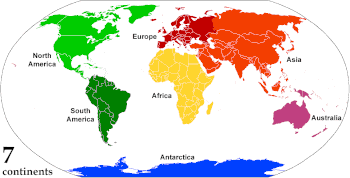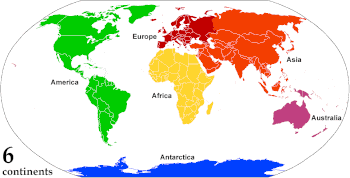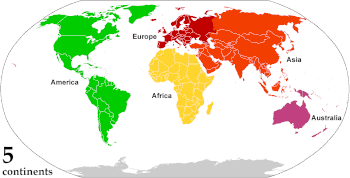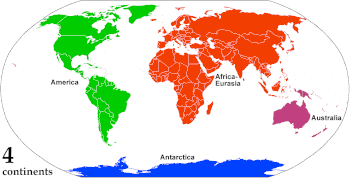
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single landmass or a part of a very large landmass, as in the case of Asia or Europe. Due to this, the number of continents varies; up to seven or as few as four geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Most English-speaking countries recognize seven regions as continents. In order from largest to smallest in area, these seven regions are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. Different variations with fewer continents merge some of these regions; examples of this are merging North America and South America into America, Asia and Europe into Eurasia, and Africa, Asia, and Europe into Afro-Eurasia.
Oceanic islands are frequently grouped with a nearby continent to divide all the world's land into geographical regions. Under this scheme, most of the island countries and territories in the Pacific Ocean are grouped together with the continent of Australia to form the geographical region Oceania.
In geology, a continent is defined as "one of Earth's major landmasses, including both dry land and continental shelves". The geological continents correspond to seven large areas of continental crust that are found on the tectonic plates, but exclude small continental fragments such as Madagascar that are generally referred to as microcontinents. Continental crust is only known to exist on Earth.
The idea of continental drift gained recognition in the 20th century. It postulates that the current continents formed from the breaking up of a supercontinent (Pangaea) that formed hundreds of millions of years ago.
Definitions and application
By convention, continents "are understood to be large, continuous, discrete masses of land, ideally separated by expanses of water". In modern schemes with five or more recognized continents, at least one pair of continents is joined by land in some fashion. The criterion "large" leads to arbitrary classification: Greenland, with a surface area of 2,166,086 square kilometres (836,330 sq mi), is only considered the world's largest island, while Australia, at 7,617,930 square kilometres (2,941,300 sq mi), is deemed the smallest continent.
Earth's major landmasses all have coasts on a single, continuous World Ocean, which is divided into a number of principal oceanic components by the continents and various geographic criteria.
Extent
The most restricted meaning of continent is that of a continuous area of land or mainland, with the coastline and any land boundaries forming the edge of the continent. In this sense, the term continental Europe (sometimes referred to in Britain as "the Continent") is used to refer to mainland Europe, excluding islands such as Great Britain, Iceland, Ireland, and Malta while the term continent of Australia may refer to the mainland of Australia, excluding New Guinea, Tasmania, and other nearby islands. Similarly, the continental United States refers to "the 49 States (including Alaska but excluding Hawaii) located on the continent of North America, and the District of Columbia."
From the perspective of geology or physical geography, continent may be extended beyond the confines of continuous dry land to include the shallow, submerged adjacent area (the continental shelf) and the islands on the shelf (continental islands), as they are structurally part of the continent.
From this perspective, the edge of the continental shelf is the true edge of the continent, as shorelines vary with changes in sea level. In this sense the islands of Great Britain and Ireland are part of Europe, while Australia and the island of New Guinea together form a continent.

As a cultural construct, the concept of a continent may go beyond the continental shelf to include oceanic islands and continental fragments. In this way, Iceland is considered a part of Europe, and Madagascar a part of Africa. Extrapolating the concept to its extreme, some geographers group the Australian continental landmass with other islands in the Pacific Ocean into one "quasi-continent" called Oceania. This divides the entire land surface of Earth into continents or quasi-continents.
Separation
The criterion that each continent is a discrete landmass is commonly relaxed due to historical conventions and practical use. Of the seven most globally recognized continents, only Antarctica and Australia are completely separated from other continents by the ocean. Several continents are defined not as absolutely distinct bodies but as "more or less discrete masses of land". Africa and Asia are joined by the Isthmus of Suez, and North America and South America by the Isthmus of Panama. In both cases, there is no complete separation of these landmasses by water (disregarding the Suez Canal and the Panama Canal, which are both narrow and shallow, as well as human-made). Both of these isthmuses are very narrow compared to the bulk of the landmasses they unite.
North America and South America are treated as separate continents in the seven-continent model. However, they may also be viewed as a single continent known as America. This viewpoint was common in the United States until World War II, and remains prevalent in some Asian six-continent models. The single American continent model remains a common view in France, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Malta, Portugal, Spain, and Latin American countries.
The criterion of a discrete landmass is completely disregarded if the continuous landmass of Eurasia is classified as two separate continents (Asia and Europe). Physiographically, Europe and the Indian subcontinent are large peninsulas of the Eurasian landmass. However, Europe is considered a continent with its comparatively large land area of 10,180,000 square kilometres (3,930,000 sq mi), while the Indian subcontinent, with less than half that area, is considered a subcontinent. The alternative view—in geology and geography—that Eurasia is a single continent results in a six-continent view of the world. Some view separation of Eurasia into Asia and Europe as a residue of Eurocentrism: "In physical, cultural and historical diversity, China and India are comparable to the entire European landmass, not to a single European country. [...]." However, for historical and cultural reasons, the view of Europe as a separate continent continues in almost all categorizations.
If continents are defined strictly as discrete landmasses, embracing all the contiguous land of a body, then Africa, Asia, and Europe form a single continent which may be referred to as Afro-Eurasia. Combined with the consolidation of the Americas, this would produce a four-continent model consisting of Afro-Eurasia, America, Antarctica, and Australia.
When sea levels were lower during the Pleistocene ice ages, greater areas of continental shelf were exposed as dry land, forming land bridges between Tasmania and the Australian mainland. At those times, Australia and New Guinea were a single, continuous continent known as Sahul. Likewise, Afro-Eurasia and the Americas were joined by the Bering Land Bridge. Other islands, such as Great Britain, were joined to the mainlands of their continents. At that time, there were just three discrete landmasses in the world: Africa-Eurasia-America, Antarctica, and Australia-New Guinea (Sahul).
Number
There are several ways of distinguishing the continents:

| Number | Continents | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Four continents | Afro-Eurasia (Old World or World Island) |
America (New World) |
Antarctica | Australia | ||||
| Five continents | Africa | Eurasia | America | Antarctica | Australia | |||
| Six continents | Africa | Eurasia | North America | South America | Antarctica | Australia | ||
| Africa | Asia | Europe | America | Antarctica | Australia | |||
| Seven continents | Africa | Asia | Europe | North America | South America | Antarctica | Australia | |
- The seven-continent model is taught in most English-speaking countries, including Australia, Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States, and also in Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia, Japan, Pakistan, the Philippines, Suriname, parts of Europe and Africa.
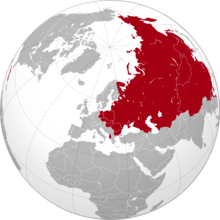
- The six-continent combined-Eurasia model is mostly used in Russia and some parts of Eastern Europe.
- The six-continent combined-America model is taught in Greece and many Romance-speaking countries—including Latin America.
- The Olympic flag's five rings represent the five inhabited continents of the combined-America model but excludes the uninhabited Antarctica.
In the English-speaking countries, geographers often use the term Oceania to denote a geographical region which includes most of the island countries and territories in the Pacific Ocean, as well as the continent of Australia.
In some non-English-speaking countries, such as China, Poland, and Russia, Oceania is considered a proper continent because their equivalent word for "continent" has a rather different meaning which can be interpreted as "a major division of land including islands" (leaning towards a region) rather than "land associated with a large landmass" (leaning towards a landmass).
Area and population
The following table provides areas given by Encyclopædia Britannica for each continent in accordance with the seven-continent model, including Australasia along with Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia as parts of Oceania. It also provides populations of continents according to 2021 estimates by the United Nations Statistics Division based on the United Nations geoscheme, which includes all of Egypt (including the Isthmus of Suez and the Sinai Peninsula) as a part of Africa, all of Armenia, Azerbaijan, Cyprus, Georgia, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, and Turkey (including East Thrace) as parts of Asia, all of Russia (including Siberia) as a part of Europe, all of Panama and the United States (including Hawaii) as parts of North America, and all of Chile (including Easter Island) as a part of South America.
| Continent | Area | Population | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | sq mi | % of total land | 2021 estimate | % of total | |
| Asia | 44,614,000 | 17,226,000 | 29.6% | 4.7 billion | 60% |
| Africa | 30,365,000 | 11,724,000 | 20.2% | 1.4 billion | 17% |
| North America | 24,230,000 | 9,360,000 | 16.4% | 600 million | 7.6% |
| South America | 17,814,000 | 6,878,000 | 11.9% | 430 million | 5.6% |
| Antarctica | 14,200,000 | 5,500,000 | 9.4% | 0 | 0% |
| Europe | 10,000,000 | 3,900,000 | 6.8% | 750 million | 9.8% |
| Oceania† | 8,511,000 | 3,286,000 | 5.7% | 40 million | 0.5% |
† Not usually considered a continent in certain countries.
Other divisions
Supercontinents

Apart from the current continents, the scope and meaning of the term continent includes past geological ones. Supercontinents, largely in evidence earlier in the geological record, are landmasses that comprise most of the world's cratons or continental cores. These have included Vaalbara, Kenorland, Columbia, Rodinia, Pannotia, and Pangaea. Over time, these supercontinents broke apart into large landmasses which formed the present continents.
Subcontinents

Certain parts of continents are recognized as subcontinents, especially the large peninsulas separated from the main continental landmass by geographical features. The most widely recognized example is the Indian subcontinent. The Arabian Peninsula, Southern Africa, the Southern Cone of South America, and Alaska in North America might be considered further examples.
In many of these cases, the "subcontinents" concerned are on different tectonic plates from the rest of the continent, providing a geological justification for the terminology. Greenland, generally reckoned as the world's largest island on the northeastern periphery of the North American Plate, is sometimes referred to as a subcontinent. This is a significant departure from the more conventional view of a subcontinent as comprising a very large peninsula on the fringe of a continent.
Where the Americas are viewed as a single continent (America), it is divided into two subcontinents (North America and South America) or three (Central America being the third). When Eurasia is regarded as a single continent, Asia and Europe are treated as subcontinents.
Submerged continents

Some areas of continental crust are largely covered by the ocean and may be considered submerged continents. Notable examples are Zealandia, emerging from the ocean primarily in New Zealand and New Caledonia, and the almost completely submerged Kerguelen Plateau in the southern Indian Ocean.
Microcontinents
Some islands lie on sections of continental crust that have rifted and drifted apart from a main continental landmass. While not considered continents because of their relatively small size, they may be considered microcontinents. Madagascar, the largest example, is usually considered an island of Africa, but its divergent evolution has caused it to be referred to as "the eighth continent" from a biological perspective.
Geological continents
Geologists use four key attributes to define a continent:
- Elevation – The landmass, whether dry or submerged beneath the ocean, should be elevated above the surrounding ocean crust.
- Geology – The landmass should contain different types of rock: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary.
- Crustal structure – The landmass should consist of the continental crust, which is thicker and has a lower seismic velocity than the oceanic crust.
- Limits and area – The landmass should have clearly-defined boundaries and an area of more than one million square kilometres.
With the addition of Zealandia in 2017, Earth currently has seven recognized geological continents: Africa, Antarctica, Australia, Eurasia, North America, South America, and Zealandia. Due to lacking the presence of Precambrian cratonic rocks, Zealandia's status as a geological continent has been disputed by some geologists. However, a study conducted in 2021 found that part of the submerged continent is indeed Precambrian, twice as old as geologists had previously thought, which is further evidence that supports the idea of Zealandia being a geological continent.
All seven geological continents are spatially isolated by geologic features.
History of the concept
Early concepts of the Old World continents

The term "continent" translates the Greek word ἤπειρος, meaning "landmass, terra firma", the proper name of Epirus and later especially used for Asia (i.e. Asia Minor).
The first distinction between continents was made by ancient Greek mariners who gave the names Europe and Asia to the lands on either side of the waterways of the Aegean Sea, the Dardanelles strait, the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus strait and the Black Sea. The names were first applied just to lands near the coast and only later extended to include the hinterlands. But the division was only carried through to the end of navigable waterways and "... beyond that point the Hellenic geographers never succeeded in laying their finger on any inland feature in the physical landscape that could offer any convincing line for partitioning an indivisible Eurasia ..."
Ancient Greek thinkers subsequently debated whether Africa (then called Libya) should be considered part of Asia or a third part of the world. Division into three parts eventually came to predominate. From the Greek viewpoint, the Aegean Sea was the center of the world; Asia lay to the east, Europe to the north and west, and Africa to the south. The boundaries between the continents were not fixed. Early on, the Europe–Asia boundary was taken to run from the Black Sea along the Rioni River (known then as the Phasis) in Georgia. Later it was viewed as running from the Black Sea through Kerch Strait, the Sea of Azov and along the Don River (known then as the Tanais) in Russia. The boundary between Asia and Africa was generally taken to be the Nile River. Herodotus in the 5th century BC objected to the whole of Egypt being split between Asia and Africa ("Libya") and took the boundary to lie along the western border of Egypt, regarding Egypt as part of Asia. He also questioned the division into three of what is really a single landmass, a debate that continues nearly two and a half millennia later.
Eratosthenes, in the 3rd century BC, noted that some geographers divided the continents by rivers (the Nile and the Don), thus considering them "islands". Others divided the continents by isthmuses, calling the continents "peninsulas". These latter geographers set the border between Europe and Asia at the isthmus between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, and the border between Asia and Africa at the isthmus between the Red Sea and the mouth of Lake Bardawil on the Mediterranean Sea.

There was no sense of continental identity within the Roman Empire. However, following the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the culture that developed in its place, linked to Latin and the Catholic church, began to associate itself with the concept of "Europe". Through the Roman period and the Middle Ages, a few writers took the Isthmus of Suez as the boundary between Asia and Africa, but most writers continued to consider it the Nile or the western border of Egypt (Gibbon). In the Middle Ages, the world was usually portrayed on T and O maps, with the T representing the waters dividing the three continents. By the middle of the 18th century, "the fashion of dividing Asia and Africa at the Nile, or at the Great Catabathmus [the boundary between Egypt and Libya] farther west, had even then scarcely passed away".
European arrival in the Americas
Christopher Columbus sailed across the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean in 1492, sparking a period of European exploration of the Americas. But despite four voyages to the Americas, Columbus never believed he had reached a new continent—he always thought it was part of Asia.
In 1501, Amerigo Vespucci and Gonçalo Coelho attempted to sail around what they considered the southern end of the Asian mainland into the Indian Ocean, passing through Fernando de Noronha. After reaching the coast of Brazil, they sailed along the coast of South America much farther south than Asia was known to extend, confirming that this was a land of continental proportions. On return to Europe, an account of the voyage, called Mundus Novus ("New World"), was published under Vespucci's name in 1502 or 1503, although it seems that it had additions or alterations by another writer. Regardless of who penned the words, Mundus Novus credited Vespucci with saying, "I have discovered a continent in those southern regions that is inhabited by more numerous people and animals than our Europe, or Asia or Africa", the first known explicit identification of part of the Americas as a continent like the other three.
Within a few years, the name "New World" began appearing as a name for South America on world maps, such as the Oliveriana (Pesaro) map of around 1504–1505. Maps of this time, though, still showed North America connected to Asia and showed South America as a separate land.

In 1507 Martin Waldseemüller published a world map, Universalis Cosmographia, which was the first to show North and South America as separate from Asia and surrounded by water. A small inset map above the main map explicitly showed for the first time the Americas being east of Asia and separated from Asia by an ocean, as opposed to just placing the Americas on the left end of the map and Asia on the right end. In the accompanying book Cosmographiae Introductio, Waldseemüller noted that the earth is divided into four parts, Europe, Asia, Africa, and the fourth part, which he named "America" after Amerigo Vespucci's first name. On the map, the word "America" was placed on part of South America.
The word continent
From the 16th century the English noun continent was derived from the term continent land, meaning continuous or connected land and translated from the Latin terra continens. The noun was used to mean "a connected or continuous tract of land" or mainland. It was not applied only to very large areas of land—in the 17th century, references were made to the continents (or mainlands) of Isle of Man, Ireland and Wales and in 1745 to Sumatra. The word continent was used in translating Greek and Latin writings about the three "parts" of the world, although in the original languages no word of exactly the same meaning as continent was used.
While continent was used on the one hand for relatively small areas of continuous land, on the other hand geographers again raised Herodotus's query about why a single large landmass should be divided into separate continents. In the mid-17th century, Peter Heylin wrote in his Cosmographie that "A Continent is a great quantity of Land, not separated by any Sea from the rest of the World, as the whole Continent of Europe, Asia, Africa." In 1727, Ephraim Chambers wrote in his Cyclopædia, "The world is ordinarily divided into two grand continents: the old and the new." And in his 1752 atlas, Emanuel Bowen defined a continent as "a large space of dry land comprehending many countries all joined together, without any separation by water. Thus Europe, Asia, and Africa is one great continent, as America is another." However, the old idea of Europe, Asia and Africa as "parts" of the world ultimately persisted with these being regarded as separate continents.
Beyond four continents
The Sanskrit text Rig Veda often dated 1500 BCE has the earliest mention of seven continents in the Earth, the text claims that the Earth has seven continents and Lord Vishnu Measured the entire universe from his first foot from the land of Earth which has 7 continents.
ato devā avantu no yato viṣṇurvicakrame | |
The Gods be gracious unto us even from the place whence Vishnu strode |
| —RigVeda transliteration of Book 1, Hymn 22, Verses 16-18 | —RigVeda translation by Ralph T.H. Griffith (1896) of Book 1, Hymn 22, Verses 16–18 |

In regard to the above-quoted verses, it is commonly accepted that there are Seven Continents or 'regions of the earth'. A. Glucklich adds that 'In the Matsya Purana, for instance, there is a seven-part map of the world ... [it has] one centre, where an immense mountain – Mount Meru (or Maha Meru, Great Meru) – stands ... The continents encircle the mountain in seven concentric circles ... It seems clear that the Himalayas were the approximate location of Mt. Meru and the text is clear that the earth has seven continents.
From the late 18th century, some geographers started to regard North America and South America as two parts of the world, making five parts in total. Overall though, the fourfold division prevailed well into the 19th century.
Europeans discovered Australia in 1606, but for some time it was taken as part of Asia. By the late 18th century, some geographers considered it a continent in its own right, making it the sixth (or fifth for those still taking America as a single continent). In 1813, Samuel Butler wrote of Australia as "New Holland, an immense island, which some geographers dignify with the appellation of another continent" and the Oxford English Dictionary was just as equivocal some decades later. It was in the 1950s that the concept of Oceania as a "great division" of the world was replaced by the concept of Australia as a continent.
Antarctica was sighted in 1820 during the First Russian Antarctic Expedition and described as a continent by Charles Wilkes on the United States Exploring Expedition in 1838, the last continent identified, although a great "Antarctic" (antipodean) landmass had been anticipated for millennia. An 1849 atlas labelled Antarctica as a continent but few atlases did so until after World War II.
Over time, the western concept of dividing the world into continents spread globally, replacing conceptions in other areas of the world. The idea of continents continued to become imbued with cultural and political meaning. In the 19th century during the Meiji period, Japanese leaders began to self-identify with the concept of being Asian, and renew relations with other "Asian" countries while conceiving of the idea of Asian solidarity against western countries. This conception of an Asian identity, as well as the idea of Asian solidarity, was later taken up by others in the region, such as Republican China and Vietnam.
From the mid-19th century, atlases published in the United States more commonly treated North and South America as separate continents, while atlases published in Europe usually considered them one continent. However, it was still not uncommon for American atlases to treat them as one continent up until World War II. From the 1950s, most U.S. geographers divided the Americas into two continents. With the addition of Antarctica, this made the seven-continent model. However, this division of the Americas never appealed to Latin Americans, who saw their region spanning an América as a single landmass, and there the conception of six continents remains dominant, as it does in scattered other countries.
Some geographers regard Europe and Asia together as a single continent, dubbed Eurasia. In this model, the world is divided into six continents, with North America and South America considered separate continents.
Geology
Geologists use the term continent in a different manner from geographers. In geology, a continent is defined by continental crust, which is a platform of metamorphic and igneous rock, largely of granitic composition. Continental crust is less dense and much thicker than oceanic crust, which causes it to "float" higher than oceanic crust on the dense underlying mantle. This explains why the continents form high platforms surrounded by deep ocean basins.
Some geologists restrict the term continent to portions of the crust built around stable regions called cratons. Cratons have largely been unaffected by mountain-building events (orogenies) since the Precambrian. A craton typically consists of a continental shield surrounded by a continental platform. The shield is a region where ancient crystalline basement rock (typically 1.5 to 3.8 billion years old) is widely exposed at the surface. The platform surrounding the shield is also composed of ancient basement rock, but with a cover of younger sedimentary rock. The continents are accretionary crustal "rafts" that, unlike the denser basaltic crust of the ocean basins, are not subjected to destruction through the plate tectonic process of subduction. This accounts for the great age of the rocks comprising the continental cratons.
The margins of geologic continents are either active or passive. An active margin is characterised by mountain building, either through a continent-on continent collision or a subduction zone. Continents grow by accreting lighter volcanic island chains and microcontinents along these active margins, forming orogens. At a passive margin, the continental crust is stretched thin by extension to form a continental shelf, which tapers off with a gradual slope covered in sediment, connecting it directly to the oceanic crust beyond. Most passive margins eventually transition into active margins: where the oceanic plate becomes too heavy due to cooling, it disconnects from the continental crust, and starts subducting below it, forming a new subduction zone.

There are many microcontinents, or continental fragments, that are built of continental crust but do not contain a craton. Some of these are fragments of Gondwana or other ancient cratonic continents: Zealandia, which includes New Zealand and New Caledonia; Madagascar; the northern Mascarene Plateau, which includes the Seychelles. Other islands, such as several in the Caribbean Sea, are composed largely of granitic rock as well, but all continents contain both granitic and basaltic crust, and there is no clear boundary as to which islands would be considered microcontinents under such a definition. The Kerguelen Plateau, for example, is largely volcanic, but is associated with the breakup of Gondwanaland and is considered a microcontinent, whereas volcanic Iceland and Hawaii are not. The British Isles, Sri Lanka, Borneo, and Newfoundland were on the margins of the Laurasian continent—only separated from the main continental landmass by inland seas flooding its margins.
The movement of plates has caused the continual formation and breakup of continents, and occasionally supercontinents, in a process called the Wilson Cycle. The supercontinent Columbia or Nuna formed during a period of 2.0–1.8 billion years ago and broke up about 1.5–1.3 billion years ago. The supercontinent Rodinia is thought to have formed about 1 billion years ago and to have embodied most or all of Earth's continents, and broken up into eight continents around 600 million years ago. The eight continents later reassembled into another supercontinent called Pangaea; Pangaea broke up into Laurasia (which became North America and Eurasia) and Gondwana (which became the remaining continents).