The amount of greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture is significant: The agriculture, forestry and land use sector contribute between 13% and 21% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Agriculture contributes towards climate change through direct greenhouse gas emissions and by the conversion of non-agricultural land such as forests into agricultural land. Emissions of nitrous oxide and methane make up over half of total greenhouse gas emission from agriculture. Animal husbandry is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions.
The agricultural food system is responsible for a significant amount of greenhouse gas emissions. In addition to being a significant user of land and consumer of fossil fuel, agriculture contributes directly to greenhouse gas emissions through practices such as rice production and the raising of livestock. The three main causes of the increase in greenhouse gases observed over the past 250 years have been fossil fuels, land use, and agriculture. Farm animal digestive systems can be put into two categories: monogastric and ruminant. Ruminant cattle for beef and dairy rank high in greenhouse-gas emissions; monogastric, or pigs and poultry-related foods, are low. The consumption of the monogastric types may yield less emissions. Monogastric animals have a higher feed-conversion efficiency, and also do not produce as much methane. Furthermore, CO2 is actually re-emitted into the atmosphere by plant and soil respiration in the later stages of crop growth, causing more greenhouse gas emissions. The amount of greenhouse gases produced during the manufacture and use of nitrogen fertilizer is estimated as around 5% of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. The single most important way to cut emissions from it is to use less fertilizers, while increasing the efficiency of their use.
There are many strategies that can be used to help soften the effects, and the further production of greenhouse gas emissions - this is also referred to as climate-smart agriculture. Some of these strategies include a higher efficiency in livestock farming, which includes management, as well as technology; a more effective process of managing manure; a lower dependence upon fossil-fuels and nonrenewable resources; a variation in the animals' eating and drinking duration, time and location; and a cutback in both the production and consumption of animal-sourced foods. A range of policies may reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the agriculture sector for a more sustainable food system.
Emissions by type of greenhouse gas
Agricultural activities emit the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide.
Carbon dioxide emissions
Activities such as tilling of fields, planting of crops, and shipment of products cause carbon dioxide emissions. Agriculture-related emissions of carbon dioxide account for around 11% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Farm practices such as reducing tillage, decreasing empty land, returning biomass residue of crop to soil, and increasing the use of cover crops can reduce carbon emissions.
Methane emissions

Methane emissions from livestock are the number one contributor to agricultural greenhouse gases globally. Livestock are responsible for 14.5% of total anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. One cow alone will emit 220 pounds of methane per year. While the residence time of methane is much shorter than that of carbon dioxide, it is 28 times more capable of trapping heat. Not only do livestock contribute to harmful emissions, but they also require a lot of land and may overgraze, which leads to unhealthy soil quality and reduced species diversity. A few ways to reduce methane emissions include switching to plant-rich diets with less meat, feeding the cattle more nutritious food, manure management, and composting.
Traditional rice cultivation is the second biggest agricultural methane source after livestock, with a near-term warming impact equivalent to the carbon-dioxide emissions from all aviation. Government involvement in agricultural policy is limited due to high demand for agricultural products like corn, wheat, and milk. The United States Agency for International Development's (USAID) global hunger and food security initiative, the Feed the Future project, is addressing food loss and waste. By addressing food loss and waste, greenhouse gas emission mitigation is also addressed. By only focusing on dairy systems of 20 value chains in 12 countries, food loss and waste could be reduced by 4-10%. These numbers are impactful and would mitigate greenhouse gas emissions while still feeding the population.
Nitrous oxide emissions

Nitrous oxide emission comes from the increased use of synthetic and organic fertilizers. Fertilizers increase crop yield production and allows the crops to grow at a faster rate. Agricultural emissions of nitrous oxide make up 6% of the United States' greenhouse gas emissions; they have increased in concentration by 30% since 1980. While 6% may appear to be a small contribution, nitrous oxide is 300 times more effective at trapping heat per pound than carbon dioxide and has a residence time of around 120 years. Different management practices such as conserving water through drip irrigation, monitoring soil nutrients to avoid overfertilization, and using cover crops in place of fertilizer application may help in reducing nitrous oxide emissions.

Emissions by type of activity
Land use changes

Agriculture contributes to greenhouse gas increases through land use in four main ways:
- CO2 releases linked to deforestation
- Methane releases from rice cultivation
- Methane releases from enteric fermentation in cattle
- Nitrous oxide releases from fertilizer application
Together, these agricultural processes comprise 54% of methane emissions, roughly 80% of nitrous oxide emissions, and virtually all carbon dioxide emissions tied to land use.
Land cover has changed majorly since 1750, as humans have deforested temperate regions. When forests and woodlands are cleared to make room for fields and pastures, the albedo of the affected area increases, which can result in either warming or cooling effects depending on local conditions. Deforestation also affects regional carbon reuptake, which can result in increased concentrations of CO2, the dominant greenhouse gas. Land-clearing methods such as slash and burn compound these effects, as the burning of biomatter directly releases greenhouse gases and particulate matter such as soot into the air. Land clearing can destroy the soil carbon sponge.
Livestock

Livestock and livestock-related activities such as deforestation and increasingly fuel-intensive farming practices are responsible for over 18% of human-made greenhouse gas emissions, including:
- 9% of global carbon dioxide emissions
- 35–40% of global methane emissions (chiefly due to enteric fermentation and manure)
- 64% of global nitrous oxide emissions (chiefly due to fertilizer use.)

Livestock activities also contribute disproportionately to land-use effects, since crops such as corn and alfalfa are cultivated in order to feed the animals.
In 2010, enteric fermentation accounted for 43% of the total greenhouse gas emissions from all agricultural activity in the world. The meat from ruminants has a higher carbon equivalent footprint than other meats or vegetarian sources of protein based on a global meta-analysis of lifecycle assessment studies. Small ruminants such as sheep and goats contribute approximately 475 million tons of carbon dioxide equivalent to GHG emissions, which constitutes around 6.5% of world agriculture sector emissions. Methane production by animals, principally ruminants, makes up an estimated 15-20% global production of methane. Research continues on the use of various seaweed species, in particular Asparegopsis armata, as a food additive that helps reduce methane production in ruminants.
Worldwide, livestock production occupies 70% of all land used for agriculture, or 30% of the land surface of the Earth. The way livestock is grazed also affects future fertility of the land. Not circulating grazing can lead to unhealthy compacted soils. The expansion of livestock farms affects the habitats of native wildlife and has led to their decline. Reduced intake of meat and dairy products is another effective approach to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Slightly over half of Europeans (51%) surveyed in 2022 support reducing the amount of meat and dairy products people may buy to combat climate change - 40% of Americans and 73% of Chinese respondents felt the same.
The Stockholm Environment Institute has suggested that livestock subsidies be phased out in a just transition.
Fertilizer production
Rice production


Global estimates


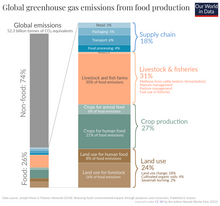
Between 2010 and 2019, agriculture, forestry and land use contributed between 13% and 21% to global greenhouse gas emissions. Nitrous oxide and methane make up over half of total greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture.
In 2020, it was estimated that the food system as a whole contributed 37% of total greenhouse gas emissions, and that this figure was on course to increase by 30–40% by 2050 due to population growth and dietary change.
Older estimates
In 2010, agriculture, forestry and land-use change were estimated to contribute 20–25% of global annual emissions.
Mitigation
| Food Types | Greenhouse Gas Emissions (g CO2-Ceq per g protein) |
|---|---|
| Ruminant Meat | 62
|
| Recirculating Aquaculture | 30
|
| Trawling Fishery | 26
|
| Non-recirculating Aquaculture | 12
|
| Pork | 10
|
| Poultry | 10
|
| Dairy | 9.1
|
| Non-trawling Fishery | 8.6
|
| Eggs | 6.8
|
| Starchy Roots | 1.7
|
| Wheat | 1.2
|
| Maize | 1.2
|
| Legumes | 0.25
|
In developed countries
Agriculture is often not included in government emissions reductions plans. For example, the agricultural sector is exempt from the EU emissions trading scheme which covers around 40% of the EU greenhouse gas emissions.
Several mitigation measures for use in developed countries have been proposed:
- breeding more resilient crop varieties, and diversification of crop species
- using improved agroforestry species
- capture and retention of rainfall, and use of improved irrigation practices
- Increasing forest cover and Agroforestry
- use of emerging water harvesting techniques (such as contour trenching)
Research in New Zealand estimated that switching agricultural production towards a healthier diet while reducing greenhouse gas emissions would cost approxiately 1% of the agricultural sector's export revenue, which is an order of magnitude less than the estimated health system savings from a healthier diet.
In developing countries
Agriculture is responsible for over a quarter of total global greenhouse gas emissions. Given that agriculture's share in global gross domestic product (GDP) is about 4%, these figures suggest that agricultural activities produce high levels of greenhouse gases. Innovative agricultural practices and technologies can play a role in climate change mitigation and adaptation. This adaptation and mitigation potential is nowhere more pronounced than in developing countries where agricultural productivity remains low; poverty, vulnerability and food insecurity remain high; and the direct effects of climate change are expected to be especially harsh. Creating the necessary agricultural technologies and harnessing them to enable developing countries to adapt their agricultural systems to changing climate will require innovations in policy and institutions as well. In this context, institutions and policies can play an important role at multiple scales.
State- or NGO-sponsored projects can help farmers be more resilient to climate change, such as irrigation infrastructure that provides a dependable water source as rains become more erratic. Water catchment systems that collect water during the rainy season to be used during dry periods can also be used to mitigate the effects of climate change. Some programs, like the Asociación de Cooperación para el Desarrollo Rural de Occidente (C.D.R.O.), a Guatemalan program funded by the United States' government until 2017, focus on agroforestry and weather monitoring systems to help farmers adapt. The organization provided residents with resources to plant new, more adaptable crops to alongside their typical maize to protect the corn from variable temperatures, frost, etc. C.D.R.O. also set up a weather monitoring system to help predict extreme weather events, and would send residents text messages to warn them about periods of frosts, extreme heat, humidity, or drought. Projects focusing on irrigation, water catchment, agroforestry, and weather monitoring can help Central American residents adapt to climate change.
The Agricultural Model Intercomparison and Improvement Project (AgMIP) was developed in 2010 to evaluate agricultural models and intercompare their ability to predict climate impacts. In sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, South America and East Asia, AgMIP regional research teams (RRTs) are conducting integrated assessments to improve understanding of agricultural impacts of climate change (including biophysical and economic impacts) at national and regional scales. Other AgMIP initiatives include global gridded modeling, data and information technology (IT) tool development, simulation of crop pests and diseases, site-based crop-climate sensitivity studies, and aggregation and scaling.
At the 2019 United Nations Climate Summit, the Global EverGreening Alliance announced an initiative to promote agroforestry and conservation farming. One of its goals is to sequester carbon from the atmosphere. The coalition aims to restore tree cover to a territory of 5.75 million square kilometres, achieve a healthy tree-grass balance on a territory of 6.5 million square kilometres, and increase carbon capture in a territory of 5 million square kilometres.By 2050 the restored land should sequester 20 billion tons of carbon annually. The first phase of the initiative is the "Grand African Savannah Green Up" project. In 2019, millions of families had already implemented these methods, and the average territory covered with trees in the farms in Sahel reached 16%.
Climate-smart agriculture
Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) (or climate resilient agriculture) is an integrated approach to managing land to help adapt agricultural methods, livestock and crops to the effects of climate change and, where possible, counteract it by reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, while taking into account the growing world population to ensure food security. The emphasis is not simply on carbon farming or sustainable agriculture, but also on increasing agricultural productivity.
CSA has three pillars: increasing agricultural productivity and incomes; adapting and building resilience to climate change; and reducing or removing greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture. There are different actions listed to counter the future challenges for crops and plants. For example, with regard to rising temperatures and heat stress, CSA recommends the production of heat tolerant crop varieties, mulching, water management, shade house, boundary trees, carbon sequestration, and appropriate housing and spacing for cattle. CSA seeks to stabilize crop production while mitigating the adverse impacts of climate change while maximizing food security.