The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline (recession) observed in national economies globally that occurred between 2007 and 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At the time, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded that it was the most severe economic and financial meltdown since the Great Depression. One result was a serious disruption of normal international relations.
The causes of the Great Recession include a combination of vulnerabilities that developed in the financial system, along with a series of triggering events that began with the bursting of the United States housing bubble in 2005–2012. When housing prices fell and homeowners began to abandon their mortgages, the value of mortgage-backed securities held by investment banks declined in 2007–2008, causing several to collapse or be bailed out in September 2008. This 2007–2008 phase was called the subprime mortgage crisis. The combination of banks unable to provide funds to businesses, and homeowners paying down debt rather than borrowing and spending, resulted in the Great Recession that began in the U.S. officially in December 2007 and lasted until June 2009, thus extending over 19 months. As with most other recessions, it appears that no known formal theoretical or empirical model was able to accurately predict the advance of this recession, except for minor signals in the sudden rise of forecast probabilities, which were still well under 50%.
The recession was not felt equally around the world; whereas most of the world's developed economies, particularly in North America, South America and Europe, fell into a severe, sustained recession, many more recently developed economies suffered far less impact, particularly China, India and Indonesia, whose economies grew substantially during this period. Similarly, Oceania suffered minimal impact, in part due to its proximity to Asian markets.
Terminology
Two senses of the word "recession" exist: one sense referring broadly to "a period of reduced economic activity" and ongoing hardship; and the more precise sense used in economics, which is defined operationally, referring specifically to the contraction phase of a business cycle, with two or more consecutive quarters of GDP contraction (negative GDP growth rate).
The definition of "great" is amount or intensity considerably above the normal or average and, contrary to some common beliefs, does not infer a positive connotation, merely large in size or scope.
Under the academic definition, the recession ended in the United States in June or July 2009.
Robert Kuttner argues, " 'The Great Recession,' is a misnomer. We should stop using it. Recessions are mild dips in the business cycle that are either self-correcting or soon cured by modest fiscal or monetary stimulus. Because of the continuing deflationary trap, it would be more accurate to call this decade's stagnant economy The Lesser Depression or The Great Deflation."
Overview
The Great Recession met the IMF criteria for being a global recession only in the single calendar year 2009. That IMF definition requires a decline in annual real world GDP per‑capita. Despite the fact that quarterly data are being used as recession definition criteria by all G20 members, representing 85% of the world GDP, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) has decided—in the absence of a complete data set—not to declare/measure global recessions according to quarterly GDP data. The seasonally adjusted PPP‑weighted real GDP for the G20‑zone, however, is a good indicator for the world GDP, and it was measured to have suffered a direct quarter on quarter decline during the three quarters from Q3‑2008 until Q1‑2009, which more accurately mark when the recession took place at the global level.
According to the U.S. National Bureau of Economic Research (the official arbiter of U.S. recessions) the recession began in December 2007 and ended in June 2009, and thus extended over eighteen months.
The years leading up to the crisis were characterized by an exorbitant rise in asset prices and associated boom in economic demand. Further, the U.S. shadow banking system (i.e., non-depository financial institutions such as investment banks) had grown to rival the depository system yet was not subject to the same regulatory oversight, making it vulnerable to a bank run.
US mortgage-backed securities, which had risks that were hard to assess, were marketed around the world, as they offered higher yields than U.S. government bonds. Many of these securities were backed by subprime mortgages, which collapsed in value when the U.S. housing bubble burst during 2006 and homeowners began to default on their mortgage payments in large numbers starting in 2007.
The emergence of sub-prime loan losses in 2007 began the crisis and exposed other risky loans and over-inflated asset prices. With loan losses mounting and the fall of Lehman Brothers on September 15, 2008, a major panic broke out on the inter-bank loan market. There was the equivalent of a bank run on the shadow banking system, resulting in many large and well established investment banks and commercial banks in the United States and Europe suffering huge losses and even facing bankruptcy, resulting in massive public financial assistance (government bailouts).
The global recession that followed resulted in a sharp drop in international trade, rising unemployment and slumping commodity prices. Several economists predicted that recovery might not appear until 2011 and that the recession would be the worst since the Great Depression of the 1930s. Economist Paul Krugman once commented on this as seemingly the beginning of "a second Great Depression".
Governments and central banks responded with fiscal policy and monetary policy initiatives to stimulate national economies and reduce financial system risks. The recession renewed interest in Keynesian' economic ideas on how to combat recessionary conditions. Economists advise that the stimulus measures such as quantitative easing (pumping money into the system) and holding down central bank wholesale lending interest rate should be withdrawn as soon as economies recover enough to "chart a path to sustainable growth".
The distribution of household incomes in the United States became more unequal during the post-2008 economic recovery. Income inequality in the United States grew from 2005 to 2012 in more than two-thirds of metropolitan areas. Median household wealth fell 35% in the US, from $106,591 to $68,839 between 2005 and 2011.
Causes
1. Central banks' gold reserves: $0.845 trillion.
2. M0 (paper money): $3.9 trillion.
3. Traditional (fractional reserve) banking assets: $39 trillion.
4. Shadow banking assets: $62 trillion.
5. Other assets: $290 trillion.
6. Bail-out money (early 2009): $1.9 trillion.
Panel reports
The majority report provided by US Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission, composed of six Democratic and four Republican appointees, reported its findings in January 2011. It concluded that "the crisis was avoidable and was caused by:
- Widespread failures in financial regulation, including the Federal Reserve's failure to stem the tide of toxic mortgages;
- Dramatic breakdowns in corporate governance including too many financial firms acting recklessly and taking on too much risk;
- An explosive mix of excessive borrowing and risk by households and Wall Street that put the financial system on a collision course with crisis;
- Key policy makers ill prepared for the crisis, lacking a full understanding of the financial system they oversaw; and systemic breaches in accountability and ethics at all levels."
There were two Republican dissenting FCIC reports. One of them, signed by three Republican appointees, concluded that there were multiple causes. In his separate dissent to the majority and minority opinions of the FCIC, Commissioner Peter J. Wallison of the American Enterprise Institute (AEI) primarily blamed U.S. housing policy, including the actions of Fannie & Freddie, for the crisis. He wrote: "When the bubble began to deflate in mid-2007, the low quality and high risk loans engendered by government policies failed in unprecedented numbers."
In its "Declaration of the Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy," dated November 15, 2008, leaders of the Group of 20 cited the following causes:
During a period of strong global growth, growing capital flows, and prolonged stability earlier this decade, market participants sought higher yields without an adequate appreciation of the risks and failed to exercise proper due diligence. At the same time, weak underwriting standards, unsound risk management practices, increasingly complex and opaque financial products, and consequent excessive leverage combined to create vulnerabilities in the system. Policy-makers, regulators and supervisors, in some advanced countries, did not adequately appreciate and address the risks building up in financial markets, keep pace with financial innovation, or take into account the systemic ramifications of domestic regulatory actions.
Federal Reserve Chair Ben Bernanke testified in September 2010 before the FCIC regarding the causes of the crisis. He wrote that there were shocks or triggers (i.e., particular events that touched off the crisis) and vulnerabilities (i.e., structural weaknesses in the financial system, regulation and supervision) that amplified the shocks. Examples of triggers included: losses on subprime mortgage securities that began in 2007 and a run on the shadow banking system that began in mid-2007, which adversely affected the functioning of money markets. Examples of vulnerabilities in the private sector included: financial institution dependence on unstable sources of short-term funding such as repurchase agreements or Repos; deficiencies in corporate risk management; excessive use of leverage (borrowing to invest); and inappropriate usage of derivatives as a tool for taking excessive risks. Examples of vulnerabilities in the public sector included: statutory gaps and conflicts between regulators; ineffective use of regulatory authority; and ineffective crisis management capabilities. Bernanke also discussed "Too big to fail" institutions, monetary policy, and trade deficits.
Narratives
There are several "narratives" attempting to place the causes of the recession into context, with overlapping elements. Five such narratives include:
- There was the equivalent of a bank run on the shadow banking system, which includes investment banks and other non-depository financial entities. This system had grown to rival the depository system in scale yet was not subject to the same regulatory safeguards. Its failure disrupted the flow of credit to consumers and corporations.
- The U.S. economy was being driven by a housing bubble. When it burst, private residential investment (i.e., housing construction) fell by over four percent of GDP. Consumption enabled by bubble-generated housing wealth also slowed. This created a gap in annual demand (GDP) of nearly $1 trillion. The U.S. government was unwilling to make up for this private sector shortfall.
- Record levels of household debt accumulated in the decades preceding the crisis resulted in a balance sheet recession (similar to debt deflation) once housing prices began falling in 2006. Consumers began paying off debt, which reduces their consumption, slowing down the economy for an extended period while debt levels are reduced.
- U.S. government policies encouraged home ownership even for those who could not afford it, contributing to lax lending standards, unsustainable housing price increases, and indebtedness.
- Wealthy and middle-class house flippers with mid-to-good credit scores created a speculative bubble in house prices, and then wrecked local housing markets and financial institutions after they defaulted on their debt en masse.
Underlying narratives #1–3 is a hypothesis that growing income inequality and wage stagnation encouraged families to increase their household debt to maintain their desired living standard, fueling the bubble. Further, this greater share of income flowing to the top increased the political power of business interests, who used that power to deregulate or limit regulation of the shadow banking system.
Narrative #5 challenges the popular claim that subprime borrowers with shoddy credit caused the crisis by buying homes they couldn't afford. This narrative is supported by new research showing that the biggest growth of mortgage debt during the U.S. housing boom came from those with good credit scores in the middle and top of the credit score distribution—and that these borrowers accounted for a disproportionate share of defaults.
Trade imbalances and debt bubbles
The Economist wrote in July 2012 that the inflow of investment dollars required to fund the U.S. trade deficit was a major cause of the housing bubble and financial crisis: "The trade deficit, less than 1% of GDP in the early 1990s, hit 6% in 2006. That deficit was financed by inflows of foreign savings, in particular from East Asia and the Middle East. Much of that money went into dodgy mortgages to buy overvalued houses, and the financial crisis was the result."
In May 2008, NPR explained in their Peabody Award winning program "The Giant Pool of Money" that a vast inflow of savings from developing nations flowed into the mortgage market, driving the U.S. housing bubble. This pool of fixed income savings increased from around $35 trillion in 2000 to about $70 trillion by 2008. NPR explained this money came from various sources, "[b]ut the main headline is that all sorts of poor countries became kind of rich, making things like TVs and selling us oil. China, India, Abu Dhabi, Saudi Arabia made a lot of money and banked it."
Describing the crisis in Europe, Paul Krugman wrote in February 2012 that: "What we're basically looking at, then, is a balance of payments problem, in which capital flooded south after the creation of the euro, leading to overvaluation in southern Europe."
Monetary policy
Another narrative about the origin has been focused on the respective parts played by the public monetary policy (in the US notably) and by the practices of private financial institutions. In the U.S., mortgage funding was unusually decentralised, opaque, and competitive, and it is believed that competition between lenders for revenue and market share contributed to declining underwriting standards and risky lending.
While Alan Greenspan's role as Chairman of the Federal Reserve has been widely discussed, the main point of controversy remains the lowering of the Federal funds rate to 1% for more than a year, which, according to Austrian theorists, injected huge amounts of "easy" credit-based money into the financial system and created an unsustainable economic boom), there is also the argument that Greenspan's actions in the years 2002–2004 were actually motivated by the need to take the U.S. economy out of the early 2000s recession caused by the bursting of the dot-com bubble—although by doing so he did not help avert the crisis, but only postpone it.
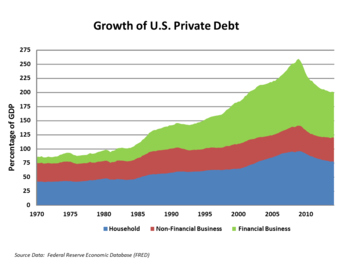
High private debt levels
Another narrative focuses on high levels of private debt in the US economy. USA household debt as a percentage of annual disposable personal income was 127% at the end of 2007, versus 77% in 1990. Faced with increasing mortgage payments as their adjustable rate mortgage payments increased, households began to default in record numbers, rendering mortgage-backed securities worthless. High private debt levels also impact growth by making recessions deeper and the following recovery weaker. Robert Reich claims the amount of debt in the US economy can be traced to economic inequality, assuming that middle-class wages remained stagnant while wealth concentrated at the top, and households "pull equity from their homes and overload on debt to maintain living standards".
The IMF reported in April 2012: "Household debt soared in the years leading up to the downturn. In advanced economies, during the five years preceding 2007, the ratio of household debt to income rose by an average of 39 percentage points, to 138 percent. In Denmark, Iceland, Ireland, the Netherlands, and Norway, debt peaked at more than 200 percent of household income. A surge in household debt to historic highs also occurred in emerging economies such as Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, and Lithuania. The concurrent boom in both house prices and the stock market meant that household debt relative to assets held broadly stable, which masked households' growing exposure to a sharp fall in asset prices. When house prices declined, ushering in the global financial crisis, many households saw their wealth shrink relative to their debt, and, with less income and more unemployment, found it harder to meet mortgage payments. By the end of 2011, real house prices had fallen from their peak by about 41% in Ireland, 29% in Iceland, 23% in Spain and the United States, and 21% in Denmark. Household defaults, underwater mortgages (where the loan balance exceeds the house value), foreclosures, and fire sales are now endemic to a number of economies. Household deleveraging by paying off debts or defaulting on them has begun in some countries. It has been most pronounced in the United States, where about two-thirds of the debt reduction reflects defaults."
Pre-recession warnings
The onset of the economic crisis took most people by surprise. A 2009 paper identifies twelve economists and commentators who, between 2000 and 2006, predicted a recession based on the collapse of the then-booming housing market in the United States: Dean Baker, Wynne Godley, Fred Harrison, Michael Hudson, Eric Janszen, Med Jones Steve Keen, Jakob Brøchner Madsen, Jens Kjaer Sørensen, Kurt Richebächer, Nouriel Roubini, Peter Schiff, and Robert Shiller.
Housing bubbles
By 2007, real estate bubbles were still under way in many parts of the world, especially in the United States, France, the United Kingdom, Spain, The Netherlands, Australia, the United Arab Emirates, New Zealand, Ireland, Poland, South Africa, Greece, Bulgaria, Croatia, Norway, Singapore, South Korea, Sweden, Finland, Argentina, the Baltic states, India, Romania, the Ukraine and China. U.S. Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan said in mid-2005 that "at a minimum, there's a little 'froth' [in the U.S. housing market]...it's hard not to see that there are a lot of local bubbles".
The Economist, writing at the same time, went further, saying, "[T]he worldwide rise in house prices is the biggest bubble in history". Real estate bubbles are (by definition of the word "bubble") followed by a price decrease (also known as a housing price crash) that can result in many owners holding negative equity (a mortgage debt higher than the current value of the property).
Ineffective or inappropriate regulation
Regulations encouraging lax lending standards
Several analysts, such as Peter Wallison and Edward Pinto of the American Enterprise Institute, have asserted that private lenders were encouraged to relax lending standards by government affordable housing policies. They cite The Housing and Community Development Act of 1992, which initially required that 30 percent or more of Fannie's and Freddie's loan purchases be related to affordable housing. The legislation gave HUD the power to set future requirements. These rose to 42 percent in 1995 and 50 percent in 2000, and by 2008 (under the G.W. Bush Administration) a 56 percent minimum was established. To fulfill the requirements, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac established programs to purchase $5 trillion in affordable housing loans, and encouraged lenders to relax underwriting standards to produce those loans.
These critics also cite, as inappropriate regulation, "The National Homeownership Strategy: Partners in the American Dream ("Strategy"), which was compiled in 1995 by Henry Cisneros, President Clinton's HUD Secretary. In 2001, the independent research company, Graham Fisher & Company, stated: "While the underlying initiatives of the [Strategy] were broad in content, the main theme ... was the relaxation of credit standards."
The Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) is also identified as one of the causes of the recession, by some critics. They contend that lenders relaxed lending standards in an effort to meet CRA commitments, and they note that publicly announced CRA loan commitments were massive, totaling $4.5 trillion in the years between 1994 and 2007.
However, the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission (FCIC) Democratic majority report concluded that Fannie & Freddie "were not a primary cause" of the crisis and that CRA was not a factor in the crisis. Further, since housing bubbles appeared in multiple countries in Europe as well, the FCIC Republican minority dissenting report also concluded that U.S. housing policies were not a robust explanation for a wider global housing bubble. The hypothesis that a primary cause of the crisis was U.S. government housing policy requiring banks to make risky loans has been widely disputed, with Paul Krugman referring to it as "imaginary history".
One of the other challenges with blaming government regulations for essentially forcing banks to make risky loans is the timing. Subprime lending increased from around 10% of mortgage origination historically to about 20% only from 2004 to 2006, with housing prices peaking in 2006. Blaming affordable housing regulations established in the 1990s for a sudden spike in subprime origination is problematic at best. A more proximate government action to the sudden rise in subprime lending was the SEC relaxing lending standards for the top investment banks during an April 2004 meeting with bank leaders. These banks increased their risk-taking shortly thereafter, significantly increasing their purchases and securitization of lower-quality mortgages, thus encouraging additional subprime and Alt-A lending by mortgage companies. This action by its investment bank competitors also resulted in Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac taking on more risk.
The Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act (1999), which reduced the regulation of banks by allowing commercial and investment banks to merge, has also been blamed for the crisis, by Nobel Prize-winning economist Joseph Stiglitz among others.
Derivatives
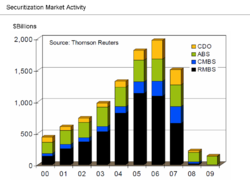
Several sources have noted the failure of the US government to supervise or even require transparency of the financial instruments known as derivatives. Derivatives such as credit default swaps (CDSs) were unregulated or barely regulated. Michael Lewis noted CDSs enabled speculators to stack bets on the same mortgage securities. This is analogous to allowing many persons to buy insurance on the same house. Speculators that bought CDS protection were betting significant mortgage security defaults would occur, while the sellers (such as AIG) bet they would not. An unlimited amount could be wagered on the same housing-related securities, provided buyers and sellers of the CDS could be found. When massive defaults occurred on underlying mortgage securities, companies like AIG that were selling CDS were unable to perform their side of the obligation and defaulted; U.S. taxpayers paid over $100 billion to global financial institutions to honor AIG obligations, generating considerable outrage.
A 2008 investigative article in the Washington Post found leading government officials at the time (Federal Reserve Board Chairman Alan Greenspan, Treasury Secretary Robert Rubin, and SEC Chairman Arthur Levitt) vehemently opposed any regulation of derivatives. In 1998, Brooksley E. Born, head of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, put forth a policy paper asking for feedback from regulators, lobbyists, and legislators on the question of whether derivatives should be reported, sold through a central facility, or whether capital requirements should be required of their buyers. Greenspan, Rubin, and Levitt pressured her to withdraw the paper and Greenspan persuaded Congress to pass a resolution preventing CFTC from regulating derivatives for another six months — when Born's term of office would expire. Ultimately, it was the collapse of a specific kind of derivative, the mortgage-backed security, that triggered the economic crisis of 2008.
Shadow banking system
Paul Krugman wrote in 2009 that the run on the shadow banking system was the fundamental cause of the crisis. "As the shadow banking system expanded to rival or even surpass conventional banking in importance, politicians and government officials should have realised that they were re-creating the kind of financial vulnerability that made the Great Depression possible – and they should have responded by extending regulations and the financial safety net to cover these new institutions. Influential figures should have proclaimed a simple rule: anything that does what a bank does, anything that has to be rescued in crises the way banks are, should be regulated like a bank." He referred to this lack of controls as "malign neglect".
During 2008, three of the largest U.S. investment banks either went bankrupt (Lehman Brothers) or were sold at fire sale prices to other banks (Bear Stearns and Merrill Lynch). The investment banks were not subject to the more stringent regulations applied to depository banks. These failures exacerbated the instability in the global financial system. The remaining two investment banks, Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs, potentially facing failure, opted to become commercial banks, thereby subjecting themselves to more stringent regulation but receiving access to credit via the Federal Reserve. Further, American International Group (AIG) had insured mortgage-backed and other securities but was not required to maintain sufficient reserves to pay its obligations when debtors defaulted on these securities. AIG was contractually required to post additional collateral with many creditors and counter-parties, touching off controversy when over $100 billion of U.S. taxpayer money was paid out to major global financial institutions on behalf of AIG. While this money was legally owed to the banks by AIG (under agreements made via credit default swaps purchased from AIG by the institutions), a number of Congressmen and media members expressed outrage that taxpayer money was used to bail out banks.
Economist Gary Gorton wrote in May 2009:
Unlike the historical banking panics of the 19th and early 20th centuries, the current banking panic is a wholesale panic, not a retail panic. In the earlier episodes, depositors ran to their banks and demanded cash in exchange for their checking accounts. Unable to meet those demands, the banking system became insolvent. The current panic involved financial firms "running" on other financial firms by not renewing sale and repurchase agreements (repo) or increasing the repo margin ("haircut"), forcing massive deleveraging, and resulting in the banking system being insolvent.
The Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission reported in January 2011:
In the early part of the 20th century, we erected a series of protections – the Federal Reserve as a lender of last resort, federal deposit insurance, ample regulations – to provide a bulwark against the panics that had regularly plagued America's banking system in the 19th century. Yet, over the past 30-plus years, we permitted the growth of a shadow banking system – opaque and laden with short term debt – that rivaled the size of the traditional banking system. Key components of the market – for example, the multitrillion-dollar repo lending market, off-balance-sheet entities, and the use of over-the-counter derivatives – were hidden from view, without the protections we had constructed to prevent financial meltdowns. We had a 21st-century financial system with 19th-century safeguards.
Systemic crisis
The financial crisis and the recession have been described as a symptom of another, deeper crisis by a number of economists. For example, Ravi Batra argues that growing inequality of financial capitalism produces speculative bubbles that burst and result in depression and major political changes. Feminist economists Ailsa McKay and Margunn Bjørnholt argue that the financial crisis and the response to it revealed a crisis of ideas in mainstream economics and within the economics profession, and call for a reshaping of both the economy, economic theory and the economics profession. They argue that such a reshaping should include new advances within feminist economics and ecological economics that take as their starting point the socially responsible, sensible and accountable subject in creating an economy and economic theories that fully acknowledge care for each other as well as the planet.
Effects
Effects on the United States
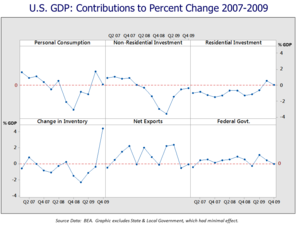
The Great Recession had a significant economic and political impact on the United States. While the recession technically lasted from December 2007 – June 2009 (the nominal GDP trough), many important economic variables did not regain pre-recession (November or Q4 2007) levels until 2011–2016. For example, real GDP fell $650 billion (4.3%) and did not recover its $15 trillion pre-recession level until Q3 2011. Household net worth, which reflects the value of both stock markets and housing prices, fell $11.5 trillion (17.3%) and did not regain its pre-recession level of $66.4 trillion until Q3 2012. The number of persons with jobs (total non-farm payrolls) fell 8.6 million (6.2%) and did not regain the pre-recession level of 138.3 million until May 2014. The unemployment rate peaked at 10.0% in October 2009 and did not return to its pre-recession level of 4.7% until May 2016.
A key dynamic slowing the recovery was that both individuals and businesses paid down debts for several years, as opposed to borrowing and spending or investing as had historically been the case. This shift to a private sector surplus drove a sizable government deficit. However, the federal government held spending at about $3.5 trillion from fiscal years 2009–2014 (thereby decreasing it as a percent of GDP), a form of austerity. Then-Fed Chair Ben Bernanke explained during November 2012 several of the economic headwinds that slowed the recovery:
- The housing sector did not rebound, as was the case in prior recession recoveries, as the sector was severely damaged during the crisis. Millions of foreclosures had created a large surplus of properties and consumers were paying down their debts rather than purchasing homes.
- Credit for borrowing and spending by individuals (or investing by corporations) was not readily available as banks paid down their debts.
- Restrained government spending following initial stimulus efforts (i.e., austerity) was not sufficient to offset private sector weaknesses.
On the political front, widespread anger at banking bailouts and stimulus measures (begun by President George W. Bush and continued or expanded by President Obama) with few consequences for banking leadership, were a factor in driving the country politically rightward starting in 2010. The Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) was the largest of the bailouts. In 2008, TARP allocated $426.4 billion to various major financial institutions. However, the US collected $441.7 billion in return from these loans in 2010, recording a profit of $15.3 billion. Nonetheless, there was a political shift from the Democratic party. Examples include the rise of the Tea Party and the loss of Democratic majorities in subsequent elections. President Obama declared the bailout measures started under the Bush administration and continued during his administration as completed and mostly profitable as of December 2014. As of January 2018, bailout funds had been fully recovered by the government, when interest on loans is taken into consideration. A total of $626B was invested, loaned, or granted due to various bailout measures, while $390B had been returned to the Treasury. The Treasury had earned another $323B in interest on bailout loans, resulting in an $87B profit. Economic and political commentators have argued the Great Recession was also an important factor in the rise of populist sentiment that resulted in the election of President Trump in 2016, and left-wing populist Bernie Sanders' candidacy for the Democratic nomination.
Effects on Europe
The crisis in Europe generally progressed from banking system crises to sovereign debt crises, as many countries elected to bail out their banking systems using taxpayer money. Greece was different in that it faced large public debts rather than problems within its banking system. Several countries received bailout packages from the troika (European Commission, European Central Bank, International Monetary Fund), which also implemented a series of emergency measures.
Many European countries embarked on austerity programs, reducing their budget deficits relative to GDP from 2010 to 2011. For example, according to the CIA World Factbook Greece improved its budget deficit from 10.4% GDP in 2010 to 9.6% in 2011. Iceland, Italy, Ireland, Portugal, France, and Spain also improved their budget deficits from 2010 to 2011 relative to GDP.
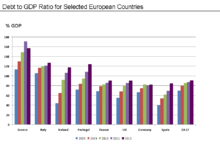
However, with the exception of Germany, each of these countries had public-debt-to-GDP ratios that increased (i.e., worsened) from 2010 to 2011, as indicated in the chart at right. Greece's public-debt-to-GDP ratio increased from 143% in 2010 to 165% in 2011 to 185% in 2014. This indicates that despite improving budget deficits, GDP growth was not sufficient to support a decline (improvement) in the debt-to-GDP ratio for these countries during this period. Eurostat reported that the debt to GDP ratio for the 17 Euro area countries together was 70.1% in 2008, 79.9% in 2009, 85.3% in 2010, and 87.2% in 2011.
According to the CIA World Factbook, from 2010 to 2011, the unemployment rates in Spain, Greece, Italy, Ireland, Portugal, and the UK increased. France had no significant changes, while in Germany and Iceland the unemployment rate declined. Eurostat reported that Eurozone unemployment reached record levels in September 2012 at 11.6%, up from 10.3% the prior year. Unemployment varied significantly by country.
Economist Martin Wolf analysed the relationship between cumulative GDP growth from 2008 to 2012 and total reduction in budget deficits due to austerity policies (see chart at right) in several European countries during April 2012. He concluded that: "In all, there is no evidence here that large fiscal contractions [budget deficit reductions] bring benefits to confidence and growth that offset the direct effects of the contractions. They bring exactly what one would expect: small contractions bring recessions and big contractions bring depressions." Changes in budget balances (deficits or surpluses) explained approximately 53% of the change in GDP, according to the equation derived from the IMF data used in his analysis.
Economist Paul Krugman analysed the relationship between GDP and reduction in budget deficits for several European countries in April 2012 and concluded that austerity was slowing growth, similar to Martin Wolf. He also wrote: "... this also implies that 1 euro of austerity yields only about 0.4 euros of reduced deficit, even in the short run. No wonder, then, that the whole austerity enterprise is spiraling into disaster."
Britain's decision to leave the European Union in 2016 has been partly attributed to the after-effects of the Great Recession on the country.
Countries that avoided recession
Poland and Slovakia were the only two members of the European Union to avoid a GDP recession during the Great Recession. As of December 2009, the Polish economy had not entered recession nor even contracted, while its IMF 2010 GDP growth forecast of 1.9 percent was expected to be upgraded. Analysts identified several causes for the positive economic development in Poland: Extremely low levels of bank lending and a relatively very small mortgage market; the relatively recent dismantling of EU trade barriers and the resulting surge in demand for Polish goods since 2004; Poland being the recipient of direct EU funding since 2004; lack of over-dependence on a single export sector; a tradition of government fiscal responsibility; a relatively large internal market; the free-floating Polish zloty; low labour costs attracting continued foreign direct investment; economic difficulties at the start of the decade, which prompted austerity measures in advance of the world crisis.
While India, Uzbekistan, China, and Iran experienced slowing growth, they did not enter recessions.
South Korea narrowly avoided technical recession in the first quarter of 2009. The International Energy Agency stated in mid September that South Korea could be the only large OECD country to avoid recession for the whole of 2009. It was the only developed economy to expand in the first half of 2009.
Australia avoided a technical recession after experiencing only one quarter of negative growth in the fourth quarter of 2008, with GDP returning to positive in the first quarter of 2009.
The financial crisis did not affect developing countries to a great extent. Experts see several reasons: Africa was not affected because it is not fully integrated in the world market. Latin America and Asia seemed better prepared, since they have experienced crises before. In Latin America, for example, banking laws and regulations are very stringent. Bruno Wenn of the German DEG suggests that Western countries could learn from these countries when it comes to regulations of financial markets.
Timeline of effects
The table below displays all national recessions appearing in 2006-2013 (for the 71 countries with available data), according to the common recession definition, saying that a recession occurred whenever seasonally adjusted real GDP contracts quarter on quarter, through minimum two consecutive quarters. Only 11 out of the 71 listed countries with quarterly GDP data (Poland, Slovakia, Moldova, India, China, South Korea, Indonesia, Australia, Uruguay, Colombia and Bolivia) escaped a recession in this time period.
The few recessions appearing early in 2006-07 are commonly never associated to be part of the Great Recession, which is illustrated by the fact that only two countries (Iceland and Jamaica) were in recession in Q4-2007.
One year before the maximum, in Q1-2008, only six countries were in recession (Iceland, Sweden, Finland, Ireland, Portugal and New Zealand). The number of countries in recession was 25 in Q2‑2008, 39 in Q3‑2008 and 53 in Q4‑2008. At the steepest part of the Great Recession in Q1‑2009, a total of 59 out of 71 countries were simultaneously in recession. The number of countries in recession was 37 in Q2‑2009, 13 in Q3‑2009 and 11 in Q4‑2009. One year after the maximum, in Q1‑2010, only seven countries were in recession (Greece, Croatia, Romania, Iceland, Jamaica, Venezuela and Belize).
The recession data for the overall G20-zone (representing 85% of all GWP), depict that the Great Recession existed as a global recession throughout Q3‑2008 until Q1‑2009.
Subsequent follow-up recessions in 2010‑2013 were confined to Belize, El Salvador, Paraguay, Jamaica, Japan, Taiwan, New Zealand and 24 out of 50 European countries (including Greece). As of October 2014, only five out of the 71 countries with available quarterly data (Cyprus, Italy, Croatia, Belize and El Salvador), were still in ongoing recessions. The many follow-up recessions hitting the European countries, are commonly referred to as being direct repercussions of the European sovereign‑debt crisis.
| Country[a] | Recession period(s) during 2006‑2013 (measured by quarter-on-quarter changes of seasonally adjusted real GDP, as per the latest revised Q3-2013 data from 10 January 2014)[b] |
|---|---|
| Albania | Q1-2007 until Q2-2007 (6 months) Q3-2009 until Q4-2009 (6 months) Q4-2011 until Q1-2012 (6 months) |
| Argentina | Q4-2008 until Q2-2009 (9 months) Q1-2012 until Q2-2012 (6 months) Q3-2013 until Q3-2014 (12 months) Q3-2015 until Q3-2016 (15 months) |
| Australia | None |
| Austria | Q2-2008 until Q2-2009 (15 months) Q3-2011 until Q4-2011 (6 months) |
| Belgium | Q3-2008 until Q1-2009 (9 months) Q2-2012 until Q1-2013 (12 months) |
| Belize | Q1-2006 until Q2-2006 (6 months) Q1-2007 until Q3-2007 (9 months) Q4-2008 until Q1-2009 (6 months) Q4-2009 until Q1-2010 (6 months) Q1-2011 until Q2-2011 (6 months) Q2-2013 until Ongoing (48 months) |
| Bolivia | None |
| Brazil | Q4-2008 until Q1-2009 (6 months) Q1-2014 until Q4-2016 (36 months) |
| Bulgaria | Q1-2009 until Q2-2009 (6 months) |
| Canada | Q4-2008 until Q2-2009 (9 months) |
| Chile | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) |
| China | None |
| Colombia | None |
| Costa Rica | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) |
| Croatia | Q3-2008 until Q2-2010 (24 months) Q3-2011 until Q4-2012 (18 months) Q2-2013 until Q2 2014 (15 months) |
| Cyprus | Q1-2009 until Q4-2009 (12 months) Q3-2011 until Q4-2014 (42 months) |
| Czech Republic | Q4-2008 until Q2-2009 (9 months) Q4-2011 until Q1-2013 (18 months) |
| Denmark | Q3-2008 until Q2-2009 (12 months) Q3-2011 until Q4-2011 (6 months) Q4-2012 until Q1-2013 (6 months) |
| Ecuador | Q4-2006 until Q1-2007 (6 months) Q1-2009 until Q3-2009 (9 months) |
| El Salvador | Q3-2008 until Q2-2009 (12 months) |
| Estonia | Q3-2008 until Q3-2009 (15 months) Q1-2013 until Q2-2013 (6 months) |
| EU (28 member states) | Q2-2008 until Q2-2009 (15 months) Q4-2011 until Q2-2012 (9 months) Q4-2012 until Q1-2013 (6 months) |
| Eurozone (17 member states) | Q2-2008 until Q2-2009 (15 months) Q4-2011 until Q1-2013 (18 months) |
| Finland | Q1-2008 until Q2-2009 (18 months) Q2-2012 until Q1-2015 (36 months) |
| France | Q2-2008 until Q2-2009 (15 months) Q4-2012 until Q1-2013 (6 months) |
| G20 (43 member states, PPP-weighted GDP)[e] | Q3-2008 until Q1-2009 (9 months) |
| Germany | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) |
| Greece | Q3-2008 until Q2-2014 (63 months) Q1-2015 until Q1-2017 (27 months) |
| Hong Kong | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) |
| Hungary | Q1-2007 until Q2-2007 (6 months) Q2-2008 until Q3-2009 (18 months) Q2-2011 until Q3-2011 (6 months) Q1-2012 until Q4-2012 (12 months) |
| Iceland | Q4-2007 until Q2-2008 (9 months) Q4-2008 until Q1-2009 (6 months) Q3-2009 until Q2-2010 (12 months) |
| India | None |
| Indonesia | None |
| Ireland | Q2-2007 until Q3-2007 (6 months) Q1-2008 until Q4-2009 (24 months) Q3-2011 until Q2-2013 (24 months) |
| Israel | Q4-2008 until Q1-2009 (6 months) |
| Italy | Q3-2007 until Q4-2007 (6 months) Q2-2008 until Q2-2009 (15 months) Q3-2011 until Q3-2013 (27 months) Q1-2014 until Q4-2014 (12 months) |
| Jamaica | Q3-2007 until Q4-2007 (6 months) Q3-2008 until Q1-2009 (9 months) Q4-2009 until Q2-2010 (9 months) Q4-2011 until Q1-2012 (6 months) Q4-2012 until Q1-2013 (6 months) |
| Japan | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) Q4-2010 until Q2-2011 (9 months) Q2-2012 until Q3-2012 (6 months) |
| Kazakhstan | Q3-2008 until Q1-2009 (9 months) |
| Latvia | Q1-2008 until Q3-2009 (18 months) Q1-2010 until Q2-2010 (12 months) |
| Lithuania | Q3-2008 until Q2-2009 (12 months) |
| Luxembourg | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) |
| Macedonia | Q1-2009 until Q3-2009 (9 months) Q1-2012 until Q2-2012 (6 months) (not qoq-data, but quarters compared with same quarter of last year)[b] Q1-2012 until Q2-2012 (6 months) |
| Malaysia | Q3-2008 until Q1-2009 (9 months) |
| Malta | Q4-2008 until Q1-2009 (6 months) |
| Mexico | Q3-2008 until Q2-2009 (12 months) |
| Moldova | None[g] |
| Netherlands | Q2-2008 until Q2-2009 (15 months) Q2-2011 until Q1-2012 (12 months) Q3-2012 until Q2-2013 (12 months) |
| New Zealand | Q1-2008 until Q2-2009 (18 months) Q3-2010 until Q4-2010 (6 months) |
| Norway | Q1-2009 until Q2-2009 (6 months) Q2-2010 until Q3-2010 (6 months) Q1-2011 until Q2-2011 (6 months) |
| OECD | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) |
| Paraguay | Q3-2008 until Q1-2009 (9 months) Q2-2011 until Q3-2011 (6 months) |
| Peru | Q4-2008 until Q2-2009 (9 months) |
| Philippines | Q4-2008 until Q1-2009 (6 months) |
| Poland | None |
| Portugal | Q2-2007 until Q3-2007 (6 months) Q1-2008 until Q1-2009 (15 months) Q4-2010 until Q1-2013 (30 months) |
| Romania | Q4-2008 until Q2-2009 (9 months) Q4-2009 until Q1-2010 (6 months) Q4-2011 until Q1-2012 (6 months) |
| Russia | Q3-2008 until Q2-2009 (12 months) Q4-2014 until Q4-2016 (27 months) |
| Serbia | Q2-2008 until Q2-2009 (15 months) Q2-2011 until Q1-2012 (12 months) Q3-2012 until Q4-2012 (6 months) |
| Singapore | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) |
| Slovakia | None |
| Slovenia | Q3-2008 until Q2-2009 (12 months) Q3-2011 until Q4-2013 (24 months) |
| South Africa | Q4-2008 until Q2-2009 (9 months) |
| South Korea | None |
| Spain | Q2-2008 until Q4-2009 (21 months) Q2-2011 until Q2-2013 (27 months) |
| Sweden | Q1-2008 until Q1-2009 (15 months) |
| Switzerland | Q4-2008 until Q2-2009 (9 months) |
| Taiwan | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) Q3-2011 until Q4-2011 (6 months) |
| Thailand | Q4-2008 until Q1-2009 (6 months) |
| Turkey | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) |
| Ukraine | Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (12 months) Q3-2012 until Q4-2012 (6 months) |
| United Kingdom | Q2-2008 until Q2-2009 (15 months) |
| United States | Q3-2008 until Q2-2009 (12 months) |
| Uruguay | None |
| Venezuela | Q1-2009 until Q1-2010 (15 months) |
- Moldova had as of January 2014 only published seasonally adjusted real GDP data until Q4-2010, with the statistics office still to publish data for 2011-13.
Country specific details about recession timelines
Iceland fell into an economic depression in 2008 following the collapse of its banking system (see 2008–2011 Icelandic financial crisis). By mid-2012 Iceland is regarded as one of Europe's recovery success stories largely as a result of a currency devaluation that has effectively reduced wages by 50%--making exports more competitive.
The following countries had a recession starting in the fourth quarter of 2007: United States,
The following countries had a recession already starting in the first quarter of 2008: Latvia, Ireland, New Zealand, and Sweden.
The following countries/territories had a recession starting in the second quarter of 2008: Japan, Hong Kong, Singapore, Italy, Turkey, Germany, United Kingdom, the Eurozone, the European Union, and OECD.
The following countries/territories had a recession starting in the third quarter of 2008: Spain, and Taiwan.
The following countries/territories had a recession starting in the fourth quarter of 2008: Switzerland.
South Korea miraculously avoided recession with GDP returning positive at a 0.1% expansion in the first quarter of 2009.
Of the seven largest economies in the world by GDP, only China avoided a recession in 2008. In the year to the third quarter of 2008 China grew by 9%. Until recently Chinese officials considered 8% GDP growth to be required simply to create enough jobs for rural people moving to urban centres. This figure may more accurately be considered to be 5–7% now that the main growth in working population is receding.
Ukraine went into technical depression in January 2009 with a GDP growth of −20%, when comparing on a monthly basis with the GDP level in January 2008. Overall the Ukrainian real GDP fell 14.8% when comparing the entire part of 2009 with 2008. When measured quarter-on-quarter by changes of seasonally adjusted real GDP, Ukraine was more precisely in recession/depression throughout the four quarters from Q2-2008 until Q1-2009 (with respective qoq-changes of: -0.1%, -0.5%, -9.3%, -10.3%), and the two quarters from Q3-2012 until Q4-2012 (with respective qoq-changes of: -1.5% and −0.8%).
Japan was in recovery in the middle of the decade 2000s but slipped back into recession and deflation in 2008. The recession in Japan intensified in the fourth quarter of 2008 with a GDP growth of −12.7%, and deepened further in the first quarter of 2009 with a GDP growth of −15.2%.
On February 26, 2009, an Economic Intelligence Briefing was added to the daily intelligence briefings prepared for the President of the United States. This addition reflects the assessment of U.S. intelligence agencies that the global financial crisis presents a serious threat to international stability.
Business Week stated in March 2009 that global political instability is rising fast because of the global financial crisis and is creating new challenges that need managing. The Associated Press reported in March 2009 that: United States "Director of National Intelligence Dennis Blair has said the economic weakness could lead to political instability in many developing nations." Even some developed countries are seeing political instability. NPR reports that David Gordon, a former intelligence officer who now leads research at the Eurasia Group, said: "Many, if not most, of the big countries out there have room to accommodate economic downturns without having large-scale political instability if we're in a recession of normal length. If you're in a much longer-run downturn, then all bets are off."
Political scientists have argued that the economic stasis triggered social churning that got expressed through protests on a variety of issues across the developing world. In Brazil, disaffected youth rallied against a minor bus-fare hike; in Turkey, they agitated against the conversion of a park to a mall and in Israel, they protested against high rents in Tel Aviv. In all these cases, the ostensible immediate cause of the protest was amplified by the underlying social suffering induced by the great recession.
In January 2009, the government leaders of Iceland were forced to call elections two years early after the people of Iceland staged mass protests and clashed with the police because of the government's handling of the economy. Hundreds of thousands protested in France against President Sarkozy's economic policies. Prompted by the financial crisis in Latvia, the opposition and trade unions there organised a rally against the cabinet of premier Ivars Godmanis. The rally gathered some 10–20 thousand people. In the evening the rally turned into a Riot. The crowd moved to the building of the parliament and attempted to force their way into it, but were repelled by the state's police. In late February many Greeks took part in a massive general strike because of the economic situation and they shut down schools, airports, and many other services in Greece. Police and protesters clashed in Lithuania where people protesting the economic conditions were shot with rubber bullets. Communists and others rallied in Moscow to protest the Russian government's economic plans. However the impact was mild in Russia, whose economy gained from high oil prices.
Asian countries saw various degrees of protest. Protests have also occurred in China as demands from the west for exports have been dramatically reduced and unemployment has increased. Beyond these initial protests, the protest movement has grown and continued in 2011. In late 2011, the Occupy Wall Street protest took place in the United States, spawning several offshoots that came to be known as the Occupy movement.
In 2012 the economic difficulties in Spain increased support for secession movements. In Catalonia, support for the secession movement exceeded. On September 11, a pro-independence march drew a crowd that police estimated at 1.5 million.
Policy responses
The financial phase of the crisis led to emergency interventions in many national financial systems. As the crisis developed into genuine recession in many major economies, economic stimulus meant to revive economic growth became the most common policy tool. After having implemented rescue plans for the banking system, major developed and emerging countries announced plans to relieve their economies. In particular, economic stimulus plans were announced in China, the United States, and the European Union. In the final quarter of 2008, the financial crisis saw the G-20 group of major economies assume a new significance as a focus of economic and financial crisis management.
United States policy responses
The U.S. government passed the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008 (EESA or TARP) during October 2008. This law included $700 billion in funding for the "Troubled Assets Relief Program" (TARP). Following a model initiated by the United Kingdom bank rescue package, $205 billion was used in the Capital Purchase Program to lend funds to banks in exchange for dividend-paying preferred stock.
On 17 February 2009, U.S. President Barack Obama signed the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, an $787 billion stimulus package with a broad spectrum of spending and tax cuts. Over $75 billion of the package was specifically allocated to programs which help struggling homeowners. This program was referred to as the Homeowner Affordability and Stability Plan.
The U.S. Federal Reserve (central bank) lowered interest rates and significantly expanded the money supply to help address the crisis. The New York Times reported in February 2013 that the Fed continued to support the economy with various monetary stimulus measures: "The Fed, which has amassed almost $3 trillion in Treasury and mortgage-backed securities to promote more borrowing and lending, is expanding those holdings by $85 billion a month until it sees clear improvement in the labor market. It plans to hold short-term interest rates near zero even longer, at least until the unemployment rate falls below 6.5 percent."
Asia-Pacific policy responses
On September 15, 2008, China cut its interest rate for the first time since 2002. Indonesia reduced its overnight rate, at which commercial banks can borrow overnight funds from the central bank, by two percentage points to 10.25 percent. The Reserve Bank of Australia injected nearly $1.5 billion into the banking system, nearly three times as much as the market's estimated requirement. The Reserve Bank of India added almost $1.32 billion, through a refinance operation, its biggest in at least a month.
On November 9, 2008, the Chinese economic stimulus program, a RMB¥ 4 trillion ($586 billion) stimulus package, was announced by the central government of the People's Republic of China in its biggest move to stop the global financial crisis from hitting the world's second largest economy. A statement on the government's website said the State Council had approved a plan to invest 4 trillion yuan ($586 billion) in infrastructure and social welfare by the end of 2010. The stimulus package was invested in key areas such as housing, rural infrastructure, transportation, health and education, environment, industry, disaster rebuilding, income-building, tax cuts, and finance.
Later that month, China's export driven economy was starting to feel the impact of the economic slowdown in the United States and Europe despite the government already cutting key interest rates three times in less than two months in a bid to spur economic expansion. On November 28, 2008, the Ministry of Finance of the People's Republic of China and the State Administration of Taxation jointly announced a rise in export tax rebate rates on some labour-intensive goods. These additional tax rebates took place on December 1, 2008.
The stimulus package was welcomed by world leaders and analysts as larger than expected and a sign that by boosting its own economy, China is helping to stabilise the global economy. News of the announcement of the stimulus package sent markets up across the world. However, Marc Faber claimed that he thought China was still in recession on January 16.
In Taiwan, the central bank on September 16, 2008, said it would cut its required reserve ratios for the first time in eight years. The central bank added $3.59 billion into the foreign-currency interbank market the same day. Bank of Japan pumped $29.3 billion into the financial system on September 17, 2008, and the Reserve Bank of Australia added $3.45 billion the same day.
In developing and emerging economies, responses to the global crisis mainly consisted in low-rates monetary policy (Asia and the Middle East mainly) coupled with the depreciation of the currency against the dollar. There were also stimulus plans in some Asian countries, in the Middle East and in Argentina. In Asia, plans generally amounted to 1 to 3% of GDP, with the notable exception of China, which announced a plan accounting for 16% of GDP (6% of GDP per year).
European policy responses
Until September 2008, European policy measures were limited to a small number of countries (Spain and Italy). In both countries, the measures were dedicated to households (tax rebates) reform of the taxation system to support specific sectors such as housing. The European Commission proposed a €200 billion stimulus plan to be implemented at the European level by the countries. At the beginning of 2009, the UK and Spain completed their initial plans, while Germany announced a new plan.
On September 29, 2008, the Belgian, Luxembourg and Dutch authorities partially nationalised Fortis. The German government bailed out Hypo Real Estate.
On October 8, 2008, the British Government announced a bank rescue package of around £500 billion ($850 billion at the time). The plan comprises three parts. The first £200 billion would be made in regard to the banks in liquidity stack. The second part will consist of the state government increasing the capital market within the banks. Along with this, £50 billion will be made available if the banks needed it, finally the government will write off any eligible lending between the British banks with a limit to £250 billion.
In early December 2008, German Finance Minister Peer Steinbrück indicated a lack of belief in a "Great Rescue Plan" and reluctance to spend more money addressing the crisis. In March 2009, The European Union Presidency confirmed that the EU was at the time strongly resisting the US pressure to increase European budget deficits.
From 2010, the United Kingdom began a fiscal consolidation program to reduce debt and deficit levels while at the same time stimulating economic recovery. Other European countries also began fiscal consolidation with similar aims.
Global responses
Most political responses to the economic and financial crisis has been taken, as seen above, by individual nations. Some coordination took place at the European level, but the need to cooperate at the global level has led leaders to activate the G-20 major economies entity. A first summit dedicated to the crisis took place, at the Heads of state level in November 2008 (2008 G-20 Washington summit).
The G-20 countries met in a summit held on November 2008 in Washington to address the economic crisis. Apart from proposals on international financial regulation, they pledged to take measures to support their economy and to coordinate them, and refused any resort to protectionism.
Another G-20 summit was held in London on April 2009. Finance ministers and central banks leaders of the G-20 met in Horsham, England, on March to prepare the summit, and pledged to restore global growth as soon as possible. They decided to coordinate their actions and to stimulate demand and employment. They also pledged to fight against all forms of protectionism and to maintain trade and foreign investments. These actions will cost $1.1tn.
They also committed to maintain the supply of credit by providing more liquidity and recapitalising the banking system, and to implement rapidly the stimulus plans. As for central bankers, they pledged to maintain low-rates policies as long as necessary. Finally, the leaders decided to help emerging and developing countries, through a strengthening of the IMF.
Policy recommendations
IMF recommendation
The IMF stated in September 2010 that the financial crisis would not end without a major decrease in unemployment as hundreds of millions of people were unemployed worldwide. The IMF urged governments to expand social safety nets and to generate job creation even as they are under pressure to cut spending. The IMF also encouraged governments to invest in skills training for the unemployed and even governments of countries, similar to that of Greece, with major debt risk to first focus on long-term economic recovery by creating jobs.
Raising interest rates
The Bank of Israel was the first to raise interest rates after the global recession began. It increased rates in August 2009.
On October 6, 2009, Australia became the first G20 country to raise its main interest rate, with the Reserve Bank of Australia moving rates up from 3.00% to 3.25%.
The Norges Bank of Norway and the Reserve Bank of India raised interest rates in March 2010.
On November 2, 2017 the Bank of England raised interest rates for the first time since March 2009 from 0.25% to 0.5% in an attempt to curb inflation.
Comparisons with the Great Depression
On April 17, 2009, the then head of the IMF Dominique Strauss-Kahn said that there was a chance that certain countries may not implement the proper policies to avoid feedback mechanisms that could eventually turn the recession into a depression. "The free-fall in the global economy may be starting to abate, with a recovery emerging in 2010, but this depends crucially on the right policies being adopted today." The IMF pointed out that unlike the Great Depression, this recession was synchronised by global integration of markets. Such synchronized recessions were explained to last longer than typical economic downturns and have slower recoveries.
Olivier Blanchard, IMF Chief Economist, stated that the percentage of workers laid off for long stints has been rising with each downturn for decades but the figures have surged this time. "Long-term unemployment is alarmingly high: in the United States, half the unemployed have been out of work for over six months, something we have not seen since the Great Depression." The IMF also stated that a link between rising inequality within Western economies and deflating demand may exist. The last time that the wealth gap reached such skewed extremes was in 1928–1929.
See also
- Basel Accords
- Collateralized debt obligation
- 2000s commodities boom
- Economic bubble
- Financial crisis of 2007–08
- Fractional-reserve banking
- Great Recession in Europe
- Great Recession in the United States
- Great Regression
- International relations since 1989
- Kondratiev wave
- Lost Decade
- Peak oil
- Savings and loan crisis
- Stock market crash
- COVID-19 recession
- The Disrupted (film)