| Islamic State | |
|---|---|
الدولة الإسلامية ad-Dawlah al-Islāmiyah | |
| Also known as | IS, ISIS, ISIL, Daesh |
| Founder | Abu Musab al-Zarqawi † |
| Leaders |
|
1999–present | |
| Group(s) | Unorganized cells |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Unknown (March 2019 – present) |
Former | |
| Active regions |  IS territory, in grey, at the time of its greatest territorial extent (May 2015) |
|---|
Additional opponents | |
| Battles and wars | Primary target of |
|---|---|
The Islamic State (IS), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL; /ˈaɪsɪl/), Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS; /ˈaɪsɪs/), and by its Arabic acronym Da'ish or Daesh (داعش, Dāʿish, IPA: [ˈdaːʕɪʃ]), is a transnational militant Islamist terrorist group and former unrecognised quasi-state that follows the Salafi jihadist branch of Sunni Islam. It was founded by Abu Musab al-Zarqawi in 1999 and gained global prominence in 2014, when its militants conquered large territories in northwestern Iraq and eastern Syria, aided by the Syrian civil war. By the end of 2015, it ruled an area with an estimated population of twelve million people, where it enforced its interpretation of Islamic law, administered an annual budget of more than US$1 billion, and had more than 30,000 fighters under its command. After years of intense and grinding combat with American, Iraqi, and Kurdish forces, by 2019 it had lost all its Middle Eastern territories and returned to insurgency tactics in the regions it once controlled, operating from remote hideouts and continuing its propaganda efforts, which have gained it a strong following in northern and Sahelian Africa.
From 2003 to 2013, the group pledged allegiance to al-Qaeda (mostly under the name "Islamic State of Iraq") and participated in the Iraqi insurgency against the United States and its allies. The group changed its name again to "Islamic State of Iraq and Levant" for about a year, before proclaiming itself to be a worldwide caliphate, called simply the Islamic State (الدولة الإسلامية, ad-Dawlah al-Islāmiyah). As a caliphate, it demanded the religious, political, and military obedience of Muslims worldwide, despite the rejection of its legitimacy by mainstream Muslims and its statehood by the United Nations and various governments.
For the next few years the Iraqi Armed Forces and the Syrian Democratic Forces beat back "the Islamic State" and degraded its financial and military infrastructure, assisted by advisors, weapons, training, supplies and airstrikes by the American-led coalition, and later by Russian airstrikes, bombings, cruise missile attacks and scorched-earth tactics across Syria, which focused mostly on razing opposition strongholds rather than IS bases. By March 2019, IS lost one of its last significant territories in the Middle East.
Designated a terrorist organisation by the United Nations and others, the group was known for its massive human rights abuses: genocide against Yazidis and Christians on a historic scale, systematic persecution of Shia Muslims; its videos of beheadings (and other kinds of executions) of soldiers, journalists, and aid workers; as well as its destruction of cultural heritage sites.
Name
In April 2013, having expanded into Syria, the group adopted the name ad-Dawlah al-Islāmiyah fī 'l-ʿIrāq wa-sh-Shām (الدولة الإسلامية في العراق والشام). As al-Shām is a region often compared with the Levant or Greater Syria, the group's name has been variously translated as "Islamic State of Iraq and al-Sham", "Islamic State of Iraq and Syria" (both abbreviated as ISIS), or "Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant" (abbreviated as ISIL).
While the use of either one or the other acronym has been the subject of debate, the distinction between the two and its relevance has been considered not so great. Of greater relevance is the name Daesh, which is an acronym of ISIL's Arabic name ad-Dawlah al-Islamīyah fī l-ʻIrāq wa-sh-Shām. Dāʿish (داعش), or Daesh. This name has been widely used by ISIL's Arabic-speaking detractors, for example when referring to the group whilst speaking amongst themselves, although—and to a certain extent because—it is considered derogatory, as it resembles the Arabic words Daes ("one who crushes, or tramples down, something underfoot") and Dāhis (loosely translated: "one who sows discord"). Within areas under its control, ISIL considers use of the name Daesh punishable by flogging.
In late June 2014, the group renamed itself ad-Dawlah al-Islāmiyah (lit. 'Islamic State' or IS), declaring itself a worldwide caliphate. The name "Islamic State" and the group's claim to be a caliphate have been widely rejected, with the UN, various governments, and mainstream Muslim groups refusing to use the new name. The group's declaration of a new caliphate in June 2014 and its adoption of the name "Islamic State" have been criticised and ridiculed by Muslim scholars and rival Islamists both inside and outside the territory it controls.
In a speech in September 2014, United States President Barack Obama said that ISIL was neither "Islamic" (on the basis that no religion condones the killing of innocents) nor was it a "state" (in that no government recognises the group as a state), while many object to using the name "Islamic State" owing to the far-reaching religious and political claims to authority which that name implies. The United Nations Security Council, the United States, Canada, Turkey, Australia, the United Kingdom and other countries generally call the group "ISIL", while much of the Arab world uses the Arabic acronym "Dāʻish" (or "Daesh"). France's Foreign Minister Laurent Fabius said "This is a terrorist group and not a state. I do not recommend using the term Islamic State because it blurs the lines between Islam, Muslims, and Islamists. The Arabs call it 'Daesh' and I will be calling them the 'Daesh cutthroats'." Retired general John Allen, the U.S. envoy appointed to co-ordinate the coalition; U.S. Army Lieutenant General James Terry, head of operations against the group; and Secretary of State John Kerry had all shifted towards use of the term Daesh by December 2014, which nonetheless remained a pejorative in 2021.
In 2014, Dar al-Ifta al-Misriyyah dubbed ISIS as QSIS for "al-Qaeda Separatists in Iraq and Syria", arguing that ISIL does not represent the vast majority of Muslims.
Purpose and strategy
Ideology
IS is a theocracy, proto-state, and a Salafi jihadist group. ISIL's ideology has been described as a hybrid of Qutbism, Takfirism, Salafism, Salafi jihadism, Wahhabism, and Sunni Islamist fundamentalism. Although ISIL claims to adhere to the Salafi theology of Ibn Taymiyyah, it rebels against traditional Salafi interpretations as well as the four Sunni schools of law and anathematises the majority of Salafis as heretics. ISIL ideologues rarely uphold adherence to Islamic scholarship and law manuals for reference, mostly preferring to derive rulings based on self-interpretation of the Qur'an and Muslim traditions.
According to Robert Manne, there is a "general consensus" that the ideology of the Islamic State is "primarily based upon the writings of the radical Egyptian Muslim Brotherhood theoretician Sayyid Qutb". The Muslim Brotherhood began the trend of political Islamism in the 20th century, seeking gradual establishment of a new Caliphate, a comprehensive Islamic society ruled by sharia law. Qutb's doctrines of Jahiliyya (pre-Islamic ignorance), Hakimiyya (Divine Sovereignty), and Takfir of entire societies formed a radicalised vision of the Muslim Brotherhood's political Islam project. Qutbism became the precursor to all Jihadist thought, from Abdullah Azzam to Zawahiri and to Daesh. Alongside Sayyid Qutb, the most invoked ideological figures of ISIS include Ibn Taymiyya, Abdullah Azzam, and Abu Bakr Naji.
ISIL's first leader Abu Omar al-Baghdadi was radicalised as a Muslim Brotherhood member during his youth. Motaz Al-Khateeb states that religious texts and Islamic jurisprudence "alone cannot explain the emergence" of Daesh since the Muslim Brotherhood and Daesh "draw on the same Islamic jurisprudence" but "are diametrically opposite" in strategy and behavior. Through the official statement of beliefs originally released by al-Baghdadi in 2007 and subsequently updated since June 2014, ISIL defined its creed as "a middle way between the extremist Kharijites and the lax Murji'ites". ISIL's ideology represents radical Jihadi-Salafi Islam, a strict, puritanical form of Sunni Islam. Muslim organisations like Islamic Networks Group (ING) in America have argued against this interpretation of Islam. ISIL promotes religious violence, and regards Muslims who do not agree with its interpretations as infidels or apostates.
According to Hayder al Khoei, ISIL's philosophy is represented by the symbolism in the Black Standard variant of the legendary battle flag of Muhammad that it has adopted: the flag shows the Seal of Muhammad within a white circle, with the phrase above it, "There is no god but Allah". This symbolism is said to symbolize ISIL's belief that it represents the restoration of the caliphate of early Islam, with all the political, religious and eschatological ramifications that this would imply.
Abu Abdullah al-Muhajir, an Egyptian Jihadist theoretician and ideologue is considered as the key inspiration for early figures of IS.[ Al-Muhajir's legal manual on violence, Fiqh ad-Dima (The Jurisprudence of Jihad or The Jurisprudence of Blood), was adopted by ISIL as its standard reference for justifying its extraordinary acts of violence. The book has been described by counter-terrorism scholar Orwa Ajjoub as rationalising and justifying "suicide operations, the mutilation of corpses, beheading, and the killing of children and non-combatants." His theological and legal justifications influenced ISIL, al-Qaeda, and Boko Haram, as well as several other jihadi terrorist groups. Numerous media outlets have compared his reference manual to Abu Bakr Naji's Management of Savagery, widely read among ISIS's commanders and fighters.
ISIL adheres to global jihadist principles and follows the hard-line ideology of al-Qaeda and many other modern-day jihadist groups.
For their guiding principles, the leaders of the Islamic State ... are open and clear about their almost exclusive commitment to the Wahhabi movement of Sunni Islam. The group circulates images of Wahhabi religious textbooks from Saudi Arabia in the schools it controls. Videos from the group's territory have shown Wahhabi texts plastered on the sides of an official missionary van.
— David D. Kirkpatrick, The New York Times
According to The Economist, Saudi practices followed by the group include the establishment of religious police to root out "vice" and enforce attendance at salat prayers, the widespread use of capital punishment, and the destruction or re-purposing of any non-Sunni religious buildings. Bernard Haykel has described ISIL leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi's creed as "a kind of untamed Wahhabism". Senior Saudi religious leaders have issued statements condemning ISIL and attempting to distance the group from official Saudi religious beliefs.
What connection, if any, there is between Salafi-Jihadism of Daesh and Wahhabism and Salafism proper is disputed. ISIS borrowed two elements of Qutbism and 20th century Islamism into its version of Wahhabi worldview. While Wahhabism shuns violent rebellion against earthly rulers, ISIS embraces political call to revolutions. While historically Wahhabis were not champion activists of a Caliphate, ISIS borrowed the idea of restoration of a global Caliphate.
Although the religious character of ISIS is mostly Wahhabi, it departs from Wahhabi tradition in four critical aspects: dynastic alliance, call to establish a global caliphate, sheer violence, and apocalyptism.
ISIS did not follow the pattern of the first three Saudi states in allying the religious mission of the Najdi ulema with the Al Saud family, rather they consider them apostates. The call for a global caliphate is another departure from Wahhabism. The caliphate, understood in Islamic law as the ideal Islamic polity uniting all Muslim territories, does not figure much in traditional Najdi writings. Ironically, Wahhabism emerged as an anti-caliphate movement.
Although violence was not absent in the First Saudi State, Islamic State's displays of beheading, immolation, and other forms of violence aimed at inspiring fear are not in imitation of early Saudi practices. They were introduced by Abu Musab Al-Zarqawi, former leader of Al-Qaeda in Iraq, who took inspiration from the Egyptian Jihadi scholar, Abu Abdallah Al Muhajir. It is the latter's legal manual on violence, popularly known as Fiqh ad-Dima (The Jurisprudence of Blood), that is the Islamic State's standard reference for justifying its acts of violence. The Islamic State's apocalyptic dimension also lacks a mainstream Wahhabi precedent.
ISIL aims to return to the early days of Islam, rejecting all innovations in the religion, which it believes corrupts its original spirit. It condemns later caliphates and the Ottoman Empire for deviating from what it calls pure Islam and seeks to revive the original Qutbist project of the restoration of a global caliphate that is governed by a strict Salafi-Jihadi doctrine. Following Salafi-Jihadi doctrines, ISIL condemns the followers of secular law as disbelievers, putting the current Saudi Arabian government in that category.
ISIL believes that only a legitimate authority can undertake the leadership of jihad and that the first priority over other areas of combat, such as fighting non-Muslim countries, is the purification of Islamic society. For example, ISIL regards the Palestinian Sunni group Hamas as apostates who have no legitimate authority to lead jihad and see fighting Hamas as the first step towards confrontation by ISIL with Israel.
Yemeni journalist Abdulelah Haider Shaye said:
The Islamic State was drafted by Sayyid Qutb, taught by Abdullah Azzam, globalized by Osama bin Laden, transferred to reality by Abu Musab al-Zarqawi, and implemented by al-Baghdadis: Abu Omar and Abu Bakr.
— Hassan Hassan, The Sectarianism of the Islamic State: Ideological Roots and Political Context.
The Islamic State added a focus on sectarianism to a layer of radical views. In particular, it linked itself to the Salafi-jihadi movement that evolved out of the Afghan jihad.
— Hassan Hassan, The Sectarianism of the Islamic State: Ideological Roots and Political Context.
Islamic eschatology
One difference between ISIL and other Islamist and jihadist movements, including al-Qaeda, is the group's emphasis on eschatology and apocalypticism – that is, a belief in a final Day of Judgment by God. ISIL believes that it will defeat the army of "Rome" at the town of Dabiq. ISIL also believes that after al-Baghdadi there will be only four more legitimate caliphs.
The noted scholar of militant Islamism Will McCants writes:
References to the End Times fill Islamic State propaganda. It's a big selling point with foreign fighters, who want to travel to the lands where the final battles of the apocalypse will take place. The civil wars raging in those countries today [Iraq and Syria] lend credibility to the prophecies. The Islamic State has stoked the apocalyptic fire. ... For Bin Laden's generation, the apocalypse wasn't a great recruiting pitch. Governments in the Middle East two decades ago were more stable, and sectarianism was more subdued. It was better to recruit by calling to arms against corruption and tyranny than against the Antichrist. Today, though, the apocalyptic recruiting pitch makes more sense than before.
— William McCants, The ISIS Apocalypse: The History, Strategy, and Doomsday Vision of the Islamic State
Goals
Since at latest 2004, a significant goal of the group has been the foundation of a Sunni Islamic state. Specifically, ISIL has sought to establish itself as a caliphate, an Islamic state led by a group of religious authorities under a supreme leader – the caliph – who is believed to be the successor to Muhammad. In June 2014, ISIL published a document in which it claimed to have traced the lineage of its leader al-Baghdadi back to Muhammad, and upon proclaiming a new caliphate on 29 June, the group appointed al-Baghdadi as its caliph. As caliph, he demanded the allegiance of all devout Muslims worldwide, according to Islamic jurisprudence (fiqh).
ISIL has detailed its goals in its Dabiq magazine, saying it will continue to seize land and take over the entire Earth until its:
Blessed flag...covers all eastern and western extents of the Earth, filling the world with the truth and justice of Islam and putting an end to the falsehood and tyranny of jahiliyyah [state of ignorance], even if America and its coalition despise such.
— 5th edition of Dabiq, the Islamic State's English-language magazine
According to German journalist Jürgen Todenhöfer, who spent ten days embedded with ISIL in Mosul, the view he kept hearing was that ISIL wants to "conquer the world", and that all who do not believe in the group's interpretation of the Quran will be killed. Todenhöfer was struck by the ISIL fighters' belief that "all religions who agree with democracy have to die", and by their "incredible enthusiasm" – including enthusiasm for killing "hundreds of millions" of people.
When the caliphate was proclaimed, ISIL stated: "The legality of all emirates, groups, states and organisations becomes null by the expansion of the khilafah's [caliphate's] authority and the arrival of its troops to their areas." This was a rejection of the political divisions in Southwestern Asia that were established by the UK and France during World War I in the Sykes–Picot Agreement.
All non-Muslim areas would be targeted for conquest after the Muslim lands were dealt with, according to the Islamist manual Management of Savagery.
Strategy

Documents found after the death of Samir Abd Muhammad al-Khlifawi, a former colonel in the intelligence service of the Iraqi Air Force before the US invasion who had been described as "the strategic head" of ISIL, detailed planning for the ISIL takeover of northern Syria which made possible "the group's later advances into Iraq". Al-Khlifawi called for the infiltration of areas to be conquered with spies who would find out "as much as possible about the target towns: Who lived there, who was in charge, which families were religious, which Islamic school of religious jurisprudence they belonged to, how many mosques there were, who the imam was, how many wives and children he had and how old they were". Following this surveillance and espionage would come murder and kidnapping – "the elimination of every person who might have been a potential leader or opponent". In Raqqa, after rebel forces drove out the Assad regime and ISIL infiltrated the town, "first dozens and then hundreds of people disappeared".
Security and intelligence expert Martin Reardon has described ISIL's purpose as being to psychologically "break" those under its control, "so as to ensure their absolute allegiance through fear and intimidation", while generating "outright hate and vengeance" among its enemies. Jason Burke, a journalist writing on Salafi jihadism, has written that ISIL's goal is to "terrorize, mobilize [and] polarize". Its efforts to terrorise are intended to intimidate civilian populations and force governments of the target enemy "to make rash decisions that they otherwise would not choose". It aims to mobilise its supporters by motivating them with, for example, spectacular deadly attacks deep in Western territory (such as the November 2015 Paris attacks), to polarise by driving Muslim populations – particularly in the West – away from their governments, thus increasing the appeal of ISIL's self-proclaimed caliphate among them, and to: "Eliminate neutral parties through either absorption or elimination". Journalist Rukmini Maria Callimachi also emphasises ISIL's interest in polarisation or in eliminating what it calls the "grey zone" between the black (non-Muslims) and white (ISIL). "The gray is moderate Muslims who are living in the West and are happy and feel engaged in the society here."
A work published online in 2004 entitled Management of Savagery (Idarat at Tawahoush), described by several media outlets as influential on ISIL and intended to provide a strategy to create a new Islamic caliphate, recommended a strategy of attack outside its territory in which fighters would "Diversify and widen the vexation strikes against the Crusader-Zionist enemy in every place in the Islamic world, and even outside of it if possible, so as to disperse the efforts of the alliance of the enemy and thus drain it to the greatest extent possible."
The group has been accused of attempting to "bolster morale" and distract attention from its loss of territory to enemies by staging terror attacks abroad (such as the 2016 Berlin truck attack, the 6 June 2017 attacks on Tehran, the 22 May 2017 bombing in Manchester, and the 3 June 2017 attacks in London that ISIL claimed credit for).
Organisation
Raqqa in Syria was under ISIL control from 2013 and in 2014 it became the group's de facto capital city. On 17 October 2017, following a lengthy battle that saw massive destruction to the city, the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) announced the full capture of Raqqa from ISIL.
Leadership and governance

From 2013 to 2019, ISIL was headed and run by Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, the Islamic State's self-styled Caliph. Before their deaths, he had two deputy leaders, Abu Muslim al-Turkmani for Iraq and Abu Ali al-Anbari (also known as Abu Ala al-Afri) for Syria, both ethnic Turkmen. Advising al-Baghdadi were a cabinet of senior leaders, while its operations in Iraq and Syria are controlled by local 'emirs,' who head semi-autonomous groups which the Islamic State refers to as its provinces. Beneath the leaders are councils on finance, leadership, military matters, legal matters (including decisions on executions) foreign fighters' assistance, security, intelligence and media. In addition, a shura council has the task of ensuring that all decisions made by the governors and councils comply with the group's interpretation of sharia. While al-Baghdadi had told followers to "advise me when I err" in sermons, according to observers "any threat, opposition, or even contradiction is instantly eradicated".
According to Iraqis, Syrians, and analysts who study the group, almost all of ISIL's leaders—including the members of its military and security committees and the majority of its emirs and princes—are former Iraqi military and intelligence officers, specifically former members of Saddam Hussein's Ba'ath government who lost their jobs and pensions in the de-Ba'athification process after that regime was overthrown. The former Chief Strategist in the Office of the Coordinator for Counterterrorism of the US State Department, David Kilcullen, has said that "There undeniably would be no Isis if we had not invaded Iraq." It has been reported that Iraqis and Syrians have been given greater precedence over other nationalities within ISIL because the group needs the loyalties of the local Sunni populations in both Syria and Iraq in order to be sustainable. Other reports, however, have indicated that Syrians are at a disadvantage to foreign members, with some native Syrian fighters resenting "favouritism" allegedly shown towards foreigners over pay and accommodation.
In August 2016, media reports based on briefings by Western intelligence agencies suggested that ISIL had a multilevel secret service known in Arabic as Emni, established in 2014, that has become a combination of an internal police force and an external operations directorate complete with regional branches. The unit was believed to be under the overall command of ISIL's most senior Syrian operative, spokesman and propaganda chief Abu Mohammad al-Adnani until his death by airstrike in late August 2016.
On 27 October 2019, the United States conducted a special operation targeting al-Baghdadi's compound in Barisha, Idlib, Northwest Syria. The attack resulted in al-Baghdadi's death; caught by surprise and unable to escape, al-Baghdadi detonated a suicide vest, deliberately killing both himself and two children who had been living in the compound prior to the assault. U.S. President Donald Trump stated in a televised announcement that Baghdadi had, in fact, died during the operation and that American forces used support from helicopters, jets and drones through airspace controlled by Russia and Turkey. He said that "Russia treated us great... Iraq was excellent. We really had great cooperation" and Turkey knew they were going in. He thanked Turkey, Russia, Syria, Iraq and the Syrian Kurdish forces for their support. The Turkish Defence Ministry also confirmed on Sunday that Turkish and U.S. military authorities exchanged and coordinated information ahead of an attack in Syria's Idlib. Fahrettin Altun, a senior aide to Turkish President Tayyib Erdogan, also stated, among other things, that "Turkey was proud to help the United States, our NATO ally, bring a notorious terrorist to justice" and that Turkey "will continue to work closely with the United States and others to combat terrorism in all its forms and manifestations." Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov declined to say if the United States had told Russia about the raid in advance but said that its result if confirmed, represented a serious contribution by the United States to combat terrorism. Russia had previously claimed Baghdadi was killed in May 2019 by their airstrike.
In September 2019, a statement attributed to ISIL's propaganda arm, the Amaq news agency, claimed that Abdullah Qardash was named as al-Baghdadi's successor. Analysts dismissed this statement as a fabrication, and relatives were reported as saying that Qardash died in 2017. Rita Katz, a terrorism analyst and the co-founder of SITE Intelligence, noted that the alleged statement used a different font when compared to other statements and it was never distributed on Amaq or ISIL channels.
On 29 October 2019, Trump stated on social media that al-Baghdadi's "number one replacement" had been killed by American forces, without giving a name. A U.S. official later confirmed that Trump was referring to ISIL spokesman and senior leader Abul-Hasan al-Muhajir, who was killed in a U.S. airstrike in Syria two days earlier. On 31 October, ISIL named Abu Ibrahim al-Hashemi al-Qurayshi as Baghdadi's successor. On 3 February 2022, it was reported by a US official that al-Hashimi killed himself and members of his family by triggering an explosive device during a counter-terrorism raid by the US Joint Special Operations Command. On 30 November 2022, ISIL announced that their unidentified leader had been killed in battle and named a successor, providing no additional information other than his pseudonym. A spokesman for U.S. Central Command confirmed that ISIL's leader had been killed in mid-October by anti-government rebels in southern Syria. On 16 February 2023, senior ISIS leader Hamza al-Homsi blew himself up in a U.S.-led raid in Syria.
Civilians in Islamic State-controlled areas
In 2014, The Wall Street Journal estimated that eight million people lived in the Islamic State. The United Nations Commission on Human Rights has stated that IS "seeks to subjugate civilians under its control and dominate every aspect of their lives through terror, indoctrination, and the provision of services to those who obey". Civilians, as well as the Islamic State itself, have released footage of some of the human rights abuses.
Social control of civilians was by imposition of IS's reading of sharia law, enforced by morality police forces known as Al-Hisbah and the all-women Al-Khanssaa Brigade, a general police force, courts, and other entities managing recruitment, tribal relations, and education. Al-Hisbah was led by Abu Muhammad al-Jazrawi.
In 2015, IS published a penal code including floggings, amputations, crucifixions, etc.
Military
Number of combatants
| Country | Fighters |
|---|---|
| Russia | 5,000
|
| Tunisia | 4,000
|
| Jordan | 3,950
|
| Saudi Arabia | 3,244
|
| Turkey | 3,000
|
| Uzbekistan | 2,500
|
| France | 1,910
|
| Morocco | 1,699
|
| Tajikistan | 1,502
|
| China | 1,000
|
| Germany | 960
|
| Lebanon | 900
|
| Azerbaijan | 900
|
| Kyrgyzstan | 863
|
| United Kingdom | 860
|
| Indonesia | 800
|
| Kazakhstan | 600
|
| Libya | 600
|
| Egypt | 500
|
| Turkmenistan | 500
|
| Belgium | 500
|
Estimates of the size of ISIL's military have varied widely, from tens of thousands up to 200,000. In early 2015, journalist Mary Anne Weaver estimated that half of ISIL fighters were foreigners. A UN report estimated a total of 15,000 fighters from over 80 countries were in ISIL's ranks in November 2014. US intelligence estimated an increase to around 20,000 foreign fighters in February 2015, including 3,400 from the Western world. In September 2015, the CIA estimated that 30,000 foreign fighters had joined ISIL.
According to Abu Hajjar, a former senior leader of ISIL, foreign fighters receive food, petrol and housing, but unlike native Iraqi or Syrian fighters, they do not receive payment in wages. Since 2012, more than 3000 people from the central Asian countries have gone to Syria, Iraq or Afghanistan to join the Islamic State or Jabhat al Nusra.
Conventional weapons
ISIL relies mostly on captured weapons with major sources including Saddam Hussein's Iraqi stockpiles from the 2003–11 Iraq insurgency and weapons from government and opposition forces fighting in the Syrian Civil War and during the post-US withdrawal Iraqi insurgency. The captured weapons, including armour, guns, surface-to-air missiles, and even some aircraft, enabled rapid territorial growth and facilitated the capture of additional equipment. For example, ISIL captured US-made TOW anti-tank missiles supplied by the United States and Saudi Arabia to the Free Syrian Army in Syria. Ninety percent of the group's weapons ultimately originated in China, Russia or Eastern Europe according to Conflict Armament Research.
Non-conventional weapons
The group uses truck and car bombs, suicide bombers and IEDs, and has used chemical weapons in Iraq and Syria. ISIL captured nuclear materials from Mosul University in July 2014, but is unlikely to be able to convert them into weapons. In September 2015 a US official stated that ISIL was manufacturing and using mustard agent in Syria and Iraq, and had an active chemical weapons research team. ISIL has also used water as a weapon of war. The group closed the gates of the smaller Nuaimiyah dam in Fallujah in April 2014, flooding the surrounding regions, while cutting the water supply to the Shia-dominated south. Around 12,000 families lost their homes and 200 square kilometres (77 sq mi) of villages and fields were either flooded or dried up. The economy of the region also suffered with destruction of cropland and electricity shortages. During the Battle of Mosul, commercially available quadcopters and drones were being used by ISIL as surveillance and weapons delivery platforms using improvised cradles to drop grenades and other explosives. One ISIL drone base was struck and destroyed by two Royal Air Force Tornado using two Paveway IV guided bombs.
Women
ISIL publishes material directed at women, with media groups encouraging them to play supportive roles within ISIL, such as providing first aid, cooking, nursing and sewing skills, in order to become "good wives of jihad". In 2015, it was estimated that western women made up over 550, or 10%, of ISIL's western foreign fighters.
Until 2016, women were generally confined to a "women's house" upon arrival which they were forbidden to leave. These houses were often small, dirty and infested with vermin and food supply was scarce. There they remained until they either had found a husband, or the husband they arrived with had completed his training. After being allowed to leave the confinement, women still generally spent most of their days indoors where their lives are devoted to caring for their husbands and the vast majority of women in the conflict area have children. Mothers play an important role passing on ISIL ideology to their children. Widows are encouraged to remarry.
In a document entitled Women in the Islamic State: Manifesto and Case Study released by the media wing of ISIL's all-female Al-Khanssaa Brigade, emphasis is given to the paramount importance of marriage and motherhood (as early as nine years old). Women should live a life of "sedentariness", fulfilling her "divine duty of motherhood" at home, with a few exceptions like teachers and doctors. Equality for women is opposed, as is education on non-religious subjects, the "worthless worldly sciences".
Communications
Finances
According to a 2015 study by the Financial Action Task Force, ISIL's five primary sources of revenue are as follows (listed in order of significance):
- proceeds from the occupation of territory (including control of banks, petroleum reservoirs, taxation, extortion, and robbery of economic assets)
- kidnapping for ransom
- donations from Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar and other Gulf states, often disguised as meant for "humanitarian charity"
- material support provided by foreign fighters
- fundraising through modern communication networks
Since 2012, ISIL has produced annual reports giving numerical information on its operations, somewhat in the style of corporate reports, seemingly in a bid to encourage potential donors.
In 2014, the RAND Corporation analysed ISIL's funding sources from documents captured between 2005 and 2010. It found that outside donations amounted to only 5% of the group's operating budgets, and that cells inside Iraq were required to send up to 20% of the income generated from kidnapping, extortion rackets and other activities to the next level of the group's leadership, which would then redistribute the funds to provincial or local cells that were in difficulties or needed money to conduct attacks. In 2016, RAND estimated that ISIL finances from its largest source of income — oil revenues and the taxes it extracts from people under its control — had fallen from about US$1.9 billion in 2014 to US$870 million in 2016.
In mid-2014, the Iraqi National Intelligence Service obtained information that ISIL had assets worth US$2 billion, making it the richest jihadist group in the world. About three-quarters of this sum was said to looted from Mosul's central bank and commercial banks in the city. However, doubt was later cast on whether ISIL was able to retrieve anywhere near that sum from the central bank, and even on whether the looting had actually occurred.
In 2022 the company Lafarge was found guilty in paying ISIS for the operation of its facilities. "In 2013-2014 the company transferred $6,000,000 to ISIL so they could continue company operations. This allowed the company to earn $70 million in sales revenue from a plant it operated in northern Syria, prosecutors said." Lafarge, which merged with Holcim in 2015, agreed to pay $778 million in forfeiture and fines as part of a plea agreement to not be convicted and sentenced to prison for providing material support to a terrorist organization. No Lafarge executives were charged in the United States, while French authorities arrested some of the executives involved but didn't provide names. The U.S. court lists six unnamed Lafarge executives. Lafarge evacuated the cement plant in September 2014, Afterwards ISIS took possession of the remaining cement and sold it for an estimated $3.21 million. SIX Swiss Exchange trading suspended trading for Holcim shares before the news became public. After trading resumed shares rose by 3.2%.
Monetary system
ISIL attempted to create a modern gold dinar by minting gold, silver, and copper coins, based on the coinage used by the Umayyad Caliphate in the seventh century. Despite a propaganda push for the currency, adoption appeared to have been minimal and its internal economy was effectively dollarised, even with regards to its own fines.
Education
The education in ISIL held territory was organised by the Diwan of Education. ISIL introduced its own curriculum which did not include lessons in history, music, geography or art, but included lectures in Islamic Law, Sharia, and Jihad. The Diwan of Education was often in competition with the Diwan of Outreach and Mosques which organised educational centres focused on the sharia.
History
| History of the Islamic State |
|---|
 |

The group was founded in 1999 by Jordanian Salafi jihadist Abu Musab al-Zarqawi under the name Jamāʻat al-Tawḥīd wa-al-Jihād (lit. 'The Organisation of Monotheism and Jihad'). In a letter published by the Coalition Provisional Authority in February 2004, Zarqawi wrote that jihadis should use bombings to start an open sectarian war so that Sunnis from the Islamic world would mobilise against assassinations carried out by Shia, specifically the Badr Brigade, against Ba'athists and Sunnis.
Territorial control and claims

 Ansar al-Sharia
Ansar al-Sharia  ISIL
ISILAs a self-proclaimed worldwide caliphate, ISIL claims religious, political and military authority over all Muslims worldwide, and that "the legality of all emirates, groups, states, and organisations, becomes null by the expansion of the khilāfah's [caliphate's] authority and arrival of its troops to their areas".
In Iraq and Syria, ISIL used many of those countries' existing governorate boundaries to subdivide territory it conquered and claimed; it called these divisions wilayah or provinces. By June 2015, ISIL had also established official "provinces" in Libya, Egypt (Sinai Peninsula), Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Algeria, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nigeria and the North Caucasus. ISIL received pledges of allegiance and publish media releases via groups in Somalia, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Myanmar, Thailand and the Philippines, but it has not announced any further official branches, instead identifying new affiliates as simply "soldiers of the caliphate".

By March 2019, ISIL had lost most of its territory in its former core areas in Syria and Iraq, and was reduced to a desert pocket as well as insurgent cells, which they lost in September 2020.
Through late 2020 and early 2021, IS African affiliates had once again seized territory and settlements in conflicts such as the Boko Haram insurgency, in Nigeria and the Insurgency in Cabo Delgado, in Mozambique. Notable takeovers by IS include Mocímboa da Praia and the Sambisa Forest. On 17 November 2021, IS supporters urge establishment of "New Provinces" in Indonesia. In October 2022, IS's Sahel province captured the rural committee and town of Ansongo in Mali.
International reaction
International criticism
The group has attracted widespread criticism internationally for its extremism, from governments and international bodies such as the United Nations and Amnesty International. On 24 September 2014, United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon stated: "As Muslim leaders around the world have said, groups like ISIL – or Da'ish – have nothing to do with Islam, and they certainly do not represent a state. They should more fittingly be called the 'Un-Islamic Non-State'." ISIL has been classified a terrorist organisation by the United Nations, the European Union and its member states, the United States, Russia, India, Turkey, Saudi Arabia and many other countries (see § Classification). Over 60 countries are directly or indirectly waging war against ISIL (see § Countries and groups at war with IS). The group was described as a cult in a Huffington Post column by notable cult authority Steven Hassan.
Twitter has removed many accounts used to spread IS propaganda, and Google developed a "Redirect Method" which identifies individuals searching for IS-related material and redirects them to content which challenges IS narratives.
Islamic criticism
The group's declaration of a caliphate has been criticised and its legitimacy has been disputed by Middle Eastern governments, by Sunni Muslim theologians and historians as well as other jihadist groups.
Religious leaders and organisations
Around the world, Islamic religious leaders have overwhelmingly condemned ISIL's ideology and actions, arguing that the group has strayed from the path of true Islam and that its actions do not reflect the religion's real teachings or virtues.
Extremism within Islam goes back to the seventh century, to the Khawarijes. From their essentially political position, the Kharijites developed extreme doctrines which set them apart from both mainstream Sunni and Shia Muslims. They were particularly noted for adopting a radical approach to takfir, whereby they declared other Muslims to be unbelievers and therefore deemed worthy of death. Other scholars have also described the group not as Sunnis, but as Khawarij. Sunni critics, including Salafi and jihadist muftis such as Adnan al-Aroor and Abu Basir al-Tartusi, say that ISIL and related terrorist groups are not Sunnis, but are instead modern-day Kharijites (Muslims who have stepped outside the mainstream of Islam) serving an imperial anti-Islamic agenda.
ISIS has been excommunicated from Islam by a number of scholars. Sheikh Muhammad al-Yaqoubi enumerated in his book, Refuting ISIS, that their form of Kharijism has removed them from Islam and fighting them is a religious duty, stating: "ISIS' leaders are people of unbelief and misguidance, and Muslims should not be lured by their jihad or deceived by their propaganda, as their actions speak louder than their words." Abd al-Aziz ibn Baz, the former Grand Mufti of Saudi Arabia, also stated that Kharijites are not Muslims, saying: "the majority are of the opinion that they are disobedient and misguided innovators, though they do not deem them unbelievers. However, the correct opinion is that they are unbelievers."
In late August 2014, the Grand Mufti of Saudi Arabia, Abdul-Aziz ibn Abdullah Al ash-Sheikh, condemned ISIL and al-Qaeda saying, "Extremist and militant ideas and terrorism which spread decay on Earth, destroying human civilization, are not in any way part of Islam, but are enemy number one of Islam, and Muslims are their first victims". In late September 2014, 126 Sunni imams and Islamic scholars—primarily Sufi—from around the Muslim world signed an open letter to the Islamic State's leader al-Baghdadi, explicitly rejecting and refuting his group's interpretations of Islamic scriptures, the Quran and hadith, which it used in order to justify its actions. "[You] have misinterpreted Islam into a religion of harshness, brutality, torture and murder ... this is a great wrong and an offence to Islam, to Muslims and to the entire world", the letter states. It rebukes the Islamic State for its killing of prisoners, describing the killings as "heinous war crimes" and its persecution of the Yazidis of Iraq as "abominable". Referring to the "self-described 'Islamic State'", the letter censures the group for carrying out killings and acts of brutality under the guise of jihad—holy struggle—saying that its "sacrifice" without legitimate cause, goals and intention "is not jihad at all, but rather, warmongering and criminality". It also accuses the group of instigating fitna—sedition—by instituting slavery under its rule in contravention of the anti-slavery consensus of the Islamic scholarly community.

The current Grand Imam of al-Azhar and former president of al-Azhar University, Ahmed el-Tayeb, has strongly condemned the Islamic State, stating that it is acting "under the guise of this holy religion and have given themselves the name 'Islamic State' in an attempt to export their false Islam". Citing the Quran, he stated: "The punishment for those who wage war against God and his Prophet and who strive to sow corruption on earth is death, crucifixion, the severing of hands and feet on opposite sides or banishment from the land. This is the disgrace for them in this world and in the hereafter, they will receive grievous torment." Although el-Tayeb has been criticised for not expressly stating that the Islamic State is heretical, the Ash'ari school of Islamic theology, to which el-Tayeb belongs, does not allow calling a person who follows the shahada an apostate. El-Tayeb has strongly come out against the practice of takfirism (declaring a Muslim an apostate) which is used by the Islamic State to "judge and accuse anyone who doesn't tow their line with apostasy and outside the realm of the faith" declaring "Jihad on peaceful Muslims" using "flawed interpretations of some Qur'anic texts, the prophet's Sunna, and the Imams' views believing incorrectly, that they are leaders of Muslim armies fighting infidel peoples, in unbelieving lands".
In late December 2015, nearly 70,000 Indian Muslim clerics associated with the Indian Barelvi movement issued a fatwa condemning ISIL and similar organisations, saying they are "not Islamic organisations". Approximately 1.5 million Sunni Muslim followers of this movement have formally decried violent extremists.
Mehdi Hasan, a political journalist in the UK, said in the New Statesman,
Whether Sunni or Shia, Salafi or Sufi, conservative or liberal, Muslims – and Muslim leaders – have almost unanimously condemned and denounced ISIL not merely as un-Islamic but actively anti-Islamic.
Hassan Hassan, an analyst at the Delma Institute, wrote in The Guardian that because the Islamic State "bases its teachings on religious texts that mainstream Muslim clerics do not want to deal with head on, new recruits leave the camp feeling that they have stumbled on the true message of Islam".
Theologian and Qatar-based TV broadcaster Yusuf al-Qaradawi stated: "[The] declaration issued by the Islamic State is void under sharia and has dangerous consequences for the Sunnis in Iraq and for the revolt in Syria", adding that the title of caliph can "only be given by the entire Muslim nation", not by a single group. He also stated on his official website "United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the leaders of Daesh (ISIS/ISIL) terrorist group are from one species and they are two sides of the same coin". In a similar vein, the Syrian Islamic scholar Muhammad al-Yaqoubi says, "[t]he followers of ISIS do not want to adhere to Islamic law but rather they want to twist Islamic law to conform to their fantasies. To this end, they pick and choose the evidences that corroborate their misguidance, despite being weak or abrogated."
Academics Robyn Creswell and Bernard Haykel of The New Yorker have criticised ISIL's execution of Muslims for breach of traditional sharia law while violating it simultaneously themselves (encouraging women to emigrate to its territory, travelling without a Wali—male guardian—and in violation of his wishes). as well as its love of archaic imagery (horsemen and swords) while engaging in bid'ah (religious innovation) in establishing female religious police (known as Al-Khansaa Brigade).
Two days after the beheading of Hervé Gourdel, hundreds of Muslims gathered in the Grand Mosque of Paris to show solidarity against the beheading. The protest was led by the leader of the French Council of the Muslim Faith, Dalil Boubakeur, and was joined by thousands of other Muslims around the country under the slogan "Not in my name". French president François Hollande said Gourdel's beheading was "cowardly" and "cruel", and confirmed that airstrikes would continue against ISIL in Iraq. Hollande also called for three days of national mourning, with flags flown at half-mast throughout the country and said that security would be increased throughout Paris.
Other jihadist groups
According to The New York Times, "All of the most influential jihadist theorists are criticising the Islamic State as deviant, calling its self-proclaimed caliphate null and void" and they have denounced it for its beheadings of journalists and aid workers. ISIL is widely denounced by a broad range of Islamic clerics, including Saudi and al-Qaeda-oriented clerics. Muhammad al-Yaqoubi states, "It is enough of a proof of the extreme ideology of ISIS that the top leaders of Salafi-Jihadism have disclaimed it." Other critics of ISIL's brand of Sunni Islam include Salafists who previously publicly supported jihadist groups such as al-Qaeda: for example, the Saudi government official Saleh Al-Fawzan, known for his extremist views, who claims that ISIL is a creation of "Zionists, Crusaders and Safavids", and the Jordanian-Palestinian writer Abu Muhammad al-Maqdisi, the former spiritual mentor to Abu Musab al-Zarqawi, who was released from prison in Jordan in June 2014 and accused ISIL of driving a wedge between Muslims.
An Islamic Front sharia court judge in Aleppo, Mohamed Najeeb Bannan, stated: "The legal reference is the Islamic Sharia. The cases are different, from robberies to drug use, to moral crimes. It's our duty to look at any crime that comes to us... After the regime has fallen, we believe that the Muslim majority in Syria will ask for an Islamic state. Of course, it's very important to point out that some say the Islamic Sharia will cut off people's hands and heads, but it only applies to criminals. And to start off by killing, crucifying etc. That is not correct at all." In response to being asked what the difference between the Islamic Front's and ISIL's version of sharia would be, he said, "One of their mistakes is before the regime has fallen, and before they've established what in Sharia is called Tamkeen [having a stable state], they started applying Sharia, thinking God gave them permission to control the land and establish a Caliphate. This goes against the beliefs of religious scholars around the world. This is what [IS] did wrong. This is going to cause a lot of trouble. Anyone who opposes [IS] will be considered against Sharia and will be severely punished."
Al-Qaeda and al-Nusra have been trying to take advantage of ISIL's rise, by attempting to present themselves as "moderate" compared to "extremist" ISIL, although they have the same aim of establishing sharia and a caliphate, but doing so in a more gradual manner. Al-Nusra has criticised the way in which ISIL fully and immediately institutes sharia in the areas that fall under its control, since it alienates people too much. It supports the gradual, slower approach favoured by al-Qaeda, preparing society to accept sharia and indoctrinating people through education before implementing the hudud aspects in sharia, which they believe supports punishments such as throwing homosexuals from the top of buildings, chopping limbs off, and public stoning. Al-Nusra and ISIL are both hostile towards the Druze. However, while al-Nusra has typically destroyed Druze shrines and pressured them to convert to Sunni Islam, ISIL regards the entire Druze community as a valid target for violence, as it does the Yazidis.
In February 2014, Ayman al-Zawahiri, the leader of Al-Qaeda, announced that his group Al-Qaeda had cut ties with the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant and denounced ISIL after being unable to reconcile a conflict between them and the al-Qaeda affiliate al-Nusra Front.
In September 2015, Ayman al-Zawahiri, the leader of al-Qaeda, called for consultation (shura) within the "prophetic method" to be used when establishing the caliphate, criticising al-Baghdadi for not following the required steps. Al-Zawahiri has called upon ISIL members to close ranks and join al-Qaeda in fighting against Assad, the Shia, Russia, Europe, and America and to stop the infighting between jihadist groups. He called upon jihadists to establish Islamic entities in Egypt and the Levant, slowly implementing sharia before establishing a caliphate, and has called for violent assaults against America and the West.
The Jaysh al-Islam group within the Islamic Front criticised ISIL, saying: "They killed the people of Islam and leave the idol worshippers ... They use the verses talking about the disbelievers and implement it on the Muslims". The main criticism of defectors from ISIL has been that the group is fighting and killing other Sunni Muslims, as opposed to just non-Sunnis being brutalised. In one case, a supposed defector from ISIL executed two activists of a Syrian opposition group in Turkey who had sheltered them.
Other commentaries
Scholar Ian Almond criticised the media commentators, the lack of balance in reporting, and the "way we are learning to talk about ISIS." While there was talk about 'radical evil' and 'radical Islam', Almond found it striking because "some of the most revered and oft-quoted figures in our Western political tradition have been capable of the most vicious acts of savagery – and yet all we ever hear about is how much the Middle East has to learn from us." Almond goes on to cite how Winston Churchill "wanted to gas women and children", how Ronald Reagan's Central American policies "disembowelled more children than ISIS," how President Barack Obama's "planes and drones have dropped bombs on as many schoolchildren as ISIS," how former secretary of state Madeleine Albright commented on the deaths of Iraqi children killed by sanctions, how Henry Kissinger and Margaret Thatcher "assisted in the torture and disappearance of thousands of Chilean students and labour activists... For anyone familiar with the history of both U.S. and European torture and murder over the past 150 years, it might not be all that hyperbolic to say that in ISIS, what we see more than anything else is a more expansive, explicit version of our own cruelties. In bombing ISIS and its would-be imperialism, we are really bombing a version of ourselves."
Author and commentator Tom Engelhardt attributed the rise of ISIL and the destruction that followed to what he dubbed as America's drive to establish its own caliphate in the region.
A leader article in the New Scientist magazine contextualised ISIL within the nation state construct. Although the group is described as medieval in the pejorative sense, "it is also hyper-modern, interested in few of the trappings of a conventional state apart from its own brutal brand of law enforcement. In fact, it is more of a network than a nation, having made canny use of social media to exert influence far beyond its geographical base."
Designation as a terrorist organisation
| Organisation | Date | Body | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multinational organisations | |||
| 18 October 2004 (as al-Qaeda in Iraq) 30 May 2013 (after separation from al‑Qaeda) |
United Nations Security Council |
| |
| 2004 | EU Council (via adoption of UN al-Qaeda Sanctions List) |
| |
| Nations | |||
| March 2001 (as part of al-Qaeda) 20 June 2014 (after separation from al‑Qaeda) |
Home Office |
| |
| 17 December 2004 (as al-Qaeda in Iraq) | United States Department of State |
| |
| 2 March 2005 (as al-Qaeda in Iraq) 14 December 2013 (after separation from al‑Qaeda) |
Attorney-General for Australia |
| |
| 20 August 2012 | Parliament of Canada |
| |
| 10 October 2006 (as al-Qaeda in Iraq) 30 May 2013 (after separation from al‑Qaeda) |
Ministry of Foreign Affairs |
| |
| 30 October 2013 | Grand National Assembly of Turkey |
| |
| 7 March 2014 | Royal decree of the King of Saudi Arabia |
| |
| 1 August 2014 | Counter-Terrorism National Agency (BNPT) |
| |
| 20 August 2014 | United Arab Emirates Cabinet |
| |
| 24 September 2014 | Ministry of Foreign Affairs |
| |
| 8 October 2014 | Swiss Federal Council |
| |
| 30 November 2014 | The Cairo Court for Urgent Matters |
| |
| 16 December 2014 | Ministry of Home Affairs | ||
| 29 December 2014 | Supreme Court of Russia |
| |
| 25 March 2015 | Kyrgyz State Committee of National Security |
| |
| 23 March 2020 | Ministry of Home Affairs |
| |
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
|
|
| |
| 29 August 2015 | Ministry of Interior |
| |
| Public Security Intelligence Agency |
| ||
| 26 November 2015 | National Security Bureau |
| |
| Ministry of Public Security |
| ||
| 4 September 2019 | National Assembly of Venezuela |
| |
| 3 July 2020 | Via the Anti-Terrorism Act |
| |
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
| |||
| 3 July 2022 (as Khorasan Province) | Taliban |
| |
The United Nations Security Council in its Resolution 1267 (1999) described Osama bin Laden and his al-Qaeda associates as operators of a network of terrorist training camps. The UN's Al-Qaida Sanctions Committee first listed ISIL in its Sanctions List under the name "Al-Qaida in Iraq" on 18 October 2004, as an entity/group associated with al-Qaeda. On 2 June 2014, the group was added to its listing under the name "Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant". The European Union adopted the UN Sanctions List in 2002.

Many world leaders and government spokespeople have called ISIL a terrorist group or banned it, without their countries having formally designated it as such. The following are examples:
The Government of Germany banned ISIL in September 2014. Activities banned include donations to the group, recruiting fighters, holding ISIL meetings and distributing its propaganda, flying ISIL flags, wearing ISIL symbols and all ISIL activities. "The terror organisation Islamic State is a threat to public safety in Germany as well", said German politician Thomas de Maizière. He added, "Today's ban is directed solely against terrorists who abuse religion for their criminal goals." Being a member of ISIL is also illegal in accordance with § 129a and § 129b of the German criminal code.
In October 2014, Switzerland banned ISIL's activities in the country, including propaganda and financial support of the fighters, with prison sentences as potential penalties.
In mid-December 2014, India banned ISIL after the arrest of an operator of a pro-ISIL Twitter account.
Pakistan designated ISIL as a banned organisation in late August 2015, under which all elements expressing sympathy for the group would be blacklisted and sanctioned.
After its 2022 Ulema gathering, the Taliban banned all Afghans from associating with the local Khorasan Province branch of IS in July 2022, and labeled it a "false sect".
Media sources worldwide have described ISIL as a terrorist organisation.
Following the D-ISIS Ministerial in June 2023, Minister Belkin announced Abdallah Makki Muslih al-Rufay’i and Abu Bakr ibn Muhammad ibn ‘Ali al-Mainuki, as terrorists under Executive Order 13224.
Militia, cult, territorial authority, and other classifications
By 2014, ISIL was increasingly being viewed as a militia in addition to a terrorist group and a cult. As major Iraqi cities fell to ISIL in June 2014, Jessica Lewis, a former US Army intelligence officer at the Institute for the Study of War, described ISIL at that time as
not a terrorism problem anymore, [but rather] an army on the move in Iraq and Syria, and they are taking terrain. They have shadow governments in and around Baghdad, and they have an aspirational goal to govern. I don't know whether they want to control Baghdad, or if they want to destroy the functions of the Iraqi state, but either way the outcome will be disastrous for Iraq.

Lewis has called ISIL
an advanced military leadership. They have incredible command and control and they have a sophisticated reporting mechanism from the field that can relay tactics and directives up and down the line. They are well-financed, and they have big sources of manpower, not just the foreign fighters, but also prisoner escapees.
Former US Defense Secretary Chuck Hagel saw an "imminent threat to every interest we have", but former top counter-terrorism adviser Daniel Benjamin derided such talk as a "farce" that panics the public.
Former British Foreign Secretary David Miliband concluded that the 2003 invasion of Iraq caused the creation of ISIL.
Writing for The Guardian, Pankaj Mishra rejects the idea that the group is a resurgence of medieval Islam, saying instead:
In actuality, Isis is the canniest of all traders in the flourishing international economy of disaffection: the most resourceful among all those who offer the security of collective identity to isolated and fearful individuals. It promises, along with others who retail racial, national and religious supremacy, to release the anxiety and frustrations of the private life into the violence of the global.
On 28 January 2017, President Donald Trump issued a National Security Presidential Memorandum which called for a comprehensive plan to destroy ISIL to be formulated by the Defense Department within 30 days.
Supporters
A United Nations report from May 2015 showed that 25,000 "foreign terrorist fighters" from 100 countries had joined "Islamist" groups, many of them working for ISIL or al-Qaeda.
According to a June 2015 Reuters report that cited "jihadist ideologues" as a source, 90% of ISIL's fighters in Iraq were Iraqi, and 70% of its fighters in Syria were Syrian. The article stated that the group had 40,000 fighters and 60,000 supporters across its two primary strongholds in Iraq and Syria. According to scholar Fawaz Gerges writing in ISIS: A History, some "30 percent of the senior figures" in ISIL's military command were former army and police officers from the disbanded Iraqi security forces, turned towards Sunni Islamism and drawn to ISIL by the US de-Ba'athification policy following the US invasion of Iraq.
A 2014 analysis of 2,195,000 Arabic-language social media posts cited by The Guardian had 47% of the postings from Qatar, 35% from Pakistan, 31% from Belgium and almost 24% from UK classified as supportive of ISIL. According to a 2015 poll by Pew Research Center, Muslim populations of various Muslim-majority countries have overwhelmingly negative views of ISIL, with the highest percentage of those expressing favorable views not exceeding 14%. In most of these countries, concerns about Islamic extremism have been growing.
There are at least 10,000 ISIL prisoners and more than 100,000 ISIL family members and other displaced persons in several camps across the Kurdish areas in Syria.
Countries and groups at war with IS

Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve
Other state-based opponents
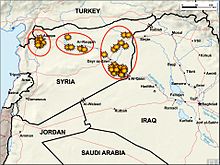
Territories held by ISIL at its late 2015 peak
ISIL's claims to territory have brought it into armed conflict with many governments, militias and other armed groups. International rejection of ISIL as a terrorist entity and rejection of its claim to even exist have placed it in conflict with countries around the world.
Global Coalition to Counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
The Global Coalition to Counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), also referred to as the Counter-ISIL Coalition or Counter-DAESH Coalition, is a US-led group of nations and non-state actors that have committed to "work together under a common, multifaceted, and long-term strategy to degrade and defeat ISIL/Daesh". According to a joint statement issued by 59 national governments and the European Union on 3 December 2014, participants in the Counter-ISIL Coalition are focused on multiple lines of effort:
- Supporting military operations, capacity building, and training;
- Stopping the flow of foreign terrorist fighters;
- Cutting off ISIL/Daesh's access to financing and funding;
- Addressing associated humanitarian relief and crises; and
- Exposing ISIL/Daesh's true nature (ideological delegitimisation).
Operation Inherent Resolve is the operational name given by the US to military operations against ISIL and Syrian al-Qaeda affiliates. Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF–OIR) is co-ordinating the military portion of the response. The Arab League, European Union, NATO, and GCC are part of the Counter-ISIL Coalition: According to the Pentagon, by December 2017 over 80,000 ISIL fighters had been killed in Iraq and Syria by CJTF-OIR airstrikes. By then the coalition had flown over 170,000 sorties, 75–80% of combat sorties were conducted by the military of the United States, with the other 20–25% by Australia, Canada, Denmark, France, Jordan, Belgium, the Netherlands, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom. According to the UK-based monitoring group Airwars, the air strikes and artillery of US-led coalition killed as many as 6,000 civilians in Iraq and Syria by the end of 2017.
Lebanon, which the U.S. considers part of the Global Coalition, fought off several incursions by ISIL, with the largest engagements taking place from June 2014 to August 2017, when several thousand ISIL fighters invaded from Syria and occupied Lebanese territory. The U.S. and UK-backed Lebanese Army succeeded in repulsing this invasion, killing or capturing over 1,200 ISIL fighters in the process.
On 21 December 2019, over 33 Islamist militants were killed in Mali by French forces using attack helicopters, drones and ground troops, alongside the border with Mauritania where an Al-Qaeda-linked group operates.
Other state opponents not part of the Counter-ISIL Coalition

![]() Iran – military advisors, training, ground troops in Iraq and Syria, and air power in Syria, beside Iranian borders (see Iranian intervention in Iraq)
Iran – military advisors, training, ground troops in Iraq and Syria, and air power in Syria, beside Iranian borders (see Iranian intervention in Iraq)

![]() Russia – arms supplier to Iraqi and Syrian governments. Security operations within state borders in 2015. Airstrikes in Syria (see Russian military intervention in the Syrian Civil War).
Russia – arms supplier to Iraqi and Syrian governments. Security operations within state borders in 2015. Airstrikes in Syria (see Russian military intervention in the Syrian Civil War).
![]() Azerbaijan – security operations within state borders
Azerbaijan – security operations within state borders
![]() Pakistan – Military deployment over Saudi Arabia-Iraq border. Arresting ISIL figures in Pakistan.
Pakistan – Military deployment over Saudi Arabia-Iraq border. Arresting ISIL figures in Pakistan.
![]() Yemen (Supreme Political Council)
Yemen (Supreme Political Council)
![]() Afghanistan – security operations within state borders (see Islamic State–Taliban conflict)
Afghanistan – security operations within state borders (see Islamic State–Taliban conflict)
Other non-state opponents
 al-Qaeda
al-Qaeda al-Nusra Front—with localised truces and co-operation at times
al-Nusra Front—with localised truces and co-operation at times- al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula
- al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb
- Al-Shabaab
 Taliban
Taliban Hamas
HamasHezbollah
 Houthis
Houthis Kurdistan Workers' Party—ground troops in Iraqi Kurdistan and in Syrian Kurdistan
Kurdistan Workers' Party—ground troops in Iraqi Kurdistan and in Syrian Kurdistan Syrian Democratic Forces
Syrian Democratic Forces Nineveh Plain Protection Units – an Assyrian Christian militia in the Nineveh Plains in Northern Iraq
Nineveh Plain Protection Units – an Assyrian Christian militia in the Nineveh Plains in Northern Iraq Amal Movement
Amal Movement Syrian Resistance – Suqur al-Furat
Syrian Resistance – Suqur al-Furat Liwa al-Quds
Liwa al-Quds Liwa Abu al-Fadhal al-Abbas
Liwa Abu al-Fadhal al-Abbas Abu al-Fadl al-Abbas Forces
Abu al-Fadl al-Abbas Forces Islamic Jihad Movement in Palestine
Islamic Jihad Movement in Palestine Arab Nationalist Guard
Arab Nationalist Guard Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine – General Command
Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine – General Command Fatah al-Intifada
Fatah al-Intifada Syrian Revolutionary Command Council
Syrian Revolutionary Command Council Mujahideen Shura Council (Syria)
Mujahideen Shura Council (Syria) Unified Military Command of Eastern Ghouta
Unified Military Command of Eastern Ghouta Fatah Halab
Fatah Halab Mare' Operations Room
Mare' Operations Room Golan Regiment
Golan RegimentMukhtar Army
Al-Qaeda

Al-Nusra Front is a branch of al-Qaeda operating in Syria. Al-Nusra has launched many attacks and bombings, mostly against targets affiliated with or supportive of the Syrian government. There have been media reports that many of al-Nusra's foreign fighters have left to join al-Baghdadi's ISIL.
In February 2014, after continued tensions, al-Qaeda publicly disavowed any relations with ISIL. However, ISIL and al-Nusra Front still cooperate with each other occasionally when they fight against the Syrian government.
The two groups [ISIL and al-Nusra] share a nihilistic worldview, a loathing for modernity, and for the West. They subscribe to the same perverted interpretations of Islam. Other common traits include a penchant for suicide attacks, and sophisticated exploitation of the internet and social media. Like ISIL, several Al Qaeda franchises are interested in taking and holding territory; AQAP has been much less successful at it. The main differences between Al Qaeda and ISIL are largely political—and personal. Over the past decade, Al Qaeda has twice embraced ISIL (and its previous manifestations) as brothers-in-arms.
— Bobby Ghosh, "ISIL and Al Qaeda: Terror's frenemies", Quartz
On 10 September 2015, an audio message was released by al-Qaeda's leader Ayman al-Zawahiri criticising ISIL's self-proclaimed caliphate and accusing it of "sedition". This was described by some media outlets as a "declaration of war". However, although al-Zawahiri denied ISIL's legitimacy, he suggested that there was still room for cooperation against common enemies, and said that if he were in Iraq, he would fight alongside ISIL.
Human rights abuse and war crime findings
In July 2014, the BBC reported the United Nations' chief investigator as stating: "Fighters from the Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) may be added to a list of war crimes suspects in Syria." By June 2014, according to United Nations reports, ISIL had killed hundreds of prisoners of war.
In November 2014, the UN Commission of Inquiry on Syria said that ISIL was committing crimes against humanity. A report by Human Rights Watch in November 2014 accused ISIL groups in control of Derna, Libya of war crimes and human rights abuses and of terrorising residents. Human Rights Watch documented three apparent summary executions and at least ten public floggings by the Islamic Youth Shura Council, which joined ISIL in November. It also documented the beheading of three Derna residents and dozens of seemingly politically motivated assassinations of judges, public officials, members of the security forces and others. Sarah Leah Watson, Director of HRW Middle East and North Africa, said: "Commanders should understand that they may face domestic or international prosecution for the grave rights abuses their forces are committing."
Speaking of ISIL's methods, the United Nations Commission on Human Rights has stated that the group "seeks to subjugate civilians under its control and dominate every aspect of their lives through terror, indoctrination, and the provision of services to those who obey".
ISIL and Al-Qaeda were both reported for exploiting Turkey-Syria earthquake event for their propaganda.










