| Energy development | |||||||||||||||||||||||||

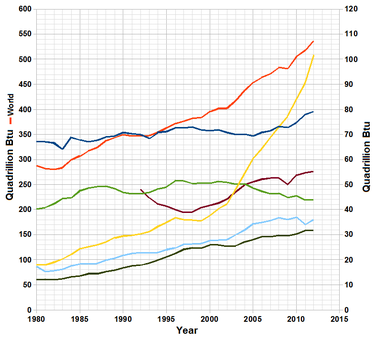
World total primary energy production
US Energy Use/Flow in 2011

Energy flow charts show the relative size
of primary energy resources and end uses in the United States, with
fuels compared on a common energy unit basis (2011: 97.3 quads).[3]
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Societies use energy for transportation, manufacturing, illumination, heating and air conditioning, and communication, for industrial, commercial, and domestic purposes. Energy resources may be classified as primary resources, where the resource can be used in substantially its original form, or as secondary resources, where the energy source must be converted into a more conveniently usable form. Non-renewable resources are significantly depleted by human use, whereas renewable resources are produced by ongoing processes that can sustain indefinite human exploitation.
Thousands of people are employed in the energy industry. The conventional industry comprises the petroleum industry, the natural gas industry, the electrical power industry, and the nuclear industry. New energy industries include the renewable energy industry, comprising alternative and sustainable manufacture, distribution, and sale of alternative fuels.
Classification of resources
Energy resources may be classified as primary resources, suitable for end use without conversion to another form, or secondary resources, where the usable form of energy required substantial conversion from a primary source. Examples of primary energy resources are wind power, solar power, wood fuel, fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas, and uranium. Secondary resources are those such as electricity, hydrogen, or other synthetic fuels.
Another important classification is based on the time required to regenerate an energy resource. "Renewable" resources are those that recover their capacity in a time significant by human needs. Examples are hydroelectric power or wind power, when the natural phenomena that are the primary source of energy are ongoing and not depleted by human demands. Non-renewable resources are those that are significantly depleted by human usage and that will not recover their potential significantly during human lifetimes. An example of a non-renewable energy source is coal, which does not form naturally at a rate that would support human use.
Fossil fuels
The Moss Landing Power Plant in California is a fossil-fuel power station that burns natural gas in a turbine to produce electricity
Fossil fuel (primary non-renewable fossil) sources burn coal or hydrocarbon fuels, which are the remains of the decomposition of plants and animals. There are three main types of fossil fuels: coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Another fossil fuel, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), is principally derived from the production of natural gas. Heat from burning fossil fuel is used either directly for space heating and process heating, or converted to mechanical energy for vehicles, industrial processes, or electrical power generation. These fossil fuels are part of the carbon cycle and thus allow stored solar energy to be used today.
The use of fossil fuels in the 18th and 19th Century set the stage for the Industrial Revolution.
Fossil fuels make up the bulk of the world's current primary energy sources. In 2005, 81% of the world's energy needs was met from fossil sources.[4] The technology and infrastructure already exist for the use of fossil fuels. Liquid fuels derived from petroleum deliver a great deal of usable energy per unit of weight or volume, which is advantageous when compared with lower energy density sources such as a battery. Fossil fuels are currently economical for decentralised energy use.
Energy dependence on imported fossil fuels creates energy security risks for dependent countries. Oil dependence in particular has led to war,[10] funding of radicals,[11] monopolization,[12] and socio-political instability.[13]
Fossil fuels are non-renewable resources, which will eventually decline in production [14] and become exhausted. While the processes that created fossil fuels are ongoing, fuels are consumed far more quickly than the natural rate of replenishment. Extracting fuels becomes increasingly costly as society consumes the most accessible fuel deposits.[15] Extraction of fossil fuels results in environmental degradation, such as the strip mining and mountaintop removal of coal.
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the efficiency of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier fuel into kinetic energy or work. The fuel economy is the energy efficiency of a particular vehicle, is given as a ratio of distance travelled per unit of fuel consumed. Weight-specific efficiency (efficiency per unit weight) may be stated for freight, and passenger-specific efficiency (vehicle efficiency per passenger). The inefficient atmospheric combustion (burning) of fossil fuels in vehicles, buildings, and power plants contributes to urban heat islands.[16]
Conventional production of oil has peaked, conservatively, between 2007 and 2010. In 2010, it was estimated that an investment in non-renewable resources of $8 trillion would be required to maintain current levels of production for 25 years.[17] In 2010, governments subsidized fossil fuels by an estimated $500 billion a year.[18] Fossil fuels are also a source of greenhouse gas emissions, leading to concerns about global warming if consumption is not reduced.
The combustion of fossil fuels leads to the release of pollution into the atmosphere. The fossil fuels are mainly carbon compounds. During combustion, carbon dioxide is released, and also nitrogen oxides, soot and other fine particulates. Man-made carbon dioxide according to the IPCC contributes to global warming.[19] Other emissions from fossil fuel power station include sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons, volatile organic compounds (VOC), mercury, arsenic, lead, cadmium, and other heavy metals including traces of uranium.[20][21]
A typical coal plant generates billions of kilowatt hours per year.[22]
Nuclear
Fission
American nuclear powered ships,(top to bottom) cruisers USS Bainbridge, the USS Long Beach and the USS Enterprise, the longest ever naval vessel, and the first nuclear-powered aircraft carrier.
Picture taken in 1964 during a record setting voyage of 26,540 nmi
(49,190 km) around the world in 65 days without refueling. Crew members
are spelling out Einstein's mass-energy equivalence formula E = mc2 on the flight deck.
The Russian nuclear-powered icebreaker NS Yamal on a joint scientific expedition with the NSF in 1994
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear fission to generate useful heat and electricity. Fission of uranium produces nearly all economically significant nuclear power. Radioisotope thermoelectric generators form a very small component of energy generation, mostly in specialized applications such as deep space vehicles.
Nuclear power plants, excluding naval reactors, provided about 5.7% of the world's energy and 13% of the world's electricity in 2012.[23]
In 2013, the IAEA report that there are 437 operational nuclear power reactors,[24] in 31 countries,[25] although not every reactor is producing electricity.[26] In addition, there are approximately 140 naval vessels using nuclear propulsion in operation, powered by some 180 reactors.[27][28][29] As of 2013, attaining a net energy gain from sustained nuclear fusion reactions, excluding natural fusion power sources such as the Sun, remains an ongoing area of international physics and engineering research. More than 60 years after the first attempts, commercial fusion power production remains unlikely before 2050.[30]
There is an ongoing debate about nuclear power.[31][32][33] Proponents, such as the World Nuclear Association, the IAEA and Environmentalists for Nuclear Energy contend that nuclear power is a safe, sustainable energy source that reduces carbon emissions.[34] Opponents, such as Greenpeace International and NIRS, contend that nuclear power poses many threats to people and the environment.[35][36][37]
Nuclear power plant accidents include the Chernobyl disaster (1986), Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster (2011), and the Three Mile Island accident (1979).[38] There have also been some nuclear submarine accidents.[38][39][40] In terms of lives lost per unit of energy generated, analysis has determined that nuclear power has caused less fatalities per unit of energy generated than the other major sources of energy generation. Energy production from coal, petroleum, natural gas and hydropower has caused a greater number of fatalities per unit of energy generated due to air pollution and energy accident effects. However, the economic costs of nuclear power accidents is high, and meltdowns can take decades to clean up. The human costs of evacuations of affected populations and lost livelihoods is also significant.[46][47]
Comparing Nuclear's latent cancer deaths, such as cancer with other energy sources immediate deaths per unit of energy generated(GWeyr). This study does not include fossil fuel related cancer and other indirect deaths created by the use of fossil fuel consumption in its "severe accident" classification, which would be an accident with more than 5 fatalities.
Nuclear power is a low carbon power generation method of producing electricity, with an analysis of the literature on its total life cycle emission intensity finding that it is similar to renewable sources in a comparison of greenhouse gas(GHG) emissions per unit of energy generated.[48] Since the 1970s, nuclear fuel has displaced about 64 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent(GtCO2-eq) greenhouse gases, that would have otherwise resulted from the burning of oil, coal or natural gas in fossil-fuel power stations.[49]
As of 2012, according to the IAEA, worldwide there were 68 civil nuclear power reactors under construction in 15 countries,[24] approximately 28 of which in the Peoples Republic of China (PRC), with the most recent nuclear power reactor, as of May 2013, to be connected to the electrical grid, occurring on February 17, 2013 in Hongyanhe Nuclear Power Plant in the PRC.[50] In the United States, two new Generation III reactors are under construction at Vogtle. U.S. nuclear industry officials expect five new reactors to enter service by 2020, all at existing plants.[51] In 2013, four aging, uncompetitive, reactors were permanently closed.[52][53]
Japan's 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident, which occurred in a reactor design from the 1960s, prompted a rethink of nuclear safety and nuclear energy policy in many countries.[54] Germany decided to close all its reactors by 2022, and Italy has banned nuclear power.[54] Following Fukushima, in 2011 the International Energy Agency halved its estimate of additional nuclear generating capacity to be built by 2035.[55][56]
Recent experiments in extraction of uranium use polymer ropes that are coated with a substance that selectively absorbs uranium from seawater. This process could make the considerable volume of uranium dissolved in seawater exploitable for energy production. Since ongoing geologic processes carry uranium to the sea in amounts comparable to the amount that would be extracted by this process, in a sense the sea-borne uranium becomes a sustainable resource.[57][58]
Fission economics

The 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, the second worst nuclear incident, displaced 50,000 households after radioactive material leaked into the air, soil and sea.[59] Radiation checks led to bans on some shipments of vegetables and fish.[60]
The economics of new nuclear power plants is a controversial subject, since there are diverging views on this topic, and multibillion-dollar investments ride on the choice of an energy source. Nuclear power plants typically have high capital costs for building the plant, but low direct fuel costs.
In recent years there has been a slowdown of electricity demand growth and financing has become more difficult, which affects large projects such as nuclear reactors, with very large upfront costs and long project cycles which carry a large variety of risks.[61] In Eastern Europe, a number of long-established projects are struggling to find finance, notably Belene in Bulgaria and the additional reactors at Cernavoda in Romania, and some potential backers have pulled out.[61] Where cheap gas is available and its future supply relatively secure, this also poses a major problem for nuclear projects.[61]
Analysis of the economics of nuclear power must take into account who bears the risks of future uncertainties. To date all operating nuclear power plants were developed by state-owned or regulated utility monopolies[63][64] where many of the risks associated with construction costs, operating performance, fuel price, and other factors were borne by consumers rather than suppliers. Many countries have now liberalized the electricity market where these risks, and the risk of cheaper competitors emerging before capital costs are recovered, are borne by plant suppliers and operators rather than consumers, which leads to a significantly different evaluation of the economics of new nuclear power plants.[65]
Two of the four EPRs under construction (in Finland and France) are significantly behind schedule and substantially over cost.[66] Following the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, costs are likely to go up for currently operating and new nuclear power plants, due to increased requirements for on-site spent fuel management and elevated design basis threats.[67] While first of their kind designs, such as the EPRs under construction are behind schedule and over-budget, of the seven South Korean APR-1400s presently under construction worldwide, two are in S.Korea at the Hanul Nuclear Power Plant and four are at the largest nuclear station construction project in the world as of 2016, in the United Arab Emirates at the planned Barakah nuclear power plant. The first reactor, Barakah-1 is 85% completed and on schedule for grid-connection during 2017.[68][69]
Renewable sources

Renewable energy is generally defined as energy that comes from resources which are naturally replenished on a human timescale such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves and geothermal heat.[70] Renewable energy replaces conventional fuels in four distinct areas: electricity generation, hot water/space heating, motor fuels, and rural (off-grid) energy services.[71]
About 16% of global final energy consumption presently comes from renewable resources, with 10% [72] of all energy from traditional biomass, mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from hydroelectricity. New renewables (small hydro, modern biomass, wind, solar, geothermal, and biofuels) account for another 3% and are growing rapidly.[73] At the national level, at least 30 nations around the world already have renewable energy contributing more than 20% of energy supply. National renewable energy markets are projected to continue to grow strongly in the coming decade and beyond.[74] Wind power, for example, is growing at the rate of 30% annually, with a worldwide installed capacity of 282,482 megawatts (MW) at the end of 2012.
Renewable energy resources exist over wide geographical areas, in contrast to other energy sources, which are concentrated in a limited number of countries. Rapid deployment of renewable energy and energy efficiency is resulting in significant energy security, climate change mitigation, and economic benefits.[75] In international public opinion surveys there is strong support for promoting renewable sources such as solar power and wind power.[76]
While many renewable energy projects are large-scale, renewable technologies are also suited to rural and remote areas and developing countries, where energy is often crucial in human development.[77] United Nations' Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon has said that renewable energy has the ability to lift the poorest nations to new levels of prosperity.[78]
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity is electric power generated by hydropower; the force of falling or flowing water. In 2015 hydropower generated 16.6% of the world's total electricity and 70% of all renewable electricity and is expected to increase about 3.1% each year for the next 25 years.
Hydropower is produced in 150 countries, with the Asia-Pacific region generating 32 percent of global hydropower in 2010. China is the largest hydroelectricity producer, with 721 terawatt-hours of production in 2010, representing around 17 percent of domestic electricity use. There are now three hydroelectricity plants larger than 10 GW: the Three Gorges Dam in China, Itaipu Dam across the Brazil/Paraguay border, and Guri Dam in Venezuela.[80]
The cost of hydroelectricity is relatively low, making it a competitive source of renewable electricity. The average cost of electricity from a hydro plant larger than 10 megawatts is 3 to 5 U.S. cents per kilowatt-hour.[80] Hydro is also a flexible source of electricity since plants can be ramped up and down very quickly to adapt to changing energy demands. However, damming interrupts the flow of rivers and can harm local ecosystems, and building large dams and reservoirs often involves displacing people and wildlife.[80] Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, the project produces no direct waste, and has a considerably lower output level of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide than fossil fuel powered energy plants.[81]
Wind
Wind power is widely used in Europe, Asia, and the United States.[83] Several countries have achieved relatively high levels of wind power penetration, such as 21% of stationary electricity production in Denmark,[84] 18% in Portugal,[84] 16% in Spain,[84] 14% in Ireland,[85] and 9% in Germany in 2010.[84][86]:11 By 2011, at times over 50% of electricity in Germany and Spain came from wind and solar power.[87][88] As of 2011, 83 countries around the world are using wind power on a commercial basis.[86]:11
Many of the world's largest onshore wind farms are located in the United States, China, and India. Most of the world's largest offshore wind farms are located in Denmark, Germany and the United Kingdom. The two largest offshore wind farm are currently the 630 MW London Array and Gwynt y Môr.
| Wind farm | Current capacity (MW) |
Country | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alta (Oak Creek-Mojave) | 1,320 | [89] | |
| Jaisalmer Wind Park | 1,064 | [90] | |
| Roscoe Wind Farm | 781 | [91] | |
| Horse Hollow Wind Energy Center | 735 | [92][93] | |
| Capricorn Ridge Wind Farm | 662 | [92][93] | |
| Fântânele-Cogealac Wind Farm | 600 | [94] | |
| Fowler Ridge Wind Farm | 599 | [95] |
Solar

Part of the 354 MW SEGS solar complex in northern San Bernardino County, California
Solar energy, radiant light and heat from the sun, is harnessed using a range of ever-evolving technologies such as solar heating, solar photovoltaics, solar thermal electricity, solar architecture and artificial photosynthesis.[96][97]
Solar technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on the way they capture, convert and distribute solar energy. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic panels and solar thermal collectors to harness the energy. Passive solar techniques include orienting a building to the Sun, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light dispersing properties, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air.
In 2011, the International Energy Agency said that "the development of affordable, inexhaustible and clean solar energy technologies will have huge longer-term benefits. It will increase countries’ energy security through reliance on an indigenous, inexhaustible and mostly import-independent resource, enhance sustainability, reduce pollution, lower the costs of mitigating climate change, and keep fossil fuel prices lower than otherwise. These advantages are global. Hence the additional costs of the incentives for early deployment should be considered learning investments; they must be wisely spent and need to be widely shared".[96] More than 100 countries use solar PV.
The Topaz Solar Farm is one of the world's largest solar power stations
Photovoltaics (PV) is a method of generating electrical power by converting solar radiation into direct current electricity using semiconductors that exhibit the photovoltaic effect. Photovoltaic power generation employs solar panels composed of a number of solar cells containing a photovoltaic material. Materials presently used for photovoltaics include monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon, amorphous silicon, cadmium telluride, and copper indium gallium selenide/sulfide. Due to the increased demand for renewable energy sources, the manufacturing of solar cells and photovoltaic arrays has advanced considerably in recent years.
Solar photovoltaics is a sustainable energy source.[98] By the end of 2011, a total of 71.1 GW[99] had been installed, sufficient to generate 85 TWh/year.[100] And by end of 2012, the 100 GW installed capacity milestone was achieved.[101] Solar photovoltaics is now, after hydro and wind power, the third most important renewable energy source in terms of globally installed capacity. In 2016, after another year of rapid growth, solar generated 1.3% of global power.[102]
Driven by advances in technology and increases in manufacturing scale and sophistication, the cost of photovoltaics has declined steadily since the first solar cells were manufactured,[103] and the levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) from PV is competitive with conventional electricity sources in an expanding list of geographic regions. Net metering and financial incentives, such as preferential feed-in tariffs for solar-generated electricity, have supported solar PV installations in many countries.[104] The Energy Payback Time (EPBT), also known as energy amortization, depends on the location's annual solar insolation and temperature profile, as well as on the used type of PV-technology. For conventional crystalline silicon photovoltaics, the EPBT is higher than for thin-film technologies such as CdTe-PV or CPV-systems. Moreover, the payback time decreased in the recent years due to a number of improvements such as solar cell efficiency and more economic manufacturing processes. As of 2014, photovoltaics recoup on average the energy needed to manufacture them in 0.7 to 2 years. This results in about 95% of net-clean energy produced by a solar rooftop PV system over a 30-year life-time.[105]:30 Installations may be ground-mounted (and sometimes integrated with farming and grazing) or built into the roof or walls of a building (either building-integrated photovoltaics or simply rooftop).
Biofuels

A bus fueled by biodiesel
Information on pump regarding ethanol fuel blend up to 10%, California
A biofuel is a fuel that contains energy from geologically recent carbon fixation. These fuels are produced from living organisms. Examples of this carbon fixation occur in plants and microalgae. These fuels are made by a biomass conversion (biomass refers to recently living organisms, most often referring to plants or plant-derived materials). This biomass can be converted to convenient energy containing substances in three different ways: thermal conversion, chemical conversion, and biochemical conversion. This biomass conversion can result in fuel in solid, liquid, or gas form. This new biomass can be used for biofuels. Biofuels have increased in popularity because of rising oil prices and the need for energy security.
Bioethanol is an alcohol made by fermentation, mostly from carbohydrates produced in sugar or starch crops such as corn or sugarcane. Cellulosic biomass, derived from non-food sources, such as trees and grasses, is also being developed as a feedstock for ethanol production. Ethanol can be used as a fuel for vehicles in its pure form, but it is usually used as a gasoline additive to increase octane and improve vehicle emissions. Bioethanol is widely used in the USA and in Brazil. Current plant design does not provide for converting the lignin portion of plant raw materials to fuel components by fermentation.
Biodiesel is made from vegetable oils and animal fats. Biodiesel can be used as a fuel for vehicles in its pure form, but it is usually used as a diesel additive to reduce levels of particulates, carbon monoxide, and hydrocarbons from diesel-powered vehicles. Biodiesel is produced from oils or fats using transesterification and is the most common biofuel in Europe. However, research is underway on producing renewable fuels from decarboxylation[106]
In 2010, worldwide biofuel production reached 105 billion liters (28 billion gallons US), up 17% from 2009,[107] and biofuels provided 2.7% of the world's fuels for road transport, a contribution largely made up of ethanol and biodiesel.[citation needed] Global ethanol fuel production reached 86 billion liters (23 billion gallons US) in 2010, with the United States and Brazil as the world's top producers, accounting together for 90% of global production. The world's largest biodiesel producer is the European Union, accounting for 53% of all biodiesel production in 2010.[107] As of 2011, mandates for blending biofuels exist in 31 countries at the national level and in 29 states or provinces.[86]:13–14 The International Energy Agency has a goal for biofuels to meet more than a quarter of world demand for transportation fuels by 2050 to reduce dependence on petroleum and coal.[108]
Geothermal

Steam rising from the Nesjavellir Geothermal Power Station in Iceland
Geothermal energy is thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. The geothermal energy of the Earth's crust originates from the original formation of the planet (20%) and from radioactive decay of minerals (80%).[109] The geothermal gradient, which is the difference in temperature between the core of the planet and its surface, drives a continuous conduction of thermal energy in the form of heat from the core to the surface. The adjective geothermal originates from the Greek roots γη (ge), meaning earth, and θερμος (thermos), meaning hot.
Earth's internal heat is thermal energy generated from radioactive decay and continual heat loss from Earth's formation. Temperatures at the core-mantle boundary may reach over 4000 °C (7,200 °F).[110] The high temperature and pressure in Earth's interior cause some rock to melt and solid mantle to behave plastically, resulting in portions of mantle convecting upward since it is lighter than the surrounding rock. Rock and water is heated in the crust, sometimes up to 370 °C (700 °F).[111]
From hot springs, geothermal energy has been used for bathing since Paleolithic times and for space heating since ancient Roman times, but it is now better known for electricity generation. Worldwide, 11,400 megawatts (MW) of geothermal power is online in 24 countries in 2012.[112] An additional 28 gigawatts of direct geothermal heating capacity is installed for district heating, space heating, spas, industrial processes, desalination and agricultural applications in 2010.[113]
Geothermal power is cost effective, reliable, sustainable, and environmentally friendly,[114] but has historically been limited to areas near tectonic plate boundaries. Recent technological advances have dramatically expanded the range and size of viable resources, especially for applications such as home heating, opening a potential for widespread exploitation. Geothermal wells release greenhouse gases trapped deep within the earth, but these emissions are much lower per energy unit than those of fossil fuels. As a result, geothermal power has the potential to help mitigate global warming if widely deployed in place of fossil fuels.
The Earth's geothermal resources are theoretically more than adequate to supply humanity's energy needs, but only a very small fraction may be profitably exploited. Drilling and exploration for deep resources is very expensive. Forecasts for the future of geothermal power depend on assumptions about technology, energy prices, subsidies, and interest rates. Pilot programs like EWEB's customer opt in Green Power Program [115] show that customers would be willing to pay a little more for a renewable energy source like geothermal. But as a result of government assisted research and industry experience, the cost of generating geothermal power has decreased by 25% over the past two decades.[116] In 2001, geothermal energy cost between two and ten US cents per kWh.[117]
Oceanic
Marine energy or marine power (also sometimes referred to as ocean energy, ocean power, or marine and hydrokinetic energy) refers to the energy carried by ocean waves, tides, salinity, and ocean temperature differences. The movement of water in the world's oceans creates a vast store of kinetic energy, or energy in motion. This energy can be harnessed to generate electricity to power homes, transport and industries.The term marine energy encompasses both wave power i.e. power from surface waves, and tidal power i.e. obtained from the kinetic energy of large bodies of moving water. Offshore wind power is not a form of marine energy, as wind power is derived from the wind, even if the wind turbines are placed over water. The oceans have a tremendous amount of energy and are close to many if not most concentrated populations. Ocean energy has the potential of providing a substantial amount of new renewable energy around the world.
100% renewable energy
The incentive to use 100% renewable energy, for electricity, transport, or even total primary energy supply globally, has been motivated by global warming and other ecological as well as economic concerns. Renewable energy use has grown much faster than anyone anticipated.[118] The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has said that there are few fundamental technological limits to integrating a portfolio of renewable energy technologies to meet most of total global energy demand.[119] At the national level, at least 30 nations around the world already have renewable energy contributing more than 20% of energy supply. Also, Professors S. Pacala and Robert H. Socolow have developed a series of "stabilization wedges" that can allow us to maintain our quality of life while avoiding catastrophic climate change, and "renewable energy sources," in aggregate, constitute the largest number of their "wedges." [120]Mark Z. Jacobson says producing all new energy with wind power, solar power, and hydropower by 2030 is feasible and existing energy supply arrangements could be replaced by 2050. Barriers to implementing the renewable energy plan are seen to be "primarily social and political, not technological or economic". Jacobson says that energy costs with a wind, solar, water system should be similar to today's energy costs.[121]
Similarly, in the United States, the independent National Research Council has noted that "sufficient domestic renewable resources exist to allow renewable electricity to play a significant role in future electricity generation and thus help confront issues related to climate change, energy security, and the escalation of energy costs … Renewable energy is an attractive option because renewable resources available in the United States, taken collectively, can supply significantly greater amounts of electricity than the total current or projected domestic demand." .[122]
Critics of the "100% renewable energy" approach include Vaclav Smil and James E. Hansen. Smil and Hansen are concerned about the variable output of solar and wind power, but Amory Lovins argues that the electricity grid can cope, just as it routinely backs up nonworking coal-fired and nuclear plants with working ones.[123]
Google spent $30 million on their RE
Increased energy efficiency
A spiral-type integrated compact fluorescent lamp, which has been popular among North American consumers since its introduction in the mid-1990s[125]
Although increasing the efficiency of energy use is not energy development per se, it may be considered under the topic of energy development since it makes existing energy sources available to do work.[126]:22
Efficient energy use reduces the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to maintain a comfortable temperature. Installing fluorescent lamps or natural skylights reduces the amount of energy required for illumination compared to incandescent light bulbs. Compact fluorescent lights use two-thirds less energy and may last 6 to 10 times longer than incandescent lights. Improvements in energy efficiency are most often achieved by adopting an efficient technology or production process.[127]
Reducing energy use may save consumers money, if the energy savings offsets the cost of an energy efficient technology. Reducing energy use reduces emissions. According to the International Energy Agency, improved energy efficiency in buildings, industrial processes and transportation could reduce the world's energy needs in 2050 by one third, and help control global emissions of greenhouse gases.[128]
Energy efficiency and renewable energy are said to be the twin pillars of sustainable energy policy.[129] In many countries energy efficiency is also seen to have a national security benefit because it can be used to reduce the level of energy imports from foreign countries and may slow down the rate at which domestic energy resources are depleted.
It's been discovered "that for OECD countries, wind, geothermal, hydro and nuclear have the lowest hazard rates among energy sources in production". [130]
Transmission
An elevated section of the Alaska Pipeline
While new sources of energy are only rarely discovered or made possible by new technology, distribution technology continually evolves.[131] The use of fuel cells in cars, for example, is an anticipated delivery technology.[132] This section presents the various delivery technologies that have been important to historic energy development. They all rely in way on the energy sources listed in the previous section.
Shipping and pipelines
Coal, petroleum and their derivatives are delivered by boat, rail, or road. Petroleum and natural gas may also be delivered by pipeline, and coal via a Slurry pipeline. Fuels such as gasoline and LPG may also be delivered via aircraft. Natural gas pipelines must maintain a certain minimum pressure to function correctly. The higher costs of ethanol transportation and storage are often prohibitive.[133]Wired energy transfer
Electrical grid – pylons and cables distribute power
Electricity grids are the networks used to transmit and distribute power from production source to end user, when the two may be hundreds of kilometres away. Sources include electrical generation plants such as a nuclear reactor, coal burning power plant, etc. A combination of sub-stations and transmission lines are used to maintain a constant flow of electricity. Grids may suffer from transient blackouts and brownouts, often due to weather damage. During certain extreme space weather events solar wind can interfere with transmissions. Grids also have a predefined carrying capacity or load that cannot safely be exceeded. When power requirements exceed what's available, failures are inevitable. To prevent problems, power is then rationed.
Industrialised countries such as Canada, the US, and Australia are among the highest per capita consumers of electricity in the world, which is possible thanks to a widespread electrical distribution network. The US grid is one of the most advanced, although infrastructure maintenance is becoming a problem. CurrentEnergy provides a realtime overview of the electricity supply and demand for California, Texas, and the Northeast of the US. African countries with small scale electrical grids have a correspondingly low annual per capita usage of electricity. One of the most powerful power grids in the world supplies power to the state of Queensland, Australia.
Wireless energy transfer
Wireless power transfer is a process whereby electrical energy is transmitted from a power source to an electrical load that does not have a built-in power source, without the use of interconnecting wires. Currently available technology is limited to short distances and relatively low power level.Orbiting solar power collectors would require wireless transmission of power to Earth. The proposed method involves creating a large beam of microwave-frequency radio waves, which would be aimed at a collector antenna site on the Earth. Formidable technical challenges exist to ensure the safety and profitability of such a scheme.
Storage
The Ffestiniog Power Station in Wales, United Kingdom. Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH) is used for grid energy storage.
Energy storage is accomplished by devices or physical media that store energy to perform useful operation at a later time. A device that stores energy is sometimes called an accumulator.
All forms of energy are either potential energy (e.g. Chemical, gravitational, electrical energy, temperature differential, latent heat, etc.) or kinetic energy (e.g. momentum). Some technologies provide only short-term energy storage, and others can be very long-term such as power to gas using hydrogen or methane and the storage of heat or cold between opposing seasons in deep aquifers or bedrock. A wind-up clock stores potential energy (in this case mechanical, in the spring tension), a battery stores readily convertible chemical energy to operate a mobile phone, and a hydroelectric dam stores energy in a reservoir as gravitational potential energy. Ice storage tanks store ice (thermal energy in the form of latent heat) at night to meet peak demand for cooling. Fossil fuels such as coal and gasoline store ancient energy derived from sunlight by organisms that later died, became buried and over time were then converted into these fuels. Even food (which is made by the same process as fossil fuels) is a form of energy stored in chemical form.
History
Energy generators past and present at Doel, Belgium: 17th-century windmill Scheldemolen and 20th-century Doel Nuclear Power Station
Since prehistory, when humanity discovered fire to warm up and roast food, through the Middle Ages in which populations built windmills to grind the wheat, until the modern era in which nations can get electricity splitting the atom. Man has sought endlessly for energy sources.
Except nuclear, geothermal and tidal, all other energy sources are from current solar isolation or from fossil remains of plant and animal life that relied upon sunlight. Ultimately, solar energy itself is the result of the Sun's nuclear fusion. Geothermal power from hot, hardened rock above the magma of the Earth's core is the result of the decay of radioactive materials present beneath the Earth's crust, and nuclear fission relies on man-made fission of heavy radioactive elements in the Earth's crust; in both cases these elements were produced in supernova explosions before the formation of the solar system.
Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, the question of the future of energy supplies has been of interest. In 1865, William Stanley Jevons published The Coal Question in which he saw that the reserves of coal were being depleted and that oil was an ineffective replacement. In 1914, U.S. Bureau of Mines stated that the total production was 5.7 billion barrels (910,000,000 m3). In 1956, Geophysicist M. King Hubbert deduces that U.S. oil production would peak between 1965 and 1970 and that oil production will peak "within half a century" on the basis of 1956 data. In 1989, predicted peak by Colin Campbell[134] In 2004, OPEC estimated, with substantial investments, it would nearly double oil output by 2025[135]
Sustainability
Energy consumption from 1989 to 1999
The environmental movement has emphasized sustainability of energy use and development.[136] Renewable energy is sustainable in its production; the available supply will not be diminished for the foreseeable future - millions or billions of years. "Sustainability" also refers to the ability of the environment to cope with waste products, especially air pollution. Sources which have no direct waste products (such as wind, solar, and hydropower) are brought up on this point. With global demand for energy growing, the need to adopt various energy sources is growing. Energy conservation is an alternative or complementary process to energy development. It reduces the demand for energy by using it efficiently.
Resilience
Energy consumption per capita (2001). Red hues indicate increase, green hues decrease of consumption during the 1990s.
Some observers contend that idea of "energy independence" is an unrealistic and opaque concept.[137] The alternative offer of "energy resilience" is a goal aligned with economic, security, and energy realities. The notion of resilience in energy was detailed in the 1982 book Brittle Power: Energy Strategy for National Security.[138] The authors argued that simply switching to domestic energy would not be secure inherently because the true weakness is the interdependent and vulnerable energy infrastructure of the United States. Key aspects such as gas lines and the electrical power grid are centralized and easily susceptible to disruption. They conclude that a "resilient energy supply" is necessary for both national security and the environment. They recommend a focus on energy efficiency and renewable energy that is decentralized.[139]
In 2008, former Intel Corporation Chairman and CEO Andrew Grove looked to energy resilience, arguing that complete independence is unfeasible given the global market for energy.[140] He describes energy resilience as the ability to adjust to interruptions in the supply of energy. To that end, he suggests the U.S. make greater use of electricity.[141] Electricity can be produced from a variety of sources. A diverse energy supply will be less affected by the disruption in supply of any one source. He reasons that another feature of electrification is that electricity is "sticky" – meaning the electricity produced in the U.S. is to stay there because it cannot be transported overseas. According to Grove, a key aspect of advancing electrification and energy resilience will be converting the U.S. automotive fleet from gasoline-powered to electric-powered. This, in turn, will require the modernization and expansion of the electrical power grid. As organizations such as The Reform Institute have pointed out, advancements associated with the developing smart grid would facilitate the ability of the grid to absorb vehicles en masse connecting to it to charge their batteries.[142]
Present and future
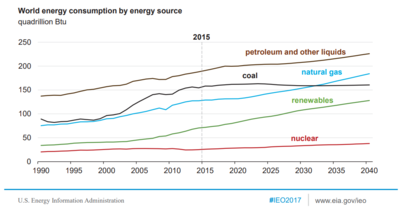
Outlook—World Energy Consumption by Fuel (as of 2011)[143]
Increasing share of energy consumption by developing nations[144]
Extrapolations from current knowledge to the future offer a choice of energy futures.[145] Predictions parallel the Malthusian catastrophe hypothesis. Numerous are complex models based scenarios as pioneered by Limits to Growth. Modeling approaches offer ways to analyze diverse strategies, and hopefully find a road to rapid and sustainable development of humanity. Short term energy crises are also a concern of energy development. Extrapolations lack plausibility, particularly when they predict a continual increase in oil consumption.[citation needed]
Energy production usually requires an energy investment. Drilling for oil or building a wind power plant requires energy. The fossil fuel resources that are left are often increasingly difficult to extract and convert. They may thus require increasingly higher energy investments. If investment is greater than the value of the energy produced by the resource, it is no longer an effective energy source. These resources are no longer an energy source but may be exploited for value as raw materials. New technology may lower the energy investment required to extract and convert the resources, although ultimately basic physics sets limits that cannot be exceeded.
Between 1950 and 1984, as the Green Revolution transformed agriculture around the globe, world grain production increased by 250%. The energy for the Green Revolution was provided by fossil fuels in the form of fertilizers (natural gas), pesticides (oil), and hydrocarbon fueled irrigation.[146] The peaking of world hydrocarbon production (peak oil) may lead to significant changes, and require sustainable methods of production.[147] One vision of a sustainable energy future involves all human structures on the earth's surface (i.e., buildings, vehicles and roads) doing artificial photosynthesis (using sunlight to split water as a source of hydrogen and absorbing carbon dioxide to make fertilizer) efficiently than plants.[148]
With contemporary space industry's economic activity[149][150] and the related private spaceflight, with the manufacturing industries, that go into Earth's orbit or beyond, delivering them to those regions will require further energy development.[151][152] Researchers have contemplated space-based solar power for collecting solar power for use on Earth. Space-based solar power has been in research since the early 1970s. Space-based solar power would require construction of collector structures in space. The advantage over ground-based solar power is higher intensity of light, and no weather to interrupt power collection.