In the context of the United States, secession primarily refers to the voluntary withdrawal of one or more states from the Union that constitutes the United States; but may loosely refer to leaving a state or territory to form a separate territory or new state, or to the severing of an area from a city or county within a state. Advocates for secession are called disunionists by their contemporaries in various historical documents.
Threats and aspirations to secede from the United States, or arguments justifying secession, have been a feature of the country's politics almost since its birth. Some have argued for secession as a constitutional right and others as from a natural right of revolution. In Texas v. White (1869), the Supreme Court ruled unilateral secession unconstitutional, while commenting that revolution or consent of the states could lead to a successful secession.
The most serious attempt at secession was advanced in the years 1860 and 1861 as 11 Southern states each declared secession from the United States, and joined together to form the Confederate States of America. This movement collapsed in 1865 with the defeat of Confederate forces by Union armies in the American Civil War.
The American Revolution
The Declaration of Independence states:
We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.—That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed,—That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it, and to institute new Government, laying its foundation on such principles and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their Safety and Happiness.
Historian Pauline Maier argues that this narrative asserted "the right of revolution, which was, after all, the right Americans were exercising in 1776"; and notes that Thomas Jefferson's language incorporated ideas explained at length by a long list of 17th-century writers, including John Milton, Algernon Sidney, John Locke, and other English and Scottish commentators, all of whom had contributed to the development of the Whig tradition in 18th-century Britain.
The right of revolution expressed in the Declaration was immediately followed with the observation that long-practiced injustice is tolerated until sustained assaults on the rights of the entire people have accumulated enough force to oppress them; then they may defend themselves. This reasoning was not original to the Declaration, but can be found in many prior political writings: Locke's Two Treatises of Government (1690); the Fairfax Resolves of 1774; Jefferson's own Summary View of the Rights of British America; the first Constitution of Virginia, which was enacted five days prior to the Declaration; and Thomas Paine's Common Sense (1776):
Prudence, indeed, will dictate that Governments long established should not be changed for light and transient causes; ...mankind are more disposed to suffer, while Evils are sufferable, than to right themselves by abolishing the Forms ("of Government", editor's addition) to which they are accustomed. But when a long train of abuses and usurpations, pursuing...a design to reduce them under absolute Despotism, it is their right, it is their duty, to throw off such Government, and to provide new Guards for their future security.
Gordon S. Wood quotes President John Adams: "Only repeated, multiplied oppressions placing it beyond all doubt that their rulers had formed settled plans to deprive them of their liberties, could warrant the concerted resistance of the people against their government".
Civil War–era political and legal views on secession
Overview
With origins in the question of states' rights, the issue of secession was argued in many forums and advocated from time to time in both the North and South in the decades after adopting the Constitution and before the American Civil War. Historian Maury Klein described the contemporary debate: "Was the Republic a unified nation in which the individual states had merged their sovereign rights and identities forever, or was it a federation of sovereign states joined together for specific purposes from which they could withdraw at any time?" He observed that "the case can be made that no result of the [American Civil] war was more important than the destruction, once and for all...of the idea of secession".
Historian Forrest McDonald argued that after adopting the Constitution, "there were no guidelines, either in theory or in history, as to whether the compact could be dissolved and, if so, on what conditions". However, during "the founding era, many a public figure...declared that the states could interpose their powers between their citizens and the power of the federal government, and talk of secession was not unknown". But according to McDonald, to avoid resorting to the violence that had accompanied the Revolution, the Constitution established "legitimate means for constitutional change in the future". In effect, the Constitution "completed and perfected the Revolution".
Whatever the intentions of the Founders, threats of secession and disunion were a constant in the political discourse of Americans preceding the Civil War. Historian Elizabeth R. Varon wrote:
[O]ne word [disunion] contained, and stimulated, their [Americans'] fears of extreme political factionalism, tyranny, regionalism, economic decline, foreign intervention, class conflict, gender disorder, racial strife, widespread violence and anarchy, and civil war, all of which could be interpreted as God's retribution for America's moral failings. Disunion connoted the dissolution of the republic—the failure of the Founders' efforts to establish a stable and lasting representative government. For many Americans in the North and the South, disunion was a nightmare, a tragic cataclysm that would reduce them to the kind of fear and misery that seemed to pervade the rest of the world. And yet, for many other Americans, disunion served as the main instrument by which they could achieve their political goals.
Abandoning the Articles of Confederation
In late 1777 the Second Continental Congress approved the Articles of Confederation for ratification by the individual states. The Confederation government was administered de facto by the Congress under the provisions of the approved (final) draft of the Articles until they achieved ratification—and de jure status—in early 1781. In 1786 delegates of five states (the Annapolis Convention) called for a convention of delegates in Philadelphia to amend the Articles, which would require the unanimous consent of all thirteen states.
The delegates to the Philadelphia Convention convened and deliberated from May to September 1787. Instead of pursuing their official charge they returned a draft (new) Constitution, proposed for constructing and administering a new federal—later also known as "national"—government. They further proposed that the draft Constitution not be submitted to the Congress (where it would require unanimous approval of the states); instead that it be presented directly to the states for ratification in special ratification conventions, and that approval by a minimum of nine state conventions would suffice to adopt the new Constitution and initiate the new federal government; and that only those states ratifying the Constitution would be included in the new government. (For a time, eleven of the original states operated under the Constitution without two non-ratifying states, Rhode Island and North Carolina.) In effect, the delegates proposed to abandon and replace the Articles of Confederation rather than amend them.
Because the Articles had specified a "perpetual union", various arguments have been offered to explain the apparent contradiction (and presumed illegality) of abandoning one form of government and creating another that did not include the members of the original. One explanation was that the Articles of Confederation simply failed to protect the vital interests of the individual states. Necessity then, rather than legality, was the practical factor in abandoning the Articles.
According to historian John Ferling, by 1786 the Union under the Articles was falling apart. James Madison of Virginia and Alexander Hamilton of New York—they who joined together to vigorously promote a new Constitution—urged that renewed stability of the Union government was critically needed to protect property and commerce. Both founders were strong advocates for a more powerful central government; they published The Federalist Papers to advocate their cause and became known as the federalists. (Because of his powerful advocacy Madison was later accorded the honorific "Father of the Constitution".) Ferling wrote:
Rumors of likely secessionist movements were unleashed. There was buzz as well that some states planned to abandon the American Union and form a regional confederacy. America, it was said, would go the way of Europe, and ultimately three or four, or more confederacies would spring up. ... Not only would these confederations be capable of taking steps that were beyond the ability of Congress under the articles, but in private some portrayed such a step in a positive light, in as much as the regional union could adopt constitutions that secured property rights and maintained order.
Other arguments that justified abandoning the Articles of Confederation pictured the Articles as an international compact between unconsolidated, sovereign states, any one of which was empowered to renounce the compact at will. (This as opposed to a consolidated union that "totally annihilated, without any power of revival" the sovereign states.) The Articles required that all states were obliged to comply with all requirements of the agreement; thus, permanence was linked to compliance.
'Compliance' was typically perceived as a matter of interpretation by each individual state. Emerich de Vattel, a recognized authority on international law, wrote at the time that "Treaties contain promises that are perfect and reciprocal. If one of the allies fails in his engagements, the other may ... disengage himself in his promises, and ... break the treaty." Thus, each state could unilaterally 'secede' from the Articles of Confederation at will; this argument for abandoning the Articles—for its weakness in the face of secession—was used by advocates for the new Constitution and was featured by James Madison in Federalist No. 43.
St. George Tucker, an influential jurist in the early republic era, and especially in the South, argued that abandoning the Articles of Confederation was the same as seceding from the Articles government. In 1803, he wrote that the unanimous dissolution of the Articles Confederation in 1789 by Act of Congress was legal precedent for future secession(s) from the Constitution one state at a time by state legislatures.
And since the seceding states, by establishing a new constitution and form of federal government among themselves, without the consent of the rest, have shown that they consider the right to do so whenever the occasion may, in their opinion require it, we may infer that the right has not been diminished by any new compact which they may since have entered into, since none could be more solemn or explicit than the first, nor more binding upon the contracting partie[s]."
Others, such as Chief Justice John Marshall who had been a Virginia delegate to its Ratification (Federal) Convention, denied that ratifying the Constitution was a precedent for a future one-off dissolution of the Union by an isolated state or states. Writing in 1824, exactly midway between the fall of the Articles of Confederation and the rise of a second self-described American Confederacy, Marshal summarized the issue thusly: "Reference has been made to the political situation of these states, anterior to [the Constitution's] formation. It has been said that they were sovereign, were completely independent, and were connected with each other only by a league. This is true. But, when these allied sovereigns converted their league into a government, when they converted their congress of ambassadors, deputed to deliberate on their common concerns, and to recommend measures of general utility, into a legislature, empowered to enact laws on the most interesting subjects, the whole character in which the states appear underwent a change."
Nationalists for Union in the antebellum America argued the opposite of secession; that indeed the new Constitution inherited perpetuity from the language in the Articles and from other actions done prior to the Constitution. Historian Kenneth Stampp explains their view:
Lacking an explicit clause in the Constitution with which to establish the Union's perpetuity, the nationalists made their case, first, with a unique interpretation of the history of the country prior to the Philadelphia Convention; second, with inferences drawn from certain passages of the Constitution; and third, with careful selections from the speeches and writings of the Founding Fathers. The historical case begins with the postulate that the Union is older than the states. It quotes the reference in the Declaration of Independence to "these united colonies", contends that the Second Continental Congress actually called the states into being [i.e., "colonies" no longer], notes the provision for a perpetual Union in the Articles of Confederation, and ends with the reminder that the preamble to the new Constitution gives as one of its purposes the formation of "a more perfect Union".
Adopting the Constitution
Constitutional scholar Akhil Reed Amar argues that the permanence of the Union of the states changed significantly when the U.S. Constitution replaced the Articles of Confederation. This action "signaled its decisive break with the Articles' regime of state sovereignty". By adopting a constitution—rather than a treaty, or a compact, or an instrument of confederacy, etc.—that created a new body of government designed to be senior to the several states, and by approving the particular language and provisions of that new Constitution, the framers and voters made it clear that the fates of the individual states were (severely) changed; and that the new United States was:
Not a "league", however firm; not a "confederacy" or a "confederation"; not a compact on among "sovereign' states"—all these high profile and legally freighted words from the Articles were conspicuously absent from the Preamble and every other operative part of the Constitution. The new text proposed a fundamentally different legal framework.
Patrick Henry adamantly opposed adopting the Constitution because he interpreted its language to replace the sovereignty of the individual states, including that of his own Virginia. He gave his strong voice to the anti-federalist cause in opposition to the federalists led by Madison and Hamilton. Questioning the nature of the proposed new federal government, Henry asked:
The fate ... of America may depend on this. ... Have they made a proposal of a compact between the states? If they had, this would be a confederation. It is otherwise most clearly a consolidated government. The question turns, sir, on that poor little thing—the expression, We, the people, instead of the states, of America. ...
The federalists acknowledged that national sovereignty would be transferred by the new Constitution to the whole of the American people—indeed, regard the expression, "We the people ...". They argued, however, that Henry exaggerated the extent to which a consolidated government was being created and that the states would serve a vital role within the new republic even though their national sovereignty was ending. Tellingly, on the matter of whether states retained a right to unilaterally secede from the United States, the federalists made it clear that no such right would exist under the Constitution.
Amar specifically cites the example of New York's ratification as suggestive that the Constitution did not countenance secession. Anti-federalists dominated the Poughkeepsie Convention that would ratify the Constitution. Concerned that the new compact might not sufficiently safeguard states' rights, the anti-federalists sought to insert into the New York ratification message language to the effect that "there should be reserved to the state of New York a right to withdraw herself from the union after a certain number of years." The Madison federalists opposed this, with Hamilton, a delegate at the Convention, reading aloud in response a letter from James Madison stating: "the Constitution requires an adoption in toto, and for ever" [emphasis added]. Hamilton and John Jay then told the Convention that in their view, reserving "a right to withdraw [was] inconsistent with the Constitution, and was no ratification". The New York convention ultimately ratified the Constitution without including the "right to withdraw" language proposed by the anti-federalists.
Amar explains how the Constitution impacted on state sovereignty:
In dramatic contrast to Article VII–whose unanimity rule that no state can bind another confirms the sovereignty of each state prior to 1787 – Article V does not permit a single state convention to modify the federal Constitution for itself. Moreover, it makes clear that a state may be bound by a federal constitutional amendment even if that state votes against the amendment in a properly convened state convention. And this rule is flatly inconsistent with the idea that states remain sovereign after joining the Constitution, even if they were sovereign before joining it. Thus, ratification of the Constitution itself marked the moment when previously sovereign states gave up their sovereignty and legal independence.
Natural right of revolution versus right of secession
Debates on the legality of secession often looked back to the example of the American Revolution and the Declaration of Independence. Law professor Daniel Farber defined what he considered the borders of this debate:
What about the original understanding? The debates contain scattered statements about the permanence or impermanence of the Union. The occasional reference to the impermanency of the Constitution are hard to interpret. They might have referred to a legal right to revoke ratification. But they equally could have referred to an extraconstitutional right of revolution, or to the possibility that a new national convention would rewrite the Constitution, or simply to the factual possibility that the national government might break down. Similarly, references to the permanency of the Union could have referred to the practical unlikelihood of withdrawal rather than any lack of legal power. The public debates seemingly do not speak specifically to whether ratification under Article VII was revocable.
In the public debate over the Nullification Crisis the separate issue of secession was also discussed. James Madison, often referred to as "The Father of the Constitution", strongly opposed the argument that secession was permitted by the Constitution. In a March 15, 1833, letter to Daniel Webster (congratulating him on a speech opposing nullification), Madison discussed "revolution" versus "secession":
I return my thanks for the copy of your late very powerful Speech in the Senate of the United S. It crushes "nullification" and must hasten the abandonment of "Secession". But this dodges the blow by confounding the claim to secede at will, with the right of seceding from intolerable oppression. The former answers itself, being a violation, without cause, of a faith solemnly pledged. The latter is another name only for revolution, about which there is no theoretic controversy.
Thus Madison affirms an extraconstitutional right to revolt against conditions of "intolerable oppression"; but if the case cannot be made (that such conditions exist), then he rejects secession—as a violation of the Constitution.
During the crisis, President Andrew Jackson, published his Proclamation to the People of South Carolina, which made a case for the perpetuity of the Union; plus, he provided his views re the questions of "revolution" and "secession":
But each State having expressly parted with so many powers as to constitute jointly with the other States a single nation, cannot from that period possess any right to secede, because such secession does not break a league, but destroys the unity of a nation, and any injury to that unity is not only a breach which would result from the contravention of a compact, but it is an offense against the whole Union. [emphasis added] To say that any State may at pleasure secede from the Union, is to say that the United States are not a nation because it would be a solecism to contend that any part of a nation might dissolve its connection with the other parts, to their injury or ruin, without committing any offense. Secession, like any other revolutionary act, may be morally justified by the extremity of oppression; but to call it a constitutional right, is confounding the meaning of terms, and can only be done through gross error, or to deceive those who are willing to assert a right, but would pause before they made a revolution, or incur the penalties consequent upon a failure.
Some twenty-eight years after Jackson spoke, President James Buchanan gave a different voice—one much more accommodating to the views of the secessionists and the 'slave' states—in the midst of the pre-War secession crisis. In his final State of the Union address to Congress, on December 3, 1860, he acknowledged his view that the South, "after having first used all peaceful and constitutional means to obtain redress, would be justified in revolutionary resistance to the Government of the Union"; but he also drew his apocalyptic vision of the results to be expected from secession:
In order to justify secession as a constitutional remedy, it must be on the principle that the Federal Government is a mere voluntary association of States, to be dissolved at pleasure by any one of the contracting parties. [emphasis added] If this be so, the Confederacy [here referring to the existing Union] is a rope of sand, to be penetrated and dissolved by the first adverse wave of public opinion in any of the States. In this manner our thirty-three States may resolve themselves into as many petty, jarring, and hostile republics, each one retiring from the Union without responsibility whenever any sudden excitement might impel them to such a course. By this process a Union might be entirely broken into fragments in a few weeks which cost our forefathers many years of toil, privation, and blood to establish.
Alien and Sedition Acts
In response to the 1798 Alien and Sedition Acts—advanced by the Federalist Party—John Taylor of the Virginia House of Delegates spoke out, urging Virginia to secede from the United States. He argued—as one of many vociferous responses by the Jeffersonian Republicans—the sense of the Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions, adopted in 1798 and 1799, which reserved to those States the rights of secession and interposition (nullification).
Thomas Jefferson, while sitting as Vice President of the United States in 1799, wrote to James Madison of his conviction in "a reservation of th[ose] rights resulting to us from these palpable violations [the Alien and Sedition Acts]" and, if the federal government did not return to
"the true principles of our federal compact, [he was determined to] sever ourselves from that union we so much value, rather than give up the rights of self government which we have reserved, and in which alone we see liberty, safety and happiness."[emphasis added]
Here Jefferson is arguing in a radical voice (and in a private letter) that he would lead a movement for secession; but it is unclear whether he is arguing for "secession at will" or for "revolution" on account of "intolerable oppression" (see above), or neither. Jefferson secretly wrote (one of) the Kentucky Resolutions, which was done—again—while he was holding the office of Vice President. His biographer Dumas Malone argued that, had his actions become known at the time, Jefferson's participation might have gotten him impeached for (charged with) treason. In writing the first Kentucky Resolution, Jefferson warned that, "unless arrested at the threshold", the Alien and Sedition Acts would "necessarily drive these states into revolution and blood". Historian Ron Chernow says of this "he wasn't calling for peaceful protests or civil disobedience: he was calling for outright rebellion, if needed, against the federal government of which he was vice president." Jefferson "thus set forth a radical doctrine of states' rights that effectively undermined the constitution".
Jeffersonian Republicans were not alone in claiming "reserved rights" against the federal government. Contributing to the rancorous debates during the War of 1812, Founding Father Gouverneur Morris of Pennsylvania and New York—a Federalist, a Hamilton ally and a primary author of the Constitution who advanced the concept that Americans were citizens of a single Union of the states—was persuaded to claim that "secession, under certain circumstances, was entirely constitutional."
New England Federalists and the Hartford Convention
The election of 1800 showed Jefferson's Democratic-Republican Party to be on the rise and the Federalists to be declining, and the Federalists felt threatened by initiatives taken by their opponents. They viewed Jefferson's unilateral purchase of the Louisiana territory as violating foundational agreements between the original 13 states; Jefferson transacted the purchase in secret and refused to seek the approval of Congress. The new lands anticipated several future western states which the Federalists feared would be dominated by the Democratic-Republicans. Other things added to the Federalists' alarm, such as the impeachment of Federalist district judge John Pickering by the Jeffersonian-dominated Congress, and similar attacks on Pennsylvania state officials by the Democratic-Republican legislature. By 1804, their national leadership was decimated and their viable base was reduced to the states of Massachusetts, Connecticut, and Delaware.
Timothy Pickering of Massachusetts and a few Federalists envisioned creating a separate New England confederation, possibly combining with lower Canada to form a new pro-British nation. The Embargo Act of 1807 was seen as a threat to the economy of Massachusetts, and the state legislature debated in May 1808 how the state should respond. These debates generated isolated references to secession, but no definite plot materialized. Historian Richard Buell, Jr. suggests that "the secessionist movement of 1804 was more of a confession of despair about the future than a realistic proposal for action."
Federalist party members convened the Hartford Convention on December 15, 1814, and they addressed their opposition to the continuing war with Britain and the domination of the federal government by the "Virginia dynasty". Twenty six delegates attended; Massachusetts sent 12, Connecticut seven, and Rhode Island four. New Hampshire and Vermont declined, but two counties each from those states sent delegates. Historian Donald R. Hickey notes:
Despite pleas in the New England press for secession and a separate peace, most of the delegates taking part in the Hartford Convention were determined to pursue a moderate course. Only Timothy Bigelow of Massachusetts apparently favored extreme measures, and he did not play a major role in the proceedings.
The final report addressed issues related to the war and state defense, and it recommended several amendments to the Constitution. Massachusetts and Connecticut endorsed it, but the war ended as the delegates were returning to Washington, effectively quashing any impact that it might have had. The Jeffersonians described the convention as "a synonym for disloyalty and treason", and it became a major factor in the sharp decline of the Federalist Party.
Abolitionists for secession by the North
It is not often remembered today, as it was the South that actually attempted to secede. However, there was a movement to have the North secede, thereby escaping the Slave Power that dominated the Federal government.
Tensions began to rise between North and South by the late 1830s over slavery and related issues. Many Northerners, especially New Englanders, saw themselves as political victims of conspiracies between slave owners and western expansionists. They viewed the movements to annex Texas and to make war on Mexico as fomented by slaveholders bent on dominating western expansion and thereby the national destiny. New England abolitionist Benjamin Lundy argued that the annexation of Texas was "a long-premeditated crusade—set on foot by slaveholders, land speculators, etc., with the view of reestablishing, extending, and perpetuating the system of slavery and the slave trade".
Newspaper editors began demanding separation from the South. Wm. Lloyd Garrison called for secession in The Liberator of May 1844 with his "Address to the Friends of Freedom and Emancipation in the United States". The Constitution was created, he wrote, "at the expense of the colored population of the country", and Southerners were dominating the nation because of the Three-Fifths Compromise; now it was time "to set the captive free by the potency of truth" and to "secede from the government". Coincidentally, the New England Anti-Slavery Convention endorsed the principles of disunion by a vote of 250–24.
Support of secession began to shift to Southern states from 1846, after introduction of the Wilmot Proviso into the public debate. Southern leaders increasingly felt helpless against a powerful political group that was attacking their interests, reminiscent of Federalist alarms at the beginning of the century.
South Carolina
During the presidential term of Andrew Jackson, South Carolina had its own semi-secession movement due to the so-called 1828 Tariff of Abominations, which threatened South Carolina's economy, and South Carolina, in turn, threatened to secede from the United States (the Union). Jackson also threatened to send federal troops to put down the movement and to hang the leader of the secessionists from the highest tree in South Carolina. Also due to this, Jackson's vice president, John C. Calhoun, who supported the movement and wrote the essay "The South Carolina Exposition and Protest", became the first US vice president to resign. On May 1, 1833, Jackson wrote of nullification, "the tariff was only a pretext, and disunion and Southern confederacy the real object. The next pretext will be the negro, or slavery question." South Carolina also threatened to secede in 1850 over the issue of California's statehood. It became the first state to declare its secession from the Union on December 20, 1860, with the Declaration of the Immediate Causes Which Induce and Justify the Secession of South Carolina from the Federal Union, and it later joined with the other Southern states to form the Confederacy.
Seceded states form the Confederate States of America
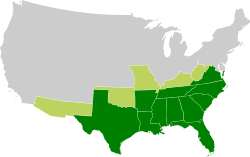
The most famous secession movement was the case of the Southern states of the United States. Secession from the United States was accepted in eleven states (and failed in two others). The seceding states joined together to form the Confederate States of America (CSA).
The eleven states of the CSA, in order of their secession dates (listed in parentheses), were: South Carolina (December 20, 1860), Mississippi (January 9, 1861), Florida (January 10, 1861), Alabama (January 11, 1861), Georgia (January 19, 1861), Louisiana (January 26, 1861), Texas (February 1, 1861), Virginia (April 17, 1861), Arkansas (May 6, 1861), North Carolina (May 20, 1861), and Tennessee (June 8, 1861). Secession was declared by pro-Confederate governments in Missouri and Kentucky (see Confederate government of Missouri and Confederate government of Kentucky), but did not become effective as it was opposed by their pro-Union state governments.
This secession movement brought about the American Civil War. The position of the Union was that the Confederacy was not a sovereign nation—and never had been, but that "the Union" was always a single nation by intent of the states themselves, from 1776 onward—and thus that a rebellion had been initiated by individuals. Historian Bruce Catton described President Abraham Lincoln's April 15, 1861, proclamation after the attack on Fort Sumter, which defined the Union's position on the hostilities:
After reciting the obvious fact that "combinations too powerful to be suppressed" by ordinary law courts and marshalls had taken charge of affairs in the seven secessionist states, it announced that the several states of the Union were called on to contribute 75,000 militia "...to suppress said combinations and to cause the laws to be duly executed." ... "And I hereby command the persons composing the combinations aforesaid to disperse, and retire peacefully to their respective abodes within twenty days from this date.
Political effects of their secession
With the departure of the Representatives and Senators from the seceding states, the makeup and organization of the 36th United States Congress changed dramatically. Vice-President and Senate President Breckinridge remained until he was replaced by Hannibal Hamlin, and then expelled, but gone was the President pro tempore (Benjamin Fitzpatrick of Alabama) and the heads of the Senate committees on Claims (Alfred Iverson Jr. of Georgia), Commerce (Clement Claiborne Clay of Alabama), the District of Columbia (Albert G. Brown of Mississippi), Finance (Robert M. T. Hunter of Virginia, expelled), Foreign Relations (James M. Mason of Virginia, expelled), Military Affairs (Jefferson Davis of Virginia), Naval Affairs (Stephen Mallory of Florida), and Public Lands (Robert Ward Johnson of Arkansas).
Within days, Kansas was admitted to the Union as a free state, an issue at the time similar to the 20th and 21st-century debate over statehood for the District of Columbia. Within a month Colorado, Nevada, and Dakota Territory followed. The end of slavery in the District of Columbia had been a goal of abolitionists since the gag rule crisis of the 1830's. The District of Columbia Compensated Emancipation Act passed in 1862, as did the Homestead Act and the Morrill Land-Grant Act of 1862, other measures the slave states had blocked.
Disputed legality of unilateral secession
The Constitution does not directly mention secession. The legality of secession was hotly debated in the 19th century. Although the Federalist Party briefly explored New England secession during the War of 1812, secession became associated with Southern states as the North's industrial power increased. The Supreme Court has consistently interpreted the Constitution to be an "indestructible" union. The Articles of Confederation explicitly state the Union is "perpetual"; the U.S. Constitution declares itself an even "more perfect union" than the Articles of Confederation. Other scholars, while not necessarily disagreeing that the secession was illegal, point out that sovereignty is often de facto an "extralegal" question. Had the Confederacy won, any illegality of its actions under U.S. law would have been rendered irrelevant, just as the undisputed illegality of American rebellion under the British law of 1775 was rendered irrelevant. Thus, these scholars argue, the illegality of unilateral secession was not firmly de facto established until the Union won the Civil War; in this view, the legal question was resolved at Appomattox.
Supreme Court rulings
Texas v. White was argued before the United States Supreme Court during the December 1868 term. Chief Justice Salmon P. Chase read the Court's decision, on April 15, 1869. Australian Professors Peter Radan and Aleksandar Pavkovic write:
Chase, [Chief Justice], ruled in favor of Texas on the ground that the Confederate state government in Texas had no legal existence on the basis that the secession of Texas from the United States was illegal. The critical finding underpinning the ruling that Texas could not secede from the United States was that, following its admission to the United States in 1845, Texas had become part of "an indestructible Union, composed of indestructible states". In practical terms, this meant that Texas has never seceded from the United States.
However, the Court's decision recognized some possibility of the divisibility "through revolution, or through consent of the States".
In 1877, the Williams v. Bruffy decision was rendered, pertaining to Civil War debts. The Court wrote regarding acts establishing an independent government that "The validity of its acts, both against the parent state and the citizens or subjects thereof, depends entirely upon its ultimate success; if it fail to establish itself permanently, all such acts perish with it; if it succeed and become recognized, its acts from the commencement of its existence are upheld as those of an independent nation."
The Union as a sovereign state
Historian Kenneth Stampp notes that a historical case against secession had been made that argued that "the Union is older than the states" and that "the provision for a perpetual Union in the Articles of Confederation" was carried over into the Constitution by the "reminder that the preamble to the new Constitution gives us one of its purposes the formation of 'a more perfect Union'". Concerning the White decision Stampp wrote:
In 1869, when the Supreme Court, in Texas v. White, finally rejected as untenable the case for a constitutional right of secession, it stressed this historical argument. The Union, the Court said, "never was a purely artificial and arbitrary relation". Rather, "It began among the Colonies. ...It was confirmed and strengthened by the necessities of war, and received definite form, and character, and sanction from the Articles of Confederation."
Texas secession from Mexico
The Republic of Texas successfully seceded from Mexico in 1836 (this, however took the form of outright rebellion against Mexico, and claimed no warrant under the Mexican Constitution to do so). Mexico refused to recognize its revolted province as an independent country, but the major nations of the world did recognize it. In 1845, Congress admitted Texas as a state. The documents governing Texas' accession to the United States of America do not mention any right of secession—although they did raise the possibility of dividing Texas into multiple states inside the Union. Mexico warned that annexation meant war and the Mexican–American War followed in 1846.
Partition of a state
Article IV, Section. 3, Clause 1 of the United States Constitutions provides:
New States may be admitted by the Congress into this Union; but no new States shall be formed or erected within the Jurisdiction of any other State; nor any State be formed by the Junction of two or more States, or parts of States, without the Consent of the Legislatures of the States concerned as well as of the Congress.
The separation referred to is not secession but partition. Some of the movements to partition states have identified themselves as "secessionist" movements.
Of the new states admitted to the Union by Congress, three were set off from already existing states, while one was established upon land claimed by an existing state after existing for several years as a de facto independent republic. They are:
- Vermont was admitted as a new state in 1791 after the legislature of New York ceded its claim to the region in 1790. New York's claim that Vermont (also known as the New Hampshire Grants) was legally a part of New York was and remains a matter of disagreement. King George III, ruled in 1764 that the region belonged to the Province of New York.
- Kentucky was a part of Virginia until it was admitted as a new state in 1792 with the consent of the legislature of Virginia in 1789.
- Maine was a part of Massachusetts until it was admitted as a new state in 1820 after the legislature of Massachusetts consented in 1819.
- West Virginia was a part of Virginia until it was admitted as a new state in 1863 after the General Assembly of the Restored Government of Virginia consented in 1862. The question of whether the legislature of Virginia consented is controversial, as Virginia was one of the Confederate states. However, antisecessionist Virginians formed a government in exile, which was recognized by the United States and approved the state's partition. Later, by its ruling in Virginia v. West Virginia (1871), the Supreme Court implicitly affirmed that the breakaway Virginia counties did have the proper consents required to become a separate state.
Many unsuccessful proposals to partition U.S. states have been drawn.
1980s–present efforts
The late 20th and early 21st centuries have seen examples of local and state secession movements. All such movements to create new states have failed. The formation in 1971 of the Libertarian Party and its national platform affirmed the right of states to secede on three vital principles: "We shall support recognition of the right to secede. Political units or areas which do secede should be recognized by the United States as independent political entities where: (1) secession is supported by a majority within the political unit, (2) the majority does not attempt suppression of the dissenting minority, and (3) the government of the new entity is at least as compatible with human freedom as that from which it seceded."
City secession
There was an attempt by Staten Island to break away from New York City in the late 1980s and early 1990s, leading to a 1993 referendum, in which 65% voted to secede. Implementation was blocked in the State Assembly by assertions that the state's constitution required a "home rule message" from New York City.
The San Fernando Valley lost a vote to separate from Los Angeles in 2002. Despite the majority (55%) of the valley within the L.A. city limits voting for secession, the city council unanimously voted to block the partition of the valley north of Mulholland Drive.
Other attempted city secession drives include Killington, Vermont, which has voted twice (2005 and 2006) to join New Hampshire; the community of Miller Beach, Indiana, originally a separate incorporated community, to split from the city of Gary in 2007 and Northeast Philadelphia to split from the city of Philadelphia in the 1980s.
A portion of the town of Calabash, North Carolina, voted to secede from the town in 1998 after receiving permission for a referendum on the issue from the state of North Carolina. Following secession, the area incorporated itself as the town of Carolina Shores. Despite the split, the towns continue to share fire and emergency services.
The town of Rough and Ready, California declared its secession from the Union as The Great Republic of Rough and Ready on 7 April 1850, largely to avoid mining taxes, but voted to rejoin the Union less than three months later on 4 July.
State secession
Some state movements seek secession from the United States itself and the formation of a nation from one or more states.
- Alaska: In November 2006, the Alaska Supreme Court held in the case Kohlhaas v. State that secession was illegal and refused to permit an initiative to be presented to the people of Alaska for a vote. The Alaskan Independence Party remains a factor in state politics, and Walter Hickel, a member of the party, was Governor from 1990 to 1994.
- California: California secession, known as #CALEXIT, was discussed by grassroots movement parties and small activist groups calling for the state to secede from the union in a pro-secessionist meeting in Sacramento on April 15, 2010. In 2015, a political action committee called Yes California Independence Committee formed to advocate California's independence from the United States. On January 8, 2016, the California Secretary of State's office confirmed that a political body called the California National Party filed the appropriate paperwork to begin qualifying as a political party. The California National Party, whose primary objective is California independence, ran a candidate for State Assembly in the June 7, 2016 primary. On November 9, 2016, after Donald Trump won the presidential election, residents of the state caused #calexit to trend on Twitter, wanting out of the country due to his win; they argue that they have the 6th largest economy in the world, and more residents than any other state in the union. 32% of Californians, and 44% of California Democrats were in favor of California secession in a March 2017 poll. The Attorney General of California approved applications by the California Freedom Coalition and others to gather signatures to put #CALEXIT on the 2018 ballot. In July 2018, the objectives of the Calexit initiative were expanded upon by including a plan to carve out an "autonomous Native American nation" that would take up the eastern part of California, and "postponing its ballot referendum approach in favor of convincing Republican states to support their breakaway efforts."
- Florida: The mock 1982 secessionist protest by the Conch Republic in the Florida Keys resulted in an ongoing source of local pride and tourist amusement. In 2015, right-wing activist Jason Patrick Sager called for Florida to secede.
- Georgia: On April 1, 2009, the Georgia State Senate passed a resolution, 43–1, that asserted the right of states to nullify federal laws under some circumstances. The resolution also asserted that if Congress, the president, or the federal judiciary took certain steps, such as establishing martial law without state consent, requiring some types of involuntary servitude, taking any action regarding religion or restricting freedom of political speech, or establishing further prohibitions of types or quantities of firearms or ammunition, the constitution establishing the United States government would be considered nullified and the union would be dissolved.
- Hawaii: The Hawaiian sovereignty movement has a number of active groups that have won some concessions from the state of Hawaii, including the offering of H.R. 258 in March 2011, which removes the words "Treaty of Annexation" from a statute. As of 2011, it had passed a committee recommendation 6–0.
- Minnesota: The Northwest Angle is a small exclave of Minnesota jutting north into Canada due to a quirk in the definitions of the US-Canada border. Because of laws restricting fishing, some residents of the Northwest Angle suggested leaving the United States and joining Canada in 1997. The following year, U.S. Representative Collin Peterson of Minnesota proposed legislation to allow the residents of the Northwest Angle, which is part of his district, to vote on seceding from the United States and joining Canada. This action succeeded in getting fishing regulations better synchronized across these international (fresh) waters.
- Montana: With the decision of the Supreme Court of the United States to hear District of Columbia v. Heller in late 2007, an early 2008 movement began in Montana involving at least 60 elected officials addressing potential secession if the Second Amendment were interpreted not to grant an individual right, citing its compact with the United States of America.
- New Hampshire: On September 1, 2012, "The New Hampshire Liberty Party was formed to promote independence from the federal government and for the individual." The Free State Project is another NH based movement that has considered secession to increase liberty. On July 23, 2001, founder of the FSP, Jason Sorens, published "Announcement: The Free State Project", in The Libertarian Enterprise, stating, "Even if we don't actually secede, we can force the federal government to compromise with us and grant us substantial liberties. Scotland and Quebec have both used the threat of secession to get large subsidies and concessions from their respective national governments. We could use our leverage for liberty."
- Oregon: Following the 2016 presidential election, Portland residents Christian Trejbal and Jennifer Rollins submitted a petition for a ballot measure relating to secession from the United States; the petitioners withdrew the measure shortly afterward, citing recent riots and death threats.
- South Carolina: In May 2010 a group formed that called itself the Third Palmetto Republic, a reference to the fact that the state claimed to be an independent republic twice before: once in 1776 and again in 1860. The group models itself after the Second Vermont Republic, and says its aims are for a free and independent South Carolina, and to abstain from any further federations.
- Texas Secession Movement: The group Republic of Texas generated national publicity for its controversial actions in the late 1990s. A small group still meets. In April 2009, Rick Perry, the Governor of Texas, raised the issue of secession in disputed comments during a speech at a Tea Party protest saying "Texas is a unique place. When we came into the union in 1845, one of the issues was that we would be able to leave if we decided to do that ... My hope is that America and Washington in particular pays attention. We've got a great union. There's absolutely no reason to dissolve it. But if Washington continues to thumb their nose at the American people, who knows what may come of that." Another group, the Texas Nationalist Movement, also seeks Texas' independence from the United States, but its methodology is to have the Texas Legislature call for a state-wide referendum on the issue (similar to the Scottish Independence vote of 2014).
- Vermont: The Second Vermont Republic, founded in 2003, is a loose network of several groups that describes itself as "a nonviolent citizens' network and think tank opposed to the tyranny of Corporate America and the U.S. government, and committed to the peaceful return of Vermont to its status as an independent republic and more broadly the dissolution of the Union". Its "primary objective is to extricate Vermont peacefully from the United States as soon as possible". They have worked closely with the Middlebury Institute created from a meeting sponsored in Vermont in 2004. On October 28, 2005, activists held the Vermont Independence Conference, "the first statewide convention on secession in the United States since North Carolina voted to secede from the Union on May 20, 1861". They also participated in the 2006 and 2007 Middlebury-organized national secessionist meetings that brought delegates from over a dozen groups.
- After Barack Obama won the 2012 presidential election, secession petitions pertaining to all fifty states were filed through the White House We the People petition website.
- After the Supreme Court of the United States rejected Texas v. Pennsylvania, Texas' attempt to invalidate 2020 election results from four states, Chairman of the Republican Party of Texas, Allen West said "Perhaps law-abiding states should bond together and form a Union of states that will abide by the Constitution." Some have interpreted this as an encouragement of secession from the United States.
Regional secession
- Republic of Lakotah: Some members of the Lakota people of Montana, Wyoming, Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota created the Republic to assert the independence of a nation that was always sovereign and did not willingly join the United States; therefore they do not consider themselves technically to be secessionists.
- Pacific Northwest: Cascadia: There have been repeated attempts to form a Bioregional Democracy Cascadia in the northwest. The core of Cascadia would be made up through the secession of the states of Washington, Oregon and the Canadian province of British Columbia, while some supporters of the movement support portions of Northern California, Southern Alaska, Idaho and Western Montana joining, to define its boundaries along ecological, cultural, economic and political boundaries.
- League of the South: The group seeks "a free and independent Southern republic" made up of the former Confederate States of America. It operated a short-lived Southern Party supporting the right of states to secede from the Union or to legally nullify federal laws.
- Red-State secession / Blue-state secession: Various editorials have proposed that states of the USA secede and then form federations only with states that have voted for the same political party. These editorials note the increasingly polarized political strife in the USA between Republican voters and Democratic voters. They propose partition of the US as a way of allowing both groups to achieve their policy goals while reducing the chances of civil war. Red states and blue states are states that typically vote for the Republican and Democratic parties, respectively.
Polling
A September 2017 Zogby International poll found that 68% of Americans were open to states of the USA seceding. A 2014 Reuters/Ipsos poll showed 24% of Americans supported their state seceding from the union if necessary; 53% opposed the idea. Republicans were somewhat more supportive than Democrats. Respondents cited issues like gridlock, governmental overreach, the possible unconstitutionality of the Affordable Care Act and a loss of faith in the federal government as reasons for desiring secession.