Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. Trigeneration or combined cooling, heat and power (CCHP) refers to the simultaneous generation of electricity and useful heating and cooling from the combustion of a fuel or a solar heat collector. The terms cogeneration and trigeneration can also be applied to the power systems simultaneously generating electricity, heat, and industrial chemicals (e.g., syngas).
Cogeneration is a more efficient use of fuel because otherwise-wasted heat from electricity generation is put to some productive use. Combined heat and power (CHP) plants recover otherwise wasted thermal energy for heating. This is also called combined heat and power district heating. Small CHP plants are an example of decentralized energy. By-product heat at moderate temperatures (100–180 °C, 212–356 °F) can also be used in absorption refrigerators for cooling.
The supply of high-temperature heat first drives a gas or steam turbine-powered generator. The resulting low-temperature waste heat is then used for water or space heating. At smaller scales (typically below 1 MW), a gas engine or diesel engine may be used. Trigeneration differs from cogeneration in that the waste heat is used for both heating and cooling, typically in an absorption refrigerator. Combined cooling, heat, and power systems can attain higher overall efficiencies than cogeneration or traditional power plants. In the United States, the application of trigeneration in buildings is called building cooling, heating, and power. Heating and cooling output may operate concurrently or alternately depending on need and system construction.
Cogeneration was practiced in some of the earliest installations of electrical generation. Before central stations distributed power, industries generating their own power used exhaust steam for process heating. Large office and apartment buildings, hotels, and stores commonly generated their own power and used waste steam for building heat. Due to the high cost of early purchased power, these CHP operations continued for many years after utility electricity became available.
Overview
Many process industries, such as chemical plants, oil refineries and pulp and paper mills, require large amounts of process heat for such operations as chemical reactors, distillation columns, steam driers and other uses. This heat, which is usually used in the form of steam, can be generated at the typically low pressures used in heating, or can be generated at much higher pressure and passed through a turbine first to generate electricity. In the turbine the steam pressure and temperature is lowered as the internal energy of the steam is converted to work. The lower-pressure steam leaving the turbine can then be used for process heat.
Steam turbines at thermal power stations are normally designed to be fed high-pressure steam, which exits the turbine at a condenser operating a few degrees above ambient temperature and at a few millimeters of mercury absolute pressure. (This is called a condensing turbine.) For all practical purposes this steam has negligible useful energy before it is condensed. Steam turbines for cogeneration are designed for extraction of some steam at lower pressures after it has passed through a number of turbine stages, with the un-extracted steam going on through the turbine to a condenser. In this case, the extracted steam causes a mechanical power loss in the downstream stages of the turbine. Or they are designed, with or without extraction, for final exhaust at back pressure (non-condensing). The extracted or exhaust steam is used for process heating. Steam at ordinary process heating conditions still has a considerable amount of enthalpy that could be used for power generation, so cogeneration has an opportunity cost.
A typical power generation turbine in a paper mill may have extraction pressures of 160 psig (1.103 MPa) and 60 psig (0.41 MPa). A typical back pressure may be 60 psig (0.41 MPa). In practice these pressures are custom designed for each facility. Conversely, simply generating process steam for industrial purposes instead of high enough pressure to generate power at the top end also has an opportunity cost. The capital and operating cost of high-pressure boilers, turbines, and generators is substantial. This equipment is normally operated continuously, which usually limits self-generated power to large-scale operations.
A combined cycle (in which several thermodynamic cycles produce electricity), may also be used to extract heat using a heating system as condenser of the power plant's bottoming cycle. For example, the RU-25 MHD generator in Moscow heated a boiler for a conventional steam powerplant, whose condensate was then used for space heat. A more modern system might use a gas turbine powered by natural gas, whose exhaust powers a steam plant, whose condensate provides heat. Cogeneration plants based on a combined cycle power unit can have thermal efficiencies above 80%.
The viability of CHP (sometimes termed utilisation factor), especially in smaller CHP installations, depends on a good baseload of operation, both in terms of an on-site (or near site) electrical demand and heat demand. In practice, an exact match between the heat and electricity needs rarely exists. A CHP plant can either meet the need for heat (heat driven operation) or be run as a power plant with some use of its waste heat, the latter being less advantageous in terms of its utilisation factor and thus its overall efficiency. The viability can be greatly increased where opportunities for trigeneration exist. In such cases, the heat from the CHP plant is also used as a primary energy source to deliver cooling by means of an absorption chiller.
CHP is most efficient when heat can be used on-site or very close to it. Overall efficiency is reduced when the heat must be transported over longer distances. This requires heavily insulated pipes, which are expensive and inefficient; whereas electricity can be transmitted along a comparatively simple wire, and over much longer distances for the same energy loss.
A car engine becomes a CHP plant in winter when the reject heat is useful for warming the interior of the vehicle. The example illustrates the point that deployment of CHP depends on heat uses in the vicinity of the heat engine.
Thermally enhanced oil recovery (TEOR) plants often produce a substantial amount of excess electricity. After generating electricity, these plants pump leftover steam into heavy oil wells so that the oil will flow more easily, increasing production. TEOR cogeneration plants in Kern County, California produce so much electricity that it cannot all be used locally and is transmitted to Los Angeles.
CHP is one of the most cost-efficient methods of reducing carbon emissions from heating systems in cold climates and is recognized to be the most energy efficient method of transforming energy from fossil fuels or biomass into electric power. Cogeneration plants are commonly found in district heating systems of cities, central heating systems of larger buildings (e.g. hospitals, hotels, prisons) and are commonly used in the industry in thermal production processes for process water, cooling, steam production or CO2 fertilization.
Types of plants
Topping cycle plants primarily produce electricity from a steam turbine. Partly expanded steam is then condensed in a heating condensor at a temperature level that is suitable e.g. district heating or water desalination.
Bottoming cycle plants produce high temperature heat for industrial processes, then a waste heat recovery boiler feeds an electrical plant. Bottoming cycle plants are only used in industrial processes that require very high temperatures such as furnaces for glass and metal manufacturing, so they are less common.
Large cogeneration systems provide heating water and power for an industrial site or an entire town. Common CHP plant types are:
- Gas turbine CHP plants using the waste heat in the flue gas of gas turbines. The fuel used is typically natural gas.
- Gas engine CHP plants use a reciprocating gas engine, which is generally more competitive than a gas turbine up to about 5 MW. The gaseous fuel used is normally natural gas. These plants are generally manufactured as fully packaged units that can be installed within a plantroom or external plant compound with simple connections to the site's gas supply, electrical distribution network and heating systems. Typical outputs and efficiences see Typical large example see
- Biofuel engine CHP plants use an adapted reciprocating gas engine or diesel engine, depending upon which biofuel is being used, and are otherwise very similar in design to a Gas engine CHP plant. The advantage of using a biofuel is one of reduced hydrocarbon fuel consumption and thus reduced carbon emissions. These plants are generally manufactured as fully packaged units that can be installed within a plantroom or external plant compound with simple connections to the site's electrical distribution and heating systems. Another variant is the wood gasifier CHP plant whereby a wood pellet or wood chip biofuel is gasified in a zero oxygen high temperature environment; the resulting gas is then used to power the gas engine.
- Combined cycle power plants adapted for CHP
- Molten-carbonate fuel cells and solid oxide fuel cells have a hot exhaust, very suitable for heating.
- Steam turbine CHP plants that use the heating system as the steam condenser for the steam turbine
- Nuclear power plants,
similar to other steam turbine power plants, can be fitted with
extractions in the turbines to bleed partially expanded steam to a
heating system. With a heating system temperature of 95 °C it is
possible to extract about 10 MW heat for every MW electricity lost. With
a temperature of 130 °C the gain is slightly smaller, about 7 MW for
every MWe lost. A review of cogeneration options is in.
Smaller cogeneration units may use a reciprocating engine or Stirling engine. The heat is removed from the exhaust and radiator. The systems are popular in small sizes because small gas and diesel engines are less expensive than small gas- or oil-fired steam-electric plants.
Some cogeneration plants are fired by biomass, or industrial and municipal solid waste (see incineration). Some CHP plants utilize waste gas as the fuel for electricity and heat generation. Waste gases can be gas from animal waste, landfill gas, gas from coal mines, sewage gas, and combustible industrial waste gas.
Some cogeneration plants combine gas and solar photovoltaic generation to further improve technical and environmental performance. Such hybrid systems can be scaled down to the building level[15] and even individual homes.
MicroCHP
Micro combined heat and power or 'Micro cogeneration" is a so-called distributed energy resource (DER). The installation is usually less than 5 kWe in a house or small business. Instead of burning fuel to merely heat space or water, some of the energy is converted to electricity in addition to heat. This electricity can be used within the home or business or, if permitted by the grid management, sold back into the electric power grid.
Delta-ee consultants stated in 2013 that with 64% of global sales the fuel cell micro-combined heat and power passed the conventional systems in sales in 2012. 20.000 units were sold in Japan in 2012 overall within the Ene Farm project. With a Lifetime of around 60,000 hours. For PEM fuel cell units, which shut down at night, this equates to an estimated lifetime of between ten and fifteen years. For a price of $22,600 before installation. For 2013 a state subsidy for 50,000 units is in place.
MicroCHP installations use five different technologies: microturbines, internal combustion engines, stirling engines, closed-cycle steam engines, and fuel cells. One author indicated in 2008 that MicroCHP based on Stirling engines is the most cost-effective of the so-called microgeneration technologies in abating carbon emissions. A 2013 UK report from Ecuity Consulting stated that MCHP is the most cost-effective method of using gas to generate energy at the domestic level. However, advances in reciprocation engine technology are adding efficiency to CHP plants, particularly in the biogas field. As both MiniCHP and CHP have been shown to reduce emissions they could play a large role in the field of CO2 reduction from buildings, where more than 14% of emissions can be saved using CHP in buildings. The University of Cambridge reported a cost-effective steam engine MicroCHP prototype in 2017 which has the potential to be commercially competitive in the following decades.
Quite recently, in some private homes, fuel cell micro-CHP plants can now be found, which can operate on hydrogen, or other fuels as natural gas or LPG. When running on natural gas, it relies on steam reforming of natural gas to convert the natural gas to hydrogen prior to use in the fuel cell. This hence still emits CO
2
(see reaction) but (temporarily) running on this can be a good solution
until the point where the hydrogen is starting to be become distributed
through the (natural gas) piping system.
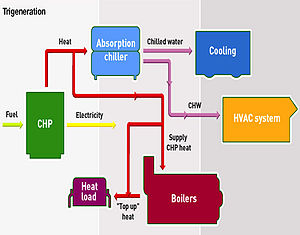
Trigeneration
A plant producing electricity, heat and cold is called a trigeneration or polygeneration plant. Cogeneration systems linked to absorption chillers or adsorption chillers use waste heat for refrigeration.
Combined heat and power district heating
In the United States, Consolidated Edison distributes 66 billion kilograms of 350 °F (180 °C) steam each year through its seven cogeneration plants to 100,000 buildings in Manhattan—the biggest steam district in the United States. The peak delivery is 10 million pounds per hour (or approximately 2.5 GW).
Industrial CHP
Cogeneration is still common in pulp and paper mills, refineries and chemical plants. In this "industrial cogeneration/CHP", the heat is typically recovered at higher temperatures (above 100 deg C) and used for process steam or drying duties. This is more valuable and flexible than low-grade waste heat, but there is a slight loss of power generation. The increased focus on sustainability has made industrial CHP more attractive, as it substantially reduces carbon footprint compared to generating steam or burning fuel on-site and importing electric power from the grid.
Utility pressures versus self generated industrial
Industrial cogeneration plants normally operate at much lower boiler pressures than utilities. Among the reasons are: 1) Cogeneration plants face possible contamination of returned condensate. Because boiler feed water from cogeneration plants has much lower return rates than 100% condensing power plants, industries usually have to treat proportionately more boiler make up water. Boiler feed water must be completely oxygen free and de-mineralized, and the higher the pressure the more critical the level of purity of the feed water. 2) Utilities are typically larger scale power than industry, which helps offset the higher capital costs of high pressure. 3) Utilities are less likely to have sharp load swings than industrial operations, which deal with shutting down or starting up units that may represent a significant percent of either steam or power demand.
Heat recovery steam generators
A heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) is a steam boiler that uses hot exhaust gases from the gas turbines or reciprocating engines in a CHP plant to heat up water and generate steam. The steam, in turn, drives a steam turbine or is used in industrial processes that require heat.
HRSGs used in the CHP industry are distinguished from conventional steam generators by the following main features:
- The HRSG is designed based upon the specific features of the gas turbine or reciprocating engine that it will be coupled to.
- Since the exhaust gas temperature is relatively low, heat transmission is accomplished mainly through convection.
- The exhaust gas velocity is limited by the need to keep head losses down. Thus, the transmission coefficient is low, which calls for a large heating surface area.
- Since the temperature difference between the hot gases and the fluid to be heated (steam or water) is low, and with the heat transmission coefficient being low as well, the evaporator and economizer are designed with plate fin heat exchangers.
Cogeneration using biomass
Biomass is emerging as one of the most important sources of renewable energy. Biomass refers to any plant or animal matter in which it is possible to be reused as a source of heat or electricity, such as sugarcane, vegetable oils, wood, organic waste and residues from the food or agricultural industries. Brazil is now considered a world reference in terms of energy generation from biomass.
A growing sector in the use of biomass for power generation is the sugar and alcohol sector, which mainly uses sugarcane bagasse as fuel for thermal and electric power generation
Power cogeneration in the sugar and alcohol sector
In the sugarcane industry, cogeneration is fuelled by the bagasse residue of sugar refining, which is burned to produce steam. Some steam can be sent through a turbine that turns a generator, producing electric power.
Energy cogeneration in sugarcane industries located in Brazil is a practice that has been growing in last years. With the adoption of energy cogeneration in the sugar and alcohol sector, the sugarcane industries are able to supply the electric energy demand needed to operate, and generate a surplus that can be commercialized.
Advantages of the cogeneration using sugarcane bagasse
In comparison with the electric power generation by means of fossil fuel-based thermoelectric plants, such as natural gas, the energy generation using sugarcane bagasse has environmental advantages due to the reduction of CO2 emissions.
In addition to the environmental advantages, cogeneration using sugarcane bagasse presents advantages in terms of efficiency comparing to thermoelectric generation, through the final destination of the energy produced. While in thermoelectric generation, part of the heat produced is lost, in cogeneration this heat has the possibility of being used in the production processes, increasing the overall efficiency of the process.[38]
Disadvantages of the cogeneration using sugarcane bagasse
In sugarcane cultivation, is usually used potassium source's containing high concentration of chlorine, such as potassium chloride (KCl). Considering that KCl is applied in huge quantities, sugarcane ends up absorbing high concentrations of chlorine.[39]
Due to this absorption, when the sugarcane bagasse is burned in the power cogeneration, dioxins [39] and methyl chloride [40] ends up being emitted. In the case of dioxins, these substances are considered very toxic and cancerous.[41][42][43]
In the case of methyl chloride, when this substance is emitted and reaches the stratosphere, it ends up being very harmful for the ozone layer, since chlorine when combined with the ozone molecule generates a catalytic reaction leading to the breakdown of ozone links.[40]
After each reaction, chlorine starts a destructive cycle with another ozone molecule. In this way, a single chlorine atom can destroy thousands of ozone molecules. As these molecules are being broken, they are unable to absorb the ultraviolet rays. As a result, the UV radiation is more intense on Earth and there is a worsening of global warming.[40]
Comparison with a heat pump
A heat pump may be compared with a CHP unit as follows. If, to supply thermal energy, the exhaust steam from the turbo-generator must be taken at a higher temperature than the system would produce most electricity at, the lost electrical generation is as if a heat pump were used to provide the same heat by taking electrical power from the generator running at lower output temperature and higher efficiency.[44] Typically for every unit of electrical power lost, then about 6 units of heat are made available at about 90 °C. Thus CHP has an effective Coefficient of Performance (COP) compared to a heat pump of 6.[45] However, for a remotely operated heat pump, losses in the electrical distribution network would need to be considered, of the order of 6%. Because the losses are proportional to the square of the current, during peak periods losses are much higher than this and it is likely that widespread (i.e. citywide application of heat pumps) would cause overloading of the distribution and transmission grids unless they were substantially reinforced.
It is also possible to run a heat driven operation combined with a heat pump, where the excess electricity (as heat demand is the defining factor on utilization) is used to drive a heat pump. As heat demand increases, more electricity is generated to drive the heat pump, with the waste heat also heating the heating fluid.
Distributed generation
Most industrial countries generate the majority of their electrical power needs in large centralized facilities with capacity for large electrical power output. These plants benefit from economy of scale, but may need to transmit electricity across long distances causing transmission losses. Cogeneration or trigeneration production is subject to limitations in the local demand and thus may sometimes need to reduce (e.g., heat or cooling production to match the demand). An example of cogeneration with trigeneration applications in a major city is the New York City steam system.
Thermal efficiency
Every heat engine is subject to the theoretical efficiency limits of the Carnot cycle or subset Rankine cycle in the case of steam turbine power plants or Brayton cycle in gas turbine with steam turbine plants. Most of the efficiency loss with steam power generation is associated with the latent heat of vaporization of steam that is not recovered when a turbine exhausts its low temperature and pressure steam to a condenser. (Typical steam to condenser would be at a few millimeters absolute pressure and on the order of 5 °C/11 °F hotter than the cooling water temperature, depending on the condenser capacity.) In cogeneration this steam exits the turbine at a higher temperature where it may be used for process heat, building heat or cooling with an absorption chiller. The majority of this heat is from the latent heat of vaporization when the steam condenses.
Thermal efficiency in a cogeneration system is defined as:
Where:
- = Thermal efficiency
- = Total work output by all systems
- = Total heat input into the system
Heat output may also be used for cooling (for example, in summer), thanks to an absorption chiller. If cooling is achieved in the same time, thermal efficiency in a trigeneration system is defined as:
Where:
- = Thermal efficiency
- = Total work output by all systems
- = Total heat input into the system
Typical cogeneration models have losses as in any system. The energy distribution below is represented as a percent of total input energy:
- Electricity = 45%
- Heat + Cooling = 40%
- Heat losses = 13%
- Electrical line losses = 2%
Conventional central coal- or nuclear-powered power stations convert about 33-45% of their input heat to electricity. Brayton cycle power plants operate at up to 60% efficiency. In the case of conventional power plants, approximately 10-15% of this heat is lost up the stack of the boiler. Most of the remaining heat emerges from the turbines as low-grade waste heat with no significant local uses, so it is usually rejected to the environment, typically to cooling water passing through a condenser. Because turbine exhaust is normally just above ambient temperature, some potential power generation is sacrificed in rejecting higher-temperature steam from the turbine for cogeneration purposes.
For cogeneration to be practical power generation and end use of heat must be in relatively close proximity (<2 km typically). Even though the efficiency of a small distributed electrical generator may be lower than a large central power plant, the use of its waste heat for local heating and cooling can result in an overall use of the primary fuel supply as great as 80%. This provides substantial financial and environmental benefits.
Costs
Typically, for a gas-fired plant the fully installed cost per kW electrical is around £400/kW (US$577), which is comparable with large central power stations.
History
Cogeneration in Europe
The EU has actively incorporated cogeneration into its energy policy via the CHP Directive. In September 2008 at a hearing of the European Parliament's Urban Lodgment Intergroup, Energy Commissioner Andris Piebalgs is quoted as saying, “security of supply really starts with energy efficiency.” Energy efficiency and cogeneration are recognized in the opening paragraphs of the European Union's Cogeneration Directive 2004/08/EC. This directive intends to support cogeneration and establish a method for calculating cogeneration abilities per country. The development of cogeneration has been very uneven over the years and has been dominated throughout the last decades by national circumstances.
The European Union generates 11% of its electricity using cogeneration. However, there is large difference between Member States with variations of the energy savings between 2% and 60%. Europe has the three countries with the world's most intensive cogeneration economies: Denmark, the Netherlands and Finland. Of the 28.46 TWh of electrical power generated by conventional thermal power plants in Finland in 2012, 81.80% was cogeneration.
Other European countries are also making great efforts to increase efficiency. Germany reported that at present, over 50% of the country's total electricity demand could be provided through cogeneration. So far, Germany has set the target to double its electricity cogeneration from 12.5% of the country's electricity to 25% of the country's electricity by 2020 and has passed supporting legislation accordingly. The UK is also actively supporting combined heat and power. In light of UK's goal to achieve a 60% reduction in carbon dioxide emissions by 2050, the government has set the target to source at least 15% of its government electricity use from CHP by 2010. Other UK measures to encourage CHP growth are financial incentives, grant support, a greater regulatory framework, and government leadership and partnership.
According to the IEA 2008 modeling of cogeneration expansion for the G8 countries, the expansion of cogeneration in France, Germany, Italy and the UK alone would effectively double the existing primary fuel savings by 2030. This would increase Europe's savings from today's 155.69 Twh to 465 Twh in 2030. It would also result in a 16% to 29% increase in each country's total cogenerated electricity by 2030.
Governments are being assisted in their CHP endeavors by organizations like COGEN Europe who serve as an information hub for the most recent updates within Europe's energy policy. COGEN is Europe's umbrella organization representing the interests of the cogeneration industry.
The European public–private partnership Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Joint Undertaking Seventh Framework Programme project ene.field deploys in 2017 up 1,000 residential fuel cell Combined Heat and Power (micro-CHP) installations in 12 states. Per 2012 the first 2 installations have taken place.
Cogeneration in the United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, the Combined Heat and Power Quality Assurance scheme regulates the combined production of heat and power. It was introduced in 1996. It defines, through calculation of inputs and outputs, "Good Quality CHP" in terms of the achievement of primary energy savings against conventional separate generation of heat and electricity. Compliance with Combined Heat and Power Quality Assurance is required for cogeneration installations to be eligible for government subsidies and tax incentives.
Cogeneration in the United States
Perhaps the first modern use of energy recycling was done by Thomas Edison. His 1882 Pearl Street Station, the world's first commercial power plant, was a combined heat and power plant, producing both electricity and thermal energy while using waste heat to warm neighboring buildings. Recycling allowed Edison's plant to achieve approximately 50 percent efficiency.
By the early 1900s, regulations emerged to promote rural electrification through the construction of centralized plants managed by regional utilities. These regulations not only promoted electrification throughout the countryside, but they also discouraged decentralized power generation, such as cogeneration.
By 1978, Congress recognized that efficiency at central power plants had stagnated and sought to encourage improved efficiency with the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA), which encouraged utilities to buy power from other energy producers.
Cogeneration plants proliferated, soon producing about 8% of all energy in the United States. However, the bill left implementation and enforcement up to individual states, resulting in little or nothing being done in many parts of the country.
The United States Department of Energy has an aggressive goal of having CHP constitute 20% of generation capacity by the year 2030. Eight Clean Energy Application Centers have been established across the nation. Their mission is to develop the required technology application knowledge and educational infrastructure necessary to lead "clean energy" (combined heat and power, waste heat recovery, and district energy) technologies as viable energy options and reduce any perceived risks associated with their implementation. The focus of the Application Centers is to provide an outreach and technology deployment program for end users, policymakers, utilities, and industry stakeholders.
High electric rates in New England and the Middle Atlantic make these areas of the United States the most beneficial for cogeneration.