| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ammonium nitrate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.680 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 0222 – with > 0.2% combustible substances 1942 – with ≤ 0.2% combustible substances 2067 – fertilizers 2426 – liquid |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| NH4NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 80.043 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless |
| Density | 1.725 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 169.6 °C (337.3 °F; 442.8 K) |
| Boiling point | approx. 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) decomposes |
| Endothermic 118 g/100 ml (0 °C) 150 g/100 ml (20 °C) 297 g/100 ml (40 °C) 410 g/100 ml (60 °C) 576 g/100 ml (80 °C) 1024 g/100 ml (100 °C)[1] | |
| -33.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| trigonal | |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | very low |
| Friction sensitivity | very low |
| Detonation velocity | 2500 m/s |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Explosive, Oxidizer |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H201, H271, H319 | |
| P220, P221, P271, P280, P264, P372 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
2085–5300 mg/kg (oral in rats, mice) |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Ammonium nitrite |
Other cations
|
Sodium nitrate Potassium nitrate Hydroxylammonium nitrate |
Related compounds
|
Ammonium perchlorate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
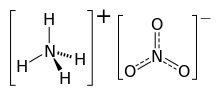
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula NH4NO3. It is a white crystalline solid consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer. Global production was estimated at 21.6 million tonnes in 2017.
Its other major use is as a component of explosive mixtures used in mining, quarrying, and civil construction. It is the major constituent of ANFO, a popular industrial explosive which accounts for 80% of explosives used in North America; similar formulations have been used in improvised explosive devices.
Many countries are phasing out its use in consumer applications due to concerns over its potential for misuse. Accidental ammonium nitrate explosions have killed thousands of people since the early 20th century.
Occurrence
Ammonium nitrate is found as the natural mineral gwihabaite – the ammonium analogue of saltpetre – in the driest regions of the Atacama Desert in Chile, often as a crust on the ground or in conjunction with other nitrate, iodate, and halide minerals. Ammonium nitrate was mined there in the past, but virtually 100% of the chemical now used is synthetic.
Production, reactions and crystalline phases
The industrial production of ammonium nitrate entails the acid-base reaction of ammonia with nitric acid:
- HNO3 + NH3 → NH4NO3
Ammonia is used in its anhydrous form (a gas) and the nitric acid is concentrated. The reaction is violent owing to its highly exothermic
nature. After the solution is formed, typically at about 83%
concentration, the excess water is evaporated off to leave an ammonium
nitrate (AN) content of 95% to 99.9% concentration (AN melt), depending
on grade. The AN melt is then made into "prills" or small beads in a spray tower,
or into granules by spraying and tumbling in a rotating drum. The
prills or granules may be further dried, cooled, and then coated to
prevent caking. These prills or granules are the typical AN products in
commerce.
The ammonia required for this process is obtained by the Haber process from nitrogen and hydrogen. Ammonia produced by the Haber process can be oxidized to nitric acid by the Ostwald process. Another production method is a variant of the nitrophosphate process:
The products, calcium carbonate and ammonium nitrate, may be separately purified or sold combined as calcium ammonium nitrate.
Ammonium nitrate can also be made via metathesis reactions:
Reactions
As ammonium nitrate is a salt, both the cation, NH4+, and the anion, NO3−, may take part in chemical reactions.
Solid ammonium nitrate decomposes on heating. At temperatures below around 300 °C, the decomposition mainly produces nitrous oxide and water:
- NH4NO3 → N2O + 2H2O
At higher temperatures, the following reaction predominates.
- 2NH4NO3 → 2N2 + O2 + 4H2O
Both decomposition reactions are exothermic and their products are gas. Under certain conditions, this can lead to a runaway reaction, with the decomposition process becoming explosive. See § disasters for details. Many ammonium nitrate disasters, with loss of lives, have occurred.
The red–orange colour in an explosion cloud is due to nitrogen dioxide, a secondary reaction product.
Crystalline phases
A number of crystalline phases of ammonium nitrate have been observed. The following occur under atmospheric pressure.
Phase Temperature (°C) Symmetry (liquid) (above 169.6) I 169.6 to 125.2 cubic II 125.2 to 84.2 tetragonal III 84.2 to 32.3 α-rhombic IV 32.3 to −16.8 β-rhombic V below −16.8 tetragonal
Both the β-rhombic to α-rhombic forms are potentially present at
ambient temperature in many parts of the world but have a 3.6%
difference in density. As a result, this phase transition and attending
change of volume, with the practical consequence that ammonium nitrate
formed as solid rocket motor
propellant develops cracks. For this reason, phase stabilized ammonium
nitrate (PSAN) which incorporates metal halides as stabilisers has been
investigated.
Applications
Fertilizer
Ammonium nitrate is an important fertilizer with NPK rating 34-0-0 (34% nitrogen). It is less concentrated than urea
(46-0-0), giving ammonium nitrate a slight transportation disadvantage.
Ammonium nitrate's advantage over urea is that it is more stable and
does not rapidly lose nitrogen to the atmosphere.
Explosives
Ammonium nitrate is an ingredient in certain explosives. Examples of explosives containing ammonium nitrate include:
- Astrolite (ammonium nitrate and hydrazine rocket fuel)
- Amatol (ammonium nitrate and TNT)
- Ammonal (ammonium nitrate and aluminum powder)
- Amatex (ammonium nitrate, TNT and RDX)
- ANFO (ammonium nitrate and fuel oil)
- DBX (ammonium nitrate, RDX, TNT and aluminum powder)
- Tovex (ammonium nitrate and methylammonium nitrate)
- Minol (explosive) (ammonium nitrate, TNT and aluminum powder)
- Goma-2 (ammonium nitrate, nitroglycol, Nitrocellulose, Dibutyl phthalate and fuel)
Mixture with fuel oil
ANFO is a mixture of 94% ammonium nitrate ("AN") and 6% fuel oil ("FO") widely used as a bulk industrial explosive. It is used in coal mining, quarrying, metal mining,
and civil construction in undemanding applications where the advantages
of ANFO's low cost and ease of use matter more than the benefits
offered by conventional industrial explosives, such as water resistance,
oxygen balance, high detonation velocity, and performance in small
diameters.
Terrorism
Ammonium nitrate-based explosives were used in the Sterling Hall bombing in Madison, Wisconsin, 1970, the Oklahoma City bombing in 1995, the 2011 Delhi bombings, the 2011 bombing in Oslo, and the 2013 Hyderabad blasts.
In November 2009, the government of the North West Frontier Province (NWFP) of Pakistan imposed a ban on ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, and calcium ammonium nitrate fertilizers in the former Malakand Division – comprising the Upper Dir, Lower Dir, Swat, Chitral, and Malakand districts of the NWFP – following reports that those chemicals were used by militants to make explosives. Due to these bans, "Potassium chlorate – the stuff that makes safety matches catch fire – has surpassed fertilizer as the explosive of choice for insurgents."
Niche uses
Ammonium nitrate is used in some instant cold packs, as its dissolution in water is highly endothermic. It also was used, in combination with independently explosive "fuels" such as guanidine nitrate, as a cheaper (but less stable) alternative to 5-aminotetrazole in the inflators of airbags manufactured by Takata Corporation, which were recalled as unsafe after killing 14 people.
A solution of ammonium nitrate with nitric acid called Cavea-b showed promise for use in spacecraft as a more energetic alternative to the common monopropellant hydrazine. A number of trials were carried out in the 1960s but the substance was not adopted by NASA.
Safety, handling, and storage
Numerous safety guidelines are available for storing and handling ammonium nitrate. Health and safety data are shown on the safety data sheets available from suppliers and from various governments.
Pure ammonium nitrate does not burn, but as a strong oxidizer, it
supports and accelerates the combustion of organic (and some inorganic)
material. It should not be stored near combustible substances.
While ammonium nitrate is stable at ambient temperature and
pressure under many conditions, it may detonate from a strong initiation
charge. It should not be stored near high explosives or blasting
agents.
Molten ammonium nitrate is very sensitive to shock and
detonation, particularly if it becomes contaminated with incompatible
materials such as combustibles, flammable liquids, acids, chlorates,
chlorides, sulfur, metals, charcoal and sawdust.
Contact with certain substances such as chlorates, mineral acids and metal sulfides, can lead to vigorous or even violent decomposition capable of igniting nearby combustible material or detonating.
Ammonium nitrate begins decomposition after melting, releasing NO
x , HNO3, NH
3 and H2O. It should not be heated in a confined space. The resulting heat and pressure from decomposition increases the sensitivity to detonation and increases the speed of decomposition. Detonation may occur at 80 atmospheres. Contamination can reduce this to 20 atmospheres.
x , HNO3, NH
3 and H2O. It should not be heated in a confined space. The resulting heat and pressure from decomposition increases the sensitivity to detonation and increases the speed of decomposition. Detonation may occur at 80 atmospheres. Contamination can reduce this to 20 atmospheres.
Ammonium nitrate has a critical relative humidity
of 59.4%, above which it will absorb moisture from the atmosphere.
Therefore, it is important to store ammonium nitrate in a tightly sealed
container. Otherwise, it can coalesce into a large, solid mass.
Ammonium nitrate can absorb enough moisture to liquefy. Blending
ammonium nitrate with certain other fertilizers can lower the critical
relative humidity.
The potential for use of the material as an explosive has
prompted regulatory measures. For example, in Australia, the Dangerous
Goods Regulations came into effect in August 2005 to enforce licensing
in dealing with such substances. Licenses are granted only to applicants (industry) with appropriate security measures in place to prevent any misuse.
Additional uses such as education and research purposes may also be
considered, but individual use will not. Employees of those with
licenses to deal with the substance are still required to be supervised
by authorized personnel and are required to pass a security and national
police check before a license may be granted.
Health hazards
Health and safety data are shown on the material safety data sheets, which are available from suppliers and can be found on the internet.
Ammonium nitrate is not hazardous to health and is usually used in fertilizer products.
Ammonium nitrate has an LD50 of 2217 mg/kg, which for comparison is about two-thirds that of table salt.
Disasters
Ammonium nitrate decomposes, non-explosively, into the gases nitrous oxide and water vapor when heated. However, it can be induced to decompose explosively by detonation.
Large stockpiles of the material can also be a major fire risk due to their supporting oxidation,
a situation which can easily escalate to detonation.
Explosions are not uncommon: relatively minor incidents occur most
years, and several large and devastating explosions have also occurred.
Examples include the Oppau explosion of 1921 (one of the largest artificial non-nuclear explosions), the Texas City disaster of 1947, the 2015 Tianjin explosions in China, and the 2020 Beirut explosion. Ammonium nitrate can explode through two mechanisms:
- Shock-to-detonation transition. An explosive charge within or in contact with a mass of ammonium nitrate causes the ammonium nitrate to detonate. Examples of such disasters are Kriewald, Morgan (present-day Sayreville, New Jersey), Oppau, and Tessenderlo.
- Deflagration to detonation transition. The ammonium nitrate explosion results from a fire that spreads into the ammonium nitrate (Texas City, TX; Brest; West, TX; Tianjin; Beirut), or from ammonium nitrate mixing with a combustible material during the fire (Repauno, Cherokee, Nadadores). The fire must be confined at least to a degree for successful transition from a fire to an explosion.

