2D structural formula and 3D models of LSD
| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /daɪ eθəl ˈæmaɪd/, /æmɪd/, or /eɪmaɪd/ |
| Synonyms | LSD, LSD-25, Acid, Delysid, others |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Dependence liability | Low |
| Addiction liability | Low-rare |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, under the tongue, intravenous |
| Drug class | Hallucinogen (serotonergic psychedelic) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 71% |
| Protein binding | Unknown |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP450) |
| Metabolites | 2-Oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD |
| Onset of action | 30–40 minutes |
| Elimination half-life | 3.6 hours |
| Duration of action | 8–12 hours |
| Excretion | Kidneys |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H25N3O |
| Molar mass | 323.44 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 80 to 85 °C (176 to 185 °F) |
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), also known as acid, is a hallucinogenic drug. Effects typically include altered thoughts, feelings, and awareness of one's surroundings. Many users see or hear things that do not exist. Dilated pupils, increased blood pressure, and increased body temperature are typical. Effects typically begin within half an hour and can last for up to 12 hours. It is used mainly as a recreational drug and for spiritual reasons.
While LSD does not appear to be addictive, tolerance with use of increasing doses may occur. Adverse psychiatric reactions such as anxiety, paranoia, and delusions are possible. Long-term flashbacks may occur despite no further use. Death as a result of LSD is very rare, though occasionally occurs via accidents. The effects of LSD are believed to occur as a result of alterations in the serotonin system. As little as 20 micrograms can produce an effect. In pure form LSD is clear or white in color, has no smell, and is crystalline. It breaks down with exposure to ultraviolet light.
In the United States, as of 2017, about 10% of people have used LSD at some point in their life, while 0.7% have used it in the last year. It was most popular in the 1960s to 1980s. LSD is typically either swallowed or held under the tongue. It is most often sold on blotter paper and less commonly as tablets or in gelatin squares. There are no known treatments for addiction, if it occurs.
LSD was first made by Albert Hofmann in 1938 from lysergic acid, a chemical from the fungus ergot. Hofmann discovered its hallucinogenic properties in 1943. In the 1950s, the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) believed the drug might be useful for mind control so tested it on people, some without their knowledge, in a program called MKUltra. LSD was sold as a medication for research purposes under the trade-name Delysid in the 1950s and 1960s. It was listed as a schedule 1 controlled substance by the United Nations in 1971. It currently has no approved medical use. In Europe, as of 2011, the typical cost of a dose was between 4.50 and 25 Euro.
Uses
Recreational
Pink elephant blotters containing LSD
LSD is commonly used as a recreational drug.
Spiritual
LSD is considered an entheogen because it can catalyze intense spiritual experiences, during which users may feel they have come into contact with a greater spiritual or cosmic order. Users sometimes report out of body experiences. In 1966, Timothy Leary established the League for Spiritual Discovery with LSD as its sacrament. Stanislav Grof has written that religious and mystical experiences observed during LSD sessions appear to be phenomenologically indistinguishable from similar descriptions in the sacred scriptures of the great religions of the world and the texts of ancient civilizations.Medical
LSD currently has no approved uses in medicine. A meta analysis concluded that a single dose was effective at reducing alcohol consumption in alcoholism. LSD has also been studied in depression, anxiety, and drug dependence, with positive preliminary results.Effects
Some symptoms reported for LSD.
Physical
LSD can cause pupil dilation, reduced appetite, and wakefulness. Other physical reactions to LSD are highly variable and nonspecific, some of which may be secondary to the psychological effects of LSD. Among the reported symptoms are numbness, weakness, nausea, hypothermia or hyperthermia, elevated blood sugar, goose bumps, heart rate increase, jaw clenching, perspiration, saliva production, mucus production, hyperreflexia, and tremors.Psychological
The most common immediate psychological effects of LSD are visual hallucinations and illusions (colloquially known as "trips"), which can vary greatly depending on how much is used and how the brain responds. Trips usually start within 20–30 minutes of taking LSD by mouth (less if snorted or taken intravenously), peak three to four hours after ingestion, and last up to 12 hours. Negative experiences, referred to as "bad trips", produce intense negative emotions, such as irrational fears and anxiety, panic attacks, paranoia, rapid mood swings, intrusive thoughts of hopelessness, wanting to harm others, and suicidal ideation. It is impossible to predict when a bad trip will occur. Good trips are stimulating and pleasurable, and typically involve feeling as if one is floating, disconnected from reality, feelings of joy or euphoria (sometimes called a "rush"), decreased inhibitions, and the belief that one has extreme mental clarity or superpowers.Sensory
Some sensory effects may include an experience of radiant colors, objects and surfaces appearing to ripple or "breathe", colored patterns behind the closed eyelids (eidetic imagery), an altered sense of time (time seems to be stretching, repeating itself, changing speed or stopping), crawling geometric patterns overlaying walls and other objects, and morphing objects. Some users, including Albert Hofmann, report a strong metallic taste for the duration of the effects.LSD causes an animated sensory experience of senses, emotions, memories, time, and awareness for 6 to 14 hours, depending on dosage and tolerance. Generally beginning within 30 to 90 minutes after ingestion, the user may experience anything from subtle changes in perception to overwhelming cognitive shifts. Changes in auditory and visual perception are typical. Visual effects include the illusion of movement of static surfaces ("walls breathing"), after image-like trails of moving objects ("tracers"), the appearance of moving colored geometric patterns (especially with closed eyes), an intensification of colors and brightness ("sparkling"), new textures on objects, blurred vision, and shape suggestibility. Some users report that the inanimate world appears to animate in an inexplicable way; for instance, objects that are static in three dimensions can seem to be moving relative to one or more additional spatial dimensions. Many of the basic visual effects resemble the phosphenes seen after applying pressure to the eye and have also been studied under the name "form constants". The auditory effects of LSD may include echo-like distortions of sounds, changes in ability to discern concurrent auditory stimuli, and a general intensification of the experience of music. Higher doses often cause intense and fundamental distortions of sensory perception such as synaesthesia, the experience of additional spatial or temporal dimensions, and temporary dissociation.
Adverse effects
Addiction
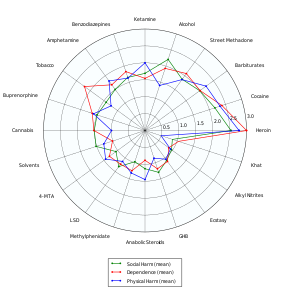
experts in psychiatry, chemistry, pharmacology, forensic science,
epidemiology, and the police and legal services engaged in delphic analysis regarding 20 popular recreational drugs. LSD was ranked 14th in dependence, 15th in physical harm, and 13th in social harm.
Of the 20 drugs ranked according to individual and societal harm by David Nutt, LSD was third to last, approximately 1/10th as harmful as alcohol. The most significant adverse effect was impairment of mental functioning while intoxicated.
Mental disorders
LSD may trigger panic attacks or feelings of extreme anxiety, known familiarly as a "bad trip." Review studies suggest that LSD likely plays a role in precipitating the onset of acute psychosis in previously healthy individuals with an increased likelihood in individuals who have a family history of schizophrenia. There is evidence that people with severe mental illnesses like schizophrenia have a higher likelihood of experiencing adverse effects from taking LSD.Suggestibility
While publicly available documents indicate that the CIA and Department of Defense have discontinued research into the use of LSD as a means of mind control, research from the 1960s suggests that both mentally ill and healthy people are more suggestible while under its influence.Flashbacks
Some individuals may experience "flashbacks" and a syndrome of long-term and occasionally distressing perceptual changes."Flashbacks" are a reported psychological phenomenon in which an individual experiences an episode of some of LSD's subjective effects after the drug has worn off, "persisting for months or years after hallucinogen use". Several studies have tried to determine the likelihood that a user of LSD, not suffering from known psychiatric conditions, will experience flashbacks. The larger studies include Blumenfeld's in 1971and Naditch and Fenwick's in 1977, which arrived at figures of 20% and 28%, respectively.
Hallucinogen persisting perception disorder (HPPD) describes a post-LSD exposure syndrome in which LSD-like visual changes are not temporary and brief, as they are in flashbacks, but instead are persistent, and cause clinically significant impairment or distress. The syndrome is a DSM-IV diagnosis. Several scientific journal articles have described the disorder. HPPD differs from flashbacks in that it is persistent and apparently entirely visual (although mood and anxiety disorders are sometimes diagnosed in the same individuals). A recent review suggests that HPPD (as defined in the DSM-IV) is uncommon and affects a distinctly vulnerable subpopulation of users.
Cancer and pregnancy
The mutagenic potential of LSD is unclear. Overall, the evidence seems to point to limited or no effect at commonly used doses. Empirical studies showed no evidence of teratogenic or mutagenic effects from use of LSD in man.Tolerance
Tolerance to LSD builds up over consistent use and cross-tolerance has been demonstrated between LSD, mescaline and psilocybin. This tolerance is probably caused by downregulation of 5-HT2A receptors in the brain and diminishes a few days after cessation of use.LSD is not addictive. Experimental evidence has demonstrated that LSD use does not yield positive reinforcement in either human or animal subjects.
Overdose
As of 2008 there were no documented fatalities attributed directly to an LSD overdose. Despite this several behavioral fatalities and suicides have occurred due to LSD. Eight individuals who accidentally consumed very high amounts by mistaking LSD for cocaine developed comatose states, hyperthermia, vomiting, gastric bleeding, and respiratory problems–however, all survived with supportive care.Reassurance in a calm, safe environment is beneficial. Agitation can be safely addressed with benzodiazepines such as lorazepam or diazepam. Neuroleptics such as haloperidol are recommended against because they may have adverse effects. LSD is rapidly absorbed, so activated charcoal and emptying of the stomach will be of little benefit, unless done within 30–60 minutes of ingesting an overdose of LSD. Sedation or physical restraint is rarely required, and excessive restraint may cause complications such as hyperthermia (over-heating) or rhabdomyolysis.
Research suggests that massive doses are not lethal, but do typically require supportive care, which may include endotracheal intubation or respiratory support. It is recommended that high blood pressure, tachycardia (rapid heart-beat), and hyperthermia, if present, are treated symptomatically, and that low blood pressure is treated initially with fluids and then with pressors if necessary. Intravenous administration of anticoagulants, vasodilators, and sympatholytics may be useful with massive doses.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Binding affinities of LSD for various receptors. The lower the dissociation constant (Ki),
the more strongly LSD binds to that receptor (i.e. with higher
affinity). The horizontal line represents an approximate value for human
plasma concentrations of LSD, and hence, receptor affinities that are
above the line are unlikely to be involved in LSD's effect. Data
averaged from data from the Ki Database
Most serotonergic psychedelics are not significantly dopaminergic, and LSD is therefore atypical in this regard. The agonism of the D2 receptor by LSD may contribute to its psychoactive effects in humans.
LSD binds to most serotonin receptor subtypes except for the 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptors. However, most of these receptors are affected at too low affinity to be sufficiently activated by the brain concentration of approximately 10–20 nM. In humans, recreational doses of LSD can affect 5-HT1A (Ki=1.1nM), 5-HT2A (Ki=2.9nM), 5-HT2B (Ki=4.9nM), 5-HT2C (Ki=23nM), 5-HT5A (Ki=9nM [in cloned rat tissues]), and 5-HT6 receptors (Ki=2.3nM). 5-HT5B receptors, which are not present in humans, also have a high affinity for LSD. The psychedelic effects of LSD are attributed to cross-activation of 5-HT2A receptor heteromers. Many but not all 5-HT2A agonists are psychedelics and 5-HT2A antagonists block the psychedelic activity of LSD. LSD exhibits functional selectivity at the 5-HT2A and 5HT2C receptors in that it activates the signal transduction enzyme phospholipase A2 instead of activating the enzyme phospholipase C as the endogenous ligand serotonin does. Exactly how LSD produces its effects is unknown, but it is thought that it works by increasing glutamate release in the cerebral cortex and therefore excitation in this area, specifically in layers IV and V. LSD, like many other drugs of recreational use, has been shown to activate DARPP-32-related pathways. The drug enhances dopamine D2 receptor protomer recognition and signaling of D2–5-HT2A receptor complexes, which may contribute to its psychotic effects.
The crystal structure of LSD bound in its active state to a serotonin receptor, specifically the 5-HT2B receptor, has recently (2017) been elucidated for the first time. The LSD-bound 5-HT2B receptor is regarded as an excellent model system for the 5-HT2A receptor and the structure of the LSD-bound 5-HT2B receptor was used in the study as a template to determine the structural features necessary for the activity of LSD at the 5-HT2A receptor. The diethylamide moiety of LSD was found to be a key component for its activity, which is in accordance with the fact that the related lysergamide lysergic acid amide (LSA) is far less hallucinogenic in comparison. LSD was found to stay bound to both the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors for an exceptionally long amount of time, which may be responsible for its long duration of action in spite of its relatively short terminal half-life. The extracellular loop 2 leucine 209 residue of the 5-HT2B receptor forms a 'lid' over LSD that appears to trap it in the receptor, and this was implicated in the potency and functional selectivity of LSD and its very slow dissociation rate from the 5-HT2 receptors.
Pharmacokinetics
The effects of LSD normally last between 6 and 12 hours depending on dosage, tolerance, body weight, and age. The Sandoz prospectus for "Delysid" warned: "intermittent disturbances of affect may occasionally persist for several days." Contrary to early reports and common belief, LSD effects do not last longer than the amount of time significant levels of the drug are present in the blood. Aghajanian and Bing (1964) found LSD had an elimination half-life of only 175 minutes (about 3 hours). However, using more accurate techniques, Papac and Foltz (1990) reported that 1 µg/kg oral LSD given to a single male volunteer had an apparent plasma half-life of 5.1 hours, with a peak plasma concentration of 5 ng/mL at 3 hours post-dose.The pharmacokinetics of LSD were not properly determined until 2015, which is not surprising for a drug with the kind of low-μg potency that LSD possesses. In a sample of 16 healthy subjects, a single mid-range 200 μg oral dose of LSD was found to produce mean maximal concentrations of 4.5 ng/mL at a median of 1.5 hours (range 0.5–4 hours) post-administration. After attainment of peak levels, concentrations of LSD decreased following first-order kinetics with a terminal half-life of 3.6 hours for up to 12 hours and then with slower elimination with a terminal half-life of 8.9 hours thereafter. The effects of the dose of LSD given lasted for up to 12 hours and were closely correlated with the concentrations of LSD present in circulation over time, with no acute tolerance observed. Only 1% of the drug was eliminated in urine unchanged whereas 13% was eliminated as the major metabolite 2-oxo-3-hydroxy-LSD (O-H-LSD) within 24 hours. O-H-LSD is formed by cytochrome P450 enzymes, although the specific enzymes involved are unknown, and it does not appear to be known whether O-H-LSD is pharmacologically active or not. The oral bioavailability of LSD was crudely estimated as approximately 71% using previous data on intravenous administration of LSD. The sample was equally divided between male and female subjects and there were no significant sex differences observed in the pharmacokinetics of LSD.
Chemistry
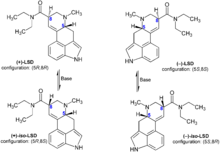
The four possible stereoisomers of LSD. Only (+)-LSD is psychoactive.
LSD is a chiral compound with two stereocenters at the carbon atoms C-5 and C-8, so that theoretically four different optical isomers of LSD could exist. LSD, also called (+)-D-LSD, has the absolute configuration (5R,8R). The C-5 isomers of lysergamides do not exist in nature and are not formed during the synthesis from d-lysergic acid. Retrosynthetically, the C-5 stereocenter could be analysed as having the same configuration of the alpha carbon of the naturally occurring amino acid L-tryptophan, the precursor to all biosynthetic ergoline compounds.
However, LSD and iso-LSD, the two C-8 isomers, rapidly interconvert in the presence of bases, as the alpha proton is acidic and can be deprotonated and reprotonated. Non-psychoactive iso-LSD which has formed during the synthesis can be separated by chromatography and can be isomerized to LSD.
Pure salts of LSD are triboluminescent, emitting small flashes of white light when shaken in the dark. LSD is strongly fluorescent and will glow bluish-white under UV light.
Synthesis
LSD is an ergoline derivative. It is commonly synthesized by reacting diethylamine with an activated form of lysergic acid. Activating reagents include phosphoryl chloride and peptide coupling reagents. Lysergic acid is made by alkaline hydrolysis of lysergamides like ergotamine, a substance usually derived from the ergot fungus on agar plate; or, theoretically possible, but impractical and uncommon, from ergine (lysergic acid amide, LSA) extracted from morning glory seeds. Lysergic acid can also be produced synthetically, eliminating the need for ergotamines.Dosage
White on White blotters (WoW) for sublingual administration
A single dose of LSD may be between 40 and 500 micrograms—an amount roughly equal to one-tenth the mass of a grain of sand. Threshold effects can be felt with as little as 25 micrograms of LSD. Dosages of LSD are measured in micrograms (µg), or millionths of a gram. By comparison, dosages of most drugs, both recreational and medicinal, are measured in milligrams (mg), or thousandths of a gram. For example, an active dose of mescaline, roughly 0.2 to 0.5 g, has effects comparable to 100 µg or less of LSD.
In the mid-1960s, the most important black market LSD manufacturer (Owsley Stanley) distributed acid at a standard concentration of 270 µg, while street samples of the 1970s contained 30 to 300 µg. By the 1980s, the amount had reduced to between 100 and 125 µg, dropping more in the 1990s to the 20–80 µg range, and even more in the 2000s (decade).
Reactivity and degradation
"LSD," writes the chemist Alexander Shulgin, "is an unusually fragile molecule… As a salt, in water, cold, and free from air and light exposure, it is stable indefinitely."LSD has two labile protons at the tertiary stereogenic C5 and C8 positions, rendering these centres prone to epimerisation. The C8 proton is more labile due to the electron-withdrawing carboxamide attachment, but removal of the chiral proton at the C5 position (which was once also an alpha proton of the parent molecule tryptophan) is assisted by the inductively withdrawing nitrogen and pi electron delocalisation with the indole ring.
LSD also has enamine-type reactivity because of the electron-donating effects of the indole ring. Because of this, chlorine destroys LSD molecules on contact; even though chlorinated tap water contains only a slight amount of chlorine, the small quantity of compound typical to an LSD solution will likely be eliminated when dissolved in tap water. The double bond between the 8-position and the aromatic ring, being conjugated with the indole ring, is susceptible to nucleophilic attacks by water or alcohol, especially in the presence of light. LSD often converts to "lumi-LSD", which is inactive in human beings.
A controlled study was undertaken to determine the stability of LSD in pooled urine samples. The concentrations of LSD in urine samples were followed over time at various temperatures, in different types of storage containers, at various exposures to different wavelengths of light, and at varying pH values. These studies demonstrated no significant loss in LSD concentration at 25 °C for up to four weeks. After four weeks of incubation, a 30% loss in LSD concentration at 37 °C and up to a 40% at 45 °C were observed. Urine fortified with LSD and stored in amber glass or nontransparent polyethylene containers showed no change in concentration under any light conditions. Stability of LSD in transparent containers under light was dependent on the distance between the light source and the samples, the wavelength of light, exposure time, and the intensity of light. After prolonged exposure to heat in alkaline pH conditions, 10 to 15% of the parent LSD epimerized to iso-LSD. Under acidic conditions, less than 5% of the LSD was converted to iso-LSD. It was also demonstrated that trace amounts of metal ions in buffer or urine could catalyze the decomposition of LSD and that this process can be avoided by the addition of EDTA.
Detection in body fluids
LSD may be quantified in urine as part of a drug abuse testing program, in plasma or serum to confirm a diagnosis of poisoning in hospitalized victims or in whole blood to assist in a forensic investigation of a traffic or other criminal violation or a case of sudden death. Both the parent drug and its major metabolite are unstable in biofluids when exposed to light, heat or alkaline conditions and therefore specimens are protected from light, stored at the lowest possible temperature and analyzed quickly to minimize losses.The apparent plasma half life of LSD is considered to be around 5.1 hours with peak plasma concentrations occurring 3 hours after administration.
History
... affected by a remarkable restlessness, combined with a slight dizziness. At home I lay down and sank into a not unpleasant intoxicated-like condition, characterized by an extremely stimulated imagination. In a dreamlike state, with eyes closed (I found the daylight to be unpleasantly glaring), I perceived an uninterrupted stream of fantastic pictures, extraordinary shapes with intense, kaleidoscopic play of colors. After some two hours this condition faded away. — Albert Hofmann, on his first experience with LSD
LSD was first synthesized on November 16, 1938 by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann at the Sandoz Laboratories in Basel, Switzerland as part of a large research program searching for medically useful ergot alkaloid derivatives. LSD's psychedelic properties were discovered 5 years later when Hofmann himself accidentally ingested an unknown quantity of the chemical. The first intentional ingestion of LSD occurred on April 19, 1943, when Hofmann ingested 250 µg of LSD. He said this would be a threshold dose based on the dosages of other ergot alkaloids. Hofmann found the effects to be much stronger than he anticipated. Sandoz Laboratories introduced LSD as a psychiatric drug in 1947 and marketed LSD as a psychiatric panacea, hailing it "as a cure for everything from schizophrenia to criminal behavior, ‘sexual perversions,’ and alcoholism.”
Albert Hofmann in 2006
Beginning in the 1950s, the US Central Intelligence Agency began a research program code named Project MKULTRA. Experiments included administering LSD to CIA employees, military personnel, doctors, other government agents, prostitutes, mentally ill patients, and members of the general public in order to study their reactions, usually without the subjects' knowledge. The project was revealed in the US congressional Rockefeller Commission report in 1975.
In 1963, the Sandoz patents expired on LSD. Several figures, including Aldous Huxley, Timothy Leary, and Al Hubbard, began to advocate the consumption of LSD. LSD became central to the counterculture of the 1960s. In the early 1960s the use of LSD and other hallucinogens was advocated by new proponents of consciousness expansion such as Leary, Huxley, Alan Watts and Arthur Koestler, and according to L. R. Veysey they profoundly influenced the thinking of the new generation of youth.
On October 24, 1968, possession of LSD was made illegal in the United States. The last FDA approved study of LSD in patients ended in 1980, while a study in healthy volunteers was made in the late 1980s. Legally approved and regulated psychiatric use of LSD continued in Switzerland until 1993.
Society and culture
Counterculture, music and art
Psychedelic art attempts to capture the visions experienced on a psychedelic trip
By the mid-1960s, the youth countercultures in California, particularly in San Francisco, had adopted the use of hallucinogenic drugs, with the first major underground LSD factory established by Owsley Stanley. From 1964, the Merry Pranksters, a loose group that developed around novelist Ken Kesey, sponsored the Acid Tests, a series of events primarily staged in or near San Francisco, involving the taking of LSD (supplied by Stanley), accompanied by light shows, film projection and discordant, improvised music known as the psychedelic symphony. The Pranksters helped popularize LSD use, through their road trips across America in a psychedelically-decorated converted school bus, which involved distributing the drug and meeting with major figures of the beat movement, and through publications about their activities such as Tom Wolfe's The Electric Kool-Aid Acid Test (1968). In both music and art, the influence of LSD was soon being more widely seen and heard thanks to the bands that participated in the Acid Tests and related events, including the Grateful Dead, Jefferson Airplane and Big Brother and the Holding Company, and through the inventive poster and album art of San Francisco-based artists like Rick Griffin, Victor Moscoso, Bonnie MacLean, Stanley Mouse and Alton Kelley, and Wes Wilson, meant to evoke the visual experience of an LSD trip.
In San Francisco's Haight-Ashbury neighborhood, brothers Ron and Jay Thelin opened the Psychedelic Shop in January 1966. The Thelins' store is regarded as the first ever head shop. The Thelins opened the store to promote safe use of LSD, which was then still legal in California. The Psychedelic Shop helped to further popularize LSD in the Haight and to make the neighborhood the unofficial capital of the hippie counterculture in the United States. Ron Thelin was also involved in organizing the Love Pageant rally, a protest held in Golden Gate park to protest California's newly adopted ban on LSD in October 1966. At the rally, hundreds of attendees took acid in unison. Although the Psychedelic Shop closed after barely a year-and-a-half in business, its role in popularizing LSD was considerable.
A similar and connected nexus of LSD use in the creative arts developed around the same time in London. A key figure in this phenomenon in the UK was British academic Michael Hollingshead, who first tried LSD in America in 1961 while he was the Executive Secretary for the Institute of British-American Cultural Exchange. After being given a large quantity of pure Sandoz LSD (which was still legal at the time) and experiencing his first "trip", Hollingshead contacted Aldous Huxley, who suggested that he get in touch with Harvard academic Timothy Leary, and over the next few years, in concert with Leary and Richard Alpert, Hollingshead played a major role in their famous LSD research at Millbrook before moving to New York City, where he conducted his own LSD experiments. In 1965 Hollingshead returned to the UK and founded the World Psychedelic Center in Chelsea, London. Among the many famous people in the UK that Hollingshead is reputed to have introduced to LSD are artist and Hipgnosis founder Storm Thorgerson, and musicians Donovan, Keith Richards, Paul McCartney, John Lennon, and George Harrison. Although establishment concern about the new drug led to it being declared an illegal drug by the Home Secretary in 1966, LSD was soon being used widely in the upper echelons of the British art and music scene, including members of the Beatles, the Rolling Stones, the Moody Blues, the Small Faces, Pink Floyd, Jimi Hendrix and others, and the products of these experiences were soon being both heard and seen by the public with singles like The Small Faces' "Itchycoo Park" and LPs like the Beatles' Sgt Pepper's Lonely Hearts Club Band and Cream's Disraeli Gears, which featured music that showed the obvious influence of the musicians' recent psychedelic excursions, and which were packaged in elaborately-designed album covers that featured vividly-coloured psychedelic artwork by artists like Peter Blake, Martin Sharp, Hapshash and the Coloured Coat (Nigel Waymouth and Michael English) and art/music collective "The Fool".
In the 1960s, musicians from psychedelic music and psychedelic rock bands began to refer (at first indirectly, and later explicitly) to the drug and attempted to recreate or reflect the experience of taking LSD in their music. A number of features are often included in psychedelic music. Exotic instrumentation, with a particular fondness for the sitar and tabla are common. Electric guitars are used to create feedback, and are played through wah wah and fuzzbox effect pedals. Elaborate studio effects are often used, such as backwards tapes, panning, phasing, long delay loops, and extreme reverb. In the 1960s there was a use of primitive electronic instruments such as early synthesizers and the theremin. Later forms of electronic psychedelia also employed repetitive computer-generated beats. Songs allegedly referring to LSD include John Prine's "Illegal Smile" and The Beatles' song Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds, although the authors of the latter song repeatedly denied this claim. Psychedelic experiences were also reflected in psychedelic art, literature and film.
LSD had a strong influence on the Grateful Dead and the culture of Deadheads, as well as the impact for artist Keith Haring, early techno music, and the jam band Phish.
Legal status
The United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances (adopted in 1971) requires the signing parties to prohibit LSD. Hence, it is illegal in all countries that were parties to the convention, including the United States, Australia, New Zealand, and most of Europe. However, enforcement of those laws varies from country to country. Medical and scientific research with LSD in humans is permitted under the 1971 UN Convention.Australia
LSD is a Schedule 9 prohibited substance in Australia under the Poisons Standard (February 2017). A Schedule 9 substance is defined as a substance which may be abused or misused, the manufacture, possession, sale or use of which should be prohibited by law except when required for medical or scientific research, or for analytical, teaching or training purposes with approval of Commonwealth and/or State or Territory Health Authorities.In Western Australia section 9 of the Misuse of Drugs Act 1981 provides for summary trial before a magistrate for possession of less than 0.004g; section 11 provides rebuttable presumptions of intent to sell or supply if the quantity is 0.002g or more, or of possession for the purpose of trafficking if 0.01g.
Canada
In Canada, LSD is a controlled substance under Schedule III of the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act. Every person who seeks to obtain the substance, without disclosing authorization to obtain such substances 30 days before obtaining another prescription from a practitioner, is guilty of an indictable offense and liable to imprisonment for a term not exceeding 3 years. Possession for purpose of trafficking is an indictable offense punishable by imprisonment for 10 years.United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, LSD is a Schedule 1 Class 'A' drug. This means it has no recognized legitimate uses and possession of the drug without a license is punishable with 7 years' imprisonment and/or an unlimited fine, and trafficking is punishable with life imprisonment and an unlimited fine (see main article on drug punishments Misuse of Drugs Act 1971).In 2000, after consultation with members of the Royal College of Psychiatrists' Faculty of Substance Misuse, the UK Police Foundation issued the Runciman Report which recommended "the transfer of LSD from Class A to Class B".
In November 2009, the UK Transform Drug Policy Foundation released in the House of Commons a guidebook to the legal regulation of drugs, After the War on Drugs: Blueprint for Regulation, which details options for regulated distribution and sale of LSD and other psychedelics.
United States
LSD is Schedule I in the United States, according to the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. This means LSD is illegal to manufacture, buy, possess, process, or distribute without a license from the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). By classifying LSD as a Schedule I substance, the DEA holds that LSD meets the following three criteria: it is deemed to have a high potential for abuse; it has no legitimate medical use in treatment; and there is a lack of accepted safety for its use under medical supervision. There are no documented deaths from chemical toxicity; most LSD deaths are a result of behavioral toxicity.There can also be substantial discrepancies between the amount of chemical LSD that one possesses and the amount of possession with which one can be charged in the US. This is because LSD is almost always present in a medium (e.g. blotter or neutral liquid), and the amount that can be considered with respect to sentencing is the total mass of the drug and its medium. This discrepancy was the subject of 1995 United States Supreme Court case, Neal v. United States.
Lysergic acid and lysergic acid amide, LSD precursors, are both classified in Schedule III of the Controlled Substances Act. Ergotamine tartrate, a precursor to lysergic acid, is regulated under the Chemical Diversion and Trafficking Act.
Mexico
In April 2009, the Mexican Congress approved changes in the General Health Law that decriminalized the possession of illegal drugs for immediate consumption and personal use, allowing a person to possess a moderate amount of LSD. The only restriction is that people in possession of drugs should not be within a 300-meter radius of schools, police departments, or correctional facilities. Marijuana, along with cocaine, opium, heroin, and other drugs were also decriminalized; their possession is not considered a crime as long as the dose does not exceed the limit established in the General Health Law. Many question this, as cocaine is as synthesised as heroin, and both are produced as extracts from plants. The law establishes very low amount thresholds and strictly defines personal dosage. For those arrested with more than the threshold allowed by the law this can result in heavy prison sentences, as they will be assumed to be small traffickers even if there are no other indications that the amount was meant for selling.Czech Republic
In the Czech Republic, until 31 December 1998 only drug possession "for other person" (i.e. intent to sell) was criminal (apart from production, importation, exportation, offering or mediation, which was and remains criminal) while possession for personal use remained legal.On 1 January 1999, an amendment of the Criminal Code, which was necessitated in order to align the Czech drug rules with the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, became effective, criminalizing possession of "amount larger than small" also for personal use (Art. 187a of the Criminal Code) while possession of small amounts for personal use became a misdemeanor.
The judicial practice came to the conclusion that the "amount larger than small" must be five to ten times larger (depending on drug) than a usual single dose of an average consumer.
Under the Regulation No. 467/2009 Coll, possession of less than 5 doses of LSD was to be considered smaller than large for the purposes of the Criminal Code and was to be treated as a misdemeanor subject to a fine equal to a parking ticket.
Ecuador
According to the 2008 Constitution of Ecuador, in its Article 364, the Ecuadorian state does not see drug consumption as a crime but only as a health concern. Since June 2013 the State drugs regulatory office CONSEP has published a table which establishes maximum quantities carried by persons so as to be considered in legal possession and that person as not a seller of drugs. The "CONSEP established, at their latest general meeting, that the 0.020 milligrams of LSD shall be considered the maximum consumer amount.Economics
Production
Glassware seized by the DEA
An active dose of LSD is very minute, allowing a large number of doses to be synthesized from a comparatively small amount of raw material. Twenty five kilograms of precursor ergotamine tartrate can produce 5–6 kg of pure crystalline LSD; this corresponds to 100 million doses. Because the masses involved are so small, concealing and transporting illicit LSD is much easier than smuggling cocaine, cannabis, or other illegal drugs.
Manufacturing LSD requires laboratory equipment and experience in the field of organic chemistry. It takes two to three days to produce 30 to 100 grams of pure compound. It is believed that LSD is not usually produced in large quantities, but rather in a series of small batches. This technique minimizes the loss of precursor chemicals in case a step does not work as expected.
Forms
Five doses of LSD, often called a "five strip"
LSD is produced in crystalline form and then mixed with excipients or redissolved for production in ingestible forms. Liquid solution is either distributed in small vials or, more commonly, sprayed onto or soaked into a distribution medium. Historically, LSD solutions were first sold on sugar cubes, but practical considerations forced a change to tablet form. Appearing in 1968 as an orange tablet measuring about 6 mm across, "Orange Sunshine" acid was the first largely available form of LSD after its possession was made illegal. Tim Scully, a prominent chemist, made some of these tablets, but said that most "Sunshine" in the USA came by way of Ronald Stark, who imported approximately thirty-five million doses from Europe.
Over a period of time, tablet dimensions, weight, shape and concentration of LSD evolved from large (4.5–8.1 mm diameter), heavyweight (≥150 mg), round, high concentration (90–350 µg/tab) dosage units to small (2.0–3.5 mm diameter) lightweight (as low as 4.7 mg/tab), variously shaped, lower concentration (12–85 µg/tab, average range 30–40 µg/tab) dosage units. LSD tablet shapes have included cylinders, cones, stars, spacecraft, and heart shapes. The smallest tablets became known as "Microdots".
After tablets came "computer acid" or "blotter paper LSD", typically made by dipping a preprinted sheet of blotting paper into an LSD/water/alcohol solution. More than 200 types of LSD tablets have been encountered since 1969 and more than 350 blotter paper designs have been observed since 1975. About the same time as blotter paper LSD came "Windowpane" (AKA "Clearlight"), which contained LSD inside a thin gelatin square a quarter of an inch (6 mm) across. LSD has been sold under a wide variety of often short-lived and regionally restricted street names including Acid, Trips, Uncle Sid, Blotter, Lucy, Alice and doses, as well as names that reflect the designs on the sheets of blotter paper. Authorities have encountered the drug in other forms—including powder or crystal, and capsule.
Modern distribution
LSD manufacturers and traffickers in the United States can be categorized into two groups: A few large-scale producers, and an equally limited number of small, clandestine chemists, consisting of independent producers who, operating on a comparatively limited scale, can be found throughout the country. As a group, independent producers are of less concern to the Drug Enforcement Administration than the larger groups because their product reaches only local markets.Many LSD dealers and chemists describe a religious or humanitarian purpose that motivates their illicit activity. Nicholas Schou's book Orange Sunshine: The Brotherhood of Eternal Love and Its Quest to Spread Peace, Love, and Acid to the World describes one such group, the Brotherhood of Eternal Love. The group was a major American LSD trafficking group in the late 1960s and early 1970s.
In the second half of the 20th century, dealers and chemists loosely associated with the Grateful Dead like Owsley Stanley, Nicholas Sand, Karen Horning, Sarah Maltzer, "Dealer McDope," and Leonard Pickard played an essential role in distributing LSD.
Mimics
LSD blotter acid mimic actually containing DOC
Different blotters which could possibly be mimics
Since 2005, law enforcement in the United States and elsewhere has seized several chemicals and combinations of chemicals in blotter paper which were sold as LSD mimics, including DOB, a mixture of DOC and DOI, 25I-NBOMe, and a mixture of DOC and DOB. Street users of LSD are often under the impression that blotter paper which is actively hallucinogenic can only be LSD because that is the only chemical with low enough doses to fit on a small square of blotter paper. While it is true that LSD requires lower doses than most other hallucinogens, blotter paper is capable of absorbing a much larger amount of material. The DEA performed a chromatographic analysis of blotter paper containing 2C-C which showed that the paper contained a much greater concentration of the active chemical than typical LSD doses, although the exact quantity was not determined. Blotter LSD mimics can have relatively small dose squares; a sample of blotter paper containing DOC seized by Concord, California police had dose markings approximately 6 mm apart. Several deaths have been attributed to 25I-NBOMe.
Research
A number of organizations—including the Beckley Foundation, MAPS, Heffter Research Institute and the Albert Hofmann Foundation—exist to fund, encourage and coordinate research into the medicinal and spiritual uses of LSD and related psychedelics. New clinical LSD experiments in humans started in 2009 for the first time in 35 years. As it is illegal in many areas of the world, potential medical uses are difficult to study.In 2001 the United States Drug Enforcement Administration stated that LSD "produces no aphrodisiac effects, does not increase creativity, has no lasting positive effect in treating alcoholics or criminals, does not produce a 'model psychosis', and does not generate immediate personality change." More recently, experimental uses of LSD have included the treatment of alcoholism and pain and cluster headache relief.
Psychedelic therapy
In the 1950s and 1960s LSD was used in psychiatry to enhance psychotherapy known as psychedelic therapy. Some psychiatrists believed LSD was especially useful at helping patients to "unblock" repressed subconscious material through other psychotherapeutic methods, and also for treating alcoholism. One study concluded, "The root of the therapeutic value of the LSD experience is its potential for producing self-acceptance and self-surrender," presumably by forcing the user to face issues and problems in that individual's psyche.Two recent reviews concluded that conclusions drawn from most of these early trials are unreliable due to serious methodological flaws. These include the absence of adequate control groups, lack of followup, and vague criteria for therapeutic outcome. In many cases studies failed to convincingly demonstrate whether the drug or the therapeutic interaction was responsible for any beneficial effects.
In recent years organizations like the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies have renewed clinical research of LSD.
Other uses
In the 1950s and 1960s, some psychiatrists (e.g. Oscar Janiger) explored the potential effect of LSD on creativity. Experimental studies attempted to measure the effect of LSD on creative activity and aesthetic appreciation.Since 2008 there has been ongoing research into using LSD to alleviate anxiety for terminally ill cancer patients coping with their impending deaths.
A 2012 meta-analysis found evidence that a single dose of LSD in conjunction with various alcoholism treatment programs was associated with a decrease in alcohol abuse, lasting for several months, but no effect was seen at one year. Adverse events included seizure, moderate confusion and agitation, nausea, vomiting, and acting in a bizarre fashion.
LSD has been used as a treatment for cluster headaches with positive results in some small studies.
Notable individuals
Some notable individuals have commented publicly on their experiences with LSD. Some of these comments date from the era when it was legally available in the US and Europe for non-medical uses, and others pertain to psychiatric treatment in the 1950s and 1960s. Still others describe experiences with illegal LSD, obtained for philosophic, artistic, therapeutic, spiritual, or recreational purposes.- Richard Feynman, a notable physicist at California Institute of Technology, tried LSD during his professorship at Caltech. Feynman largely sidestepped the issue when dictating his anecdotes; he mentions it in passing in the "O Americano, Outra Vez" section.
- Jerry Garcia stated in a July 3, 1989 interview for Relix Magazine, in response to the question "Have your feelings about LSD changed over the years?," "They haven't changed much. My feelings about LSD are mixed. It's something that I both fear and that I love at the same time. I never take any psychedelic, have a psychedelic experience, without having that feeling of, "I don't know what's going to happen." In that sense, it's still fundamentally an enigma and a mystery."
- Bill Gates implied in an interview with Playboy that he tried LSD during his youth.
- Aldous Huxley, author of Brave New World, became a user of psychedelics after moving to Hollywood. He was at the forefront of the counterculture's experimentation with psychedelic drugs, which led to his 1954 work The Doors of Perception. Dying from cancer, he asked his wife on 22 November 1963 to inject him with 100 µg of LSD. He died later that day.
- Steve Jobs, co-founder and former CEO of Apple Inc., said, "Taking LSD was a profound experience, one of the most important things in my life."
- In a 2004 interview, Paul McCartney said that The Beatles' songs "Day Tripper" and "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds" were inspired by LSD trips. Nonetheless, John Lennon consistently stated over the course of many years that the fact that the initials of "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds" spelled out L-S-D was a coincidence (the title came from a picture drawn by his son Julian) and that the band members did not notice until after the song had been released, and Paul McCartney corroborated that story. John Lennon, George Harrison, and Ringo Starr also experimented with the drug, although McCartney cautioned that "it's easy to overestimate the influence of drugs on the Beatles' music."
- Kary Mullis is reported to credit LSD with helping him develop DNA amplification technology, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993.
- Oliver Sacks, a neurologist famous for writing best-selling case histories about his patients' disorders and unusual experiences, talks about his own experiences with LSD and other perception altering chemicals, in his book, Hallucinations.