Coordinates: 33°N 44°E
| Republic of Iraq | |
|---|---|
 | |
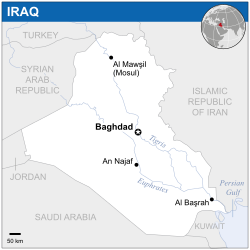 | |
| Capital and largest city | Baghdad 33°20′N 44°26′E |
| Official languages | |
| Religion | Islam |
| Demonym | Iraqi |
| Government | Federal parliamentary republic |
| Fuad Masum | |
| Haider al-Abadi | |
| Legislature | Council of Representatives |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| Area | |
• Total
| 437,072 km2 (168,754 sq mi) (58th) |
• Water (%)
| 1.1 |
| Population | |
• 2016 estimate
| 37,202,572 (36th) |
• Density
| 82.7/km2 (214.2/sq mi) (125th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate |
• Total
| $753.450 billion (34th) |
• Per capita
| $17,394[2] (71st) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total
| $202.922 billion (47th) |
• Per capita
| $5,091 (88th) |
| Gini (2012) | 29.5 low |
| HDI (2014) | medium · 121st |
| Currency | Iraqi dinar (IQD) |
| Time zone | AST (UTC+3) |
| Drives on the | right |
| Calling code | +964 |
| ISO 3166 code | IQ |
| Internet TLD | .iq |
| |
Iraq has a coastline measuring 58 km (36 miles) on the northern Persian Gulf and encompasses the Mesopotamian Alluvial Plain, the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range and the eastern part of the Syrian Desert.[6] Two major rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates, run south through Iraq and into the Shatt al-Arab near the Persian Gulf. These rivers provide Iraq with significant amounts of fertile land.
The region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, historically known as Mesopotamia, is often referred to as the cradle of civilisation. It was here that mankind first began to read, write, create laws and live in cities under an organised government—notably Uruk, from which "Iraq" is derived. The area has been home to successive civilisations since the 6th millennium BC. Iraq was the centre of the Akkadian, Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian empires. It was also part of the Median, Achaemenid, Hellenistic, Parthian, Sassanid, Roman, Rashidun, Umayyad, Abbasid, Ayyubid, Mongol, Safavid, Afsharid and Ottoman empires.
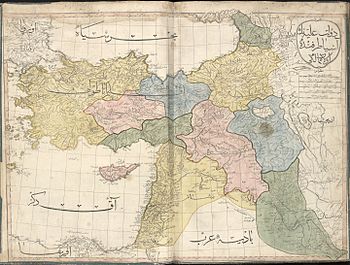
The country today known as Iraq was a region of the Ottoman Empire until the partition of the Ottoman Empire in the 20th century. It was made up of three provinces, called vilayets in the Ottoman language: Mosul Vilayet, Baghdad Vilayet, and Basra Vilayet. In April 1920 the British Mandate of Mesopotamia was created under the authority of the League of Nations. A British-backed monarchy joining these vilayets into one Kingdom was established in 1921 under Faisal I of Iraq. The Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq gained independence from the UK in 1932. In 1958, the monarchy was overthrown and the Iraqi Republic created. Iraq was controlled by the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party from 1968 until 2003. After an invasion by the United States and its allies in 2003, Saddam Hussein's Ba'ath Party was removed from power, and multi-party parliamentary elections were held in 2005. The US presence in Iraq ended in 2011, but the Iraqi insurgency continued and intensified as fighters from the Syrian Civil War spilled into the country. Out of the insurgency came a highly destructive group calling itself ISIL, which took large parts of the north and west. It has since been largely defeated. Disputes over the sovereignty of Iraqi Kurdistan continue. A referendum about the full sovereignty of Iraqi Kurdistan was held on 25 September 2017. On 9 December 2017, Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi declared victory over ISIL after the group lost its territory in Iraq.
Iraq is a founding member of the UN as well as of the Arab League, OIC, Non-Aligned Movement and the IMF. It is a federal parliamentary republic consisting of 19 governorates (provinces) and one autonomous region (Iraqi Kurdistan). The country's official religion is Islam. Culturally, Iraq has a very rich heritage and celebrates the achievements of its past in pre-Islamic times and is known for its poets. Its painters and sculptors are among the best in the Arab world, some of them being world-class as well as producing fine handicrafts, including rugs and carpets.
Name
The Arabic name العراق al-ʿIrāq has been in use since before the 6th century. There are several suggested origins for the name. One dates to the Sumerian city of Uruk (Biblical Hebrew Erech) and is thus ultimately of Sumerian origin, as Uruk was the Akkadian name for the Sumerian city of Urug, containing the Sumerian word for "city", UR. An Arabic folk etymology for the name is "deeply rooted, well-watered; fertile".During the medieval period, there was a region called ʿIrāq ʿArabī ("Arabian Iraq") for Lower Mesopotamia and ʿIrāq ʿajamī ("Foreign Iraq"), for the region now situated in Central and Western Iran. The term historically included the plain south of the Hamrin Mountains and did not include the northernmost and westernmost parts of the modern territory of Iraq. Prior to the middle of the 19th century, the term Eyraca Arabic was commonly used to describe Iraq.
The term Sawad was also used in early Islamic times for the region of the alluvial plain of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, contrasting it with the arid Arabian desert. As an Arabic word, عراق means "hem", "shore", "bank", or "edge", so that the name by folk etymology came to be interpreted as "the escarpment", viz. at the south and east of the Jazira Plateau, which forms the northern and western edge of the "al-Iraq arabi" area.
The Arabic pronunciation is [ʕiˈrɑːq]. In English, it is either /ɪˈrɑːk/ (the only pronunciation listed in the Oxford English Dictionary and the first one in Merriam-Webster's Online Dictionary) or /ɪˈræk/ (listed first by MQD), the American Heritage Dictionary, and the Random House Dictionary. The pronunciation /aɪˈræk/ is frequently heard in US media.
In accordance with the 2005 Constitution, the official name of the state is the "Republic of Iraq" (Jumhūrīyyat al-‘Irāq).
History
Pre-historic era
Between 65,000 BC and 35,000 BC northern Iraq was home to a Neanderthal culture, archaeological remains of which have been discovered at Shanidar Cave This same region is also the location of a number of pre-Neolithic cemeteries, dating from approximately 11,000 BC.Since approximately 10,000 BC, Iraq (alongside Asia Minor and The Levant) was one of centres of a Caucasoid Neolithic culture (known as Pre-Pottery Neolithic A) where agriculture and cattle breeding appeared for the first time in the world. The following Neolithic period (PPNB) is represented by rectangular houses. At the time of the pre-pottery Neolithic, people used vessels made of stone, gypsum and burnt lime (Vaisselle blanche). Finds of obsidian tools from Anatolia are evidences of early trade relations.
Further important sites of human advancement were Jarmo (circa 7100 BC), the Halaf culture and Ubaid period (between 6500 BC and 3800 BC). These periods show ever-increasing levels of advancement in agriculture, tool-making and architecture.
Ancient Iraq
Cylinder Seal, Old Babylonian Period, c.1800 BC, hematite. The king makes an animal offering to Shamash. This seal was probably made in a workshop at Sippar.
The historical period in Iraq truly begins during the Uruk period (4000 BC to 3100 BC), with the founding of a number of Sumerian cities, and the use of Pictographs, Cylinder seals and mass-produced goods.
The "Cradle of Civilization" is thus a common term for the area comprising modern Iraq as it was home to the earliest known civilisation, the Sumerian civilisation, which arose in the fertile Tigris-Euphrates river valley of southern Iraq in the Chalcolithic (Ubaid period).
It was here, in the late 4th millennium BC, that the world's first writing system and recorded history itself were born. The Sumerians were also the first to harness the wheel and create City States, and whose writings record the first evidence of Mathematics, Astronomy, Astrology, Written Law, Medicine and Organised religion.
The language of the Sumerians is a language isolate. The major city states of the early Sumerian period were; Eridu, Bad-tibira, Larsa, Sippar, Shuruppak, Uruk, Kish, Ur, Nippur, Lagash, Girsu, Umma, Hamazi, Adab, Mari, Isin, Kutha, Der and Akshak.
The cities to the north like Ashur, Arbela (modern Erbil) and Arrapha (modern Kirkuk) were also extant in what was to be called Assyria from the 25th century BC; however, at this early stage, they were Sumerian ruled administrative centres.
Victory stele of Naram-Sin of Akkad.
Bronze Age
In the 26th century BC, Eannatum of Lagash created what was perhaps the first empire in history, though this was short-lived. Later, Lugal-Zage-Si, the priest-king of Umma, overthrew the primacy of the Lagash dynasty in the area, then conquered Uruk, making it his capital, and claimed an empire extending from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean. It was during this period that the Epic of Gilgamesh originates, which includes the tale of The Great Flood.From the 29th century BC, Akkadian Semitic names began to appear on king lists and administrative documents of various city states. It remains unknown as to the origin of Akkad, where it was precisely situated and how it rose to prominence. Its people spoke Akkadian, an East Semitic language.
During the 3rd millennium BC, a cultural symbiosis developed between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism. The influences between Sumerian and Akkadian are evident in all areas, including lexical borrowing on a massive scale—and syntactic, morphological, and phonological convergence. This mutual influence has prompted scholars to refer to Sumerian and Akkadian of the 3rd millennium BC as a Sprachbund. From this period, the civilisation in Iraq came to be known as Sumero-Akkadian.
Bill of sale of a male slave and a building in Shuruppak, Sumerian tablet, circa 2600 BC.
However, the Sumerians remained generally dominant until the rise of the Akkadian Empire (2335–2124 BC), based in the city of Akkad in central Iraq. Sargon of Akkad, originally a Rabshakeh to a Sumerian king, founded the empire, he conquered all of the city states of southern and central Iraq, and subjugated the kings of Assyria, thus uniting the Sumerians and Akkadians in one state. He then set about expanding his empire, conquering Gutium, Elam and had victories that did not result into a full conquest against the Amorites and Eblaites of Ancient Syria.
After the collapse of the Akkadian Empire in the late 22nd century BC, the Gutians occupied the south for a few decades, while Assyria reasserted its independence in the north. This was followed by a Sumerian renaissance in the form of the Neo-Sumerian Empire. The Sumerians under king Shulgi conquered almost all of Iraq except the northern reaches of Assyria, and asserted themselves over the Gutians, Elamites and Amorites, destroying the first and holding off the others.
An Elamite invasion in 2004 BC brought the Sumerian revival to an end. By the mid 21st century BC, the Akkadian speaking kingdom of Assyria had risen to dominance in northern Iraq. Assyria expanded territorially into the north eastern Levant, central Iraq, and eastern Anatolia, forming the Old Assyrian Empire (circa 2035–1750 BC) under kings such as Puzur-Ashur I, Sargon I, Ilushuma and Erishum I, the latter of whom produced the most detailed set of law yet written. The south broke up into a number of Akkadian speaking states, Isin, Larsa and Eshnunna being the major ones.
During the 20th century BC, the Canaanite speaking Amorites began to migrate into southern Mesopotamia. Eventually, they began to set up small petty kingdoms in the south, as well as usurping the thrones of extant city states such as Isin, Larsa and Eshnunna.
Hammurabi, depicted as receiving his royal insignia from Shamash. Relief on the upper part of the stele of Hammurabi's code of laws.
One of these small Amorite kingdoms founded in 1894 BC contained the then small administrative town of Babylon within its borders. It remained insignificant for over a century, overshadowed by older and more powerful states, such as Assyria, Elam, Isin, Ehnunna and Larsa.
In 1792 BC, an Amorite ruler named Hammurabi came to power in this state, and immediately set about building Babylon from a minor town into a major city, declaring himself its king. Hammurabi conquered the whole of southern and central Iraq, as well as Elam to the east and Mari to the west, then engaged in a protracted war with the Assyrian king Ishme-Dagan for domination of the region, creating the short-lived Babylonian Empire. He eventually prevailed over the successor of Ishme-Dagan and subjected Assyria and its Anatolian colonies. By the middle of the eighteenth century BC, the Sumerians had lost their cultural identity and ceased to exist as a distinct people. Genetic and cultural analysis indicates that the Marsh Arabs of southern Iraq are probably their most direct modern descendants.
It is from the period of Hammurabi that southern Iraq came to be known as Babylonia, while the north had already coalesced into Assyria hundreds of years before. However, his empire was short-lived, and rapidly collapsed after his death, with both Assyria and southern Iraq, in the form of the Sealand Dynasty, falling back into native Akkadian hands. The foreign Amorites clung on to power in a once more weak and small Babylonia until it was sacked by the Indo-European speaking Hittite Empire based in Anatolia in 1595 BC. After this, another foreign people, the Language Isolate speaking Kassites, originating in the Zagros Mountains of Ancient Iran, seized control of Babylonia, where they were to rule for almost 600 years, by far the longest dynasty ever to rule in Babylon.
Iraq was from this point divided into three polities: Assyria in the north, Kassite Babylonia in the south central region, and the Sealand Dynasty in the far south. The Sealand Dynasty was finally conquered by Kassite Babylonia circa 1380 BC.
The Middle Assyrian Empire (1365–1020 BC) saw Assyria rise to be the most powerful nation in the known world. Beginning with the campaigns of Ashur-uballit I, Assyria destroyed the rival Hurrian-Mitanni Empire, annexed huge swathes of the Hittite Empire for itself, annexed northern Babylonia from the Kassites, forced the Egyptian Empire from the region, and defeated the Elamites, Phrygians, Canaanites, Phoenicians, Cilicians, Gutians, Dilmunites and Arameans. At its height, the Middle Assyrian Empire stretched from The Caucasus to Dilmun (modern Bahrain), and from the Mediterranean coasts of Phoenicia to the Zagros Mountains of Iran. In 1235 BC, Tukulti-Ninurta I of Assyria took the throne of Babylon, thus becoming the very first native Mesopotamian to rule the state.
During the Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BC), Babylonia was in a state of chaos, dominated for long periods by Assyria and Elam. The Kassites were driven from power by Assyria and Elam, allowing native south Mesopotamian kings to rule Babylonia for the first time, although often subject to Assyrian or Elamite rulers. However, these East Semitic Akkadian kings, were unable to prevent new waves of West Semitic migrants entering southern Iraq, and during the 11th century BC Arameans and Suteans entered Babylonia from The Levant, and these were followed in the late 10th to early 9th century BC by the migrant Chaldeans who were closely related to the earlier Arameans.
Iron Age
After a period of comparative decline in Assyria, it once more began to expand with the Neo Assyrian Empire (935–605 BC). This was to be the largest empire the region had yet seen, and under rulers such as Adad-Nirari II, Ashurnasirpal, Shalmaneser III, Semiramis, Tiglath-pileser III, Sargon II, Sennacherib, Esarhaddon and Ashurbanipal, Iraq became the centre of an empire stretching from Persia, Parthia and Elam in the east, to Cyprus and Antioch in the west, and from The Caucasus in the north to Egypt, Nubia and Arabia in the south.The Arabs and the Chaldeans are first mentioned in written history (circa 850 BC) in the annals of Shalmaneser III.
It was during this period that an Akkadian influenced form of Eastern Aramaic was adopted by the Assyrians as the lingua franca of their vast empire, and Mesopotamian Aramaic began to supplant Akkadian as the spoken language of the general populace of both Assyria and Babylonia. The descendant dialects of this tongue survive amongst the Mandaeans of southern Iraq and Assyrians of northern Iraq to this day.
In the late 7th century BC, the Assyrian Empire tore itself apart with a series of brutal civil wars, weakening itself to such a degree that a coalition of its former subjects; the Babylonians, Chaldeans, Medes, Persians, Parthians, Scythians and Cimmerians, were able to attack Assyria, finally bringing its empire down by 605 BC.
Babylonian and Persian periods
The short-lived Neo-Babylonian Empire (620–539 BC) succeeded that of Assyria. It failed to attain the size, power or longevity of its predecessor; however, it came to dominate The Levant, Canaan, Arabia, Israel and Judah, and to defeat Egypt. Initially, Babylon was ruled by yet another foreign dynasty, that of the Chaldeans, who had migrated to the region in the late 10th or early 9th century BC. Its greatest king, Nebuchadnezzar II, rivalled another non native ruler, the ethnically unrelated Amorite king Hammurabi, as the greatest king of Babylon. However, by 556 BC, the Chaldeans had been deposed from power by the Assyrian born Nabonidus and his son and regent Belshazzar.In the 6th century BC, Cyrus the Great of neighbouring Persia defeated the Neo-Babylonian Empire at the Battle of Opis and Iraq was subsumed into the Achaemenid Empire for nearly two centuries. The Achaemenids made Babylon their main capital. The Chaldeans and Chaldea disappeared at around this time, though both Assyria and Babylonia endured and thrived under Achaemenid rule (see Achaemenid Assyria). Little changed under the Persians, having spent three centuries under Assyrian rule, their kings saw themselves as successors to Ashurbanipal, and they retained Assyrian Imperial Aramaic as the language of empire, together with the Assyrian imperial infrastructure, and an Assyrian style of art and architecture.
The Greek-ruled Seleucid Empire (in yellow) with capital in Seleucia on the Tigris, north of Babylon.
In the late 4th century BC, Alexander the Great conquered the region, putting it under Hellenistic Seleucid rule for over two centuries. The Seleucids introduced the Indo-Anatolian and Greek term Syria to the region. This name had for many centuries been the Indo-European word for Assyria and specifically and only meant Assyria; however, the Seleucids also applied it to The Levant (Aramea, causing both the Assyria and the Assyrians of Iraq and the Arameans and The Levant to be called Syria and Syrians/Syriacs in the Greco-Roman world.
The Parthians (247 BC – 224 AD) from Persia conquered the region during the reign of Mithridates I of Parthia (r. 171–138 BC). From Syria, the Romans invaded western parts of the region several times, briefly founding Assyria Provincia in Assyria. Christianity began to take hold in Iraq (particularly in Assyria) between the 1st and 3rd centuries, and Assyria became a centre of Syriac Christianity, the Church of the East and Syriac literature. A number of independent states evolved in the north during the Parthian era, such as Adiabene, Assur, Osroene and Hatra.
The Sassanids of Persia under Ardashir I destroyed the Parthian Empire and conquered the region in 224 AD. During the 240s and 250's AD, the Sassanids gradually conquered the independent states, culminating with Assur in 256 AD. The region was thus a province of the Sassanid Empire for over four centuries, and became the frontier and battle ground between the Sassanid Empire and Byzantine Empire, with both empires weakening each other, paving the way for the Arab-Muslim conquest of Persia in the mid-7th century.
Middle Ages
The Abbasid Caliphate at its greatest extent, c. 850.
The Arab Islamic conquest in the mid-7th century AD established Islam in Iraq and saw a large influx of Arabs. Under the Rashidun Caliphate, the prophet Muhammad's cousin and son-in-law, Ali, moved his capital to Kufa when he became the fourth caliph. The Umayyad Caliphate ruled the province of Iraq from Damascus in the 7th century. (However, eventually there was a separate, independent Caliphate of Córdoba in Iberia.)
The Abbasid Caliphate built the city of Baghdad in the 8th century as its capital, and the city became the leading metropolis of the Arab and Muslim world for five centuries. Baghdad was the largest multicultural city of the Middle Ages, peaking at a population of more than a million, and was the centre of learning during the Islamic Golden Age. The Mongols destroyed the city and burned its library during the siege of Baghdad in the 13th century.
In 1257, Hulagu Khan amassed an unusually large army, a significant portion of the Mongol Empire's forces, for the purpose of conquering Baghdad. When they arrived at the Islamic capital, Hulagu Khan demanded its surrender, but the last Abbasid Caliph Al-Musta'sim refused. This angered Hulagu, and, consistent with Mongol strategy of discouraging resistance, he besieged Baghdad, sacked the city and massacred many of the inhabitants. Estimates of the number of dead range from 200,000 to a million.
The sack of Baghdad by the Mongols.
The Mongols destroyed the Abbasid Caliphate and Baghdad's House of Wisdom, which contained countless precious and historical documents. The city has never regained its previous pre-eminence as a major centre of culture and influence. Some historians believe that the Mongol invasion destroyed much of the irrigation infrastructure that had sustained Mesopotamia for millennia. Other historians point to soil salination as the culprit in the decline in agriculture.
The mid-14th-century Black Death ravaged much of the Islamic world. The best estimate for the Middle East is a death rate of roughly one-third.
In 1401, a warlord of Mongol descent, Tamerlane (Timur Lenk), invaded Iraq. After the capture of Baghdad, 20,000 of its citizens were massacred. Timur ordered that every soldier should return with at least two severed human heads to show him (many warriors were so scared they killed prisoners captured earlier in the campaign just to ensure they had heads to present to Timur). Timur also conducted massacres of the indigenous Assyrian Christian population, hitherto still the majority population in northern Mesopotamia, and it was during this time that the ancient Assyrian city of Assur was finally abandoned.
Ottoman Iraq
The 1803 Cedid Atlas, showing the area today known as Iraq divided between "Al Jazira" (pink), "Kurdistan" (blue), "Iraq" (green), and "Al Sham" (yellow).
During the late 14th and early 15th centuries, the Black Sheep Turkmen ruled the area now known as Iraq. In 1466, the White Sheep Turkmen defeated the Black Sheep and took control. From the earliest 16th century, in 1508, as with all territories of the former White Sheep Turkmen, Iraq fell into the hands of the Iranian Safavids. Owing to the century long Turco-Iranian rivalry between the Safavids and the neighbouring Ottoman Turks, Iraq would be contested between the two for more than a hundred years during the frequent Ottoman-Persian Wars.
With the Treaty of Zuhab in 1639, most of the territory of present-day Iraq eventually came under the control of Ottoman Empire as the eyalet of Baghdad as a result of wars with the neighbouring rival, Safavid Iran. Throughout most of the period of Ottoman rule (1533–1918), the territory of present-day Iraq was a battle zone between the rival regional empires and tribal alliances.
By the 17th century, the frequent conflicts with the Safavids had sapped the strength of the Ottoman Empire and had weakened its control over its provinces. The nomadic population swelled with the influx of bedouins from Najd, in the Arabian Peninsula. Bedouin raids on settled areas became impossible to curb.
During the years 1747–1831, Iraq was ruled by a Mamluk dynasty of Georgian origin who succeeded in obtaining autonomy from the Ottoman Porte, suppressed tribal revolts, curbed the power of the Janissaries, restored order and introduced a programme of modernisation of economy and military. In 1831, the Ottomans managed to overthrow the Mamluk regime and imposed their direct control over Iraq. The population of Iraq, estimated at 30 million in 800 AD, was only 5 million at the start of the 20th century.
During World War I, the Ottomans sided with Germany and the Central Powers. In the Mesopotamian campaign against the Central Powers, British forces invaded the country and initially suffered a major defeat at the hands of the Turkish army during the Siege of Kut (1915–1916). However, subsequent to this the British began to gain the upper hand, and were further aided by the support of local Arabs and Assyrians. In 1916, the British and French made a plan for the post-war division of Western Asia under the Sykes-Picot Agreement. British forces regrouped and captured Baghdad in 1917, and defeated the Ottomans. An armistice was signed in 1918. The British lost 92,000 soldiers in the Mesopotamian campaign. Ottoman losses are unknown but the British captured a total of 45,000 prisoners of war. By the end of 1918, the British had deployed 410,000 men in the area, of which 112,000 were combat troops.
British administration and independent Kingdom
British troops in Baghdad, June 1941.
The country today known as Iraq was a region of the Ottoman Empire until the partition of the Ottoman Empire in the 20th century. It was made up of three provinces, called vilayets in the Ottoman language: Mosul Vilayet, Baghdad Vilayet, and Basra Vilayet. These three provinces were joined into one Kingdom by the British after the region became a League of Nations mandate, administered under British control, with the name "State of Iraq". The British established the Hashemite king, Faisal I of Iraq, who had been forced out of Syria by the French, as their client ruler. Likewise, British authorities selected Sunni Arab elites from the region for appointments to government and ministry offices.
Faced with spiraling costs and influenced by the public protestations of the war hero T. E. Lawrence in The Times, Britain replaced Arnold Wilson in October 1920 with a new Civil Commissioner, Sir Percy Cox. Cox managed to quell a rebellion, yet was also responsible for implementing the fateful policy of close co-operation with Iraq's Sunni minority. The institution of slavery was abolished in the 1920s.
Britain granted independence to the Kingdom of Iraq in 1932, on the urging of King Faisal, though the British retained military bases, local militia in the form of Assyrian Levies, and transit rights for their forces. King Ghazi ruled as a figurehead after King Faisal's death in 1933, while undermined by attempted military coups, until his death in 1939. Ghazi was followed by his underage son, Faisal II. 'Abd al-Ilah served as Regent during Faisal's minority.
On 1 April 1941, Rashid Ali al-Gaylani and members of the Golden Square staged a coup d'état and overthrew the government of 'Abd al-Ilah. During the subsequent Anglo-Iraqi War, the United Kingdom (which still maintained air bases in Iraq) invaded Iraq for fear that the Rashid Ali government might cut oil supplies to Western nations because of his links to the Axis powers. The war started on 2 May, and the British, together with loyal Assyrian Levies, defeated the forces of Al-Gaylani, forcing an armistice on 31 May.
A military occupation followed the restoration of the pre-coup government of the Hashemite monarchy. The occupation ended on 26 October 1947, although Britain was to retain military bases in Iraq until 1954, after which the Assyrian militias were disbanded. The rulers during the occupation and the remainder of the Hashemite monarchy were Nuri as-Said, the autocratic Prime Minister, who also ruled from 1930 to 1932, and 'Abd al-Ilah, the former Regent who now served as an adviser to King Faisal II.
Republic and Ba'athist Iraq
The 14 July Revolution in 1958.
In 1958, a coup d'état known as the 14 July Revolution was led by the Brigadier General Abd al-Karim Qasim. This revolt was strongly anti-imperial and anti-monarchical in nature and had strong socialist elements. Numerous people were killed in the coup, including King Faysal II, Prince Abd al-Ilah, and Nuri al-Sa'id. Qasim controlled Iraq through military rule and in 1958 he began a process of forcibly reducing the surplus amounts of land owned by a few citizens and having the state redistribute the land. He was overthrown by Colonel Abdul Salam Arif in a February 1963 coup. After the latter's death in 1966, he was succeeded by his brother, Abdul Rahman Arif, who was overthrown by the Ba'ath Party in 1968. Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr became the first Ba'ath President of Iraq but then the movement gradually came under the control of Saddam Hussein, who acceded to the presidency and control of the Revolutionary Command Council (RCC), then Iraq's supreme executive body, in July 1979.
In 1979, the Iranian Revolution took place. Following months of cross-border raids between the two countries, Saddam declared war on Iran in September 1980, initiating the Iran–Iraq War (or First Persian Gulf War). Taking advantage of the post-revolution chaos in Iran, Iraq captured some territories in southwest of Iran, but Iran recaptured all of the lost territories within two years, and for the next six years Iran was on the offensive. The war, which ended in stalemate in 1988, had cost the lives of between half a million and 1.5 million people. In 1981, Israeli aircraft bombed an Iraqi nuclear materials testing reactor at Osirak and was widely criticised at the United Nations. During the eight-year war with Iran, Saddam Hussein extensively used chemical weapons against Iranians. In the final stages of the Iran–Iraq War, the Ba'athist Iraqi regime led the Al-Anfal Campaign, a genocidal campaign that targeted Iraqi Kurds, and led to the killing of 50,000–100,000 civilians. Chemical weapons were also used against Iraqi Shia civilians during the 1991 uprisings in Iraq.
In August 1990, Iraq invaded and annexed Kuwait. This subsequently led to military intervention by United States-led forces in the First Gulf War. The coalition forces proceeded with a bombing campaign targeting military targets and then launched a 100-hour-long ground assault against Iraqi forces in Southern Iraq and those occupying Kuwait.
Saddam Hussein meets Donald Rumsfeld during the Iran–Iraq War. Hussein ruled Iraq from 1979 until 2003.
Iraq's armed forces were devastated during the war. Shortly after it ended in 1991, Shia and Kurdish Iraqis led several uprisings against Saddam Hussein's regime, but these were successfully repressed using the Iraqi security forces and chemical weapons. It is estimated that as many as 100,000 people, including many civilians were killed. During the uprisings the US, UK, France and Turkey, claiming authority under UNSCR 688, established the Iraqi no-fly zones to protect Kurdish and Shiite populations from attacks by the Saddam regime's fixed-wing aircraft (but not helicopters).
Iraq was ordered to destroy its chemical and biological weapons and the UN attempted to compel Saddam's government to disarm and agree to a ceasefire by imposing additional sanctions on the country in addition to the initial sanctions imposed following Iraq's invasion of Kuwait. The Iraqi Government's failure to disarm and agree to a ceasefire resulted in sanctions which remained in place until 2003. The effects of the sanctions on the civilian population of Iraq have been disputed. Whereas it was widely believed that the sanctions caused a major rise in child mortality, recent research has shown that commonly cited data were fabricated by the Iraqi government and that "there was no major rise in child mortality in Iraq after 1990 and during the period of the sanctions." An oil for food program was established in 1996 to ease the effects of sanctions.
Following the 9/11 terrorist attacks, the George W. Bush administration began planning the overthrow of Saddam's government and in October 2002, the US Congress passed the Joint Resolution to Authorize the Use of United States Armed Forces Against Iraq. In November 2002, the UN Security Council passed UNSCR 1441 and in March 2003 the US and its allies invaded Iraq.
2003–2007
The April 2003 toppling of Saddam Hussein's statue in Firdos Square in Baghdad shortly after the Iraq War invasion.
On 20 March 2003, a United States-organized coalition invaded Iraq, under the pretext that Iraq had failed to abandon its weapons of mass destruction program in violation of UN Resolution 687. This claim was based on documents provided by the CIA and the British government and were later found to be unreliable.
Following the invasion, the United States established the Coalition Provisional Authority to govern Iraq. In May 2003 L. Paul Bremer, the chief executive of the CPA, issued orders to exclude Baath Party members from the new Iraqi government (CPA Order 1) and to disband the Iraqi Army (CPA Order 2). The decision dissolved the largely Sunni Iraqi Army and excluded many of the country's former government officials from participating in the country's governance, including 40,000 school teachers who had joined the Baath Party simply to keep their jobs, helping to bring about a chaotic post-invasion environment.
An insurgency against the US-led coalition-rule of Iraq began in summer 2003 within elements of the former Iraqi secret police and army, who formed guerilla units. In fall 2003, self-entitled 'jihadist' groups began targeting coalition forces. Various Sunni militias were created in 2003, for example Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad led by Abu Musab al-Zarqawi. The insurgency included intense inter-ethnic violence between Sunnis and Shias. The Abu Ghraib torture and prisoner abuse scandal came to light, late 2003 in reports by Amnesty International and Associated Press.
US Marines patrol the streets of Al Faw, October 2003.
The Mahdi Army—a Shia militia created in the summer of 2003 by Muqtada al-Sadr—began to fight Coalition forces in April 2004. 2004 saw Sunni and Shia militants fighting against each other and against the new Iraqi Interim Government installed in June 2004, and against Coalition forces, as well as the First Battle of Fallujah in April and Second Battle of Fallujah in November. The Sunni militia Jama'at al-Tawhid wal-Jihad became Al-Qaeda in Iraq in October 2004 and targeted Coalition forces as well as civilians, mainly Shia Muslims, further exacerbating ethnic tensions.
In January 2005, the first elections since the invasion took place and in October a new Constitution was approved, which was followed by parliamentary elections in December. However, insurgent attacks were common and increased to 34,131 in 2005 from 26,496 in 2004.
During 2006, fighting continued and reached its highest levels of violence, more war crimes scandals were made public, Abu Musab al-Zarqawi the leader of Al-Qaeda in Iraq was killed by US forces and Iraq's former dictator Saddam Hussein was sentenced to death for crimes against humanity and hanged. In late 2006, the US government's Iraq Study Group recommended that the US begin focusing on training Iraqi military personnel and in January 2007 US President George W. Bush announced a "Surge" in the number of US troops deployed to the country.
In May 2007, Iraq's Parliament called on the United States to set a timetable for withdrawal and US coalition partners such as the UK and Denmark began withdrawing their forces from the country. The war in Iraq has resulted in between 151,000 and 1.2 million Iraqis being killed.
2008–present
In 2008, fighting continued and Iraq's newly trained armed forces launched attacks against militants. The Iraqi government signed the US–Iraq Status of Forces Agreement, which required US forces to withdraw from Iraqi cities by 30 June 2009 and to withdraw completely from Iraq by 31 December 2011.US troops handed over security duties to Iraqi forces in June 2009, though they continued to work with Iraqi forces after the pullout. On the morning of 18 December 2011, the final contingent of US troops to be withdrawn ceremonially exited over the border to Kuwait. Crime and violence initially spiked in the months following the US withdrawal from cities in mid-2009 but despite the initial increase in violence, in November 2009, Iraqi Interior Ministry officials reported that the civilian death toll in Iraq fell to its lowest level since the 2003 invasion.
Military situation in 2015
Following the withdrawal of US troops in 2011, the insurgency continued and Iraq suffered from political instability. In February 2011, the Arab Spring protests spread to Iraq; but the initial protests did not topple the government. The Iraqi National Movement, reportedly representing the majority of Iraqi Sunnis, boycotted Parliament for several weeks in late 2011 and early 2012, claiming that the Shiite-dominated government was striving to sideline Sunnis.
In 2012 and 2013, levels of violence increased and armed groups inside Iraq were increasingly galvanised by the Syrian Civil War. Both Sunnis and Shias crossed the border to fight in Syria. In December 2012, Sunni Arabs protested against the government, whom they claimed marginalised them.
During 2013, Sunni militant groups stepped up attacks targeting the Iraq's Shia population in an attempt to undermine confidence in the Nouri al-Maliki-led government. In 2014, Sunni insurgents belonging to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) terrorist group seized control of large swathes of land including several major Iraqi cities, like Tikrit, Fallujah and Mosul creating hundreds of thousands of internally displaced persons amid reports of atrocities by ISIL fighters.
US-led anti-ISIL coalition has conducted air strikes in support of the Mosul offensive, 11 July 2017
After an inconclusive election in April 2014, Nouri al-Maliki served as caretaker-Prime-Minister.
On 11 August, Iraq's highest court ruled that PM Maliki's bloc is biggest in parliament, meaning Maliki could stay Prime Minister. By 13 August, however, the Iraqi president had tasked Haider al-Abadi with forming a new government, and the United Nations, the United States, the European Union, Saudi Arabia, Iran, and some Iraqi politicians expressed their wish for a new leadership in Iraq, for example from Haider al-Abadi. On 14 August, Maliki stepped down as PM to support Mr al-Abadi and to "safeguard the high interests of the country". The US government welcomed this as "another major step forward" in uniting Iraq. On 9 September 2014, Haider al-Abadi had formed a new government and became the new prime minister. Intermittent conflict between Sunni, Shiite and Kurdish factions has led to increasing debate about the splitting of Iraq into three autonomous regions, including Sunni Kurdistan in the northeast, a Sunnistan in the west and a Shiastan in the southeast.
In response to rapid territorial gains made by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) during the first half of 2014, and its universally-condemned executions and reported human rights abuses, many states began to intervene against it in the Iraqi Civil War (2014–present). Since the airstrikes started, ISIL has been losing ground in both Iraq and Syria. Tens of thousands of civilians have been killed in Iraq in ISIL-linked violence. The genocide of Yazidis by ISIL has led to the expulsion, flight and effective exile of the Yazidis from their ancestral lands in Northern Iraq. The 2016 Karrada bombing killed nearly 400 civilians and injured hundreds more. On 17 March 2017, a US-led coalition airstrike in Mosul killed more than 200 civilians.
Since 2015, ISIL lost territory in Iraq, including Tikrit in March and April 2015, Baiji in October 2015, Sinjar in November 2015, Ramadi in December 2015, Fallujah in June 2016 and Mosul in July 2017. By December 2017, ISIL had no remaining territory in Iraq, following the 2017 Western Iraq campaign.
In September 2017, a referendum was held regarding Kurdish independence in Iraq. 92% of Iraqi Kurds voted in favor of independence. The referendum was regarded as illegal by the federal government in Baghdad. In March 2018, Turkey launched military operations to eliminate the Kurdish separatist fighters in northern Iraq. Anti-American cleric Muqtada al-Sadr's political coalition has won Iraq's parliamentary election in May 2018.
Geography
Satellite map of Iraq.
Iraq Köppen climate classification map.
Iraq mainly consists of desert, but near the two major rivers (Euphrates and Tigris) are fertile alluvial plains, as the rivers carry about 60,000,000 m3 (78,477,037 cu yd) of silt annually to the delta. The north of the country is mostly composed of mountains; the highest point being at 3,611 m (11,847 ft) point, unnamed on the map opposite, but known locally as Cheekah Dar (black tent). Iraq has a small coastline measuring 58 km (36 mi) along the Persian Gulf. Close to the coast and along the Shatt al-Arab (known as arvandrūd: اروندرود among Iranians) there used to be marshlands, but many were drained in the 1990s.
Climate
Most of Iraq has a hot arid climate with subtropical influence. Summer temperatures average above 40 °C (104 °F) for most of the country and frequently exceed 48 °C (118.4 °F). Winter temperatures infrequently exceed 21 °C (69.8 °F) with maxima roughly 15 to 19 °C (59.0 to 66.2 °F) and night-time lows 2 to 5 °C (35.6 to 41.0 °F). Typically, precipitation is low; most places receive less than 250 mm (9.8 in) annually, with maximum rainfall occurring during the winter months. Rainfall during the summer is extremely rare, except in the far north of the country. The northern mountainous regions have cold winters with occasional heavy snows, sometimes causing extensive flooding.Government and politics
Baghdad Convention Center, the current meeting place of the Council of Representatives of Iraq.
The National Alliance is the main Shia parliamentary bloc, and was established as a result of a merger of Prime Minister Nouri Maliki's State of Law Coalition and the Iraqi National Alliance. The Iraqi National Movement is led by Iyad Allawi, a secular Shia widely supported by Sunnis. The party has a more consistent anti-sectarian perspective than most of its rivals. The Kurdistan List is dominated by two parties, the Kurdistan Democratic Party led by Masood Barzani and the Patriotic Union of Kurdistan headed by Jalal Talabani. Both parties are secular and enjoy close ties with the West.
In 2018, according to the Failed States Index, Iraq was the world's eleventh most politically unstable country. The concentration of power in the hands of Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki and growing pressure on the opposition led to growing concern about the future of political rights in Iraq. Nevertheless, progress was made and the country had risen to 11th place by 2013. In August 2014, al-Maliki's reign came to an end. He announced on 14 August 2014 that he would stand aside so that Haider Al-Abadi, who had been nominated just days earlier by newly installed President Fuad Masum, could take over. Until that point, al-Maliki had clung to power even asking the federal court to veto the president's nomination describing it as a violation of the constitution.
Transparency International ranks Iraq's government as the eighth-most-corrupt government in the world. Government payroll have increased from 1 million employees under Saddam Hussein to around 7 million employees in 2016. In combination with decreased oil prices, the government budget deficit is near 25% of GDP as of 2016.
Pro-independence rally in Iraqi Kurdistan in September 2017
Law
In October 2005, the new Constitution of Iraq was approved in a referendum with a 78% overall majority, although the percentage of support varying widely between the country's territories. The new constitution was backed by the Shia and Kurdish communities, but was rejected by Arab Sunnis. Under the terms of the constitution, the country conducted fresh nationwide parliamentary elections on 15 December 2005. All three major ethnic groups in Iraq voted along ethnic lines, as did Assyrian and Turcoman minorities.Law no. 188 of the year 1959 (Personal Status Law) made polygamy extremely difficult, granted child custody to the mother in case of divorce, prohibited repudiation and marriage under the age of 16. Article 1 of Civil Code also identifies Islamic law as a formal source of law. Iraq had no Sharia courts but civil courts used Sharia for issues of personal status including marriage and divorce. In 1995 Iraq introduced Sharia punishment for certain types of criminal offences. The code is based on French civil law as well as Sunni and Jafari (Shi'ite) interpretations of Sharia.
In 2004, the CPA chief executive L. Paul Bremer said he would veto any constitutional draft stating that sharia is the principal basis of law. The declaration enraged many local Shia clerics, and by 2005 the United States had relented, allowing a role for sharia in the constitution to help end a stalemate on the draft constitution.
The Iraqi Penal Code is the statutory law of Iraq.
Military
An Iraqi Army BMP-1 on the move.
The current military situation, 24 October 2017:
Controlled by Iraqi government
Controlled by the Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (ISIL)
Controlled by Iraqi Kurds
Iraqi security forces are composed of forces serving under the Ministry of Interior (which controls the Police and Popular Mobilization Forces) and the Ministry of Defense, as well as the Iraqi Counter Terrorism Bureau, reporting directly to the Prime Minister of Iraq, which oversees the Iraqi Special Operations Forces. Ministry of Defense forces include the Iraqi Army, the Iraqi Air Force and the Iraqi Navy. The Peshmerga are a separate armed force loyal to the Kurdistan Regional Government. The regional government and the central government disagree as to whether they are under Baghdad's authority and to what extent.
The Iraqi Army is an objective counter-insurgency force that as of November 2009 includes 14 divisions, each division consisting of 4 brigades. It is described as the most important element of the counter-insurgency fight. Light infantry brigades are equipped with small arms, machine guns, RPGs, body armour and light armoured vehicles. Mechanized infantry brigades are equipped with T-54/55 main battle tanks and BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicles. As of mid-2008, logistical problems included a maintenance crisis and ongoing supply problems.
The Iraqi Air Force is designed to support ground forces with surveillance, reconnaissance and troop lift. Two reconnaissance squadrons use light aircraft, three helicopter squadrons are used to move troops and one air transportation squadron uses C-130 transport aircraft to move troops, equipment, and supplies. It currently has 3,000 personnel. It is planned to increase to 18,000 personnel, with 550 aircraft by 2018.
The Iraqi Navy is a small force with 1,500 sailors and officers, including 800 Marines, designed to protect shoreline and inland waterways from insurgent infiltration. The navy is also responsible for the security of offshore oil platforms. The navy will have coastal patrol squadrons, assault boat squadrons and a marine battalion. The force will consist of 2,000 to 2,500 sailors by year 2010.
Foreign relations
US President Donald Trump with Iraqi Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi in 2017.
On 17 November 2008, the US and Iraq agreed to a Status of Forces Agreement, as part of the broader Strategic Framework Agreement. This agreement states "the Government of Iraq requests" US forces to temporarily remain in Iraq to "maintain security and stability" and that Iraq has jurisdiction over military contractors, and US personnel when not on US bases or on–duty.
On 12 February 2009, Iraq officially became the 186th State Party to the Chemical Weapons Convention. Under the provisions of this treaty, Iraq is considered a party with declared stockpiles of chemical weapons. Because of their late accession, Iraq is the only State Party exempt from the existing timeline for destruction of their chemical weapons. Specific criteria is in development to address the unique nature of Iraqi accession.
Iran–Iraq relations have flourished since 2005 by the exchange of high level visits: Iraqi PM Nouri al-Maliki made frequent visits to Iran, along with Jalal Talabani visiting numerous times, to help boost bilateral co-operation in all fields. A conflict occurred in December 2009, when Iraq accused Iran of seizing an oil well on the border.
Relationships with Turkey are tense, largely because of the Kurdistan Regional Government, as clashes between Turkey and the PKK continue. In October 2011, the Turkish parliament renewed a law that gives Turkish forces the ability to pursue rebels over the border in Iraq."
Human rights
See also: Human rights in ISIL-controlled territory and Mass executions in ISIL occupied Mosul Relations between Iraq and its Kurdish population have been sour in recent history, especially with Saddam Hussein's genocidal campaign against them in the 1980s. After uprisings during the early 90s, many Kurds fled their homeland and no-fly zones were established in northern Iraq to prevent more conflicts. Despite historically poor relations, some progress has been made, and Iraq elected its first Kurdish president, Jalal Talabani, in 2005. Furthermore, Kurdish is now an official language of Iraq alongside Arabic according to Article 4 of the constitution.LGBT rights in Iraq remain limited. Although decriminalised, homosexuality remains stigmatised in Iraqi society. Targeting people because of their gender identity or sexual orientation is not uncommon and is usually carried out in the name of family honour. People who dress in emo style are mistakenly associated with homosexuality and may suffer the same fate. Investigations by the BBC and other western media in 2008 and 2009, including interviews of homosexual and transgender Iraqis, showed that violence against LGBT people had significantly increased since Saddam Hussein was toppled.
Administrative divisions
 Iraq is composed of nineteen governorates (or provinces) (Arabic: muhafadhat (singular muhafadhah); Kurdish: پارێزگا Pârizgah). The governorates are subdivided into districts (or qadhas), which are further divided into sub-districts (or nawāḥī). Iraqi Kurdistan (Erbil, Dohuk, Sulaymaniyah and Halabja) is the only legally defined region within Iraq, with its own government and quasi-official army Peshmerga.
Iraq is composed of nineteen governorates (or provinces) (Arabic: muhafadhat (singular muhafadhah); Kurdish: پارێزگا Pârizgah). The governorates are subdivided into districts (or qadhas), which are further divided into sub-districts (or nawāḥī). Iraqi Kurdistan (Erbil, Dohuk, Sulaymaniyah and Halabja) is the only legally defined region within Iraq, with its own government and quasi-official army Peshmerga.
Economy
GNP per capita in Iraq from 1950 to 2008.
Global distribution of Iraqi exports in 2006.
Prior to US occupation, Iraq's centrally planned economy prohibited foreign ownership of Iraqi businesses, ran most large industries as state-owned enterprises, and imposed large tariffs to keep out foreign goods. After the 2003 Invasion of Iraq, the Coalition Provisional Authority quickly began issuing many binding orders privatising Iraq's economy and opening it up to foreign investment.
Agriculture is the main occupation of the people.
On November 20, 2004, the Paris Club of creditor nations agreed to write off 80% ($33 billion) of Iraq's $42 billion debt to Club members. Iraq's total external debt was around $120 billion at the time of the 2003 invasion, and had grown another $5 billion by 2004. The debt relief will be implemented in three stages: two of 30% each and one of 20%.
In February 2011, Citigroup included Iraq in a group of countries which it described as 'Global Growth Generators', that it argued will enjoy significant economic growth in the future.
The official currency in Iraq is the Iraqi dinar. The Coalition Provisional Authority issued new dinar coins and notes, with the notes printed by De La Rue using modern anti-forgery techniques. Jim Cramer's October 20, 2009 endorsement of the Iraqi Dinar on CNBC has further piqued interest in the investment.
Five years after the invasion, an estimated 2.4 million people were internally displaced (with a further two million refugees outside Iraq), four million Iraqis were considered food-insecure (a quarter of children were chronically malnourished) and only a third of Iraqi children had access to safe drinking water.
According to the Overseas Development Institute, international NGOs face challenges in carrying out their mission, leaving their assistance "piecemeal and largely conducted undercover, hindered by insecurity, a lack of coordinated funding, limited operational capacity and patchy information". International NGOs have been targeted and during the first 5 years, 94 aid workers were killed, 248 injured, 24 arrested or detained and 89 kidnapped or abducted.
Oil and energy
Tankers at the Basra Oil Terminal.
With its 143.1 billion barrels (2.275×1010 m3) of proved oil reserves, Iraq ranks third in the world behind Venezuela and Saudi Arabia in the amount of oil reserves. Oil production levels reached 3.4 million barrels per day by December 2012. Only about 2,000 oil wells have been drilled in Iraq, compared with about 1 million wells in Texas alone. Iraq was one of the founding members of OPEC.
During the 1970s Iraq produced up to 3.5 million barrels per day, but sanctions imposed against Iraq after its invasion of Kuwait in 1990 crippled the country's oil sector. The sanctions prohibited Iraq from exporting oil until 1996 and Iraq's output declined by 85% in the years following the First Gulf War. The sanctions were lifted in 2003 after the US-led invasion removed Saddam Hussein from power, but development of Iraq's oil resources has been hampered by the ongoing conflict.
As of 2010, despite improved security and billions of dollars in oil revenue, Iraq still generates about half the electricity that customers demand, leading to protests during the hot summer months.
The Iraq oil law, a proposed piece of legislation submitted to the Iraqi Council of Representatives in 2007, has failed to gain approval due to disagreements among Iraq's various political blocs.
According to a US Study from May 2007, between 100,000 barrels per day (16,000 m3/d) and 300,000 barrels per day (48,000 m3/d) of Iraq's declared oil production over the past four years could have been siphoned off through corruption or smuggling. In 2008, Al Jazeera reported $13 billion of Iraqi oil revenues in US care was improperly accounted for, of which $2.6 billion is totally unaccounted for. Some reports that the government has reduced corruption in public procurement of oil; however, reliable reports of bribery and kickbacks to government officials persist.
In June 2008, the Iraqi Oil Ministry announced plans to go ahead with small one- or two-year no-bid contracts to Exxon Mobil, Shell, Total and BP—once partners in the Iraq Petroleum Company—along with Chevron and smaller firms to service Iraq's largest fields. These plans were cancelled in September because negotiations had stalled for so long that the work could not be completed within the time frame, according to Iraqi oil minister Hussain al-Shahristani. Several United States senators had also criticised the deal, arguing it was hindering efforts to pass the hydrocarbon law.
On 30 June and 11 December 2009, the Iraqi ministry of oil awarded service contracts to international oil companies for some of Iraq's many oil fields. Oil fields contracted include the "super-giant" Majnoon Field, Halfaya Field, West Qurna Field and Rumaila Field. BP and China National Petroleum Corporation won a deal to develop Rumaila, the largest Iraqi oil field.
On 14 March 2014, the International Energy Agency said Iraq's oil output jumped by half a million barrels a day in February to average 3.6 million barrels a day. The country hadn't pumped that much oil since 1979, when Saddam Hussein rose to power. However, on 14 July 2014, as sectarian strife had taken hold, Kurdistan Regional Government forces seized control of the Bai Hassan and Kirkuk oilfields in the north of the country, taking them from Iraq's control. Baghdad condemned the seizure and threatened "dire consequences" if the fields were not returned.
The UN estimates that oil accounts for 99% of Iraq's revenue.
Water supply and sanitation
A reservoir in the Samawa desert Southern Iraq
Water supply and sanitation in Iraq is characterized by poor water and service quality. Three decades of war, combined with limited environmental awareness, have destroyed Iraq's water resources management system. Access to potable water differs significantly among governorates and between urban and rural areas. 91% of the entire population has access to potable water. But in rural areas, only 77% of the population has access to improved drinking water sources compared to 98% in urban areas. Large amounts of water are wasted during production.
Infrastructure
Although many infrastructure projects are underway, Iraq remains in deep housing crisis, with the war-ravaged country likely to complete only 5 percent of the 2.5 million homes it needs to build by 2016 to keep up with demand, the Minister for Construction and Housing said in September 2013.
- In 2009, the IBBC was established (Iraq Britain Business Council). The Council was established by Baroness Nicholson of Winterbourne.
- In August 2009, two American firms reached a deal with the Iraqi Government to build Basra Sports City, a new sports complex.
- In October 2012, the Emirati property firm, Emaar Properties reached a deal with the Iraqi Ministry of Construction and Housing to build and develop housing and commercial projects in Iraq.
- In January 2013, the Emirati property firm, Nakheel Properties signed a deal to build Al Nakheel City, a future town in Basra, Iraq.
Demographics
The 2016 estimate of the total Iraqi population is 37,202,572. Iraq's population was estimated to be 2 million in 1878. In 2013 Iraq's population reached 35 million amid a post-war population boom.Ethnic groups
According to the CIA World Factbook, citing a 1987 Iraqi government estimate, the population of Iraq is formed of 75-80% Arabs followed by 15% Kurds. In addition, the estimate claims that other minorities form 5% of the country's population, including the Turkmen/Turcoman, Yezidis, Shabak, Kaka'i, Bedouins, Roma, Assyrians, Circassians, Sabaean-Mandaean, and Persians. However, the International Crisis Group points out that figures from the 1987 census, as well as the 1967, 1977, and 1997 censuses, "are all considered highly problematic, due to suspicions of regime manipulation" because Iraqi citizens were only allowed to indicate belonging to either the Arab or Kurdish ethnic groups; consequently, this skewed the number of other ethnic minorities, such as Iraq's third largest ethnic group – the Turkmens/Turkomans.A report published by the European Parliamentary Research Service suggests that in 2015 there was 24 million Arabs (15 million Shia and 9 million Sunni); 4 million Sunni Kurds (plus 500,000 Shia Faili Kurds and 200,000 Kaka'i); 3 million Iraqi Turkmen/Turkoman; 1 million Black Iraqis; 500,000 Christians (including Assyrians and Armenians); 500,000 Yazidis; 250,000 Shabaks; 50,000 Roma; 3,000 Sabean-Mandaeans; 2,000 Circassians; 1,000 Baha’i; and a few dozen Jews.[200]
Around 20,000 Marsh Arabs live in southern Iraq.
Iraq has a community of 2,500 Chechens. In southern Iraq, there is a community of Iraqis of African descent, a legacy of the slavery practised in the Islamic Caliphate beginning before the Zanj Rebellion of the 9th century, and Basra's role as a key port. It is the most populous country in the Arabian Plate.
Languages
Kurdish children in Sulaymaniyah.
The main languages spoken in Iraq are Mesopotamian Arabic and Kurdish, followed by the Iraqi Turkmen/Turkoman dialect of Turkish, and the Neo-Aramaic languages (specifically Chaldean and Assyrian). Arabic and Kurdish are written with versions of the Arabic script. Since 2005, the Turkmen/Turkoman have switched from the Arabic script to the Turkish alphabet. In addition, the Neo-Aramaic languages use the Syriac script.
Other smaller minority languages include Mandaic, Shabaki, Armenian, Circassian and Persian.
Prior to the invasion in 2003, Arabic was the sole official language. Since the new Constitution of Iraq approved in June 2004, both Arabic and Kurdish are official languages,[206] while Assyrian Neo-Aramaic and the Turkmen/Turkoman dialect of Turkish (referred to as respectively "Syriac" and "Turkmen" in the constitution) are recognised regional languages.[207] In addition, any region or province may declare other languages official if a majority of the population approves in a general referendum.
According to the Iraqi constitution:
The Arabic language and the Kurdish language are the two official languages of Iraq. The right of Iraqis to educate their children in their mother tongue, such as Turkmen, Assyrian, and Armenian shall be guaranteed in government educational institutions in accordance with educational guidelines, or in any other language in private educational institutions.
Religion
Imam Ali Mosque in Najaf.
Muslim (official) 99% (Shia 55-60%, Sunni 40%), Christian <.1%, Yazidi <.1%, Sabean Mandaean <.1%, Baha'i <.1%, Zoroastrian <.1%, Hindu <0 .1="" 0.1="" a="" buddhist="" folk="" has="" href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shia_Islam" it="" jewish="" mixed="" other="" religion="" title="Shia Islam" unafilliated="">Shia
and Sunni population. The CIA World Factbook estimates that around 65% of Muslims in Iraq are Shia, and around 35% are Sunni. A 2011 Pew Research Center estimates that 51% of Muslims in Iraq are Shia, 42% are Sunni, while 5% identify themselves as "Just a Muslim". The Sunni Muslims, 12-13 million in a population of 36 million, include Arabs, most Turkomen, and Kurds.
The Sunni population complains of facing discrimination in almost all aspects of life by the government. However, former Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki denied that such discrimination occurs. Christians have lived in the area for about 2,000 years, and many descend from the pre-Arab ancient Mesopotamians-Assyrians. They numbered over 1.4 million in 1987 or 8% of the estimated population of 16.3 million and 550,000 in 1947 or 12% of the population of 4.6 millions.
Indigenous Neo Aramaic speaking Assyrians, most of whom are adherents of the Chaldean Catholic Church, Assyrian Church of the East, Ancient Church of the East, Assyrian Pentecostal Church, Syriac Orthodox Church and Syriac Catholic Church account for most of the Christian population. Estimates for the numbers of Christians suggest a decline from 8–12% in the mid-20th century to 5% in 2008 or 1.6 million. More than half of Iraqi Christians have fled to neighbouring countries since the start of the war, and many have not returned, although a number are migrating back to the traditional Assyrian homeland in the Kurdish Autonomous region.
There are also small ethno-religious minority populations of Mandaeans, Shabaks, Yarsan and Yezidis remaining. Prior to 2003 their numbers together may have been 2 million, the majority Yarsan, a non-Islamic religion with roots in pre-Islamic and pre-Christian religion. There are reports of over 100.000 conversions to Zoroastrianism in recent years. The Iraqi Jewish community, numbering around 150,000 in 1941, has almost entirely left the country.
Iraq is home to two of the world's holiest places among Shias: Najaf and Karbala.
Diaspora and refugees
Iraqi refugees in Damascus, Syria.
The dispersion of native Iraqis to other countries is known as the Iraqi diaspora. The UN High Commission for Refugees has estimated that nearly two million Iraqis have fled the country after the multinational invasion of Iraq in 2003, mostly to Syria and Jordan. The Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre estimates an additional 1.9 million are currently displaced within the country.
In 2007, the UN said that about 40% of Iraq's middle class is believed to have fled and that most are fleeing systematic persecution and have no desire to return. Refugees are mired in poverty as they are generally barred from working in their host countries. In recent years the diaspora seems to be returning with the increased security; the Iraqi government claimed that 46,000 refugees have returned to their homes in October 2007 alone.
As of 2011, nearly 3 million Iraqis have been displaced, with 1.3 million within Iraq and 1.6 million in neighbouring countries, mainly Jordan and Syria. More than half of Iraqi Christians have fled the country since the 2003 US-led invasion. According to official United States Citizenship and Immigration Services statistics, 58,811 Iraqis have been granted refugee-status citizenship as of May 25, 2011.
To escape the civil war, over 160,000 Syrian refugees of varying ethnicities have fled to Iraq since 2012. Increasing violence during the Syrian civil war led to an increasing number of Iraqis returning to their native country.
Health
In 2010, spending on healthcare accounted for 6.84% of the country's GDP. In 2008, there were 6.96 physicians and 13.92 nurses per 10,000 inhabitants. The life expectancy at birth was 68.49 years in 2010, or 65.13 years for males and 72.01 years for females. This is down from a peak life expectancy of 71.31 years in 1996.Iraq had developed a centralised free health care system in the 1970s using a hospital based, capital-intensive model of curative care. The country depended on large-scale imports of medicines, medical equipment and even nurses, paid for with oil export income, according to a "Watching Brief" report issued jointly by the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) and the World Health Organization (WHO) in July 2003. Unlike other poorer countries, which focused on mass health care using primary care practitioners, Iraq developed a Westernized system of sophisticated hospitals with advanced medical procedures, provided by specialist physicians. The UNICEF/WHO report noted that prior to 1990, 97% of the urban dwellers and 71% of the rural population had access to free primary health care; just 2% of hospital beds were privately managed.
Education
Students at the college of medicine of the University of Basrah, 2010.
The CIA World Factbook estimates that, in 2000, the adult literacy rate was 84% for males and 64% for females, with UN figures suggesting a small fall in literacy of Iraqis aged 15–24 between 2000 and 2008, from 84.8% to 82.4%. The Coalition Provisional Authority undertook a complete reform of Iraq's education system: Baathist ideology was removed from curricula and there were substantial increases in teacher salaries and training programs, which the Hussein regime neglected in the 1990s. In 2003, an estimated 80% of Iraq's 15,000 school buildings needed rehabilitation and lacked basic sanitary facilities, and most schools lacked libraries and laboratories.
Education is mandatory only through to the sixth grade, after which a national examination determines the possibility of continuing into the upper grades. Although a vocational track is available to those who do not pass the exam, few students elect that option because of its poor quality. Boys and girls generally attend separate schools beginning with seventh grade.
In 2005, obstacles to further reform were poor security conditions in many areas, a centralised system that lacked accountability for teachers and administrators, and the isolation in which the system functioned for the previous 30 years. Few private schools exist. Prior to the invasion of 2003, some 240,000 persons were enrolled in institutions of higher education.
According to the Webometrics Ranking of World Universities, the top-ranking universities in the country are the University of Dohuk (1717th worldwide), the University of Baghdad (3160th) and Babylon University (3946th).
Culture
Public holidays in Iraq include Republic Day on 14 July and the National Day on 3 October.Music
Iraqi maqam performer Muhammad al-Qubbanchi.
Iraq is known primarily for its rich maqam heritage which has been passed down orally by the masters of the maqam in an unbroken chain of transmission leading up to the present. The maqam al-Iraqi is considered to be the most noble and perfect form of maqam. Al-maqam al-Iraqi is the collection of sung poems written either in one of the sixteen meters of classical Arabic or in Iraqi dialect (Zuhayri). This form of art is recognised by UNESCO as "an intangible heritage of humanity".
Early in the 20th century, many of the most prominent musicians in Iraq were Jewish. In 1936, Iraq Radio was established with an ensemble made up entirely of Jews, with the exception of the percussion player. At the nightclubs of Baghdad, ensembles consisted of oud, qanun and two percussionists, while the same format with a ney and cello were used on the radio.
The most famous singer of the 1930s–1940s was perhaps the Jew Salima Pasha (later Salima Murad). The respect and adoration for Pasha were unusual at the time since public performance by women was considered shameful, and most female singers were recruited from brothels.
The most famous early composer from Iraq was Ezra Aharon, an oud player, while the most prominent instrumentalist was Daoud Al-Kuwaiti. Daoud and his brother Saleh formed the official ensemble for the Iraqi radio station and were responsible for introducing the cello and ney into the traditional ensemble.
Art and architecture
The Great Ziggurat of Ur near Nasiriyah.
Important cultural institutions in the capital include the Iraqi National Symphony Orchestra – rehearsals and performances were briefly interrupted during the Occupation of Iraq but have since returned to normal. The National Theatre of Iraq was looted during the 2003 invasion, but efforts are underway to restore it. The live theatre scene received a boost during the 1990s when UN sanctions limited the import of foreign films. As many as 30 cinemas were reported to have been converted to live stages, producing a wide range of comedies and dramatic productions.
Institutions offering cultural education in Baghdad include the Academy of Music, Institute of Fine Arts and the Music and Ballet school Baghdad. Baghdad also features a number of museums including the National Museum of Iraq – which houses the world's largest and finest collection of artefacts and relics of Ancient Iraqi civilisations; some of which were stolen during the Occupation of Iraq.
Facade of Temple at Hatra, declared World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1985.
The capital, Ninus or Nineveh, was taken by the Medes under Cyaxares, and some 200 years after Xenophon passed over its site, then mere mounds of earth. It remained buried until 1845, when Botta and Layard discovered the ruins of the Assyrian cities. The principal remains are those of Khorsabad, 16 km (10 mi) N.E. of Mosul; of Nimroud, supposed to be the ancient Calah; and of Kouyunjik, in all probability the ancient Nineveh. In these cities are found fragments of several great buildings which seem to have been palace-temples. They were constructed chiefly of sun-dried bricks, and all that remains of them is the lower part of the walls, decorated with sculpture and paintings, portions of the pavements, a few indications of the elevation, and some interesting works connected with the drainage.
Media
After the end of the full state control in 2003, there were a period of significant growth in the broadcast media in Iraq. Immediately, and the ban on satellite dishes is no longer in place, and by mid-2003, according to a BBC report, there were 20 radio stations from 0.15 to 17 television stations owned by Iraqis, and 200 Iraqi newspapers owned and operated. Significantly, there have been many of these newspapers in numbers disproportionate to the population of their locations. For example, in Najaf, which has a population of 300,000, is being published more than 30 newspapers and distributed.Iraqi media expert and author of a number of reports on this subject, Ibrahim Al Marashi, identifies four stages of the US invasion of Iraq in 2003 where they had been taking the steps that have significant effects on the way for the later of the Iraqi media since then. Stages are: pre-invasion preparation, and the war and the actual choice of targets, the first post-war period, and a growing insurgency and hand over power to the Iraqi Interim Government (IIG) and Prime Minister Iyad Allawi.
Cuisine
Iraqi cuisine can be traced back some 10,000 years – to the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, Assyrians and Ancient Persians. Tablets found in ancient ruins in Iraq show recipes prepared in the temples during religious festivals – the first cookbooks in the world. Ancient Iraq, or Mesopotamia, was home to many sophisticated and highly advanced civilisations, in all fields of knowledge – including the culinary arts. However, it was in the medieval era when Baghdad was the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate that the Iraqi kitchen reached its zenith. Today the cuisine of Iraq reflects this rich inheritance as well as strong influences from the culinary traditions of neighbouring Turkey, Iran and the Greater Syria area.
Some characteristic ingredients of Iraqi cuisine include – vegetables such as aubergine, tomato, okra, onion, potato, courgette, garlic, peppers and chilli, cereals such as rice, bulgur wheat and barley, pulses and legumes such as lentils, chickpeas and cannellini, fruits such as dates, raisins, apricots, figs, grapes, melon, pomegranate and citrus fruits, especially lemon and lime.
Similarly with other countries of Western Asia, chicken and especially lamb are the favourite meats. Most dishes are served with rice – usually Basmati, grown in the marshes of southern Iraq. Bulgur wheat is used in many dishes – having been a staple in the country since the days of the Ancient Assyrians.
Sport
Football is the most popular sport in Iraq. Football is a considerable uniting factor in Iraq following years of war and unrest. Basketball, swimming, weightlifting, bodybuilding, boxing, kick boxing and tennis are also popular sports.The Iraqi Football Association is the governing body of football in Iraq, controlling the Iraqi National Team and the Iraqi Premier League (also known as Dawri Al-Nokba). It was founded in 1948, and has been a member of FIFA since 1950 and the Asian Football Confederation since 1971. The biggest club in Iraq is Al-Shorta, who won back-to-back league titles in 2013 and 2014 and were the first ever winners of the Arab Champions League. The Iraqi National Football Team were the 2007 AFC Asian Cup champions after defeating Saudi Arabia in the final by 1–0 thanks to a goal by captain Younis Mahmoud and they have participated in two FIFA competitions (the 1986 FIFA World Cup and the 2009 FIFA Confederations Cup).
Technology
Mobile phones
Despite having mobile phones in the Middle East since 1995, Iraqis were only able to use mobile phones after 2003. Mobile phones were banned under Saddam's rule. In 2013, it was reported that 78% of Iraqis owned a mobile phone.Satellite
According to the Iraqi Ministry of Communication, Iraq is now in the second phase of building and launching a multipurpose strategic satellite.A project which expected to cost $600 million is ongoing in co-operation with market leaders such as Astrium and Arianespace.
Undersea cable
On 18 January 2012, Iraq was connected to the undersea communications network for the first time.This had an immense impact on internet speed, availability and usage in Iraq.
In October 2013, the Iraqi Minister for Communication ordered internet prices to be lowered by a third. This is an attempt to boost usage and comes as a result of significant improvements in Internet infrastructure in the country.