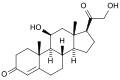
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
11β,21-Dihydroxy-3,20-dioxopregn-4-en-18-al
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.128 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Aldosterone |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C21H28O5 | |
| Molar mass | 360.450 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| H02AA01 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Aldosterone, the main mineralocorticoid hormone, is a steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands and colon. It plays a central role in the homeostatic regulation of blood pressure, plasma sodium (Na+), and potassium (K+) levels. It does so primarily by acting on the mineralocorticoid receptors in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron. It influences the reabsorption of sodium and excretion of potassium (from and into the tubular fluids, respectively) of the kidney, thereby indirectly influencing water retention or loss, blood pressure and blood volume. When dysregulated, aldosterone is pathogenic and contributes to the development and progression of cardiovascular and kidney disease. Aldosterone has exactly the opposite function of the atrial natriuretic hormone secreted by the heart.
Aldosterone is part of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. It has a plasma half-life of under 20 minutes. Drugs that interfere with the secretion or action of aldosterone are in use as antihypertensives, like lisinopril, which lowers blood pressure by blocking the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), leading to lower aldosterone secretion. The net effect of these drugs is to reduce sodium and water retention but increase retention of potassium. In other words, these drugs stimulate the excretion of sodium and water in urine, while they block the excretion of potassium.
Another example is spironolactone, a potassium-sparing diuretic of the steroidal spirolactone group, which interferes with the aldosterone receptor (among others) leading to lower blood pressure by the mechanism described above.
Aldosterone was first isolated by Simpson and Tait in 1953.
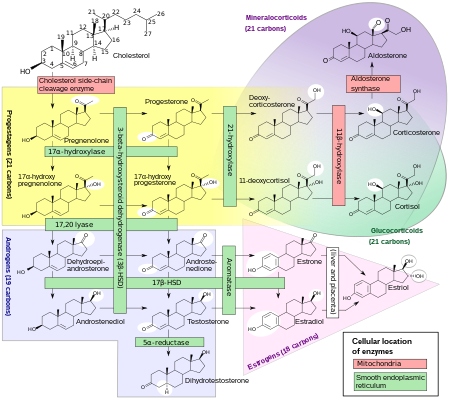
Biosynthesis
The corticosteroids are synthesized from cholesterol within the zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex. Most steroidogenic reactions are catalysed by enzymes of the cytochrome P450 family. They are located within the mitochondria and require adrenodoxin as a cofactor (except 21-hydroxylase and 17α-hydroxylase).
Aldosterone and corticosterone share the first part of their biosynthetic pathways. The last parts are mediated either by the aldosterone synthase (for aldosterone) or by the 11β-hydroxylase (for corticosterone). These enzymes are nearly identical (they share 11β-hydroxylation and 18-hydroxylation functions), but aldosterone synthase is also able to perform an 18-oxidation. Moreover, aldosterone synthase is found within the zona glomerulosa at the outer edge of the adrenal cortex; 11β-hydroxylase is found in the zona glomerulosa and zona fasciculata.
Steroidogenesis, showing aldosterone synthesis at upper-right corner.
Note: aldosterone synthase is absent in other sections of the adrenal gland.
Stimulation
Aldosterone synthesis is stimulated by several factors:
- increase in the plasma concentration of angiotensin III, a metabolite of angiotensin II
- increase in plasma angiotensin II, ACTH, or potassium levels, which are present in proportion to plasma sodium deficiencies. (The increased potassium level works to regulate aldosterone synthesis by depolarizing the cells in the zona glomerulosa, which opens the voltage-dependent calcium channels.) The level of angiotensin II is regulated by angiotensin I, which is in turn regulated by renin, a hormone secreted in the kidneys.
- Serum potassium concentrations are the most potent stimulator of aldosterone secretion.
- the ACTH stimulation test, which is sometimes used to stimulate the production of aldosterone along with cortisol to determine whether primary or secondary adrenal insufficiency is present. However, ACTH has only a minor role in regulating aldosterone production; with hypopituitarism there is no atrophy of the zona glomerulosa.
- plasma acidosis
- the stretch receptors located in the atria of the heart. If decreased blood pressure is detected, the adrenal gland is stimulated by these stretch receptors to release aldosterone, which increases sodium reabsorption from the urine, sweat, and the gut. This causes increased osmolarity in the extracellular fluid, which will eventually return blood pressure toward normal.
- adrenoglomerulotropin, a lipid factor, obtained from pineal extracts. It selectively stimulates secretion of aldosterone.
The secretion of aldosterone has a diurnal rhythm.
Biological function
Aldosterone is the primary of several endogenous members of the class of mineralocorticoids in humans. Deoxycorticosterone is another important member of this class. Aldosterone tends to promote Na+ and water retention, and lower plasma K+ concentration by the following mechanisms:
- Acting on the nuclear mineralocorticoid receptors (MR) within the principal cells of the distal tubule and the collecting duct of the kidney nephron, it upregulates and activates the basolateral Na+/K+ pumps, which pumps three sodium ions out of the cell, into the interstitial fluid and two potassium ions into the cell from the interstitial fluid. This creates a concentration gradient which results in reabsorption of sodium (Na+) ions and water (which follows sodium) into the blood, and secreting potassium (K+) ions into the urine (lumen of collecting duct).
- Aldosterone upregulates epithelial sodium channels (ENaCs) in the collecting duct and the colon, increasing apical membrane permeability for Na+ and thus absorption.
- Cl− is reabsorbed in conjunction with sodium cations to maintain the system's electrochemical balance.
- Aldosterone stimulates the secretion of K+ into the tubular lumen.
- Aldosterone stimulates Na+ and water reabsorption from the gut, salivary and sweat glands in exchange for K+.
- Aldosterone stimulates secretion of H+ via the H+/ATPase in the intercalated cells of the cortical collecting tubules
- Aldosterone upregulates expression of NCC in the distal convoluted tubule chronically and its activity acutely.
Aldosterone is responsible for the reabsorption of about 2% of
filtered sodium in the kidneys, which is nearly equal to the entire
sodium content in human blood under normal glomerular filtration rates.
Aldosterone, probably acting through mineralocorticoid receptors, may positively influence neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus.
Mineralocorticoid receptors
Steroid receptors are intracellular. The aldosterone mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) complex binds on the DNA to specific hormone response element, which leads to gene specific transcription.
Some of the transcribed genes are crucial for transepithelial sodium transport, including the three subunits of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC), the Na+/K+ pumps and their regulatory proteins serum and glucocorticoid-induced kinase, and channel-inducing factor, respectively.
The MR is stimulated by both aldosterone and cortisol, but a
mechanism protects the body from excess aldosterone receptor stimulation
by glucocorticoids (such as cortisol), which happen to be present at
much higher concentrations than mineralocorticoids in the healthy
individual. The mechanism consists of an enzyme called 11 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
(11β-HSD). This enzyme co-localizes with intracellular adrenal steroid
receptors and converts cortisol into cortisone, a relatively inactive
metabolite with little affinity for the MR. Liquorice, which contains glycyrrhetinic acid, can inhibit 11β-HSD and lead to a mineralocorticoid excess syndrome.
Control of aldosterone release from the adrenal cortex
The renin–angiotensin system, showing role of aldosterone between the adrenal glands and the kidneys
Major regulators
The role of the renin–angiotensin system
Angiotensin is involved in regulating aldosterone and is the core regulation.
Angiotensin II acts synergistically with potassium, and the potassium
feedback is virtually inoperative when no angiotensin II is present.
A small portion of the regulation resulting from angiotensin II must
take lace indirectly from decreased blood flow through the liver due to
constriction of capillaries. When the blood flow decreases so does the destruction of aldosterone by liver enzymes.
Although sustained production of aldosterone requires persistent calcium entry through low-voltage-activated Ca2+ channels,
isolated zona glomerulosa cells are considered nonexcitable, with
recorded membrane voltages that are too hyperpolarized to permit Ca2+ channels entry.
However, mouse zona glomerulosa cells within adrenal slices
spontaneously generate membrane potential oscillations of low
periodicity; this innate electrical excitability of zona glomerulosa
cells provides a platform for the production of a recurrent Ca2+ channels signal that can be controlled by angiotensin II and extracellular potassium, the 2 major regulators of aldosterone production. Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels have been detected in the zona glomerulosa of the human adrenal, which suggests that Ca2+ channel blockers may directly influence the adrenocortical biosynthesis of aldosterone in vivo.
The plasma concentration of potassium
The amount of aldosterone secreted is an indirect function of the serum potassium as probably determined by sensors in the carotid artery.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), a pituitary peptide, also has some stimulating effect on aldosterone, probably by stimulating the formation of deoxycorticosterone, a precursor of aldosterone. Aldosterone is increased by blood loss, pregnancy, and possibly by further circumstances such as physical exertion, endotoxin shock, and burns.
Miscellaneous regulators
The role of sympathetic nerves
The
aldosterone production is also affected to one extent or another by
nervous control, which integrates the inverse of carotid artery
pressure, pain, posture, and probably emotion (anxiety, fear, and hostility) (including surgical stress). Anxiety increases aldosterone, which must have evolved because of the time delay involved in migration of aldosterone into the cell nucleus.
Thus, there is an advantage to an animal's anticipating a future need
from interaction with a predator, since too high a serum content of
potassium has very adverse effects on nervous transmission.
The role of baroreceptors
Pressure-sensitive baroreceptors
are found in the vessel walls of nearly all large arteries in the
thorax and neck, but are particularly plentiful in the sinuses of the
carotid arteries and in the arch of the aorta. These specialized
receptors are sensitive to changes in mean arterial pressure. An
increase in sensed pressure results in an increased rate of firing by
the baroreceptors and a negative feedback response, lowering systemic
arterial pressure. Aldosterone release causes sodium and water
retention, which causes increased blood volume, and a subsequent
increase in blood pressure, which is sensed by the baroreceptors.
To maintain normal homeostasis these receptors also detect low blood
pressure or low blood volume, causing aldosterone to be released. This
results in sodium retention in the kidney, leading to water retention
and increased blood volume.
The plasma concentration of sodium
Aldosterone levels vary as an inverse function of sodium intake as sensed via osmotic pressure. The slope of the response of aldosterone to serum potassium is almost independent of sodium intake.
Aldosterone is increased at low sodium intakes, but the rate of
increase of plasma aldosterone as potassium rises in the serum is not
much lower at high sodium intakes than it is at low. Thus, potassium is
strongly regulated at all sodium intakes by aldosterone when the supply
of potassium is adequate, which it usually is in "primitive" diets.
Aldosterone feedback
Feedback
by aldosterone concentration itself is of a nonmorphological character
(that is, other than changes in the cells' number or structure) and is
poor, so the electrolyte feedbacks predominate, short term.
Associated clinical conditions
Hyperaldosteronism is abnormally increased levels of aldosterone, while hypoaldosteronism is abnormally decreased levels of aldosterone.
A measurement of aldosterone in blood may be termed a plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC), which may be compared to plasma renin activity (PRA) as an aldosterone-to-renin ratio.
Hyperaldosteronism
Primary aldosteronism, also known as primary hyperaldosteronism, is characterized by the overproduction of aldosterone by the adrenal glands, when not a result of excessive renin secretion. It leads to arterial hypertension (high blood pressure) associated with hypokalemia, usually a diagnostic clue. Secondary hyperaldosteronism, on the other hand, is due to overactivity of the renin–angiotensin system.
Conn's syndrome is primary hyperaldosteronism caused by an aldosterone-producing adenoma.
Depending on cause and other factors, hyperaldosteronism can be treated by surgery and/or medically, such as by aldosterone antagonists.
The ratio of renin to aldosterone is an effective screening test to screen for primary hyperaldosteronism related to adrenal adenomas. It is the most sensitive serum blood test to differentiate primary from secondary causes of hyperaldosteronism.
Blood obtained when the patient has been standing for more than 2 hours
are more sensitive than those from when the patient is lying down.
Before the test, individuals should not restrict salt and low potassium should be corrected before the test because it can suppress aldosterone secretion.
Hypoaldosteronism
An ACTH stimulation test for aldosterone can help in determining the cause of hypoaldosteronism,
with a low aldosterone response indicating a primary hypoaldosteronism
of the adrenals, while a large response indicating a secondary
hypoaldosteronism.