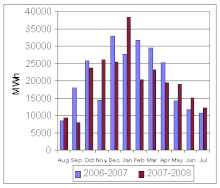
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable energy sources, such as dammed hydroelectricity or biomass, or relatively constant sources, such as geothermal power.
The use of small amounts of intermittent power has little effect on grid operations. Using larger amounts of intermittent power may require upgrades or even a redesign of the grid infrastructure. Options to absorb large shares of variable energy into the grid include using storage, improved interconnection between different variable sources to smooth out supply, using dispatchable energy sources such as hydroelectricity and having overcapacity, so that sufficient energy is produced even when weather is less favourable. More connections between the energy sector and the building, transport and industrial sectors may also help.
Background and terminology
The penetration of intermittent renewables in most power grids is low: global electricity generation in 2021 was 7% wind and 4% solar. However, in 2021 Denmark, Luxembourg and Uruguay generated over 40% of their electricity from wind and solar. Characteristics of variable renewables include their unpredictability, variability, their low running costs and the fact they are constrained to a certain location. These provide a challenge to grid operators, who must make sure supply and demand are matched. Solutions include energy storage, demand response, availability of overcapacity and sector coupling. Smaller isolated grids may be less tolerant to high levels of penetration.
Matching power demand to supply is not a problem specific to intermittent power sources. Existing power grids already contain elements of uncertainty including sudden and large changes in demand and unforeseen power plant failures. Though power grids are already designed to have some capacity in excess of projected peak demand to deal with these problems, significant upgrades may be required to accommodate large amounts of intermittent power.
Several key terms are useful for understanding the issue of intermittent power sources. These terms are not standardized, and variations may be used. Most of these terms also apply to traditional power plants.
- Intermittency or variability is the extent to which a power source fluctuates. This has two aspects: a predictable variability (such as the day-night cycle) and an unpredictable part (imperfect local weather forecasting). The term intermittent can be used to refer to the unpredictable part, with variable then referring to the predictable part.
- Dispatchability is the ability of a given power source to increase and decrease output quickly on demand. The concept is distinct from intermittency; dispatchability is one of several ways system operators match supply (generator's output) to system demand (technical loads).
- Penetration is the amount of electricity generated as a percentage of annual consumption.
- Nominal power or nameplate capacity is the maximum output of a generating plant in normal operating conditions. This is the most common number used and is typically expressed in watts (including multiples like kW, MW, GW).
- Capacity factor, average capacity factor, or load factor is the average expected output of a generator, usually over an annual period. It is expressed as a percentage of the nameplate capacity or in decimal form (e.g. 30% or 0.30).
- Firm capacity or firm power is "guaranteed by the supplier to be available at all times during a period covered by a commitment".
- Capacity credit: the amount of conventional (dispatchable) generation power that can be potentially removed from the system while keeping the reliability, usually expressed as a percentage of the nominal power.
- Foreseeability or predictability is how accurately the operator can anticipate the generation: for example tidal power varies with the tides but is completely foreseeable because the orbit of the moon can be predicted exactly, and improved weather forecasts can make wind power more predictable.
Sources
Dammed hydroelectricity, biomass and geothermal are dispatchable as each has a store of potential energy; wind and solar without storage can be decreased, but not dispatched, other than when nature provides. Between wind and solar, solar has a more variable daily cycle than wind, but is more predictable in daylight hours than wind. Like solar, tidal energy varies between on and off cycles through each day, unlike solar there is no intermittency, tides are available every day without fail.
Wind power
Grid operators use day ahead forecasting to determine which of the available power sources to use the next day, and weather forecasting is used to predict the likely wind power and solar power output available. Although wind power forecasts have been used operationally for decades, as of 2019 the IEA is organizing international collaboration to further improve their accuracy.
Wind-generated power is a variable resource, and the amount of electricity produced at any given point in time by a given plant will depend on wind speeds, air density, and turbine characteristics (among other factors). If wind speed is too low then the wind turbines will not be able to make electricity, and if it is too high the turbines will have to be shut down to avoid damage. While the output from a single turbine can vary greatly and rapidly as local wind speeds vary, as more turbines are connected over larger and larger areas the average power output becomes less variable.
- Intermittence: Regions smaller than synoptic scale (less than about 1000 km long, the size of an average country) have mostly the same weather and thus around the same wind power, unless local conditions favor special winds. Some studies show that wind farms spread over a geographically diverse area will as a whole rarely stop producing power altogether. However this is rarely the case for smaller areas with uniform geography such as Ireland, Scotland and Denmark which have several days per year with little wind power.
- Capacity factor: Wind power typically has an annual capacity factor of 25–50%, with offshore wind outperforming onshore wind.
- Dispatchability: Because wind power is not by itself dispatchable wind farms are sometimes built with storage.
- Capacity credit: At low levels of penetration, the capacity credit of wind is about the same as the capacity factor. As the concentration of wind power on the grid rises, the capacity credit percentage drops.
- Variability: Site dependent. Sea breezes are much more constant than land breezes. Seasonal variability may reduce output by 50%.
- Reliability: A wind farm has high technical reliability when the wind blows. That is, the output at any given time will only vary gradually due to falling wind speeds or storms (the latter necessitating shut downs). A typical wind farm is unlikely to have to shut down in less than half an hour at the extreme, whereas an equivalent-sized power station can fail totally instantaneously and without warning. The total shutdown of wind turbines is predictable via weather forecasting. The average availability of a wind turbine is 98%, and when a turbine fails or is shut down for maintenance it only affects a small percentage of the output of a large wind farm.
- Predictability: Although wind is variable, it is also predictable in the short term. There is an 80% chance that wind output will change less than 10% in an hour and a 40% chance that it will change 10% or more in 5 hours.
Because wind power is generated by large numbers of small generators, individual failures do not have large impacts on power grids. This feature of wind has been referred to as resiliency.
Solar power
Intermittency inherently affects solar energy, as the production of renewable electricity from solar sources depends on the amount of sunlight at a given place and time. Solar output varies throughout the day and through the seasons, and is affected by dust, fog, cloud cover, frost or snow. Many of the seasonal factors are fairly predictable, and some solar thermal systems make use of heat storage to produce grid power for a full day.
- Variability: In the absence of an energy storage system, solar does not produce power at night, little in bad weather and varies between seasons. In many countries, solar produces most energy in seasons with low wind availability and vice versa.
- Capacity factor Standard photovoltaic solar has an annual average capacity factor of 10-20%, but panels that move and track the sun have a capacity factor up to 30%. Thermal solar parabolic trough with storage 56%. Thermal solar power tower with storage 73%.
The impact of intermittency of solar-generated electricity will depend on the correlation of generation with demand. For example, solar thermal power plants such as Nevada Solar One are somewhat matched to summer peak loads in areas with significant cooling demands, such as the south-western United States. Thermal energy storage systems like the small Spanish Gemasolar Thermosolar Plant can improve the match between solar supply and local consumption. The improved capacity factor using thermal storage represents a decrease in maximum capacity, and extends the total time the system generates power.
Run-of-the-river hydroelectricity
In many countries new large dams are no longer being built, because of the environmental impact of reservoirs. Run of the river projects have continued to be built. The absence of a reservoir results in both seasonal and annual variations in electricity generated.
Tidal power
Tidal power is the most predictable of all the variable renewable energy sources. The tides reverse twice a day, but they are never intermittent, on the contrary they are completely reliable. Only 20 sites in the world have yet been identified as possible tidal power stations.
Wave power
Waves are primarily created by wind, so the power available from waves tends to follow that available from wind, but due to the mass of the water is less variable than wind power. Wind power is proportional to the cube of the wind speed, while wave power is proportional to the square of the wave height.
Solutions for their integration
The displaced dispatchable generation could be coal, natural gas, biomass, nuclear, geothermal or storage hydro. Rather than starting and stopping nuclear or geothermal it is cheaper to use them as constant base load power. Any power generated in excess of demand can displace heating fuels, be converted to storage or sold to another grid. Biofuels and conventional hydro can be saved for later when intermittents are not generating power. Alternatives to burning coal and natural gas which produce fewer greenhouse gases may eventually make fossil fuels a stranded asset that is left in the ground. Highly integrated grids favor flexibility and performance over cost, resulting in more plants that operate for fewer hours and lower capacity factors.
All sources of electrical power have some degree of variability, as do demand patterns which routinely drive large swings in the amount of electricity that suppliers feed into the grid. Wherever possible, grid operations procedure are designed to match supply with demand at high levels of reliability, and the tools to influence supply and demand are well-developed. The introduction of large amounts of highly variable power generation may require changes to existing procedures and additional investments.
The capacity of a reliable renewable power supply, can be fulfilled by the use of backup or extra infrastructure and technology, using mixed renewables to produce electricity above the intermittent average, which may be used to meet regular and unanticipated supply demands. Additionally, the storage of energy to fill the shortfall intermittency or for emergencies can be part of a reliable power supply.
In practice, as the power output from wind varies, partially loaded conventional plants, which are already present to provide response and reserve, adjust their output to compensate. While low penetrations of intermittent power may use existing levels of response and spinning reserve, the larger overall variations at higher penetrations levels will require additional reserves or other means of compensation.
Operational reserve
All managed grids already have existing operational and "spinning" reserve to compensate for existing uncertainties in the power grid. The addition of intermittent resources such as wind does not require 100% "back-up" because operating reserves and balancing requirements are calculated on a system-wide basis, and not dedicated to a specific generating plant.
Some gas, or hydro power plants are partially loaded and then controlled to change as demand changes or to replace rapidly lost generation. The ability to change as demand changes is termed "response". The ability to quickly replace lost generation, typically within timescales of 30 seconds to 30 minutes, is termed "spinning reserve".
Generally thermal plants running as peaking plants will be less efficient than if they were running as base load. Hydroelectric facilities with storage capacity (such as the traditional dam configuration) may be operated as base load or peaking plants.
Grids can contract for grid battery plants, which provide immediately available power for an hour or so, which gives time for other generators to be started up in the event of a failure, and greatly reduces the amount of spinning reserve required.
Demand response
Demand response is a change in consumption of energy to better align with supply. It can take the form of switching off loads, or absorb additional energy to correct supply/demand imbalances. Incentives have been widely created in the American, British and French systems for the use of these systems, such as favorable rates or capital cost assistance, encouraging consumers with large loads to take them offline whenever there is a shortage of capacity, or conversely to increase load when there is a surplus.
Certain types of load control allow the power company to turn loads off remotely if insufficient power is available. In France large users such as CERN cut power usage as required by the System Operator - EDF under the encouragement of the EJP tariff.
Energy demand management refers to incentives to adjust use of electricity, such as higher rates during peak hours. Real-time variable electricity pricing can encourage users to adjust usage to take advantage of periods when power is cheaply available and avoid periods when it is more scarce and expensive. Some loads such as desalination plants, electric boilers and industrial refrigeration units, are able to store their output (water and heat). Several papers also concluded that Bitcoin mining loads would reduce curtailment, hedge electricity price risk, stabilize the grid, increase the profitability of renewable energy power stations and therefore accelerate transition to sustainable energy. But others argue that Bitcoin mining can never be sustainable.
Instantaneous demand reduction. Most large systems also have a category of loads which instantly disconnect when there is a generation shortage, under some mutually beneficial contract. This can give instant load reductions (or increases).
Storage
At times of low load where non-dispatchable output from wind and solar may be high, grid stability requires lowering the output of various dispatchable generating sources or even increasing controllable loads, possibly by using energy storage to time-shift output to times of higher demand. Such mechanisms can include:
Pumped storage hydropower is the most prevalent existing technology used, and can substantially improve the economics of wind power. The availability of hydropower sites suitable for storage will vary from grid to grid. Typical round trip efficiency is 80%.
Traditional lithium-ion is the most common type used for grid-scale battery storage as of 2020. Rechargeable flow batteries can serve as a large capacity, rapid-response storage medium. Hydrogen can be created through electrolysis and stored for later use.
Flywheel energy storage systems have some advantages over chemical batteries. Along with substantial durability which allows them to be cycled frequently without noticeable life reduction, they also have very fast response and ramp rates. They can go from full discharge to full charge within a few seconds. They can be manufactured using non-toxic and environmentally friendly materials, easily recyclable once the service life is over.
Thermal energy storage stores heat. Stored heat can be used directly for heating needs or converted into electricity. In the context of a CHP plant a heat storage can serve as a functional electricity storage at comparably low costs. Ice storage air conditioning Ice can be stored inter seasonally and can be used as a source of air-conditioning during periods of high demand. Present systems only need to store ice for a few hours but are well developed.
Storage of electrical energy results in some lost energy because storage and retrieval are not perfectly efficient. Storage also requires capital investment and space for storage facilities.
Geographic diversity and complementing technologies
The variability of production from a single wind turbine can be high. Combining any additional number of turbines (for example, in a wind farm) results in lower statistical variation, as long as the correlation between the output of each turbine is imperfect, and the correlations are always imperfect due to the distance between each turbine. Similarly, geographically distant wind turbines or wind farms have lower correlations, reducing overall variability. Since wind power is dependent on weather systems, there is a limit to the benefit of this geographic diversity for any power system.
Multiple wind farms spread over a wide geographic area and gridded together produce power more constantly and with less variability than smaller installations. Wind output can be predicted with some degree of confidence using weather forecasts, especially from large numbers of turbines/farms. The ability to predict wind output is expected to increase over time as data is collected, especially from newer facilities.
Electricity produced from solar energy tends to counterbalance the fluctuating supplies generated from wind. Normally it is windiest at night and during cloudy or stormy weather, and there is more sunshine on clear days with less wind. Besides, wind energy has often a peak in the winter season, whereas solar energy has a peak in the summer season; the combination of wind and solar reduces the need for dispatchable backup power.
- In some locations, electricity demand may have a high correlation with wind output,particularly in locations where cold temperatures drive electric consumption (as cold air is denser and carries more energy).
- The allowable penetration may be increased with further investment in standby generation. For instance some days could produce 80% intermittent wind and on the many windless days substitute 80% dispatchable power like natural gas, biomass and Hydro.
- Areas with existing high levels of hydroelectric generation may ramp up or down to incorporate substantial amounts of wind. Norway, Brazil, and Manitoba all have high levels of hydroelectric generation, Quebec produces over 90% of its electricity from hydropower, and Hydro-Québec is the largest hydropower producer in the world. The U.S. Pacific Northwest has been identified as another region where wind energy is complemented well by existing hydropower. Storage capacity in hydropower facilities will be limited by size of reservoir, and environmental and other considerations.
Connecting grid internationally
It is often feasible to export energy to neighboring grids at times of surplus, and import energy when needed. This practice is common in Europe and between the US and Canada. Integration with other grids can lower the effective concentration of variable power: for instance, Denmark's high penetration of VRE, in the context of the German/Dutch/Scandinavian grids with which it has interconnections, is considerably lower as a proportion of the total system. Hydroelectricity that compensates for variability can be used across countries.
The capacity of power transmission infrastructure may have to be substantially upgraded to support export/import plans. Some energy is lost in transmission. The economic value of exporting variable power depends in part on the ability of the exporting grid to provide the importing grid with useful power at useful times for an attractive price.
Sector coupling
Demand and generation can be better matched when sectors such as mobility, heat and gas are coupled with the power system. The electric vehicle market is for instance expected to become the largest source of storage capacity. This may be a more expensive option appropriate for high penetration of variable renewables, compared to other sources of flexibility. The International Energy Agency says that sector coupling is needed to compensate for the mismatch between seasonal demand and supply.
Electric vehicles can be charged during periods of low demand and high production, and in some places send power back from the vehicle-to-grid.
Penetration
Penetration refers to the proportion of a primary energy (PE) source in an electric power system, expressed as a percentage. There are several methods of calculation yielding different penetrations. The penetration can be calculated either as:
- the nominal capacity (installed power) of a PE source divided by the peak load within an electric power system; or
- the nominal capacity (installed power) of a PE source divided by the total capacity of the electric power system; or
- the electrical energy generated by a PE source in a given period, divided by the demand of the electric power system in this period.
The level of penetration of intermittent variable sources is significant for the following reasons:
- Power grids with significant amounts of dispatchable pumped storage, hydropower with reservoir or pondage or other peaking power plants such as natural gas-fired power plants are capable of accommodating fluctuations from intermittent power more easily.
- Relatively small electric power systems without strong interconnection (such as remote islands) may retain some existing diesel generators but consuming less fuel, for flexibility until cleaner energy sources or storage such as pumped hydro or batteries become cost-effective.
In the early 2020s wind and solar produce 10% of the world's electricity, but supply in the 40-55% penetration range has already been implemented in several systems, with over 65% planned for the UK by 2030.
There is no generally accepted maximum level of penetration, as each system's capacity to compensate for intermittency differs, and the systems themselves will change over time. Discussion of acceptable or unacceptable penetration figures should be treated and used with caution, as the relevance or significance will be highly dependent on local factors, grid structure and management, and existing generation capacity.
For most systems worldwide, existing penetration levels are significantly lower than practical or theoretical maximums.
Maximum penetration limits
Maximum penetration of combined wind and solar is estimated at around 70% to 90% without regional aggregation, demand management or storage; and up to 94% with 12 hours of storage. Economic efficiency and cost considerations are more likely to dominate as critical factors; technical solutions may allow higher penetration levels to be considered in future, particularly if cost considerations are secondary.
Economic impacts of variability
Estimates of the cost of wind and solar energy may include estimates of the "external" costs of wind and solar variability, or be limited to the cost of production. All electrical plant has costs that are separate from the cost of production, including, for example, the cost of any necessary transmission capacity or reserve capacity in case of loss of generating capacity. Many types of generation, particularly fossil fuel derived, will also have cost externalities such as pollution, greenhouse gas emission, and habitat destruction which are generally not directly accounted for. The magnitude of the economic impacts is debated and will vary by location, but is expected to rise with higher penetration levels. At low penetration levels, costs such as operating reserve and balancing costs are believed to be insignificant.
Intermittency may introduce additional costs that are distinct from or of a different magnitude than for traditional generation types. These may include:
- Transmission capacity: transmission capacity may be more expensive than for nuclear and coal generating capacity due to lower load factors. Transmission capacity will generally be sized to projected peak output, but average capacity for wind will be significantly lower, raising cost per unit of energy actually transmitted. However transmission costs are a low fraction of total energy costs.
- Additional operating reserve: if additional wind and solar does not correspond to demand patterns, additional operating reserve may be required compared to other generating types, however this does not result in higher capital costs for additional plants since this is merely existing plants running at low output - spinning reserve. Contrary to statements that all wind must be backed by an equal amount of "back-up capacity", intermittent generators contribute to base capacity "as long as there is some probability of output during peak periods". Back-up capacity is not attributed to individual generators, as back-up or operating reserve "only have meaning at the system level".
- Balancing costs: to maintain grid stability, some additional costs may be incurred for balancing of load with demand. Although improvements to grid balancing can be costly, they can lead to long term savings.
In many countries for many types of variable renewable energy, from time to time the government invites companies to tender sealed bids to construct a certain capacity of solar power to connect to certain electricity substations. By accepting the lowest bid the government commits to buy at that price per kWh for a fixed number of years, or up to a certain total amount of power. This provides certainty for investors against highly volatile wholesale electricity prices. However they may still risk exchange rate volatility if they borrowed in foreign currency.
Regulation and grid planning
Britain
The operator of the British electricity system has said that it will be capable of operating zero-carbon by 2025, whenever there is enough renewable generation, and may be carbon negative by 2033. The company, National Grid Electricity System Operator, states that new products and services will help reduce the overall cost of operating the system.