 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cogentin, others |
| Other names | benzatropine (BAN UK), benztropine (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, IM, IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 12-24 hours |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
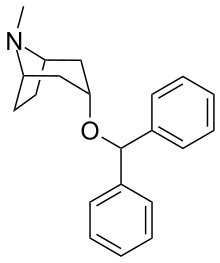
| Formula | C21H25NO |
| Molar mass | 307.437 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| | |
Benzatropine (INN[1]), known as benztropine in the United States and Japan, is a medication used to treat a type of movement disorder due to antipsychotics known as dystonia and parkinsonism. It is not useful for tardive dyskinesia. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein or muscle. Benefits are seen within two hours and last for up to ten hours.
Common side effects include dry mouth, blurry vision, nausea, and constipation. Serious side effect may include urinary retention, hallucinations, hyperthermia, and poor coordination. It is unclear if use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe. Benzatropine is an anticholinergic which works by blocking the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor.
Benzatropine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1954. It is available as a generic medication. In 2017, it was the 226th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than two million prescriptions. It is sold under the brand name Cogentin among others.
Medical uses
Benzatropine is used to reduce extrapyramidal side effects of antipsychotic treatment. Benzatropine is also a second-line drug for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It improves tremor, and may alleviate rigidity and bradykinesia. Benzatropine is also sometimes used for the treatment of dystonia, a rare disorder that causes abnormal muscle contraction, resulting in twisting postures of limbs, trunk, or face.
Adverse effects
These are principally anticholinergic:
- Dry mouth
- Blurred vision
- Cognitive changes
- Drowsiness
- Constipation
- Urinary retention
- Tachycardia
- Anorexia
- Severe delirium and hallucinations (in overdose)
While some studies suggest that use of anticholinergics increases the risk of tardive dyskinesia (a long-term side effect of antipsychotics), other studies have found no association between anticholinergic exposure and risk of developing tardive dyskinesia, although symptoms may be worsened.
Drugs that decrease cholinergic transmission may impair storage of new information into long-term memory. Anticholinergic agents can also impair time perception.
Pharmacology
Benzatropine is a centrally acting anticholinergic/antihistamine agent. It is a selective M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. Benzatropine partially blocks cholinergic activity in the basal ganglia and has also been shown to increase the availability of dopamine by blocking its reuptake and storage in central sites, and as a result, increasing dopaminergic activity. Animal studies have indicated that anticholinergic activity of benzatropine is approximately one-half that of atropine, while its antihistamine activity approaches that of mepyramine. Its anticholinergic effects have been established as therapeutically significant in the management of Parkinsonism. Benzatropine antagonizes the effect of acetylcholine, decreasing the imbalance between the neurotransmitters acetylcholine and dopamine, which may improve the symptoms of early Parkinson's disease.
Benzatropine analogues are atypical dopamine reuptake inhibitors, which might make them useful for people with akathisia secondary to antipsychotic therapy.
Benzatropine also acts as a functional inhibitor of acid sphingomyelinase (FIASMA).
Benzatropine has been also identified, by a high throughput screening approach, as a potent differentiating agent for oligodendrocytes, possibly working through M1 and M3 muscarinic receptors. In preclinical models for multiple sclerosis, benzatropine decreased clinical symptoms and enhanced re-myelination.
Other animals
In veterinary medicine, benzatropine is used to treat priapism in stallions.
Naming
Since 1959, benzatropine is the official international nonproprietary name of the medication under the INN scheme, the medication naming system coordinated by the World Health Organization; it is also the British Approved Name (BAN) given in the British Pharmacopoeia, and has been the official nonproprietary name in Australia since 2015. Regional variations of the "a" spelling are also used in French, Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish, as well as Latin (all medications are assigned a Latin name by WHO).
"Benztropine" is the official United States Adopted Name (USAN), the medication naming system coordinated by the USAN Council, co-sponsored by the American Medical Association (AMA), the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA). It is also the Japanese Accepted Name (JAN) and was used in Australia until 2015, when it was harmonized with the INN.
Both names may be modified to account for the methanesulfonate salt as which the medication is formulated: the modified INN (INNm) and BAN (BANM) is benzatropine mesilate, while the modified USAN is benztropine mesylate. The modified JAN is a hybrid form, benztropine mesilate.
The misspelling benzotropine is also occasionally seen in the literature.
