| Tunguska event | |
|---|---|
Location of the event in Siberia (modern map)
| |
| Event | Explosion in forest area (10–15 megatons of TNT) |
| Time | 30 June 1908 |
| Place | Podkamennaya Tunguska River in Siberia, Russia |
| Effects | Flattening 2,000 km2 (770 sq mi) of forest |
| Damage | Devastation to local plants and animals A few damaged buildings |
| Deaths | 0 confirmed, 3 possible |
| Cause | Probable air burst of small asteroid or comet |
| Coordinates | 60°53′09″N 101°53′40″E |
The Tunguska event was a large explosion that occurred near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River in Yeniseysk Governorate (now Krasnoyarsk Krai), Russia, on the morning of 30 June 1908 (NS). The explosion over the sparsely populated Eastern Siberian Taiga flattened an estimated 80 million trees over an area of 2,150 km2 (830 sq mi) of forest, and eyewitness reports suggest that at least three people may have died in the event. The explosion is generally attributed to the air burst of a meteoroid. It is classified as an impact event, even though no impact crater has been found; the object is thought to have disintegrated at an altitude of 5 to 10 kilometres (3 to 6 miles) rather than to have hit the surface of the Earth.
Due to the remoteness of the site and the limited instrumentation available at the time of the event, modern scientific interpretations of its cause and magnitude have relied chiefly on damage assessments and geological studies conducted many years after the fact. Studies have yielded different estimates of the meteoroid's size, on the order of 50 to 190 metres (160 to 620 feet), depending on whether the body entered with a low or high speed. It is estimated that the shock wave from the air burst would have measured 5.0 on the Richter magnitude scale, and estimates of its energy have ranged from 3–30 megatons of TNT (13–126 petajoules). An explosion of this magnitude would be capable of destroying a large metropolitan area. Since the 1908 event, there have been an estimated 1,000 scholarly papers (most in Russian) published about the Tunguska explosion. In 2013, a team of researchers published the results of an analysis of micro-samples from a peat bog near the center of the affected area which show fragments that may be of meteoritic origin.
The Tunguska event is the largest impact event on Earth in recorded history, though much larger impacts have occurred in prehistoric times. It has been mentioned numerous times in popular culture, and has also inspired real-world discussion of asteroid impact avoidance.
Description
Trees knocked over by the Tunguska blast. Photograph from the Soviet Academy of Science 1927 expedition led by Leonid Kulik.
On 30 June 1908 (cited in Russia as 17 Jun 1908, Julian Calendar, prior to implementation of the Soviet calendar in 1918), at around 07:17 local time, Evenki natives and Russian settlers in the hills northwest of Lake Baikal observed a column of bluish light, nearly as bright as the Sun,
moving across the sky. About ten minutes later, there was a flash and a
sound similar to artillery fire. Eyewitnesses closer to the explosion
reported that the source of the sound moved from the east to the north
of them. The sounds were accompanied by a shock wave that knocked people off their feet and broke windows hundreds of kilometres away.
The explosion registered at seismic stations across Eurasia, and air waves from the blast were detected in Germany, Denmark, Croatia, the United Kingdom, and as far away as Batavia and Washington, D.C. It is estimated that, in some places, the resulting shock wave was equivalent to an earthquake measuring 5.0 on the Richter magnitude scale. Over the next few days, night skies in Asia and Europe were aglow, with contemporaneous reports of photographs being successfully taken at midnight in Sweden and Scotland.
It has been theorized that this effect was due to light passing through
high-altitude ice particles that had formed at extremely low
temperatures—a phenomenon that many years later was reproduced by space shuttles. In the United States, a Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory program at the Mount Wilson Observatory in California observed a months-long decrease in atmospheric transparency consistent with an increase in suspended dust particles.
Selected eyewitness reports
Topi Tunguski, around the area where it fell. This photo is from the magazine Around the World, 1931. The original photo was taken between 1927 and 1930 (presumably no later than 14 September 1930).
Though the region of Siberia in which the explosion occurred was
extremely sparsely populated in 1908, accounts of the event from
eyewitnesses who were in the surrounding area at the time do exist.
Regional newspapers also reported the event shortly after it occurred.
According to the testimony of S. Semenov, as recorded by Russian mineralogist Leonid Kulik's expedition in 1930:
At breakfast time I was sitting by the house at Vanavara Trading Post [approximately 65 kilometres (40 mi) south of the explosion], facing north. […] I suddenly saw that directly to the north, over Onkoul's Tunguska Road, the sky split in two and fire appeared high and wide over the forest [as Semenov showed, about 50 degrees up—expedition note]. The split in the sky grew larger, and the entire northern side was covered with fire. At that moment I became so hot that I couldn't bear it as if my shirt was on fire; from the northern side, where the fire was, came strong heat. I wanted to tear off my shirt and throw it down, but then the sky shut closed, and a strong thump sounded, and I was thrown a few metres. I lost my senses for a moment, but then my wife ran out and led me to the house. After that such noise came, as if rocks were falling or cannons were firing, the Earth shook, and when I was on the ground, I pressed my head down, fearing rocks would smash it. When the sky opened up, hot wind raced between the houses, like from cannons, which left traces in the ground like pathways, and it damaged some crops. Later we saw that many windows were shattered, and in the barn, a part of the iron lock snapped.
Testimony of Chuchan of Shanyagir tribe, as recorded by I. M. Suslov in 1926:
We had a hut by the river with my brother Chekaren. We were sleeping. Suddenly we both woke up at the same time. Somebody shoved us. We heard whistling and felt strong wind. Chekaren said, 'Can you hear all those birds flying overhead?' We were both in the hut, couldn't see what was going on outside. Suddenly, I got shoved again, this time so hard I fell into the fire. I got scared. Chekaren got scared too. We started crying out for father, mother, brother, but no one answered. There was noise beyond the hut, we could hear trees falling down. Chekaren and I got out of our sleeping bags and wanted to run out, but then the thunder struck. This was the first thunder. The Earth began to move and rock, the wind hit our hut and knocked it over. My body was pushed down by sticks, but my head was in the clear. Then I saw a wonder: trees were falling, the branches were on fire, it became mighty bright, how can I say this, as if there was a second sun, my eyes were hurting, I even closed them. It was like what the Russians call lightning. And immediately there was a loud thunderclap. This was the second thunder. The morning was sunny, there were no clouds, our Sun was shining brightly as usual, and suddenly there came a second one!
Chekaren and I had some difficulty getting out from under the remains of our hut. Then we saw that above, but in a different place, there was another flash, and loud thunder came. This was the third thunder strike. Wind came again, knocked us off our feet, struck the fallen trees.
We looked at the fallen trees, watched the tree tops get snapped off, watched the fires. Suddenly Chekaren yelled "Look up" and pointed with his hand. I looked there and saw another flash, and it made another thunder. But the noise was less than before. This was the fourth strike, like normal thunder.
Now I remember well there was also one more thunder strike, but it was small, and somewhere far away, where the Sun goes to sleep.
Sibir newspaper, 2 July 1908:
On the morning of 17th of June, around 9:00, we observed an unusual natural occurrence. In the north Karelinski village [200 verst (213 km (132 mi)) north of Kirensk] the peasants saw to the northwest, rather high above the horizon, some strangely bright (impossible to look at) bluish-white heavenly body, which for 10 minutes moved downwards. The body appeared as a "pipe", i.e., a cylinder. The sky was cloudless, only a small dark cloud was observed in the general direction of the bright body. It was hot and dry. As the body neared the ground (forest), the bright body seemed to smudge, and then turned into a giant billow of black smoke, and a loud knocking (not thunder) was heard as if large stones were falling, or artillery was fired. All buildings shook. At the same time the cloud began emitting flames of uncertain shapes. All villagers were stricken with panic and took to the streets, women cried, thinking it was the end of the world.
The author of these lines was meantime in the forest about 6 versts [6.4 km] north of Kirensk and heard to the north east some kind of artillery barrage, that repeated in intervals of 15 minutes at least 10 times. In Kirensk in a few buildings in the walls facing north-east window glass shook.
Siberian Life newspaper, 27 July 1908:
When the meteorite fell, strong tremors in the ground were observed, and near the Lovat village of the Kansk uezd two strong explosions were heard, as if from large-calibre artillery.
Krasnoyaretz newspaper, 13 July 1908:
Kezhemskoe village. On the 17th an unusual atmospheric event was observed. At 7:43 the noise akin to a strong wind was heard. Immediately afterward a horrific thump sounded, followed by an earthquake that literally shook the buildings as if they were hit by a large log or a heavy rock. The first thump was followed by a second, and then a third. Then the interval between the first and the third thumps was accompanied by an unusual underground rattle, similar to a railway upon which dozens of trains are travelling at the same time. Afterward, for 5 to 6 minutes an exact likeness of artillery fire was heard: 50 to 60 salvoes in short, equal intervals, which got progressively weaker. After 1.5–2 minutes after one of the "barrages" six more thumps were heard, like cannon firing, but individual, loud and accompanied by tremors.
The sky, at the first sight, appeared to be clear. There was no wind and no clouds. Upon closer inspection to the north, i.e. where most of the thumps were heard, a kind of an ashen cloud was seen near the horizon, which kept getting smaller and more transparent and possibly by around 2–3 p.m. completely disappeared.
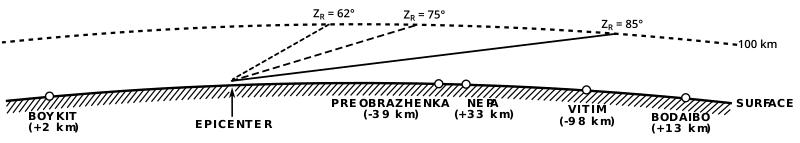
Tunguska's
trajectory and the locations of five villages projected onto a plane
normal to the Earth's surface and passing through the fireball's
approach path. The scale is given by an adopted beginning height of
100 km. Three zenith angles ZR of the apparent radiant are assumed and
the trajectories plotted by the solid, dashed, and dotted lines,
respectively. The parenthesized data are the distances of the locations
from the plane of projection: a plus sign indicates the location is
south-south west of the plane; a minus sign, north-north east of it. The
transliteration of the village names in this figure and the text is
consistent with that of Paper I and differs somewhat from the
transliteration in the current world atlases.
Scientific investigation
It
was not until more than a decade after the event that any scientific
analysis of the region took place, in part due to the isolation of the
area. In 1921, the Russian mineralogist Leonid Kulik led a team to the Podkamennaya Tunguska River basin to conduct a survey for the Soviet Academy of Sciences.
Although they never visited the central blast area, the many local
accounts of the event led Kulik to believe that the explosion had been
caused by a giant meteorite impact.
Upon returning, he persuaded the Soviet government to fund an
expedition to the suspected impact zone, based on the prospect of
salvaging meteoric iron.
Photograph from Kulik's 1929 expedition taken near the Hushmo River
Kulik led a scientific expedition to the Tunguska blast site in 1927. He hired local Evenki hunters to guide his team to the centre of the blast area, where they expected to find an impact crater. To their surprise, there was no crater to be found at ground zero.
Instead they found a zone, roughly 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) across, where
the trees were scorched and devoid of branches, but still standing
upright.
Trees more distant from the center had been partly scorched and knocked
down in a direction away from the center, creating a large radial
pattern of downed trees.
In the 1960s, it was established that the zone of leveled forest occupied an area of 2,150 km2
(830 sq mi), its shape resembling a gigantic spread-eagled butterfly
with a "wingspan" of 70 km (43 mi) and a "body length" of 55 km (34 mi).
Upon closer examination, Kulik located holes that he erroneously
concluded were meteorite holes; he did not have the means at that time
to excavate the holes.
During the following 10 years, there were three more expeditions
to the area. Kulik found several dozens of little "pothole" bogs, each
10 to 50 metres (33 to 164 feet) in diameter, that he thought might be
meteoric craters. After a laborious exercise in draining one of these bogs (the so-called "Suslov's crater", 32 m (105 ft) in diameter), he found an old tree stump
on the bottom, ruling out the possibility that it was a meteoric
crater. In 1938, Kulik arranged for an aerial photographic survey of the
area covering the central part of the leveled forest (250 square kilometres (97 sq mi)).
The original negatives of these aerial photographs (1,500 negatives,
each 18 by 18 centimetres (7.1 by 7.1 inches)) were burned in 1975 by
order of Yevgeny Krinov,
then Chairman of the Committee on Meteorites of the USSR Academy of
Sciences, as part of an initiative to dispose of hazardous nitrate film. Positive prints were preserved for further study in the Russian city of Tomsk.
Expeditions sent to the area in the 1950s and 1960s found microscopic silicate and magnetite
spheres in siftings of the soil. Similar spheres were predicted to
exist in the felled trees, although they could not be detected by
contemporary means. Later expeditions did identify such spheres in the
resin of the trees. Chemical analysis showed that the spheres contained high proportions of nickel relative to iron, which is also found in meteorites,
leading to the conclusion they were of extraterrestrial origin. The
concentration of the spheres in different regions of the soil was also
found to be consistent with the expected distribution of debris from a
meteoroid air burst.
Later studies of the spheres found unusual ratios of numerous other
metals relative to the surrounding environment, which was taken as
further evidence of their extraterrestrial origin.
Chemical analysis of peat bogs from the area also revealed numerous anomalies considered consistent with an impact event. The isotopic signatures
of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen at the layer of the bogs
corresponding to 1908 were found to be inconsistent with the isotopic
ratios measured in the adjacent layers, and this abnormality was not
found in bogs located outside the area. The region of the bogs showing
these anomalous signatures also contains an unusually high proportion of
iridium, similar to the iridium layer found in the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary.
These unusual proportions are believed to result from debris from the
falling body that deposited in the bogs. The nitrogen is believed to
have been deposited as acid rain, a suspected fallout from the explosion.
Researcher John Anfinogenov has suggested that a boulder found at
the event site, known as John's stone, is a remnant of the meteorite, but oxygen isotope analysis of the quartzite suggests that it is of hydrothermal origin, and probably related to Permian-Triassic Siberian Traps magmatism.
Earth impactor model
Comparison of possible sizes of Tunguska (TM mark) and Chelyabinsk (CM) meteoroids to the Eiffel Tower and Empire State Building
The leading scientific explanation for the explosion is the air burst of an asteroid 6–10 km (4–6 mi) above the Earth's surface.
Meteoroids enter Earth's atmosphere from outer space every day, travelling at a speed of at least 11 km/s (7 mi/s). The heat generated by compression of air in front of the body (ram pressure)
as it travels through the atmosphere is immense and most meteoroids
burn up or explode before they reach the ground. Early estimates of the
energy of the Tunguska air burst ranged from 10–15 megatons of TNT (42–63 petajoules) to 30 megatons of TNT (130 PJ), depending on the exact height of the burst as estimated when the scaling laws from the effects of nuclear weapons are employed. More recent calculations that include the effect of the object's momentum
find that more of the energy was focused downward than would be the
case from a nuclear explosion and estimate that the air burst had an
energy range from 3 to 5 megatons of TNT (13 to 21 PJ). The 15-megaton (Mt) estimate represents an energy about 1,000 times greater than that of the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima, Japan, in 1945, and roughly equal to that of the United States' Castle Bravo nuclear test in 1954 (which measured 15.2 Mt) and one-third that of the Soviet Union's Tsar Bomba test in 1961. A 2019 paper suggests the explosive power of the Tunguska event may have been around 20–30 megatons.
Since the second half of the 20th century, close monitoring of
Earth's atmosphere through infrasound and satellite observation has
shown that asteroid air bursts with energies comparable to those of
nuclear weapons routinely occur, although Tunguska-sized events, on the
order of 5–15 megatons, are much rarer. Eugene Shoemaker estimated that 20-kiloton events occur annually and that Tunguska-sized events occur about once every 300 years.
More recent estimates place Tunguska-sized events at about once every
thousand years, with 5-kiloton air bursts averaging about once per year. Most of these air bursts are thought to be caused by asteroid impactors, as opposed to mechanically weaker cometary materials, based on their typical penetration depths into the Earth's atmosphere. The largest asteroid air burst to be observed with modern instrumentation was the 500-kiloton Chelyabinsk meteor in 2013, which shattered windows and produced meteorites.
Blast pattern
The explosion's effect on the trees near the hypocentre of the explosion was similar to the effects of the conventional Operation Blowdown. These effects are caused by the blast wave
produced by large air burst explosions. The trees directly below the
explosion are stripped as the blast wave moves vertically downward, but
remain standing upright, while trees farther away are knocked over
because the blast wave is travelling closer to horizontal when it
reaches them.
Soviet experiments performed in the mid-1960s, with model forests (made of matches
on wire stakes) and small explosive charges slid downward on wires,
produced butterfly-shaped blast patterns similar to the pattern found at
the Tunguska site. The experiments suggested that the object had
approached at an angle of roughly 30 degrees from the ground and 115
degrees from north and had exploded in mid-air.
Asteroid or comet?
In 1930, the British astronomer F. J. W. Whipple suggested that the Tunguska body was a small comet. A comet is composed of dust and volatiles, such as water ice and frozen gases, and could have been completely vaporised
by the impact with Earth's atmosphere, leaving no obvious traces. The
comet hypothesis was further supported by the glowing skies (or
"skyglows" or "bright nights") observed across Eurasia for several
evenings after the impact, which are possibly explained by dust and ice
that had been dispersed from the comet's tail across the upper atmosphere. The cometary hypothesis gained a general acceptance among Soviet Tunguska investigators by the 1960s.
In 1978, Slovak astronomer Ľubor Kresák suggested that the body was a fragment of Comet Encke. This is a periodic comet with an extremely short period of three years that stays entirely within the orbit of Jupiter. It is also responsible for the Beta Taurids, an annual meteor shower with a maximum activity around 28–29 June. The Tunguska event coincided with the peak activity of that shower, and the approximate trajectory of the Tunguska object is consistent with what would be expected from a fragment of Comet Encke.
It is now known that bodies of this kind explode at frequent intervals
tens to hundreds of kilometres above the ground. Military satellites
have been observing these explosions for decades.
During 2019 astronomers searched for hypothesized asteroids ~100 metres
in diameter from the Taurid swarm between 5–11 July, and 21 July – 10
August. However, as of December 2019, there have been no reports of discoveries of any such objects.
In 1983, astronomer Zdeněk Sekanina
published a paper criticising the comet hypothesis. He pointed out that
a body composed of cometary material, travelling through the atmosphere
along such a shallow trajectory, ought to have disintegrated, whereas
the Tunguska body apparently remained intact into the lower atmosphere.
Sekanina argued that the evidence pointed to a dense, rocky object,
probably of asteroidal origin. This hypothesis was further boosted in 2001, when Farinella, Foschini, et al.
released a study calculating the probabilities based on orbital
modelling extracted from the atmospheric trajectories of the Tunguska
object. They concluded with a probability of 83% that the object moved
on an asteroidal path originating from the asteroid belt, rather than on a cometary one (probability of 17%). Proponents of the comet hypothesis have suggested that the object was an extinct comet with a stony mantle that allowed it to penetrate the atmosphere.
The chief difficulty in the asteroid hypothesis is that a stony object should have produced a large crater
where it struck the ground, but no such crater has been found. It has
been hypothesised that the passage of the asteroid through the
atmosphere caused pressures and temperatures to build up to a point
where the asteroid abruptly disintegrated in a huge explosion. The
destruction would have to have been so complete that no remnants of
substantial size survived, and the material scattered into the upper
atmosphere during the explosion would have caused the skyglows. Models
published in 1993 suggested that the stony body would have been about 60
metres (200 ft) across, with physical properties somewhere between an
ordinary chondrite and a carbonaceous chondrite.[citation needed] Typical carbonaceous chondrite substance tends to be dissolved with water rather quickly unless it is frozen.
Christopher Chyba
and others have proposed a process whereby a stony meteorite could have
exhibited the behaviour of the Tunguska impactor. Their models show
that when the forces opposing a body's descent become greater than the
cohesive force holding it together, it blows apart, releasing nearly all
of its energy at once. The result is no crater, with damage distributed
over a fairly wide radius, and all of the damage resulting from the
thermal energy released in the blast.
Three-dimensional numerical modelling of the Tunguska impact done by Utyuzhnikov and Rudenko in 2008
supports the comet hypothesis. According to their results, the comet
matter dispersed in the atmosphere, while the destruction of the forest
was caused by the shock wave.
During the 1990s, Italian researchers, coordinated by the physicist Giuseppe Longo from the University of Bologna, extracted resin
from the core of the trees in the area of impact to examine trapped
particles that were present during the 1908 event. They found high
levels of material commonly found in rocky asteroids and rarely found in
comets.
Kelly et al. (2009) contend that the impact was caused by a comet because of the sightings of noctilucent clouds
following the impact, a phenomenon caused by massive amounts of water
vapor in the upper atmosphere. They compared the noctilucent cloud
phenomenon to the exhaust plume from NASA's Endeavour space shuttle. In 2013, analysis of fragments from the Tunguska site by a joint US-European team was consistent with an iron meteorite.
The February 2013 Chelyabinsk bolide
event provided ample data for scientists to create new models for the
Tunguska event. Researchers used data from both Tunguska and Chelyabinsk
to perform a statistical study of over 50 million combinations of
bolide and entry properties that could produce Tunguska-scale damage
when breaking apart or exploding at similar altitudes. Some models
focused on combinations of properties which created scenarios with
similar effects to the tree fall pattern as well as the atmospheric and
seismic pressure waves of Tunguska. Four different computer models
produced similar results; they concluded that the likeliest candidate
for the Tunguska impactor was a stony body between 50 and 80 m (164 and
262 ft) in diameter, entering the atmosphere at roughly 55,000 km/h
(34,000 mph), exploding at 10 to 14 km (6 to 9 mi) altitude, and
releasing explosive energy equivalent to between 10 and 30 megatons.
This is similar to the blast energy equivalent of the 1980 volcanic eruption of Mount St. Helens. The researchers also concluded impactors of this size only hit the Earth at an average interval scale of millennia.
Lake Cheko
In June 2007, scientists from the University of Bologna
identified a lake in the Tunguska region as a possible impact crater
from the event. They do not dispute that the Tunguska body exploded in
mid-air but believe that a 10-metre (33 ft) fragment survived the
explosion and struck the ground. Lake Cheko is a small, bowl-shaped lake approximately 8 km (5.0 mi) north-northwest of the hypocentre.
The hypothesis has been disputed by other impact crater specialists. A 1961 investigation had dismissed a modern origin of Lake Cheko, saying that the presence of metres-thick silt deposits at the lake's bed suggests an age of at least 5,000 years,
but more recent research suggests that only a metre or so of the
sediment layer on the lake bed is "normal lacustrine sedimentation", a
depth consistent with an age of about 100 years.
Acoustic-echo soundings of the lake floor provide support for the
hypothesis that the lake was formed by the Tunguska event. The soundings
revealed a conical shape for the lake bed, which is consistent with an
impact crater.
Magnetic readings indicate a possible metre-sized chunk of rock below
the lake's deepest point that may be a fragment of the colliding body. Finally, the lake's long axis points to the hypocentre of the Tunguska explosion, about 7.0 km (4.3 mi) away. Work is still being done at Lake Cheko to determine its origins.
The main points of the study are that:
Cheko, a small lake located in Siberia close to the epicentre of the 1908 Tunguska explosion, might fill a crater left by the impact of a fragment of a cosmic body. Sediment cores from the lake's bottom were studied to support or reject this hypothesis. A 175-centimetre-long (69 in) core, collected near the center of the lake, consists of an upper c. 1-metre-thick (39 in) sequence of lacustrine deposits overlaying coarser chaotic material. 210Pb and 137Cs indicate that the transition from lower to upper sequence occurred close to the time of the Tunguska event. Pollen analysis reveals that remains of aquatic plants are abundant in the top post-1908 sequence but are absent in the lower pre-1908 portion of the core. These results, including organic C, N and δ13C data, suggest that Lake Cheko formed at the time of the Tunguska event.
In 2017, new research by Russian scientists pointed to a rejection of
the theory that Lake Cheko was created by the Tunguska event. They used
soil research to prove that the lake is 280 years old or even much
older; in any case clearly older than the Tunguska event.
Geophysical hypotheses
Though
scientific consensus is that the Tunguska explosion was caused by the
impact of a small asteroid, there are some dissenters. Astrophysicist
Wolfgang Kundt has proposed that the Tunguska event was caused by the
release and subsequent explosion of 10 million tons of natural gas from within the Earth's crust.
The basic idea is that natural gas leaked out of the crust and then
rose to its equal-density height in the atmosphere; from there, it
drifted downwind, in a sort of wick, which eventually found an ignition
source such as lightning. Once the gas was ignited, the fire streaked
along the wick, and then down to the source of the leak in the ground,
whereupon there was an explosion.
The similar verneshot hypothesis has also been proposed as a possible cause of the Tunguska event. Other research has supported a geophysical mechanism for the event.
Similar events
The Tunguska event is not the only example of an enormous unobserved explosion event. For example, the 1930 Curuçá River event in Brazil may have been an explosion of a superbolide that left no clear evidence of an impact crater. Modern developments in infrasound detection by the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization and infrared DSP satellite technology have reduced the likelihood of undetected air bursts.
A smaller air burst occurred over a populated area on 15 February 2013, at Chelyabinsk
in the Ural district of Russia. The exploding meteoroid was determined
to have been an asteroid that measured about 17–20 metres (56–66 ft)
across, with an estimated initial mass of 11,000 tonnes and which
exploded with an energy release of approximately 500 kilotons. The air burst inflicted over 1,200 injuries, mainly from broken glass falling from windows shattered by its shock wave.