| Berlin Wall | |
|---|---|
 View from the West Berlin side of graffiti art on the Wall in 1986. The Wall's "death strip", on the east side of the Wall, here follows the curve of the Luisenstadt Canal (filled in 1932). | |
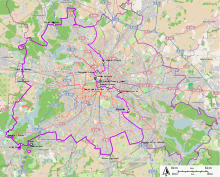
 Map of the location of the Berlin Wall, showing checkpoints | |
| General information | |
| Type | Wall |
| Country |
|
| Coordinates | 52.516°N 13.377°ECoordinates: 52.516°N 13.377°E |
| Construction started | 13 August 1961 |
| Demolished | 9 November 1989 – 1994 |
| Dimensions | |
| Other dimensions |
|
| Technical details | |
| Size | 155 km (96.3 mi) |
| Eastern Bloc |
|---|
 |
The Berlin Wall (German: Berliner Mauer, pronounced [bɛʁˌliːnɐ ˈmaʊ̯ɐ]) was a guarded concrete barrier that physically and ideologically divided Berlin from 1961 to 1989. Construction of the wall was commenced by the German Democratic Republic (GDR, East Germany) on 13 August 1961. The Wall cut off West Berlin from surrounding East Germany, including East Berlin. The barrier included guard towers placed along large concrete walls, accompanied by a wide area (later known as the "death strip") that contained anti-vehicle trenches, beds of nails and other defenses. The Eastern Bloc portrayed the Wall as protecting its population from fascist elements conspiring to prevent the "will of the people" from building a socialist state in East Germany.
GDR authorities officially referred to the Berlin Wall as the Anti-Fascist Protection Rampart (German: Antifaschistischer Schutzwall). The West Berlin city government sometimes referred to it as the "Wall of Shame", a term coined by mayor Willy Brandt in reference to the Wall's restriction on freedom of movement. Along with the separate and much longer Inner German border (IGB), which demarcated the border between East and West Germany, it came to symbolize physically the "Iron Curtain" that separated Western Europe and the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War.
Before the Wall's erection, 3.5 million East Germans circumvented Eastern Bloc emigration restrictions and defected from the GDR, many by crossing over the border from East Berlin into West Berlin; from there they could then travel to West Germany and to other Western European countries. Between 1961 and 1989, the Wall prevented almost all such emigration. During this period, over 100,000 people attempted to escape, and over 5,000 people succeeded in escaping over the Wall, with an estimated death toll ranging from 136 to more than 200 in and around Berlin.
In 1989, a series of revolutions in nearby Eastern Bloc countries—in Poland and Hungary in particular—caused a chain reaction in East Germany. In particular, the Pan-European Picnic in August 1989 set in motion a peaceful development during which the Iron Curtain largely broke, the rulers in the East came under pressure, the Berlin Wall fell and finally the Eastern Bloc fell apart. After several weeks of civil unrest, the East German government announced on 9 November 1989 that all GDR citizens could visit West Germany and West Berlin. Crowds of East Germans crossed and climbed onto the Wall, joined by West Germans on the other side in a celebratory atmosphere. Over the next few weeks, euphoric people and souvenir hunters chipped away parts of the Wall. The Brandenburg Gate, a few meters from the Berlin Wall, was opened on 22 December 1989. The demolition of the Wall officially began on 13 June 1990 and was completed in 1994. The "fall of the Berlin Wall" paved the way for German reunification, which formally took place on 3 October 1990.
Background
Post-war Germany
After the end of World War II in Europe, what remained of pre-war Germany west of the Oder-Neisse line was divided into four occupation zones (as per the Potsdam Agreement), each one controlled by one of the four occupying Allied powers: the United States, the United Kingdom, France and the Soviet Union. The capital of Berlin, as the seat of the Allied Control Council, was similarly subdivided into four sectors despite the city's location, which was fully within the Soviet zone.
Within two years, political divisions increased between the Soviets and the other occupying powers. These included the Soviets' refusal to agree to reconstruction plans making post-war Germany self-sufficient, and to a detailed accounting of industrial plants, goods and infrastructure—some of which had already been removed by the Soviets. France, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Benelux countries later met to combine the non-Soviet zones of Germany into one zone for reconstruction, and to approve the extension of the Marshall Plan.
Eastern Bloc and the Berlin airlift
Following the defeat of Nazi Germany in World War II, the Soviet Union engineered the installation of friendly Communist governments in most of the countries occupied by Soviet military forces at the end of the War, including Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Bulgaria, Romania, and the GDR, which together with Albania formed the Comecon in 1949 and later a military alliance, the Warsaw Pact. This bloc of nations was set up by the Soviets in opposition to NATO in the capitalist West in what became the Cold War.
Since the end of the War, the Soviets together with like-minded East Germans created a new Soviet-style regime in the Soviet Zone and later the GDR, on a centrally planned socialist economic model with nationalized means of production, and with repressive police state institutions, under party dictatorship of the SED similar to the party dictatorship of the Soviet Communist Party in the USSR.
At the same time, a parallel regime was established under the strict control of the Western powers in the zones of post-war Germany occupied by them, culminating in the foundation of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949, which initially claimed to be the sole legitimate power in all of Germany, East and West. The material standard of living in the Western zones of Berlin began to improve quickly, and residents of the Soviet Zone soon began leaving for the West in large numbers, fleeing hunger, poverty and repression in the Soviet Zone for a better life in the West. Soon residents of other parts of the Soviet Zone began to escape to the West through Berlin, and this migration, called in Germany "Republikflucht", deprived the Soviet Zone not only of working forces desperately needed for post-war reconstruction but disproportionately highly educated people, which came to be known as the "Brain Drain".
In 1948, in response to moves by the Western powers to establish a separate, federal system of government in the Western zones, and to extend the Marshall Plan to Germany, the Soviets instituted the Berlin Blockade, preventing people, food, materials and supplies from arriving in West Berlin by land routes through the Soviet zone. The United States, the United Kingdom, France, Canada, Australia, New Zealand and several other countries began a massive "airlift", supplying West Berlin with food and other supplies. The Soviets mounted a public relations campaign against the Western policy change. Communists attempted to disrupt the elections of 1948, preceding large losses therein, while 300,000 Berliners demonstrated for the international airlift to continue. In May 1949, Stalin lifted the blockade, permitting the resumption of Western shipments to Berlin.
The German Democratic Republic (the "GDR"; East Germany) was declared on 7 October 1949. On that day, the USSR ended the Soviet military government which had governed the Soviet Occupation Zone (Sowetische Besatzungszone) since the end of the War and handed over legal power to the Provisorische Volkskammer under the new Constitution of the GDR which came into force that day. However, until 1955, the Soviets maintained considerable legal control over the GDR state, including the regional governments, through the Sowetische Kontrollkommission and maintained a presence in various East German administrative, military, and secret police structures. Even after legal sovereignty of the GDR was restored in 1955, the Soviet Union continued to maintain considerable influence over administration and lawmaking in the GDR through the Soviet embassy and through the implicit threat of force which could be exercised through the continuing large Soviet military presence in the GDR, which was used to bloodily repress protests in East Germany in June 1953.
East Germany differed from West Germany (Federal Republic of Germany), which developed into a Western capitalist country with a social market economy and a democratic parliamentary government. Continual economic growth starting in the 1950s fueled a 20-year "economic miracle" ("Wirtschaftswunder"). As West Germany's economy grew, and its standard of living steadily improved, many East Germans wanted to move to West Germany.
Emigration westward in the early 1950s
After the Soviet occupation of Eastern Europe at the end of World War II, the majority of those living in the newly acquired areas of the Eastern Bloc aspired to independence and wanted the Soviets to leave. Taking advantage of the zonal border between occupied zones in Germany, the number of GDR citizens moving to West Germany totaled 187,000 in 1950; 165,000 in 1951; 182,000 in 1952; and 331,000 in 1953. One reason for the sharp 1953 increase was fear of potential further Sovietization, given the increasingly paranoid actions of Joseph Stalin in late 1952 and early 1953. 226,000 had fled in just the first six months of 1953.
Erection of the inner German border
By the early 1950s, the Soviet approach to controlling national movement, restricting emigration, was emulated by most of the rest of the Eastern Bloc, including East Germany. The restrictions presented a quandary for some Eastern Bloc states, which had been more economically advanced and open than the Soviet Union, such that crossing borders seemed more natural—especially where no prior border existed between East and West Germany.
Up until 1952, the demarcation lines between East Germany and the western occupied zones could be easily crossed in most places. On 1 April 1952, East German leaders met the Soviet leader Joseph Stalin in Moscow; during the discussions, Stalin's foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov proposed that the East Germans should "introduce a system of passes for visits of West Berlin residents to the territory of East Berlin [so as to stop] free movement of Western agents" in the GDR. Stalin agreed, calling the situation "intolerable". He advised the East Germans to build up their border defenses, telling them that "The demarcation line between East and West Germany should be considered a border—and not just any border, but a dangerous one ... The Germans will guard the line of defence with their lives."
Consequently, the inner German border between the two German states was closed, and a barbed-wire fence erected. The border between the Western and Eastern sectors of Berlin, however, remained open, although traffic between the Soviet and the Western sectors was somewhat restricted. This resulted in Berlin becoming a magnet for East Germans desperate to escape life in the GDR, and also a flashpoint for tension between the United States and the Soviet Union.
In 1955, the Soviets gave East Germany authority over civilian movement in Berlin, passing control to a regime not recognized in the West. Initially, East Germany granted "visits" to allow its residents access to West Germany. However, following the defection of large numbers of East Germans (known as Republikflucht) under this regime, the new East German state legally restricted virtually all travel to the West in 1956. Soviet East German ambassador Mikhail Pervukhin observed that "the presence in Berlin of an open and essentially uncontrolled border between the socialist and capitalist worlds unwittingly prompts the population to make a comparison between both parts of the city, which unfortunately does not always turn out in favour of Democratic [East] Berlin."
Berlin emigration loophole
With the closing of the inner German border officially in 1952, the border in Berlin remained considerably more accessible because it was administered by all four occupying powers. Accordingly, Berlin became the main route by which East Germans left for the West. On 11 December 1957, East Germany introduced a new passport law that reduced the overall number of refugees leaving Eastern Germany.
It had the unintended result of drastically increasing the percentage of those leaving through West Berlin from 60% to well over 90% by the end of 1958. Those caught trying to leave East Berlin were subjected to heavy penalties, but with no physical barrier and subway train access still available to West Berlin, such measures were ineffective. The Berlin sector border was essentially a "loophole" through which Eastern Bloc citizens could still escape. The 3.5 million East Germans who had left by 1961 totalled approximately 20% of the entire East German population.
An important reason that passage between East Germany and West Berlin was not stopped earlier was that doing so would cut off much of the railway traffic in East Germany. Construction of a new railway bypassing West Berlin, the Berlin outer ring, commenced in 1951. Following the completion of the railway in 1961, closing the border became a more practical proposition. (See History of rail transport in Germany.)
Brain drain
The emigrants tended to be young and well-educated, leading to the "brain drain" feared by officials in East Germany. Yuri Andropov, then the CPSU Director on Relations with Communist and Workers' Parties of Socialist Countries, wrote an urgent letter on 28 August 1958 to the Central Committee about the significant 50% increase in the number of East German intelligentsia among the refugees. Andropov reported that, while the East German leadership stated that they were leaving for economic reasons, testimony from refugees indicated that the reasons were more political than material. He stated "the flight of the intelligentsia has reached a particularly critical phase."
By 1960, the combination of World War II and the massive emigration westward left East Germany with only 61% of its population of working age, compared to 70.5% before the war. The loss was disproportionately heavy among professionals: engineers, technicians, physicians, teachers, lawyers, and skilled workers. The direct cost of manpower losses to East Germany (and corresponding gain to the West) has been estimated at $7 billion to $9 billion, with East German party leader Walter Ulbricht later claiming that West Germany owed him $17 billion in compensation, including reparations as well as manpower losses. In addition, the drain of East Germany's young population potentially cost it over 22.5 billion marks in lost educational investment. The brain drain of professionals had become so damaging to the political credibility and economic viability of East Germany that the re-securing of the German communist frontier was imperative.
The exodus of emigrants from East Germany presented two minor potential benefits: an easy opportunity to smuggle East German secret agents to West Germany, and a reduction in the number of citizens hostile to the communist regime. Neither of these advantages, however, proved particularly useful.
Start of the construction (1961)
On 15 June 1961, First Secretary of the Socialist Unity Party and GDR State Council chairman Walter Ulbricht stated in an international press conference, "Niemand hat die Absicht, eine Mauer zu errichten!" (No one has the intention of erecting a wall!). It was the first time the colloquial term Mauer (wall) had been used in this context.
The transcript of a telephone call between Nikita Khrushchev and Ulbricht, on 1 August in the same year, suggests that the initiative for the construction of the Wall came from Khrushchev. However, other sources suggest that Khrushchev had initially been wary about building a wall, fearing negative Western reaction. Nevertheless, Ulbricht had pushed for a border closure for quite some time, arguing that East Germany's very existence was at stake.
Khrushchev had become emboldened upon seeing US president John F. Kennedy's youth and inexperience, which he considered a weakness. In the 1961 Vienna summit, Kennedy made the error of admitting that the US wouldn't actively oppose the building of a barrier. A feeling of miscalculation and failure immediately afterwards was admitted by Kennedy in a candid interview with New York Times columnist James "Scotty" Reston. On Saturday, 12 August 1961, the leaders of the GDR attended a garden party at a government guesthouse in Döllnsee, in a wooded area to the north of East Berlin. There, Ulbricht signed the order to close the border and erect a wall.
At midnight, the police and units of the East German army began to close the border and, by Sunday morning, 13 August, the border with West Berlin was closed. East German troops and workers had begun to tear up streets running alongside the border to make them impassable to most vehicles and to install barbed wire entanglements and fences along the 156 kilometres (97 mi) around the three western sectors, and the 43 kilometres (27 mi) that divided West and East Berlin. The date of 13 August became commonly referred to as Barbed Wire Sunday in Germany.
The barrier was built inside East Berlin or East German territory to ensure that it did not encroach on West Berlin at any point. Generally, the Wall was only slightly inside East Berlin, but in a few places it was some distance from the legal border, most notably at Potsdamer Bahnhof and the Lenné Triangle that is now much of the Potsdamer Platz development.
Later, the initial barrier was built up into the Wall proper, the first concrete elements and large blocks being put in place on 17 August. During the construction of the Wall, National People's Army (NVA) and Combat Groups of the Working Class (KdA) soldiers stood in front of it with orders to shoot anyone who attempted to defect. Additionally, chain fences, walls, minefields and other obstacles were installed along the length of East Germany's western border with West Germany proper. A huge no man's land was cleared to provide a clear line of fire at fleeing refugees.
Immediate effects
With the closing of the east–west sector boundary in Berlin, the vast majority of East Germans could no longer travel or emigrate to West Germany. Berlin soon went from being the easiest place to make an unauthorized crossing between East and West Germany to being the most difficult. Many families were split, while East Berliners employed in the West were cut off from their jobs. West Berlin became an isolated exclave in a hostile land. West Berliners demonstrated against the Wall, led by their Mayor (Oberbürgermeister) Willy Brandt, who criticized the United States for failing to respond and went so far as to suggest to Washington what to do next. Kennedy was furious. Allied intelligence agencies had hypothesized about a wall to stop the flood of refugees, but the main candidate for its location was around the perimeter of the city. In 1961, Secretary of State Dean Rusk proclaimed, "The Wall certainly ought not to be a permanent feature of the European landscape. I see no reason why the Soviet Union should think it is—it is to their advantage in any way to leave there that monument to communist failure."
United States and UK sources had expected the Soviet sector to be sealed off from West Berlin but were surprised by how long the East Germans took for such a move. They considered the Wall as an end to concerns about a GDR/Soviet retaking or capture of the whole of Berlin; the Wall would presumably have been an unnecessary project if such plans were afloat. Thus, they concluded that the possibility of a Soviet military conflict over Berlin had decreased.
The East German government claimed that the Wall was an "anti-fascist protective rampart" (German: "antifaschistischer Schutzwall") intended to dissuade aggression from the West. Another official justification was the activities of Western agents in Eastern Europe. The Eastern German government also claimed that West Berliners were buying out state-subsidized goods in East Berlin. East Germans and others greeted such statements with skepticism, as most of the time, the border was only closed for citizens of East Germany traveling to the West, but not for residents of West Berlin travelling to the East. The construction of the Wall had caused considerable hardship to families divided by it. Most people believed that the Wall was mainly a means of preventing the citizens of East Germany from entering or fleeing to West Berlin.
Secondary response
The National Security Agency was the only American intelligence agency that was aware that East Germany was to take action to deal with the brain drain problem. On 9 August 1961, the NSA intercepted an advance warning information of the Socialist Unity Party's plan to close the intra-Berlin border between East and West Berlin completely for foot traffic. The interagency intelligence Berlin Watch Committee assessed that this intercept "might be the first step in a plan to close the border." This warning did not reach John F. Kennedy until noon on 13 August 1961, while he was vacationing in his yacht off the Kennedy Compound in Hyannis Port, Massachusetts. While Kennedy was angry that he had no advance warning, he was relieved that the East Germans and the Soviets had only divided Berlin without taking any action against West Berlin's access to the West. However, he denounced the Berlin Wall, whose erection worsened the relations between the United States and the Soviet Union.
In response to the erection of the Berlin Wall, a retired general, Lucius D. Clay, was appointed by Kennedy as his special advisor with ambassadorial rank. Clay had been the Military Governor of the US Zone of Occupation in Germany during the period of the Berlin Blockade and had ordered the first measures in what became the Berlin Airlift. He was immensely popular with the residents of West Berlin, and his appointment was an unambiguous sign that Kennedy would not compromise on the status of West Berlin. As a symbolic gesture, Kennedy sent Clay and Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson to West Berlin. They landed at Tempelhof Airport on the afternoon of Saturday, 19 August 1961 and were greeted enthusiastically by the local population.
They arrived in a city defended by three Allied brigades—one each from the UK (Berlin Infantry Brigade), the US (Berlin Brigade), and France (Forces Françaises à Berlin). On 16 August, Kennedy had given the order for them to be reinforced. Early on 19 August, the 1st Battle Group, 18th Infantry Regiment (commanded by Colonel Glover S. Johns Jr.) was alerted.
On Sunday morning, U.S. troops marched from West Germany through East Germany, bound for West Berlin. Lead elements—arranged in a column of 491 vehicles and trailers carrying 1,500 men, divided into five march units—left the Helmstedt-Marienborn checkpoint at 06:34. At Marienborn, the Soviet checkpoint next to Helmstedt on the West German-East German border, US personnel were counted by guards. The column was 160 kilometres (99 mi) long, and covered 177 kilometres (110 mi) from Marienborn to Berlin in full battle gear. East German police watched from beside trees next to the autobahn all the way along.
The front of the convoy arrived at the outskirts of Berlin just before noon, to be met by Clay and Johnson, before parading through the streets of Berlin in front of a large crowd. At 04:00 on 21 August, Lyndon Johnson left West Berlin in the hands of General Frederick O. Hartel and his brigade of 4,224 officers and men. "For the next three and a half years, American battalions would rotate into West Berlin, by autobahn, at three-month intervals to demonstrate Allied rights to the city".
The creation of the Wall had important implications for both German states. By stemming the exodus of people from East Germany, the East German government was able to reassert its control over the country: in spite of discontent with the Wall, economic problems caused by dual currency and the black market were largely eliminated. The economy in the GDR began to grow. However, the Wall proved a public relations disaster for the communist bloc as a whole. Western powers portrayed it as a symbol of communist tyranny, particularly after East German border guards shot and killed would-be defectors. Such fatalities were later treated as acts of murder by the reunified Germany.
Structure and adjacent areas
Layout and modifications
| Length (km) | Description |
|---|---|
| 156.4 | Bordering around West Berlin within 3.4m and 4.2m in height |
| 111.9 | Concrete walls |
| 44.5 | Metal mesh fence (along death strip) |
| 112.7 | Cross attachment in Potsdam |
| 43.7 | Cross attachment along the border of East and West Berlin |
| 0.5 | Remains of house fronts, land mansion bricks |
| 58.95 | Wall-shaped front wall with a height of 3.40 m |
| 68.42 | Expanded metal fence with a height of 2.90 m as a "front barrier" |
| 161 | Light strip |
| 113.85 | Limit signal and barrier fence (GSSZ) |
| 127.5 | Contact and signal fence |
| 124.3 | Border patrol |
| Actual number | Descriptions |
| 186 | Observation towers (302 in West-Berlin) |
| 31 | Implementing agencies |
| 259 | Dog runs |
| 20 | Bunkers |
- Border
- Outer strip
- Concrete wall with rounded top
- Anti vehicle ditch
- "Death strip" sand bank
- Guard road
- Lighting
- Observation towers
- Spikes or tank traps
- Electrified fence with alarms
- Inner wall
- Restricted zone
The Berlin Wall was more than 140 kilometres (87 mi) long. In June 1962, a second, parallel fence, also known as a “hinterland” wall (inner wall), was built some 100 metres (110 yd) farther into East German territory. The houses contained between the wall and fences were razed and the inhabitants relocated, thus establishing what later became known as the death strip. The death strip was covered with raked sand or gravel, rendering footprints easy to notice, easing the detection of trespassers and also enabling officers to see which guards had neglected their task; it offered no cover; and, most importantly, it offered clear fields of fire for the Wall guards.
Through the years, the Berlin Wall evolved through four versions:
- Wire fence and concrete block wall (1961)
- Improved wire fence (1962–1965)
- Improved concrete wall (1965–1975)
- Grenzmauer 75 (Border Wall 75) (1975–1989)
The "fourth-generation Wall", known officially as "Stützwandelement UL 12.11" (retaining wall element UL 12.11), was the final and most sophisticated version of the Wall. Begun in 1975 and completed about 1980, it was constructed from 45,000 separate sections of reinforced concrete, each 3.6 metres (12 ft) high and 1.2 metres (3.9 ft) wide, and cost DDM16,155,000 or about US$3,638,000. The concrete provisions added to this version of the Wall were done to prevent escapees from driving their cars through the barricades. At strategic points, the Wall was constructed to a somewhat weaker standard, so that East German and Soviet armored vehicles could easily break through in the event of war.
The top of the wall was lined with a smooth pipe, intended to make it more difficult to scale. The Wall was reinforced by mesh fencing, signal fencing, anti-vehicle trenches, barbed wire, dogs on long lines, "beds of nails" (also known as "Stalin's Carpet") under balconies hanging over the "death strip", over 116 watchtowers, and 20 bunkers with hundreds of guards. This version of the Wall is the one most commonly seen in photographs, and surviving fragments of the Wall in Berlin and elsewhere around the world are generally pieces of the fourth-generation Wall. The layout came to resemble the inner German border in most technical aspects, except that the Berlin Wall had no landmines nor spring-guns. Maintenance was performed on the outside of the wall by personnel who accessed the area outside it either via ladders or via hidden doors within the wall. These doors could not be opened by a single person, needing two separate keys in two separate keyholes to unlock.
As was the case with the inner German border, an unfortified strip of Eastern territory was left outside the wall. This outer strip was used by workers to paint over graffiti and perform other maintenance on the outside of the wall Unlike the inner German border, however, the outer strip was usually no more than four meters wide, and, in photos from the era, the exact location of the actual border in many places appears not even to have been marked. Also in contrast with the inner German border, little interest was shown by East German law enforcement in keeping outsiders off the outer strip; sidewalks of West Berlin streets even ran inside it.
Despite the East German government's general policy of benign neglect, vandals were known to have been pursued in the outer strip, and even arrested. In 1986, defector and political activist Wolfram Hasch and four other defectors were standing inside the outer strip defacing the wall when East German personnel emerged from one of the hidden doors to apprehend them. All but Hasch escaped back into the western sector. Hasch himself was arrested, dragged through the door into the death strip, and later convicted of illegally crossing the de jure border outside the wall. Graffiti artist Thierry Noir has reported having often been pursued there by East German soldiers. While some graffiti artists were chased off the outer strip, others, such as Keith Haring, were seemingly tolerated.
Surrounding municipalities
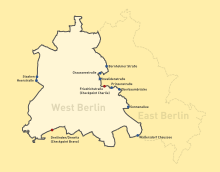
Besides the sector-sector boundary within Berlin itself, the Wall also separated West Berlin from the present-day state of Brandenburg. The following present-day municipalities, listed in counter-clockwise direction, share a border with the former West Berlin:
- Oberhavel: Mühlenbecker Land (partially), Glienicke/Nordbahn, Hohen Neuendorf, Hennigsdorf
- Havelland: Schönwalde-Glien, Falkensee, Dallgow-Döberitz
- Potsdam (urban district)
- Potsdam-Mittelmark: Stahnsdorf, Kleinmachnow, Teltow
- Teltow-Fläming: Großbeeren, Blankenfelde-Mahlow
- Dahme-Spreewald: Schönefeld (partially)
Official crossings and usage
There were nine border crossings between East and West Berlin. These allowed visits by West Berliners, other West Germans, Western foreigners and Allied personnel into East Berlin, as well as visits by GDR citizens and citizens of other socialist countries into West Berlin, provided that they held the necessary permits. These crossings were restricted according to which nationality was allowed to use it (East Germans, West Germans, West Berliners, other countries). The best known was the vehicle and pedestrian checkpoint at the corner of Friedrichstraße and Zimmerstraße (Checkpoint Charlie), which was restricted to Allied personnel and foreigners.
Several other border crossings existed between West Berlin and surrounding East Germany. These could be used for transit between West Germany and West Berlin, for visits by West Berliners into East Germany, for transit into countries neighbouring East Germany (Poland, Czechoslovakia, Denmark), and for visits by East Germans into West Berlin carrying a permit. After the 1972 agreements, new crossings were opened to allow West Berlin waste to be transported into East German dumps, as well as some crossings for access to West Berlin's exclaves (see Steinstücken).
Four autobahns connected West Berlin to West Germany, including Berlin-Helmstedt autobahn, which entered East German territory between the towns of Helmstedt and Marienborn (Checkpoint Alpha), and which entered West Berlin at Dreilinden (Checkpoint Bravo for the Allied forces) in southwestern Berlin. Access to West Berlin was also possible by railway (four routes) and by boat for commercial shipping via canals and rivers.
Non-German Westerners could cross the border at Friedrichstraße station in East Berlin and at Checkpoint Charlie. When the Wall was erected, Berlin's complex public transit networks, the S-Bahn and U-Bahn, were divided with it. Some lines were cut in half; many stations were shut down. Three western lines traveled through brief sections of East Berlin territory, passing through eastern stations (called Geisterbahnhöfe, or ghost stations) without stopping. Both the eastern and western networks converged at Friedrichstraße, which became a major crossing point for those (mostly Westerners) with permission to cross.
Crossing
West Germans and citizens of other Western countries could generally visit East Germany, often after applying for a visa at an East German embassy several weeks in advance. Visas for day trips restricted to East Berlin were issued without previous application in a simplified procedure at the border crossing. However, East German authorities could refuse entry permits without stating a reason. In the 1980s, visitors from the western part of the city who wanted to visit the eastern part had to exchange at least DM 25 into East German currency at the poor exchange rate of 1:1. It was forbidden to export East German currency from the East, but money not spent could be left at the border for possible future visits. Tourists crossing from the west had to also pay for a visa, which cost DM 5; West Berliners did not have to pay this fee.
West Berliners initially could not visit East Berlin or East Germany at all—all crossing points were closed to them between 26 August 1961 and 17 December 1963. In 1963, negotiations between East and West resulted in a limited possibility for visits during the Christmas season that year (Passierscheinregelung). Similar, very limited arrangements were made in 1964, 1965 and 1966.
In 1971, with the Four Power Agreement on Berlin, agreements were reached that allowed West Berliners to apply for visas to enter East Berlin and East Germany regularly, comparable to the regulations already in force for West Germans. However, East German authorities could still refuse entry permits.
East Berliners and East Germans could not, at first, travel to West Berlin or West Germany at all. This regulation remained in force essentially until the fall of the Wall, but over the years several exceptions to these rules were introduced, the most significant being:
- Elderly pensioners could travel to the West starting in 1964
- Visits of relatives for important family matters
- People who had to travel to the West for professional reasons (for example, artists, truck drivers, musicians, writers, etc.)
For each of these exceptions, GDR citizens had to apply for individual approval, which was never guaranteed. In addition, even if travel was approved, GDR travellers could exchange only a very small amount of East German Marks into Deutsche Marks (DM), thus limiting the financial resources available for them to travel to the West. This led to the West German practice of granting a small amount of DM annually (Begrüßungsgeld, or welcome money) to GDR citizens visiting West Germany and West Berlin to help alleviate this situation.
Citizens of other East European countries were in general subject to the same prohibition of visiting Western countries as East Germans, though the applicable exception (if any) varied from country to country.
Allied military personnel and civilian officials of the Allied forces could enter and exit East Berlin without submitting to East German passport controls, purchasing a visa or being required to exchange money. Likewise, Soviet military patrols could enter and exit West Berlin. This was a requirement of the post-war Four Powers Agreements. A particular area of concern for the Western Allies involved official dealings with East German authorities when crossing the border, since Allied policy did not recognize the authority of the GDR to regulate Allied military traffic to and from West Berlin, as well as the Allied presence within Greater Berlin, including entry into, exit from, and presence within East Berlin.
The Allies held that only the Soviet Union, and not the GDR, had the authority to regulate Allied personnel in such cases. For this reason, elaborate procedures were established to prevent inadvertent recognition of East German authority when engaged in travel through the GDR and when in East Berlin. Special rules applied to travel by Western Allied military personnel assigned to the military liaison missions accredited to the commander of Soviet forces in East Germany, located in Potsdam.
Allied personnel were restricted by policy when travelling by land to the following routes:
- Transit between West Germany and West Berlin
- Road: the Helmstedt–Berlin autobahn (A2) (checkpoints Alpha and Bravo respectively). Soviet military personnel manned these checkpoints and processed Allied personnel for travel between the two points. Military personnel were required to be in uniform when traveling in this manner.
- Rail: Western Allied military personnel and civilian officials of the Allied forces were forbidden to use commercial train service between West Germany and West Berlin, because of GDR passport and customs controls when using them. Instead, the Allied forces operated a series of official (duty) trains that traveled between their respective duty stations in West Germany and West Berlin. When transiting the GDR, the trains would follow the route between Helmstedt and Griebnitzsee, just outside West Berlin. In addition to persons traveling on official business, authorized personnel could also use the duty trains for personal travel on a space-available basis. The trains traveled only at night, and as with transit by car, Soviet military personnel handled the processing of duty train travelers. (See History of the Berlin S-Bahn.)
- Entry into and exit from East Berlin
- Checkpoint Charlie (as a pedestrian or riding in a vehicle)
As with military personnel, special procedures applied to travel by diplomatic personnel of the Western Allies accredited to their respective embassies in the GDR. This was intended to prevent inadvertent recognition of East German authority when crossing between East and West Berlin, which could jeopardize the overall Allied position governing the freedom of movement by Allied forces personnel within all Berlin.
Ordinary citizens of the Western Allied powers, not formally affiliated with the Allied forces, were authorized to use all designated transit routes through East Germany to and from West Berlin. Regarding travel to East Berlin, such persons could also use the Friedrichstraße train station to enter and exit the city, in addition to Checkpoint Charlie. In these instances, such travelers, unlike Allied personnel, had to submit to East German border controls.
Defection attempts
During the years of the Wall, around 5,000 people successfully defected to West Berlin. The number of people who died trying to cross the Wall, or as a result of the Wall's existence, has been disputed. The most vocal claims by Alexandra Hildebrandt, Director of the Checkpoint Charlie Museum and widow of the Museum's founder, estimated the death toll to be well above 200. A historic research group at the Centre for Contemporary History (ZZF) in Potsdam has confirmed at least 140 deaths. Prior official figures listed 98 as being killed.
The East German government issued shooting orders (Schießbefehl) to border guards dealing with defectors, though such orders are not the same as "shoot to kill" orders. GDR officials denied issuing the latter. In an October 1973 order later discovered by researchers, guards were instructed that people attempting to cross the Wall were criminals and needed to be shot:
Do not hesitate to use your firearm, not even when the border is breached in the company of women and children, which is a tactic the traitors have often used.
Early successful escapes involved people jumping the initial barbed wire or leaping out of apartment windows along the line, but these ended as the Wall was fortified. East German authorities no longer permitted apartments near the Wall to be occupied, and any building near the Wall had its windows boarded and later bricked up. On 15 August 1961, Conrad Schumann was the first East German border guard to escape by jumping the barbed wire to West Berlin.
On 22 August 1961, Ida Siekmann was the first casualty at the Berlin Wall: she died after she jumped out of her third floor apartment at 48 Bernauer Strasse. The first person to be shot and killed while trying to cross to West Berlin was Günter Litfin, a twenty-four-year-old tailor. He attempted to swim across the Spree to West Berlin on 24 August 1961, the same day that East German police had received shoot-to-kill orders to prevent anyone from escaping.
Another dramatic escape was carried out in April 1963 by Wolfgang Engels, a 19-year-old civilian employee of the Nationale Volksarmee (NVA). Engels stole a Soviet armored personnel carrier from a base where he was deployed and drove it right into the Wall. He was fired at and seriously wounded by border guards. But a West German policeman intervened, firing his weapon at the East German border guards. The policeman removed Engels from the vehicle, which had become entangled in the barbed wire.
East Germans successfully defected by a variety of methods: digging long tunnels under the Wall, waiting for favorable winds and taking a hot air balloon, sliding along aerial wires, flying ultralights and, in one instance, simply driving a sports car at full speed through the basic, initial fortifications. When a metal beam was placed at checkpoints to prevent this kind of defection, up to four people (two in the front seats and possibly two in the boot) drove under the bar in a sports car that had been modified to allow the roof and windscreen to come away when it made contact with the beam. They lay flat and kept driving forward. The East Germans then built zig-zagging roads at checkpoints. The sewer system predated the Wall, and some people escaped through the sewers, in a number of cases with assistance from the Unternehmen Reisebüro. In September 1962, 29 people escaped through a tunnel to the west. At least 70 tunnels were dug under the wall; only 19 were successful in allowing fugitives—about 400 persons—to escape. The East Germany authorities eventually used seismographic and acoustic equipment to detect the practice. In 1962, they planned an attempt to use explosives to destroy one tunnel, but this was not carried out as it was apparently sabotaged by a member of the Stasi.
An airborne escape was made by Thomas Krüger, who landed a Zlin Z 42M light aircraft of the Gesellschaft für Sport und Technik, an East German youth military training organization, at RAF Gatow. His aircraft, registration DDR-WOH, was dismantled and returned to the East Germans by road, complete with humorous slogans painted on it by airmen of the Royal Air Force, such as "Wish you were here" and "Come back soon".
If an escapee was wounded in a crossing attempt and lay on the death strip, no matter how close they were to the Western wall, Westerners could not intervene for fear of triggering engaging fire from the 'Grepos', the East Berlin border guards. The guards often let fugitives bleed to death in the middle of this ground, as in the most notorious failed attempt, that of Peter Fechter (aged 18) at a point near Zimmerstrasse in East Berlin. He was shot and bled to death, in full view of the Western media, on 17 August 1962. Fechter's death created negative publicity worldwide that led the leaders of East Berlin to place more restrictions on shooting in public places and provide medical care for possible "would-be escapers". The last person to be shot and killed while trying to cross the border was Chris Gueffroy on 6 February 1989, while the final person to die in an escape attempt was Winfried Freudenberg who was killed when his homemade natural gas-filled balloon crashed on 8 March 1989.
The Wall gave rise to a widespread sense of desperation and oppression in East Berlin, as expressed in the private thoughts of one resident, who confided to her diary "Our lives have lost their spirit… we can do nothing to stop them."
Concerts by Western artists and growing anti-Wall sentiment
David Bowie, 1987
On 6 June 1987, David Bowie, who earlier for several years lived and recorded in West Berlin, played a concert close to the Wall. This was attended by thousands of Eastern concertgoers across the Wall, followed by violent rioting in East Berlin. According to Tobias Ruther, these protests in East Berlin were the first in the sequence of riots that led to those of November 1989. Although other factors were probably more influential in the fall of the Wall, upon his death in 2016, the German Foreign Office tweeted "Good-bye, David Bowie. You are now among #Heroes. Thank you for helping to bring down the #wall."
Bruce Springsteen, 1988
On 19 July 1988, 16 months before the Wall came down, Bruce Springsteen and the E-Street Band, played Rocking the Wall, a live concert in East Berlin, which was attended by 300,000 in person and broadcast on television. Springsteen spoke to the crowd in German, saying: "I'm not here for or against any government. I've come to play rock 'n' roll for you in the hope that one day all the barriers will be torn down". East Germany and its FDJ youth organization were worried they were losing an entire generation. They hoped that by letting Springsteen in, they could improve their sentiment among East Germans. However, this strategy of "one step backwards, two steps forwards" backfired, and the concert only made East Germans hungrier for more of the freedoms that Springsteen epitomized. While John F. Kennedy and Ronald Reagan delivered their famous speeches from the safety of West Berlin, Springsteen's speaking out against the Wall in the middle of East Berlin added to the euphoria.
David Hasselhoff, 1989
On 31 December 1989, American TV actor and pop music singer David Hasselhoff was the headlining performer for the Freedom Tour Live concert, which was attended by over 500,000 people on both sides of the Wall. The live concert footage was directed by music video director Thomas Mignone and aired on broadcast television station Zweites Deutsches Fernsehen ZDF throughout Europe. During shooting, film crew personnel pulled people up from both sides to stand and celebrate on top of the wall. Hasselhoff sang his number one hit song "Looking For Freedom" on a platform at the end of a twenty-meter steel crane that swung above and over the Wall adjacent to the Brandenburg Gate.
Comments by politicians
On 26 June 1963, 22 months after the erection of the Berlin Wall, U.S. President John F. Kennedy visited West Berlin. Speaking from a platform erected on the steps of Rathaus Schöneberg for an audience of 450,000 and straying from the prepared script, he declared in his Ich bin ein Berliner speech the support of the United States for West Germany and the people of West Berlin in particular:
Two thousand years ago, the proudest boast was civis romanus sum ["I am a Roman citizen"]. Today, in the world of freedom, the proudest boast is "Ich bin ein Berliner!"... All free men, wherever they may live, are citizens of Berlin, and therefore, as a free man, I take pride in the words "Ich bin ein Berliner!"
The message was aimed as much at the Soviets as it was at Berliners and was a clear statement of U.S. policy in the wake of the construction of the Berlin Wall. The speech is considered one of Kennedy's best, both a significant moment in the Cold War and a high point of the New Frontier. It was a great morale boost for West Berliners, who lived in an exclave deep inside East Germany and feared a possible East German occupation.
Former British prime minister Margaret Thatcher commented in 1982:
Every stone bears witness to the moral bankruptcy of the society it encloses.
In a speech at the Brandenburg Gate commemorating the 750th anniversary of Berlin on 12 June 1987, U.S. President Ronald Reagan challenged Mikhail Gorbachev, then the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, to tear down the Wall as a symbol of increasing freedom in the Eastern Bloc:
We welcome change and openness; for we believe that freedom and security go together, that the advance of human liberty can only strengthen the cause of world peace. There is one sign the Soviets can make that would be unmistakable, that would advance dramatically the cause of freedom and peace. General Secretary Gorbachev, if you seek peace, if you seek prosperity for the Soviet Union and eastern Europe, if you seek liberalization, come here to this gate. Mr. Gorbachev, open this gate. Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this Wall!
In January 1989 GDR leader Erich Honecker predicted that the Wall would stand for 50 or 100 more years if the conditions that had caused its construction did not change.
Fall
Due to the increasing economic problems in the Eastern Bloc and the failure of the USSR to intervene in relation to the individual communist states, the brackets of the Eastern Bloc slowly began to loosen from the end of the 1980s. One example is the fall of the communist government in neighboring Poland's 1989 Polish legislative election. Also in June 1989, the Hungarian government began dismantling the electrified fence along its border with Austria (with Western TV crews present) although the border was still very closely guarded and escape was almost impossible.
The opening of a border gate between Austria and Hungary at the Pan-European Picnic on 19 August 1989, which was based on an idea by Otto von Habsburg to test the reaction of Mikhail Gorbachev, then triggered a peaceful chain reaction, at the end of which there was no longer the GDR and the Eastern Bloc had disintegrated. Because with the non-reaction of the USSR and the GDR to the mass exodus, the media-informed Eastern Europeans could feel the increasing loss of power of their governments and more and more East Germans were now trying to flee via Hungary. Erich Honecker explained to the Daily Mirror regarding the Paneuropean picnic and thus showed his people his own inaction: "Habsburg distributed leaflets far into Poland, on which the East German holidaymakers were invited to a picnic. When they came to the picnic, they were given gifts, food and Deutsche Mark, and then they were persuaded to come to the West." Then, in September, more than 13,000 East German tourists escaped through Hungary to Austria. This set up a chain of events. The Hungarians prevented many more East Germans from crossing the border and returned them to Budapest. These East Germans flooded the West German embassy and refused to return to East Germany.
The East German government responded by disallowing any further travel to Hungary but allowed those already there to return to East Germany. This triggered similar events in neighboring Czechoslovakia. This time, however, the East German authorities allowed people to leave, provided that they did so by train through East Germany. This was followed by mass demonstrations within East Germany itself. Protest demonstrations spread throughout East Germany in September 1989. Initially, protesters were mostly people wanting to leave to the West, chanting "Wir wollen raus!" ("We want out!"). Then protestors began to chant "Wir bleiben hier!" ("We are staying here!"). This was the start of what East Germans generally call the "Peaceful Revolution" of late 1989. The protest demonstrations grew considerably by early November. The movement neared its height on 4 November, when half a million people gathered to demand political change, at the Alexanderplatz demonstration, East Berlin's large public square and transportation hub. On 9 October 1989, the police and army units were given permission to use force against those assembled, but this did not deter the church service and march from taking place, which gathered 70,000 people.
The longtime leader of East Germany, Erich Honecker, resigned on 18 October 1989 and was replaced by Egon Krenz that day.
The wave of refugees leaving East Germany for the West kept increasing. By early November refugees were finding their way to Hungary via Czechoslovakia, or via the West German Embassy in Prague. This was tolerated by the new Krenz government, because of long-standing agreements with the communist Czechoslovak government, allowing free travel across their common border. However, this movement of people grew so large it caused difficulties for both countries. To ease the difficulties, the politburo led by Krenz decided on 9 November to allow refugees to exit directly through crossing points between East Germany and West Germany, including between East and West Berlin. Later the same day, the ministerial administration modified the proposal to include private, round-trip, and travel. The new regulations were to take effect the next day.
Günter Schabowski, the party boss in East Berlin and the spokesman for the SED Politburo, had the task of announcing the new regulations. However, he had not been involved in the discussions about the new regulations and had not been fully updated. Shortly before a press conference on 9 November, he was handed a note announcing the changes, but given no further instructions on how to handle the information. These regulations had only been completed a few hours earlier and were to take effect the following day, so as to allow time to inform the border guards. But this starting time delay was not communicated to Schabowski. At the end of the press conference, Schabowski read out loud the note he had been given. A reporter, ANSA's Riccardo Ehrman, asked when the regulations would take effect. After a few seconds' hesitation, Schabowski replied, "As far as I know, it takes effect immediately, without delay". After further questions from journalists, he confirmed that the regulations included the border crossings through the Wall into West Berlin, which he had not mentioned until then. He repeated that it was immediate in an interview with American journalist Tom Brokaw.
Excerpts from Schabowski's press conference were the lead story on West Germany's two main news programs that night—at 7:17 p.m. on ZDF's heute and at 8 p.m. on ARD's Tagesschau. As ARD and ZDF had broadcast to nearly all of East Germany since the late 1950s and had become accepted by the East German authorities, the news was broadcast there as well simultaneously. Later that night, on ARD's Tagesthemen, anchorman Hanns Joachim Friedrichs proclaimed, "This 9 November is a historic day. The GDR has announced that, starting immediately, its borders are open to everyone. The gates in the Wall stand open wide."
After hearing the broadcast, East Germans began gathering at the Wall, at the six checkpoints between East and West Berlin, demanding that border guards immediately open the gates. The surprised and overwhelmed guards made many hectic telephone calls to their superiors about the problem. At first, they were ordered to find the "more aggressive" people gathered at the gates and stamp their passports with a special stamp that barred them from returning to East Germany—in effect, revoking their citizenship. However, this still left thousands of people demanding to be let through "as Schabowski said we can". It soon became clear that no one among the East German authorities would take personal responsibility for issuing orders to use lethal force, so the vastly outnumbered soldiers had no way to hold back the huge crowd of East German citizens. Finally, at 10:45 p.m. on 9 November, Harald Jäger, the commander of the Bornholmer Straße border crossing yielded, allowing for the guards to open the checkpoints and allowing people through with little or no identity checking. As the Ossis swarmed through, they were greeted by Wessis waiting with flowers and champagne amid wild rejoicing. Soon afterward, a crowd of West Berliners jumped on top of the Wall, and were soon joined by East German youngsters. The evening of 9 November 1989 is known as the night the Wall came down.
Another border crossing to the south may have been opened earlier. An account by Heinz Schäfer indicates that he also acted independently and ordered the opening of the gate at Waltersdorf-Rudow a couple of hours earlier. This may explain reports of East Berliners appearing in West Berlin earlier than the opening of the Bornholmer Straße border crossing.
Thirty years after the fall of the Berlin Wall, The Guardian collected short stories from 9 November 1989 by five German writers who reflect on the day. In this, Kathrin Schmidt remembers comically: 'I downed almost an entire bottle of schnapps'.
Legacy
Remains of the Wall adjacent to the Topography of Terror, August 2007
A "BERLINER MAUER 1961–1989" plaque near Checkpoint Charlie signifying where the Wall stood
Display of two sections of the Wall and a "You are leaving" sign at Fort Gordon, Georgia, USA
Czech hedgehog anti-tank obstacles and the Wall
An exhibition dedicated to the 25th anniversary to the Berlin Wall destruction was located at Potsdamer Platz Arkaden
Little is left of the Wall at its original site, which was destroyed almost in its entirety. Three long sections are still standing: an 80-metre-long (260 ft) piece of the first (westernmost) wall at the Topography of Terror, site of the former Gestapo headquarters, halfway between Checkpoint Charlie and Potsdamer Platz; a longer section of the second (easternmost) wall along the Spree River near the Oberbaumbrücke, nicknamed East Side Gallery; and a third section that is partly reconstructed, in the north at Bernauer Straße, which was turned into a memorial in 1999. Other isolated fragments, lampposts, other elements, and a few watchtowers also remain in various parts of the city.
- The former leadership in the Schlesischen Busch in the vicinity of the Puschkinallee—the listed, twelve-meter high watchtower stands in a piece of the wall strip, which has been turned into a park, near the Lohmühleninsel.
- The former "Kieler Eck" (Kiel Corner) on Kieler Strasse in Mitte, close to the Berlin-Spandau Schifffahrtskanal—the tower is protected as a historic monument and now surrounded on three sides by new buildings. It houses a memorial site named after the Wallopfer Günter Litfin, who was shot at Humboldthafen in August 1961. The memorial site, which is run by the initiative of his brother Jürgen Liftin, can be viewed after registration.
- The former management office at Nieder Neuendorf, in the district of Hennigsdorf of the same name—here is the permanent exhibition on the history of the border installations between the two German states.
- The former management station at Bergfelde, today the district of Hohen Neuendorf—The tower is located in an already reforested area of the border strip and is used together with surrounding terrain as a nature protection tower by the Deutschen Waldjugend.
- The only one of the much slimmer observation towers (BT-11) in the Erna-Berger-Strasse also in Mitte—however, was moved by a few meters for construction work and is no longer in the original location; There is an exhibition about the wall in the area of the Potsdamer Platz in planning.
Nothing still accurately represents the Wall's original appearance better than a very short stretch at Bernauer Straße associated with the Berlin Wall Documentation Center. Other remnants are badly damaged by souvenir seekers. Fragments of the Wall were taken and some were sold around the world. Appearing both with and without certificates of authenticity, these fragments are now a staple on the online auction service eBay as well as German souvenir shops. Today, the eastern side is covered in graffiti that did not exist while the Wall was guarded by the armed soldiers of East Germany. Previously, graffiti appeared only on the western side. Along some tourist areas of the city centre, the city government has marked the location of the former Wall by a row of cobblestones in the street. In most places only the "first" wall is marked, except near Potsdamer Platz where the stretch of both walls is marked, giving visitors an impression of the dimension of the barrier system.
After the fall of the Berlin Wall, there were initiatives that they want to preserve the death strip walkways and redevelop it into a hiking and cycling area, known as Berliner Mauerweg. It is part of the initiative by the Berlin Senate since 2005.
Cultural differences
For many years after reunification, people in Germany talked about cultural differences between East and West Germans (colloquially Ossis and Wessis), sometimes described as Mauer im Kopf (The wall in the head). A September 2004 poll found that 25 percent of West Germans and 12 percent of East Germans wished that East and West should be separated again by a "Wall". A poll taken in October 2009 on the occasion of the 20th anniversary of the fall of the Wall indicated, however, that only about a tenth of the population was still unhappy with the unification (8 percent in the East; 12 percent in the West). Although differences are still perceived between East and West, Germans make similar distinctions between North and South.
A 2009 poll conducted by Russia's VTsIOM, found that more than half of all Russians do not know who built the Berlin Wall. Ten percent of people surveyed thought Berlin residents built it themselves. Six percent said Western powers built it and four percent thought it was a "bilateral initiative" of the Soviet Union and the West. Fifty-eight percent said they did not know who built it, with just 24 percent correctly naming the Soviet Union and its then-communist ally East Germany.
Wall segments around the world
Not all segments of the Wall were ground up as the Wall was being torn down. Many segments have been given to various institutions in the world. They can be found, for instance, in presidential and historical museums, lobbies of hotels and corporations, at universities and government buildings, and in public spaces in different countries of the world.
50th anniversary commemoration
On 13 August 2011, Germany marked the 50th anniversary of East Germany beginning the erection of the Berlin Wall. Chancellor Angela Merkel joined with President Christian Wulff and Berlin Mayor Klaus Wowereit at the Bernauer Straße memorial park to remember lives and liberty. Speeches extolled freedom and a minute of silence at noon honored those who died trying to flee to the West. "It is our shared responsibility to keep the memory alive and to pass it on to the coming generations as a reminder to stand up for freedom and democracy to ensure that such injustice may never happen again." entreated Mayor Wowereit. "It has been shown once again: Freedom is invincible at the end. No wall can permanently withstand the desire for freedom", proclaimed President Wulff.
Related media
Documentaries
Documentary films specifically about the Berlin Wall include:
- The Tunnel (December 1962), an NBC News Special documentary film.
- The Road to the Wall (1962), a documentary film.
- Something to Do with the Wall (1991), a documentary about the fall of the Berlin Wall by Ross McElwee and Marilyn Levine, originally conceived as a commemoration of the 25th anniversary of its construction.
- Rabbit à la Berlin (2009), a documentary film, directed by Bartek Konopka, told from the point of view of a group of wild rabbits that inhabited the zone between the two walls.
- "30 years ago, the fall of the Berlin Wall - the end of the Cold War". (2019) a documentary film by André Bossuroy, 26 min, ARTE, Europe for Citizens Programme of the European Union. 22 October 2019.
- The American Sector (2020), a documentary by Courtney Stephens and Pacho Velez that tracks down the wall segments located in the U.S.
Feature films
Fictional films featuring the Berlin Wall have included:
- Escape from East Berlin (1962), American-West German film inspired by story of 29 East Germans that tunneled under the wall
- The Spy Who Came in from the Cold (1965), a Cold War classic set on both sides of The Wall, from the eponymous book by John le Carré, directed by Martin Ritt.
- The Boy and the Ball and the Hole in the Wall (1965), Spanish-Mexican co-production.
- Funeral in Berlin (1966), a spy movie starring Michael Caine, directed by Guy Hamilton.
- Casino Royale (1967), a film featuring a segment centred on a house apparently bisected by the Wall.
- The Wicked Dreams of Paula Schultz (1968), a Cold War spy farce about an Olympic athlete who defects, directed by George Marshall.
- Berlin Tunnel 21 (1981), a made-for-TV movie about a former American officer leading an attempt to build a tunnel underneath The Wall as a rescue route.
- Night Crossing (1982), a British-American drama film starring John Hurt, Jane Alexander, and Beau Bridges, based on the true story of the Strelzyk and Wetzel families, who on 16 September 1979, attempted to escape from East Germany to West Germany in a homemade hot air balloon, during the days of the Inner German border-era.
- The Innocent (1993), a film about the joint CIA/MI6 operation to build a tunnel under East Berlin in the 1950s, directed by John Schlesinger.
- The Tunnel (2001), a dramatization of a collaborative tunnel under the Wall, filmed by Roland Suso Richter.
- Good Bye Lenin! (2003), film set during German unification that depicts the fall of the Wall through archive footage
- Open The Wall (2014), featuring a dramatized story of the East-German border guard who was the first to let East Berliners cross the border to West Berlin on 9 November 1989.
- Bridge of Spies (2015), featuring a dramatized subplot about Frederic Pryor, in which an American economics graduate student visits his German girlfriend in East Berlin just as the Berlin Wall is being built. He tries to bring her back into West Berlin but is stopped by Stasi agents and arrested as a spy.
Literature
Some novels specifically about the Berlin Wall include:
- John le Carré, The Spy Who Came in from the Cold (1963), classic Cold War spy fiction.
- Len Deighton, Berlin Game (1983), classic Cold War spy fiction
- T.H.E. Hill, The Day Before the Berlin Wall: Could We Have Stopped It? – An Alternate History of Cold War Espionage, 2010 – based on a legend told in Berlin in the 1970s.
- John Marks' The Wall (1999) in which an American spy defects to the East just hours before the Wall falls.
- Marcia Preston's West of the Wall (2007, published as Trudy's Promise in North America), in which the heroine, left behind in East Berlin, waits for news of her husband after he makes his escape over the Berlin Wall.
- Peter Schneider's The Wall Jumper, (1984; German: Der Mauerspringer, 1982), the Wall plays a central role in this novel set in Berlin of the 1980s.
Music
Music related to the Berlin Wall includes:
- Stationary Traveller (1984), a concept album by Camel that takes the theme of families and friends split up by the building of the Berlin Wall.
- "West of the Wall", a 1962 top 40 hit by Toni Fisher, which tells the tale of two lovers separated by the newly built Berlin Wall.
- "Holidays in the Sun", a song by the English punk rock band Sex Pistols which prominently mentions the Wall, specifically singer Johnny Rotten's fantasy of digging a tunnel under it.
- David Bowie's "Heroes", inspired by the image of a couple kissing at the Berlin Wall (in reality, the couple was his producer Tony Visconti and backup singer Antonia Maaß). The song (which, along with the album of the same name, were recorded in Berlin), makes lyrical references to the kissing couple, and to the "Wall of Shame" ("the shame was on the other side"). Upon Bowie's death, the Federal Foreign Office paid homage to Bowie on Twitter: see also above
- "Over de muur" (1984), a song by the Dutch pop band Klein Orkest, about the differences between East and West Berlin during the period of the Berlin Wall.
- "Chippin' Away" (1990), a song by Tom Fedora, performed by Crosby, Stills & Nash on the Berlin Wall, which appeared on Graham Nash's solo album Innocent Eyes (1986).
- "Hedwig and the Angry Inch," a rock opera whose genderqueer protagonist Hedwig Robinson was born in East Berlin and later, living in the United States, describes herself as "the new Berlin Wall" standing between "East and West, slavery and freedom, man and woman, top and bottom." As a result, she says, people are moved to "decorate" her with "blood, graffiti and spit." (1998)
- The music video for Liza Fox's song "Free" (2013) contains video clips of the fall of the Berlin Wall.
Visual art
Artworks related to the Berlin Wall include:
- In 1982, the West-German artist Elsner created about 500 artworks along the former border strip around West Berlin as part of his work series Border Injuries. On one of his actions he tore down a large part of the Wall, installed a prepared foil of 3x2m in it, and finished the painting there before the border soldiers on patrol could detect him. This performance was recorded on video. His actions are well-documented both in newspapers from that time and in recent scientific publications.
- The Day the Wall Came Down, 1996 and 1998 sculptures by Veryl Goodnight, which depict five horses leaping over actual pieces of the Berlin Wall.
Games
Video games related to the Berlin Wall include:
- The Berlin Wall (1991), a video game.
- SimCity 3000 (1999), a video game featuring a scenario taking place at the end of the Cold War, wherein the player is given five years within the game to demolish the Wall and re-unite East and West Berlin; the longer it takes to complete the goal, the more riots take place in the city.
- The Call of Duty: Black Ops (2010) "First Strike" downloadable content pack includes a multiplayer map (called ("Berlin Wall") that takes place at the Berlin Wall.
- The introductory video to the Civilization VI video game expansion "Rise and Fall" depicts a woman striking the wall with a sledgehammer.
- Ostalgie: The Berlin Wall (2018), video game by Kremlingames, where the player, playing as the leader of the GDR from 1989 to 1991, can take down the Berlin Wall themselves or as a result of events in the game, or keep the wall intact as long as the country exists.
- In April 2018 game publisher Playway S.A. announced that Polish game studio K202 was working on The Berlin Wall video game, which was released in November 2019.