A camera phone is a mobile phone which is able to capture photographs and often record video using one or more built-in digital cameras. It can also send the resulting image wirelessly and conveniently. The first color commercial camera phone was the Kyocera Visual Phone VP-210, released in Japan in May 1999.
Most camera phones are smaller and simpler than the separate digital cameras. In the smartphone era, the steady sales increase of camera phones caused point-and-shoot camera sales to peak about 2010 and decline thereafter. The concurrent improvement of smartphone camera technology, and its other multifunctional benefits, have led to it gradually replacing compact point-and-shoot cameras.
Most modern smartphones only have a menu choice to start a camera application program and an on-screen button to activate the shutter. Some also have a separate camera button, for quickness and convenience. Few mobile phones such as the 2009 Samsung i8000 Omnia II have a two-level shutter button to resemble the point-and-shoot intuition from dedicated digital cameras. A few camera phones are designed to resemble separate low-end digital compact cameras in appearance and to some degree in features and picture quality, and are branded as both mobile phones and cameras - an example being Samsung Galaxy S4 Zoom.
The principal advantages of camera phones are cost and compactness; indeed for a user who carries a mobile phone anyway, the addition is negligible. Smartphones that are camera phones may run mobile applications to add capabilities such as geotagging and image stitching. Also, modern smartphones can use their touch screens to direct their camera to focus on a particular object in the field of view, giving even an inexperienced user a degree of focus control exceeded only by seasoned photographers using manual focus. However, the touch screen, being a general purpose control, lacks the agility of a separate camera's dedicated buttons and dial(s).
Starting in the mid-2010s, some advanced camera phones feature optical image stabilisation (OIS), larger sensors, bright lenses, 4K video and even optical zoom, for which a few use a physical zoom lens. Multiple lenses and multi-shot night modes are also familiar. Since the late 2010s, high-end smartphones typically have multiple lenses with different functions, to make more use of a device's limited physical space. Common lens functions include an ultrawide sensor, a telephoto sensor, a macro sensor, and a depth sensor. Some phone cameras have a label that indicates the lens manufacturer, megapixel count, or features such as autofocus or zoom ability for emphasis, including the Samsung Omnia II (2009), Samsung Galaxy S II (2011), Sony Xperia Z1 (2013) and some successors, Nokia Lumia 1020 (2013), and the Samsung Galaxy S20 (2020).
Technology
Camera
Mobile phone cameras typically feature CMOS active-pixel image sensors (CMOS sensors) due to largely reduced power consumption compared to charge-coupled device (CCD) type cameras, which few camera phones use. Some use CMOS back-illuminated sensors, which use even less energy, at higher price than CMOS and CCD.
The usual fixed-focus lenses and smaller sensors limit performance in poor lighting. Lacking a physical shutter, some have a long shutter lag. Photoflash by the typical internal LED source illuminates less intensely over a much longer exposure time than a flash strobe, and none has a hot shoe for attaching an external flash. Optical zoom and tripod screws are rare and some also lack a USB connection or a removable memory card. Most have Bluetooth and WiFi, and can make geotagged photographs. Some of the more expensive camera phones have only a few of these technical disadvantages, but with bigger image sensors (a few are up to 1", such as the Panasonic Lumix DMC-CM1), their capabilities approach those of low-end point-and-shoot cameras. The few hybrid camera phones such as Samsung Galaxy S4 Zoom and K Zoom were equipped with real optical zoom lenses.
As camera phone technology has progressed, lens design has evolved from a simple double Gauss or Cooke triplet to many molded plastic aspheric lens elements made with varying dispersion and refractive indexes. Some phone cameras also apply distortion (optics), vignetting, and various optical aberration corrections to the image before it is compressed into a jpeg format.
Few smartphones such as LG initially with the 2014 G3 are equipped with a time-of-flight camera with infrared laser beam assisted auto focus. A thermal imaging camera has initially been implemented in 2016 on the Caterpillar S60.
High dynamic range imaging merges multiple images with different exposure values for a balanced brightness across the image and was first implemented in early 2010s smartphones such as the Samsung Galaxy S III and iPhone 5. The earliest known smartphone to feature high dynamic range filming is the Sony Xperia Z, 2013, where frames are arrayed by changing the exposure every two lines of pixels to create a spatially varying exposure (SVE).
As of 2019, high-end camera phones can also produce advance video with capability up to 4K at 60 frames per second for smoothness.
Zooming
Most camera phones have a digital zoom feature, which may allow zooming without quality loss if a lower resolution than the highest image sensor resolution is selected, as it makes use of image sensors' spare resolution. For example, at twice digital zoom, only a quarter of the image sensor resolution is available. A few have optical zoom, and several have a few cameras with different field of view, combined with digital zoom as a hybrid zoom feature. For example, the Huawei P30 Pro uses a "periscope" 5x telephoto camera with up to 10x digital zoom, resulting in 50x hybrid zoom. An external camera can be added, coupled wirelessly to the phone by Wi-Fi. They are compatible with most smartphones. Windows Phones can be configured to operate as a camera even if the phone is asleep.
Physical location
When viewed vertically from behind, the rear camera module on some mobile phones is located in the top center, while other mobile phones have cameras located in the upper left corner. The latter has benefits in terms of ergonomy due to the lower likelihood of covering and soiling the lens when held horizontally, as well as more efficient packing of tight physical device space due to neighbouring components not having to be built around the lens.
Image format and mode
Images are usually saved in the JPEG file format. Since the mid-2010s, some high-end camera phones have a RAW photography feature, HDR, and "Bokeh mode". Phones with Android 5.0 Lollipop and later versions can install phone apps that provide similar features.
Audio recording
Mobile phones with multiple microphones usually allow video recording with stereo audio. Samsung, Sony, and HTC initially implemented it in 2012 on their Samsung Galaxy S3, Sony Xperia S, and HTC One X. Apple implemented stereo audio starting with the 2018 iPhone Xs family and iPhone XR.
Files and directories
Like dedicated (stand-alone) digital cameras, mobile phone camera software usually stores pictures and video files in a directory called DCIM/ in the internal memory, with numbered or dated file names. The former prevents missing out files during file transfers and facilitates counting files, while the latter facilitates searching files by date/time, regardless of file attribute resets during transfer and possible lack of in-file metadata date/time information .
Some can store this media in external memory (secure digital card or USB on the go pen drive).
Multimedia Messaging Service
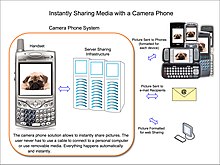
Camera phones can share pictures almost instantly and automatically via a sharing infrastructure integrated with the carrier network. Early developers including Philippe Kahn envisioned a technology that would enable service providers to "collect a fee every time anyone snaps a photo". The resulting technologies, Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) and Sha-Mail, were developed parallel to and in competition to open Internet-based mobile communication provided by GPRS and later 3G networks.
The first commercial camera phone complete with infrastructure was the J-SH04, made by Sharp Corporation; it had an integrated CCD sensor, with the Sha-Mail (Picture-Mail in Japanese) infrastructure developed in collaboration with Kahn's LightSurf venture, and marketed from 2001 by J-Phone in Japan today owned by Softbank.It was also the world's first cellular mobile camera phone. The first commercial deployment in North America of camera phones was in 2004. The Sprint wireless carriers deployed over one million camera phones manufactured by Sanyo and launched by the PictureMail infrastructure (Sha-Mail in English) developed and managed by LightSurf.
While early phones had Internet connectivity, working web browsers and email-programs, the phone menu offered no way of including a photo in an email or uploading it to a web site. Connecting cables or removable media that would enable the local transfer of pictures were also usually missing. Modern smartphones have almost unlimited connectivity and transfer options with photograph attachment features.
External camera
During 2003 (as camera phones were gaining popularity), in Europe some phones without cameras had support for MMS and external cameras that could be connected with a small cable or directly to the data port at the base of the phone. The external cameras were comparable in quality to those fitted on regular camera phones at the time, typically offering VGA resolution.
One of these examples was the Nokia Fun Camera (model number PT-3) announced together with the Nokia 3100 in June 2003. The idea was for it to be used on devices without a built-in camera (connected via the Pop-Port interface) and be able to transfer images taken on the camera (VGA resolution and a flash) directly to the phone to be stored or sent via MMS.
In 2013-2014 Sony and other manufacturers announced add-on camera modules for smartphones called lens-style cameras. They have larger sensors and lenses than those in a camera phone but lack a viewfinder, display and most controls. They can be mounted to an Android or iOS phone or tablet and use its display and controls. Lens-style cameras include:
- Sony SmartShot QX series, announced and released in mid 2013. They include the DSC-QX100/B, the large Sony ILCE-QX1, and the small Sony DSC-QX30.
- Kodak PixPro smart lens camera series, announced in 2014.
- Vivicam smart lens camera series from Vivitar/Sakar, announced in 2014.
- HTC RE HTC also announced an external camera module for smartphones, which can capture 16 MP still shots and Full HD videos. The RE Module is also waterproof and dustproof, so it can be used in a variety of conditions.
External cameras for thermal imaging also became available in late 2014.
Microscope attachments were available from several manufacturers in 2019, as are adapters for connecting an astronomical telescope.
Limitations
- Mobile phone form factors are small. They lack space for a large image sensor and dedicated knobs and buttons for easier ergonomy.
- Controls work by a touchscreen menu system. The photographer must look at the menu instead of looking at the target.
- Dedicated cameras have a compartment housing the memory card and battery. For most it is easily accessible by hand, allowing uninterrupted operation when storage or energy is exhausted (hot swapping). Meanwhile, the battery can be charged externally. Most mobile phones have a non-replaceable battery and many lack a memory card slot entirely. Others have a memory card slot inside a tray, requiring a tool for access.
- Mobile phone operating systems are not able to boot immediately like the firmwares of dedicated digital cameras/camcorders, and are prone to interference from processes running in background.
- Dedicated digital cameras, even low-budget ones, are typically equipped with a photoflash capacitor-discharging Xenon flash, larger and by far more powerful than LED lamps found on mobile phones.
- Due to the default orientation of mobile phones being vertical, inexperienced users might intuitively be encouraged to film vertically, making a portrait mode poorly suited to the usual horizontal screens used at home.
- Due to their comparatively thin form factor, smartphones are typically unable to stand upright on their own and must be leaned, whereas dedicated digital cameras and camcorders typically have a flat bottom that lets them stand upright.
- Smartphones lack dedicated stable tripod mounts, and can only be mounted through a less stable device that grips the unit's edges.
Software
Users may use bundled camera software, or install alternative software.
The graphical user interface typically features a virtual on-screen shutter button located towards the usual home button and charging port side, and a thumbnail previewing the last photo. There may be an option to utilize volume keys for photo, video, or zoom. Specific objects can usually be focused on by tapping on the viewfinder, and exposure may adjust accordingly; there may be an option to capture a photo with each tap.
Exposure value may be adjustable by swiping vertically after tapping to focus or through a separate menu option. It may be possible to lock focus and exposure by holding the touch for a short time, and exposure value may remain adjustable in this state. These gestures may be available while filming and for the front camera.
Retaining focus also has in the past been implemented through holding the virtual shutter button. Another common use of holding the shutter button is burst shot, where multiple photos are captured in quick succession, with varying resolutions, speeds, and sequential limits among devices, and possibly with an option to adjust between speed and resolution.
Lock screens typically allow the user to launch the camera without unlocking to prevent missing moments. This may be implemented through an icon swiped away from. Launching from anywhere may be possible through double-press of stand-by or home button, or a dedicated shutter button if present.
Camera software on more recent and higher-end smartphones (e.g. Samsung since 2015) allows for more manual control of parameters such as exposure and focus. This was first featured in 2013 on the camera-centric Samsung Galaxy S4 Zoom and Nokia Lumia 1020, but was later expanded among smartphones.
The camera software may indicate the estimated number of remaining photographs until exhausted space, the current video file size, and remaining space storage while recording, as done on early-2010s Samsung smartphones.
Video recording
Video recording may be implemented as a separate camera mode, or merged on the first viewfinder page as done since the Samsung Galaxy S4 until the S9. Specific resolutions may be implemented as separate camera mode, like Sony has done with 4K (2160p) on the Xperia Z2.
During video recording, it may be possible to capture still photos, possibly with a higher resolution than the video itself. For example, the Samsung Galaxy S4 captures still photos during video recording at 9.6 Megapixels, which is the largest 16:9 aspect ratio crop of the 13-Megapixel 4:3 image sensor.
Parameters adjustable during video recording may include flashlight illumination, focus, exposure, light sensitivity (ISO), and white balance. Some settings may only be adjustable while idle and locked while filming, such as light sensitivity and exposure on the Samsung Galaxy S7.
Recording time may be limited by software to fixed durations at specific resolutions, after which recording can be restarted. For example, 2160p (4K) recording is capped to five minutes on Samsung flagship smartphones released before 2016, ten minutes on the Galaxy Note 7, four minutes on the Galaxy Alpha, and six minutes on the HTC One M9. The camera software may temporarily disable recording while a high device temperature is detected.
"Slow motion" (high frame rate) video may be stored as real-time video which retains the original image sensor frame rate and audio track, or slowed down and muted. While the latter allows slow-motion playback on older video player software which lacks playback speed control, the former can act both as real-time video and as slow-motion video, and is preferable for editing as the playback speed and duration indicated in the video editor are real-life equivalent.
Camera settings may appear as a menu on top of an active viewfinder in the background, or as a separate page, the former of which allows returning to the viewfinder immediately without having to wait for it to initiate again. The settings may appear as a grid or a list. On Apple iOS, some camera settings such as video resolution are located separately in the system settings, outside the camera application.
The range of selectable resolution levels for photos and videos varies among camera software. There may be settings for frame rate and bit rate, as on the LG V10, where they are implemented independently within a supported pixel rate (product of resolution and frame rate).
When the selected photo or video resolution is below that of the image sensor, digital zooming may allow limited magnification without quality loss by cropping into the image sensor's spare resolution. This is known as "lossless digital zoom". Zooming is typically implemented through pinch and may additionally be controllable through a slider. On early-2010s Samsung Galaxy smartphones, a square visualized the magnification.
Other functionality
The ability to take photographs and film from both front and rear cameras simultaneously was first implemented in 2013 on the Samsung Galaxy S4, where the two video tracks are stored picture-in-picture. An implementation with separate video tracks within a file or separate video files is not known yet.
High-dynamic-range imaging, also referred to as "rich tone", keeps brightness across the image within a visible range. Camera software may have an option for automatically toggling it depending on necessity. Deacativated HDR may be desirable as HDR may add shutter lag, ghosting from merged photos, and discard EXIF meta data. A possible option allows retaining both HDR and non-HDR variants of the same photo. HDR may be supported for panorama shots and video recording, if supported by the image sensor.
Voice commands were first featured in 2012 on the camera software of the Samsung Galaxy S3, and the ability to take a photo after a short countdown initiated by hand gesture was first featured in 2015 on the Galaxy S6.
The camera effects introduced by Samsung on the Galaxy S3 or S4 including "best photo" which automatically picks a photo and "drama shot" for multiplying moving objects and "eraser" which can remove moving objects, were merged to "shot & more" on the Galaxy S5, allowing retrospectively applying them to a burst of eight images stored in a single file.
In 2014, HTC implemented several visual effect features as part of their dual-camera setup on the One M8, including weather, 3D tilting, and focus adjustment after capture, branded "uFocus". The last was branded "Selective Focus" by Samsung, additionally with the "pan focus" option to make the entire depth of field appear in focus.
Camera software may have an option for automatically capturing a photograph or video when launched.
Some smartphones since the mid-2010s have the ability to attach short videos surrounding or following the moment to a photo. Apple has branded this feature as "live photo", and Samsung as "motion photo".
Shortcuts to settings in the camera viewfinder may be customizable.
A "remote viewfinder" feature has been implemented into few smartphones' camera software (Samsung Galaxy S4, S4 Zoom, Note 3, S5, K Zoom, Alpha), where the viewfinder and camera controls are cast to a supported device through WiFi Direct.
An artificial intelligence that notifies of flaws after each photograph such as blinking eyes, misfocus, blur, and shake, was first implemented in 2018 on the Samsung Galaxy Note 9. Later phones from other manufacturers have more advanced IA features.
History
The camera phone, like many complex systems, is the result of converging and enabling technologies. Compared to digital cameras, a consumer-viable camera in a mobile phone would require far less power and a higher level of camera electronics integration to permit the miniaturization.
The metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) active pixel sensor (APS) was developed by Tsutomu Nakamura at Olympus in 1985. The complementary MOS (CMOS) active pixel sensor (CMOS sensor) "camera-on-a-chip" was later developed by Eric Fossum and his team in the early 1990s. This was an important step towards realizing the modern camera phone as described in a March 1995 Business Week article. While the first camera phones (e.g. J-SH04) successfully marketed by J-Phone in Japan used charge-coupled device (CCD) sensors rather than CMOS sensors, more than 90% of camera phones sold today use CMOS image sensor technology.
Another important enabling factor was advances in data compression, due to the impractically high memory and bandwidth requirements of uncompressed media. The most important compression algorithm is the discrete cosine transform (DCT), a lossy compression technique that was first proposed by Nasir Ahmed while he was working at the University of Texas in 1972. Camera phones were enabled by DCT-based compression standards, including the H.26x and MPEG video coding standards introduced from 1988 onwards, and the JPEG image compression standard introduced in 1992.
Experiments
There were several early videophones and cameras that included communication capability. Some devices experimented with integration of the device to communicate wirelessly with the Internet, which would allow instant media sharing with anyone anywhere. The DELTIS VC-1100 by Japanese company Olympus was the world's first digital camera with cellular phone transmission capability, revealed in the early 1990s and released in 1994. In 1995, Apple experimented with the Apple Videophone/PDA. There was also a digital camera with cellular phone designed by Shosaku Kawashima of Canon in Japan in May 1997. In Japan, two competing projects were run by Sharp and Kyocera in 1997. Both had cell phones with integrated cameras. However, the Kyocera system was designed as a peer-to-peer video-phone as opposed to the Sharp project which was initially focused on sharing instant pictures. That was made possible when the Sharp devices was coupled to the Sha-mail infrastructure designed in collaboration with American technologist Kahn. The Kyocera team was led by Kazumi Saburi. In 1995, work by James Greenwold of Bureau Of Technical Services, in Chippewa Falls, Wisconsin, was developing a pocket video camera for surveillance purposes. By 1999, the Tardis recorder was in prototype and being used by the government. Bureau Of Technical Services advanced further by the patent No. 6,845,215,B1 on "Body-Carryable, digital Storage medium, Audio/Video recording Assembly".
A camera phone was patented by Kari-Pekka Wilska, Reijo Paajanen, Mikko Terho and Jari Hämäläinen, four employees at Nokia, in 1994. Their patent application was filed with the Finnish Patent and Registration Office on May 19, 1994, followed by several filings around the world making it a global family of patent applications. The patent application specifically described the combination as either a separate digital camera connected to a cell phone or as an integrated system with both sub-systems combined in a single unit. Their patent application design included all of the basic functions camera phones implemented for many years: the capture, storage, and display of digital images and the means to transmit the images over the radio frequency channel. On August 12, 1998, the United Kingdom granted patent GB 2289555B and on July 30, 2002, the USPTO granted US Patent 6427078B1 based on the original Finnish Patent and Registration Office application to Wilska, Paajanen, Terho and Hämäläinen.
On June 11, 1997, Philippe Kahn instantly shared the first pictures from the maternity ward where his daughter Sophie was born. In the hospital waiting room he devised a way to connect his laptop to his digital camera and to his cell phone for transmission to his home computer. This improvised system transmitted his pictures to more than 2,000 family, friends and associates around the world. Kahn's improvised connections augured the birth of instant visual communications. Kahn's cell phone transmission is the first known publicly shared picture via a cell phone.
Commercialization
The first commercial camera phone was the Kyocera Visual Phone VP-210, released in Japan in May 1999. It was called a "mobile videophone" at the time, and had a 110,000-pixel front-facing camera. It stored up to 20 JPEG digital images, which could be sent over e-mail, or the phone could send up to two images per second over Japan's Personal Handy-phone System (PHS) cellular network. The Samsung SCH-V200, released in South Korea in June 2000, was also one of the first phones with a built-in camera. It had a TFT liquid-crystal display (LCD) and stored up to 20 digital photos at 350,000-pixel resolution. However, it could not send the resulting image over the telephone function, but required a computer connection to access photos. The first mass-market camera phone was the J-SH04, a Sharp J-Phone model sold in Japan in November 2000. It could instantly transmit pictures via cell phone telecommunication.
Cameras on cell phones proved popular right from the start, as indicated by the J-Phone in Japan having had more than half of its subscribers using cell phone cameras in two years. The world soon followed. In 2003, more camera phones were sold worldwide than stand-alone digital cameras largely due to growth in Japan and Korea. In 2005, Nokia became the world's most sold digital camera brand. In 2006, half of the world's mobile phones had a built-in camera. In 2006, Thuraya released the first satellite phone with an integrated camera. The Thuraya SG-2520 was manufactured by Korean company APSI and ran Windows CE. In 2008, Nokia sold more camera phones than Kodak sold film-based simple cameras, thus becoming the biggest manufacturer of any kind of camera. In 2010, the worldwide number of camera phones totaled more than a billion. Since 2010, most mobile phones, even cheapest ones, are being sold with a camera. High-end camera phones usually had a relatively good lens and high resolution.
Higher resolution camera phones started to appear in the 2010s. 12-megapixel camera phones have been produced by at least two companies. To highlight the capabilities of the Nokia N8 (Big CMOS Sensor) camera, Nokia created a short film, The Commuter, in October 2010. The seven-minute film was shot entirely on the phone's 720p camera. A 14-megapixel smartphone with 3× optical zoom was announced in late 2010. In 2011, the first phones with dual rear cameras were released to the market but failed to gain traction. Originally, dual rear cameras were implemented as a way to capture 3D content, which was something that electronics manufacturers were pushing back then. Several years later, the release of the iPhone 7 would popularize this concept, but instead using the second lens as a wide angle lens. In 2012, Nokia announced Nokia 808 PureView. It features a 41-megapixel 1/1.2-inch sensor and a high-resolution f/2.4 Zeiss all-aspherical one-group lens. It also features Nokia's PureView Pro technology, a pixel oversampling technique that reduces an image taken at full resolution into a lower resolution picture, thus achieving higher definition and light sensitivity, and enables lossless zoom. In mid-2013, Nokia announced the Nokia Lumia 1020. In 2014, the HTC one M8 introduced the concept of having a camera as a depth sensor. In late 2016, Apple introduced the iPhone 7 Plus, one of the phones to popularize a dual camera setup. The iPhone 7 Plus included a main 12 MP camera along with a 12 MP telephoto camera which allowed for 2x optical zoom and Portrait Mode for the first time in a smartphone. In early 2018 Huawei released a new flagship phone, the Huawei P20 Pro, with the first triple camera lens setup. Making up its three sensors (co-engineered with Leica) are a 40 megapixel RGB lens, a 20 megapixel monochrome lens, and an 8 megapixel telephoto lens. Some features on the Huawei P20 Pro include 3x optical zoom, and 960 fps slow motion. In late 2018, Samsung released a new mid-range smartphone, the Galaxy A9 (2018) with the world's first quad camera setup. The quadruple camera setup features a primary 24MP f/1.7 sensor for normal photography, an ultra-wide 8MP f/2.4 sensor with a 120 degrees viewing angle, a telephoto 10MP f/2.4 with 2x optical zoom and a 5MP depth sensor for effects such as Bokeh. Nokia 9 PureView was released in 2019 featuring penta-lens camera system.
In 2019, Samsung announced the Galaxy A80, which has only rear cameras. When the user wants to take a selfie, the cameras automatically slide out of the back and rotate towards the user. This is known as a pop-up camera, and it allows smartphone displays to cover the entire front of the phone body without a notch or a punch hole on the top of the screen. Samsung, Xiaomi, OnePlus, and other manufacturers adopted a system where the camera "pops" out of the phone's body. Also in 2019, Samsung developed and began commercialization of 64 and 108-megapixel cameras for phones. The 108 MP sensor was developed in cooperation with Chinese electronics company Xiaomi and both sensors are capable of pixel binning, which combines the signals of 4 or 9 pixels, and makes the 4 or 9 pixels act as a single, larger pixel. A larger pixel can capture more light (resulting in a higher ISO rating and lower image noise). Under display cameras are under development, which would place a camera under a special display that would allow the camera to see through the display.
Manufacturers
Major manufacturers of cameras for phones include Sony, Toshiba, ST Micro, Sharp, Omnivision, and Aptina (Now part of ON Semiconductor).
Social impact
Personal photography allows people to capture and construct personal and group memory, maintain social relationships as well as expressing their identity. The hundreds of millions of camera phones sold every year provide the same opportunities, yet these functions are altered and allow for a different user experience. As mobile phones are constantly carried, they allow for capturing moments at any time. Mobile communication also allows for immediate transmission of content (for example via Multimedia Messaging Services), which cannot be reversed or regulated. Brooke Knight observes that "the carrying of an external, non-integrated camera (like a DSLR) always changes the role of the wearer at an event, from participant to photographer". The camera phone user, on the other hand, can remain a participant in whatever moment they photograph. Photos taken on a camera phone serve to prove the physical presence of the photographer. The immediacy of sharing and the liveness that comes with it allows the photographs shared through camera phones to emphasize their indexing of the photographer.
While phones have been found useful by tourists and for other common civilian purposes, as they are cheap, convenient, and portable; they have also posed controversy, as they enable secret photography. A user may pretend to be simply talking on the phone or browsing the internet, drawing no suspicion while photographing a person or place in non-public areas where photography is restricted, or against that person's wishes. Camera phones have enabled everyone to exercise freedom of speech by quickly communicating to others what they see with their own eyes. In most democratic free countries, there are no restrictions against photography in public and thus camera phones enable new forms of citizen journalism, fine art photography, and recording one's life experiences for facebooking or blogging.
Camera phones have also been very useful to street photographers and social documentary photographers as they enable them to take pictures of strangers in the street without them noticing, thus allowing the artist/photographer to get close to subjects and take more lively photos. While most people are suspect of secret photography, artists who do street photography (like Henri Cartier-Bresson did), photojournalists and photographers documenting people in public (like the photographers who documented the Great Depression in 1930s America) must often work unnoticed as their subjects are often unwilling to be photographed or are not aware of legitimate uses of secret photography like those photos that end up in fine art galleries and journalism.
As a network-connected device, megapixel camera phones are playing significant roles in crime prevention, journalism and business applications as well as individual uses. They can also be used for activities such as voyeurism, invasion of privacy, and copyright infringement. Because they can be used to share media almost immediately, they are a potent personal content creation tool.
Camera phones limit the "right to be let alone", since this recording tool is always present. A security bug can allow attackers to spy on users through a phone camera.
In January 2007, New York City Mayor Michael Bloomberg announced a plan to encourage people to use their camera phones to capture crimes happening in progress or dangerous situations and send them to emergency responders. The program enables people to send their images or video directly to 911. The service went live in 2020.
Camera phones have also been used to discreetly take photographs in museums, performance halls, and other places where photography is prohibited. However, as sharing can be instantaneous, even if the action is discovered, it is too late, as the image is already out of reach, unlike a photo taken by a digital camera that only stores images locally for later transfer. However, as the newer digital cameras support Wi-Fi, a photographer can perform photography with a DSLR and instantly post the photo on the internet through the mobile phone's Wi-Fi and 3G capabilities.
Apart from street photographers and social documentary photographers or cinematographers, camera phones have also been used successfully by war photographers. The small size of the camera phone allows a war photographer to secretly film the men and women who fight in a war, without them realizing that they have been photographed, thus the camera phone allows the war photographer to document wars while maintaining her or his safety.
In 2010, in Ireland the annual "RTÉ 60 second short award" was won by 15-year-old Laura Gaynor, who made her winning cartoon,"Piece of Cake" on her Sony Ericsson C510 camera phone. In 2012, director and writer Eddie Brown Jr. made the reality thriller Camera Phone, one of the first commercial produced movies using camera phones as the story's perspective. The film is a reenactment of an actual case, and the names were changed to protect those involved. Some modern camera phones (in 2013–2014) have big sensors, thus allowing a street photographer or any other kind of photographer to take photos of similar quality to a semi-professional camera.
Camera as an interaction device
The cameras of smartphones are used as input devices in numerous research projects and commercial applications. A commercially successful example is the use of QR codes attached to physical objects. QR codes can be sensed by the phone using its camera and provide an according link to related digital content, usually a URL. Another approach is using camera images to recognize objects. Content-based image analysis is used to recognize physical objects such as advertisement posters to provide information about the object. Hybrid approaches use a combination of un-obtrusive visual markers and image analysis. An example is to estimate the pose of the camera phone to create a real-time overlay for a 3D paper globe.
Some smartphones can provide an augmented reality overlay for 2D objects and to recognize multiple objects on the phone using a stripped down object recognition algorithm as well as using GPS and compass. A few can translate text from a foreign language. Auto-geotagging can show where a picture is taken, promoting interactions and allowing a photo to be mapped with others for comparison.
Smartphones can use their front camera (of lesser performance as compared to rear camera) facing the user for purposes like self-portraiture (selfie) and videoconferencing.
Smartphones can usually not fixed on a tripod, which can make problems at filming or at taking pictures with long exposure times.
Laws
Camera phones, or more specifically, widespread use of such phones as cameras by the general public, has increased exposure to laws relating to public and private photography. The laws that relate to other types of cameras also apply to camera phones. There are no special laws for camera phones. Enforcing bans on camera phones has proven nearly impossible. They are small and numerous and their use is easy to hide or disguise, making it hard for law enforcement and security personnel to detect or stop use. Total bans on camera phones would also raise questions about freedom of speech and the freedom of the press, since camera phone ban would prevent a citizen or a journalist (or a citizen journalist) from communicating to others a newsworthy event that could be captured with a camera phone.
From time to time, organizations and places have prohibited or restricted the use of camera phones and other cameras because of the privacy, security, and copyright issues they pose. Such places include the Pentagon, federal and state courts, museums, schools, theaters, and local fitness clubs. Saudi Arabia, in April 2004, banned the sale of camera phones nationwide for a time before reallowing their sale in December 2004 (although pilgrims on the Hajj were allowed to bring in camera phones). There is the occasional anecdote of camera phones linked to industrial espionage and the activities of paparazzi (which are legal but often controversial), as well as some hacking into wireless operators' network.
Notable events involving camera phones
- The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake was the first global news event where the majority of the first day news footage was no longer provided by professional news crews, but rather by citizen journalists, using primarily camera phones.
- On November 17, 2006, during a performance at the Laugh Factory comedy club, comedian Michael Richards was recorded responding to hecklers with racial slurs by a member of the audience using a camera phone. The video was widely circulated in television and internet news broadcasts.
- On December 30, 2006, the execution of former Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein was recorded by a video camera phone, and made widely available on the Internet. A guard was arrested a few days later.
- Camera phone video and photographs taken in the immediate aftermath of the 7 July 2005 London bombings were featured worldwide. CNN executive Jonathan Klein predicts camera phone footage will be increasingly used by news organizations.
- Camera phone digital images helped to spread the 2009 Iranian election protests.
- Camera phones recorded the BART Police shooting of Oscar Grant.
Camera phone photography
Photography produced specifically with phone cameras has become an art form in its own right. Work in this genre is sometimes referred to as iPhoneography (whether for photographs taken with an iPhone, or any brand of smart phone). The movement, though already a few years old, became mainstream with the advent of the iPhone and its App Store which provided better, easier, and more creative tools for people to shoot, process, and share their work.
Reportedly, the first gallery exhibition to feature iPhoneography exclusively opened on June 30, 2010: "Pixels at an Exhibition" was held in Berkeley, California, organized and curated by Knox Bronson and Rae Douglass. Around the same time, the photographer Damon Winter used Hipstamatic to make photos of the war in Afghanistan. A collection of these was published November 21, 2010 in the New York Times in a series titled "A Grunt's Life", earning an international award (3rd) sponsored by RJI, Donald W. Reynolds Journalism Institute. Also in Afghanistan, in 2011, photojournalist David Guttenfelder used an iPhone and the Polarize application. In 2013, National Geographic published a photo feature in which phoneographer Jim Richardson used his iPhone 5s to photograph the Scottish Highlands.