From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pet



A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive/cute appearances, intelligence, and relatable personalities, but some pets may be taken in on an altruistic basis (such as a stray animal) and accepted by the owner regardless of these characteristics.
Two of the most popular pets are dogs and cats. Other animals commonly kept include rabbits; ferrets; pigs; rodents such as gerbils, hamsters, chinchillas, rats, mice, and guinea pigs; birds such as parrots, passerines, and fowls; reptiles such as turtles, lizards, snakes, and iguanas; aquatic pets such as fish, freshwater snails, and saltwater snails; amphibians such as frogs and salamanders; and arthropod pets such as tarantulas and hermit crabs. Smaller pets include rodents, while the equine and bovine group include the largest companion animals.
Pets provide their owners, or guardians, both physical and emotional benefits. Walking a dog can provide both the human and the dog with exercise, fresh air, and social interaction. Pets can give companionship to people who are living alone or elderly adults who do not have adequate social interaction with other people. There is a medically approved class of therapy animals that are brought to visit confined humans, such as children in hospitals or elders in nursing homes. Pet therapy utilizes trained animals and handlers to achieve specific physical, social, cognitive, or emotional goals with patients.
People most commonly get pets for companionship, to protect a home or property, or because of the perceived beauty or attractiveness of the animals. A 1994 Canadian study found that the most common reasons for not owning a pet were lack of ability to care for the pet when traveling (34.6%), lack of time (28.6%), and lack of suitable housing (28.3%), with dislike of pets being less common (19.6%). Some scholars, ethicists, and animal rights organizations have raised concerns over keeping pets because of the lack of autonomy and the objectification of non-human animals.
Pet popularity
In China, spending on domestic animals has grown from an estimated $3.12 billion in 2010 to $25 billion in 2018. The Chinese people own 51 million dogs and 41 million cats, with pet owners often preferring to source pet food internationally. There are a total of 755 million pets, increased from 389 million in 2013.
According to a survey promoted by Italian family associations in 2009, it is estimated that there are approximately 45 million pets in Italy. This includes 7 million dogs, 7.5 million cats, 16 million fish, 12 million birds, and 10 million snakes.
A 2007 survey by the University of Bristol found that 26% of UK households owned cats and 31% owned dogs, estimating total domestic populations of approximately 10.3 million cats and 10.5 million dogs in 2006. The survey also found that 47.2% of households with a cat had at least one person educated to degree level, compared with 38.4% of homes with dogs.
Sixty-eight percent of U.S. households, or about 85 million families, own a pet, according to the 2017-2018 National Pet Owners Survey conducted by the American Pet Products Association (APPA). This is up from 56 percent of U.S. households in 1988, the first year the survey was conducted. There are approximately 86.4 million pet cats and approximately 78.2 million pet dogs in the United States, and a United States 2007–2008 survey showed that dog-owning households outnumbered those owning cats, but that the total number of pet cats was higher than that of dogs. The same was true for 2011. In 2013, pets outnumbered children four to one in the United States.
Most popular pets in the U.S. (millions) Pet Global population U.S. population U.S. inhabited households U.S. average per inhabited household Cat 202 93.6 38.2 2.45 Dog 171 77.5 45.6 1.70 Fish N/A 171.7 13.3 12.86 Small mammals N/A 15.9 5.3 3.00 Birds N/A 15.0 6.0 2.50 Reptiles & amphibians N/A 13.6 4.7 2.89 Equine N/A 13.3 3.9 3.41
Effects on pets' health
Keeping animals as pets may be detrimental to their health if certain requirements are not met. An important issue is inappropriate feeding, which may produce clinical effects. The consumption of chocolate or grapes by dogs, for example, may prove fatal. Certain species of houseplants can also prove toxic if consumed by pets. Examples include philodendrons and Easter lilies, which can cause severe kidney damage to cats, and poinsettias, begonia, and aloe vera, which are mildly toxic to dogs. For birds, chocolate can be deadly, and foods intended for human consumption, such as bread, crackers, and dairy items, can potentially cause health problems.
Housepets, particularly dogs and cats in industrialized societies, are highly susceptible to obesity. Overweight pets have been shown to be at a higher risk of developing diabetes, liver problems, joint pain, kidney failure, and cancer. Lack of exercise and high-caloric diets are considered to be the primary contributors to pet obesity.
Effects of pets on their caregivers' health


Health benefits
It is widely believed among the public, and among many scientists, that pets probably bring mental and physical health benefits to their owners; a 1987 NIH statement cautiously argued that existing data was "suggestive" of a significant benefit. A recent dissent comes from a 2017 RAND study, which found that at least in the case of children, having a pet per se failed to improve physical or mental health by a statistically significant amount; instead, the study found children who were already prone to being healthy were more likely to get pets in the first place. Conducting long-term randomized trials to settle the issue would be costly or infeasible.
Observed correlations
Pets might have the ability to stimulate their caregivers, in particular the elderly, giving people someone to take care of, someone to exercise with, and someone to help them heal from a physically or psychologically troubled past. Animal company can also help people to preserve acceptable levels of happiness despite the presence of mood symptoms like anxiety or depression. Having a pet may also help people achieve health goals, such as lowered blood pressure, or mental goals, such as decreased stress. There is evidence that having a pet can help a person lead a longer, healthier life. In a 1986 study of 92 people hospitalized for coronary ailments, within a year, 11 of the 29 patients without pets had died, compared to only 3 of the 52 patients who had pets. Having pet(s) was shown to significantly reduce triglycerides, and thus heart disease risk, in the elderly. A study by the National Institute of Health found that people who owned dogs were less likely to die as a result of a heart attack than those who did not own one. There is some evidence that pets may have a therapeutic effect in dementia cases. Other studies have shown that for the elderly, good health may be a requirement for having a pet, and not a result. Dogs trained to be guide dogs can help people with vision impairment. Dogs trained in the field of Animal-Assisted Therapy (AAT) can also benefit people with other disabilities.
Pets in long-term care institutions
People residing in a long-term care facility, such as a hospice or nursing home, may experience health benefits from pets. Pets help them to cope with the emotional issues related to their illness. They also offer physical contact with another living creature, something that is often missing in an elder's life. Pets for nursing homes are chosen based on the size of the pet, the amount of care that the breed needs, and the population and size of the care institution. Appropriate pets go through a screening process and, if it is a dog, additional training programs to become a therapy dog. There are three types of therapy dogs: facility therapy dogs, animal-assisted therapy dogs, and therapeutic visitation dogs. The most common therapy dogs are therapeutic visitation dogs. These dogs are household pets whose handlers take time to visit hospitals, nursing homes, detention facilities, and rehabilitation facilities. Different pets require varying amounts of attention and care; for example, cats may have lower maintenance requirements than dogs.
Connection with community
In addition to providing health benefits for their owners, pets also impact the social lives of their owners and their connection to their community. There is some evidence that pets can facilitate social interaction. Assistant Professor of Sociology at the University of Colorado at Boulder, Leslie Irvine has focused her attention on pets of the homeless population. Her studies of pet ownership among the homeless found that many modify their life activities for fear of losing their pets. Pet ownership prompts them to act responsibly, with many making a deliberate choice not to drink or use drugs, and to avoid contact with substance abusers or those involved in any criminal activity for fear of being separated from their pet. Additionally, many refuse to house in shelters if their pet is not allowed to stay with them.
Health risks
Health risks that are associated with pets include:
- Aggravation of allergies and asthma caused by dander and fur or feathers
- Falling injuries. Tripping over pets, especially dogs causes more than 86,000 falls serious enough to prompt a trip to the emergency room each year in the United States. Among elderly and disabled people, these falls have resulted in life-threatening injuries and broken bones.
- Injury, mauling, and sometimes death caused by pet bites and attacks
- Disease or parasites due to animal hygiene problems, lack of appropriate treatment, and undisciplined behavior (feces and urine)
- Stress caused by the behavior of animals
- Anxiety over who will care for the animal should the owner no longer be able to do so
Legislation
Treaties
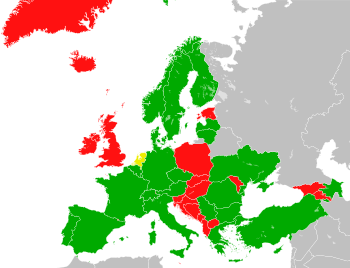
| | Signed and ratified | | Acceded or succeeded |
| | Only signed | | Not signed (CoE member states) |
| | Not signed (non-CoE member states) |
The European Convention for the Protection of Pet Animals is a 1987 treaty of the Council of Europe – but accession to the treaty is open to all states in the world – to promote the welfare of pet animals and ensure minimum standards for their treatment and protection. It went into effect on 1 May 1992, and as of June 2020, it has been ratified by 24 states.
National and local laws
Ownership or guardianship
Pets have commonly been considered private property, owned by individual persons. Many legal protections have existed (historically and today) with the intention of safeguarding pets' and other animals' well-being. Since the year 2000, a small but increasing number of jurisdictions in North America have enacted laws redefining pet's owners as guardians. Intentions have been characterized as simply changing attitudes and perceptions but not legal consequences to working toward legal personhood for pets themselves. Some veterinarians and breeders have opposed these moves. The question of pets' legal status can arise with concern to purchase or adoption, custody, divorce, estate and inheritance, injury, damage, and veterinary malpractice.
Limitations on species
States, cities, and towns in Western countries commonly enact local ordinances to limit the number or kind of pets a person may keep personally or for business purposes. Prohibited pets may be specific to certain breeds such as pit bulls or Rottweilers, they may apply to general categories of animals (such as livestock, exotic animals, wild animals, and canid or felid hybrids), or they may simply be based on the animal's size. Additional or different maintenance rules and regulations may also apply. Condominium associations and owners of rental properties also commonly limit or forbid tenants' keeping of pets.
In Belgium and the Netherlands, the government publishes white lists and black lists (called 'positive' and 'negative lists') with animal species that are designated to be appropriate to be kept as pets (positive) or not (negative). The Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy originally established its first positive list (positieflijst) per 1 February 2015 for a set of 100 mammals (including cats, dogs and production animals) deemed appropriate as pets on the recommendations of Wageningen University. Parliamentary debates about such a pet list date back to the 1980s, with continuous disagreements about which species should be included and how the law should be enforced. In January 2017, the white list was expanded to 123 species, while the black list that had been set up was expanded (with animals like the brown bear and two great kangaroo species) to contain 153 species unfit for petting, such as the armadillo, the sloth, the European hare, and the wild boar.
Killing and eating pets
In January 2011, the Belgian Federal Agency for the Safety of the Food Chain stated that people are not allowed to kill random cats walking in their garden, but "nowhere in the law does it say that you can't eat your cat, dog, rabbit, fish or whatever. You just have to kill them in an animal-friendly way." Since 1 July 2014, it is illegal in the Netherlands for owners to kill their own cats and dogs kept as pets. Parakeets, guinea pigs, hamsters and other animals may still be killed by their owners, but nonetheless when owners mistreat their companion animals (for example, in the process of killing them), the owners can still be prosecuted under Dutch law.
Environmental impact
Pets have a considerable environmental impact, especially in countries where they are common or held in high densities. For instance, the 163 million dogs and cats kept in the United States consume about 20% of the amount of dietary energy that humans do and an estimated 33% of the animal-derived energy. They produce about 30% ± 13%, by mass, as much feces as Americans, and through their diet, constitute about 25–30% of the environmental impacts from animal production in terms of the use of land, water, fossil fuel, phosphate, and biocides. Dog and cat animal product consumption is responsible for the release of up to 64 ± 16 million tons CO2-equivalent methane and nitrous oxide, two powerful greenhouse gasses. Americans are the largest pet owners in the world, but pet ownership in the US has considerable environmental costs.
Types
While many people have kept many different species of animals in captivity over the course of human history, only a relative few have been kept long enough to be considered domesticated. Other types of animal, notably monkeys, have never been domesticated but are still sold and kept as pets. Some wild animals are kept as pets, such as tigers, even though this is illegal. There is a market for illegal pets.
Domesticated
Domesticated pets are most common. A domesticated animal is a species that has been made fit for a human environment, by being consistently kept in captivity and selectively bred over a long enough period of time that it exhibits marked differences in behavior and appearance from its wild relatives. Domestication contrasts with taming, which is simply when an un-domesticated, wild animal has become tolerant of human presence, and perhaps even enjoys it.
Large mammals that might be kept as pets include: alpaca, camel, cattle, donkey, goat, horse, llama, pig, and sheep. Small mammals that might be kept as pets include: ferret, hedgehog, rabbit, sugar glider, and rodents, including rat, mouse, hamster, guinea pig, gerbil, and chinchilla. Other mammals include cat, dog, monkey, and domesticated silver fox.
Birds kept as pets include companion parrots like the budgie and cockatiel, fowl such as chickens, turkeys, ducks, geese, and quail, columbines, and passerines, namely finches and canaries.
Fish kept as pets include: goldfish, koi, Siamese fighting fish (Betta), barb, guppy, molly, Japanese rice fish (Medaka), and oscar.
Arthropods kept as pets include bees, such as honey bees and stingless bees, Silk moth, and ant farms.
Reptiles and amphibians kept as pets include snakes, turtles, axolotl, frogs and salamanders.
Wild animals

Wild animals are kept as pets. The term wild in this context specifically applies to any species of animal which has not undergone a fundamental change in behavior to facilitate a close co-existence with humans. Some species may have been bred in captivity for a considerable length of time, but are still not recognized as domesticated.
Generally, wild animals are recognized as not suitable to keep as pets, and this practice is completely banned in many places. In other areas, certain species are allowed to be kept, and it is usually required for the owner to obtain a permit. It is considered animal cruelty by some, as most often, wild animals require precise and constant care that is very difficult to meet in captive conditions. Many large and instinctively aggressive animals are extremely dangerous, and numerous times have they killed their handlers.
History
Prehistory
Archaeology suggests that human ownership of dogs as pets may date back to at least 12,000 years ago.
Ancient history
Ancient Greeks and Romans would openly grieve for the loss of a dog, evidenced by inscriptions left on tombstones commemorating their loss. The surviving epitaphs dedicated to horses are more likely to reference a gratitude for the companionship that had come from war horses rather than race horses. The latter may have chiefly been commemorated as a way to further the owner's fame and glory. In Ancient Egypt, dogs and baboons were kept as pets and buried with their owners. Dogs were given names, which is significant as Egyptians considered names to have magical properties.
Victorian era: the rise of modern pet keeping
Throughout the 17th and 18th-century pet keeping in the modern sense gradually became accepted throughout Britain. Initially, aristocrats kept dogs for both companionship and hunting. Thus, pet keeping was a sign of elitism within society. By the 19th century, the rise of the middle class stimulated the development of pet keeping and it became inscribed within the bourgeois culture.
Economy
As the popularity of pet-keeping in the modern sense rose during the Victorian era, animals became a fixture within urban culture as commodities and decorative objects. Pet keeping generated a commercial opportunity for entrepreneurs. By the mid-19th century, nearly twenty thousand street vendors in London dealt with live animals. The popularity of animals also developed a demand for animal goods such as accessories and guides for pet keeping. Pet care developed into a big business by the end of the nineteenth century.
Profiteers also sought out pet stealing as a means for economic gain. Utilizing the affection that owners had for their pets, professional dog stealers would capture animals and hold them for ransom. The development of dog stealing reflects the increased value of pets. Pets gradually became defined as the property of their owners. Laws were created that punished offenders for their burglary.
Social
Pets and animals also had social and cultural implications throughout the nineteenth century. The categorization of dogs by their breeds reflected the hierarchical, social order of the Victorian era. The pedigree of a dog represented the high status and lineage of their owners and reinforced social stratification. Middle-class owners valued the ability to associate with the upper-class through ownership of their pets. The ability to care for a pet signified respectability and the capability to be self-sufficient. According to Harriet Ritvo, the identification of "elite animal and elite owner was not a confirmation of the owner's status but a way of redefining it."
Entertainment
The popularity of dog and pet keeping generated animal fancy. Dog fanciers showed enthusiasm for owning pets, breeding dogs, and showing dogs in various shows. The first dog show took place on 28 June 1859 in Newcastle and focused mostly on sporting and hunting dogs. However, pet owners produced an eagerness to demonstrate their pets as well as have an outlet to compete. Thus, pet animals gradually were included within dog shows. The first large show, which would host one thousand entries, took place in Chelsea in 1863. The Kennel Club was created in 1873 to ensure fairness and organization within dog shows. The development of the Stud Book by the Kennel Club defined policies, presented a national registry system of purebred dogs, and essentially institutionalized dog shows.
Pet ownership by non-humans
Pet ownership by animals in the wild, as an analogue to the human phenomenon, has not been observed and is likely non-existent in nature. One group of capuchin monkeys was observed appearing to care for a marmoset, a fellow New World monkey species, however observations of chimpanzees apparently "playing" with small animals like hyraxes have ended with the chimpanzees killing the animals and tossing the corpses around.
A 2010 study states that human relationships with animals have an exclusive human cognitive component and that pet-keeping is a fundamental and ancient attribute of the human species. Anthropomorphism, or the projection of human feelings, thoughts and attributes on to animals, is a defining feature of human pet-keeping. The study identifies it as the same trait in evolution responsible for domestication and concern for animal welfare. It is estimated to have arisen at least 100,000 years before present (ybp) in Homo sapiens.
It is debated whether this redirection of human nurturing behaviour towards non-human animals, in the form of pet-keeping, was maladaptive, due to being biologically costly, or whether it was positively selected for. Two studies suggest that the human ability to domesticate and keep pets came from the same fundamental evolutionary trait and that this trait provided a material benefit in the form of domestication that was sufficiently adaptive to be positively selected for. A 2011 study suggests that the practical functions that some pets provide, such as assisting hunting or removing pests, could have resulted in enough evolutionary advantage to allow for the persistence of this behaviour in humans and outweigh the economic burden held by pets kept as playthings for immediate emotional rewards. Two other studies suggest that the behaviour constitutes an error, side effect or misapplication of the evolved mechanisms responsible for human empathy and theory of mind to cover non-human animals which has not sufficiently impacted its evolutionary advantage in the long run.
Animals in captivity, with the help of caretakers, have been considered to have owned "pets". Examples of this include Koko the gorilla who had several pet cats, Tonda the orangutan and a pet cat and Tarra the elephant and a dog named Bella.






