Proterozoic snowball periods | ||||||
−1000 — – −950 — – −900 — – −850 — – −800 — – −750 — – −700 — – −650 — – −600 — – −550 — | ← Gaskiers (millions of years ago) | |||||
| ||||||
Estimate of Proterozoic glacial periods.
Dating of pre-Gaskiers glaciations is uncertain. As for the Kaigas, its very existence is doubted by some. The Huronian glaciation, is not shown, there is a lack of any significant evidence for a Snowball Earth during the time period. | ||||||
The Snowball Earth is a geohistorical hypothesis that proposes during one or more of Earth's icehouse climates, the planet's surface became entirely or nearly entirely frozen with no liquid oceanic or surface water exposed to the atmosphere. The most academically referred period of such global glaciation is believed to have occurred sometime before 650 mya during the Cryogenian period.
Proponents of the hypothesis argue that it best explains sedimentary deposits that are generally believed to be of glacial origin at tropical palaeolatitudes and other enigmatic features in the geological record. Opponents of the hypothesis contest the geological evidence for global glaciation and the geophysical feasibility of an ice- or slush-covered ocean, and they emphasize the difficulty of escaping an all-frozen condition. Several unanswered questions remain, including whether Earth was a full snowball or a "slushball" with a thin equatorial band of open (or seasonally open) water. The snowball-Earth episodes are proposed to have occurred before the sudden radiation of multicellular bioforms known as the Cambrian explosion. The most recent snowball episode may have triggered the evolution of multicellularity.
History
−4500 — – — – −4000 — – — – −3500 — – — – −3000 — – — – −2500 — – — – −2000 — – — – −1500 — – — – −1000 — – — – −500 — – — – 0 — |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
First evidence for ancient glaciation
Long before the idea of a global glaciation was first proposed, a series of discoveries occurred that accumulated evidence for ancient Precambrian glaciations. The first of these discoveries was published in 1871 by J. Thomson, who found ancient glacier-reworked material (tillite) in Islay, Scotland. Similar findings followed in Australia (1884) and India (1887). A fourth and very illustrative finding, which came to be known as "Reusch's Moraine," was reported by Hans Reusch in northern Norway in 1891. Many other findings followed, but their understanding was hampered by the rejection (at the time) of continental drift.
Global glaciation proposed
Douglas Mawson, an Australian geologist and Antarctic explorer, spent much of his career studying the stratigraphy of the Neoproterozoic in South Australia, where he identified thick and extensive glacial sediments. As a result, late in his career, he speculated about the possibility of global glaciation.
Mawson's ideas of global glaciation, however, were based on the mistaken assumption that the geographic position of Australia, and those of other continents where low-latitude glacial deposits are found, have remained constant through time. With the advancement of the continental drift hypothesis, and eventually plate tectonic theory, came an easier explanation for the glaciogenic sediments—they were deposited at a time when the continents were at higher latitudes.
In 1964, the idea of global-scale glaciation reemerged when W. Brian Harland published a paper in which he presented palaeomagnetic data showing that glacial tillites in Svalbard and Greenland were deposited at tropical latitudes. From this data and the sedimentological evidence that the glacial sediments interrupt successions of rocks commonly associated with tropical to temperate latitudes, he argued that an ice age occurred that was so extreme that it resulted in marine glacial rocks being deposited in the tropics.
In the 1960s, Mikhail Budyko, a Soviet climatologist, developed a simple energy-balance climate model to investigate the effect of ice cover on global climate. Using this model, Budyko found that if ice sheets advanced far enough out of the polar regions, a feedback loop ensued where the increased reflectiveness (albedo) of the ice led to further cooling and the formation of more ice, until the entire Earth was covered in ice and stabilized in a new ice-covered equilibrium. While Budyko's model showed that this ice-albedo stability could happen, he concluded that it had, in fact, never happened, as his model offered no way to escape from such a feedback loop.
In 1971, Aron Faegre, an American physicist, showed that a similar energy-balance model predicted three stable global climates, one of which was snowball Earth. This model introduced Edward Norton Lorenz's concept of intransitivity, indicating that there could be a major jump from one climate to another, including to snowball Earth.
The term "snowball Earth" was coined by Joseph Kirschvink in a short paper published in 1992 within a lengthy volume concerning the biology of the Proterozoic eon. The major contributions from this work were: (1) the recognition that the presence of banded iron formations is consistent with such a global glacial episode, and (2) the introduction of a mechanism by which to escape from a completely ice-covered Earth—specifically, the accumulation of CO2 from volcanic outgassing leading to an ultra-greenhouse effect.
Franklyn Van Houten's discovery of a consistent geological pattern in which lake levels rose and fell is now known as the "Van Houten cycle". His studies of phosphorus deposits and banded iron formations in sedimentary rocks made him an early adherent of the snowball Earth hypothesis postulating that the planet's surface froze more than 650 Ma.
Interest in the notion of a snowball Earth increased dramatically after Paul F. Hoffman and his co-workers applied Kirschvink's ideas to a succession of Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks in Namibia and elaborated upon the hypothesis in the journal Science in 1998 by incorporating such observations as the occurrence of cap carbonates.
In 2010, Francis A. Macdonald, assistant professor at Harvard in the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, and others, reported evidence that Rodinia was at equatorial latitude during the Cryogenian period with glacial ice at or below sea level, and that the associated Sturtian glaciation was global.
Evidence
The snowball Earth hypothesis was originally devised to explain geological evidence for the apparent presence of glaciers at tropical latitudes. According to modelling, an ice–albedo feedback would result in glacial ice rapidly advancing to the equator once the glaciers spread to within 25° to 30° of the equator. Therefore, the presence of glacial deposits within the tropics suggests global ice cover.
Critical to an assessment of the validity of the theory, therefore, is an understanding of the reliability and significance of the evidence that led to the belief that ice ever reached the tropics. This evidence must prove three things:
- that a bed contains sedimentary structures that could have been created only by glacial activity;
- that the bed lay within the tropics when it was deposited.
- that glaciers were active at different global locations at the same time, and that no other deposits of the same age are in existence.
This last point is very difficult to prove. Before the Ediacaran, the biostratigraphic markers usually used to correlate rocks are absent; therefore there is no way to prove that rocks in different places across the globe were deposited at the same time. The best that can be done is to estimate the age of the rocks using radiometric methods, which are rarely accurate to better than a million years or so.
The first two points are often the source of contention on a case-to-case basis. Many glacial features can also be created by non-glacial means, and estimating the approximate latitudes of landmasses even as recently as 200 Ma can be riddled with difficulties.
Palaeomagnetism
The snowball Earth hypothesis was first posited to explain what were then considered to be glacial deposits near the equator. Since tectonic plates move slowly over time, ascertaining their position at a given point in Earth's long history is not easy. In addition to considerations of how the recognizable landmasses could have fit together, the latitude at which a rock was deposited can be constrained by palaeomagnetism.
When sedimentary rocks form, magnetic minerals within them tend to align with Earth's magnetic field. Through the precise measurement of this palaeomagnetism, it is possible to estimate the latitude (but not the longitude) where the rock matrix was formed. Palaeomagnetic measurements have indicated that some sediments of glacial origin in the Neoproterozoic rock record were deposited within 10 degrees of the equator, although the accuracy of this reconstruction is in question. This palaeomagnetic location of apparently glacial sediments (such as dropstones) has been taken to suggest that glaciers extended from land to sea level in tropical latitudes at the time the sediments were deposited. It is not clear whether this implies a global glaciation or the existence of localized, possibly land-locked, glacial regimes. Others have even suggested that most data do not constrain any glacial deposits to within 25° of the equator.
Skeptics suggest that the palaeomagnetic data could be corrupted if Earth's ancient magnetic field was substantially different from today's. Depending on the rate of cooling of Earth's core, it is possible that during the Proterozoic, the magnetic field did not approximate a simple dipolar distribution, with north and south magnetic poles roughly aligning with the planet's axis as they do today. Instead, a hotter core may have circulated more vigorously and given rise to 4, 8 or more poles. Palaeomagnetic data would then have to be re-interpreted, as the sedimentary minerals could have aligned pointing to a "west pole" rather than the north magnetic pole. Alternatively, Earth's dipolar field could have been oriented such that the poles were close to the equator. This hypothesis has been posited to explain the extraordinarily rapid motion of the magnetic poles implied by the Ediacaran palaeomagnetic record; the alleged motion of the north magnetic pole would occur around the same time as the Gaskiers glaciation.
Another weakness of reliance on palaeomagnetic data is the difficulty in determining whether the magnetic signal recorded is original, or whether it has been reset by later activity. For example, a mountain-building orogeny releases hot water as a by-product of metamorphic reactions; this water can circulate to rocks thousands of kilometers away and reset their magnetic signature. This makes the authenticity of rocks older than a few million years difficult to determine without painstaking mineralogical observations. Moreover, further evidence is accumulating that large-scale remagnetization events have taken place which may necessitate revision of the estimated positions of the palaeomagnetic poles.
There is currently only one deposit, the Elatina deposit of Australia, that was indubitably deposited at low latitudes; its depositional date is well-constrained, and the signal is demonstrably original.
Low-latitude glacial deposits


Sedimentary rocks that are deposited by glaciers have distinctive features that enable their identification. Long before the advent of the snowball Earth hypothesis, many Neoproterozoic sediments had been interpreted as having a glacial origin, including some apparently at tropical latitudes at the time of their deposition. However, many sedimentary features traditionally associated with glaciers can also be formed by other means. Thus the glacial origin of many of the key occurrences for snowball Earth has been contested. As of 2007, there was only one "very reliable"—still challenged—datum point identifying tropical tillites, which makes statements of equatorial ice cover somewhat presumptuous. However, evidence of sea-level glaciation in the tropics during the Sturtian glaciation is accumulating. Evidence of possible glacial origin of sediment includes:
- Dropstones (stones dropped into marine sediments), which can be deposited by glaciers or other phenomena.
- Varves (annual sediment layers in periglacial lakes), which can form at higher temperatures.
- Glacial striations (formed by embedded rocks scraped against bedrock): similar striations are from time to time formed by mudflows or tectonic movements.
- Diamictites (poorly sorted conglomerates). Originally described as glacial till, most were in fact formed by debris flows.
Open-water deposits
It appears that some deposits formed during the snowball period could only have formed in the presence of an active hydrological cycle. Bands of glacial deposits up to 5,500 meters thick, separated by small (meters) bands of non-glacial sediments, demonstrate that glaciers melted and re-formed repeatedly for tens of millions of years; solid oceans would not permit this scale of deposition. It is considered possible that ice streams such as seen in Antarctica today could have caused these sequences. Further, sedimentary features that could only form in open water (for example: wave-formed ripples, far-traveled ice-rafted debris and indicators of photosynthetic activity) can be found throughout sediments dating from the snowball-Earth periods. While these may represent "oases" of meltwater on a completely frozen Earth, computer modelling suggests that large areas of the ocean must have remained ice-free, arguing that a "hard" snowball is not plausible in terms of energy balance and general circulation models.
Carbon isotope ratios
There are two stable isotopes of carbon in sea water: carbon-12 (12C) and the rare carbon-13 (13C), which makes up about 1.109 percent of carbon atoms. Biochemical processes, of which photosynthesis is one, tend to preferentially incorporate the lighter 12C isotope. Thus ocean-dwelling photosynthesizers, both protists and algae, tend to be very slightly depleted in 13C, relative to the abundance found in the primary volcanic sources of Earth's carbon. Therefore, an ocean with photosynthetic life will have a lower 13C/12C ratio within organic remains and a higher ratio in corresponding ocean water. The organic component of the lithified sediments will remain very slightly, but measurably, depleted in 13C.
Silicate weathering, an inorganic process by which carbon dioxide is drawn out of the atmosphere and deposited in rock, also fractionates carbon. The emplacement of several large igneous provinces shortly before the Cryogenian and the subsequent chemical weathering of the enormous continental flood basalts created by them, aided by the breakup of Rodinia that exposed many of these flood basalts to warmer, moister conditions closer to the coast and accelerated chemical weathering, is also believed to have caused a major positive shift in carbon isotopic ratios and contributed to the beginning of the Sturtian glaciation.
During the proposed episode of snowball Earth, there are rapid and extreme negative excursions in the ratio of 13C to 12C. Close analysis of the timing of 13C 'spikes' in deposits across the globe allows the recognition of four, possibly five, glacial events in the late Neoproterozoic.
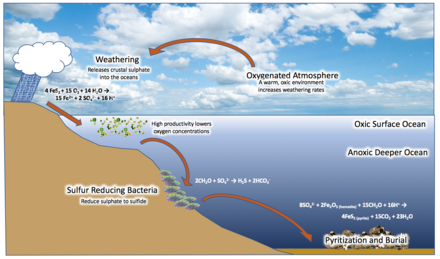
Banded iron formations

Banded iron formations (BIF) are sedimentary rocks of layered iron oxide and iron-poor chert. In the presence of oxygen, iron naturally rusts and becomes insoluble in water. The banded iron formations are commonly very old and their deposition is often related to the oxidation of Earth's atmosphere during the Palaeoproterozoic era, when dissolved iron in the ocean came in contact with photosynthetically produced oxygen and precipitated out as iron oxide.
The bands were produced at the tipping point between an anoxic and an oxygenated ocean. Since today's atmosphere is oxygen-rich (nearly 21% by volume) and in contact with the oceans, it is not possible to accumulate enough iron oxide to deposit a banded formation. The only extensive iron formations that were deposited after the Palaeoproterozoic (after 1.8 billion years ago) are associated with Cryogenian glacial deposits.
For such iron-rich rocks to be deposited there would have to be anoxia in the ocean, so that much dissolved iron (as ferrous oxide) could accumulate before it met an oxidant that would precipitate it as ferric oxide. For the ocean to become anoxic it must have limited gas exchange with the oxygenated atmosphere. Proponents of the hypothesis argue that the reappearance of BIF in the sedimentary record is a result of limited oxygen levels in an ocean sealed by sea-ice. Near the end of a glaciation period, a reestablishment of gas exchange between the ocean and atmosphere oxidised seawater rich in ferrous iron would occur. A positive shift in δ56FeIRMM-014 from the lower to upper layers of Cryogenian BIFs may reflect an increase in ocean acidification, as the upper layers were deposited as more and more oceanic ice cover melted away and more carbon dioxide was dissolved by the ocean.
Opponents of the hypothesis suggest that the rarity of the BIF deposits may indicate that they formed in inland seas. Being isolated from the oceans, such lakes could have been stagnant and anoxic at depth, much like today's Black Sea; a sufficient input of iron could provide the necessary conditions for BIF formation. A further difficulty in suggesting that BIFs marked the end of the glaciation is that they are found interbedded with glacial sediments; such interbedding has been suggested to be an artefact of Milankovitch cycles, which would have periodically warmed the seas enough to allow gas exchange between the atmosphere and ocean and precipitate BIFs.
Cap carbonate rocks

Around the top of Neoproterozoic glacial deposits there is commonly a sharp transition into a chemically precipitated sedimentary limestone or dolomite metres to tens of metres thick. These cap carbonates sometimes occur in sedimentary successions that have no other carbonate rocks, suggesting that their deposition is result of a profound aberration in ocean chemistry.

These cap carbonates have unusual chemical composition as well as strange sedimentary structures that are often interpreted as large ripples. The formation of such sedimentary rocks could be caused by a large influx of positively charged ions, as would be produced by rapid weathering during the extreme greenhouse following a snowball Earth event. The δ13C isotopic signature of the cap carbonates is near −5 ‰, consistent with the value of the mantle—such a low value could be taken to signify an absence of life, since photosynthesis usually acts to raise the value; alternatively the release of methane deposits could have lowered it from a higher value and counterbalance the effects of photosynthesis.
The mechanism involved in the formation of cap carbonates is not clear, but the most cited explanation suggests that at the melting of a snowball Earth, water would dissolve the abundant CO2 from the atmosphere to form carbonic acid, which would fall as acid rain. This would weather exposed silicate and carbonate rock (including readily attacked glacial debris), releasing large amounts of calcium, which when washed into the ocean would form distinctively textured layers of carbonate sedimentary rock. Such an abiotic "cap carbonate" sediment can be found on top of the glacial till that gave rise to the snowball Earth hypothesis.
However, there are some problems with the designation of a glacial origin to cap carbonates. The high carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere would cause the oceans to become acidic and dissolve any carbonates contained within—starkly at odds with the deposition of cap carbonates. The thickness of some cap carbonates is far above what could reasonably be produced in the relatively quick deglaciations. The cause is further weakened by the lack of cap carbonates above many sequences of clear glacial origin at a similar time and the occurrence of similar carbonates within the sequences of proposed glacial origin. An alternative mechanism, which may have produced the Doushantuo cap carbonate at least, is the rapid, widespread release of methane. This accounts for incredibly low—as low as −48 ‰—δ13C values—as well as unusual sedimentary features which appear to have been formed by the flow of gas through the sediments.
Changing acidity
Isotopes of boron suggest that the pH of the oceans dropped dramatically before and after the Marinoan glaciation. This may indicate a buildup of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, some of which would dissolve into the oceans to form carbonic acid. Although the boron variations may be evidence of extreme climate change, they need not imply a global glaciation.
Space dust
Earth's surface is very depleted in iridium, which primarily resides in Earth's core. The only significant source of the element at the surface is cosmic particles that reach Earth. During a snowball Earth, iridium would accumulate on the ice sheets, and when the ice melted the resulting layer of sediment would be rich in iridium. An iridium anomaly has been discovered at the base of the cap carbonate formations and has been used to suggest that the glacial episode lasted for at least 3 million years, but this does not necessarily imply a global extent to the glaciation; indeed, a similar anomaly could be explained by the impact of a large meteorite.
Cyclic climate fluctuations
Using the ratio of mobile cations to those that remain in soils during chemical weathering (the chemical index of alteration), it has been shown that chemical weathering varied in a cyclic fashion within a glacial succession, increasing during interglacial periods and decreasing during cold and arid glacial periods. This pattern, if a true reflection of events, suggests that the "snowball Earths" bore a stronger resemblance to Pleistocene ice age cycles than to a completely frozen Earth.
In addition, glacial sediments of the Port Askaig tillite formation in Scotland clearly show interbedded cycles of glacial and shallow marine sediments. The significance of these deposits is highly reliant upon their dating. Glacial sediments are difficult to date, and the closest dated bed to the Port Askaig group is 8 km stratigraphically above the beds of interest. Its dating to 600 Ma means the beds can be tentatively correlated to the Sturtian glaciation, but they may represent the advance or retreat of a snowball Earth.
Mechanisms
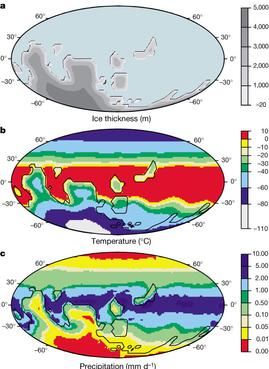
The initiation of a snowball Earth event would involve some initial cooling mechanism, which would result in an increase in Earth's coverage of snow and ice. The increase in Earth's coverage of snow and ice would in turn increase Earth's albedo, which would result in positive feedback for cooling. If enough snow and ice accumulates, run-away cooling would result. This positive feedback is facilitated by an equatorial continental distribution, which would allow ice to accumulate in the regions closer to the equator, where solar radiation is most direct.
Many possible triggering mechanisms could account for the beginning of a snowball Earth, such as the eruption of a supervolcano, a reduction in the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases such as methane and/or carbon dioxide, changes in Solar energy output, or perturbations of Earth's orbit. Regardless of the trigger, initial cooling results in an increase in the area of Earth's surface covered by ice and snow, and the additional ice and snow reflects more solar energy back to space, further cooling Earth and further increasing the area of Earth's surface covered by ice and snow. This positive feedback loop could eventually produce a frozen equator as cold as modern Antarctica.
Global warming associated with large accumulations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere over millions of years, emitted primarily by volcanic activity, is the proposed trigger for melting a snowball Earth. Due to positive feedback for melting, the eventual melting of the snow and ice covering most of Earth's surface would require as little as a millennium.
Initiation of glaciation
A tropical distribution of the continents is, perhaps counter-intuitively, necessary to allow the initiation of a snowball Earth. Tropical continents are more reflective than open ocean and so absorb less of the Sun's heat: most absorption of solar energy on Earth today occurs in tropical oceans. Further, tropical continents are subject to more rainfall, which leads to increased river discharge and erosion. When exposed to air, silicate rocks undergo weathering reactions which remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These reactions proceed in the general form
- Rock-forming mineral + CO2 + H2O → cations + bicarbonate + SiO2
An example of such a reaction is the weathering of wollastonite:
- CaSiO3 + 2 CO2 + H2O → Ca2+ + SiO2 + 2 HCO−
3
The released calcium cations react with the dissolved bicarbonate in the ocean to form calcium carbonate as a chemically precipitated sedimentary rock. This transfers carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, from the air into the geosphere, and, in steady-state on geologic time scales, offsets the carbon dioxide emitted from volcanoes into the atmosphere.
As of 2003, a precise continental distribution during the Neoproterozoic was difficult to establish because there were too few suitable sediments for analysis. Some reconstructions point towards polar continents—which have been a feature of all other major glaciations, providing a point upon which ice can nucleate. Changes in ocean circulation patterns may then have provided the trigger of snowball Earth.
Additional factors that may have contributed to the onset of the Neoproterozoic snowball include the introduction of atmospheric free oxygen, which may have reached sufficient quantities to react with methane in the atmosphere, oxidizing it to carbon dioxide, a much weaker greenhouse gas, and a younger—thus fainter—Sun, which would have emitted 6 percent less radiation in the Neoproterozoic.
Normally, as Earth gets colder due to natural climatic fluctuations and changes in incoming solar radiation, the cooling slows these weathering reactions. As a result, less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere and Earth warms as this greenhouse gas accumulates—this 'negative feedback' process limits the magnitude of cooling. During the Cryogenian, however, Earth's continents were all at tropical latitudes, which made this moderating process less effective, as high weathering rates continued on land even as Earth cooled. This caused ice to advance beyond the polar regions. Once ice advanced to within 30° of the equator, a positive feedback could ensue such that the increased reflectiveness (albedo) of the ice led to further cooling and the formation of more ice, until the whole Earth is ice-covered.
Polar continents, because of low rates of evaporation, are too dry to allow substantial carbon deposition—restricting the amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide that can be removed from the carbon cycle. A gradual rise of the proportion of the isotope 13C relative to 12C in sediments pre-dating "global" glaciation indicates that CO2 draw-down before snowball Earths was a slow and continuous process. The start of snowball Earths are marked by a sharp downturn in the δ13C value of sediments, a hallmark that may be attributed to a crash in biological productivity as a result of the cold temperatures and ice-covered oceans.
In January 2016, Gernon et al. proposed a "shallow-ridge hypothesis" involving the breakup of Rodinia, linking the eruption and rapid alteration of hyaloclastites along shallow ridges to massive increases in alkalinity in an ocean with thick ice cover. Gernon et al. demonstrated that the increase in alkalinity over the course of glaciation is sufficient to explain the thickness of cap carbonates formed in the aftermath of Snowball Earth events.
Dating of the Sturtian glaciation's onset has found it to be coeval with the emplacement of a large igneous province in the tropics. Weathering of this equatorial large igneous province is believed to have sucked enough carbon dioxide out of the air to enable the development of major glaciation.
During the frozen period

Global temperature fell so low that the equator was as cold as modern-day Antarctica. This low temperature was maintained by the high albedo of the ice sheets, which reflected most incoming solar energy into space. A lack of heat-retaining clouds, caused by water vapor freezing out of the atmosphere, amplified this effect. Degassing of carbon dioxide has been speculated to have been unusually low during the Cryogenian, enabling the persistence of global glaciation.
Breaking out of global glaciation
The carbon dioxide levels necessary to thaw Earth have been estimated as being 350 times what they are today, about 13% of the atmosphere. Since Earth was almost completely covered with ice, carbon dioxide could not be withdrawn from the atmosphere by release of alkaline metal ions weathering out of siliceous rocks. Over 4 to 30 million years, enough CO2 and methane, mainly emitted by volcanoes but also produced by microbes converting organic carbon trapped under the ice into the gas, would accumulate to finally cause enough greenhouse effect to make surface ice melt in the tropics until a band of permanently ice-free land and water developed; this would be darker than the ice and thus absorb more energy from the Sun—initiating a "positive feedback".
The first areas to become free of permanent ice cover may have been in the mid-latitudes rather than in the tropics, because a rapid hydrological cycle would have inhibited the melting of ice at low latitudes. As these mid-latitude regions became ice free, dust from them blew over onto ice sheets elsewhere, decreasing their albedo and accelerating the process of deglaciation. Destabilization of substantial deposits of methane hydrates locked up in low-latitude permafrost may also have acted as a trigger and/or strong positive feedback for deglaciation and warming.[67]
Methanogens were an important contributor to the deglaciation of the Marinoan Snowball Earth. The return of high primary productivity in surficial waters fueled extensive microbial sulphur reduction, causing deeper waters to become highly euxinic. Euxinia caused the formation of large amounts of methyl sulphides, which in turn was converted into methane by methanogens. A major negative nickel isotope excursion confirms high methanogenic activity during this period of deglaciation and global warming.
On the continents, the melting of glaciers would release massive amounts of glacial deposit, which would erode and weather. The resulting sediments supplied to the ocean would be high in nutrients such as phosphorus, which combined with the abundance of CO2 would trigger a cyanobacteria population explosion, which would cause a relatively rapid reoxygenation of the atmosphere and may have contributed to the rise of the Ediacaran biota and the subsequent Cambrian explosion—a higher oxygen concentration allowing large multicellular lifeforms to develop. Although the positive feedback loop would melt the ice in geological short order, perhaps less than 1,000 years, replenishment of atmospheric oxygen and depletion of the CO2 levels would take further millennia.
It is possible that carbon dioxide levels fell enough for Earth to freeze again; this cycle may have repeated until the continents had drifted to more polar latitudes. More recent evidence suggests that with colder oceanic temperatures, the resulting higher ability of the oceans to dissolve gases led to the carbon content of sea water being more quickly oxidized to carbon dioxide. This leads directly to an increase of atmospheric carbon dioxide, enhanced greenhouse warming of Earth's surface, and the prevention of a total snowball state.
During millions of years, cryoconite would have accumulated on and inside the ice. Psychrophilic microorganisms, volcanic ash and dust from ice-free locations would settle on ice covering several million square kilometers. Once the ice started to melt, these layers would become visible and darken the icy surfaces, helping to accelerate the process. Also, ultraviolet light from the Sun produced hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) when it hit water molecules. Normally H2O2 breaks down in sunlight, but some would have been trapped inside the ice. When the glaciers started to melt, it would have been released in both the ocean and the atmosphere, where it was split into water and oxygen molecules, increasing atmospheric oxygen.
Slushball Earth hypothesis
While the presence of glaciers is not disputed, the idea that the entire planet was covered in ice is more contentious, leading some scientists to posit a "slushball Earth", in which a band of ice-free, or ice-thin, waters remains around the equator, allowing for a continued hydrologic cycle. This hypothesis appeals to scientists who observe certain features of the sedimentary record that can only be formed under open water or rapidly moving ice (which would require somewhere ice-free to move to). Recent research observed geochemical cyclicity in clastic rocks, showing that the snowball periods were punctuated by warm spells, similar to ice age cycles in recent Earth history. Attempts to construct computer models of a snowball Earth have struggled to accommodate global ice cover without fundamental changes in the laws and constants which govern the planet.
A less extreme snowball Earth hypothesis involves continually evolving continental configurations and changes in ocean circulation. Synthesised evidence has produced slushball Earth models where the stratigraphic record does not permit postulating complete global glaciations. Kirschvink's original hypothesis had recognised that warm tropical puddles would be expected to exist in a snowball Earth.
Scientific dispute
The argument against the hypothesis is evidence of fluctuation in ice cover and melting during "snowball Earth" deposits. Evidence for such melting comes from evidence of glacial dropstones, geochemical evidence of climate cyclicity, and interbedded glacial and shallow marine sediments. A longer record from Oman, constrained to 13°N, covers the period from 712 to 545 million years ago—a time span containing the Sturtian and Marinoan glaciations—and shows both glacial and ice-free deposition. The snowball Earth hypothesis does not explain the alternation of glacial and interglacial events, nor the oscillation of glacial sheet margins.
There have been difficulties in recreating a snowball Earth with global climate models. Simple GCMs with mixed-layer oceans can be made to freeze to the equator; a more sophisticated model with a full dynamic ocean (though only a primitive sea ice model) failed to form sea ice to the equator. In addition, the levels of CO2 necessary to melt a global ice cover have been calculated to be 130,000 ppm, which is considered by some to be unreasonably large.
Strontium isotopic data have been found to be at odds with proposed snowball Earth models of silicate weathering shutdown during glaciation and rapid rates immediately post-glaciation. Therefore, methane release from permafrost during marine transgression was proposed to be the source of the large measured carbon excursion in the time immediately after glaciation.
"Zipper rift" hypothesis
Nick Eyles suggests that the Neoproterozoic Snowball Earth was in fact no different from any other glaciation in Earth's history, and that efforts to find a single cause are likely to end in failure. The "zipper rift" hypothesis proposes two pulses of continental "unzipping"—first, the breakup of Rodinia, forming the proto-Pacific Ocean; then the splitting of the continent Baltica from Laurentia, forming the proto-Atlantic—coincided with the glaciated periods. The associated tectonic uplift would form high plateaus, just as the East African Rift is responsible for high topography; this high ground could then host glaciers.
Banded iron formations have been taken as unavoidable evidence for global ice cover, since they require dissolved iron ions and anoxic waters to form; however, the limited extent of the Neoproterozoic banded iron deposits means that they may have formed in inland seas rather than in frozen oceans. Such seas can experience a wide range of chemistries; high rates of evaporation could concentrate iron ions, and a periodic lack of circulation could allow anoxic bottom water to form. Continental rifting, with associated subsidence, tends to produce such landlocked water bodies. This rifting, and associated subsidence, would produce the space for the fast deposition of sediments, negating the need for an immense and rapid melting to raise the global sea levels.
High-obliquity hypothesis
A competing hypothesis to explain the presence of ice on the equatorial continents was that Earth's axial tilt was quite high, in the vicinity of 60°, which would place Earth's land in high "latitudes", although supporting evidence is scarce. A less extreme possibility would be that it was merely Earth's magnetic pole that wandered to this inclination, as the magnetic readings which suggested ice-filled continents depend on the magnetic and rotational poles being relatively similar. In either of these two situations, the freeze would be limited to relatively small areas, as is the case today; severe changes to Earth's climate are not necessary.
Inertial interchange true polar wander
The evidence for low-latitude glacial deposits during the supposed snowball Earth episodes has been reinterpreted via the concept of inertial interchange true polar wander. This hypothesis, created to explain palaeomagnetic data, suggests that Earth's orientation relative to its axis of rotation shifted one or more times during the general time-frame attributed to snowball Earth. This could feasibly produce the same distribution of glacial deposits without requiring any of them to have been deposited at equatorial latitude. While the physics behind the proposition is sound, the removal of one flawed data point from the original study rendered the application of the concept in these circumstances unwarranted.
Survival of life through frozen periods

A tremendous glaciation would curtail photosynthetic life on Earth, thus depleting atmospheric oxygen, and thereby allowing non-oxidized iron-rich rocks to form. Detractors argue that this kind of glaciation would have made life extinct entirely. However, microfossils such as stromatolites and oncolites prove that, in shallow marine environments at least, life did not suffer any perturbation. Instead life developed a trophic complexity and survived the cold period unscathed. Proponents counter that it may have been possible for life to survive in these ways:
- In reservoirs of anaerobic and low-oxygen life powered by chemicals in deep oceanic hydrothermal vents surviving in Earth's deep oceans and crust; but photosynthesis would not have been possible there.
- Under the ice layer, in chemolithotrophic (mineral-metabolizing) ecosystems theoretically resembling those in existence in modern glacier beds, high-alpine and Arctic talus permafrost, and basal glacial ice. This is especially plausible in areas of volcanism or geothermal activity.
- In pockets of liquid water within and under the ice caps, similar to Lake Vostok in Antarctica. In theory, this system may resemble microbial communities living in the perennially frozen lakes of the Antarctic dry valleys. Photosynthesis can occur under ice up to 20 m thick, and at the temperatures predicted by models, equatorial sublimation would prevent equatorial ice thickness from exceeding 10 m.
- As eggs and dormant cells and spores deep-frozen into ice during the most severe phases of the frozen period.
- In small regions of open sea water: polynya. These natural ice holes can occur from the action of winds, currents or a local heat source (e.g. geothermal), even if the surrounding sea is completely frozen over. They could preserve enclaves of photosynthesizers (not multicellular plants, which did not yet exist) with access to light and CO2 to generate trace amounts of oxygen, enough to sustain some oxygen-dependent organisms. It is not necessary that a hole form in the ice, merely that some parts of the ice become thin enough to admit light. These small regions may have occurred in deep ocean, far from Rodinia or its remnants as it broke apart and drifted on the tectonic plates.
- In layers of "dirty ice" on top of the ice sheet covering shallow seas below. Animals and mud from the sea would be frozen into the base of the ice and gradually concentrate on the top as the ice above evaporates. Small ponds of water would teem with life thanks to the flow of nutrients through the ice. Such environments may have covered approximately 12 per cent of the global surface area.
- In small oases of liquid water, as would be found near geothermal hotspots resembling Iceland today.
- In nunatak areas in the tropics, where daytime tropical sun or volcanic heat heated bare rock sheltered from cold wind and made small temporary melt pools, which would freeze at sunset.[citation needed]
- Oxygenated subglacial meltwater, along with iron-rich sediments dissolved in the glacial water, created a meltwater oxygen pump when it entered the ocean, where it provided eukaryotes with some oxygen, and both photosynthetic and chemosynthetic organisms with sufficient nutrients to support an ecosystem. The freshwater would also mix with the hypersaline seawater, which created areas less hostile to eukaryotic life than elsewhere in the ocean.
However, organisms and ecosystems, as far as it can be determined by the fossil record, do not appear to have undergone the significant change that would be expected by a mass extinction. With the advent of more precise dating, a phytoplankton extinction event which had been associated with snowball Earth was shown to precede glaciations by 16 million years. Even if life were to cling on in all the ecological refuges listed above, a whole-Earth glaciation would result in a biota with a noticeably different diversity and composition. This change in diversity and composition has not yet been observed—in fact, the organisms which should be most susceptible to climatic variation emerge unscathed from the snowball Earth. One rebuttal to this is the fact that in many of these places where an argument is made against a mass extinction caused by snowball Earth, the Cryogenian fossil record is impoverished.
Implications
A snowball Earth has profound implications in the history of life on Earth. While many refugia have been postulated, global ice cover would certainly have ravaged ecosystems dependent on sunlight. Geochemical evidence from rocks associated with low-latitude glacial deposits have been interpreted to show a crash in oceanic life during the glacials.
Because about half of the oceans' water was frozen solid as ice, the remaining water would be twice as salty as it is today, lowering its freezing point. When the ice sheet melted under a hot atmosphere rich in carbon dioxide, it would cover the oceans with a layer of warm (50°C) freshwater up to 2 kilometres thick. Only after the warm surface water mixed with the colder and deeper saltwater did the sea return to a warmer and less salty state. The melting of the ice may have presented many new opportunities for diversification, and may indeed have driven the rapid evolution which took place at the end of the Cryogenian period. Global ice cover, if it existed, may—in concert with geothermal heating—have led to a lively, well mixed ocean with great vertical convective circulation.
Effect on early evolution

The Neoproterozoic was a time of remarkable diversification of multicellular organisms, including animals. Organism size and complexity increased considerably after the end of the snowball glaciations. This rapid development of multicellular organisms may have been the result of increased evolutionary pressures resulting from multiple icehouse-hothouse cycles; in this sense, snowball Earth episodes may have "pumped" evolution. Alternatively, fluctuating copper levels and rising oxygen may have played a part. Many Sturtian diamictites unconformably overlie copper-mineralised strata in Greenland, North America, Australia, and Africa; the glacial breakup and erosion of rocks heavily enriched in copper during the Sturtian glaciation, combined with the chemical weathering of the Franklin Large Igneous Province, greatly elevated copper concentrations in the ocean. Because copper is an essential component of many proteins involved in mitigating oxygen toxicity, synthesising adenosine triphosphate, and producing elastin and collagen, among other biological functions, this spike in copper concentrations was essential to the explosive evolution of multicellular life throughout the latter portion of the Neoproterozoic. Elevated copper concentrations persisted into the Cambrian explosion at the beginning of the Phanerozoic and likely influenced its course too.
One hypothesis which has been gaining currency in recent years: that early snowball Earths did not so much affect the evolution of life on Earth as result from it. In fact the two hypotheses are not mutually exclusive. The idea is that Earth's life forms affect the global carbon cycle and so major evolutionary events alter the carbon cycle, redistributing carbon within various reservoirs within the biosphere system and in the process temporarily lowering the atmospheric (greenhouse) carbon reservoir until the revised biosphere system settled into a new state. The cool period of the Huronian glaciation is speculated to be linked to the decline in the atmospheric content of greenhouse gases during the Great Oxygenation Event. Similarly, the possible snowball Earth of the Precambrian's Cryogenian between 580 and 850 million years ago (and which itself had a number of distinct episodes) could be related to the rise of more advanced multicellular animal life and life's colonisation of the land. However, a very recent study, based on findings of previous studies, suggested land plant evolution was driven by the Cryogenian glaciations, which they also theorized to be the reason why the Zygnematophyceae (sister group of land plants) became unicellular and cryophilic, lost their flagella and evolved sexual conjugation.
Occurrence and timing
Palaeoproterozoic
The Snowball Earth hypothesis has been invoked to explain glacial deposits in the Huronian Supergroup of Canada, though the palaeomagnetic evidence that suggests ice sheets at low latitudes is contested, and stratigraphic evidence clearly shows only three distinct depositions of glacial material (the Ramsay, Bruce and Gowganda Formations) separated by significant periods without. The glacial sediments of the Makganyene formation of South Africa are slightly younger than the Huronian glacial deposits (~2.25 billion years old) and were possibly deposited at tropical latitudes. It has been proposed that rise of free oxygen that occurred during the Great Oxygenation Event removed atmospheric methane through oxidation. As the solar irradiance was notably weaker at the time, Earth's climate may have relied on methane, a powerful greenhouse gas, to maintain surface temperatures above freezing. In the absence of this methane greenhousing, temperatures plunged and a global glaciation could have occurred between 2.5 and 2.2 Gya, during the Siderian and Rhyacian periods of the Paleoproterozoic era.
Neoproterozoic
There were three or four significant ice ages during the late Neoproterozoic. Of these, the Marinoan was the most significant, and the Sturtian glaciations were also widespread. Even the leading snowball proponent Hoffman agrees that the 350 thousand-year-long Gaskiers glaciation did not lead to global glaciation, although it was probably as intense as the late Ordovician glaciation. The status of the Kaigas "glaciation" or "cooling event" is currently unclear; some scientists do not recognise it as a glacial, others suspect that it may reflect poorly dated strata of Sturtian association, and others believe it may indeed be a third ice age. It was certainly less significant than the Sturtian or Marinoan glaciations, and probably not global in extent. Emerging evidence suggests that Earth underwent a number of glaciations during the Neoproterozoic, which would stand strongly at odds with the snowball hypothesis.
Karoo Ice Age
Before the theory of continental drift, glacial deposits in Carboniferous strata in tropical continental areas such as India and South America led to speculation that the Karoo Ice Age glaciation reached into the tropics. However, a continental reconstruction shows that ice was in fact constrained to the polar parts of the supercontinent Gondwana.