In electromagnetism, the Mie solution to Maxwell's equations (also known as the Lorenz–Mie solution, the Lorenz–Mie–Debye solution or Mie scattering) describes the scattering of an electromagnetic plane wave by a homogeneous sphere. The solution takes the form of an infinite series of spherical multipole partial waves. It is named after German physicist Gustav Mie.
The term Mie solution is also used for solutions of Maxwell's equations for scattering by stratified spheres or by infinite cylinders, or other geometries where one can write separate equations for the radial and angular dependence of solutions. The term Mie theory is sometimes used for this collection of solutions and methods; it does not refer to an independent physical theory or law. More broadly, the "Mie scattering" formulas are most useful in situations where the size of the scattering particles is comparable to the wavelength of the light, rather than much smaller or much larger.
Mie scattering (sometimes referred to as a non-molecular scattering or aerosol particle scattering) takes place in the lower 4,500 m (15,000 ft) of the atmosphere, where many essentially spherical particles with diameters approximately equal to the wavelength of the incident ray may be present. Mie scattering theory has no upper size limitation, and converges to the limit of geometric optics for large particles.
Introduction

A modern formulation of the Mie solution to the scattering problem on a sphere can be found in many books, e.g., J. A. Stratton's Electromagnetic Theory. In this formulation, the incident plane wave, as well as the scattering field, is expanded into radiating spherical vector spherical harmonics. The internal field is expanded into regular vector spherical harmonics. By enforcing the boundary condition on the spherical surface, the expansion coefficients of the scattered field can be computed.
For particles much larger or much smaller than the wavelength of the scattered light there are simple and accurate approximations that suffice to describe the behavior of the system. But for objects whose size is within a few orders of magnitude of the wavelength, e.g., water droplets in the atmosphere, latex particles in paint, droplets in emulsions, including milk, and biological cells and cellular components, a more detailed approach is necessary.
The Mie solution is named after its developer, German physicist Gustav Mie. Danish physicist Ludvig Lorenz and others independently developed the theory of electromagnetic plane wave scattering by a dielectric sphere.
The formalism allows the calculation of the electric and magnetic fields inside and outside a spherical object and is generally used to calculate either how much light is scattered (the total optical cross section), or where it goes (the form factor). The notable features of these results are the Mie resonances, sizes that scatter particularly strongly or weakly. This is in contrast to Rayleigh scattering for small particles and Rayleigh–Gans–Debye scattering (after Lord Rayleigh, Richard Gans and Peter Debye) for large particles. The existence of resonances and other features of Mie scattering makes it a particularly useful formalism when using scattered light to measure particle size.
Approximations
Rayleigh approximation (scattering)

Rayleigh scattering describes the elastic scattering of light by spheres that are much smaller than the wavelength of light. The intensity I of the scattered radiation is given by
where I0 is the light intensity before the interaction with the particle, R is the distance between the particle and the observer, θ is the scattering angle, λ is the wavelength of light under consideration, n is the refractive index of the particle, and d is the diameter of the particle.
It can be seen from the above equation that Rayleigh scattering is strongly dependent upon the size of the particle and the wavelengths. The intensity of the Rayleigh scattered radiation increases rapidly as the ratio of particle size to wavelength increases. Furthermore, the intensity of Rayleigh scattered radiation is identical in the forward and reverse directions.
The Rayleigh scattering model breaks down when the particle size becomes larger than around 10% of the wavelength of the incident radiation. In the case of particles with dimensions greater than this, Mie's scattering model can be used to find the intensity of the scattered radiation. The intensity of Mie scattered radiation is given by the summation of an infinite series of terms rather than by a simple mathematical expression. It can be shown, however, that scattering in this range of particle sizes differs from Rayleigh scattering in several respects: it is roughly independent of wavelength and it is larger in the forward direction than in the reverse direction. The greater the particle size, the more of the light is scattered in the forward direction.
The blue colour of the sky results from Rayleigh scattering, as the size of the gas particles in the atmosphere is much smaller than the wavelength of visible light. Rayleigh scattering is much greater for blue light than for other colours due to its shorter wavelength. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, its blue component is Rayleigh scattered strongly by atmospheric gases but the longer wavelength (e.g. red/yellow) components are not. The sunlight arriving directly from the Sun therefore appears to be slightly yellow, while the light scattered through rest of the sky appears blue. During sunrises and sunsets, the effect of Rayleigh scattering on the spectrum of the transmitted light is much greater due to the greater distance the light rays have to travel through the high-density air near the Earth's surface.
In contrast, the water droplets that make up clouds are of a comparable size to the wavelengths in visible light, and the scattering is described by Mie's model rather than that of Rayleigh. Here, all wavelengths of visible light are scattered approximately identically, and the clouds therefore appear to be white or grey.
Rayleigh–Gans approximation
The Rayleigh–Gans approximation is an approximate solution to light scattering when the relative refractive index of the particle is close to that of the environment, and its size is much smaller in comparison to the wavelength of light divided by |n − 1|, where n is the refractive index:
where is the wavevector of the light (), and refers to the linear dimension of the particle. The former condition is often referred as optically soft and the approximation holds for particles of arbitrary shape.
Anomalous diffraction approximation of van de Hulst
The anomalous diffraction approximation is valid for large (compared to wavelength) and optically soft spheres; soft in the context of optics implies that the refractive index of the particle (m) differs only slightly from the refractive index of the environment, and the particle subjects the wave to only a small phase shift. The extinction efficiency in this approximation is given by
where Q is the efficiency factor of scattering, which is defined as the ratio of the scattering cross-section and geometrical cross-section πa2.
The term p = 4πa(n − 1)/λ has as its physical meaning the phase delay of the wave passing through the centre of the sphere, where a is the sphere radius, n is the ratio of refractive indices inside and outside of the sphere, and λ the wavelength of the light.
This set of equations was first described by van de Hulst in (1957).
Mathematics

The scattering by a spherical nanoparticle is solved exactly regardless of the particle size. We consider scattering by a plane wave propagating along the z-axis polarized along the x-axis. Dielectric and magnetic permeabilities of a particle are and , and and for the environment.
In order to solve the scattering problem, we write first the solutions of the vector Helmholtz equation in spherical coordinates, since the fields inside and outside the particles must satisfy it. Helmholtz equation:
In addition to the Helmholtz equation, the fields must satisfy the conditions and , . Vector spherical harmonics possess all the necessary properties, introduced as follows:
- — magnetic harmonics (TE),
- — electric harmonics (TM),
where
and — Associated Legendre polynomials, and — any of the spherical Bessel functions.
Next, we expand the incident plane wave in vector spherical harmonics:
Here the superscript means that in the radial part of the functions are spherical Bessel functions of the first kind. The expansion coefficients are obtained by taking integrals of the form
In this case, all coefficients at are zero, since the integral over the angle in the numerator is zero.
Then the following conditions are imposed:
- Interface conditions on the boundary between the sphere and the environment (which allow us to relate the expansion coefficients of the incident, internal, and scattered fields)
- The condition that the solution is bounded at the origin (therefore, in the radial part of the generating functions , spherical Bessel functions of the first kind are selected for the internal field),
- For a scattered field, the asymptotics at infinity corresponds to a diverging spherical wave (in connection with this, for the scattered field in the radial part of the generating functions spherical Hankel functions of the first kind are chosen).
Scattered fields are written in terms of a vector harmonic expansion as
Here the superscript means that in the radial part of the functions are spherical Hankel functions of the first kind (those of the second kind would have ), and ,
Internal fields:
is the wave vector outside the particle is the wave vector in the medium from the particle material, and are the refractive indices of the medium and the particle.
After applying the interface conditions, we obtain expressions for the coefficients:
where
- with being the radius of the sphere.
and represent the spherical functions of Bessel and Hankel of the first kind, respectively.
Scattering and extinction cross-sections
Values commonly calculated using Mie theory include efficiency coefficients for extinction , scattering , and absorption . These efficiency coefficients are ratios of the cross section of the respective process, , to the particle protected area, , where a is the particle radius. According to the definition of extinction,
- and .
The scattering and extinction coefficients can be represented as the infinite series:
The contributions in these sums, indexed by n, correspond to the orders of a multipole expansion with n = 1 being the dipole term, n = 2 being the quadrupole term, and so forth.
Application to larger particles
If the size of the particle is equal to several wavelengths in the material, then the scattered fields have some features. Further, the form of the electric field is key, since the magnetic field is obtained from it by taking the curl.
All Mie coefficients depend on the frequency and have maximums when the denominator is close to zero (exact equality to zero is achieved for complex frequencies). In this case, it is possible, that the contribution of one specific harmonic dominates in scattering. Then at large distances from the particle, the radiation pattern of the scattered field will be similar to the corresponding radiation pattern of the angular part of vector spherical harmonics. The harmonics correspond to electric dipoles (if the contribution of this harmonic dominates in the expansion of the electric field, then the field is similar to the electric dipole field), correspond to the electric field of the magnetic dipole, and - electric and magnetic quadrupoles, and - octupoles, and so on. The maxima of the scattering coefficients (as well as the change of their phase to ) are called multipole resonances, and zeros can be called anapoles.
The dependence of the scattering cross-section on the wavelength and the contribution of specific resonances strongly depends on the particle material. For example, for a gold particle with a radius of 100 nm, the contribution of the electric dipole to scattering predominates in the optical range, while for a silicon particle there are pronounced magnetic dipole and quadrupole resonances. For metal particles, the peak visible in the scattering cross-section is also called localized plasmon resonance.
In the limit of small particles or long wavelengths, the electric dipole contribution dominates in the scattering cross-section.
Other directions of the incident plane wave
In case of x-polarized plane wave, incident along the z-axis, decompositions of all fields contained only harmonics with m= 1, but for an arbitrary incident wave this is not the case. For a rotated plane wave, the expansion coefficients can be obtained, for example, using the fact that during rotation, vector spherical harmonics are transformed through each other by Wigner D-matrixes.
In this case, the scattered field will be decomposed by all possible harmonics:
Then the scattering cross section will be expressed in terms of the coefficients as follows:
Kerker effect
The Kerker effect is a phenomenon in scattering directionality, which occurs when different multipole responses are presented and not negligible.

In 1983, in the work of Kerker, Wang and Giles, the direction of scattering by particles with was investigated. In particular, it was shown that for hypothetical particles with backward scattering is completely suppressed. This can be seen as an extension to a spherical surface of Giles' and Wild's results for reflection at a planar surface with equal refractive indices where reflection and transmission is constant and independent of angle of incidence.
In addition, scattering cross sections in the forward and backward directions are simply expressed in terms of Mie coefficients:
For certain combinations of coefficients, the expressions above can be minimized.
So, for example, when terms with can be neglected (dipole approximation), , corresponds to the minimum in backscattering (magnetic and electric dipoles are equal in magnitude and are in phase, this is also called first Kerker or zero-backward intensity condition). And corresponds to minimum in forward scattering, this is also called second Kerker condition (or near-zero forward intensity condition). From the optical theorem, it is shown that for a passive particle is not possible. For the exact solution of the problem, it is necessary to take into account the contributions of all multipoles. The sum of the electric and magnetic dipoles forms Huygens source
For dielectric particles, maximum forward scattering is observed at wavelengths longer than the wavelength of magnetic dipole resonance, and maximum backward scattering at shorter ones.
Later, other varieties of the effect were found. For example, the transverse Kerker effect, with nearly complete simultaneous suppression of both forward and backward scattered fields (side-scattering patterns), optomechanical Kerker effect, in acoustic scattering, and also found in plants.
There is also a short Video on YouTube with an explanation of the effect.
Dyadic Green's function of a sphere
Green's function is a solution to the following equation:
where — identity matrix for , and for . Since all fields are vectorial, the Green function is a 3 by 3 matrix and is called a dyadic. If polarization is induced in the system, when the fields are written as
In the same way as the fields, the Green's function can be decomposed into vector spherical harmonics. Dyadic Green's function of a free space a:
In the presence of a sphere, the Green's function is also decomposed into vector spherical harmonics. Its appearance depends on the environment in which the points and are located.
When both points are outside the sphere ():
where the coefficients are :
When both points are inside the sphere () :
Coefficients:
Source is inside the sphere and observation point is outside ():
coefficients:
Source is outside the sphere and observation point is inside () :
coefficients:
Computational codes
Mie solutions are implemented in a number of programs written in different computer languages such as Fortran, MATLAB, and Mathematica. These solutions approximate an infinite series, and provide as output the calculation of the scattering phase function, extinction, scattering, and absorption efficiencies, and other parameters such as asymmetry parameters or radiation torque. Current usage of the term "Mie solution" indicates a series approximation to a solution of Maxwell's equations. There are several known objects that allow such a solution: spheres, concentric spheres, infinite cylinders, clusters of spheres and clusters of cylinders. There are also known series solutions for scattering by ellipsoidal particles. A list of codes implementing these specialized solutions is provided in the following:
- Codes for electromagnetic scattering by spheres – solutions for a single sphere, coated spheres, multilayer sphere, and cluster of spheres;
- Codes for electromagnetic scattering by cylinders – solutions for a single cylinder, multilayer cylinders, and cluster of cylinders.
A generalization that allows a treatment of more generally shaped particles is the T-matrix method, which also relies on a series approximation to solutions of Maxwell's equations.
See also external links for other codes and calculators.
Applications
Mie theory is very important in meteorological optics, where diameter-to-wavelength ratios of the order of unity and larger are characteristic for many problems regarding haze and cloud scattering. A further application is in the characterization of particles by optical scattering measurements. The Mie solution is also important for understanding the appearance of common materials like milk, biological tissue and latex paint.
Atmospheric science
Mie scattering occurs when the diameters of atmospheric particulates are similar to or larger than the wavelengths of the light. Dust, pollen, smoke and microscopic water droplets that form clouds are common causes of Mie scattering. Mie scattering occurs mostly in the lower portions of the atmosphere, where larger particles are more abundant, and dominates in cloudy conditions.
Cancer detection and screening
Mie theory has been used to determine whether scattered light from tissue corresponds to healthy or cancerous cell nuclei using angle-resolved low-coherence interferometry.
Clinical laboratory analysis
Mie theory is a central principle in the application of nephelometric based assays, widely used in medicine to measure various plasma proteins. A wide array of plasma proteins can be detected and quantified by nephelometry.
Magnetic particles
A number of unusual electromagnetic scattering effects occur for magnetic spheres. When the relative permittivity equals the permeability, the back-scatter gain is zero. Also, the scattered radiation is polarized in the same sense as the incident radiation. In the small-particle (or long-wavelength) limit, conditions can occur for zero forward scatter, for complete polarization of scattered radiation in other directions, and for asymmetry of forward scatter to backscatter. The special case in the small-particle limit provides interesting special instances of complete polarization and forward-scatter-to-backscatter asymmetry.
Metamaterial
Mie theory has been used to design metamaterials. They usually consist of three-dimensional composites of metal or non-metallic inclusions periodically or randomly embedded in a low-permittivity matrix. In such a scheme, the negative constitutive parameters are designed to appear around the Mie resonances of the inclusions: the negative effective permittivity is designed around the resonance of the Mie electric dipole scattering coefficient, whereas negative effective permeability is designed around the resonance of the Mie magnetic dipole scattering coefficient, and doubly negative material (DNG) is designed around the overlap of resonances of Mie electric and magnetic dipole scattering coefficients. The particle usually have the following combinations:
- one set of magnetodielectric particles with values of relative permittivity and permeability much greater than one and close to each other;
- two different dielectric particles with equal permittivity but different size;
- two different dielectric particles with equal size but different permittivity.
In theory, the particles analyzed by Mie theory are commonly spherical but, in practice, particles are usually fabricated as cubes or cylinders for ease of fabrication. To meet the criteria of homogenization, which may be stated in the form that the lattice constant is much smaller than the operating wavelength, the relative permittivity of the dielectric particles should be much greater than 1, e.g. to achieve negative effective permittivity (permeability).
Particle sizing
Mie theory is often applied in laser diffraction analysis to inspect the particle sizing effect. While early computers in the 1970s were only able to compute diffraction data with the more simple Fraunhofer approximation, Mie is widely used since the 1990s and officially recommended for particles below 50 micrometers in guideline ISO 13320:2009.
Mie theory has been used in the detection of oil concentration in polluted water.
Mie scattering is the primary method of sizing single sonoluminescing bubbles of air in water and is valid for cavities in materials, as well as particles in materials, as long as the surrounding material is essentially non-absorbing.
Parasitology
It has also been used to study the structure of Plasmodium falciparum, a particularly pathogenic form of malaria.
Extensions
In 1986, P. A. Bobbert and J. Vlieger extended the Mie model to calculate scattering by a sphere in a homogeneous medium placed on flat surface: the Bobbert–Vlieger (BV) model. Like the Mie model, the extended model can be applied to spheres with a radius nearly the wavelength of the incident light. The model has been implemented in C++ source code. Recent developments are related to scattering by ellipsoid. The contemporary studies go to well known research of Rayleigh.


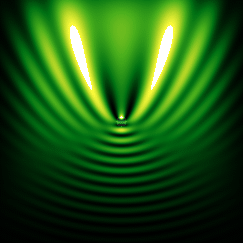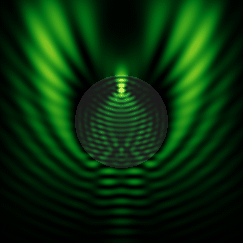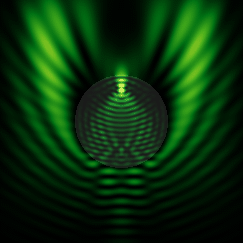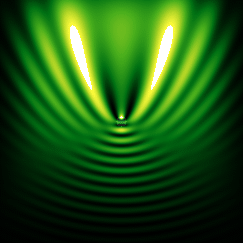








































![{\displaystyle c_{n}(\omega )={\frac {\mu _{1}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho )-\mu _{1}\left[\rho j_{n}(\rho )\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}{\mu _{1}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})-\mu \left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f0a86291790bed49bd6f16912fede3f699b0f1d5)
![{\displaystyle d_{n}(\omega )={\frac {\mu _{1}n_{1}n\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho )-\mu _{1}n_{1}n\left[\rho j_{n}(\rho )\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}{\mu n_{1}^{2}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})-\mu _{1}n^{2}\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1f53e6324063f56935547c233205312256fd28d0)
![{\displaystyle b_{n}(\omega )={\frac {\mu _{1}\left[\rho j_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})-\mu \left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'j_{n}(\rho )}{\mu _{1}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})-\mu \left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ce3d49d4dfd99578bee9eb83d67b99b840640411)
![{\displaystyle a_{n}(\omega )={\frac {\mu n_{1}^{2}\left[\rho j_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})-\mu _{1}n^{2}\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'j_{n}(\rho )}{\mu n_{1}^{2}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})-\mu _{1}n^{2}\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bc8da43bf1f051625390492adc95b338ae73b338)

























![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}C_{\text{sca}}={\frac {2\pi }{\pi a^{2}k^{2}}}\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }{\frac {n(n+1)}{(2n+1)}}&\times \left[\sum _{m=1}^{n}{\frac {(n+m)!}{(n-m)!}}\left(|D_{Memn}|^{2}+|D_{Momn}|^{2}+|D_{Nemn}|^{2}+|D_{Nomn}|^{2}\right)\right.\\&+\left.{\vphantom {\sum _{}}}2|D_{Me0n}|^{2}+2|D_{Ne0n}|^{2}\right].\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ed7606fc0d4a1f654ac69061b6d2b23470b084be)















![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}&{\hat {\bf {G}}}^{0}({\mathbf {r} ,\mathbf {r} ',k})\\{}={}&{\frac {\mathbf {e_{r}} \otimes \mathbf {e_{r}} }{k^{2}}}\delta (\mathbf {r} -\mathbf {r} ')+{\frac {ik}{4\pi }}\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\sum _{m=0}^{n}(2-\delta _{m,0}){\frac {2n+1}{n(n+1)}}{\frac {(n-m)!}{(n+m)!}}\cdot {}\\&\quad {\begin{cases}{\begin{aligned}\left(\left(\mathbf {M} _{emn}^{(1)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {M} }_{emn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ']\right.\right.&+\left.\left.\mathbf {M} _{omn}^{(1)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {M} }_{omn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ']\right)\right.\\&+\left.\left({\mathbf {N} }_{emn}^{(1)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {N} }_{emn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ']+\mathbf {N} _{omn}^{(1)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {N} }_{omn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ']\right)\right)\end{aligned}}&{\text{if }}r<r'\\{\begin{aligned}\left(\left(\mathbf {M} _{emn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {M} }_{emn}^{(1)}[k,\mathbf {r} ']\right.\right.&+\left.\left.\mathbf {M} _{omn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {M} }_{omn}^{(1)}[k,\mathbf {r} ']\right)\right.\\&+\left.\left({\mathbf {N} }_{emn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {N} }_{emn}^{(1)}[k,\mathbf {r} ']+\mathbf {N} _{omn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {N} }_{omn}^{(1)}[k,\mathbf {r} ']\right)\right)\end{aligned}}&{\text{if }}r>r'\end{cases}}\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d8c84d774a37a08cf4a61266b0ff1db003fd15bc)



![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}&{\hat {\bf {G}}}^{00}({\mathbf {r} ,\mathbf {r} ',k,k_{1}})\\{}={}&{\hat {\bf {G}}}^{0}({\mathbf {r} ,\mathbf {r} ',k})+{\frac {ik}{4\pi }}\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\sum _{m=0}^{n}(2-\delta _{m,0}){\frac {2n+1}{n(n+1)}}{\frac {(n-m)!}{(n+m)!}}\cdot {}\\&\quad \left(a_{n}^{(0)}(\omega )\left(\mathbf {M} _{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {M} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ']\right)+b_{n}^{(0)}(\omega )\left({\mathbf {N} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {N} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ']\right)\right)\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e677851cfa72a7561a7ee960e3504963872653ee)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}a_{n}^{(0)}(\omega )&={\frac {\mu /\mu _{1}\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'j_{n}(\rho )-\left[\rho j_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})}{\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})-\mu /\mu _{1}\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}},\\b_{n}^{(0)}(\omega )&={\frac {n^{2}\mu _{1}/\mu \left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'j_{n}(\rho )-n_{1}^{2}\left[\rho j_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})}{n_{1}^{2}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})-n^{2}\mu _{1}/\mu \left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}}.\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/092998f5055a75474335786015e209b00676ff60)

![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}&{\hat {\bf {G}}}^{11}({\mathbf {r} ,\mathbf {r} ',k,k_{1}})\\{}={}&{\hat {\bf {G}}}^{0}({\mathbf {r} ,\mathbf {r} ',k_{1}})+{\frac {ik_{1}}{4\pi }}\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\sum _{m=0}^{n}(2-\delta _{m,0}){\frac {2n+1}{n(n+1)}}{\frac {(n-m)!}{(n+m)!}}\cdot {}\\&\quad \left(c_{n}^{(1)}(\omega )\left(\mathbf {M} _{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(1)}[k_{1},\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {M} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(1)}[k_{1},\mathbf {r} ']\right)+d_{n}^{(1)}(\omega )\left({\mathbf {N} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(1)}[k_{1},\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {N} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(1)}[k_{1},\mathbf {r} ']\right)\right),\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1a3cb288cc8399bed8d6b2cfcba9b38a285e0de2)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}c_{n}^{(1)}(\omega )&={\frac {\mu _{1}/\mu \left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'h_{n}(\rho _{1})-\left[\rho _{1}h_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}{\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )-\mu _{1}/\mu \left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})}},\\d_{n}^{(1)}(\omega )&={\frac {n_{1}^{2}\mu /\mu _{1}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'h_{n}(\rho _{1})-n^{2}\left[\rho _{1}h_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}{n^{2}\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )-n_{1}^{2}\mu /\mu _{1}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})}}.\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/74935abf30c5a80f31aed8aac72b9004c9fe8b06)

![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}&{\hat {\bf {G}}}^{01}({\mathbf {r} ,\mathbf {r} ',k,k_{1}})\\{}={}&{\frac {ik_{1}}{4\pi }}\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\sum _{m=0}^{n}(2-\delta _{m,0}){\frac {2n+1}{n(n+1)}}{\frac {(n-m)!}{(n+m)!}}\cdot {}\\&\quad \left(a_{n}^{(1)}(\omega )(\mathbf {M} _{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {M} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(1)}[k_{1},\mathbf {r} '])+b_{n}^{(1)}(\omega )\left(\mathbf {N} _{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(3)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {N} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(1)}[k_{1},\mathbf {r} ']\right)\right)\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b2e9f6e18a17997c073166a089c0b5bef56bc67f)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}a_{n}^{(1)}(\omega )&={\frac {\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho _{1})-\left[\rho _{1}h_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})}{\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )-\mu _{1}/\mu \left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})}},\\b_{n}^{(1)}(\omega )&={\frac {nn_{1}\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho _{1})-nn_{1}\left[\rho _{1}h_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})}{n^{2}\mu _{1}/\mu \left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )-n_{1}^{2}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})}}.\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d928f22514238ddb00dec0b8e87e1d60913f2cb5)

![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}&{\hat {\bf {G}}}^{10}({\mathbf {r} ,\mathbf {r} ',k,k_{1}})\\{}={}&{\frac {ik}{4\pi }}\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\sum _{m=0}^{n}(2-\delta _{m,0}){\frac {2n+1}{n(n+1)}}{\frac {(n-m)!}{(n+m)!}}\cdot {}\\&\quad \left(c_{n}^{(0)}(\omega )(\mathbf {M} _{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(1)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {M} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(3)}[k_{1},\mathbf {r} '])+d_{n}^{(0)}(\omega )({\mathbf {N} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(1)}[k,\mathbf {r} ]\otimes {\mathbf {N} }_{^{e}_{o}mn}^{(3)}[k_{1},\mathbf {r} '])\right)\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/44ed16735b8d15e1d0f9422239dba82f47b37db9)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}c_{n}^{(0)}(\omega )&={\frac {\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho )-\left[\rho j_{n}(\rho )\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}{\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})-\mu /\mu _{1}\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}},\\d_{n}^{(0)}(\omega )&={\frac {nn_{1}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho )-nn_{1}\left[\rho j_{n}(\rho )\right]'h_{n}(\rho )}{n_{1}^{2}\mu /\mu _{1}\left[\rho h_{n}(\rho )\right]'j_{n}(\rho _{1})-n^{2}\left[\rho _{1}j_{n}(\rho _{1})\right]'j_{n}(\rho )}}.\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/23f1fc04f97455456a7dd07fb30d0e769c8754ec)






