| |

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dinitrogen monoxide
| |
| Other names
: Laughing gas, sweet air, protoxide of nitrogen, hyponitrous oxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 8137358 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.017 |
| E number | E942 (glazing agents, ...) |
| 2153410 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | QX1350000 |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1070 (compressed) 2201 (liquid) |
| Properties | |
| N 2O | |
| Molar mass | 44.013 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless gas |
| Density | 1.977 g/L (gas) |
| Melting point | −90.86 °C (−131.55 °F; 182.29 K) |
| Boiling point | −88.48 °C (−127.26 °F; 184.67 K) |
| 1.5 g/L (15 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, ether, sulfuric acid |
| log P | 0.35 |
| Vapor pressure | 5150 kPa (20 °C) |
| −18.9·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.000516 (0 °C, 101,325 kPa) |
| Structure | |
| linear, C∞v | |
| 0.166 D | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S |
219.96 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
+82.05 kJ mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| N01AX13 (WHO) | |
| |
| Inhalation | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| 0.004% | |
| 5 minutes | |
| Respiratory | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Ilo.org, ICSC 0067 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | Nonflammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Nitric oxide Dinitrogen trioxide Nitrogen dioxide Dinitrogen tetroxide Dinitrogen pentoxide | |
Related compounds
|
Ammonium nitrate Azide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or nitrous, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula N
2O. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slight metallic scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidizer similar to molecular oxygen. It is soluble in water.
Nitrous oxide has significant medical uses, especially in surgery and dentistry, for its anaesthetic and pain reducing effects. Its name "laughing gas", coined by Humphry Davy, is due to the euphoric effects upon inhaling it, a property that has led to its recreational use as a dissociative anaesthetic. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. It also is used as an oxidizer in rocket propellants, and in motor racing to increase the power output of engines.
Nitrous oxide occurs in small amounts in the atmosphere, but recently has been found to be a major scavenger of stratospheric ozone, with an impact comparable to that of CFCs. It is estimated that 30% of the N
2O in the atmosphere is the result of human activity, chiefly agriculture.
Uses
Rocket motors
Nitrous oxide may be used as an oxidizer in a rocket
motor. This is advantageous over other oxidisers in that it is much
less toxic, and due to its stability at room temperature is also easier
to store and relatively safe to carry on a flight. As a secondary
benefit, it may be decomposed readily to form breathing air. Its high
density and low storage pressure (when maintained at low temperature)
enable it to be highly competitive with stored high-pressure gas
systems.
In a 1914 patent, American rocket pioneer Robert Goddard suggested nitrous oxide and gasoline as possible propellants for a liquid fueled rocket. Nitrous oxide has been the oxidizer of choice in several hybrid rocket designs (using solid fuel with a liquid or gaseous oxidizer). The combination of nitrous oxide with hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene fuel has been used by SpaceShipOne and others. It also is notably used in amateur and high power rocketry with various plastics as the fuel.
Nitrous oxide also may be used in a monopropellant rocket. In the presence of a heated catalyst, N
2O will decompose exothermically into nitrogen and oxygen, at a temperature of approximately 1,070 °F (577 °C). Because of the large heat release, the catalytic action rapidly becomes secondary, as thermal autodecomposition becomes dominant. In a vacuum thruster, this may provide a monopropellant specific impulse (Isp) of as much as 180 s. While noticeably less than the Isp available from hydrazine thrusters (monopropellant or bipropellant with dinitrogen tetroxide), the decreased toxicity makes nitrous oxide an option worth investigating.
2O will decompose exothermically into nitrogen and oxygen, at a temperature of approximately 1,070 °F (577 °C). Because of the large heat release, the catalytic action rapidly becomes secondary, as thermal autodecomposition becomes dominant. In a vacuum thruster, this may provide a monopropellant specific impulse (Isp) of as much as 180 s. While noticeably less than the Isp available from hydrazine thrusters (monopropellant or bipropellant with dinitrogen tetroxide), the decreased toxicity makes nitrous oxide an option worth investigating.
Nitrous oxide is said to deflagrate at approximately 600 °C (1,112 °F) at a pressure of 309 psi (21 atmospheres). At 600 psi for example, the required ignition energy is only 6 joules, whereas N
2O at 130 psi a 2500-joule ignition energy input is insufficient.
2O at 130 psi a 2500-joule ignition energy input is insufficient.
Internal combustion engine
In vehicle racing, nitrous oxide (often referred to as just "nitrous") allows the engine to burn more fuel by providing more oxygen than air alone, resulting in a more powerful combustion. The gas is not flammable at a low pressure/temperature, but it delivers more oxygen
than atmospheric air by breaking down at elevated temperatures.
Therefore, it often is mixed with another fuel that is easier to
deflagrate. Nitrous oxide is a strong oxidant, roughly equivalent to
hydrogen peroxide, and much stronger than oxygen gas.
Nitrous oxide is stored as a compressed liquid; the evaporation and expansion of liquid nitrous oxide in the intake manifold
causes a large drop in intake charge temperature, resulting in a denser
charge, further allowing more air/fuel mixture to enter the cylinder.
Sometimes nitrous oxide is injected into (or prior to) the intake
manifold, whereas other systems directly inject, right before the
cylinder (direct port injection) to increase power.
The technique was used during World War II by Luftwaffe aircraft with the GM-1 system to boost the power output of aircraft engines.
Originally meant to provide the Luftwaffe standard aircraft with
superior high-altitude performance, technological considerations limited
its use to extremely high altitudes. Accordingly, it was only used by
specialized planes such as high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft, high-speed bombers, and high-altitude interceptor aircraft. It sometimes could be found on Luftwaffe aircraft also fitted with another engine-boost system, MW 50, a form of water injection for aviation engines that used methanol for its boost capabilities.
One of the major problems of using nitrous oxide in a
reciprocating engine is that it can produce enough power to damage or
destroy the engine. Very large power increases are possible, and if the
mechanical structure of the engine is not properly reinforced, the
engine may be severely damaged, or destroyed, during this kind of
operation. It is very important with nitrous oxide augmentation of petrol engines to maintain proper operating temperatures and fuel levels to prevent "pre-ignition",
or "detonation" (sometimes referred to as "knock"). Most problems that
are associated with nitrous oxide do not come from mechanical failure
due to the power increases. Since nitrous oxide allows a much denser
charge into the cylinder, it dramatically increases cylinder pressures.
The increased pressure and temperature can cause problems such as
melting the piston or valves. It also may crack or warp the piston or
head and cause pre-ignition due to uneven heating.
Automotive-grade liquid nitrous oxide differs slightly from medical-grade nitrous oxide. A small amount of sulfur dioxide (SO
2) is added to prevent substance abuse. Multiple washes through a base (such as sodium hydroxide) can remove this, decreasing the corrosive properties observed when SO
2 is further oxidized during combustion into sulfuric acid, making emissions cleaner.
2) is added to prevent substance abuse. Multiple washes through a base (such as sodium hydroxide) can remove this, decreasing the corrosive properties observed when SO
2 is further oxidized during combustion into sulfuric acid, making emissions cleaner.
Aerosol propellant
Food grade N
2O whippets
2O whippets
The gas is approved for use as a food additive (also known as E942), specifically as an aerosol spray propellant. Its most common uses in this context are in aerosol whipped cream canisters and cooking sprays.
The gas is extremely soluble in fatty compounds. In aerosol
whipped cream, it is dissolved in the fatty cream until it leaves the
can, when it becomes gaseous and thus creates foam. Used in this way, it
produces whipped cream four times the volume of the liquid, whereas
whipping air into cream only produces twice the volume. If air were used
as a propellant, oxygen would accelerate rancidification
of the butterfat, but nitrous oxide inhibits such degradation. Carbon
dioxide cannot be used for whipped cream because it is acidic in water,
which would curdle the cream and give it a seltzer-like "sparkling"
sensation.
The whipped cream produced with nitrous oxide is unstable,
however, and will return to a more liquid state within half an hour to
one hour.Thus, the method is not suitable for decorating food that will not be served immediately.
During December 2016, some manufacturers reported a shortage of
aerosol whipped creams in the United States due to an explosion at the Air Liquide nitrous oxide facility in Florida
in late August. With a major facility offline, the disruption caused a
shortage resulting in the company diverting the supply of nitrous oxide
to medical clients rather than to food manufacturing. The shortage came
during the Christmas and holiday season when canned whipped cream use is normally at its highest.
Similarly, cooking spray, which is made from various types of oils combined with lecithin (an emulsifier), may use nitrous oxide as a propellant. Other propellants used in cooking spray include food-grade alcohol and propane.
Medicine
Medical grade N
2O tanks used in dentistry
2O tanks used in dentistry
Nitrous oxide has been used in dentistry and surgery, as an anesthetic and analgesic, since 1844.
In the early days, the gas was administered through simple inhalers consisting of a breathing bag made of rubber cloth. Today, the gas is administered in hospitals by means of an automated relative analgesia machine, with an anesthetic vaporizer and a medical ventilator, that delivers a precisely dosed and breath-actuated flow of nitrous oxide mixed with oxygen in a 2:1 ratio.
Nitrous oxide is a weak general anesthetic,
and so is generally not used alone in general anaesthesia, but used as a
carrier gas (mixed with oxygen) for more powerful general anesthetic
drugs such as sevoflurane or desflurane. It has a minimum alveolar concentration of 105% and a blood/gas partition coefficient of 0.46. The use of nitrous oxide in anesthesia, however, can increase the risk of postoperative nausea and vomiting.
Dentists use a simpler machine, that only delivers a N
2O/O
2 mixture for the patient to inhale while conscious. The patient is kept conscious throughout the procedure, and retains adequate mental faculties to respond to questions and instructions from the dentist.
2O/O
2 mixture for the patient to inhale while conscious. The patient is kept conscious throughout the procedure, and retains adequate mental faculties to respond to questions and instructions from the dentist.
Inhalation of nitrous oxide is used frequently to relieve pain associated with childbirth, trauma, oral surgery, and acute coronary syndrome (includes heart attacks). Its use during labor has been shown to be a safe and effective aid for birthing women. Its use for acute coronary syndrome is of unknown benefit.
In Britain and Canada, Entonox and Nitronox are used commonly by
ambulance crews (including unregistered practitioners) as a rapid and
highly effective analgesic gas.
50% nitrous oxide can be considered for use by trained
non-professional first aid responders in prehospital settings, given the
relative ease and safety of administering 50% nitrous oxide as an
analgesic. The rapid reversibility of its effect would also prevent it
from precluding diagnosis.
Recreational use
Aquatint depiction of a laughing gas party in the nineteenth century
Whippit remnants of recreational drug use, the Netherlands, 2017
Recreational inhalation of nitrous oxide, with the purpose of causing euphoria and/or slight hallucinations, began as a phenomenon for the British upper class in 1799, known as "laughing gas parties".
Starting in the nineteenth century, widespread availability of
the gas for medical and culinary purposes allowed the recreational use
to expand greatly, throughout the world. In the United Kingdom, as of
2014, nitrous oxide was estimated to be used by almost half a million
young people at nightspots, festivals, and parties. The legality of that use varies greatly from country to country, and even from city to city in some countries.
Safety
The major safety hazards of nitrous oxide come from the fact that it is a compressed liquefied gas, an asphyxiation risk, and a dissociative anesthetic.
While relatively non-toxic, nitrous oxide has a number of
recognized ill effects on human health, whether through breathing it in
or by contact of the liquid with skin or eyes.
Nitrous oxide is a significant occupational hazard
for surgeons, dentists, and nurses. Because nitrous oxide is minimally
metabolized in humans (with a rate of 0.004%), it retains its potency
when exhaled into the room by the patient, and can pose an intoxicating
and prolonged exposure hazard to the clinic staff if the room is poorly
ventilated. Where nitrous oxide is administered, a continuous-flow
fresh-air ventilation system or N
2O scavenger system is used to prevent a waste-gas buildup.
2O scavenger system is used to prevent a waste-gas buildup.
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
recommends that workers' exposure to nitrous oxide should be controlled
during the administration of anesthetic gas in medical, dental, and
veterinary operators. It set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 25 ppm (46 mg/m3) to escaped anesthetic.
Mental and manual impairment
Exposure to nitrous oxide causes short-term decreases in mental performance, audiovisual ability, and manual dexterity.
These effects coupled with the induced spatial and temporal
disorientation could result in physical harm to the user from
environmental hazards.
Neurotoxicity and neuroprotection
Like other NMDA antagonists, N
2O was suggested to produce neurotoxicity in the form of Olney's lesions in rodents upon prolonged (several hour) exposure. New research has arisen suggesting that Olney's lesions do not occur in humans, however, and similar drugs such as ketamine are now believed not to be acutely neurotoxic. It has been argued that, because N
2O has a very short duration under normal circumstances, it is less likely to be neurotoxic than other NMDA antagonists. Indeed, in rodents, short-term exposure results in only mild injury that is rapidly reversible, and neuronal death occurs only after constant and sustained exposure. Nitrous oxide also may cause neurotoxicity after extended exposure because of hypoxia. This is especially true of non-medical formulations such as whipped-cream chargers (also known as "whippets" or "nangs"), which never contain oxygen, since oxygen makes cream rancid.
2O was suggested to produce neurotoxicity in the form of Olney's lesions in rodents upon prolonged (several hour) exposure. New research has arisen suggesting that Olney's lesions do not occur in humans, however, and similar drugs such as ketamine are now believed not to be acutely neurotoxic. It has been argued that, because N
2O has a very short duration under normal circumstances, it is less likely to be neurotoxic than other NMDA antagonists. Indeed, in rodents, short-term exposure results in only mild injury that is rapidly reversible, and neuronal death occurs only after constant and sustained exposure. Nitrous oxide also may cause neurotoxicity after extended exposure because of hypoxia. This is especially true of non-medical formulations such as whipped-cream chargers (also known as "whippets" or "nangs"), which never contain oxygen, since oxygen makes cream rancid.
Additionally, nitrous oxide depletes vitamin B12 levels. This can cause serious neurotoxicity if the user has preexisting vitamin B12 deficiency.
Nitrous oxide at 75% by volume reduces ischemia-induced neuronal
death induced by occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in rodents, and
decreases NMDA-induced Ca2+ influx in neuronal cell cultures, a critical event involved in excitotoxicity.
Oxygen deprivation
If
pure nitrous oxide is inhaled without oxygen mixed in, this can
eventually lead to oxygen deprivation resulting in loss of blood
pressure, fainting and even heart attacks. This can occur if the user
inhales large quantities continuously, as with a strap-on mask connected
to a gas canister. It can also happen if the user engages in excessive
breath-holding or uses any other inhalation system that cuts off their
supply of fresh air.
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Long-term exposure to nitrous oxide may cause vitamin B12 deficiency. It inactivates the cobalamin form of vitamin B12 by oxidation. Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency, including sensory neuropathy, myelopathy, and encephalopathy, may occur within days or weeks of exposure to nitrous oxide anaesthesia in people with subclinical vitamin B12 deficiency.
Symptoms are treated with high doses of vitamin B12, but recovery can be slow and incomplete.
People with normal vitamin B12 levels have stores to
make the effects of nitrous oxide insignificant, unless exposure is
repeated and prolonged (nitrous oxide abuse). Vitamin B12 levels should be checked in people with risk factors for vitamin B12 deficiency prior to using nitrous oxide anesthesia.
Prenatal development
Several
experimental studies in rats indicate that chronic exposure of pregnant
females to nitrous oxide may have adverse effects on the developing
fetus.
Chemical/physical risks
At
room temperature (20 °C (68 °F)) the saturated vapor pressure is
50.525 bar, rising up to 72.45 bar at 36.4 °C (97.5 °F)—the critical temperature. The pressure curve is thus unusually sensitive to temperature. Liquid nitrous oxide acts as a good solvent for many organic compounds; liquid mixtures may form shock sensitive explosives.
As with many strong oxidizers, contamination of parts with fuels
have been implicated in rocketry accidents, where small quantities of
nitrous/fuel mixtures explode due to "water hammer"-like effects
(sometimes called "dieseling"—heating due to adiabatic compression of gases can reach decomposition temperatures).
Some common building materials such as stainless steel and aluminium
can act as fuels with strong oxidizers such as nitrous oxide, as can
contaminants that may ignite due to adiabatic compression.
There also have been incidents where nitrous oxide decomposition in plumbing has led to the explosion of large tanks.
Mechanism of action
The pharmacological mechanism of action of N
2O in medicine is not fully known. However, it has been shown to directly modulate a broad range of ligand-gated ion channels, and this likely plays a major role in many of its effects. It moderately blocks NMDA and β2-subunit-containing nACh channels, weakly inhibits AMPA, kainate, GABAC, and 5-HT3 receptors, and slightly potentiates GABAA and glycine receptors. It also has been shown to activate two-pore-domain K+ channels. While N
2O affects quite a few ion channels, its anesthetic, hallucinogenic, and euphoriant effects are likely caused predominantly, or fully, via inhibition of NMDA receptor-mediated currents. In addition to its effects on ion channels, N
2O may act to imitate nitric oxide (NO) in the central nervous system, and this may be related to its analgesic and anxiolytic properties. Nitrous oxide is 30-40 times more soluble than nitrogen.
2O in medicine is not fully known. However, it has been shown to directly modulate a broad range of ligand-gated ion channels, and this likely plays a major role in many of its effects. It moderately blocks NMDA and β2-subunit-containing nACh channels, weakly inhibits AMPA, kainate, GABAC, and 5-HT3 receptors, and slightly potentiates GABAA and glycine receptors. It also has been shown to activate two-pore-domain K+ channels. While N
2O affects quite a few ion channels, its anesthetic, hallucinogenic, and euphoriant effects are likely caused predominantly, or fully, via inhibition of NMDA receptor-mediated currents. In addition to its effects on ion channels, N
2O may act to imitate nitric oxide (NO) in the central nervous system, and this may be related to its analgesic and anxiolytic properties. Nitrous oxide is 30-40 times more soluble than nitrogen.
The effects of inhaling sub-anesthetic doses of Nitrous Oxide
have been known to vary, based on several factors, including settings
and individual differences, however, from his discussion, Jay (2008) suggests that it has been reliably known to induce the following states and sensations:
- Intoxication
- Euphoria/dysphoria
- Spatial disorientation
- Temporal disorientation
- Reduced pain sensitivity
A minority of users also will present with uncontrolled vocalizations
and muscular spasms. These effects generally disappear minutes after
removal of the nitrous oxide source.
Euphoric effect
In rats, N
2O stimulates the mesolimbic reward pathway via inducing dopamine release and activating dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens, presumably through antagonisation of NMDA receptors localized in the system. This action has been implicated in its euphoric effects, and notably, appears to augment its analgesic properties as well.
2O stimulates the mesolimbic reward pathway via inducing dopamine release and activating dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens, presumably through antagonisation of NMDA receptors localized in the system. This action has been implicated in its euphoric effects, and notably, appears to augment its analgesic properties as well.
It is remarkable, however, that in mice, N
2O blocks amphetamine-induced carrier-mediated dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and behavioral sensitization, abolishes the conditioned place preference (CPP) of cocaine and morphine, and does not produce reinforcing (or aversive) effects of its own. Effects of CPP of N
2O in rats are mixed, consisting of reinforcement, aversion, and no change. In contrast, it is a positive reinforcer in squirrel monkeys, and is well known as a drug of abuse in humans. These discrepancies in response to N
2O may reflect species variation or methodological differences. In human clinical studies, N
2O was found to produce mixed responses, similarly to rats, reflecting high subjective individual variability.
2O blocks amphetamine-induced carrier-mediated dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and behavioral sensitization, abolishes the conditioned place preference (CPP) of cocaine and morphine, and does not produce reinforcing (or aversive) effects of its own. Effects of CPP of N
2O in rats are mixed, consisting of reinforcement, aversion, and no change. In contrast, it is a positive reinforcer in squirrel monkeys, and is well known as a drug of abuse in humans. These discrepancies in response to N
2O may reflect species variation or methodological differences. In human clinical studies, N
2O was found to produce mixed responses, similarly to rats, reflecting high subjective individual variability.
Anxiolytic effect
In behavioural tests of anxiety, a low dose of N
2O is an effective anxiolytic, and this anti-anxiety effect is associated with enhanced activity of GABAA receptors, as it is partially reversed by benzodiazepine receptor antagonists. Mirroring this, animals that have developed tolerance to the anxiolytic effects of benzodiazepines are partially tolerant to N
2O. Indeed, in humans given 30% N
2O, benzodiazepine receptor antagonists reduced the subjective reports of feeling "high", but did not alter psychomotor performance, in human clinical studies.
2O is an effective anxiolytic, and this anti-anxiety effect is associated with enhanced activity of GABAA receptors, as it is partially reversed by benzodiazepine receptor antagonists. Mirroring this, animals that have developed tolerance to the anxiolytic effects of benzodiazepines are partially tolerant to N
2O. Indeed, in humans given 30% N
2O, benzodiazepine receptor antagonists reduced the subjective reports of feeling "high", but did not alter psychomotor performance, in human clinical studies.
Analgesic effect
The analgesic effects of N
2O are linked to the interaction between the endogenous opioid system and the descending noradrenergic system. When animals are given morphine chronically, they develop tolerance to its pain-killing effects, and this also renders the animals tolerant to the analgesic effects of N
2O. Administration of antibodies that bind and block the activity of some endogenous opioids (not β-endorphin) also block the antinociceptive effects of N
2O. Drugs that inhibit the breakdown of endogenous opioids also potentiate the antinociceptive effects of N
2O. Several experiments have shown that opioid receptor antagonists applied directly to the brain block the antinociceptive effects of N
2O, but these drugs have no effect when injected into the spinal cord.
2O are linked to the interaction between the endogenous opioid system and the descending noradrenergic system. When animals are given morphine chronically, they develop tolerance to its pain-killing effects, and this also renders the animals tolerant to the analgesic effects of N
2O. Administration of antibodies that bind and block the activity of some endogenous opioids (not β-endorphin) also block the antinociceptive effects of N
2O. Drugs that inhibit the breakdown of endogenous opioids also potentiate the antinociceptive effects of N
2O. Several experiments have shown that opioid receptor antagonists applied directly to the brain block the antinociceptive effects of N
2O, but these drugs have no effect when injected into the spinal cord.
Conversely, α2-adrenoceptor antagonists block the pain-reducing effects of N
2O when given directly to the spinal cord, but not when applied directly to the brain. Indeed, α2B-adrenoceptor knockout mice or animals depleted in norepinephrine are nearly completely resistant to the antinociceptive effects of N
2O. Apparently N
2O-induced release of endogenous opioids causes disinhibition of brain stem noradrenergic neurons, which release norepinephrine into the spinal cord and inhibit pain signalling. Exactly how N
2O causes the release of endogenous opioid peptides remains uncertain.
2O when given directly to the spinal cord, but not when applied directly to the brain. Indeed, α2B-adrenoceptor knockout mice or animals depleted in norepinephrine are nearly completely resistant to the antinociceptive effects of N
2O. Apparently N
2O-induced release of endogenous opioids causes disinhibition of brain stem noradrenergic neurons, which release norepinephrine into the spinal cord and inhibit pain signalling. Exactly how N
2O causes the release of endogenous opioid peptides remains uncertain.
Properties and reactions
Nitrous oxide is a colorless, non-toxic gas with a faint, sweet odor.
Nitrous oxide supports combustion by releasing the dipolar bonded oxygen radical, thus it can relight a glowing splint.
N
2O is inert at room temperature and has few reactions. At elevated temperatures, its reactivity increases. For example, nitrous oxide reacts with NaNH
2 at 460 K (187 °C) to give NaN
3 :
2O is inert at room temperature and has few reactions. At elevated temperatures, its reactivity increases. For example, nitrous oxide reacts with NaNH
2 at 460 K (187 °C) to give NaN
3 :
- 2 NaNH
2 + N
2O → NaN
3 + NaOH + NH
3
The above reaction is the route adopted by the commercial chemical
industry to produce azide salts, which are used as detonators.
History
The gas was first synthesised in 1772 by English natural philosopher and chemist Joseph Priestley who called it phlogisticated nitrous air or inflammable nitrous air. Priestley published his discovery in the book Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air (1775), where he described how to produce the preparation of "nitrous air diminished", by heating iron filings dampened with nitric acid.
Early use
"LIVING MADE EASY"
A satirical print from 1830 depicting Humphry Davy administering a dose of laughing gas to a woman
A satirical print from 1830 depicting Humphry Davy administering a dose of laughing gas to a woman
The first important use of nitrous oxide was made possible by Thomas Beddoes and James Watt, who worked together to publish the book Considerations on the Medical Use and on the Production of Factitious Airs (1794).
This book was important for two reasons. First, James Watt had invented
a novel machine to produce "Factitious Airs" (i.e. nitrous oxide) and a
novel "breathing apparatus" to inhale the gas. Second, the book also
presented the new medical theories by Thomas Beddoes, that tuberculosis and other lung diseases could be treated by inhalation of "Factitious Airs".
Sir Humphry Davy’s Researches chemical and philosophical: chiefly concerning nitrous oxide (1800), pages 556 and 557 (right), outlining potential anaesthetic properties of nitrous oxide in relieving pain during surgery
The machine to produce "Factitious Airs" had three parts: a furnace
to burn the needed material, a vessel with water where the produced gas
passed through in a spiral pipe (for impurities to be "washed off"), and
finally the gas cylinder with a gasometer where the gas produced,
"air", could be tapped into portable air bags (made of airtight oily
silk). The breathing apparatus consisted of one of the portable air bags
connected with a tube to a mouthpiece. With this new equipment being
engineered and produced by 1794, the way was paved for clinical trials, which began in 1798 when Thomas Beddoes established the "Pneumatic Institution for Relieving Diseases by Medical Airs" in Hotwells (Bristol). In the basement of the building, a large-scale machine was producing the gases under the supervision of a young Humphry Davy, who was encouraged to experiment with new gases for patients to inhale. The first important work of Davy was examination of the nitrous oxide, and the publication of his results in the book: Researches, Chemical and Philosophical (1800).
In that publication, Davy notes the analgesic effect of nitrous oxide
at page 465 and its potential to be used for surgical operations at page
556. Davy coined the name "laughing gas" for nitrous oxide.
Despite Davy's discovery that inhalation of nitrous oxide could
relieve a conscious person from pain, another 44 years elapsed before
doctors attempted to use it for anesthesia. The use of nitrous oxide as a recreational drug at "laughing gas parties", primarily arranged for the British upper class,
became an immediate success beginning in 1799. While the effects of the
gas generally make the user appear stuporous, dreamy, and sedated, some
people also "get the giggles" in a state of euphoria, and frequently
erupt in laughter.
One of the earliest commercial producers in the U.S. was George Poe, cousin of the poet Edgar Allan Poe, who also was the first to liquefy the gas.
Anaesthetic use
The first time nitrous oxide was used as an anaesthetic drug in the treatment of a patient was when dentist Horace Wells, with assistance by Gardner Quincy Colton and John Mankey Riggs, demonstrated insensitivity to pain from a dental extraction on 11 December 1844. In the following weeks, Wells treated the first 12–15 patients with nitrous oxide in Hartford, Connecticut, and according to his own record, only failed in two cases. In spite of these convincing results having been reported by Wells to the medical society in Boston
in December 1844, this new method was not immediately adopted by other
dentists. The reason for this was most likely that Wells, in January
1845 at his first public demonstration to the medical faculty in Boston,
had been partly unsuccessful, leaving his colleagues doubtful regarding
its efficacy and safety. The method did not come into general use until 1863, when Gardner Quincy Colton successfully started to use it in all his "Colton Dental Association" clinics, that he had just established in New Haven and New York City. Over the following three years, Colton and his associates successfully administered nitrous oxide to more than 25,000 patients. Today, nitrous oxide is used in dentistry as an anxiolytic, as an adjunct to local anesthetic.
Nitrous oxide was not found to be a strong enough anaesthetic for use in major surgery in hospital settings, however. Instead, diethyl ether, being a stronger and more potent anaesthetic, was demonstrated and accepted for use in October 1846, along with chloroform in 1847. When Joseph Thomas Clover
invented the "gas-ether inhaler" in 1876, however, it became a common
practice at hospitals to initiate all anesthetic treatments with a mild
flow of nitrous oxide, and then gradually increase the anesthesia
with the stronger ether or chloroform. Clover's gas-ether inhaler was
designed to supply the patient with nitrous oxide and ether at the same
time, with the exact mixture being controlled by the operator of the
device. It remained in use by many hospitals until the 1930s. Although hospitals today are using a more advanced anesthetic machine,
these machines still use the same principle launched with Clover's
gas-ether inhaler, to initiate the anesthesia with nitrous oxide,
before the administration of a more powerful anesthetic.
As a patent medicine
Colton's popularization of nitrous oxide led to its adoption by a number of less than reputable quacksalvers, who touted it as a cure for consumption, scrofula, catarrh, and other diseases of the blood, throat, and lungs. Nitrous oxide treatment was administered and licensed as a patent medicine by the likes of C. L. Blood and Jerome Harris in Boston and Charles E. Barney of Chicago.
Production
Reviewing various methods of producing nitrous oxide is published.
Industrial methods
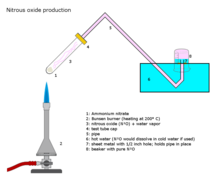
Nitrous oxide production
Nitrous oxide is prepared on an industrial scale by careful heating of ammonium nitrate at about 250 C, which decomposes into nitrous oxide and water vapor.
- NH
4NO
3 → 2 H
2O + N
2O
The addition of various phosphate salts favors formation of a purer gas at slightly lower temperatures. This reaction may be difficult to control, resulting in detonation.
Laboratory methods
The
decomposition of ammonium nitrate is also a common laboratory method
for preparing the gas. Equivalently, it can be obtained by heating a
mixture of sodium nitrate and ammonium sulfate:
- 2 NaNO
3 + (NH
4)2SO
4 → Na
2SO
4 + 2 N
2O+ 4 H
2O.
Another method involves the reaction of urea, nitric acid, and sulfuric acid:
- 2 (NH2)2CO + 2 HNO
3+ H
2SO
4 → - 2 N
2O + 2 CO
2 + (NH4)2SO4 + 2H
2O.
Direct oxidation of ammonia with a manganese dioxide-bismuth oxide catalyst has been reported: cf. Ostwald process.
- 2 NH
3 + 2 O
2 → N
2O + 3 H
2O
Hydroxylammonium chloride reacts with sodium nitrite
to give nitrous oxide. If the nitrite is added to the hydroxylamine
solution, the only remaining by-product is salt water. If the
hydroxylamine solution is added to the nitrite solution (nitrite is in
excess), however, then toxic higher oxides of nitrogen also are formed:
- NH
3OHCl + NaNO
2 → N
2O + NaCl + 2 H
2O
Treating HNO
3 with SnCl
2 and HCl also has been demonstrated:
3 with SnCl
2 and HCl also has been demonstrated:
- 2 HNO
3 + 8 HCl + 4 SnCl
2 → 5 H
2O + 4 SnCl
4 + N
2O
Hyponitrous acid decomposes to N2O and water with a half-life of 16 days at 25 °C at pH 1–3.
- H2N2O2→ H2O + N2O
Atmospheric occurrence
Nitrous oxide is a minor component of Earth's atmosphere, currently with a concentration of about 0.330 ppm.
Emissions by source
As of 2010, it was estimated that about 29.5 million tonnes of N
2O (containing 18.8 million tonnes of nitrogen) were entering the atmosphere each year; of which 64% were natural, and 36% due to human activity.
2O (containing 18.8 million tonnes of nitrogen) were entering the atmosphere each year; of which 64% were natural, and 36% due to human activity.
Most of the N
2O emitted into the atmosphere, from natural and anthropogenic sources, is produced by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi in soils and oceans. Soils under natural vegetation are an important source of nitrous oxide, accounting for 60% of all naturally produced emissions. Other natural sources include the oceans (35%) and atmospheric chemical reactions (5%).
2O emitted into the atmosphere, from natural and anthropogenic sources, is produced by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi in soils and oceans. Soils under natural vegetation are an important source of nitrous oxide, accounting for 60% of all naturally produced emissions. Other natural sources include the oceans (35%) and atmospheric chemical reactions (5%).
The main components of anthropogenic emissions are fertilized
agricultural soils and livestock manure (42%), runoff and leaching of
fertilizers (25%), biomass burning (10%), fossil fuel combustion and
industrial processes (10%), biological degradation of other
nitrogen-containing atmospheric emissions (9%), and human sewage (5%). Agriculture enhances nitrous oxide production through soil cultivation, the use of nitrogen fertilizers,
and animal waste handling. These activities stimulate
naturally-occurring bacteria to produce more nitrous oxide. Nitrous
oxide emissions from soil can be challenging to measure as they vary
markedly over time and space, and the majority of a year's emissions may
occur when conditions are favorable during "hot moments" and/or at favorable locations known as "hotspots".
Among industrial emissions, the production of nitric acid and adipic acid are the largest sources of nitrous oxide emissions. The adipic acid emissions specifically arise from the degradation of the nitrolic acid intermediate derived from nitration of cyclohexanone.
Biological processes
Natural processes that generate nitrous oxide may be classified as nitrification and denitrification. Specifically, they include:
- aerobic autotrophic nitrification, the stepwise oxidation of ammonia (NH
3) to nitrite (NO−
2) and to nitrate (NO−
3) - anaerobic heterotrophic denitrification, the stepwise reduction of NO−
3 to NO−
2, nitric oxide (NO), N
2O and ultimately N
2, where facultative anaerobe bacteria use NO−
3 as an electron acceptor in the respiration of organic material in the condition of insufficient oxygen (O
2) - nitrifier denitrification, which is carried out by autotrophic NH
3−oxidizing bacteria and the pathway whereby ammonia (NH
3) is oxidised to nitrite (NO−
2), followed by the reduction of NO−
2 to nitric oxide (NO), N
2O and molecular nitrogen (N
2) - heterotrophic nitrification
- aerobic denitrification by the same heterotrophic nitrifiers
- fungal denitrification
- non-biological chemodenitrification
These processes are affected by soil chemical and physical properties
such as the availability of mineral nitrogen and organic matter,
acidity, and soil type; as well as climate-related factors such as soil
temperature and water content.
The emission of the gas to the atmosphere is limited greatly by
its consumption inside the cells, by a process catalyzed by the enzyme nitrous oxide reductase.
Environmental impact
Greenhouse effect
Greenhouse gas trends
Nitrous oxide has significant global warming potential as a greenhouse gas.
On a per-molecule basis, considered over a 100-year-period, nitrous
oxide has 298 times the atmospheric heat-trapping ability of carbon
dioxide (CO
2), however, because of its low concentration (less than 1/1000 of that of CO
2), its contribution to the greenhouse effect is less than one-third that of carbon dioxide, and also less than water vapor and methane. On the other hand, since 38% or more of the N
2O entering the atmosphere is the result of human activity, and its concentration has increased 15% since 1750, control of nitrous oxide is considered part of efforts to curb greenhouse gas emissions.
2), however, because of its low concentration (less than 1/1000 of that of CO
2), its contribution to the greenhouse effect is less than one-third that of carbon dioxide, and also less than water vapor and methane. On the other hand, since 38% or more of the N
2O entering the atmosphere is the result of human activity, and its concentration has increased 15% since 1750, control of nitrous oxide is considered part of efforts to curb greenhouse gas emissions.
A 2008 study by Nobel Laureate Paul Crutzen
suggests that the amount of nitrous oxide release attributable to
agricultural nitrate fertilizers has been seriously underestimated, most
of which presumably, would come under soil and oceanic release in the
Environmental Protection Agency data.
Globally, about 40 percent of total N2O emissions come from human
activities.2 Nitrous oxide is emitted from agriculture, transportation,
and industry activities, described below.
•Agriculture. Nitrous oxide can result from various agricultural soil
management activities, such as synthetic and organic fertilizer
application and other cropping practices, the management of manure, or
burning of agricultural residues. Agricultural soil management is the
largest source of N2O emissions in the United States, accounting for
about 77 percent of total U.S. N2O emissions in 2016.
•Fuel Combustion. Nitrous oxide is emitted when fuels are burned. The
amount of N2O emitted from burning fuels depends on the type of fuel and
combustion technology, maintenance, and operating practices.
•Industry. Nitrous oxide is generated as a byproduct during the
production of nitric acid, which is used to make synthetic commercial
fertilizer, and in the production of adipic acid, which is used to make
fibers, like nylon, and other synthetic products.
Ozone layer depletion
Nitrous oxide also has been implicated in thinning of the ozone layer. A new study suggests that N
2O emission currently is the single most important ozone-depleting substance (ODS) emission and is expected to remain the largest throughout the twenty-first century.
2O emission currently is the single most important ozone-depleting substance (ODS) emission and is expected to remain the largest throughout the twenty-first century.
Legality
In the United States, possession of nitrous oxide is legal under federal law and is not subject to DEA purview. It is, however, regulated by the Food and Drug Administration
under the Food Drug and Cosmetics Act; prosecution is possible under
its "mis-branding" clauses, prohibiting the sale or distribution of
nitrous oxide for the purpose of human consumption.
Many states have laws regulating the possession, sale, and
distribution of nitrous oxide. Such laws usually ban distribution to
minors or limit the amount of nitrous oxide that may be sold without
special license. For example, in the state of California, possession for recreational use is prohibited and qualifies as a misdemeanor.
In August 2015, the Council of the London Borough of Lambeth (UK) banned the use of the drug for recreational purposes, making offenders liable to an on-the-spot fine of up to £1,000.
In New Zealand, the Ministry of Health
has warned that nitrous oxide is a prescription medicine, and its sale
or possession without a prescription, is an offense under the Medicines
Act.
This statement would seemingly prohibit all non-medicinal uses of
nitrous oxide, although it is implied that only recreational use will be
targeted legally.
In India, transfer of nitrous oxide from bulk cylinders to smaller, more transportable E-type, 1590 liter-capacity tanks, is legal when the intended use of the gas is for medical anesthesia.