| Nephrotic syndrome | |
|---|---|
 | |
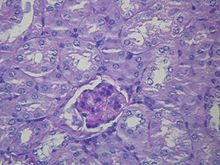
| Microscopic image of diabetic glomerulosclerosis, the main cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults. | |
| Specialty | Nephrology |
| Symptoms | Swelling, weight gain, feeling tired, foamy urine |
| Complications | Blood clots, infections, high blood pressure |
| Causes | Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, membranous nephropathy, minimal change disease, diabetes, lupus |
| Diagnostic method | Urine testing, kidney biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Nephritic syndrome, cirrhosis, severe malnutrition |
| Treatment | Directed at underlying cause |
| Frequency | 5 per 100,000 per year |
Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes protein in the urine, low blood albumin levels, high blood lipids, and significant swelling. Other symptoms may include weight gain, feeling tired, and foamy urine. Complications may include blood clots, infections, and high blood pressure.
Causes include a number of kidney diseases such as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, membranous nephropathy, and minimal change disease. It may also occur as a complication of diabetes or lupus. The underlying mechanism typically involves damage to the glomeruli of the kidney. Diagnosis is typically based on urine testing and sometimes a kidney biopsy. It differs from nephritic syndrome in that there are no red blood cells in the urine.
Treatment is directed at the underlying cause. Other efforts include managing high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and infection risk. A low salt diet and limiting fluids is often recommended. About 5 per 100,000 people are affected per year. The usual underlying cause varies between children and adults.
Signs and symptoms
Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by large amounts of proteinuria (>3.5 g per 1.73 m2 body surface area per day, or > 40 mg per square meter body surface area per hour in children), hypoalbuminemia (< 2.5 g/dl), hyperlipidaemia, and edema that begins in the face. Lipiduria (lipids in urine) can also occur, but is not essential for the diagnosis of nephrotic syndrome. Hyponatremia also occurs with a low fractional sodium excretion.
Hyperlipidaemia is caused by two factors:
- Hypoproteinemia stimulates protein synthesis in the liver, resulting in the overproduction of lipoproteins.
- Lipid catabolism is decreased due to lower levels of lipoprotein lipase, the main enzyme involved in lipoprotein breakdown. Cofactors, such as apolipoprotein C2 may also be lost by increased filtration of proteins.
A few other characteristics seen in nephrotic syndrome are:
- The most common sign is excess fluid
in the body due to the serum hypoalbuminemia. Lower serum oncotic
pressure causes fluid to accumulate in the interstitial tissues. Sodium
and water retention aggravates the edema. This may take several forms:
- Puffiness around the eyes, characteristically in the morning.
- Pitting edema over the legs.
- Fluid in the pleural cavity causing pleural effusion. More commonly associated with excess fluid is pulmonary edema.
- Fluid in the peritoneal cavity causing ascites.
- Generalized edema throughout the body known as anasarca.
- Most of the people with nephrotic syndrome are normotensive but hypertension (rarely) may also occur.
- Anaemia (iron resistant microcytic hypochromic type) maybe present due to transferrin loss.
- Dyspnea may be present due to pleural effusion or due to diaphragmatic compression with ascites.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased due to increased fibrinogen & other plasma contents.
- Some people may notice foamy or frothy urine, due to a lowering of the surface tension by the severe proteinuria. Actual urinary complaints such as haematuria or oliguria are uncommon, though these are seen commonly in nephritic syndrome.
- May have features of the underlying cause, such as the rash associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, or the neuropathy associated with diabetes.
- Examination should also exclude other causes of gross edema—especially the cardiovascular and liver system.
- Muehrcke's nails; white lines (leukonychia) that extend all the way across the nail and lie parallel to the lunula
The main signs of nephrotic syndrome are:
- A proteinuria of greater than 3.5 g /24 h /1.73 m2 (between 3 and 3.5 g/24 h /1.73 m2 is considered to be proteinuria in the nephrotic range) or greater than 40 mg/h/m2 in children. The ratio between urinary concentrations of albumin and creatinine can be used in the absence of a 24-hour urine test for total protein. This coefficient will be greater than 200–400 mg/mmol in nephrotic syndrome. This pronounced loss of proteins is due to an increase in glomerular permeability that allows proteins to pass into the urine instead of being retained in the blood. Under normal conditions a 24-hour urine sample should not exceed 80 milligrams or 10 milligrams per decilitre.
- A hypoalbuminemia of less than 2.5 g/dL, that exceeds the liver clearance level, that is, protein synthesis in the liver is insufficient to increase the low blood protein levels.
- Edema is thought to be caused by two mechanisms. The first being hypoalbuminemia which lowers the oncotic pressure within vessels resulting in hypovolemia and subsequent activation of the renin–angiotensin system and thus retention of sodium and water. Additionally, it is thought that albumin causes a direct effect on the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) on the principal cell that leads to the reabsorption of sodium and water. Nephrotic syndrome edema initially appears in parts of the lower body (such as the legs) and in the eyelids. In the advanced stages it also extends to the pleural cavity and peritoneum (ascites) and can even develop into a generalized anasarca.
- Hyperlipidaemia is caused by an increase in the synthesis of low and very low-density lipoproteins in the liver that are responsible for the transport of cholesterol and triglycerides. There is also an increase in the liver synthesis of cholesterol.
- Thrombophilia, or hypercoagulability, is a greater predisposition for the formation of blood clots that is caused by a decrease in the levels of antithrombin III in the blood due to its loss in urine.
- Lipiduria or loss of lipids in the urine is indicative of glomerular pathology due to an increase in the filtration of lipoproteins.
Complications
Nephrotic syndrome can be associated with a series of complications that can affect an individual's health and quality of life:
- Thromboembolic disorders: particularly those caused by a decrease in blood antithrombin III levels due to leakage. Antithrombin III counteracts the action of thrombin. Thrombosis usually occurs in the kidney veins although it can also occur in arteries. Treatment is with oral anticoagulants (not heparin as heparin acts via anti-thrombin 3 which is lost in the proteinuria so it will be ineffective.) Hypercoagulopathy due to extravasation of fluid from the blood vessels (edema) is also a risk for venous thrombosis.
- Infections: The increased susceptibility of people with nephrotic syndrome to infections can be a result of the leakage of immunoglobulins from the blood, the loss of proteins in general and the presence of oedematous fluid (which acts as a breeding ground for infections). The most common infection is peritonitis, followed by lung, skin and urinary infections, meningoencephalitis and in the most serious cases septicaemia. The most notable of the causative organisms are Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae.
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis can develop where there is ascites present. This is a frequent development in children but very rarely found in adults.
- Acute kidney failure due to hypovolemia: the loss of vascular fluid into the tissues (edema) produces a decreased blood supply to the kidneys that causes a loss of kidney function. Thus it is a tricky task to get rid of excess fluid in the body while maintaining circulatory euvolemia.
- Pulmonary edema: the loss of proteins from blood plasma and the consequent fall in oncotic pressure causes an abnormal accumulation of liquid in the lungs causing hypoxia and dyspnoea.
- Hypothyroidism: deficiency of the thyroglobulin transport protein thyroxin (a glycoprotein that is rich in iodine and is found in the thyroid gland) due to decreased thyroid binding globulin.
- Vitamin D deficiency can occur. Vitamin D binding protein is lost.
- Hypocalcaemia: lack of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (the way that vitamin D is stored in the body). As vitamin D regulates the amount of calcium present in the blood, a decrease in its concentration will lead to a decrease in blood calcium levels. It may be significant enough to cause tetany. Hypocalcaemia may be relative; calcium levels should be adjusted based on the albumin level and ionized calcium levels should be checked.
- Microcytic hypochromic anaemia: iron deficiency caused by the loss of ferritin (compound used to store iron in the body). It is iron-therapy resistant.
- Protein malnutrition: this occurs when the amount of protein that is lost in the urine is greater than that ingested, this leads to a negative nitrogen balance.
- Growth retardation: can occur in cases of relapse or resistance to therapy. Causes of growth retardation are protein deficiency from the loss of protein in urine, anorexia (reduced protein intake), and steroid therapy (catabolism).
- Cushing's syndrome
Causes
Histological
image of a normal kidney glomerulus. It is possible to see a glomerulus
in the centre of the image surrounded by kidney tubules.
Nephrotic syndrome has many causes and may either be the result of a
glomerular disease that can be either limited to the kidney, called primary nephrotic syndrome (primary glomerulonephrosis), or a condition that affects the kidney and other parts of the body, called secondary nephrotic syndrome.
Primary glomerulonephrosis
Primary causes of nephrotic syndrome are usually described by their histology:
- Minimal change disease (MCD): is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in children. It owes its name to the fact that the nephrons appear normal when viewed with an optical microscope as the lesions are only visible using an electron microscope. Another symptom is a pronounced proteinuria.
- Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS): is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults. It is characterized by the appearance of tissue scarring in the glomeruli. The term focal is used as some of the glomeruli have scars, while others appear intact; the term segmental refers to the fact that only part of the glomerulus suffers the damage.
- Membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN): The inflammation of the glomerular membrane causes increased leaking in the kidney. It is not clear why this condition develops in most people, although an auto-immune mechanism is suspected.
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN): is the inflammation of the glomeruli along with the deposit of antibodies in their membranes, which makes filtration difficult.
- Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN): (Usually presents as a nephritic syndrome) A person's glomeruli are present in a crescent moon shape. It is characterized clinically by a rapid decrease in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) by at least 50% over a short period, usually from a few days to 3 months.
They are considered to be "diagnoses of exclusion", i.e. they are diagnosed only after secondary causes have been excluded.
Secondary glomerulonephrosis
Diabetic glomerulonephritis in a person with nephrotic syndrome.
Secondary causes of nephrotic syndrome have the same histologic
patterns as the primary causes, though they may exhibit some difference
suggesting a secondary cause, such as inclusion bodies. They are usually described by the underlying cause.
- Diabetic nephropathy: is a complication that occurs in some diabetics. Excess blood sugar accumulates in the kidney causing them to become inflamed and unable to carry out their normal function. This leads to the leakage of proteins into the urine.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus: this autoimmune disease can affect a number of organs, among them the kidney, due to the deposit of immunocomplexes that are typical to this disease. The disease can also cause lupus nephritis.
- Sarcoidosis: This disease does not usually affect the kidney but, on occasions, the accumulation of inflammatory granulomas (collection of immune cells) in the glomeruli can lead to nephrotic syndrome.
- Syphilis: kidney damage can occur during the secondary stage of this disease (between 2 and 8 weeks from onset).
- Hepatitis B: certain antigens present during hepatitis can accumulate in the kidneys and damage them.
- Sjögren's syndrome: this autoimmune disease causes the deposit of immunocomplexes in the glomeruli, causing them to become inflamed, this is the same mechanism as occurs in systemic lupus erythematosus.
- HIV: the virus's antigens provoke an obstruction in the glomerular capillary's lumen that alters normal kidney function.
- Amyloidosis: the deposit of amyloid substances (proteins with anomalous structures) in the glomeruli modifying their shape and function.
- Multiple myeloma: kidney impairment is caused by the accumulation and precipitation of light chains, which form casts in the distal tubules, resulting in kidney obstruction. In addition, myeloma light chains are also directly toxic on proximal kidney tubules, further adding to kidney dysfunction.
- Vasculitis: inflammation of the blood vessels at a glomerular level impedes the normal blood flow and damages the kidney.
- Cancer: as happens in myeloma, the invasion of the glomeruli by cancerous cells disturbs their normal functioning.
- Genetic disorders: congenital nephrotic syndrome is a rare genetic disorder in which the protein nephrin, a component of the glomerular filtration barrier, is altered.
- Drugs ( e.g. gold salts, penicillin, captopril): gold salts can cause a more or less important loss of proteins in urine as a consequence of metal accumulation. Penicillin is nephrotoxic in people with kidney failure and captopril can aggravate proteinuria.
By histologic pattern
Membranous nephropathy (MN)
- Sjögren's syndrome
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Sarcoidosis
- Drugs (such as corticosteroids, gold, intravenous heroin)
- Malignancy (cancer)
- Bacterial infections, e.g. leprosy & syphilis
- Protozoal infections, e.g. malaria
Minimal change disease (MCD)
- Drugs, especially NSAIDs in the elderly
- Malignancy, especially Hodgkin's lymphoma
- Allergy
- Bee sting
Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis
Genetics
Over 50 mutations are known to be associated with this condition.
Pathophysiology
Drawing of the kidney glomerulus.
The kidney glomerulus filters the blood that arrives at the kidney.
It is formed of capillaries with small pores that allow small molecules
to pass through that have a molecular weight of less than 40,000 Daltons, but not larger macromolecules such as proteins.
In nephrotic syndrome, the glomeruli are affected by an inflammation or a hyalinization (the formation of a homogenous crystalline material within cells) that allows proteins such as albumin, antithrombin or the immunoglobulins to pass through the cell membrane and appear in urine.
Albumin is the main protein in the blood that is able to maintain an oncotic pressure, which prevents the leakage of fluid into the extracellular medium and the subsequent formation of edemas.
As a response to hypoproteinemia the liver commences a compensatory mechanism involving the synthesis of proteins, such as alpha-2 macroglobulin and lipoproteins. An increase in the latter can cause the hyperlipidemia associated with this syndrome.
Diagnosis
Urinalysis will be able to detect high levels of proteins and occasionally microscopic haematuria.
Ultrasound of a kidney with nephrotic syndrome. There is a hyperechoic kidney without demarcation of the cortex and medulla.
Along with obtaining a complete medical history, a series of biochemical
tests are required in order to arrive at an accurate diagnosis that
verifies the presence of the illness. In addition, imaging of the
kidneys (for structure and presence of two kidneys) is sometimes carried
out, and/or a biopsy of the kidneys. The first test will be a
urinalysis to test for high levels of proteins,
as a healthy subject excretes an insignificant amount of protein in
their urine. The test will involve a 24-hour bedside urinary total
protein estimation. The urine sample is tested for proteinuria (>3.5 g per 1.73 m2 per 24 hours). It is also examined for urinary casts, which are more a feature of active nephritis. Next a blood screen, comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) will look for hypoalbuminemia: albumin levels of ≤2.5 g/dL (normal=3.5-5 g/dL). Then a Creatinine Clearance CCr test will evaluate kidney function particularly the glomerular filtration capacity. Creatinine
formation is a result of the breakdown of muscular tissue, it is
transported in the blood and eliminated in urine. Measuring the
concentration of organic compounds in both liquids evaluates the capacity of the glomeruli to filter blood. Electrolytes and urea levels may also be analysed at the same time as creatinine (EUC test) in order to evaluate kidney function.
A lipid profile will also be carried out as high levels of cholesterol (hypercholesterolemia), specifically elevated LDL, usually with concomitantly elevated VLDL, is indicative of nephrotic syndrome.
A kidney biopsy may also be used as a more specific and invasive test method. A study of a sample's anatomical pathology may then allow the identification of the type of glomerulonephritis involved.
However, this procedure is usually reserved for adults as the majority
of children suffer from minimal change disease that has a remission rate
of 95% with corticosteroids.[30] A biopsy is usually only indicated for children that are corticosteroid resistant as the majority suffer from focal and segmental glomeruloesclerosis.
Further investigations are indicated if the cause is not clear including analysis of auto-immune markers (ANA, ASOT, C3, cryoglobulins, serum electrophoresis), or ultrasound of the whole abdomen.
Classification
A broad classification of nephrotic syndrome based on underlying cause:
| Nephrotic syndrome | |||||||||||||||||||
| Primary | Secondary | ||||||||||||||||||
Nephrotic syndrome is often classified histologically:
Differential diagnosis
Some
symptoms that are present in nephrotic syndrome, such as edema and
proteinuria, also appear in other illnesses. Therefore, other
pathologies need to be excluded in order to arrive at a definitive
diagnosis.
- Edema: in addition to nephrotic syndrome there are two other disorders that often present with edema; these are heart failure and liver failure. Congestive heart failure can cause liquid retention in tissues as a consequence of the decrease in the strength of ventricular contractions. The liquid is initially concentrated in the ankles but it subsequently becomes generalized and is called anasarca. People with congestive heart failure also experience an abnormal swelling of the heart cardiomegaly, which aids in making a correct diagnosis. Jugular venous pressure can also be elevated and it might be possible to hear heart murmurs. An echocardiogram is the preferred investigation method for these symptoms. Liver failure caused by cirrhosis, hepatitis and other conditions such as alcoholism, IV drug use or some hereditary diseases can lead to swelling in the lower extremities and the abdominal cavity. Other accompanying symptoms include jaundice, dilated veins over umbilicus (caput medusae), scratch marks (due to widespread itching, known as pruritus), enlarged spleen, spider angiomata, encephalopathy, bruising, nodular liver and anomalies in the liver function tests. Less frequently symptoms associated with the administration of certain pharmaceutical drugs have to be discounted. These drugs promote the retention of liquid in the extremities such as occurs with NSAIs, some antihypertensive drugs, the adrenal corticosteroids and sex hormones.
Acute fluid overload
can cause edema in someone with kidney failure. These people are known
to have kidney failure, and have either drunk too much or missed their
dialysis. In addition, when Metastatic cancer
spreads to the lungs or abdomen it causes effusions and fluid
accumulation due to obstruction of lymphatic vessels and veins, as well
as serous exudation.
- Proteinuria: the loss of proteins from the urine is caused by many pathological agents and infection by these agents has to be ruled out before it can be certain that a person has nephrotic syndrome. Multiple myeloma can cause a proteinuria that is not accompanied by hypoalbuminemia, which is an important aid in making a differential diagnosis; other potential causes of proteinuria include asthenia, weight loss or bone pain. In diabetes mellitus there is an association between increases in glycated hemoglobin levels and the appearance of proteinuria. Other causes are amyloidosis and certain other allergic and infectious diseases.
Treatment
The treatment of nephrotic syndrome can be symptomatic or can directly address the injuries caused to the kidney.
Symptomatic
The objective of this treatment is to treat the imbalances brought about by the illness: edema, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipemia, hypercoagulability and infectious complications.
- Edema: a return to an unswollen state is the prime
objective of this treatment of nephrotic syndrome. It is carried out
through the combination of a number of recommendations:
- Rest: depending on the seriousness of the edema and taking into account the risk of thrombosis caused by prolonged bed rest.
- Medical nutrition therapy: based on a diet with the correct energy intake and balance of proteins that will be used in synthesis processes and not as a source of calories. A total of 35 kcal/kg body weight/day is normally recommended. This diet should also comply with two more requirements: the first is to not consume more than 1 g of protein/kg body weight/ day, as a greater amount could increase the degree of proteinuria and cause a negative nitrogen balance. People are usually recommended lean cuts of meat, fish, and poultry. The second guideline requires that the amount of water ingested is not greater than the level of diuresis. In order to facilitate this the consumption of salt must also be controlled, as this contributes to water retention. It is advisable to restrict the ingestion of sodium to 1 or 2 g/day, which means that salt cannot be used in cooking and salty foods should also be avoided. Foods high in sodium include seasoning blends (garlic salt, Adobo, season salt, etc.) canned soups, canned vegetables containing salt, luncheon meats including turkey, ham, bologna, and salami, prepared foods, fast foods, soy sauce, ketchup, and salad dressings. On food labels, compare milligrams of sodium to calories per serving. Sodium should be less than or equal to calories per serving.
- Medication: The pharmacological treatment of edema is based on diuretic medications (especially loop diuretics, such as furosemide). In severe cases of edema (or in cases with physiological repercussions, such as scrotal, preputial or urethral edema) or in peoeple with one of a number of severe infections (such as sepsis or pleural effusion), the diuretics can be administered intravenously. This occurs where the risk from plasmatic expansion is considered greater than the risk of severe hypovolemia, which can be caused by the strong diuretic action of intravenous treatment. The procedure is the following:
- Analyse haemoglobin and haematocrit levels.
- A solution of 25% albumin is used that is administered for only 4 hours in order to avoid pulmonary edema.
- Haemoglobin and haematocrit levels are analysed again: if the haematocrit value is less than the initial value (a sign of correct expansion) the diuretics are administered for at least 30 minutes. If the haematocrit level is greater than the initial one this is a contraindication for the use of diuretics as they would increase said value.
- It may be necessary to give a person potassium or require a change in dietary habits if the diuretic drug causes hypokalaemia as a side effect.
- Hypoalbuminemia: is treated using the medical nutrition therapy described as a treatment for edema. It includes a moderate intake of foods rich in animal proteins.
- Hyperlipidaemia: depending of the seriousness of the condition it can be treated with medical nutrition therapy as the only treatment or combined with drug therapy. The ingestion of cholesterol should be less than 300 mg/day, which will require a switch to foods that are low in saturated fats. Avoid saturated fats such as butter, cheese, fried foods, fatty cuts of red meat, egg yolks, and poultry skin. Increase unsaturated fat intake, including olive oil, canola oil, peanut butter, avocadoes, fish and nuts. In cases of severe hyperlipidaemia that are unresponsive to nutrition therapy the use of hypolipidemic drugs, may be necessary (these include statins, fibrates and resinous sequesters of bile acids).
- Thrombophilia: low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) may be appropriate for use as a prophylactic in some circumstances, such as in asymptomatic people that have no history of suffering from thromboembolism. When the thrombophilia is such that it leads to the formation of blood clots, heparin is given for at least 5 days along with oral anticoagulants (OAC). During this time and if the prothrombin time is within its therapeutic range (between 2 and 3), it may be possible to suspend the LMWH while maintaining the OACs for at least 6 months.
- Infectious complications: an appropriate course of antibacterial drugs can be taken according to the infectious agent.
In addition to these key imbalances, vitamin D and calcium are also
taken orally in case the alteration of vitamin D causes a severe
hypocalcaemia, this treatment has the goal of restoring physiological
levels of calcium in the person.
- Achieving better blood glucose level control if the person is diabetic.
- Blood pressure control. ACE inhibitors are the drug of choice. Independent of their blood pressure lowering effect, they have been shown to decrease protein loss.
Kidney damage
The treatment of kidney damage may reverse or delay the progression of the disease. Kidney damage is treated by prescribing drugs:
- Corticosteroids: the result is a decrease in the proteinuria and the risk of infection as well as a resolution of the edema. Prednisone is usually prescribed at a dose of 60 mg/m2 of body surface area/day in a first treatment for 4–8 weeks. After this period the dose is reduced to 40 mg/m2
for a further 4 weeks. People suffering a relapse or children are
treated with prednisolone 2 mg/kg/day till urine becomes negative for
protein. Then, 1.5 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks. Frequent relapses treated by: cyclophosphamide or nitrogen mustard or ciclosporin or levamisole. People can respond to prednisone in a number of different ways:
- People with Corticosteroid sensitive or early steroid-responder: the subject responds to the corticosteroids in the first 8 weeks of treatment. This is demonstrated by a strong diuresis and the disappearance of edemas, and also by a negative test for proteinuria in three urine samples taken during the night.
- People with Corticosteroid resistant or late steroid-responder: the proteinuria persists after the 8-week treatment. The lack of response is indicative of the seriousness of the glomerular damage, which could develop into chronic kidney failure.
- People with Corticosteroid intolerant : complications such as hypertension appear, and they gain a lot of weight and can develop aseptic or avascular necrosis of the hip or knee, cataracts and thrombotic phenomena and/or embolisms.
- People with Corticosteroid dependent : proteinuria appears when the dose of corticosteroid is decreased or there is a relapse in the first two weeks after treatment is completed.
The susceptibility testing in vitro to glucocorticoids on the
person's peripheral blood mononuclear cells is associated with the
number of new cases of not optimal clinical responses: the most
sensitive people in vitro have shown a higher number of cases of
corticodependence, while the most resistant people in vitro showed a
higher number of cases of ineffective therapy.
- Immunosupressors (cyclophosphamide): only indicated in recurring nephrotic syndrome in corticosteroid dependent or intolerant people. In the first two cases the proteinuria has to be negated before treatment with the immunosuppressor can begin, which involves a prolonged treatment with prednisone. The negation of the proteinuria indicates the exact moment when treatment with cyclophosphamide can begin. The treatment is continued for 8 weeks at a dose of 3 mg/kg/day, the immunosuppression is halted after this period. In order to be able to start this treatment the person should not be suffering from neutropenia nor anaemia, which would cause further complications. A possible side effect of the cyclophosphamide is alopecia. Complete blood count tests are carried out during the treatment in order to give advance warning of a possible infection.
Prognosis
The
prognosis for nephrotic syndrome under treatment is generally good
although this depends on the underlying cause, the age of the person and
their response to treatment. It is usually good in children, because minimal change disease responds very well to steroids and does not cause chronic kidney failure. Any relapses that occur become less frequent over time; the opposite occurs with mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis, in which the kidney fails within three years of the disease developing, making dialysis necessary and subsequent kidney transplant.
In addition children under the age of 5 generally have a poorer
prognosis than prepubescents, as do adults older than 30 years of age as
they have a greater risk of kidney failure.
Other causes such as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis frequently lead to end stage kidney disease. Factors associated with a poorer prognosis in these cases include level of proteinuria, blood pressure control and kidney function (GFR).
Without treatment nephrotic syndrome has a very bad prognosis especially rapidly progressing glomerulonephritis, which leads to acute kidney failure after a few months.
Epidemiology
Nephrotic syndrome can affect any age, although it is mainly found in adults with a ratio of adults to children of 26 to 1.
The syndrome presents in different ways in the two groups: the most frequent glomerulopathy in children is minimal change disease (66% of cases), followed by focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (8%) and mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis (6%).
In adults the most common disease is mesangiocapillary
glomerulonephritis (30-40%), followed by focal and segmental
glomeruloesclerosis (15-25%) and minimal change disease (20%). The
latter usually presents as secondary and not primary as occurs in
children. Its main cause is diabetic nephropathy. It usually presents in a person from their 40s or 50s.
Of the glomerulonephritis cases approximately 60% to 80% are primary, while the remainder are secondary.
There are also differences in epidemiology between the sexes, the
disease is more common in men than in women by a ratio of 2 to 1.
The epidemiological data also reveals information regarding the most common way that symptoms develop in people with nephrotic syndrome:
spontaneous remission occurs in up to 20% or 30% of cases during the
first year of the illness. However, this improvement is not definitive
as some 50% to 60% of people with Nephrotic syndrome die and / or
develop chronic kidney failure 6 to 14 years after this remission. On
the other hand, between 10% and 20% of people have continuous episodes
of remissions and relapses
without dying or jeopardizing their kidney. The main causes of death
are cardiovascular, as a result of the chronicity of the syndrome, and
thromboembolic accidents.