People with HIV-AIDS up to 2016
The spread of HIV/AIDS has affected millions of people worldwide; AIDS is considered a pandemic. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that in 2016 there were 36.7 million people worldwide living with HIV/AIDS, with 1.8 million new HIV infections per year and 1 million deaths due to AIDS. In 2016, UNAIDS
estimated: 2.1 million children (less than 15 years) worldwide were living
with HIV/ AIDS and 17.8 million women (15+ years) worldwide were living
with HIV/ AIDS. In 2011, UNAIDS estimated: 1.8 million new HIV infections in sub-Saharan Africa compared to 2.4 million new infections in 2001 a 25% decline.
Between 2005-2011, the number of deaths from AIDS-related causes in
sub-Saharan Africa declined by 32%,1.8 million to 1.2 million. From 2009
and 2011, the number of children newly infected with HIV fell in sub-Saharan Africa fell by 24%.
Misconceptions about HIV and AIDS arise from several
different sources, from simple ignorance and misunderstandings about
scientific knowledge regarding HIV infections and the cause of AIDS to
misinformation propagated by individuals and groups with ideological
stances that deny
a causative relationship between HIV infection and the development of
AIDS. Below is a list and explanations of some common misconceptions and
their rebuttals.
The relationship between HIV and AIDS
HIV is the same as AIDS
HIV is an acronym for human immunodeficiency virus, which is the virus that causes AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Contracting HIV can lead to the development of AIDS or stage 3 HIV, which causes serious damage to the immune system. While this virus is the underlying cause of AIDS, not all HIV-positive individuals have AIDS, as HIV can remain in a latent state for many years.
If undiagnosed or left untreated, HIV usually progresses to AIDS,
defined as possessing a CD4+ lymphocyte count under 200 cells/μl or HIV
infection plus co-infection with an AIDS-defining opportunistic
infection. HIV cannot be cured, but it can be treated, and its
transmission can be halted. Treating HIV can prevent new infections,
which is the key to ultimately defeating AIDS.
Treatment
Cure
A bottle containing Stribild tablets (medication used to treat HIV). Stribild is a combination drug containing tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, emtricitabine, elvitegravir and cobicistat.
Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy (HAART) in many cases allows the stabilization of the patient's symptoms, partial recovery of CD4+ T-cell levels, and reduction in viremia
(the level of virus in the blood) to low or near-undetectable levels.
Disease-specific drugs can also alleviate symptoms of AIDS and even cure
specific AIDS-defining conditions in some cases. Medical treatment can
reduce HIV infection in many cases to a survivable chronic condition.
However, these advances do not constitute a cure, since current
treatment regimens cannot eradicate latent HIV from the body.
High levels of HIV-1 (often HAART-resistant) develop if treatment
is stopped, if compliance with treatment is inconsistent, or if the
virus spontaneously develops resistance to an individual's regimen. Antiretroviral treatment known as post-exposure prophylaxis reduces the chance of acquiring an HIV infection when administered within 72 hours of exposure to HIV.
These problems mean that while HIV-positive people with low viremia are
less likely to infect others, the chance of transmission always exists.
In addition, people on HAART may still become sick.
Sexual intercourse with a virgin will cure AIDS
The myth that sex with a virgin will cure AIDS is prevalent in South Africa. Sex with an uninfected virgin does not cure an HIV-infected
person, and such contact will expose the uninfected individual to HIV,
potentially further spreading the disease. This myth has gained
considerable notoriety as the perceived reason for certain sexual abuse and child molestation occurrences, including the rape of infants, in South Africa.
Sexual intercourse with an animal will avoid or cure AIDS
In 2002, the National Council of Societies for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (NSPCA) in Johannesburg, South Africa, recorded beliefs amongst youths that sex with animals is a means to avoid AIDS or cure it if infected.
As with "virgin cure" beliefs, there is no scientific evidence
suggesting a sexual act can actually cure AIDS, and no plausible
mechanism by which it could do so has ever been proposed. While the risk
of contracting HIV via sex with animals is likely much lower than with
humans due to HIV's inability to infect animals, the practice of
bestiality still has the ability to infect humans with other fatal zoonotic diseases.
HIV antibody testing is unreliable
Diagnosis of infection using antibody testing is a well-established technique in medicine. HIV antibody
tests exceed the performance of most other infectious disease tests in
both sensitivity (the ability of the screening test to give a positive
finding when the person tested truly has the disease) and specificity
(the ability of the test to give a negative finding when the subjects
tested are free of the disease under study). Many current HIV antibody
tests have sensitivity and specificity in excess of 96% and are
therefore extremely reliable.
While most patients with HIV show an antibody response after six weeks,
window periods vary and may occasionally be as long as three months.
Progress in testing methodology has enabled detection of viral
genetic material, antigens, and the virus itself in bodily fluids and
cells. While not widely used for routine testing due to high cost and
requirements in laboratory equipment, these direct testing techniques
have confirmed the validity of the antibody tests.
Positive HIV antibody tests are usually followed up by retests and tests for antigens, viral genetic material and the virus itself, providing confirmation of actual infection.
HIV infection
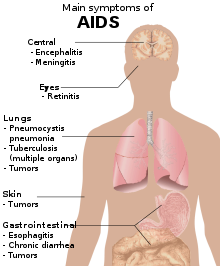
Symptoms of acute HIV infection
HIV can be spread through casual contact with an HIV infected individual
Symptoms of AIDS
One cannot become infected with HIV through normal contact in social
settings, schools, or in the workplace. One cannot be infected by
shaking someone's hand, by hugging or "dry" kissing someone, by using
the same toilet or drinking from the same glass as an HIV-infected person, or by being exposed to coughing or sneezing by an infected person. Saliva
carries a negligible viral load, so even open-mouthed kissing is
considered a low risk. However, if the infected partner or both of the
performers have blood in their mouth due to cuts, open sores, or gum disease, the risk is higher. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
(CDC) has only recorded one case of possible HIV transmission through
kissing (involving an HIV-infected man with significant gum disease and a
sexual partner also with significant gum disease), and the Terence Higgins Trust says that this is essentially a no-risk situation.
Other interactions that could theoretically result in person-to-person transmission include caring for nose bleeds
and home health care procedures, yet there are very few recorded
incidents of transmission occurring in these ways. A handful of cases of
transmission via biting have occurred, though this is extremely rare.
HIV-positive individuals can be detected by their appearance
Due
to media images of the effects of AIDS, many people believe that
individuals infected with HIV always appear a certain way, or at least
appear different from an uninfected, healthy person. In fact, disease
progression can occur over a long period of time before the onset of
symptoms, and as such, HIV infections cannot be detected based on
appearance.
HIV cannot be transmitted through oral sex
Contracting HIV through oral sex is not impossible, but it is much lower than from anal sex and penile–vaginal intercourse.
HIV is transmitted by mosquitoes
When mosquitoes
bite a person, they do not inject the blood of a previous victim into
the person they bite next. Mosquitoes do, however, inject their saliva into their victims, which may carry diseases such as dengue fever, malaria, yellow fever, or West Nile virus and can infect a bitten person with these diseases. HIV is not transmitted in this manner.
On the other hand, a mosquito may have HIV-infected blood in its gut,
and if swatted on the skin of a human who then scratches it,
transmission is hypothetically possible, though this risk is extremely small, and no cases have yet been identified through this route.
HIV survives for only a short time outside the body
HIV can survive at room temperature outside the body for hours if dry (provided that initial concentrations are high), and for weeks if wet (in used syringes/needles).
However, the amounts typically present in bodily fluids do not survive
nearly as long outside the body—generally no more than a few minutes if
dry. Again, the amount of time is longer if wet, especially in syringes/needles and related equipment.
HIV can infect only homosexual men and drug users
Irrespective to sexual orientation, HIV can transmit from one person
to another if an engaging partner is HIV positive. In the United States,
the main route of infection is via homosexual anal sex, while for women transmission is primarily through heterosexual contact. Nevertheless, HIV can infect anybody, regardless of age, sex, ethnicity, or sexual orientation.
It is true that anal sex (regardless of the gender of the receptive
partner) carries a higher risk of infection than most sex acts, but most
penetrative sex acts between any individuals carry some risk. Properly
used condoms can reduce this risk.
An HIV-infected female cannot have children
HIV-infected women remain fertile, although in late stages of HIV disease a pregnant woman may have a higher risk of miscarriage.
Normally, the risk of transmitting HIV to the unborn child is between
15 and 30%. However, this may be reduced to just 2–3% if patients
carefully follow medical guidelines.
HIV cannot be the cause of AIDS because the body develops a vigorous antibody response to the virus
This reasoning ignores numerous examples of viruses other than HIV that can be pathogenic after evidence of immunity appears. Measles virus may persist for years in brain cells, eventually causing a chronic neurologic disease despite the presence of antibodies. Viruses such as Cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex virus, and Varicella zoster
may be activated after years of latency even in the presence of
abundant antibodies. In other animals, viral relatives of HIV with long
and variable latency periods, such as visna virus in sheep, cause central nervous system damage even after the production of antibodies.
HIV has a well-recognized capacity to mutate to evade the ongoing immune response of the host.
Only a small number of CD4+ T-cells are infected by HIV, not enough to damage the immune system
Although
the fraction of CD4+ T-cells that is infected with HIV at any given
time is never high (only a small subset of activated cells serve as
ideal targets of infection), several groups have shown that rapid cycles
of death of infected cells and infection of new target cells occur
throughout the course of the disease. Macrophages and other cell types are also infected with HIV and serve as reservoirs for the virus.
Furthermore, like other viruses, HIV is able to suppress the
immune system by secreting proteins that interfere with it. For example,
HIV's coat protein, gp120, sheds from viral particles and binds to the CD4
receptors of otherwise healthy T-cells; this interferes with the normal
function of these signalling receptors. Another HIV protein, Tat, has been demonstrated to suppress T cell activity.
Infected lymphocytes express the Fas ligand, a cell-surface protein that triggers the death of neighboring uninfected T-cells expressing the Fas receptor.
This "bystander killing" effect shows that great harm can be caused to
the immune system even with a limited number of infected cells.
History of HIV/AIDS
The cover page of MMWR in July 3, 1981. The first major public info regarding (what later became known as) AIDS/HIV.
The current consensus is that HIV was introduced to North America by a Haitian immigrant who contracted it while working in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the early 1960s, or from another person who worked there during that time. In 1981 on June 5, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC) publish a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report
(MMWR), describing cases of a rare lung infection, Pneumocystis carinii
pneumonia (PCP), from five healthy, gay men in Los Angeles. This
edition would later become MMWR's first official reporting of the AIDS epidemic in North America.
By year-end, a cumulative total of 270 reported cases of severe immune
deficiency was founded amid gay men, 121 out of the 270 reported cases
had died.
On September 24 in 1982, CDC started to use the term “AIDS” (acquired
immune deficiency syndrome) for the first time, and released the first
case definition of AIDS: “a disease at least moderately predictive of a
defect in cell-mediated immunity, occurring in a person with no known
case for diminished resistance to that disease.” Than an edition in March 4,1983 of the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report
(MMWR), notes that CDC founded most cases of AIDS have been reported
among homosexual men with multiple sexual partners, injection drug
users, Haitians, and hemophiliacs. The report suggests that AIDS may be
caused by an infectious agent that is transmitted sexually or through
exposure to blood or blood products and issues recommendations for
preventing transmission.
Although most cases founded of HIV/AIDS were founded in gay men on
January 7, 1983 CDC reported cases of AIDS in female sexual partners of
males with AIDS.
In 1984 Scientists identified the virus that causes AIDS, which was
first named after the T-cells affected by the strain and is now called
HIV or human immunodeficiency virus.
Afterwards, A Canadian flight attendant, dubbed "Patient Zero," dies of
AIDS-related complications. His sexual connection to several of the
first victims of HIV is erroneously reported that he is responsible for
introducing the virus into North America. By this time there were 8,000
confirmed cases in the U.S., resulting in an alarming 3,500 deaths.
On September 17,1985 President Ronald Reagan for the first time
mentioned AIDS and vowed in a letter to Congress to make AIDS a priority. In 1987 the FDA approved AZT which is the first antiretroviral drug for treating AIDS.
The Ad Council partners with AMFAR and the National AIDS Network in
1989 launched a national AIDS education campaign. This was the first ad
campaign in the U.S. to use the word "condom." One of the campaign's
slogans were "Using it won't kill you. Not using it might."
Singer Paul Jabara starts the Red Ribbon Foundation in 1991, which
begins distributing ribbons as a symbol of tolerance for those living
with HIV/AIDS.
At the 11th International AIDS Conference in Vancouver, combination
antiretroviral treatment is presented for the first time. These drugs
are shown to be effective against HIV.
Media outlets in 1997 started to report that for the first time since
the epidemic of AIDS/HIV began, the AIDS death rate had declined in the
U.S. thanks to the success of drug therapies.
Researchers from the University of Alabama at Birmingham reported a
discovery in 1999 of HIV-1 in a subspecies of chimpanzee. They believed
this to be the source of the virus and theorize that human hunters
contracted it when exposed to infected blood.
Later in 2003, The FDA approved the first of a new type of anti-HIV
drug called Fuzeon (also known as enfuvirtide or T-20). This drug is
designed to prevent the entry of HIV into human cells.
George W. Bush launched PEPFAR in 2004, the U.S. President's Emergency
Plan to combat AIDS worldwide. "This historic commitment is the largest
by any nation to combat a single disease internationally," according to
the PEPFAR website.
President Obama removed a travel ban in 2009 that prevented
HIV-positive people from entering the U.S. This leads to the
announcement that the International AIDS Conference will be held in the
U.S. for the first time in more than 20 years.
During 2012 UNAIDS announced that new HIV infections had dropped more
than 50% in 25 low- and middle-income countries, and the number of
people getting antiretroviral treatment had increased 63% in the past
two years. More than 34 million people are still living with HIV,
according to global estimates.
Origin of AIDS through human–monkey sexual intercourse
While HIV is most likely a mutated form of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), a disease present only in chimpanzees and African monkeys, highly plausible explanations for the transfer of the disease between species (zoonosis) exist not involving sexual intercourse. In particular, the African chimpanzees and monkeys which carry SIV are often hunted
for food, and epidemiologists theorize that the disease may have
appeared in humans after hunters came into blood-contact with monkeys
infected with SIV that they had killed. The first known instance of HIV in a human was found in a person who died in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1959, and a recent study dates the last common ancestor of HIV and SIV to between 1884 and 1914 by using a molecular clock approach.
Tennessee State Senator Stacey Campfield
was the subject of controversy in 2012 after stating that AIDS was the
result of a human having sexual intercourse with a monkey.
AIDS denialism
There is no AIDS in Africa, as AIDS is nothing more than a new name for old diseases
The diseases that have come to be associated with AIDS in Africa, such as cachexia, diarrheal diseases and tuberculosis have long been severe burdens there. However, high rates of mortality from these diseases, formerly confined to the elderly and malnourished, are now common among HIV-infected young and middle-aged people, including well-educated members of the middle class.
For example, in a study in Côte d'Ivoire, HIV-seropositive individuals with pulmonary tuberculosis were 17 times more likely to die within six months than HIV-seronegative individuals with pulmonary tuberculosis. In Malawi, mortality over three years among children who had received recommended childhood immunizations
and who survived the first year of life was 9.5 times higher among
HIV-seropositive children than among HIV-seronegative children. The
leading causes of death were wasting and respiratory conditions. Elsewhere in Africa, findings are similar.
HIV is not the cause of AIDS
There is broad scientific consensus that HIV is the cause of AIDS, but some individuals reject this consensus, including biologist Peter Duesberg, biochemist David Rasnick, journalist/activist Celia Farber, conservative writer Tom Bethell, and intelligent design advocate Phillip E. Johnson. (Some one-time skeptics have since rejected AIDS denialism, including physiologist Robert Root-Bernstein, and physician and AIDS researcher Joseph Sonnabend.)
A great deal is known about the pathogenesis
of HIV disease, even though important details remain to be elucidated.
However, a complete understanding of the pathogenesis of a disease is
not a prerequisite to knowing its cause. Most infectious agents have
been associated with the disease they cause long before their pathogenic
mechanisms have been discovered. Because research in pathogenesis is
difficult when precise animal models are unavailable, the
disease-causing mechanisms in many diseases, including tuberculosis and hepatitis B, are poorly understood, but the pathogens responsible are very well established.
AZT and other antiretroviral drugs, not HIV, cause AIDS
The vast majority of people with AIDS never received antiretroviral
drugs, including those in developed countries prior to the licensure of AZT in 1987. Even today, very few individuals in developing countries have access to these medications.
In the 1980s, clinical trials
enrolling patients with AIDS found that AZT given as single-drug
therapy conferred a modest (and short-lived) survival advantage compared
to placebo.
Among HIV-infected patients who had not yet developed AIDS,
placebo-controlled trials found that AZT given as a single-drug therapy
delayed, for a year or two, the onset of AIDS-related illnesses. The
lack of excess AIDS cases and death in the AZT arms of these
placebo-controlled trials effectively counters the argument that AZT
causes AIDS.
Subsequent clinical trials found that patients receiving two-drug
combinations had up to 50% increases in time to progression to AIDS and
in survival when compared to people receiving single-drug therapy. In
more recent years, three-drug combination therapies have produced
another 50–80% improvements in progression to AIDS and in survival when
compared to two-drug regimens in clinical trials.
Use of potent anti-HIV combination therapies has contributed to
dramatic reductions in the incidence of AIDS and AIDS-related deaths in
populations where these drugs are widely available, an effect which
would be unlikely if antiretroviral drugs caused AIDS.
Behavioral factors such as recreational drug use and multiple sexual partners—not HIV—account for AIDS
The proposed behavioral causes of AIDS, such as multiple sexual partners and long-term recreational drug use,
have existed for many years. The epidemic of AIDS, characterized by the
occurrence of formerly rare opportunistic infections such as Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), did not occur in the United States until a previously unknown human retrovirus—HIV—spread through certain communities.
Compelling evidence against the hypothesis that behavioral
factors cause AIDS comes from recent studies that have followed cohorts
of homosexual
men for long periods of time and found that only HIV-seropositive men
develop AIDS. For example, in a prospectively studied cohort in Vancouver, British Columbia,
715 homosexual men were followed for a median of 8.6 years. Among 365
HIV-positive individuals, 136 developed AIDS. No AIDS-defining illnesses
occurred among 350 seronegative men, despite the fact that these men
reported appreciable use of nitrite inhalants ("poppers") and other recreational drugs, and frequent receptive anal intercourse (Schechter et al., 1993).
Other studies show that among homosexual men and injection-drug
users, the specific immune deficit that leads to AIDS—a progressive and
sustained loss of CD4+ T-cells—is extremely rare in the absence of other immunosuppressive conditions. For example, in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study,
more than 22,000 T-cell determinations in 2,713 HIV-seronegative
homosexual men revealed only one individual with a CD4+ T-cell count
persistently lower than 300 cells/µl of blood, and this individual was
receiving immunosuppressive therapy.
In a survey of 229 HIV-seronegative injection-drug users in New York City,
mean CD4+ T-cell counts of the group were consistently more than 1000
cells/µl of blood. Only two individuals had two CD4+ T-cell measurements
of less than 300/µl of blood, one of whom died with cardiac disease and
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma listed as the cause of death.
AIDS among transfusion recipients is due to underlying diseases that necessitated the transfusion, rather than to HIV
This
notion is contradicted by a report by the Transfusion Safety Study
Group (TSSG), which compared HIV-negative and HIV-positive blood
recipients who had been given blood transfusions
for similar diseases. Approximately 3 years following blood
transfusion, the mean CD4+ T-cell count in 64 HIV-negative recipients
was 850/µl of blood, while 111 HIV-seropositive individuals had average
CD4+ T-cell counts of 375/µl of blood. By 1993, there were 37 cases of
AIDS in the HIV-infected group, but not a single AIDS-defining illness
in the HIV-seronegative transfusion recipients.
High usage of clotting factor concentrate, not HIV, leads to CD4+ T-cell depletion and AIDS in hemophiliacs
This view is contradicted by many studies. For example, among HIV-seronegative patients with hemophilia A
enrolled in the Transfusion Safety Study, no significant differences in
CD4+ T-cell counts were noted between 79 patients with no or minimal
factor treatment and 52 with the largest amount of lifetime treatments.
Patients in both groups had CD4+ T-cell-counts within the normal range.
In another report from the Transfusion Safety Study, no instances of
AIDS-defining illnesses were seen among 402 HIV-seronegative
hemophiliacs who had received factortherapy.
In a cohort in the United Kingdom, researchers matched 17 HIV-seropositive hemophiliacs
with 17 HIV-seronegative hemophiliacs with regard to clotting factor
concentrate usage over a ten-year period. During this time, 16
AIDS-defining clinical events occurred in 9 patients, all of whom were
HIV-seropositive. No AIDS-defining illnesses occurred among the
HIV-negative patients. In each pair, the mean CD4+ T-cell count during
follow-up was, on average, 500 cells/µl lower in the HIV-seropositive
patient.
Among HIV-infected hemophiliacs, Transfusion Safety Study
investigators found that neither the purity nor the amount of factor
VIII therapy had a deleterious effect on CD4+ T-cell counts.
Similarly, the Multicenter Hemophilia Cohort Study found no association
between the cumulative dose of plasma concentrate and incidence of AIDS
among HIV-infected hemophiliacs.
The distribution of AIDS cases casts doubt on HIV as the cause. Viruses are not gender-specific, yet only a small proportion of AIDS cases are among women
The distribution of AIDS cases, whether in the
United States or elsewhere in the world, invariably mirrors the
prevalence of HIV in a population. In the United States, HIV first
appeared in populations of injection-drug users (a majority of whom are male) and gay
men. HIV is spread primarily through unprotected sex, the exchange of
HIV-contaminated needles, or cross-contamination of the drug solution
and infected blood during intravenous drug use. Because these behaviors
show a gender skew—Western men are more likely to take illegal drugs
intravenously than Western women, and men are more likely to report
higher levels of the riskiest sexual behaviors, such as unprotected anal intercourse—it is not surprising that a majority of U.S. AIDS cases have occurred in men.
Women in the United States, however, are increasingly becoming
HIV-infected, usually through the exchange of HIV-contaminated needles
or sex with an HIV-infected male. The CDC
estimates that 30 percent of new HIV infections in the United States in
1998 were in women. As the number of HIV-infected women has risen, so
too has the number of female AIDS patients in the United States.
Approximately 23% of U.S. adult/adolescent AIDS cases reported to the
CDC in 1998 were among women. In 1998, AIDS was the fifth leading cause
of death among women aged 25 to 44 in the United States, and the third
leading cause of death among African-American women in that age group.
In Africa, HIV was first recognized in sexually active heterosexuals,
and AIDS cases in Africa have occurred at least as frequently in women
as in men. Overall, the worldwide distribution of HIV infection and AIDS
between men and women is approximately 1 to 1. In sub-Saharan Africa,
57% of adults with HIV are women, and young women aged 15 to 24 are
more than three times as likely to be infected as young men.
HIV is not the cause of AIDS because many individuals with HIV have not developed AIDS
HIV
infections have a prolonged and variable course. The median period of
time between infection with HIV and the onset of clinically apparent
disease is approximately 10 years in industrialized countries, according to prospective studies of homosexual men in which dates of seroconversion
are known. Similar estimates of asymptomatic periods have been made for
HIV-infected blood-transfusion recipients, injection-drug users and
adult hemophiliacs.
As with many diseases, a number of factors can influence the
course of HIV disease. Factors such as age or genetic differences
between individuals, the level of virulence of the individual strain of
virus, as well as exogenous influences such as co-infection with other
microbes may determine the rate and severity of HIV disease expression.
Similarly, some people infected with hepatitis B, for example, show no symptoms or only jaundice and clear their infection, while others suffer disease ranging from chronic liver inflammation to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Co-factors probably also determine why some smokers develop lung cancer while others do not.
HIV is not the cause of AIDS because some people have symptoms associated with AIDS but are not infected with HIV
Most AIDS symptoms result from the development of opportunistic infections and cancers associated with severe immunosuppression secondary to HIV.
However, immunosuppression has many other potential causes. Individuals who take glucocorticoids or immunosuppressive drugs to prevent transplant rejection or to treat autoimmune diseases can have increased susceptibility to unusual infections, as do individuals with certain genetic conditions, severe malnutrition and certain kinds of cancers. There is no evidence suggesting that the numbers of such cases have risen, while abundant epidemiologic evidence shows a very large rise in cases of immunosuppression among individuals who share one characteristic: HIV infection.
The diseases associated with AIDS, such as Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP) and Mycobacterium avium complex
(MAC), are not caused by HIV, but rather result from the
immunosuppression caused by HIV disease. As the immune system of an
HIV-infected individual weakens, he or she becomes susceptible to the
particular viral, fungal, and bacterial infections common in the community. For example, HIV-infected people in the Midwestern United States are much more likely than people in New York City to develop histoplasmosis,
which is caused by a fungus. A person in Africa is exposed to pathogens
different from individuals in an American city. Children may be exposed
to infectious agents different from adults.
HIV is the underlying cause of the condition named AIDS, but the
additional conditions that may affect an AIDS patient are dependent upon
the endemic pathogens to which the patient may be exposed.
AIDS can be prevented with complementary or alternative medicine
Many HIV-infected people turn to complementary and alternative medicine, such as traditional medicine, especially in areas where conventional therapies are less widespread.
However, the overwhelming majority of scientifically rigorous research
indicates little or negative effect on patient outcomes such as
HIV-symptom severity and disease duration, and mixed outcomes on
psychological well-being.
It is important that patients notify their healthcare provider prior to
beginning any treatment, as certain alternative therapies may interfere
with conventional treatment.