| |
| Introduced | 21 September 1997 |
|---|---|
| Compatible hardware | Personal computers, gaming consoles, smart devices, televisions, printers, security cameras |
Wi-Fi (/ˈwaɪfaɪ/) is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks in the world, used globally in home and small office networks to link devices together and to a wireless router to connect them to the Internet, and in wireless access points in public places like coffee shops, hotels, libraries, and airports to provide visitors with Internet connectivity for their mobile devices.
Wi-Fi is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term "Wi-Fi Certified" to products that successfully complete interoperability certification testing. As of 2017, the Wi-Fi Alliance consisted of more than 800 companies from around the world. As of 2019, over 3.05 billion Wi-Fi-enabled devices are shipped globally each year.
Wi-Fi uses multiple parts of the IEEE 802 protocol family and is designed to work seamlessly with its wired sibling, Ethernet. Compatible devices can network through wireless access points with each other as well as with wired devices and the Internet. Different versions of Wi-Fi are specified by various IEEE 802.11 protocol standards, with different radio technologies determining radio bands, maximum ranges, and speeds that may be achieved. Wi-Fi most commonly uses the 2.4 gigahertz (120 mm) UHF and 5 gigahertz (60 mm) SHF radio bands; these bands are subdivided into multiple channels. Channels can be shared between networks, but, within range, only one transmitter can transmit on a channel at a time.

Wi-Fi's radio bands have relatively high absorption and work best for line-of-sight use. Many common obstructions such as walls, pillars, home appliances, etc. may greatly reduce range, but this also helps minimize interference between different networks in crowded environments. An access point range is about 20 m (66 ft) indoors, while some access points claim up to a 150 m (490 ft) range outdoors. Hotspot coverage can be as small as a single room with walls that block radio waves or as large as many square kilometres using many overlapping access points with roaming permitted between them. Over time, the speed and spectral efficiency of Wi-Fi have increased. As of 2019, some versions of Wi-Fi, running on suitable hardware at close range, can achieve speeds of 9.6 Gbit/s (gigabit per second).
History
A 1985 ruling by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission released parts of the ISM bands for unlicensed use for communications. These frequency bands include the same 2.4 GHz bands used by equipment such as microwave ovens, and are thus subject to interference.
In 1991, the NCR Corporation in the Netherlands with AT&T Corporation invented the precursor to 802.11, intended for use in cashier systems, under the name WaveLAN. NCR's Vic Hayes, who held the chair of IEEE 802.11 for 10 years, along with Bell Labs engineer Bruce Tuch, approached the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) to create a standard and were involved in designing the initial 802.11b and 802.11a standards within the IEEE. They have both been subsequently inducted into the Wi-Fi NOW Hall of Fame.
At about the same time in Australia, a prototype test bed for a wireless local area network (WLAN) was developed in 1992 by a team of researchers from the Radiophysics Division of the CSIRO (Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation) in Australia, led by Dr John O'Sullivan.
The first version of the 802.11 protocol was released in 1997, and provided up to 2 Mbit/s link speeds. This was updated in 1999 with 802.11b to permit 11 Mbit/s link speeds.
In 1999, the Wi-Fi Alliance formed as a trade association to hold the Wi-Fi trademark under which most IEEE 802.11 products are sold.
The major commercial breakthrough came with Apple Inc. adopting Wi-Fi for their iBook series of laptops in 1999. It was the first mass consumer product to offer Wi-Fi network connectivity, which was then branded by Apple as AirPort. This was in collaboration with the same group that helped create the standard: Vic Hayes, Bruce Tuch, Cees Links, Rich McGinn, and others from Lucent.
Wi-Fi uses a large number of patents held by many different organizations. Australia, the United States and The Netherlands simultaneously claim the invention of Wi-Fi. A consensus has not been reached globally and is a controversial topic. In 2009, the Australian CSIRO was awarded $200 Million after a patent settlement with 14 technology companies, with a further $220 Million awarded in 2012 after legal proceedings with 23 companies.
In 2016, the CSIRO's WLAN prototype test bed was chosen as Australia's contribution to the exhibition A History of the World in 100 Objects held in the National Museum of Australia.
Etymology and terminology
The name Wi-Fi, commercially used at least as early as August 1999, was coined by the brand-consulting firm Interbrand. The Wi-Fi Alliance had hired Interbrand to create a name that was "a little catchier than 'IEEE 802.11b Direct Sequence'." According to Phil Belanger, a founding member of the Wi-Fi Alliance, the term Wi-Fi was chosen from a list of ten names that Interbrand proposed. Interbrand also created the Wi-Fi logo. The yin-yang Wi-Fi logo indicates the certification of a product for interoperability.
The Wi-Fi Alliance used the advertising slogan "The Standard for Wireless Fidelity" for a short time after the brand name was created, and the Wi-Fi Alliance was also called the "Wireless Fidelity Alliance Inc." in some publications. The name is often written as WiFi, Wifi, or wifi, but these are not approved by the Wi-Fi Alliance. IEEE is a separate, but related, organization and their website has stated "WiFi is a short name for Wireless Fidelity".
Other technologies intended for fixed points, including Motorola Canopy, are usually called fixed wireless. Alternative wireless technologies include Zigbee, Z-Wave, Bluetooth and mobile phone standards.
To connect to a Wi-Fi LAN, a computer must be equipped with a wireless network interface controller. The combination of a computer and an interface controller is called a station. Stations are identified by one or more MAC addresses.
Wi-Fi nodes often operate in infrastructure mode in which all communications go through a base station. Ad hoc mode refers to devices communicating directly with each other, without communicating with an access point.
A service set is the set of all the devices associated with a particular Wi-Fi network. Devices in a service set need not be on the same wavebands or channels. A service set can be local, independent, extended, mesh, or a combination. Each service set has an associated identifier, a 32-byte service set identifier (SSID), which identifies the network. The SSID is configured within the devices that are part of the network. A basic service set (BSS) is a group of stations that share the same wireless channel, SSID, and other settings that have wirelessly connected, usually to the same access point. Each BSS is identified by a MAC address called the BSSID.
Certification

The IEEE does not test equipment for compliance with their standards. The Wi-Fi Alliance was formed in 1999 to establish and enforce standards for interoperability and backward compatibility, and to promote wireless local-area-network technology. The Wi-Fi Alliance enforces the use of the Wi-Fi brand to technologies based on the IEEE 802.11 standards from the IEEE. Manufacturers with membership in the Wi-Fi Alliance, whose products pass the certification process, gain the right to mark those products with the Wi-Fi logo. Specifically, the certification process requires conformance to the IEEE 802.11 radio standards, the WPA and WPA2 security standards, and the EAP authentication standard. Certification may optionally include tests of IEEE 802.11 draft standards, interaction with cellular-phone technology in converged devices, and features relating to security set-up, multimedia, and power-saving.
Not every Wi-Fi device is submitted for certification. The lack of Wi-Fi certification does not necessarily imply that a device is incompatible with other Wi-Fi devices. The Wi-Fi Alliance may or may not sanction derivative terms, such as Super Wi-Fi, coined by the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to describe proposed networking in the UHF TV band in the US.
Versions and generations
| Generation | IEEE standard |
First Approved |
Maximum link rate (Mbit/s) |
Radio frequency (GHz) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi 7 | 802.11be | 2019-03-21 | 721 to 46120 | 2.4 | 5 | 6 |
| Wi-Fi 6/6E | 802.11ax | 2014-03-27 | 600 to 9608 | 2.4 | 5 | 6 |
| Wi-Fi 5 | 802.11ac | 2008-09-26 | 433 to 6933 | ↓ | 5 | |
| Wi-Fi 4 | 802.11n | 2003-09-11 | 72 to 600 | 2.4 | 5 | |
| (Wi-Fi 3)* | 802.11g | 2000-09-21 | 6 to 54 | 2.4 |
| |
| (Wi-Fi 2)* | 802.11a | 1997-09-16 | 5 | |||
| (Wi-Fi 1)* | 802.11b | 1997-12-09 | 1 to 11 | 2.4 | ||
| (Wi-Fi 0)* | 802.11 | 1991-03-21 | 1 to 2 | 2.4 | ||
| *(Wi-Fi 0, 1, 2, 3, are unbranded common usage) | ||||||
Equipment frequently supports multiple versions of Wi-Fi. To communicate, devices must use a common Wi-Fi version. The versions differ between the radio wavebands they operate on, the radio bandwidth they occupy, the maximum data rates they can support and other details. Some versions permit the use of multiple antennas, which permits greater speeds as well as reduced interference.
Historically, the equipment listed the versions of Wi-Fi supported using the name of the IEEE standards. In 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance introduced simplified Wi-Fi generational numbering to indicate equipment that supports Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) and Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax). These generations have a high degree of backward compatibility with previous versions. The alliance has stated that the generational level 4, 5, or 6 can be indicated in the user interface when connected, along with the signal strength.
The list of most important versions of Wi-Fi is: 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4), 802.11h, 802.11i, 802.11-2007, 802.11-2012, 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5), 802.11ad, 802.11af, 802.11-2016, 802.11ah, 802.11ai, 802.11aj, 802.11aq, 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), 802.11ay.
Uses
Internet
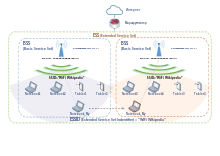
Wi-Fi technology may be used to provide local network and Internet access to devices that are within Wi-Fi range of one or more routers that are connected to the Internet. The coverage of one or more interconnected access points can extend from an area as small as a few rooms to as large as many square kilometres. Coverage in the larger area may require a group of access points with overlapping coverage. For example, public outdoor Wi-Fi technology has been used successfully in wireless mesh networks in London. An international example is Fon.
Wi-Fi provides services in private homes, businesses, as well as in public spaces. Wi-Fi hotspots may be set up either free of charge or commercially, often using a captive portal webpage for access. Organizations, enthusiasts, authorities and businesses, such as airports, hotels, and restaurants, often provide free or paid-use hotspots to attract customers, to provide services to promote business in selected areas. Routers often incorporate a digital subscriber line modem or a cable modem and a Wi-Fi access point, are frequently set up in homes and other buildings, to provide Internet access for the structure.
Similarly, battery-powered routers may include a mobile broadband modem and a Wi-Fi access point. When subscribed to a cellular data carrier, they allow nearby Wi-Fi stations to access the Internet. Many smartphones have a built-in mobile hotspot capability of this sort, though carriers often disable the feature, or charge a separate fee to enable it. Standalone devices such as MiFi- and WiBro-branded devices provide the capability. Some laptops that have a cellular modem card can also act as mobile Internet Wi-Fi access points.
Many traditional university campuses in the developed world provide at least partial Wi-Fi coverage. Carnegie Mellon University built the first campus-wide wireless Internet network, called Wireless Andrew, at its Pittsburgh campus in 1993 before Wi-Fi branding originated. By February 1997, the CMU Wi-Fi zone was fully operational. Many universities collaborate in providing Wi-Fi access to students and staff through the Eduroam international authentication infrastructure.
City-wide

In the early 2000s, many cities around the world announced plans to construct citywide Wi-Fi networks. There are many successful examples; in 2004, Mysore (Mysuru) became India's first Wi-Fi-enabled city. A company called WiFiyNet has set up hotspots in Mysore, covering the whole city and a few nearby villages.
In 2005, St. Cloud, Florida and Sunnyvale, California, became the first cities in the United States to offer citywide free Wi-Fi (from MetroFi). Minneapolis has generated $1.2 million in profit annually for its provider.
In May 2010, the then London mayor Boris Johnson pledged to have London-wide Wi-Fi by 2012. Several boroughs including Westminster and Islington already had extensive outdoor Wi-Fi coverage at that point.
New York City announced a city-wide campaign to convert old phone booths into digitized "kiosks" in 2014. The project, titled LinkNYC, has created a network of kiosks which serve as public Wi-Fi hotspots, high-definition screens and landlines. Installation of the screens began in late 2015. The city government plans to implement more than seven thousand kiosks over time, eventually making LinkNYC the largest and fastest public, government-operated Wi-Fi network in the world. The UK has planned a similar project across major cities of the country, with the project's first implementation in the Camden borough of London.
Officials in South Korea's capital Seoul are moving to provide free Internet access at more than 10,000 locations around the city, including outdoor public spaces, major streets, and densely populated residential areas. Seoul will grant leases to KT, LG Telecom, and SK Telecom. The companies will invest $44 million in the project, which was to be completed in 2015.
Geolocation
Wi-Fi positioning systems use the positions of Wi-Fi hotspots to identify a device's location.
Motion detection
Wi-Fi sensing is used in applications such as motion detection and gesture recognition.
Operational principles
Wi-Fi stations communicate by sending each other data packets: blocks of data individually sent and delivered over radio. As with all radio, this is done by the modulation and demodulation of carrier waves. Different versions of Wi-Fi use different techniques, 802.11b uses DSSS on a single carrier, whereas 802.11a, Wi-Fi 4, 5 and 6 use multiple carriers on slightly different frequencies within the channel (OFDM).
As with other IEEE 802 LANs, stations come programmed with a globally unique 48-bit MAC address (often printed on the equipment) so that each Wi-Fi station has a unique address. The MAC addresses are used to specify both the destination and the source of each data packet. Wi-Fi establishes link-level connections, which can be defined using both the destination and source addresses. On the reception of a transmission, the receiver uses the destination address to determine whether the transmission is relevant to the station or should be ignored. A network interface normally does not accept packets addressed to other Wi-Fi stations.
Channels are used half duplex and can be time-shared by multiple networks. When communication happens on the same channel, any information sent by one computer is locally received by all, even if that information is intended for just one destination. The network interface card interrupts the CPU only when applicable packets are received: the card ignores information not addressed to it. The use of the same channel also means that the data bandwidth is shared, such that, for example, available data bandwidth to each device is halved when two stations are actively transmitting.
A scheme known as carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) governs the way stations share channels. With CSMA/CA stations attempt to avoid collisions by beginning transmission only after the channel is sensed to be "idle", but then transmit their packet data in its entirety. However, for geometric reasons, it cannot completely prevent collisions. A collision happens when a station receives multiple signals on a channel at the same time. This corrupts the transmitted data and can require stations to re-transmit. The lost data and re-transmission reduces throughput, in some cases severely.
Waveband
The 802.11 standard provides several distinct radio frequency ranges for use in Wi-Fi communications: 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, 3.6 GHz, 4.9 GHz, 5 GHz, 5.9 GHz and 60 GHz bands. Each range is divided into a multitude of channels. In the standards, channels are numbered at 5 MHz spacing within a band (except in the 60 GHz band, where they are 2.16 GHz apart), and the number refers to the centre frequency of the channel. Although channels are numbered at 5 MHz spacing, transmitters generally occupy at least 20 MHz, and standards allow for channels to be bonded together to form wider channels for higher throughput.
Countries apply their own regulations to the allowable channels, allowed users and maximum power levels within these frequency ranges. 802.11b/g/n can use the 2.4 GHz band, operating in the United States under FCC Part 15 Rules and Regulations. In this frequency band equipment may occasionally suffer interference from microwave ovens, cordless telephones, USB 3.0 hubs, and Bluetooth devices.
Spectrum assignments and operational limitations are not consistent worldwide: Australia and Europe allow for an additional two channels (12, 13) beyond the 11 permitted in the United States for the 2.4 GHz band, while Japan has three more (12–14). In the US and other countries, 802.11a and 802.11g devices may be operated without a licence, as allowed in Part 15 of the FCC Rules and Regulations.
802.11a/h/j/n/ac/ax can use the 5 GHz U-NII band, which, for much of the world, offers at least 23 non-overlapping 20 MHz channels rather than the 2.4 GHz frequency band, where the channels are only 5 MHz wide. In general, lower frequencies have longer range but have less capacity. The 5 GHz bands are absorbed to a greater degree by common building materials than the 2.4 GHz bands and usually give a shorter range.
As 802.11 specifications evolved to support higher throughput, the protocols have become much more efficient in their use of bandwidth. Additionally, they have gained the ability to aggregate (or 'bond') channels together to gain still more throughput where the bandwidth is available. 802.11n allows for double radio spectrum/bandwidth (40 MHz- 8 channels) compared to 802.11a or 802.11g (20 MHz). 802.11n can also be set to limit itself to 20 MHz bandwidth to prevent interference in dense communities. In the 5 GHz band, 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, and 160 MHz bandwidth signals are permitted with some restrictions, giving much faster connections.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Communication stack

Wi-Fi is part of the IEEE 802 protocol family. The data is organized into 802.11 frames that are very similar to Ethernet frames at the data link layer, but with extra address fields. MAC addresses are used as network addresses for routing over the LAN.
Wi-Fi's MAC and physical layer (PHY) specifications are defined by IEEE 802.11 for modulating and receiving one or more carrier waves to transmit the data in the infrared, and 2.4, 3.6, 5, 6, or 60 GHz frequency bands. They are created and maintained by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802). The base version of the standard was released in 1997 and has had many subsequent amendments. The standard and amendments provide the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi brand. While each amendment is officially revoked when it is incorporated in the latest version of the standard, the corporate world tends to market to the revisions because they concisely denote capabilities of their products. As a result, in the market place, each revision tends to become its own standard.
In addition to 802.11 the IEEE 802 protocol family has specific provisions for Wi-Fi. These are required because Ethernet's cable-based media are not usually shared, whereas with wireless all transmissions are received by all stations within the range that employ that radio channel. While Ethernet has essentially negligible error rates, wireless communication media are subject to significant interference. Therefore, the accurate transmission is not guaranteed so delivery is, therefore, a best-effort delivery mechanism. Because of this, for Wi-Fi, the Logical Link Control (LLC) specified by IEEE 802.2 employs Wi-Fi's media access control (MAC) protocols to manage retries without relying on higher levels of the protocol stack.
For internetworking purposes, Wi-Fi is usually layered as a link layer (equivalent to the physical and data link layers of the OSI model) below the internet layer of the Internet Protocol. This means that nodes have an associated internet address and, with suitable connectivity, this allows full Internet access.
Modes
Infrastructure
In infrastructure mode, which is the most common mode used, all communications go through a base station. For communications within the network, this introduces an extra use of the airwaves but has the advantage that any two stations that can communicate with the base station can also communicate through the base station, which enormously simplifies the protocols.
Ad hoc and Wi-Fi direct
Wi-Fi also allows communications directly from one computer to another without an access point intermediary. This is called ad hoc Wi-Fi transmission. Different types of ad hoc networks exist. In the simplest case network nodes must talk directly to each other. In more complex protocols nodes may forward packets, and nodes keep track of how to reach other nodes, even if they move around.
Ad hoc mode was first described by Chai Keong Toh in his 1996 patent of wireless ad hoc routing, implemented on Lucent WaveLAN 802.11a wireless on IBM ThinkPads over a size nodes scenario spanning a region of over a mile. The success was recorded in Mobile Computing magazine (1999) and later published formally in IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2002 and ACM SIGMETRICS Performance Evaluation Review, 2001.
This wireless ad hoc network mode has proven popular with multiplayer handheld game consoles, such as the Nintendo DS, PlayStation Portable, digital cameras, and other consumer electronics devices. Some devices can also share their Internet connection using ad hoc, becoming hotspots or "virtual routers".
Similarly, the Wi-Fi Alliance promotes the specification Wi-Fi Direct for file transfers and media sharing through a new discovery- and security-methodology. Wi-Fi Direct launched in October 2010.
Another mode of direct communication over Wi-Fi is Tunneled Direct-Link Setup (TDLS), which enables two devices on the same Wi-Fi network to communicate directly, instead of via the access point.
Multiple access points

An Extended Service Set may be formed by deploying multiple access points that are configured with the same SSID and security settings. Wi-Fi client devices typically connect to the access point that can provide the strongest signal within that service set.
Increasing the number of Wi-Fi access points for a network provides redundancy, better range, support for fast roaming, and increased overall network-capacity by using more channels or by defining smaller cells. Except for the smallest implementations (such as home or small office networks), Wi-Fi implementations have moved toward "thin" access points, with more of the network intelligence housed in a centralized network appliance, relegating individual access points to the role of "dumb" transceivers. Outdoor applications may use mesh topologies.
Performance
Wi-Fi operational range depends on factors such as the frequency band, radio power output, receiver sensitivity, antenna gain, and antenna type as well as the modulation technique. Also, the propagation characteristics of the signals can have a big impact.
At longer distances, and with greater signal absorption, speed is usually reduced.
Transmitter power
Compared to cell phones and similar technology, Wi-Fi transmitters are low-power devices. In general, the maximum amount of power that a Wi-Fi device can transmit is limited by local regulations, such as FCC Part 15 in the US. Equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) in the European Union is limited to 20 dBm (100 mW).
To reach requirements for wireless LAN applications, Wi-Fi has higher power consumption compared to some other standards designed to support wireless personal area network (PAN) applications. For example, Bluetooth provides a much shorter propagation range between 1 and 100 metres (1 and 100 yards) and so in general has a lower power consumption. Other low-power technologies such as Zigbee have fairly long range, but much lower data rate. The high power consumption of Wi-Fi makes battery life in some mobile devices a concern.
Antenna
An access point compliant with either 802.11b or 802.11g, using the stock omnidirectional antenna might have a range of 100 m (0.062 mi). The same radio with an external semi parabolic antenna (15 dB gain) with a similarly equipped receiver at the far end might have a range over 20 miles.
Higher gain rating (dBi) indicates further deviation (generally toward the horizontal) from a theoretical, perfect isotropic radiator, and therefore the antenna can project or accept a usable signal further in particular directions, as compared to a similar output power on a more isotropic antenna. For example, an 8 dBi antenna used with a 100 mW driver has a similar horizontal range to a 6 dBi antenna being driven at 500 mW. Note that this assumes that radiation in the vertical is lost; this may not be the case in some situations, especially in large buildings or within a waveguide. In the above example, a directional waveguide could cause the low-power 6 dBi antenna to project much further in a single direction than the 8 dBi antenna, which is not in a waveguide, even if they are both driven at 100 mW.
On wireless routers with detachable antennas, it is possible to improve range by fitting upgraded antennas that provide a higher gain in particular directions. Outdoor ranges can be improved to many kilometres (miles) through the use of high gain directional antennas at the router and remote device(s).
 |
 |
 |
 |
MIMO (multiple-input and multiple-output)
Wi-Fi 4 and higher standards allow devices to have multiple antennas on transmitters and receivers. Multiple antennas enable the equipment to exploit multipath propagation on the same frequency bands giving much higher speeds and longer range.
Wi-Fi 4 can more than double the range over previous standards.
The Wi-Fi 5 standard uses the 5 GHz band exclusively, and is capable of multi-station WLAN throughput of at least 1 gigabit per second, and a single station throughput of at least 500 Mbit/s. As of the first quarter of 2016, The Wi-Fi Alliance certifies devices compliant with the 802.11ac standard as "Wi-Fi CERTIFIED ac". This standard uses several signal processing techniques such as multi-user MIMO and 4X4 Spatial Multiplexing streams, and wide channel bandwidth (160 MHz) to achieve its gigabit throughput. According to a study by IHS Technology, 70% of all access point sales revenue in the first quarter of 2016 came from 802.11ac devices.
Radio propagation
With Wi-Fi signals line-of-sight usually works best, but signals can transmit, absorb, reflect, refract, diffract and up and down fade through and around structures, both man-made and natural. Wi-Fi signals are very strongly affected by metallic structures (including rebar in concrete, low-e coatings in glazing) and water (such as found in vegetation.)
Due to the complex nature of radio propagation at typical Wi-Fi frequencies, particularly around trees and buildings, algorithms can only approximately predict Wi-Fi signal strength for any given area in relation to a transmitter. This effect does not apply equally to long-range Wi-Fi, since longer links typically operate from towers that transmit above the surrounding foliage.
Mobile use of Wi-Fi over wider ranges is limited, for instance, to uses such as in an automobile moving from one hotspot to another. Other wireless technologies are more suitable for communicating with moving vehicles.
Distance records
Distance records (using non-standard devices) include 382 km (237 mi) in June 2007, held by Ermanno Pietrosemoli and EsLaRed of Venezuela, transferring about 3 MB of data between the mountain-tops of El Águila and Platillon. The Swedish Space Agency transferred data 420 km (260 mi), using 6 watt amplifiers to reach an overhead stratospheric balloon.
Interference

Wi-Fi connections can be blocked or the Internet speed lowered by having other devices in the same area. Wi-Fi protocols are designed to share the wavebands reasonably fairly, and this often works with little to no disruption. To minimize collisions with Wi-Fi and non-Wi-Fi devices, Wi-Fi employs Carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA), where transmitters listen before transmitting and delay transmission of packets if they detect that other devices are active on the channel, or if noise is detected from adjacent channels or non-Wi-Fi sources. Nevertheless, Wi-Fi networks are still susceptible to the hidden node and exposed node problem.
A standard speed Wi-Fi signal occupies five channels in the 2.4 GHz band. Interference can be caused by overlapping channels. Any two channel numbers that differ by five or more, such as 2 and 7, do not overlap (no adjacent-channel interference). The oft-repeated adage that channels 1, 6, and 11 are the only non-overlapping channels is, therefore, not accurate. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are the only group of three non-overlapping channels in North America. However, whether the overlap is significant depends on physical spacing. Channels that are four apart interfere a negligible amount – much less than reusing channels (which causes co-channel interference) – if transmitters are at least a few metres apart. In Europe and Japan where channel 13 is available, using Channels 1, 5, 9, and 13 for 802.11g and 802.11n is viable and recommended.
However, many 2.4 GHz 802.11b and 802.11g access-points default to the same channel on initial startup, contributing to congestion on certain channels. Wi-Fi pollution, or an excessive number of access points in the area, can prevent access and interfere with other devices' use of other access points as well as with decreased signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) between access points. These issues can become a problem in high-density areas, such as large apartment complexes or office buildings with many Wi-Fi access points.
Other devices use the 2.4 GHz band: microwave ovens, ISM band devices, security cameras, Zigbee devices, Bluetooth devices, video senders, cordless phones, baby monitors, and, in some countries, amateur radio, all of which can cause significant additional interference. It is also an issue when municipalities or other large entities (such as universities) seek to provide large area coverage. On some 5 GHz bands interference from radar systems can occur in some places. For base stations that support those bands they employ Dynamic Frequency Selection which listens for radar, and if it is found, it will not permit a network on that band.
These bands can be used by low power transmitters without a licence, and with few restrictions. However, while unintended interference is common, users that have been found to cause deliberate interference (particularly for attempting to locally monopolize these bands for commercial purposes) have been issued large fines.
Throughput
Various layer-2 variants of IEEE 802.11 have different characteristics. Across all flavours of 802.11, maximum achievable throughputs are either given based on measurements under ideal conditions or in the layer-2 data rates. This, however, does not apply to typical deployments in which data are transferred between two endpoints of which at least one is typically connected to a wired infrastructure, and the other is connected to an infrastructure via a wireless link.
This means that typically data frames pass an 802.11 (WLAN) medium and are being converted to 802.3 (Ethernet) or vice versa.
Due to the difference in the frame (header) lengths of these two media, the packet size of an application determines the speed of the data transfer. This means that an application that uses small packets (e.g. VoIP) creates a data flow with high overhead traffic (low goodput).
Other factors that contribute to the overall application data rate are the speed with which the application transmits the packets (i.e. the data rate) and the energy with which the wireless signal is received. The latter is determined by distance and by the configured output power of the communicating devices.
The same references apply to the attached throughput graphs, which show measurements of UDP throughput measurements. Each represents an average throughput of 25 measurements (the error bars are there, but barely visible due to the small variation), is with specific packet size (small or large), and with a specific data rate (10 kbit/s – 100 Mbit/s). Markers for traffic profiles of common applications are included as well. This text and measurements do not cover packet errors but information about this can be found at the above references. The table below shows the maximum achievable (application-specific) UDP throughput in the same scenarios (same references again) with various WLAN (802.11) flavours. The measurement hosts have been 25 metres (yards) apart from each other; loss is again ignored.
Hardware


Wi-Fi allows wireless deployment of local area networks (LANs). Also, spaces where cables cannot be run, such as outdoor areas and historical buildings, can host wireless LANs. However, building walls of certain materials, such as stone with high metal content, can block Wi-Fi signals.
A Wi-Fi device is a short-range wireless device. Wi-Fi devices are fabricated on RF CMOS integrated circuit (RF circuit) chips.
Since the early 2000s, manufacturers are building wireless network adapters into most laptops. The price of chipsets for Wi-Fi continues to drop, making it an economical networking option included in ever more devices.
Different competitive brands of access points and client network-interfaces can inter-operate at a basic level of service. Products designated as "Wi-Fi Certified" by the Wi-Fi Alliance are backward compatible. Unlike mobile phones, any standard Wi-Fi device works anywhere in the world.
Access point

A wireless access point (WAP) connects a group of wireless devices to an adjacent wired LAN. An access point resembles a network hub, relaying data between connected wireless devices in addition to a (usually) single connected wired device, most often an Ethernet hub or switch, allowing wireless devices to communicate with other wired devices.
Wireless adapter

Wireless adapters allow devices to connect to a wireless network. These adapters connect to devices using various external or internal interconnects such as PCI, miniPCI, USB, ExpressCard, Cardbus, and PC Card. As of 2010, most newer laptop computers come equipped with built-in internal adapters.
Router
Wireless routers integrate a Wireless Access Point, Ethernet switch, and internal router firmware application that provides IP routing, NAT, and DNS forwarding through an integrated WAN-interface. A wireless router allows wired and wireless Ethernet LAN devices to connect to a (usually) single WAN device such as a cable modem, DSL modem, or optical modem. A wireless router allows all three devices, mainly the access point and router, to be configured through one central utility. This utility is usually an integrated web server that is accessible to wired and wireless LAN clients and often optionally to WAN clients. This utility may also be an application that is run on a computer, as is the case with as Apple's AirPort, which is managed with the AirPort Utility on macOS and iOS.
Bridge
Wireless network bridges can act to connect two networks to form a single network at the data-link layer over Wi-Fi. The main standard is the wireless distribution system (WDS).
Wireless bridging can connect a wired network to a wireless network. A bridge differs from an access point: an access point typically connects wireless devices to one wired network. Two wireless bridge devices may be used to connect two wired networks over a wireless link, useful in situations where a wired connection may be unavailable, such as between two separate homes or for devices that have no wireless networking capability (but have wired networking capability), such as consumer entertainment devices; alternatively, a wireless bridge can be used to enable a device that supports a wired connection to operate at a wireless networking standard that is faster than supported by the wireless network connectivity feature (external dongle or inbuilt) supported by the device (e.g., enabling Wireless-N speeds (up to the maximum supported speed on the wired Ethernet port on both the bridge and connected devices including the wireless access point) for a device that only supports Wireless-G). A dual-band wireless bridge can also be used to enable 5 GHz wireless network operation on a device that only supports 2.4 GHz wireless and has a wired Ethernet port.
Repeater
Wireless range-extenders or wireless repeaters can extend the range of an existing wireless network. Strategically placed range-extenders can elongate a signal area or allow for the signal area to reach around barriers such as those pertaining in L-shaped corridors. Wireless devices connected through repeaters suffer from an increased latency for each hop, and there may be a reduction in the maximum available data throughput. Besides, the effect of additional users using a network employing wireless range-extenders is to consume the available bandwidth faster than would be the case whereby a single user migrates around a network employing extenders. For this reason, wireless range-extenders work best in networks supporting low traffic throughput requirements, such as for cases whereby a single user with a Wi-Fi-equipped tablet migrates around the combined extended and non-extended portions of the total connected network. Also, a wireless device connected to any of the repeaters in the chain has data throughput limited by the "weakest link" in the chain between the connection origin and connection end. Networks using wireless extenders are more prone to degradation from interference from neighbouring access points that border portions of the extended network and that happen to occupy the same channel as the extended network.
Embedded systems

The security standard, Wi-Fi Protected Setup, allows embedded devices with a limited graphical user interface to connect to the Internet with ease. Wi-Fi Protected Setup has 2 configurations: The Push Button configuration and the PIN configuration. These embedded devices are also called The Internet of Things and are low-power, battery-operated embedded systems. Several Wi-Fi manufacturers design chips and modules for embedded Wi-Fi, such as GainSpan.
Increasingly in the last few years (particularly as of 2007), embedded Wi-Fi modules have become available that incorporate a real-time operating system and provide a simple means of wirelessly enabling any device that can communicate via a serial port. This allows the design of simple monitoring devices. An example is a portable ECG device monitoring a patient at home. This Wi-Fi-enabled device can communicate via the Internet.
These Wi-Fi modules are designed by OEMs so that implementers need only minimal Wi-Fi knowledge to provide Wi-Fi connectivity for their products.
In June 2014, Texas Instruments introduced the first ARM Cortex-M4 microcontroller with an onboard dedicated Wi-Fi MCU, the SimpleLink CC3200. It makes embedded systems with Wi-Fi connectivity possible to build as single-chip devices, which reduces their cost and minimum size, making it more practical to build wireless-networked controllers into inexpensive ordinary objects.
Network security
The main issue with wireless network security is its simplified access to the network compared to traditional wired networks such as Ethernet. With wired networking, one must either gain access to a building (physically connecting into the internal network), or break through an external firewall. To access Wi-Fi, one must merely be within the range of the Wi-Fi network. Most business networks protect sensitive data and systems by attempting to disallow external access. Enabling wireless connectivity reduces security if the network uses inadequate or no encryption.
An attacker who has gained access to a Wi-Fi network router can initiate a DNS spoofing attack against any other user of the network by forging a response before the queried DNS server has a chance to reply.
Securing methods
A common measure to deter unauthorized users involves hiding the access point's name by disabling the SSID broadcast. While effective against the casual user, it is ineffective as a security method because the SSID is broadcast in the clear in response to a client SSID query. Another method is to only allow computers with known MAC addresses to join the network, but determined eavesdroppers may be able to join the network by spoofing an authorized address.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption was designed to protect against casual snooping but it is no longer considered secure. Tools such as AirSnort or Aircrack-ng can quickly recover WEP encryption keys. Because of WEP's weakness the Wi-Fi Alliance approved Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) which uses TKIP. WPA was specifically designed to work with older equipment usually through a firmware upgrade. Though more secure than WEP, WPA has known vulnerabilities.
The more secure WPA2 using Advanced Encryption Standard was introduced in 2004 and is supported by most new Wi-Fi devices. WPA2 is fully compatible with WPA. In 2017, a flaw in the WPA2 protocol was discovered, allowing a key replay attack, known as KRACK.

A flaw in a feature added to Wi-Fi in 2007, called Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS), let WPA and WPA2 security be bypassed, and effectively broken in many situations. The only remedy as of late 2011 was to turn off Wi-Fi Protected Setup, which is not always possible.
Virtual Private Networks can be used to improve the confidentiality of data carried through Wi-Fi networks, especially public Wi-Fi networks.
A URI using the WIFI scheme can specify the SSID, encryption type, password/passphrase, and if the SSID is hidden or not, so users can follow links from QR codes, for instance, to join networks without having to manually enter the data. A MECARD-like format is supported by Android and iOS 11+.
- Common format:
WIFI:S:<SSID>;T:<WEP|WPA|blank>;P:<PASSWORD>;H:<true|false|blank>; - Sample
WIFI:S:MySSID;T:WPA;P:MyPassW0rd;;
Data security risks
The older wireless encryption-standard, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), has been shown easily breakable even when correctly configured. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA and WPA2) encryption, which became available in devices in 2003, aimed to solve this problem. Wi-Fi access points typically default to an encryption-free (open) mode. Novice users benefit from a zero-configuration device that works out-of-the-box, but this default does not enable any wireless security, providing open wireless access to a LAN. To turn security on requires the user to configure the device, usually via a software graphical user interface (GUI). On unencrypted Wi-Fi networks connecting devices can monitor and record data (including personal information). Such networks can only be secured by using other means of protection, such as a VPN or secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Transport Layer Security (HTTPS).
Wi-Fi Protected Access encryption (WPA2) is considered secure, provided a strong passphrase is used. In 2018, WPA3 was announced as a replacement for WPA2, increasing security; it rolled out on 26 June.
Piggybacking
Piggybacking refers to access to a wireless Internet connection by bringing one's computer within the range of another's wireless connection, and using that service without the subscriber's explicit permission or knowledge.
During the early popular adoption of 802.11, providing open access points for anyone within range to use was encouraged to cultivate wireless community networks, particularly since people on average use only a fraction of their downstream bandwidth at any given time.
Recreational logging and mapping of other people's access points have become known as wardriving. Indeed, many access points are intentionally installed without security turned on so that they can be used as a free service. Providing access to one's Internet connection in this fashion may breach the Terms of Service or contract with the ISP. These activities do not result in sanctions in most jurisdictions; however, legislation and case law differ considerably across the world. A proposal to leave graffiti describing available services was called warchalking.
Piggybacking often occurs unintentionally – a technically unfamiliar user might not change the default "unsecured" settings to their access point and operating systems can be configured to connect automatically to any available wireless network. A user who happens to start up a laptop in the vicinity of an access point may find the computer has joined the network without any visible indication. Moreover, a user intending to join one network may instead end up on another one if the latter has a stronger signal. In combination with automatic discovery of other network resources (see DHCP and Zeroconf) this could lead wireless users to send sensitive data to the wrong middle-man when seeking a destination (see man-in-the-middle attack). For example, a user could inadvertently use an unsecured network to log into a website, thereby making the login credentials available to anyone listening, if the website uses an insecure protocol such as plain HTTP without TLS.
On an unsecured access point, an unauthorized user can obtain security information (factory preset passphrase and/or Wi-Fi Protected Setup PIN) from a label on a wireless access point and use this information (or connect by the Wi-Fi Protected Setup pushbutton method) to commit unauthorized and/or unlawful activities.
Societal aspects
Wireless internet access has become much more embedded in society. It has thus changed how the society functions in many ways.
Influence on developing countries
Over half the world does not have access to the internet, prominently rural areas in developing nations. Technology that has been implemented in more developed nations is often costly and low energy efficient. This has led to developing nations using more low-tech networks, frequently implementing renewable power sources that can solely be maintained through solar power, creating a network that is resistant to disruptions such as power outages. For instance, in 2007 a 450 km (280 mile) network between Cabo Pantoja and Iquitos in Peru was erected in which all equipment is powered only by solar panels. These long-range Wi-Fi networks have two main uses: offer internet access to populations in isolated villages, and to provide healthcare to isolated communities. In the case of the aforementioned example, it connects the central hospital in Iquitos to 15 medical outposts which are intended for remote diagnosis.
Work habits
Access to Wi-Fi in public spaces such as cafes or parks allows people, in particular freelancers, to work remotely. While the accessibility of Wi-Fi is the strongest factor when choosing a place to work (75% of people would choose a place that provides Wi-Fi over one that does not), other factors influence the choice of specific hotspots. These vary from the accessibility of other resources, like books, the location of the workplace, and the social aspect of meeting other people in the same place. Moreover, the increase of people working from public places results in more customers for local businesses thus providing an economic stimulus to the area.
Additionally, in the same study it has been noted that wireless connection provides more freedom of movement while working. Both when working at home or from the office it allows the displacement between different rooms or areas. In some offices (notably Cisco offices in New York) the employees do not have assigned desks but can work from any office connecting their laptop to Wi-Fi hotspot.
Housing
The internet has become an integral part of living. 81.9% of American households have internet access. Additionally, 89% of American households with broadband connect via wireless technologies. 72.9% of American households have Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi networks have also affected how the interior of homes and hotels are arranged. For instance, architects have described that their clients no longer wanted only one room as their home office, but would like to work near the fireplace or have the possibility to work in different rooms. This contradicts architect's pre-existing ideas of the use of rooms that they designed. Additionally, some hotels have noted that guests prefer to stay in certain rooms since they receive a stronger Wi-Fi signal.
Health concerns
The World Health Organization (WHO) says, "no health effects are expected from exposure to RF fields from base stations and wireless networks", but notes that they promote research into effects from other RF sources. (a category used when "a causal association is considered credible, but when chance, bias or confounding cannot be ruled out with reasonable confidence"), this classification was based on risks associated with wireless phone use rather than Wi-Fi networks.
The United Kingdom's Health Protection Agency reported in 2007 that exposure to Wi-Fi for a year results in the "same amount of radiation from a 20-minute mobile phone call".
A review of studies involving 725 people who claimed electromagnetic hypersensitivity, "...suggests that 'electromagnetic hypersensitivity' is unrelated to the presence of an EMF, although more research into this phenomenon is required."
Alternatives
Several other wireless technologies provide alternatives to Wi-Fi for different use cases:
- Bluetooth, a short-distance network
- Bluetooth Low Energy, a low-power variant of Bluetooth
- Zigbee, a low-power, low data rate, short-distance communication protocol
- Cellular networks, used by smartphones
- WiMAX, for providing long range wireless internet connectivity
- LoRa, for long range wireless with low data rate
Some alternatives are "no new wires", re-using existing cable:
- G.hn, which uses existing home wiring, such as phone and power lines
Several wired technologies for computer networking, which provide viable alternatives to Wi-Fi: