A natural product is a chemical compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis (both semisynthesis and total synthesis) and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients.
Within the field of organic chemistry, the definition of natural products is usually restricted to organic compounds isolated from natural sources that are produced by the pathways of primary or secondary metabolism. Within the field of medicinal chemistry, the definition is often further restricted to secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites are not essential for survival, but nevertheless provide organisms that produce them an evolutionary advantage. Many secondary metabolites are cytotoxic and have been selected and optimized through evolution for use as "chemical warfare" agents against prey, predators, and competing organisms.
Natural sources may lead to basic research on potential bioactive components for commercial development as lead compounds in drug discovery. Although natural products have inspired numerous drugs, drug development from natural sources has received declining attention in the 21st century by pharmaceutical companies, partly due to unreliable access and supply, intellectual property, cost, and profit concerns, seasonal or environmental variability of composition, and loss of sources due to rising extinction rates.
Classes
The broadest definition of natural product is anything that is produced by life, and includes the likes of biotic materials (e.g. wood, silk), bio-based materials (e.g. bioplastics, cornstarch), bodily fluids (e.g. milk, plant exudates), and other natural materials (e.g. soil, coal).
Natural products may be classified according to their biological function, biosynthetic pathway, or source. Depending on the sources, the number of known natural product molecules ranges between 300,000 and 400,000.
Function
Following Albrecht Kossel's original proposal in 1891, natural products are often divided into two major classes, the primary and secondary metabolites. Primary metabolites have an intrinsic function that is essential to the survival of the organism that produces them. Secondary metabolites in contrast have an extrinsic function that mainly affects other organisms. Secondary metabolites are not essential to survival but do increase the competitiveness of the organism within its environment. Because of their ability to modulate biochemical and signal transduction pathways, some secondary metabolites have useful medicinal properties.
Natural products especially within the field of organic chemistry are often defined as primary and secondary metabolites. A more restrictive definition limiting natural products to secondary metabolites is commonly used within the fields of medicinal chemistry and pharmacognosy.
Primary metabolites
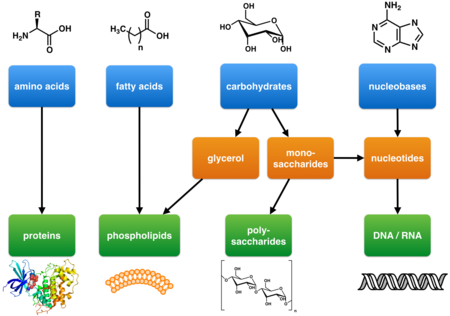
Primary metabolites as defined by Kossel are components of basic metabolic pathways that are required for life. They are associated with essential cellular functions such as nutrient assimilation, energy production, and growth/development. They have a wide species distribution that span many phyla and frequently more than one kingdom. Primary metabolites include carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids, and nucleic acids which are the basic building blocks of life.
Primary metabolites that are involved with energy production include respiratory and photosynthetic enzymes. Enzymes in turn are composed of amino acids and often non-peptidic cofactors that are essential for enzyme function. The basic structure of cells and of organisms are also composed of primary metabolites. These include cell membranes (e.g. phospholipids), cell walls (e.g. peptidoglycan, chitin), and cytoskeletons (proteins).
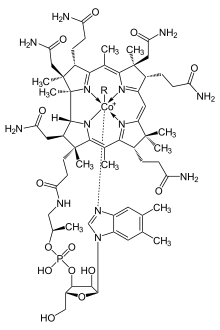
Primary metabolite enzymatic cofactors include members of the vitamin B family. Vitamin B1 as thiamine diphosphate is a coenzyme for pyruvate dehydrogenase, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, and transketolase which are all involved in carbohydrate metabolism. Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) is a constituent of FMN and FAD which are necessary for many redox reactions. Vitamin B3 (nicotinic acid or niacin), synthesized from tryptophan is a component of the coenzymes NAD+ and NADP+ which in turn are required for electron transport in the Krebs cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, as well as many other redox reactions. Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) is a constituent of coenzyme A, a basic component of carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism as well as the biosynthesis of fatty acids and polyketides. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxol, pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine) as pyridoxal 5′-phosphate is a cofactor for many enzymes especially transaminases involve in amino acid metabolism. Vitamin B12 (cobalamins) contain a corrin ring similar in structure to porphyrin and is an essential coenzyme for the catabolism of fatty acids as well for the biosynthesis of methionine.
DNA and RNA which store and transmit genetic information are composed of nucleic acid primary metabolites.
First messengers are signaling molecules that control metabolism or cellular differentiation. These signaling molecules include hormones and growth factors in turn are composed of peptides, biogenic amines, steroid hormones, auxins, gibberellins etc. These first messengers interact with cellular receptors which are composed of proteins. Cellular receptors in turn activate second messengers are used to relay the extracellular message to intracellular targets. These signaling molecules include the primary metabolites cyclic nucleotides, diacyl glycerol etc.
Secondary metabolites
Secondary in contrast to primary metabolites are dispensable and not absolutely required for survival. Furthermore, secondary metabolites typically have a narrow species distribution.
Secondary metabolites have a broad range of functions. These include pheromones that act as social signaling molecules with other individuals of the same species, communication molecules that attract and activate symbiotic organisms, agents that solubilize and transport nutrients (siderophores etc.), and competitive weapons (repellants, venoms, toxins etc.) that are used against competitors, prey, and predators. For many other secondary metabolites, the function is unknown. One hypothesis is that they confer a competitive advantage to the organism that produces them. An alternative view is that, in analogy to the immune system, these secondary metabolites have no specific function, but having the machinery in place to produce these diverse chemical structures is important and a few secondary metabolites are therefore produced and selected for.
General structural classes of secondary metabolites include alkaloids, phenylpropanoids, polyketides, and terpenoids.
Biosynthesis
The biosynthetic pathways leading to the major classes of natural products are described below.
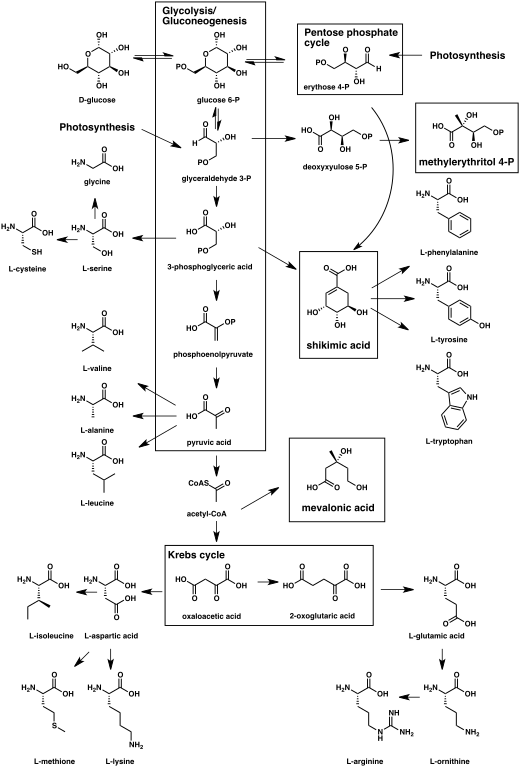
- Photosynthesis or gluconeogenesis → monosaccharides → polysaccharides (cellulose, chitin, glycogen etc.)
- Acetate pathway → fatty acids and polyketides
- Shikimate pathway → aromatic amino acids and phenylpropanoids
- Mevalonate pathway and methyletrythritol phosphate pathway → terpenoids and steroids
- Amino acids → alkaloids
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are an essential energy source for most life forms. In addition, polysaccharides formed from simpler carbohydrates are important structural components of many organisms such the cell walls of bacteria and plants.
Carbohydrate are the products of plant photosynthesis and animal gluconeogenesis. Photosynthesis produces initially 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde, a three carbon atom containing sugar (a triose). This triose in turn may be converted into glucose (a six carbon atom containing sugar) or a variety of pentoses (five carbon atom containing sugars) through the Calvin cycle. In animals, the three carbon precursors lactate or glycerol can be converted into pyruvate which in turn can be converted into carbohydrates in the liver.
Fatty acids and polyketides
Through the process of glycolysis sugars are broken down into acetyl-CoA. In an ATP dependent enzymatically catalyzed reaction, acetyl-CoA is carboxylated to form malonyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA undergo a Claisen condensation with lose of carbon dioxide to form acetoacetyl-CoA. Additional condensation reactions produce successively higher molecular weight poly-β-keto chains which are then converted into other polyketides. The polyketide class of natural products have diverse structures and functions and include prostaglandins and macrolide antibiotics.
One molecule of acetyl-CoA (the "starter unit") and several molecules malonyl-CoA (the "extender units") are condensed by fatty acid synthase to produce fatty acids. Fatty acid are essential components of lipid bilayers that form cell membranes as well as fat energy stores in animals.
Sources
Natural products may be extracted from the cells, tissues, and secretions of microorganisms, plants and animals. A crude (unfractionated) extract from any one of these sources will contain a range of structurally diverse and often novel chemical compounds. Chemical diversity in nature is based on biological diversity, so researchers collect samples from around the world to analyze and evaluate in drug discovery screens or bioassays. This effort to search for biologically active natural products is known as bioprospecting.
Pharmacognosy provides the tools to detect, isolate and identify bioactive natural products that could be developed for medicinal use. When an "active principle" is isolated from a traditional medicine or other biological material, this is known as a "hit". Subsequent scientific and legal work is then performed to validate the hit (eg. elucidation of mechanism of action, confirmation that there is no intellectual property conflict). This is followed by the hit to lead stage of drug discovery, where derivatives of the active compound are produced in an attempt to improve its potency and safety. In this and related ways, modern medicines can be developed directly from natural sources.
Although traditional medicines and other biological material are considered an excellent source of novel compounds, the extraction and isolation of these compounds can be a slow, expensive and inefficient process. For large scale manufacture therefore, attempts may be made to produce the new compound by total synthesis or semisynthesis. Because natural products are generally secondary metabolites with complex chemical structures, their total/semisynthesis is not always commercially viable. In these cases, efforts can be made to design simpler analogues with comparable potency and safety that are amenable to total/semisynthesis.
Prokaryotic
Bacteria
The serendipitous discovery and subsequent clinical success of penicillin prompted a large-scale search for other environmental microorganisms that might produce anti-infective natural products. Soil and water samples were collected from all over the world, leading to the discovery of streptomycin (derived from Streptomyces griseus), and the realization that bacteria, not just fungi, represent an important source of pharmacologically active natural products. This, in turn, led to the development of an impressive arsenal of antibacterial and antifungal agents including amphotericin B, chloramphenicol, daptomycin and tetracycline (from Streptomyces spp.), the polymyxins (from Paenibacillus polymyxa), and the rifamycins (from Amycolatopsis rifamycinica).
Although most of the drugs derived from bacteria are employed as anti-infectives, some have found use in other fields of medicine. Botulinum toxin (from Clostridium botulinum) and bleomycin (from Streptomyces verticillus) are two examples. Botulinum, the neurotoxin responsible for botulism, can be injected into specific muscles (such as those controlling the eyelid) to prevent muscle spasm. Also, the glycopeptide bleomycin is used for the treatment of several cancers including Hodgkin's lymphoma, head and neck cancer, and testicular cancer. Newer trends in the field include the metabolic profiling and isolation of natural products from novel bacterial species present in underexplored environments. Examples include symbionts or endophytes from tropical environments, subterranean bacteria found deep underground via mining/drilling, and marine bacteria.
Archaea
Because many Archaea have adapted to life in extreme environments such as polar regions, hot springs, acidic springs, alkaline springs, salt lakes, and the high pressure of deep ocean water, they possess enzymes that are functional under quite unusual conditions. These enzymes are of potential use in the food, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries, where biotechnological processes frequently involve high temperatures, extremes of pH, high salt concentrations, and / or high pressure. Examples of enzymes identified to date include amylases, pullulanases, cyclodextrin glycosyltransferases, cellulases, xylanases, chitinases, proteases, alcohol dehydrogenase, and esterases. Archaea represent a source of novel chemical compounds also, for example isoprenyl glycerol ethers 1 and 2 from Thermococcus S557 and Methanocaldococcus jannaschii, respectively.
Eukaryotic
Fungi
Several anti-infective medications have been derived from fungi including penicillin and the cephalosporins (antibacterial drugs from Penicillium rubens and Cephalosporium acremonium, respectively) and griseofulvin (an antifungal drug from Penicillium griseofulvum). Other medicinally useful fungal metabolites include lovastatin (from Pleurotus ostreatus), which became a lead for a series of drugs that lower cholesterol levels, cyclosporin (from Tolypocladium inflatum), which is used to suppress the immune response after organ transplant operations, and ergometrine (from Claviceps spp.), which acts as a vasoconstrictor, and is used to prevent bleeding after childbirth. Asperlicin (from Aspergillus alliaceus) is another example. Asperlicin is a novel antagonist of cholecystokinin, a neurotransmitter thought to be involved in panic attacks, and could potentially be used to treat anxiety.
Plants
Plants are a major source of complex and highly structurally diverse chemical compounds (phytochemicals), this structural diversity attributed in part to the natural selection of organisms producing potent compounds to deter herbivory (feeding deterrents). Major classes of phytochemical include phenols, polyphenols, tannins, terpenes, and alkaloids. Though the number of plants that have been extensively studied is relatively small, many pharmacologically active natural products have already been identified. Clinically useful examples include the anticancer agents paclitaxel and omacetaxine mepesuccinate (from Taxus brevifolia and Cephalotaxus harringtonii, respectively), the antimalarial agent artemisinin (from Artemisia annua), and the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor galantamine (from Galanthus spp.), used to treat Alzheimer's disease. Other plant-derived drugs, used medicinally and/or recreationally include morphine, cocaine, quinine, tubocurarine, muscarine, and nicotine.
Animals
Animals also represent a source of bioactive natural products. In particular, venomous animals such as snakes, spiders, scorpions, caterpillars, bees, wasps, centipedes, ants, toads, and frogs have attracted much attention. This is because venom constituents (peptides, enzymes, nucleotides, lipids, biogenic amines etc.) often have very specific interactions with a macromolecular target in the body (e.g. α-bungarotoxin from cobras). As with plant feeding deterrents, this biological activity is attributed to natural selection, organisms capable of killing or paralyzing their prey and/or defending themselves against predators being more likely to survive and reproduce.
Because of these specific chemical-target interactions, venom constituents have proved important tools for studying receptors, ion channels, and enzymes. In some cases, they have also served as leads in the development of novel drugs. For example, teprotide, a peptide isolated from the venom of the Brazilian pit viper Bothrops jararaca, was a lead in the development of the antihypertensive agents cilazapril and captopril. Also, echistatin, a disintegrin from the venom of the saw-scaled viper Echis carinatus was a lead in the development of the antiplatelet drug tirofiban.
In addition to the terrestrial animals and amphibians described above, many marine animals have been examined for pharmacologically active natural products, with corals, sponges, tunicates, sea snails, and bryozoans yielding chemicals with interesting analgesic, antiviral, and anticancer activities. Two examples developed for clinical use include ω-conotoxin (from the marine snail Conus magus) and ecteinascidin 743 (from the tunicate Ecteinascidia turbinata). The former, ω-conotoxin, is used to relieve severe and chronic pain, while the latter, ecteinascidin 743 is used to treat metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. Other natural products derived from marine animals and under investigation as possible therapies include the antitumour agents discodermolide (from the sponge Discodermia dissoluta), eleutherobin (from the coral Erythropodium caribaeorum), and the bryostatins (from the bryozoan Bugula neritina).
Medical uses
Natural products sometimes have pharmacological activity that can be of therapeutic benefit in treating diseases. Moreover, synthetic analogs of natural products with improved potency and safety can be prepared and therefore natural products are often used as starting points for drug discovery. Natural product constituents have inspired numerous drug discovery efforts that eventually gained approval as new drugs.
Traditional medicine
Indigenous peoples and ancient civilizations experimented with various plant and animal parts to determine what effect they might have. Through trial and error in isolated cases, traditional healers or shamans found some sources to provide therapeutic effect, representing knowledge of a crude drug that was passed down through generations in such practices as traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurveda. Extracts of some natural products led to modern discovery of their active constituents and eventually to the development of new drugs.
Modern natural product-derived drugs
A large number of currently prescribed drugs have been either directly derived from or inspired by natural products.
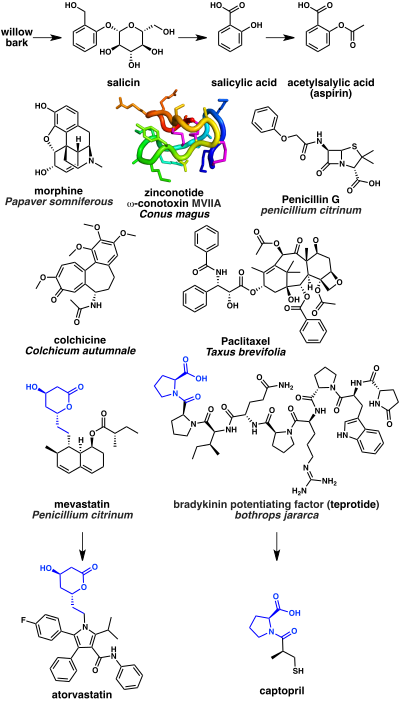
Some of the oldest natural product based drugs are analgesics. The bark of the willow tree has been known from antiquity to have pain relieving properties. This is due to presence of the natural product salicin which in turn may be hydrolyzed into salicylic acid. A synthetic derivative acetylsalicylic acid better known as aspirin is a widely used pain reliever. Its mechanism of action is inhibition of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme. Another notable example is opium is extracted from the latex from Papaver somniferous (a flowering poppy plant). The most potent narcotic component of opium is the alkaloid morphine which acts as an opioid receptor agonist. A more recent example is the N-type calcium channel blocker ziconotide analgesic which is based on a cyclic peptide cone snail toxin (ω-conotoxin MVIIA) from the species Conus magus.
A significant number of anti-infectives are based on natural products. The first antibiotic to be discovered, penicillin, was isolated from the mold Penicillium. Penicillin and related beta lactams work by inhibiting DD-transpeptidase enzyme that is required by bacteria to cross link peptidoglycan to form the cell wall.
Several natural product drugs target tubulin, which is a component of the cytoskeleton. These include the tubulin polymerization inhibitor colchicine isolated from the Colchicum autumnale (autumn crocus flowering plant), which is used to treat gout. Colchicine is biosynthesized from the amino acids phenylalanine and tryptophan. Paclitaxel, in contrast, is a tubulin polymerization stabilizer and is used as a chemotherapeutic drug. Paclitaxel is based on the terpenoid natural product taxol, which is isolated from Taxus brevifolia (the pacific yew tree).
A class of drugs widely used to lower cholesterol are the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, for example atorvastatin. These were developed from mevastatin, a polyketide produced by the fungus Penicillium citrinum. Finally, a number natural product drugs are used to treat hypertension and congestive heart failure. These include the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor captopril. Captopril is based on the peptidic bradykinin potentiating factor isolated from venom of the Brazilian arrowhead viper (Bothrops jararaca).
Limiting and enabling factors
Numerous challenges limit the use of natural products for drug discovery, resulting in 21st century preference by pharmaceutical companies to dedicate discovery efforts toward high-throughput screening of pure synthetic compounds with shorter timelines to refinement. Natural product sources are often unreliable to access and supply, have a high probability of duplication, inherently create intellectual property concerns about patent protection, vary in composition due to sourcing season or environment, and are susceptible to rising extinction rates.
The biological resource for drug discovery from natural products remains abundant, with small percentages of microorganisms, plant species, and insects assessed for bioactivity. In enormous numbers, bacteria and marine microorganisms remain unexamined. As of 2008, the field of metagenomics was proposed to examine genes and their function in soil microbes, but most pharmaceutical firms have not exploited this resource fully, choosing instead to develop "diversity-oriented synthesis" from libraries of known drugs or natural sources for lead compounds with higher potential for bioactivity.
Isolation and purification
All natural products begin as mixtures with other compounds from the natural source, often very complex mixtures, from which the product of interest must be isolated and purified. The isolation of a natural product refers, depending on context, either to the isolation of sufficient quantities of pure chemical matter for chemical structure elucidation, derivitzation/degradation chemistry, biological testing, and other research needs (generally milligrams to grams, but historically, often more), or to the isolation of "analytical quantities" of the substance of interest, where the focus is on identification and quantitation of the substance (e.g. in biological tissue or fluid), and where the quantity isolated depends on the analytical method applied (but is generally always sub-microgram in scale). The ease with which the active agent can be isolated and purified depends on the structure, stability, and quantity of the natural product. The methods of isolation applied toward achieving these two distinct scales of product are likewise distinct, but generally involve extraction, precipitation, adsorptions, chromatography, and sometimes crystallizations. In both cases, the isolated substance is purified to chemical homogeneity, i.e. specific combined separation and analytical methods such as LC-MS methods are chosen to be "orthogonal"—achieving their separations based on distinct modes of interaction between substance and isolating matrix—with the goal being repeated detection of only a single species present in the putative pure sample. Early isolation is almost inevitably followed by structure determination, especially if an important pharmacologic activity is associated with the purified natural product.
Structure determination refers to methods applied to determine the chemical structure of an isolated, pure natural product, a process that involves an array of chemical and physical methods that have changed markedly over the history of natural products research; in earliest days, these focused on chemical transformation of unknown substances into known substances, and measurement of physical properties such as melting point and boiling point, and related methods for determining molecular weight. In the modern era, methods focus on mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance methods, often multidimensional, and, when feasible, small molecule crystallography. For instance, the chemical structure of penicillin was determined by Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin in 1945, work for which she later received a Nobel Prize in Chemistry (1964).
Synthesis
Many natural products have very complex structures. The perceived complexity of a natural product is a qualitative matter, consisting of consideration of its molecular mass, the particular arrangements of substructures (functional groups, rings etc.) with respect to one another, the number and density of those functional groups, the stability of those groups and of the molecule as a whole, the number and type of stereochemical elements, the physical properties of the molecule and its intermediates (which bear on the ease of its handling and purification), all of these viewed in the context of the novelty of the structure and whether preceding related synthetic efforts have been successful (see below for details). Some natural products, especially those less complex, are easily and cost-effectively prepared via complete chemical synthesis from readily available, simpler chemical ingredients, a process referred to as total synthesis (especially when the process involves no steps mediated by biological agents). Not all natural products are amenable to total synthesis, cost-effective or otherwise. In particular, those most complex often are not. Many are accessible, but the required routes are simply too expensive to allow synthesis on any practical or industrial scale. However, to be available for further study, all natural products must yield to isolation and purification. This may suffice if isolation provides appropriate quantities of the natural product for the intended purpose (e.g. as a drug to alleviate disease). Drugs such as penicillin, morphine, and paclitaxel proved to be affordably acquired at needed commercial scales solely via isolation procedures (without any significant synthetic chemistry contributing). However, in other cases, needed agents are not available without synthetic chemistry manipulations.
Semisynthesis
The process of isolating a natural product from its source can be costly in terms of committed time and material expense, and it may challenge the availability of the relied upon natural resource (or have ecological consequences for the resource). For instance, it has been estimated that the bark of an entire yew tree (Taxus brevifolia) would have to be harvested to extract enough paclitaxel for just a single dose of therapy. Furthermore, the number of structural analogues obtainable for structure–activity analysis (SAR) simply via harvest (if more than one structural analogue is even present) is limited by the biology at work in the organism, and so outside of the experimentalist's control.
In such cases where the ultimate target is harder to come by, or limits SAR, it is sometimes possible to source a middle-to-late stage biosynthetic precursor or analogue from which the ultimate target can be prepared. This is termed semisynthesis or partial synthesis. With this approach, the related biosynthetic intermediate is harvested and then converted to the final product by conventional procedures of chemical synthesis.
This strategy can have two advantages. Firstly, the intermediate may be more easily extracted, and in higher yield, than the ultimate desired product. An example of this is paclitaxel, which can be manufactured by extracting 10-deacetylbaccatin III from T. brevifolia needles, then carrying out a four-step synthesis. Secondly, the route designed between semisynthetic starting material and ultimate product may permit analogues of the final product to be synthesized. The newer generation semisynthetic penicillins are an illustration of the benefit of this approach.
Total synthesis
In general, the total synthesis of natural products is a non-commercial research activity, aimed at deeper understanding of the synthesis of particular natural product frameworks, and the development of fundamental new synthetic methods. Even so, it is of tremendous commercial and societal importance. By providing challenging synthetic targets, for example, it has played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry. Prior to the development of analytical chemistry methods in the twentieth century, the structures of natural products were affirmed by total synthesis (so-called "structure proof by synthesis"). Early efforts in natural products synthesis targeted complex substances such as cobalamin (vitamin B12), an essential cofactor in cellular metabolism.
Symmetry
Examination of dimerized and trimerized natural products has shown that an element of bilateral symmetry is often present. Bilateral symmetry refers to a molecule or system that contains a C2, Cs, or C2v point group identity. C2 symmetry tends to be much more abundant than other types of bilateral symmetry. This finding sheds light on how these compounds might be mechanistically created, as well as providing insight into the thermodynamic properties that make these compounds more favorable. Density functional theoretical (DFT), Hartree Fock, and semiempirical calculations also show some favorability for dimerization in natural products due to evolution of more energy per bond than the equivalent trimer or tetramer. This is proposed to be due to steric hindrance at the core of the molecule, as most natural products dimerize and trimerize in a head-to-head fashion rather than head-to-tail.
Research and teaching
Research and teaching activities related to natural products fall into a number of diverse academic areas, including organic chemistry, medicinal chemistry, pharmacognosy, ethnobotany, traditional medicine, and ethnopharmacology. Other biological areas include chemical biology, chemical ecology, chemogenomics, systems biology, molecular modeling, chemometrics, and chemoinformatics.
Chemistry
Natural products chemistry is a distinct area of chemical research which was important in the development and history of chemistry. Isolating and identifying natural products has been important to source substances for early preclinical drug discovery research, to understand traditional medicine and ethnopharmacology, and to find pharmacologically useful areas of chemical space. To achieve this, many technological advances have been made, such as the evolution of technology associated with chemical separations, and the development of modern methods in chemical structure determination such as NMR. In addition, natural products are prepared by organic synthesis, to provide confirmation of their structure, or to give access to larger quantities of natural products of interest. In this process, the structure of some natural products have been revised, and the challenge of synthesising natural products has led to the development of new synthetic methodology, synthetic strategy, and tactics. In this regard, natural products play a central role in the training of new synthetic organic chemists, and are a principal motivation in the development of new variants of old chemical reactions (e.g., the Evans aldol reaction), as well as the discovery of completely new chemical reactions (e.g., the Woodward cis-hydroxylation, Sharpless epoxidation, and Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions).
Biochemistry
The biosynthesis of natural products is interest. Knowledge of the biosynthesis enables improved routes to valuable natural products. This knowledge can then be used to access larger quantities of natural products with interesting biological activity, and allow medicinally useful natural products, such as alkaloids to be produced more efficiently and economically.
History
Foundations of organic and natural product chemistry
The concept of natural products dates back to the early 19th century, when the foundations of organic chemistry were laid. Organic chemistry was regarded at that time as the chemistry of substances that plants and animals are composed of. It was a relatively complex form of chemistry and stood in stark contrast to inorganic chemistry, the principles of which had been established in 1789 by the Frenchman Antoine Lavoisier in his work Traité Élémentaire de Chimie.
Isolation
Lavoisier showed at the end of the 18th century that organic substances consisted of a limited number of elements: primarily carbon and hydrogen and supplemented by oxygen and nitrogen. He quickly focused on the isolation of these substances, often because they had an interesting pharmacological activity. Plants were the main source of such compounds, especially alkaloids and glycosides. It was long been known that opium, a sticky mixture of alkaloids (including codeine, morphine, noscapine, thebaine, and papaverine) from the opium poppy (Papaver somniferum), possessed a narcotic and at the same time mind-altering properties. By 1805, morphine had already been isolated by the German chemist Friedrich Sertürner and in the 1870s it was discovered that boiling morphine with acetic anhydride produced a substance with a strong pain suppressive effect: heroin. In 1815, Eugène Chevreul isolated cholesterol, a crystalline substance, from animal tissue that belongs to the class of steroids, and in 1820 strychnine, an alkaloid was isolated.
Synthesis
A second important step was the synthesis of organic compounds. Whereas the synthesis of inorganic substances had been known for a long time, the synthesis of organic substances was a difficult hurdle. In 1827 the Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius held that an indispensable force of nature for the synthesis of organic compounds, called vital force or life force, was needed. This philosophical idea, vitalism, well into the 19th century had many supporters, even after the introduction of the atomic theory. The idea of vitalism especially fitted in with beliefs in medicine; the most traditional healing practices believed that disease was the result of some imbalance in the vital energies that distinguishes life from nonlife. A first attempt to break the vitalism idea in science was made in 1828, when the German chemist Friedrich Wöhler succeeded in synthesizing urea, a natural product found in urine, by heating ammonium cyanate, an inorganic substance:
This reaction showed that there was no need for a life force in order to prepare organic substances. This idea, however, was initially met with a high degree of skepticism, and only 20 years later, with the synthesis of acetic acid from carbon by Adolph Wilhelm Hermann Kolbe, was the idea accepted. Organic chemistry has since developed into an independent area of research dedicated to the study of carbon-containing compounds, since that element in common was detected in a variety of nature-derived substances. An important factor in the characterization of organic materials was on the basis of their physical properties (such as melting point, boiling point, solubility, crystallinity, or color).
Structural theories
A third step was the structure elucidation of organic substances: although the elemental composition of pure organic substances (irrespective of whether they were of natural or synthetic origin) could be determined fairly accurately, the molecular structure was still a problem. The urge to do structural elucidation resulted from a dispute between Friedrich Wöhler and Justus von Liebig, who both studied a silver salt of the same composition but had different properties. Wöhler studied silver cyanate, a harmless substance, while von Liebig investigated silver fulminate, a salt with explosive properties. The elemental analysis shows that both salts contain equal quantities of silver, carbon, oxygen and nitrogen. According to the then prevailing ideas, both substances should possess the same properties, but this was not the case. This apparent contradiction was later solved by Berzelius's theory of isomers, whereby not only the number and type of elements are of importance to the properties and chemical reactivity, but also the position of atoms in within a compound. This was a direct cause for the development of structure theories, such as the radical theory of Jean-Baptiste Dumas and the substitution theory of Auguste Laurent. However, it took until 1858 before by August Kekulé formulated a definite structure theory. He posited that carbon is tetravalent and can bind to itself to form carbon chains as they occur in natural products.
Expanding the concept
The concept of natural product, which initially based on organic compounds that could be isolated from plants, was extended to include animal material in the middle of the 19th century by the German Justus von Liebig. Hermann Emil Fischer in 1884, turned his attention to the study of carbohydrates and purines, work for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1902. He also succeeded to make synthetically in the laboratory in a variety of carbohydrates, including glucose and mannose. After the discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928, fungi and other micro-organisms were added to the arsenal of sources of natural products.
Milestones
By the 1930s, several large classes of natural products were known. Important milestones included:
- Terpenes, first systematically studied by Otto Wallach (Nobel Prize 1910) and later by Leopold Ružička (Nobel Prize 1939)
- Dyes based on porphins (including chlorophyll and heme), studied by Richard Willstätter (Nobel Prize 1915) and Hans Fischer (Nobel Prize 1930)
- Steroids, studied by Heinrich Otto Wieland (Nobel Prize 1927) and Adolf Windaus (Nobel Prize 1928)
- Carotenoids, studied by Paul Karrer (Nobel Prize 1937)
- Vitamins, studied among others by Paul Karrer, Adolf Windaus, Robert R. Williams, Norman Haworth (Nobel Prize 1937), Richard Kuhn (Nobel Prize 1938) and Albert Szent-Györgyi
- Hormones studied by Adolf Butenandt (Nobel Prize 1939) and Edward Calvin Kendall (Nobel Prize 1950)
- Alkaloids and anthocyanins, studied by, among others, Robert Robinson (Nobel Prize 1947)