enhanced requirements related to severe accident prevention and mitigation. The deployment of various Gen III plant designs started in the last 15 years worldwide and now practically only Gen III reactors are constructed and commissioned. These latest technology 10-10 fatalities/GWh, see Figure 3.5-1 (of Part A). The fatality rates characterizing state-of-the art Gen III NPPs are the lowest of all the electricity generation technologies.
Chernobyl steam explosion
The Chernobyl steam explosion was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine. A steam explosion and graphite fire released large quantities of radioactive contamination into the atmosphere, which spread over much of Western USSR and Europe. It is considered the worst nuclear power plant accident in history, and is one of only two classified as a level 7 event on the International Nuclear Event Scale (the other being the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster). The battle to contain the contamination and avert a greater catastrophe ultimately involved over 500,000 workers and cost an estimated 18 billion rubles, crippling the Soviet economy. The accident raised concerns about the safety of the nuclear power industry, slowing its expansion for a number of years.
Despite the fact the Chernobyl disaster became a nuclear power safety debate icon, there were other nuclear accidents in USSR at the Mayak nuclear weapons production plant (nearby Chelyabinsk, Russia) and total radioactive emissions in Chelyabinsk accidents of 1949, 1957 and 1967 together were significantly higher than in Chernobyl. However, the region near Chelyabinsk was and is much more sparsely populated than the region around Chernobyl.
The United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) has conducted 20 years of detailed scientific and epidemiological research on the effects of the Chernobyl accident. Apart from the 57 direct deaths in the accident itself, UNSCEAR predicted in 2005 that up to 4,000 additional cancer deaths related to the accident would appear "among the 600 000 persons receiving more significant exposures (liquidators working in 1986–87, evacuees, and residents of the most contaminated areas)". According to BBC, "It is conclusive that around 5,000 cases of thyroid cancer—most of which were treated and cured—were caused by the contamination. Many suspect that the radiation has caused or will cause other cancers, but the evidence is patchy. Amid reports of other health problems—including birth defects—it still is not clear if any can be attributed to radiation". Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus have been burdened with the continuing and substantial decontamination and health care costs of the Chernobyl disaster.
Fukushima disaster
Following an earthquake, tsunami, and failure of cooling systems at Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant and issues concerning other nuclear facilities in Japan on 11 March 2011, a nuclear emergency was declared. This was the first time a nuclear emergency had been declared in Japan, and 140,000 residents within 20 km (12 mi) of the plant were evacuated. Explosions and a fire resulted in increased levels of radiation, sparking a stock market collapse and panic-buying in supermarkets. The UK, France and some other countries advised their nationals to consider leaving Tokyo, in response to fears of spreading nuclear contamination. The accidents drew attention to ongoing concerns over Japanese nuclear seismic design standards and caused other governments to re-evaluate their nuclear programs. John Price, a former member of the Safety Policy Unit at the UK's National Nuclear Corporation, said that it "might be 100 years before melting fuel rods can be safely removed from Japan's Fukushima nuclear plant".
Three Mile Island accident
The Three Mile Island accident was a core meltdown in Unit 2 (a pressurized water reactor manufactured by Babcock & Wilcox) of the Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station in Dauphin County, Pennsylvania near Harrisburg, United States in 1979. It was the most significant accident in the history of the US commercial nuclear power generating industry, resulting in the release of approximately 2.5 million curies of radioactive noble gases, and approximately 15 curies of iodine-131. Cleanup started in August 1979 and officially ended in December 1993, with a total cleanup cost of about $1 billion. The incident was rated a five on the seven-point International Nuclear Event Scale: Accident With Wider Consequences.
The health effects of the Three Mile Island nuclear accident are widely, but not universally, agreed to be very low level. However, there was an evacuation of 140,000 pregnant women and pre-school age children from the area. The accident crystallized anti-nuclear safety concerns among activists and the general public, resulted in new regulations for the nuclear industry, and has been cited as a contributor to the decline of new reactor construction that was already underway in the 1970s.
New reactor designs
The nuclear power industry has moved to improve engineering design. Generation IV reactors are now in late stage design and development to improve safety, sustainability, efficiency, and cost. Key to the latest designs is the concept of passive nuclear safety. Passive nuclear safety does not require operator actions or electronic feedback in order to shut down safely in the event of a particular type of emergency (usually overheating resulting from a loss of coolant or loss of coolant flow). This is in contrast to older-yet-common reactor designs, where the natural tendency for the reaction was to accelerate rapidly from increased temperatures. In such a case, cooling systems must be operative to prevent meltdown. Past design mistakes like Fukushima in Japan did not anticipate that a tsunami generated by an earthquake would disable the backup systems that were supposed to stabilize the reactor after the earthquake. New reactors with passive nuclear safety eliminate this failure mode.
The United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission has formally engaged in pre-application activities with four applicants who have Generation IV reactors. Of those four applicants' designs, two are molten salt reactors, one is a compact fast reactor, and one is a Modular High temperature gas-cooled reactor.
Whistleblowers
Health effects on population near nuclear power plants and workers
A major concern in the nuclear debate is what the long-term effects of living near or working in a nuclear power station are. These concerns typically center on the potential for increased risks of cancer. However, studies conducted by non-profit, neutral agencies have found no compelling evidence of correlation between nuclear power and risk of cancer.
There has been considerable research done on the effect of low-level radiation on humans. Debate on the applicability of Linear no-threshold model versus Radiation hormesis and other competing models continues, however, the predicted low rate of cancer with low dose means that large sample sizes are required in order to make meaningful conclusions. A study conducted by the National Academy of Sciences found that carcinogenic effects of radiation does increase with dose. The largest study on nuclear industry workers in history involved nearly a half-million individuals and concluded that a 1–2% of cancer deaths were likely due to occupational dose. This was on the high range of what theory predicted by LNT, but was "statistically compatible".
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) has a factsheet that outlines 6 different studies. In 1990 the United States Congress requested the National Cancer Institute to conduct a study of cancer mortality rates around nuclear plants and other facilities covering 1950 to 1984 focusing on the change after operation started of the respective facilities. They concluded in no link. In 2000 the University of Pittsburgh found no link to heightened cancer deaths in people living within 5 miles of plant at the time of the Three Mile Island accident. The same year, the Illinois Public Health Department found no statistical abnormality of childhood cancers in counties with nuclear plants. In 2001 the Connecticut Academy of Science and Engineering confirmed that radiation emissions were negligibly low at the Connecticut Yankee Nuclear Power Plant. Also that year, the American Cancer Society investigated cancer clusters around nuclear plants and concluded no link to radiation noting that cancer clusters occur regularly due to unrelated reasons. Again in 2001, the Florida Bureau of Environmental Epidemiology reviewed claims of increased cancer rates in counties with nuclear plants, however, using the same data as the claimants, they observed no abnormalities.
Scientists learned about exposure to high level radiation from studies of the effects of bombing populations at Hiroshima and Nagasaki. However, it is difficult to trace the relationship of low level radiation exposure to resulting cancers and mutations. This is because the latency period between exposure and effect can be 25 years or more for cancer and a generation or more for genetic damage. Since nuclear generating plants have a brief history, it is early to judge the effects.
Most human exposure to radiation comes from natural background radiation. Natural sources of radiation amount to an average annual radiation dose of 295 millirems (0.00295 sieverts). The average person receives about 53 mrem (0.00053 Sv) from medical procedures and 10 mrem from consumer products per year, as of May 2011. According to the National Safety Council, people living within 50 miles (80 km) of a nuclear power plant receive an additional 0.01 mrem per year. Living within 50 miles of a coal plant adds 0.03 mrem per year.
In its 2000 report, "Sources and effects of ionizing radiation", the UNSCEAR also gives some values for areas where the radiation background is very high. You can for example have some value like 370 nanograys per hour (0.32 rad/a) on average in Yangjiang, China (meaning 3.24 mSv per year or 324 mrem), or 1,800 nGy/h (1.6 rad/a) in Kerala, India (meaning 15.8 mSv per year or 1580 mrem). They are also some other "hot spots", with some maximum values of 17,000 nGy/h (15 rad/a) in the hot springs of Ramsar, Iran (that would be equivalent to 149 mSv per year pr 14,900 mrem per year). The highest background seem to be in Guarapari with a reported 175 mSv per year (or 17,500 mrem per year), and 90,000 nGy/h (79 rad/a) maximum value given in the UNSCEAR report (on the beaches). A study made on the Kerala radiation background, using a cohort of 385,103 residents, concludes that "showed no excess cancer risk from exposure to terrestrial gamma radiation" and that "Although the statistical power of the study might not be adequate due to the low dose, our cancer incidence study [...] suggests it is unlikely that estimates of risk at low doses are substantially greater than currently believed."
Current guidelines established by the NRC, require extensive emergency planning, between nuclear power plants, Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), and the local governments. Plans call for different zones, defined by distance from the plant and prevailing weather conditions and protective actions. In the reference cited, the plans detail different categories of emergencies and the protective actions including possible evacuation.
A German study on childhood cancer in the vicinity of nuclear power plants called "the KiKK study" was published in December 2007. According to Ian Fairlie, it "resulted in a public outcry and media debate in Germany which has received little attention elsewhere". It has been established "partly as a result of an earlier study by Körblein and Hoffmann which had found statistically significant increases in solid cancers (54%), and in leukemia (76%) in children aged less than 5 within 5 km (3.1 mi) of 15 German nuclear power plant sites. It red a 2.2-fold increase in leukemias and a 1.6-fold increase in solid (mainly embryonal) cancers among children living within 5 km of all German nuclear power stations." In 2011 a new study of the KiKK data was incorporated into an assessment by the Committee on Medical Aspects of Radiation in the Environment (COMARE) of the incidence of childhood leukemia around British nuclear power plants. It found that the control sample of population used for comparison in the German study may have been incorrectly selected and other possible contributory factors, such as socio-economic ranking, were not taken into consideration. The committee concluded that there is no significant evidence of an association between risk of childhood leukemia (in under 5-year olds) and living in proximity to a nuclear power plant.
European Commission Joint Research Centre report of 2021 (see above) concluded:
The average annual exposure to a member of the public, due to effects attributable to nuclear energy-based electricity production is about 0.2 microsievert, which is ten thousand times less than the average annual dose due to the natural background radiation. According to the LCIA (Life Cycle Impact Analysis) studies analysed in Chapter 3.4 of Part A, the total impact on human health of both the radiological and non-radiological emissions from the nuclear energy chain are comparable with the human health impact from offshore wind energy.
Safety culture in host nations
Some developing countries which plan to go nuclear have very poor industrial safety records and problems with political corruption. Inside China, and outside the country, the speed of the nuclear construction program has raised safety concerns. Prof. He Zuoxiu, who was involved with China's atomic bomb program, has said that plans to expand production of nuclear energy twentyfold by 2030 could be disastrous, as China was seriously underprepared on the safety front.
China's fast-expanding nuclear sector is opting for cheap technology that "will be 100 years old by the time dozens of its reactors reach the end of their lifespans", according to diplomatic cables from the US embassy in Beijing. The rush to build new nuclear power plants may "create problems for effective management, operation and regulatory oversight" with the biggest potential bottleneck being human resources—"coming up with enough trained personnel to build and operate all of these new plants, as well as regulate the industry". The challenge for the government and nuclear companies is to "keep an eye on a growing army of contractors and subcontractors who may be tempted to cut corners". China is advised to maintain nuclear safeguards in a business culture where quality and safety are sometimes sacrificed in favor of cost-cutting, profits, and corruption. China has asked for international assistance in training more nuclear power plant inspectors.
Nuclear proliferation and terrorism concerns
Opposition to nuclear power is frequently linked to opposition to nuclear weapons. Anti-nuclear scientist Mark Z. Jacobson, believes the growth of nuclear power has "historically increased the ability of nations to obtain or enrich uranium for nuclear weapons". However, many countries have civilian nuclear power programs, while not developing nuclear weapons, and all civilian reactors are covered by IAEA non-proliferation safeguards, including international inspections at the plants.
Iran has developed a nuclear power program under IAEA treaty controls, and attempted to develop a parallel nuclear weapons program in strict separation of the latter to avoid IAEA inspections. Modern light water reactors used in most civilian nuclear power plants cannot be used to produce weapons-grade uranium.
A 1993–2013 Megatons to Megawatts Program successfully led to recycling 500 tonnes of Russian warhead-grade high-enriched uranium (equivalent to 20,008 nuclear warheads) to low-enriched uranium used as fuel for civilian power plants and was the most successful non-proliferation program in history.
Four AP1000 reactors, which were designed by the American Westinghouse Electric Company are currently, as of 2011, being built in China and a further two AP1000 reactors are to be built in the US. Hyperion Power Generation, which is designing modular reactor assemblies that are proliferation resistant, is a privately owned US corporation, as is Terrapower which has the financial backing of Bill Gates and his Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Vulnerability of plants to attack
Development of covert and hostile nuclear installations was occasionally prevented by military operations in what is described as "radical counter-proliferation" activities.
- Operation Gunnerside (1943), by Allies, against heavy water factory in German-occupied Norway
- Operation Scorch Sword (1980), by Iran, against construction site of Osirak nuclear complex construction site in Iraq.
- Operation Opera (1981), by Israel, against the same Osirak site in Iraq.
- Iraqi air force attacks on unfinished Bushehr nuclear plant in Iran during Iraq-Iran war (1986, 1987).
- Operation Outside the Box (2007), by Israel, against a suspected Al Kibar nuclear construction site in Syria.
No military operations were targeted against live nuclear reactors and no operations resulted in nuclear incidents. No terrorist attacks targeted live reactors, with the only recorded quasi-terrorist attacks on a nuclear power plant construction sites by anti-nuclear activists:
- 1977–1982 ETA performed numerous attacks, including bombings and kidnappings, against Lemóniz Nuclear Power Plant constructions site and its personnel
- 18 January 1982 when environmental activist Chaïm Nissim fired RPG rockets at Superphénix reactor construction site in France, causing no damage
According to a 2004 report by the U.S. Congressional Budget Office, "The human, environmental, and economic costs from a successful attack on a nuclear power plant that results in the release of substantial quantities of radioactive material to the environment could be great." The United States 9/11 Commission has said that nuclear power plants were potential targets originally considered for the 11 September 2001 attacks. If terrorist groups could sufficiently damage safety systems to cause a core meltdown at a nuclear power plant, and/or sufficiently damage spent fuel pools, such an attack could lead to a widespread radioactive contamination.
New reactor designs have features of passive safety, such as the flooding of the reactor core without active intervention by reactor operators. But these safety measures have generally been developed and studied with respect to accidents, not to the deliberate reactor attack by a terrorist group. However, the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission now also requires new reactor license applications to consider security during the design stage.
Use of waste byproduct as a weapon
There is a concern if the by-products of nuclear fission (the nuclear waste generated by the plant) were to be left unprotected it could be stolen and used as a radiological weapon, colloquially known as a "dirty bomb". No actual terrorist attacks involving "dirty bomb" were ever recorded, although cases of illegal trade of fissile material happened.
There are additional concerns that the transportation of nuclear waste along roadways or railways opens it up for potential theft. The United Nations has since called upon world leaders to improve security in order to prevent radioactive material falling into the hands of terrorists, and such fears have been used as justifications for centralized, permanent, and secure waste repositories and increased security along transportation routes.
The spent fissile fuel is not radioactive enough to create any sort of effective nuclear weapon, in a traditional sense where the radioactive material is the means of explosion. Nuclear reprocessing plants also acquire uranium from spent reactor fuel and take the remaining waste into their custody.
Public opinion
Support for nuclear power varies between countries and has changed significantly over time.
Trends and future prospects
Following the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, the International Energy Agency halved its estimate of additional nuclear generating capacity to be built by 2035. Platts has reported that "the crisis at Japan's Fukushima nuclear plants has prompted leading energy-consuming countries to review the safety of their existing reactors and cast doubt on the speed and scale of planned expansions around the world". In 2011, The Economist reported that nuclear power "looks dangerous, unpopular, expensive and risky", and that "it is replaceable with relative ease and could be forgone with no huge structural shifts in the way the world works".
In September 2011, German engineering giant Siemens announced it will withdraw entirely from the nuclear industry, as a response to the Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan. The company is to boost its work in the renewable energy sector. Commenting on the German government's policy to close nuclear plants, Werner Sinn, president of the Ifo Institute for Economic Research at the University of Munich, stated: "It is wrong to shut down the atomic power plants, because this is a cheap source of energy, and wind and solar power are by no means able to provide a replacement. They are much more expensive, and the energy that comes out is of inferior quality. Energy-intensive industries will move out, and the competitiveness of the German manufacturing sector will be reduced or wages will be depressed."
But with regard to the proposition that "Improved communication by industry might help to overcome current fears regarding nuclear power", Princeton University Physicist M. V. Ramana says that the basic problem is that there is "distrust of the social institutions that manage nuclear energy", and a 2001 survey by the European Commission found that "only 10.1 percent of Europeans trusted the nuclear industry". This public distrust is periodically reinforced by safety violations by nuclear companies, or through ineffectiveness or corruption on the part of nuclear regulatory authorities. Once lost, says Ramana, trust is extremely difficult to regain. Faced with public antipathy, the nuclear industry has "tried a variety of strategies to persuade the public to accept nuclear power", including the publication of numerous "fact sheets" that discuss issues of public concern. Ramana says that none of these strategies have been very successful.
In March 2012, E.ON UK and RWE npower announced they would be pulling out of developing new nuclear power plants in the UK, placing the future of nuclear power in the UK in doubt. More recently, Centrica (who own British Gas) pulled out of the race on 4 February 2013 by letting go its 20% option on four new nuclear plants. Cumbria county council (a local authority) turned down an application for a final waste repository on 30 January 2013 – there is currently no alternative site on offer.
In terms of current nuclear status and future prospects:
- Ten new reactors were connected to the grid, In 2015, the highest number since 1990, but expanding Asian nuclear programs are balanced by retirements of aging plants and nuclear reactor phase-outs. Seven reactors were permanently shut down.
- 441 operational reactors had a worldwide net capacity of 382,855 megawatts of electricity in 2015. However, some reactors are classified as operational, but are not producing any power.
- 67 new nuclear reactors were under construction in 2015, including four EPR units. The first two EPR projects, in Finland and France, were meant to lead a nuclear renaissance but both are facing costly construction delays. Construction commenced on two Chinese EPR units in 2009 and 2010. The Chinese units were to start operation in 2014 and 2015, but the Chinese government halted construction because of safety concerns. China's National Nuclear Safety Administration carried out on-site inspections and issued a permit to proceed with function tests in 2016. Taishan 1 is expected to start up in the first half of 2017 and Taishan 2 is scheduled to begin operating by the end of 2017.
In February 2020, the world's first open-source platform for the design, construction, and financing of nuclear power plants, OPEN100, was launched in the United States. This project aims to provide a clear pathway to a sustainable, low cost, zero-carbon future. Collaborators in the OPEN100 project include Framatome, Studsvik, the UK's National Nuclear Laboratory, Siemens, Pillsbury, the Electric Power Research Institute, the US Department of Energy's Idaho National Laboratory, and Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
In October 2020, the U.S. Department of Energy announced selecting two U.S.-based teams to receive $160 million in initial funding under the new Advanced Reactor Demonstration Program (ARDP). TerraPower LLC (Bellevue, WA) and X-energy (Rockville, MD) were each awarded $80 million to build two advanced nuclear reactors that can be operational within seven years.